Engaging with NCLEX PN Study Guide on a regular basis can help students identify areas of weakness and focus their study efforts accordingly.
NCLEX Surgery Questions - NCLEX Questions On Surgery
Surgery NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
A client tells the nurse on admission that she is uneasy about having to leave her children with a relative while being in the hospital for surgery. What should the nurse do?
(a) Reassure the client that her children will be fine and she should stop worrying.
(b) Contact the relative to determine his/her capacity to be an adequate care provider.
(c) Encourage the client to call the children to make sure they are doing well.
(d) Gather more information about the client’s feelings about the childcare arrangements.
Answer:
(d) Gather more information about the client’s feelings about the childcare arrangements.
Explanation:
The health history is conducted to ascertain a client’s state of wellness or illness. A personal dialogue between a client and a nurse is conducted to obtain information. To achieve a relationship of mutual trust and respect, the nurse must have the ability to communicate a sincere interest in the client. The therapeutic communication must be adapted to the responses, problems, and needs of the client. Reassurance and the remaining options do not demonstrate that the nurse is genuinely interested in the client’s needs.
Question 2.
The client has a latex allergy. What should the nurse teach the client to do before having surgery? Select all that apply.
(a) Determine that there will be a latex-safe environment for surgery.
(b) Report symptoms experienced with the latex allergy (e.g., rhinitis, conjunctivitis, flushing).
(c) Notify the health care providers (HCPs) at the surgery center.
(d) Wear a stainless steel medical alert bracelet into the surgical suite.
(e) Ask to have the surgery at a hospital.
Answer:
(a) Determine that there will be a latex-safe environment for surgery.
(b) Report symptoms experienced with the latex allergy (e.g., rhinitis, conjunctivitis, flushing).
(c) Notify the health care providers (HCPs) at the surgery center.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c) Treatment and diagnostic evaluation must be done in a latex-safe environment. Signs and symptoms of latex allergy may range from mild to anaphylaxis. Clients with latex allergy are advised to notify their HCPs and to wear a medical ID however, all metal and jewelry must be removed prior to surgery as they could conduct an electrical current. The surgery can be safely performed at a free-standing surgery center as long as latex precautions are observed.
Question 3.
When the nurse asks the client who is having abdominal surgery today if the client understands the procedure, the client replies, “No, not really; I talked about several different things with my surgeon, and I’m just not sure.” What should the nurse do next?
(a) Teach the client all the details of the planned procedure.
(b) Utilize a second witness when the client signs for consent.
(c) Notify the surgeon of the client’s expressed lack of understanding.
(d) Administer the prescribed preoperative narcotics and/or sedatives.
Answer:
(c) Notify the surgeon of the client’s expressed lack of understanding.
Explanation:
It is the surgeon’s responsibility to discuss the planned procedure and review the risks, benefits, and alternatives to the planned procedure. If the client verbalizes that he or she does not understand the procedure that is planned, it is the nurse’s responsibility to notify the surgeon of this lack of understanding right away, prior to any other/additional nursing actions.
In this case, when the client verbalizes a lack of understanding, the nurse should not teach about the procedure; the surgeon needs to do this. The nurse cannot assist the client to sign for consent Q and should not administer narcotics or sedatives until the client understands and agrees to the procedure.
Question 4.
During preadmission testing for same-day surgery, a client states that she has added garlic each day to her diet to help control her blood pressure. What should the nurse ask the client next?
(a) “What type of surgery are you having?”
(b) “What is your normal blood pressure?”
(c) “How much garlic are you eating?”
(d) “What type of anesthesia are you having?”
Answer:
(c) “How much garlic are you eating?”
Explanation:
Garlic has anticoagulant properties and may pose a problem with bleeding if enough has been taken too close to surgery. Therefore, the nurse must obtain more quantifiable details about the client’s statement. The type of surgical procedure, anesthesia, and blood pressure status are not affected by garlic.
Question 5.
When removing protective covering, what action should this nurse (see figure) take to avoid spreading nosocomial infections?
(a) Remove the face mask.
(b) Place the face mask over the mouth and nose before removing the hair covering.
(c) Wash hands before tying the strings on the mask.
(d) Tie the dangling strings of the mask around the neck.
Answer:
(a) Remove the face mask.
Explanation:
The nurse should remove the face mask. The face mask contains nasal and oral droplets, which are easily transmitted to the hands as the mask dangles when left hanging around the neck. When a face mask is not worn over the mouth and nose, it should be completely removed.
Question 6.
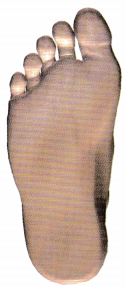
The client is to have surgery on the fourth metatarsal. Identify the place on the illustration below where the client should confirm the operative site to the health care provider.
Answer:
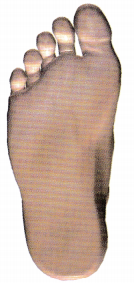
Explanation:
This is the correct surgical site.
Question 7.
The nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who is scheduled for a lumbar laminectomy. The nurse should report which finding to the surgeon?
(a) pimple on the lower back
(b) abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG)
(c) hearing aid
(d) allergy to iodine
Answer:
(a) pimple on the lower back
Explanation:
A pimple close to the incision site may be reason for the surgeon to cancel the surgical procedure because it increases the risk of infection. If the client had an abnormal ECG, the nurse would notify the anesthesiologist who will be administering the anesthesia. The anesthesiologist is the decisionmaker regarding the implications of the anesthesia on the cardiac system.
The surgical team should be notified of the client’s hearing disability, but the surgeon, who has already met the client, does not need to be notified. The surgical team should be notified of the client’s allergy to iodine, and it should be documented in all the appropriate places, but the surgeon would not need to be notified in advance of the surgical procedure.
Question 8.
Prior to going to surgery, the client tells the nurse that it is not possible to hear without a hearing aid and asks to wear it to surgery and recovery. What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) Explain to the client that it is policy not to take personal items to surgery because they may be lost or broken.
(b) Tell the client that a nurse will bring the hearing aid to the postanesthesia care unit as soon as the client wakes up.
(c) Explain to the client that the premedication that will cause sleepiness and it will not be necessary to hear anything.
(d) Call the surgery unit to explain the client’s concern, and ask if the client can wear the hearing aid to surgery.
Answer:
(d) Call the surgery unit to explain the client’s concern, and ask if the client can wear the hearing aid to surgery.
Explanation:
The nurse serves as a client advocate when helping in addressing a client’s concern. The nurse should call the operating room and inform the intraoperative nurse about the client’s request. A special container with correct identification can be prepared so that when the client is anesthetized and her hearing aid is removed, it will not be lost or broken. It is usual policy not to send personal belongings to surgery because they are easily broken or lost in the transfer of an anesthetized client with higher priority needs, but special needs do exist.
In some instances, the nurse does bring a client’s personal belongings to the postanesthesia care unit, but in this case, the item involves the client’s ability to communicate. Because the trend is to use little premedication, clients are more alert and may want to talk with their surgical team before going to sleep. Decreasing the client’s anxieties preoperatively affects the amount of medication used to induce the client and her overall psychological and physiologic status. Telling the client that she will not need to hear is insensitive.
Question 9.
The adult daughters of an older adult client inform the nurse that they fully expect their father to be combative after surgery. Preoperatively, they request that the nurse put all four side rails up and use restraints to keep him safe. What should the nurse tell the daughters?
(a) “Certainly; we will want to be sure to keep your father safe too.”
(b) “We will call the health care provider to get a prescription right away. ”
(c) "We will first try to keep him safe without restraint.”
(d) “Restraint use is prohibited at our hospital at all times.”
Answer:
(c) "We will first try to keep him safe without restraint.”
Explanation:
A least-restraint environment should always be provided as much as possible. Nursing staff are required to attempt lesser restrictive alternatives (e.g., use of family or sitter, reorienta-tion, distraction, or a toileting schedule) prior to notifying the provider of the need for restraints. Nursing staff are also required to document clinical conditions requiring restraint, lesser restrictive alternatives attempted, and client/family education provided regarding restraint use.
Provider prescrip-tions for restraints must be time limited and specific regarding the type of restraint. Additionally, if restraints are implemented, nursing staff must monitor clients for safety (including skin checks and range of motion) and provide frequent food/fluids/ toileting
Question 10.
Prior to surgery, the client is to take nothing by mouth after 0400. Which statement indicates the client did not follow the preoperative directions? The client:
(a) ate a gelatin dessert at 0330.
(b) brushed the teeth at 0400 but did not swallow.
(c) held a cold washcloth against the lips.
(d) smoked a cigarette at 0600.
Answer:
(d) smoked a cigarette at 0600.
Explanation:
The client has deficient knowledge if he smoked a cigarette after 0400 because, even though he did not have anything to eat or drink, smoking has increased the production of gastric hydrochloric acid, which can increase the risk of aspiration in an anesthetized client. The client consumed the gelatin dessert prior to the 0400 restriction for being NPO. Comfort measures, such as brushing the teeth without swallowing or holding a cold washcloth against the lips, are acceptable for a client who is to have nothing by mouth.
Question 11.
The surgeon prescribes cefazolin 1 g to be given IV at 0730 when the client’s surgery is scheduled at 0800. What is the primary reason to start the antibiotic exactly at 0730?
(a) Legally the medication has to be given at the prescribed time.
(b) The antibiotic is most effective in preventing infection if it is given 30 to 60 minutes before the operative incision is made.
(c) The postoperative dose of cefazolin needs to be started exactly 8 hours after the preoperative dose of cefazolin.
(d) The peak and titer levels are needed for antibiotic therapy.
Answer:
(b) The antibiotic is most effective in preventing infection if it is given 30 to 60 minutes before the operative incision is made.
Explanation:
The antibiotic is most effective in preventing infection, according to research, if it is given 30 to 60 minutes before the operative incision is made. When the surgeon prescribes the antibiotic to be given at a specific time related to the scheduled time of the surgical procedure, it is imperative that the antibiotic is given on time.
Legally, the nurse considers 30 minutes on either side of the scheduled time to be acceptable for administering medications: however, in this situation, giving the antibiotic 30 minutes too soon can make the prophylactic antibiotic ineffective. The postoperative dose of antibiotic is not timed according to the preoperative dose. Peak and titer levels are measured for some antibiotics, but in this case, the primary reason is to have the antibiotic infused before the time of the incision.
Question 12.
Which approach is the best way for the nurse to begin the preoperative interview?
Walk in the client's room:
(a) and ask, “Are you Mrs. Smith?”
(b) sit down, and take the client’s blood pressure.
(c) sit down, maintain eye contact, and make an introduction.
(d) and ask the client's name.
Answer:
(c) sit down, maintain eye contact, and make an introduction.
Explanation:
Nurses should provide the preoperative client individual and sincere attention by meeting the client at eye level and introducing themselves by name and role. The nurse should ask the client to tell her full name rather than asking if she is Mrs. Smith because there might be another client by that name on the schedule. Nurses should not start the physical assessment or ask the client’s name without first identifying themselves and their role out of courtesy and to relieve the client’s anxiety in the new environment of the surgical experience.
Question 13.
A client who is to receive general anesthesia has a serum potassium level of 5.8 mEq/L (5.8 mmol/L). What should be the nurse’s first response?
(a) Call the operating room to cancel the surgery.
(b) Send the client to surgery.
(c) Make a note on the client’s record.
(d) Notify the anesthesiologist.
Answer:
(d) Notify the anesthesiologist.
Explanation:
The nurse should notify the anesthesiologist because a serum potassium level of 5.8 mEq/L (5.8 mmol/L) places the client at risk for arrhythmias when under general anesthesia. It is not the role of the nurse to cancel surgery. The nurse should not automatically send a client with abnormal laboratory findings to surgery because the procedure may be canceled.
Once the client is inside the operating room and sterile supplies have been opened up for the procedure, the client is usually charged. The nurse should call ahead of time to communicate the abnormal laboratory result instead of noting the finding on the client’s record. The information on the record should not be reviewed until after the client has been transported to the operating room and the supplies have been opened.
Question 14.
Prior to being transported to the surgery suite, the nurse asks the client whether the client has any allergies. The client responds, “Does anyone communicate with anyone? I’ve been asked that question over and over!” What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “I’m sorry! I just have to ask that question for the record.”
(b) “It’s an important question, and we just have to check.”
(c) “You will hear it again and again as you go through surgery.”
(d) “This question is asked for verification and safety with each new phase of treatment.”
Answer:
(d) “This question is asked for verification and safety with each new phase of treatment.”
Explanation:
Clients should be made aware that some questions are asked for verification and safety with each new phase of treatment. Indicating that the nurse is sorry, or needs to check several times, or telling the client that the question will be asked again does not tell the client why it is necessary to continue to verify information essential to the client’s safety.
Question 15.
On the day of surgery, a client with diabetes who takes insulin on a sliding scale is to have nothing by mouth and all medications withheld. The client’s 0600 glucose level is 300 mg/dL (16.7 mmol/L). What should the nurse do?
(a) Withhold all medications.
(b) Administer the insulin dose dictated by the sliding scale.
(c) Call the health care provider (HCP) for specific prescriptions based on the glucose level.
(d) Notify the surgery department.
Answer:
(c) Call the health care provider (HCP) for specific prescriptions based on the glucose level.
Explanation:
The nurse should notify the HCP directly for specific prescriptions based on the client’s glucose level. The nurse cannot ignore the elevated glucose level. The surgical experience is stressful, and the client needs specific insulin coverage during the perioperative period. The nurse should not administer the insulin without checking with the surgeon because there are specific prescriptions to withhold all medications. It is not necessary to notify the surgery department unless the HCP cancels the surgery.
Question 16.
The nurse is preparing a preoperative teaching plan for a client who is undergoing a bilateral breast reduction. Which aspect of the plan is the
priority?
(a) reduction of risk potential
(b) physiologic adaptation
(c) psychosocial integrity
(d) health promotion and maintenance
Answer:
(c) psychosocial integrity
Explanation:
Psychosocial integrity issues, including coping mechanisms, situational role changes, and body image changes, are more common in a client who undergoes elective cosmetic surgical procedures. Reduction of risk potential, physiologic adaptation, and health promotion and maintenance are greater needs for clients who are undergoing surgical correction of functional, anatomic, or physiologic defects in nonelective surgical procedures.
Question 17.
A client is scheduled to have an elective mandibular osteotomy to correct a mandibular fracture sustained in an accident 6 months earlier. Which statement by the client indicates to the nurse that the client is having difficulty coping?
(a) “I’ll be glad to have my jaw fixed because my wife thinks I don’t look like myself.”
(b) “I’m somewhat afraid to have the surgery, but I feel OK about it.”
(c) “My wife will help me, but I don’t think I’ll need that much help.”
(d) “I’m ready to get this over with.”
Answer:
(a) “I’ll be glad to have my jaw fixed because my wife thinks I don’t look like myself.”
Explanation:
A client should not elect surgery to meet someone else’s needs. The nurse should encourage the client to share his feelings and his perception of the deformity and to clarify his reasons for electing to have the surgery. It is normal to be somewhat afraid, and it is good if a client says he feels “OK” about the surgery. The fact that a client believes that his wife will help him after surgery and that he will also be relatively independent reflects appropriate adaptation. It is a common feeling among preoperative clients that they are ready to “get this over with,” indicating that the waiting period is stressful.
Question 18.
The nurse is assessing a client’s nutritional status before surgery. Which observation would indicate poor nutrition in a 5-foot 7-inch (170 cm) female client who is 21 years of age?
(a) poor posture
(b) brittle nails
(c) dull expression
(d) weight of 128 lb (58.1 kg)
Answer:
(b) brittle nails
Explanation:
Brittle nails indicate poor nutrition. Poor posture indicates that the client does not stand up straight and use her muscles to support herself. A dull expression reflects the client’s affect and emotional status. The client’s weight of 128 lb (58.1 kg) is within normal range.
Question 19.
An older adult is being discharged following a repair of an inguinal hernia. The client is independent and lives alone, but the client’s family lives 60 miles from the client’s house. When at home, the client is to cleanse and inspect the incision for signs of infection. The client and family are able to read and understand written instructions. When giving discharge instructions, what should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Explain the instructions to the client.
(b) Ask the client to demonstrate the procedure.
(c) Explain the instructions to a family member.
(d) Provide written instructions for the client.
(e) Give the family a link to a video showing the procedure.
Answer:
(a) Explain the instructions to the client.
(b) Ask the client to demonstrate the procedure.
(d) Provide written instructions for the client.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d) The nurse should explain and demonstrate the discharge instructions and then ask the client to give a return demonstration. The Joint Commission and Health Canada require that discharge instructions be written for the postoperative client. Clients need to be given discharge instructions orally and in written form because of stress, medications, and the volume of material to be learned.
Explaining all the instructions to a family member and giving them a link to a video is important but does not replace the need for written instructions. Since the family does not live nearby, the nurse must be certain the client can manage the instructions by herself.
Question 20.
A client is admitted for an arthroscopy of the right shoulder through same-day surgery. Which nurse is responsible for starting the client’s discharge planning?
(a) preadmission nurse
(b) preoperative nurse
(c) intraoperative nurse
(d) postoperative nurse
Answer:
(a) preadmission nurse
Explanation:
The preadmission nurse, the first person in contact with the client, starts the discharge planning for the client undergoing surgery. All nurses involved with the client, from preadmission through postoperative recovery, should continue to reinforce the discharge plan.
Question 21.
The nurse is preparing to administer a preoperative medication that includes a sedative to a client who is having abdominal surgery. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Have the family present.
(b) Ensure that the operative area has been shaved.
(c) Have the client empty the bladder.
(d) Make sure the client is covered with a warm blanket.
Answer:
(c) Have the client empty the bladder.
Explanation:
The nurse should have the client empty the bladder before the premedication is administered. This will be more comfortable and safe for the client. The purpose of the premedication is to decrease anxiety and promote a relaxed state. The client must have an empty bladder before being transferred to the operating room, where the client will be immobilized and receive IV fluids.
The family does not have to be present, but it is usually desired. Shaving the operative area is not generally recommended because it can cause small nicks that harbor bacteria. If the client must be shaved, it is usually done in the operating room holding area. The client should be comfortable at all times and offered a warm blanket before or after the premedication.
Question 22.
Before surgery, a client expresses a fear of surgery because 10 years ago the client’s sister died in surgery related to complications of anesthesia. What should the nurse do?
(a) Reassure the client that technology has changed over the last 10 years.
(b) Encourage the client to further express concerns.
(c) Explain to the client that it is normal to be afraid.
(d) Ask the client if any family members had trouble when they had surgery.
Answer:
(d) Ask the client if any family members had trouble when they had surgery.
Explanation:
The nurse should immediately think of the congenital metabolic tendency for malignant hyperthermia, which occurs in the presence of certain kinds of anesthetics. Whenever a preoperative client states that a family member has had problems with anesthesia or surgery, the nurse should inquire about the nature of the problems and whether other family members have had similar problems.
Reassuring the client that technology has changed will do little to affect her fears and misses the opportunity to evaluate the risk for malignant hyperthermia. Encouraging the client to further express her concerns and reassuring her that her feelings are normal are important, but missing a familial tendency of malignant hyperthermia could be fatal.
Question 23.
The nurse is preparing to start an intravenous infusion and has raised the head of the client’s bed. After the nurse applies gloves to insert an IV catheter, the client begins to rub the eyes and wipe away nasal drainage. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Distract the client’s attention.
(b) Assess the client for pain.
(c) Remove the gloves and assess the client’s vital signs.
(d) Lower the head of the client’s bed.
Answer:
(c) Remove the gloves and assess the client’s vital signs.
Explanation:
Although most clinical agencies use latex- free materials, the nurse should assess the vital signs of the client who exhibits urticaria, rhinitis, and conjunctivitis a few seconds after coming in contact with rubber gloves, a plastic catheter, plastic IV tubing, or a plastic IV solution bag.
The nurse should recognize that these symptoms indicate that a type I allergic reaction is occurring. Although many health care agencies now use latex-free materials, it is possible that the products contain latex or other materials that might be precipitating the client’s allergic response. The client does not need to be distracted or assessed for pain. It is not necessary to lower the head of the bed.
Question 24.
When evaluating a client’s preoperative cognitive-perceptual pattern, which question should the nurse ask the client?
(a) “Do you have difficulty swallowing?”
(b) "Do you need special equipment to walk?”
(c) “Do you smoke?”
(d) "Do you wear glasses?”
Answer:
(d) "Do you wear glasses?”
Explanation:
The nurse would ask whether the client wears glasses to evaluate the client’s preoperative cognitive-perceptual pattern. Asking about the client’s swallowing pattern would evaluate the client’s nutritional-metabolic pattern. Asking about the client’s need for special equipment to walk would evaluate the client’s activity-exercise pattern. Asking about the client’s history of smoking would evaluate the client’s health perception-health management pattern.
Question 25.
When attempting to check the pupils of a client scheduled to receive general anesthesia, the nurse notices that the client has trouble tilting the head back. What is the primary concern related to this finding?
(a) The client has limited movement of the neck.
(b) The client may have postoperative neck pain.
(c) The client is at risk for difficult intubation.
(d) The ability to assess the client’s pupils is limited.
Answer:
(c) The client is at risk for difficult intubation.
Explanation:
The client is at risk for a difficult intubation because the neck must be hyperextended to pass the endotracheal tube. Assessment of the pupils should not be limited. If the client is positioned appropriately during surgery, there is no risk of postoperative neck pain or limited neck movement.
Question 26.
A client is to have a below-the-knee amputation. Prior to the surgery, what should the circulating nurse in the operating room do?
(a) Insert a Foley catheter.
(b) Start an intravenous infusion.
(c) Initiate a time-out.
(d) Verify that the surgeon possesses the degree of expertise needed.
Answer:
(c) Initiate a time-out.
Explanation:
The Universal Protocol is used to prevent wrong site, wrong procedure, and wrong person surgery. Actions included in the protocol are as follows: conduct a preprocedure verification process, mark the procedure site, and perform a time-out . Exceptions to the Universal Protocol are routine or “minor” procedures, such as venipuncture, peripheral IV line placement, insertion of oral/nasal drainage or feeding tubes, or Foley catheter insertion.
Prior to closure, the surgeon or circulating nurse will initiate a time-out to verbally confirm a review of informed consent and procedures completed: all specimens are identified, accounted for, and accurately labeled; and all foreign bodies have been removed. The chief of surgery and medical director
are the ones who will verify the surgeons’ levels of expertise.
Question 27.
The nurse is developing a plan to teach a client deep-breathing exercises to expand collapsed alveoli and prevent postoperative atelectasis and pneumonia. What information should be included in the plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Splint or support the incision to promote maximal comfort.
(b) Inhale slowly through the nostrils; exhale through pursed lips.
(c) Hold the breath for about 5 seconds to expand the alveoli.
(d) Repeat this breathing method 5 to 10 times hourly.
(e) Close one nostril while inhaling.
Answer:
(a) Splint or support the incision to promote maximal comfort.
(b) Inhale slowly through the nostrils; exhale through pursed lips.
(c) Hold the breath for about 5 seconds to expand the alveoli.
(d) Repeat this breathing method 5 to 10 times hourly.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) Splinting the incision is important to avoid stress on the surgical site and to promote comfort so that the client will adhere to the plan of care. Inhaling through the nostrils and exhaling through pursed lips are important to bring in adequate oxygen and clear out carbon dioxide; however, closing one nostril when inhaling would be inap-propriate and ineffective.
The most important step is asking the client to hold the inhaled breath for about 5 seconds, which keeps the alveoli expanded. This step should be stressed the most. Repeating the exercise 5 to 10 times hourly is the second most important point to emphasize in this teaching plan.
Question 28.
The nurse receives the preoperative blood work report for a client who is scheduled to undergo surgery. Which laboratory finding should the nurse report to the surgeon and anesthesiologist?
(a) red blood cells, 4.5 million/mm3 (4.5 x 1012/L)
(b) creatinine, 2.6 mg/dL (198 pmol/L)
(c) hemoglobin, 12.2 g/dL (122 g/L)
(d) blood urea nitrogen, 15 mg/dL (5.4 mmol/L)
Answer:
(b) creatinine, 2.6 mg/dL (198 pmol/L)
Explanation:
The nurse should call the surgeon for a serum creatinine level of 2.6 mg/dL (198 pmol/L), which is higher than the normal range of 0.1 to 0.4 mg/dL (8 to 31 pmol/L). An elevated serum creatinine value indicates that the kidneys are not filtering effectively and has important implications for the surgical client because many anesthesia and analgesia medications need to be filtered out through the renal system. The red blood cell count, hemoglobin level, and blood urea nitrogen level are within normal limits and do not need to be reported to the surgeon.
Question 29.
client will receive IV midazolam hydro-chloride during surgery. Which finding indicates a therapeutic effect?
(a) amnesia
(b) nausea
(c) mild agitation
(d) blurred vision
Answer:
(a) amnesia
Explanation:
Midazolam hydrochloride causes antegrade amnesia or decreased ability to remember events that occurred around the time of sedation. Nausea, mild agitation, and blurred vision are adverse effects of midazolam.
Question 30.
When administering IV midazolam hydrochloride to a client, what should the nurse do?
(a) Assess the blood pressure.
(b) Monitor the pulse oximeter.
(c) Have client take deep breaths.
(d) Help the client relax.
Answer:
(c) Have client take deep breaths.
Explanation:
The client should be encouraged to take slow, deep breaths because midazolam hydrochloride is a respiratory depressant. The nurse should assess the client’s blood pressure, monitor the pulse oximeter, and keep the client calm and relaxed, but the client will slip into very shallow, ineffective breathing if not encouraged to deep breathe
Question 31.
When the nurse administers IV midazolam hydrochloride, the client demonstrates signs of an overdose. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Ventilate with an oxygenated bag-valve mask.
(b) Prepare ECG paddles in case the client has a cardiac arrest.
(c) Administer 0.5 mL 1:1,000 epinephrine.
(d) Titrate flumazenil to reverse the effects of the midazolam hydrochloride.
Answer:
(a) Ventilate with an oxygenated bag-valve mask.
Explanation:
The nurse should have a bag-valve mask in the client’s room because midazolam hydrochloride can lead to respiratory arrest if it is administered too quickly. The client does not need to be shocked back into a normal rhythm or to receive epinephrine unless cardiac compromise developed after the respiratory arrest. The client would receive titrated dosing of flumazenil to reverse the midazolam, but first the nurse should ventilate the client.
Question 32.
Metoclopramide is prescribed as a premedication for a client about to undergo a gastroduode- noscopy. What expected therapeutic effect of this drug should the nurse assess in this client?
(a) increased gastric pH
(b) increased gastric emptying
(c) reduced anxiety
(d) inhibited respiratory secretions
Answer:
(b) increased gastric emptying
Explanation:
Metoclopramide is an antiemetic given because of its gastric emptying ability, which is necessary in gastrointestinal procedures. It does not increase gastric pH, reduce anxiety, or inhibit respiratory secretions.
Question 33.
What therapeutic outcome does the nurse expect for a client who has received a premedication of glycopyrrolate?
(a) increased heart rate
(b) increased respiratory rate
(c) decreased secretions
(d) decreased amnesia
Answer:
(c) decreased secretions
Explanation:
Glycopyrrolate is an anticholinergic given for its ability to reduce oral and respiratory secretions before general anesthesia. Increased heart rate and respiratory rate would be adverse effects of the drug. Amnesia should not be an effect of the drug.
Question 34.
Atropine sulfate is contraindicated as a pre-operative medication for which client?
A client with:
(a) diabetes.
(b) glaucoma.
(c) pyelonephritis.
(d) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Answer:
(b) glaucoma.
Explanation:
Atropine is contraindicated in clients with glaucoma because it increases intraocular pressure. It is not contraindicated in clients with diabetes, pyelonephritis, or COPD.
Question 35.
A client is to receive enoxaparin 6 hours before the scheduled time of laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy. Which effect does the nurse recognize as an intended therapeutic action of the enoxaparin?
(a) increase in red blood cell production
(b) reduction of postoperative thrombi
(c) decrease in postoperative bleeding
(d) promotion of tissue healing
Answer:
(b) reduction of postoperative thrombi
Explanation:
Research findings have shown that enoxa- parin and low-dose heparin given 6 to 12 hours preoperatively reduce the incidence of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary emboli by 60% in clients who are at risk for deep vein thrombosis, such as those who are placed in the lithotomy position. Enoxaparin has no effect on red blood cell production, postoperative bleeding, or tissue healing.
Question 36.
During the preoperative interview, the nurse obtains information about the client’s medication history. Which information is not necessary to record about the client?
(a) current use of medications, herbs, and vitamins
(b) over-the-counter medication use in the last 6 weeks
(c) steroid use in the last year
(d) all drugs taken in the last 18 months
Answer:
(d) all drugs taken in the last 18 months
Explanation:
The nurse does not need to ask about all drugs used in the last 18 months unless the client is still taking them. The nurse does need to know all drugs the client is currently taking, including herbs and vitamins, over-the-counter medications such as aspirin taken in the past 6 weeks, the amount of alcohol consumed, and use of illegal drugs, because these can interfere with the anesthetic and analgesic agents. Steroid use is of concern because it can suppress the adrenal cortex for up to 1 year, and supplemental steroids may need to be administered in times of stress such as surgery.
Question 37.
When the nurse is conducting a preoperative interview with a client who is having a vaginal hysterectomy, the client states that she forgot to tell her surgeon that she had a total hip replacement 3 years ago. Why should the nurse communicate this information to the perioperative nurse?
(a) The prosthesis may cause a problem with the electrosurgical unit used to control bleeding.
(b) The client should not have her hip externally rotated when she is positioned for the procedure.
(c) The perioperative nurse can inform the rest of the team about the total hip replacement.
(d) There is not enough time to notify the surgeon and note this finding on the history and physical information before the procedure.
Answer:
(b) The client should not have her hip externally rotated when she is positioned for the procedure.
Explanation:
The nurse should notify the surgery department and document the past surgery in the medical record U in the preoperative notes so that the client’s hip is not externally rotated and the hip dislocated while she is in the lithotomy position. The prosthesis should not be a problem as long as the perioperative nurse places the return electrode away from the prosthesis site. The perioperative nurse will inform the rest of the team, but the primary reason to inform the perioperative nurse is related to safe positioning of the client. The surgeon should enter this information on the client’s medical record at this time.

Question 38.
The nurse learns that a client who is scheduled for a tonsillectomy has been taking 40 mg of oral prednisone daily for the last week for poison ivy on the leg. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Document the prednisone with current medications.
(b) Notify the surgeon of the poison iv.
(c) Notify the anesthesiologist of the prednisone administration.
(d) Send the client to surgery.
Answer:
(c) Notify the anesthesiologist of the prednisone administration.
Explanation:
The nurse should notify the anesthesiologist because supplemental prednisone suppresses the adrenal cortex’s natural ability to produce increased corticosteroids in times of stress such as surgery. The anesthesiologist may need to prescribe supplemental steroid coverage during the perioperative period. The nurse should document the pred-nisone with current medications, but it is a priority to inform the anesthesiologist. Because the poison ivy is not in the surgical field, the surgeon does not need to be called regarding the skin disruption.
Question 39.
A client who is scheduled for an open chole-cystectomy has been smoking a pack of cigarettes a day for 20 years. For which postoperative complication is the client most at risk?
(a) deep vein thrombosis
(b) atelectasis
(c) delayed wound healing
(d) prolonged immobility
Answer:
(b) atelectasis
Explanation:
The client who has a significant cigarette smoking history and an operative manipulation close to the diaphragm (the gallbladder is against the liver) is at increased risk for atelectasis and pneumonia. Postoperatively, this client will be reluctant to deep breathe because of pain, in addition to having residual lung damage from smoking. Therefore, the client is at greater-than-average risk for pulmonary complications.
The client does not have an increased risk of prolonged immobility (unless slowed by a respiratory problem), deep vein thrombosis (as long as the client performs leg exercises), or delayed wound healing (as long as the client maintains appropriate nutrition).
Question 40.
The nurse explains to a family that they cannot go with the client past the doors that separate the public from the restricted area of the operating room suite. What is the purpose of this restriction?
(a) protection of the privacy of clients
(b) prevention of electrical sparks that could ignite the anesthetic gases
(c) separation of the family from the surgical team during the operation
(d) maintenance of an aseptic environment to prevent infection
Answer:
(d) maintenance of an aseptic environment to prevent infection
Explanation:
The purpose of separating the public from the restricted-attire area of the operating room is to provide an aseptic environment and prevent contamination of the environment by organisms. The client’s privacy is protected, but the main purpose is infection control. Anesthetics currently in use do not pose a risk of being ignited.
Question 41.
Which client is most at risk for potential hazards from the surgical experience?
(a) an 80-year-old client
(b) a 50-year-old client
(c) a 30-year-old client
(d) a 15-year-old client
Answer:
(a) an 80-year-old client
Explanation:
The 80-year-old client is at greater risk because an older adult client is more likely to have comorbid conditions, a less effective immune system, and less collagen in the integumentary system.
Question 42.
The nurse teaches a client who had cystoscopy about the urge to void when the procedure is over. What other information should the nurse tell the client to expect to do?
(a) Ignore the urge to void.
(b) Increase intake of fluids.
(c) Ask for the bedpan.
(d) Ring for assistance to go to the bathroom.
Answer:
(b) Increase intake of fluids.
Explanation:
After a scope or catheter has been inserted into the urethra, the mucosal membrane is irritated, and the client feels the need to void even though the bladder may not be full. The nurse should encourage the client to force fluids to make the urine dilute. The client should not ignore the urge to void. The client should be encouraged to use the bathroom; there is no need to use the bedpan. The client does not need assistance to the bathroom because this procedure does not require any anesthesia except a topical anesthetic for the male client.
Question 43.
Which nursing intervention is most important in preventing postoperative complications?
(a) progressive diet planning
(b) pain management
(c) bowel and elimination monitoring
(d) early ambulation
Answer:
(d) early ambulation
Explanation:
Early ambulation is the most significant general nursing measure to prevent postoperative complications and has been advocated for more than 40 years. Walking the client increases vital capacity and maintains normal respiratory functioning, stimulates circulation, prevents venous stasis, improves gastrointestinal and genitourinary function, increases muscle tone, and increases wound healing. The client should maintain a healthy diet, manage pain, and have regular bowel movements. However, early ambulation is the most important intervention.
Question 44.
When the nurse is preparing a teaching plan for an adult client about general anesthesia induction, which explanation by the nurse would be most appropriate?
(a) “Your premedication will put you to sleep.”
(b) “You will breathe in an inhalant anesthetic mixed with oxygen through a facial mask and receive intravenous medication to make you sleepy.”
(c) “You will receive intravenous medication to make you sleepy.”
(d) “You will breathe in medication through a facial mask to make you sleepy.”
Answer:
(b) “You will breathe in an inhalant anesthetic mixed with oxygen through a facial mask and receive intravenous medication to make you sleepy.”
Explanation:
Adult clients are induced for general anesthesia by breathing in an inhalant anesthetic mixed with oxygen through a facial mask and receiving intravenous medication to make them sleepy. Clients are not induced with the premedication. Clients usually are not induced with the intravenous infusion or the mask alone.
Question 45.
A client who had a gastrectomy has been in the postanesthesia recovery room for 30 minutes when the vital signs suddenly change. The nurse checks the recovery room record (see chart). In addition to notifying the health care provider, what other action should the nurse take immediately?
|
Date |
06/30 |
06/30 |
06/30 |
|
Time |
1345 |
1400 |
1415 |
|
Pulse |
70 |
82 |
90 |
|
Respiration |
12 |
14 |
20 |
|
Bloood Pressure |
100/60 |
110/70 |
140/90 |
|
Temperature |
98° F (36.7°C) |
99°F(37.2°C) |
102°F (38.9°C) |
(a) Administer dantrolene.
(b) Elevate the head of the bed 30 degrees.
(c) Administer a bolus of IV fluids.
(d) Insert an indwelling urinary catheter.
Answer:
(a) Administer dantrolene.
Explanation:
The client is demonstrating signs of malignant hyperthermia. Unless the body is cooled and the influx of calcium into the muscle cells is reversed, lethal cardiac arrhythmia and hypermetabolism occur. The client’s body temperature can rise as high as 109°F (42.8°C) as body muscles contract. Dantrolene, an IV skeletal muscle relaxant, is used to reverse muscle rigidity. Elevating the head of the bed will not reverse the hyperthermia. Adding fluids and inserting an indwelling urinary catheter are not immediately beneficial steps in reversing the progression of malignant hyperthermia.
Question 46.
To decrease a female client’s anxiety about being placed in the lithotomy position for surgery, what should the nurse do?
(a) Explain in detail what will occur in the operating room.
(b) Determine what the client is concerned about.
(c) Pad the stirrups for comfort.
(d) Reassure the client that an all-female surgical team will be present.
Answer:
(b) Determine what the client is concerned about.
Explanation:
The nurse should first attempt to find out what the client’s concerns are and address them. Providing too much information with details can increase the client’s anxiety and does not address specific concerns. Padding the stirrups will provide comfort, but this does not address concerns. Having an all-female team may or may not be the source of the client’s concerns and probably is not possible.
Question 47.
A client is to receive medication by a con-tinuous nerve block route. Prior to insertion of the catheter by the anesthesiologist, what information must the nurse document? Select all that apply.
(a) vital signs
(b) weakness/numbness
(c) location of pain
(d) results of laboratory tests
(e) allergies
Answer:
(a) vital signs
(b) weakness/numbness
(c) location of pain
(e) allergies
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e) Prior to the catheter insertion, the nurse must document location of pain and pain rating, level of consciousness (LOC), vital signs, and weakness or numbness, especially in the legs. The nurse should also ask if the client has allergies before medication administration. It is not the nurse’s responsibility to chart laboratory results; the
Question 48.
Prior to placement of an epidural/intrathecal catheter, what should the nurse instruct the client to do while the catheter is in place? Select all that apply.
(a) Take showers instead of baths.
(b) Tell the nurse about having nausea or vomiting.
(c) Call for assistance with turning or repositioning while in bed.
(d) Inform the nurse of numbness or weakness in the legs.
(e) Take shallow breaths to prevent dislodging the catheter.
(f) Call the nurse if the catheter becomes dislodged.
Answer:
(b) Tell the nurse about having nausea or vomiting.
(c) Call for assistance with turning or repositioning while in bed.
(d) Inform the nurse of numbness or weakness in the legs.
(f) Call the nurse if the catheter becomes dislodged.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d) (f) Complications may develop when a client is receiving medication via epidural, intrathecal, or continuous nerve block routes. The nurse should inform the health care provider (HCP) Q if there is a dislodged catheter, disconnected tubing, or an occluded line. The nurse must also notify the HCP if the client has nausea or vomiting as the movement involved could dislodge the catheter.
Numbness or weakness in the legs could also indicated a dislodged catheter, and the nurse must assess the client for these signs and report them if they occur. The client should call for assistance when getting out of bed or ambulating. The client should not take a shower or a bath while the cath-eter is in place. The client does not need to take shallow breaths, and the nurse should encourage the client to breathe normally and take deep breaths regularly.
Question 49.
A client arrives from surgery to the postanesthesia care unit. Which respiratory assessment should the nurse complete first?
(a) oxygen saturation
(b) respiratory rate
(c) breath sounds
(d) airway flow
Answer:
(d) airway flow
Explanation:
Airway flow is always the first assessment. Once the nurse establishes that the client has a patent airway, the pulse oximeter is applied to measure the oxygen saturation, the respiratory rate is counted, and the breath sounds are auscultated bilaterally.
Question 50.
The nurse is assessing a client who had epidural anesthesia 4 hours ago. What should the nurse assess first?
(a) bladder distention
(b) headache
(c) postoperative pain
(d) ability to move the legs
Answer:
(a) bladder distention
Explanation:
The last area to regain sensation is the perineal area, and the nurse should check the client for a distended bladder. The client has received a large volume of IV fluids since the epidural was inserted, and the client may not feel the urge to void or may be unable to void. In that case, the nurse should obtain a prescription to catheterize the client before the bladder becomes so distended as to cause bladder spasms. The nurse should assess for a spinal headache, postoperative pain, and the client’s ability to move after determining whether the bladder is distended.
Question 51.
When assessing a client who has had spinal anesthesia, which finding is expected?
(a) The client feels pain before moving the legs.
(b) The blood pressure is significantly increased.
(c) Sensation returns to the toes first and then progresses to the perineal area.
(d) The client has a headache while in the lying position.
Answer:
(c) Sensation returns to the toes first and then progresses to the perineal area.
Explanation:
Spinal anesthesia is an extensive conduction nerve block that is produced when a local anesthetic is introduced into the subarachnoid space at the lumbar level. A few minutes after induction of a spinal anesthetic, anesthesia and paralysis affect the toes and perineum and then, gradually, the legs and abdomen.
When the autonomic nervous system is blocked, vasodilation occurs and hypotension occurs. The client will feel sensation to the toes before the perineal area. A spinal headache due to loss of fluid is a severe headache that occurs while in the upright position but is relieved in the lying position
Question 52.
The nurse in the postanesthesia care unit notes that one of the client’s pupils is larger than the other. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Rate the client on the Glasgow Coma Scale.
(b) Administer oxygen.
(c) Check the client’s baseline data.
(d) Call the surgeon.
Answer:
(c) Check the client’s baseline data.
Explanation:
The nurse should check the client’s baseline data to ascertain whether the client’s pupil has always been enlarged or this is a new finding. The preoperative assessment is valuable as the baseline for comparison of all subsequent assessments made throughout the perioperative period. The nurse may determine that a more involved neurologic examination is indicated or may choose to assess other signs using the Glasgow Coma Scale, administer oxygen, or call the surgeon, but the nurse still needs to know the baseline data before proceeding.
Question 53.
A client is admitted to the postanesthesia care unit following a left hip replacement. The initial nursing assessment is as follows: temperature, 96.6°F (35.9°C); pulse, 90 bpm; respiration rate, 14 breaths/min; and blood pressure, 128/80 mm Hg. The client only responds with moaning when spoken to. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Observe the surgical dressing.
(b) Position the client on the right side.
(c) Remove the oral airway remaining from surgery.
(d) Administer sedation reversal agent such as flumazenil.
Answer:
(b) Position the client on the right side.
Explanation:
During the immediate postanesthesia period, the unconscious client should be positioned on the side to maintain an open airway and promote drainage of secretions; because of the type of surgery, the client should be positioned on the right side. Removing the oral airway and observing the surgical dressing are appropriate, but other actions should be implemented before these.
Respiratory depression can occur in a client after a procedure requiring sedation. If the client cannot be aroused, the sedation drugs can be reversed by administering a sedation reversal agent, but this client’s respiratory rate is 14, and the client is moaning, indicating expected recovery from anesthetics.
Question 54.
The surgical floor receives a client from the postanesthesia care unit. Ten minutes ago, the final assessment in the postanesthesia care unit indicated that the client had a patent airway and stable vital signs. The client’s pain level was 2. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Check the dressing for signs of bleeding.
(b) Empty any peri-incisional drains.
(c) Reassess the client’s pain level.
(d) Determine if the client has a full bladder.
Answer:
(a) Check the dressing for signs of bleeding.
Explanation:
The nurse should check the dressing for signs of bleeding to establish a baseline for future assessments of the dressing and to verify that there is no obvious sign of hemorrhage. The nurse does not need to empty peri-incisional drains at this time.
All drains should have been emptied and reconstituted by the postanesthesia care nurse before the client was transferred to the surgical floor. Assessing the client’s pain level and assessing the bladder are important; however, it is more important to assess the surgical site for bleeding because hemorrhage is a life-threatening complication of any surgical procedure.
Question 55.
A client with impaired cardiac functioning is having abdominal surgery. Sodium thiopental is being used during anesthesia induction. What should the nurse monitor the client for during the surgery?
(a) bradycardia
(b) complete muscle relaxation
(c) hypotension
(d) tachypnea
Answer:
(c) hypotension
Explanation:
Sodium pentothal, a short-acting barbiturate, can cause hypotension, which may be especially problematic for the client with impaired cardiac functioning. Sodium pentothal does not cause bradycardia, complete muscle relaxation, hypertension, or tachypnea.
Question 56.
A client received propofol as the induction and maintenance agent for general anesthesia. What outcome of this drug should the nurse expect?
(a) minimal nausea and vomiting
(b) hypertension
(c) slow induction of anesthesia
(d) small tremors of the skeletal muscles
Answer:
(a) minimal nausea and vomiting
Explanation:
Propofol, a nonbarbiturate anesthetic, causes less nausea and vomiting than do other induction agents because of a direct antiemetic action. It does not cause hypertension or skeletal muscle movement, and it does not act slowly.
Question 57.
A 250-lb (113-kg) male client is recovering from general anesthesia. The client’s vital signs are: pulse, 150 bpm; blood pressure, 90/50 mm Hg; respiratory rate, 28 breaths/min; tympanic temperature, 99.8°F (37.7°C); The client has rigid muscles. How should the nurse interpret these findings?
(a) The client is recovering as expected from the anesthesia; the nurse should continue monitoring him.
(b) The client is exhibiting the effects of excessive blood loss experienced in the operating room; the nurse should increase the rate of his IV infusion.
(c) The client is in the early stages of malignant hyperthermia; the nurse should obtain emergency medications and notify the anesthesiologist.
(d) The client is in pain; the nurse should offer him pain medication.
Answer:
(c) The client is in the early stages of malignant hyperthermia; the nurse should obtain emergency medications and notify the anesthesiologist.
Explanation:
A heart rate of 150 bpm or greater, hypotension, and muscle rigidity are early signs of malignant hyperthermia. The nurse should quickly assemble emergency supplies and personnel because malignant hyperthermia is potentially and rapidly fatal in more than 50% of cases. Rapid, extreme rise in temperature is a late sign.
Another factor influencing the analysis is that the client has a large body frame, and having large, bulky muscles is a risk factor for malignant hyperthermia. The client's vital signs are well out of the range of normal; analysis of the data and swift intervention are indicated. Excessive blood loss is unlikely, and the data do not support this conclusion. Although clients do have changes in vital signs when in acute pain, the nurse would expect the client to be hypertensive, not hypotensive.
Question 58.
The nurse is assessing a client recovering from anesthesia. Which finding is an early indicator of hypoxemia?
(a) somnolence
(b) restlessness
(c) chills
(d) urgency
Answer:
(b) restlessness
Explanation:
One of the earliest signs of hypoxia is restlessness and agitation. Decreased level of consciousness and somnolence are later signs of hypoxia. Chills can be related to the anesthetic agent used but are not indicative of hypoxia. Urgency is not related to hypoxia.
Question 59.
When administering flumazenil intravenously for reversal of sedation, what should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Administer the medication as a 2-mg bolus.
(b) Give the medication undiluted in incremental doses.
(c) Be alert for shivering and hypotension.
(d) Use only a free-flowing IV line in a large vein.
(e) Monitor the client’s level of consciousness.
Answer:
(b) Give the medication undiluted in incremental doses.
(c) Be alert for shivering and hypotension.
(d) Use only a free-flowing IV line in a large vein.
(e) Monitor the client’s level of consciousness.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d), (e) Flumazenil should be administered in small quantities such as 0.2 mg over 15 to 30 seconds but never as a bolus. Flumazenil may be given undiluted in incremental doses. Adverse effects of flumazenil may include shivering and hypotension. The nurse should monitor the client’s level of consciousness while recovering from sedation. Flumazenil should be administered through a free- flowing IV line in a large vein because extravasation causes local irritation,
Question 60.
An 80-year-old client had spinal anesthesia for a transurethral resection of the prostate and received 4,000 mL of room temperature isotonic bladder irrigation. He now has continuous irrigation through a three-way indwelling urinary catheter. Which postoperative nursing intervention is most important to include in his plan of care?
(a) Empty the catheter drainage bag.
(b) Cover the client with warm blankets.
(c) Hang new bags of irrigation.
(d) Turn the client.
Answer:
(b) Cover the client with warm blankets.
Explanation:
It is important for the nurse to cover this client with warm blankets because he is at high risk for hypothermia secondary to age, spinal anesthesia, placement in a lithotomy position in the cool operating room for 1.5 hours, instillation of 4,000 mL of room temperature bladder irrigation, and ongoing bladder irrigation.
Spinal anesthesia causes vasodilation, which results in heat loss from the core to the periphery. The nurse will empty the catheter drainage bag and hang new bags of irrigation as needed, but the client’s potential for hypothermia should be addressed first. The client will not be turned at this time.
Question 61.
Which client is expected to retain anesthetic agents longest?
A client who is:
(a) 6 feet 2 inches tall (188 cm) and weighs 250lb (113 kg)
(b) 5 feet 4 inches (163 cm) tall and weighs 110lb (49.9 kg)
(c) 5 feet 1 inches (155 cm) tall and weighs 200lb (90.7 kg)
(d) 5 feet 7 inches (170 cm) tall and weighs 145lb (65.8 kg)
Answer:
(c) 5 feet 1 inches (155 cm) tall and weighs 200lb (90.7 kg)
Explanation:
The client who is 5 feet 1 inch tall (155 cm) and weighs 200 lb (90.7 kg) would be expected to retain the anesthetic agents longer because adipose tissue absorbs the drug before the desired systemic effect is reached for anesthesia maintenance. Nursing interventions are aimed at encouraging the obese client to turn, cough, and deep breathe despite feeling sleepy and tired. The sooner this client ambulates, the sooner the retained anesthesia will be worked out of the adipose tissue.
Question 62.
Prior having a broken arm casted, the client received an intravenous regional nerve block (Bier block). Following surgery, the casted arm is elevated on a pillow. What action should the nurse encourage the client to avoid until sensation returns?
(a) holding the operated arm close to the face
(b) holding the operated arm with the unoperatedarm
(c) using the unoperated arm
(d) using pain medication
Answer:
(a) holding the operated arm close to the face
Explanation:
The nurse should encourage the client to avoid holding the operated arm, the arm with the intravenous regional nerve block (Bier block), close to the face because the client does not have motor control over it. With the cast in place, the client could hit the eye, nose, or mouth and cause soft tissue damage. It is acceptable for the client to hold the operated arm with the unoperated arm or to use the unoperated arm. The nurse should administer the analgesic before the intravenous regional anesthetic completely wears off so that the pain does not peak before pain medication is administered.
Question 63.
The health care provider prescribed intravenous naloxone to reverse the respiratory depression from morphine administration. After administration of the naloxone, what should the nurse do?
(a) Check respirations in 5 minutes because naloxone is immediately effective in relieving respiratory depression.
(b) Check respirations in 30 minutes because the effects of morphine will have worn off by then.
(c) Monitor respirations frequently for 4 to 6 hours because the client may need repeated doses of naloxone.
(d) Monitor respirations each time the client receives morphine sulfate 10 mg IM.
Answer:
(c) Monitor respirations frequently for 4 to 6 hours because the client may need repeated doses of naloxone.
Explanation:
The nurse should monitor the client’s respirations closely for 4 to 6 hours because naloxone has a shorter duration of action than do opioids. The client may need repeated doses of naloxone to prevent or treat a recurrence of the respiratory depression. Naloxone is usually effective in a few minutes; however, its effects last only 1 to 2 hours, and ongoing monitoring of the client’s respiratory rate will be necessary. The client’s dosage of morphine will be decreased or a new drug will be prescribed to prevent another instance of respiratory depression.
Question 64.
When administering naloxone, the nurse should monitor the surgical client closely for which clinical manifestation?
(a) restlessness
(b) dizziness
(c) bleeding
(d) urine retention
Answer:
(a) restlessness
Explanation:
The nurse should monitor the client who has received naloxone for side effects such as restlessness, agitation, and potential cardiac arrhythmias. Bleeding, dizziness, and urine retention are not typical side effects of naloxone.
Question 65.
The nurse is to administer midazolam 2.5 mg. The medication is available in a 5-mg/mL vial. How many mL should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal point .................. mL.
Answer:
0.5 mL. To obtain the answer, treat the volume to be administered as X.
Explanation:
imm
5x = 2.5
x = 2.5/5 = 0.5
Question 66.
On the first day after abdominal surgery, the nurse auscultates a client’s abdomen for bowel sounds; there are none. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Ask another nurse to validate the absence of bowel sounds.
(c) Encourage the client to take more ice chips.
(d) Document assessment findings in the client’s medical record.
Answer:
(d) Document assessment findings in the client’s medical record.
Explanation:
Bowel sounds are not present until the 3rd or 4th postoperative day; the nurse should document the assessment findings. Since this is an expected finding it is not necessary to notify the HCP or have another nurse validate the findings. Too many ice chips may promote abdominal distention, especially if the client is not ambulating in the intermediate postoperative period.
Question 67.
Three days after a cholecystectomy, a client states, “I feel like my stomach is going to burst.” The client is taking a regular diet. After determining that vital signs are stable, in which order of priority from first to last does the nurse assist the client? All options must be used.
(a) Position the client on the right side.
(b) Offer 120 mL of hot liquids.
(c) Auscultate for bowel sounds.
(d) Encourage ambulation.
Answer:
(c) Auscultate for bowel sounds.
(b) Offer 120 mL of hot liquids.
(a) Position the client on the right side.
(d) Encourage ambulation.
Explanation:
(c), (b), (a), (d) The nurse first auscultates the abdomen for bowel sounds to determine if peristalsis has resumed and is present. The nurse then administers hot liquids to stimulate peristalsis and promote expulsion of the gas that is causing the client to be uncomfortable. Positioning the client on the right side permits gas to rise along the transverse colon and facilitates its release. Abdominal distention may be minimized by early and frequent ambulation, which stimulates intestinal motility. The nurse also assists the client to ambulate.
Question 68.
The nurse assesses that a client is restless and becoming agitated in the immediate postoperative period. The client’s oxygen saturation is 91%. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Administer a sedative.
(b) Offer ice chips.
(c) Administer oxygen.
(d) Apply wrist restraints.
Answer:
(c) Administer oxygen.
Explanation:
Restlessness in the immediate postoperative period may be a sign of cerebral hypoxia as a result of depression on the central nervous from anesthetic agents and sedatives. Administering sedatives would depress the central nervous system further. A client may aspirate ice chips when he or she is restless. Wrist restraints may increase agitation and cannot be used without justification.
Question 69.
A client requests a narcotic analgesic shortly after the oncoming nurse receives change-of-shift report. The nurse who is leaving reported that the client had received morphine 10 mg (IM) 2 hours ago. In what order from first to last should the oncoming registered nurse (RN) perform the actions? All options must be used.
(a) Take the client’s vital signs.
(b) Asses the client for pain using a pain scale.
(c) Review the prescription for dose and frequency of administration.
(d) Determine the client’s sedation level using the Opioid-induced Sedation Scale.
Answer:
(b) Asses the client for pain using a pain scale.
(a) Take the client’s vital signs.
(c) Review the prescription for dose and frequency of administration.
Explanation:
(b), (a), (c), The oncoming nurse should first assess the client for pain using a pain scale. Next, the nurse should check the client’s vital signs, and then check the client’s level of sedation using a scale that assesses levels of sedation for clients receiving opioids such as the Opioid-induced Sedation Scale. Last, the nurse should review the prescription to see how often and at what dose the client can receive the pain medication
Question 70.
A client is prescribed morphine sulfate intramuscularly (IM). Which is true regarding administration of this controlled substance?
(a) Morphine may only be administered by a registered nurse.
(b) Another nurse must observe disposal of unused medication.
(c) Another nurse must validate administration of the medication.
(d) A registered nurse must observe the licensed practical/vocational nurse administer the medication.
Answer:
(b) Another nurse must observe disposal of unused medication.
Explanation:
Morphine sulfate and other narcotics are carefully controlled by state and federal guidelines, including observation and documentation of any unused (“wasted”) medication. While administering morphine intravenously is not within the scope of practice of a licensed nurse, IM morphine may be given by a registered or licensed nurse without observation or validation by another nurse.
Question 71.
A client who is a Jehovah’s Witness consented to surgery only and not to receiving any blood products, including autotransfusion. During surgery, the client lost blood, the blood pressure dropped, and two units of blood were administered. Following surgery, during handover the nurse was informed that the blood had been administered. In which order, from first to last should the nurse complete these tasks?
(a) Complete an incident report.
(b) Initiate an ethics consultation.
(c) Notify the unit manager.
(d) Inform the next oncoming nurse during hand off of care report.
Answer:
(b) Initiate an ethics consultation.
(c) Notify the unit manager.
(a) Complete an incident report.
(d) Inform the next oncoming nurse during hand off of care report.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (a), (d) Anyone (client, family, nurse) can initiate an ethics consultation for guidance in the event an ethical or legal concern arises. As a requirement for accreditation, ethics teams are available for consultation at all times, and the nurse could initiate a request for this consultation. The nurse manager would be notified shortly after the ethics consultation request.
The nurse manager wall consult with corporate legal and risk management related to the next steps. An incident report would be completed, and all parties would be notified including the surgeon and client. During shift hand off care report, the oncoming nurse would be informed of the incident and the actions completed.
Question 72.
On the day of surgery, a client has been breathing room air. The vital signs are normal, and the O2 saturation is 89%. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Lower the head of the bed.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Assist the client to take several deep breaths and cough.
(d) Administer oxygen by nasal cannula as prescribed at 2 L/min.
Answer:
(c) Assist the client to take several deep breaths and cough.
Explanation:
Deep breathing and coughing help to increase lung expansion and prevent the accumulation of secretions in postoperative clients. An CL saturation of 89% is not an unexpected or emergent finding immediately following surgery. Frequent coughing and deep breathing will likely quickly remedy an O2 saturation of 89% but will also effec-tively help to prevent atelectasis and pneumonia in the remainder of the postoperative period.
It is not necessary to notify the HCP QJ prior to intervening with coughing/deep breathing, and it is not appropriate to position this client with the head of the bed lower because this would make it more difficult for the client to expectorate secretions. Oxygen may be necessary, but the nurse should assist the client to cough and deep breathe first, in an attempt to improve his oxygenation and saturation.
Question 73.
A client has been unable to void since having abdominal surgery 7 hours ago. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Encourage the client to increase oral fluid intake.
(b) Insert an intermittent urinary catheter.
(c) Use an ultrasound bladder scanner to determine urine volume in the bladder.
(d) Assist the client up to the toilet to attempt to void.
Answer:
(d) Assist the client up to the toilet to attempt to void.
Explanation:
Urinary retention is common following abdominal surgery. The nurse should first assist the client to an anatomically comfortable position to void prior to resorting to other strategies such as cauterization. If the client is unable to void, the nurse can use a bladder scanner to determine the volume of retained urine, and then, if necessary, use an intermittent urinary catheter. While increasing fluid intake is important, it will not help the client void now.
Question 74.
Following abdominal surgery, a client refuses to deep breathe and cough every 2 hours as prescribed. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Ask the client’s wife to insist that the client take the deep breaths every 2 hours.
(b) Respect the client’s wishes, and turn the client from side to side more frequently.
(c) Suggest that the client increase the daily fluid intake to at least 2,500 mL.
(d) Explain the risks of not expanding the lungs and why the exercise is important.
Answer:
(d) Explain the risks of not expanding the lungs and why the exercise is important.
Explanation:
Following surgery, clients are at risk for respiratory complications and should take the necessary actions to prevent these. The nurse should first be sure that the client understands how to do the exercises and the potential complications if they are not done. It is not the wife’s responsibility to make the client do the exercise, but she can help. Increasing fluid intake and frequent turning are appropriate, but these measures are not sufficient for aerating the lungs.

Question 75.
Eight hours after laparoscopic abdominal surgery, a client has a distended bladder and is unable to void in bed using a urinal. The client can be out of bed as tolerated, but has not done so yet. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Assist the client to stand at the bedside to use the urinal.
(b) Pour running water over perineum to stimulate emptying of the bladder.
(c) Encourage the client to ambulate to prevent further bladder distention.
(d) Notify the health care provider to request a prescription for catheterization.
Answer:
(a) Assist the client to stand at the bedside to use the urinal.
Explanation:
The nurse should first try to facilitate the client’s ability to void by having the client stand at the bedside and use the urinal. Pouring running water over the perineum is a strategy that could be used if the client cannot void in a standing position. Ambulation will not help the client void. If such conservative methods fail, the nurse should obtain a prescription to catheterize the client, but an indwelling urinary catheter increases the risk of urinary tract infection because microbes ascend the catheter and travel to the bladder.
Question 76.
The nurse is assessing the level of consciousness for a client who just had open heart surgery. When asked, the client can give his name but is not sure about where he is or the time of day. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the surgeon.
(b) Rub the client’s sternum to arouse the client.
(c) Encourage the client’s wife to orient the client.
(d) Tell the client where he is and the time of day.
Answer:
(d) Tell the client where he is and the time of day.
Explanation:
The first cognitive response that returns after anesthesia is orientation to person. The nurse assesses this by asking the client his name. Orientation to place and time usually occurs after orientation by the nurse because of confusion from anesthesia and waking in an unfamiliar place.
The nurse can then continue to assess and document the client’s cognitive ability to remember information. The nurse does not need to notify the surgeon. The client’s cognitive response is normal. It is not necessary to ask the wife to reorient the client; however, she can continue to talk to him and help him regain consciousness.
Question 77.
Following surgery, a client is receiving 1,000 mL normal saline (IV) with 40 mEq (40 mmol/L) KC1, which has been prescribed to be infused at 125 mL/h. The client states, “My IV hurts.” What should the nurse do first?
(a) Contact the client’s health care provider (HCP) for a different IV prescription.
(b) Slow down the infusion to a keep-open rate (20 to 50 mL/h).
(c) Assess the IV site for signs of phlebitis, extravasation, or IV-related infection.
(d) Check the hanging parenteral fluid and administration set for documentation as to when they were last changed.
Answer:
(c) Assess the IV site for signs of phlebitis, extravasation, or IV-related infection.
Explanation:
Potassium in an IV solution may be irritating to a vein. The nurse should assess the IV site before taking any of the other actions listed. The infusion may have to be slowed and/or stopped, and the HCP contacted. An outdated parenteral fluid setup does not cause pain, but it may be a source of infection.
Question 78.
A nurse is assessing a client when she returns from same-day surgery for a dilatation and curettage. The nurse checks preoperative vital signs at 0830 to compare them with the current vital signs at 2230 (see chart). What should the nurse do first?
|
Pulse |
70 |
82 |
90 |
|
Respiration |
12 |
14 |
20 |
|
Bloood Pressure |
100/60 |
110/70 |
140/90 |
|
Temperature |
98° F (36.7°C) |
99°F(37.2°C) |
102°F (38.9°C) |
(a) CalI the health care provider for pain medication.
(b) Cover the client with warmed blankets.
(c) Administer oxygen at 4 L/min.
(d) Increase the IV fluid rate.
Answer:
(b) Cover the client with warmed blankets.
Explanation:
The client’s body temperature dropped 2.5°F (1.4°C) from the preoperative to postoperative phase. The client lost heat during the preoperative period. The client has not had time to regain the heat she has lost and should not be discharged postoperatively until her postoperative vital signs, which include body temperature, are closer to her preoperative vital signs.
The client’s pulse rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure have compensated according to the client’s hypothermic state and will reflect changes as the client warms up. There are no indications that the client needs more pain medication, oxygen, or IV fluids.
Question 79.
The nurse is caring for a client receiving morphine in an intravenous infusion using a patient-controlled anesthesia pump (PCA) for relief of postoperative pain. On assessment, the client’s vital signs are as follows: heart rate, 84 bpm; respirations, 8 breaths/min; blood pressure, 104/56 mm Hg; and oxygen saturation of 88% on room air. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Contact the health care provider (HCP) to request a prescription for naloxone.
(b) Stop the infusion of morphine.
(c) Assist the client to sit and stimulate coughing/deep breathing.
(d) Call the rapid response team.
Answer:
(c) Assist the client to sit and stimulate coughing/deep breathing.
Explanation:
The client still has a respiratory rate of 8; the nurse should first assist the client to sit and stimulate the client to take deep breaths and cough. This action will also help the nurse to determine what the client’s level of sedation is if the client is too sedated to cooperate with coughing/deep breathing, it will be important to slow or stop the infusion of narcotics and to consider contacting the HCP for a prescription for naloxone. The client is still breathing, so it is not necessary to call the rapid response team
Question 80.
A client had a colectomy 8V2 hours ago and has received 1,500 mL of dextrose 5% in water with normal saline solution. The client has just used a patient-controlled analgesia pump to administer morphine for pain, has been repositioned for comfort, and has stable pulse rate, respirations, and blood pressure. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Check that the family is comfortable.
(b) Assess vital signs following the use of morphine.
(c) Dim the lights in the room.
(d) Increase nasal oxygen from 2 to 3 L.
Answer:
(c) Dim the lights in the room.
Explanation:
The nurse is helping the client manage pain and comfort level. The nurse has completed the assessment of the client and should now dim the lights and create a quiet environment. Such non- pharmacologic measures as adjusting the light level in the room facilitate pain management. Decreasing stimulation from the environment, such as brightness to the optic nerve, promotes the client’s ability to relax skeletal muscles and fall asleep.
It is too soon to reassess vital signs. Checking that the family is comfortable is important, but it is not the next thing to do for this client. Increasing the oxygen flow rate is not indicated and, if needed, should have been done before repositioning the client.
Question 81.
A client who had an esophageal hernia repair 4 hours ago has a pulse rate of 90 bpm; respiration rate of 16 breaths/min; blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg; pulse oximeter of 91%, on room air; and a temperature of 100.4°F (38°C). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Obtain a culture of the incision.
(b) Notify the surgeon to obtain an antibiotic prescription.
(c) Offer pain medication.
(d) Assist the client to a sitting position to take deep breaths.
Answer:
(d) Assist the client to a sitting position to take deep breaths.
Explanation:
When a postoperative client has a temperature elevation to >100°F (37.8°C) in the first 24 hours after surgery, the temperature elevation is usually related to atelectasis. Because this client had upper abdominal surgery with manipulation around the diaphragm, the client is more prone to guarding the operative site and shallow breathing. Encouraging the client to take deep breaths and use incentive spirometry is an appropriate measure to prevent atelectasis and pulmonary infection.
The nurse must assist the client in filling the alveoli in the lower posterior lobes of the lungs. An incentive spirometer is a good visual biofeedback instrument that the client had practiced with preoperatively. Changing the client’s position from lying to sitting for deep breathing will expand alveoli in the lower posterior lobes. There is no indication that a surgical wound infection is occurring. An antibiotic is not indicated at this time. Pain medication will decrease respirations, and the client is not indicating pain at the moment.
Question 82.
After teaching the client how to use the patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump, the nurse determines that the client understands the use of the PCA when the client makes which statement?
(a) “It’s OK for my family to press the button for me if I’m too tired to do it myself.”
(b) “I should wait until the pain is really bad before I push the button to get more pain medicine.”
(c) “The machine will only give me the prescribed amount of pain medication even if I push the button too soon.”
(d) “I have to be careful about pushing the button too many times or I will overdose myself.”
Answer:
(c) “The machine will only give me the prescribed amount of pain medication even if I push the button too soon.”
Explanation:
The client must be able to verbalize understanding about receiving no more pain medication than is prescribed no matter how many times the button is pushed. Only the client should press the button for the PCA. The client should administer the pain medication when the pain is first noticed, well before the pain is out of control. One of the advantages of the PCA is that the amount of pain medication is controlled; therefore, overdosing is not a client concern when using a PCA.
Question 83.
A client had a total abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral oophorectomy for ovarian carcinoma yesterday. She received 2 mg of morphine sulfate IV by patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) 10 minutes ago. The nurse was assisting her from the bed to a chair when the client felt dizzy and fell into the chair. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Discontinue the PCA pump.
(b) Administer oxygen.
(c) Take the client’s blood pressure.
(d) Assist the client back to bed.
Answer:
(c) Take the client’s blood pressure.
Explanation:
The nurse should take the client’s blood pressure. She is likely experiencing orthostatic hypotension. The PCA pump does not need to be discontinued because as soon as the blood pressure stabilizes the pain medication can be resumed. Administering oxygen is not necessary unless the oxygen saturation also drops. The client should sit in the chair until the blood pressure stabilizes.
Question 84.
Immediately following pelvic surgery, a client has an indwelling urinary catheter. Which nursing action would be most helpful to prevent a catheter-related urinary tract infection?
(a) Provide catheter and perineal care twice daily.
(b) Monitor the color, clarity, and amount of urine output.
(c) Advocate for limited use of and duration of indwelling urinary catheters.
(d) Palpate for lower abdominal distension once per shift.
Answer:
(c) Advocate for limited use of and duration of indwelling urinary catheters.
Explanation:
Urinary catheters should be limited in use and duration only as needed for client care. The guideline also specifies that if used, the catheter should be inserted using aseptic technique, secured to provide unobstructed flow and drainage, and maintained in a way that protects sterility of the catheter and the drainage system. It is not necessary to provide catheter care or cleanse the meatus as these can be a source of introducing an infection; it is not necessary to check for bladder distention if the catheter is draining correctly.
Question 85.
A nurse is instructing a client who had abdominal surgery that day to do deep-breathing exercises. In which order from first to last should the nurse teach the client to perform diaphragmatic breathing and coughing? All options must be used.
(a) Inhale through the nose.
(b) Cough deeply from the lungs.
(c) Exhale through pursed lips.
(d) Splint the incisional site.
Answer:
(d) Splint the incisional site.
(a) Inhale through the nose.
(c) Exhale through pursed lips.
(b) Cough deeply from the lungs.
Explanation:
(d), (a), (c), (b) The client must first splint the incision to avoid increased intolerable pain, or he or she may not cooperate with the pulmonary ventilation. The next step is to inhale oxygen to expand the alveoli for a few seconds and then exhale carbon dioxide in successive steps 5 to 10 times. The client should try to cough on the end of the exhalation to remove retained secretions from the larger airways.
Question 86.
The postoperative nursing assessment of a client’s ability to swallow fluids before providing oral fluids is based on the type of anesthesia given. Which client would not have delayed fluid restrictions?
The client who had:
(a) a bronchoscopy under local anesthesia.
(b) a transurethral resection of a bladder tumor under general anesthesia.
(c) a repair of carpal tunnel syndrome under local anesthesia.
(d) an inguinal herniorrhaphy with spinal and intravenous conscious sedation.
Answer:
(c) a repair of carpal tunnel syndrome under local anesthesia.
Explanation:
The client who has not had the gag reflex anesthetized is the client who had a repair of the carpal tunnel syndrome under local anesthesia because the area being anesthetized was the tissue in the wrist. The client who had a bronchoscopy received a local anesthetic on the vocal cords, and the nurse should check the gag reflex or ability to swallow before administering fluids.
Clients who had general anesthesia or intravenous conscious sedation received medication for central nervous system sedation, and the nurse should assess the level of consciousness and ability to swallow before administering fluids.
Question 87.
The client has just returned to bed following the first ambulation since abdominal surgery. The client’s heart rate and blood pressure are slightly elevated; oxygen saturation is 91% on room air. The client reports being “a little short of breath,” but does not have dizziness or pain. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Obtain a 12-lead ECG.
(b) Administer pain medication.
(c) Allow the client to rest for a few minutes, then reassess.
(d) Request new activity prescriptions from the health care provider.
Answer:
(c) Allow the client to rest for a few minutes, then reassess.
Explanation:
The client is experiencing activity intolerance, which is common following the first ambulation following surgery. The nurse should allow the client to rest and continue to monitor vital signs. Since the client is not dizzy or in pain, the nurse should wait to see if the client recovers from ambu-lating and reports having pain prior to administering pain medication. There is no need to request different activity prescriptions; it will still be important for the client to ambulate. The client is not having chest pain; it is not necessary to obtain a 12-lead ECG.
Question 88.
Eight hours following bowel surgery, the nurse observes that the client’s urine output has decreased from 50 to 20 mL/h. The nurse should assess the client further for which condition?
(a) bowel obstruction
(b) adverse effect of opioid analgesics
(c) hemorrhage
(d) hypertension
Answer:
(c) hemorrhage
Explanation:
When the urine output is < 30 mL/h, the nurse should assess for potential causes such as hypovolemia or hemorrhage. The nurse should assess and evaluate the client’s vital signs, intake and output, dressing, and available laboratory values and notify the health care provider (HCP). Bowel obstruction, although possible after surgery, is characterized most notably by abdominal distention and absent bowel sounds, not decreased urine output. The nurse would not expect the client to have hypertension, but rather hypotension.
Question 89.
A client who had a left thoracoscopy sustained an injury secondary to the surgery position. The nurse should assess the client for which sign?
(a) foot drop
(b) knee swelling and pain
(c) tingling in the arm
(d) absence of the Achilles reflex
Answer:
(c) tingling in the arm
Explanation:
A client who had a left thoracoscopy is placed in the lateral position, in which the most common injury is an injury to the brachial plexus. Numbness and tingling in the arm suggests a brachial plexus injury. There is no undue pressure on the ankles or knees during thoracic surgery
Question 90.
The nurse is evaluating a client who is using a flow incentive spirometer (see figure) following abdominal surgery 1 day ago. The client is performing the procedure correctly when the client does what? Select all that apply.
(a) inhales before using the spirometer
(b) inhales for 3 seconds following fully expanding the lungs
(c) coughs after using the spirometer
(d) uses the spirometer once every 8 hours
(e) exhales passively before using the spirometer
(f) sits upright
Answer:
(b) inhales for 3 seconds following fully expanding the lungs
(c) coughs after using the spirometer
(e) exhales passively before using the spirometer
(f) sits upright
Explanation:
(b), (c), (e), (f) The client should be in an upright position when using the spirometer. The client should exhale fully prior to using the spirometer and then inhale to expand the lungs and continue inhaling for 3 more seconds. The client should relax and exhale before inhaling for the next use of the spirometer. The client should cough and clear retained secretions following the use of the spirometer. The client should use the spirometer every 2 hours during the immediate postoperative period.
Question 91.
The nurse is teaching a client how to take care of an incision at home. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “Don’t touch your incision before your next appointment.”
(b) “Clean your incision three times a day with hydrogen peroxide and water.”
(c) “Don’t be concerned about uneven lumps under the suture lines.”
(d) “If the staples don’t come out by themselves before your next appointment, the surgeon will remove them.”
Answer:
(c) “Don’t be concerned about uneven lumps under the suture lines.”
Explanation:
The nurse should inform the client that as the incision heals, uneven lumps might appear under the incision line because the collagen is growing new tissue at different rates. Eventually, the lumps will even out, and the tissue will be smooth. The client can touch the incision with clean hands as needed to perform incisional care. The client should not clean the incision with hydrogen peroxide because it may dry out the natural skin oils. The surgeon will remove the staples for the client.
Question 92.
The nurse is removing the client’s staples from an abdominal incision when the client sneezes and the incision splits open, exposing the intestines. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Press the emergency alarm to call the resuscitation team.
(b) Cover the abdominal organs with sterile dressings moistened with sterile normal saline.
(c) Have all visitors and family leave the room.
(d) Call the surgeon to come to the client’s room immediately.
Answer:
(b) Cover the abdominal organs with sterile dressings moistened with sterile normal saline.
Explanation:
When a wound eviscerates (abdominal organs protruding through the opened incision), the nurse should cover the open area with a sterile dressing moistened with sterile normal saline and then cover it with a dry dressing. The surgeon should then be notified to take the client back to the operating room to close the incision under general anesthesia.
The nurse should not press the emergency alarm because this is not a cardiac or respiratory arrest. The nurse should have the visitors and family leave the room to decrease the chance of airborne contamination, but the primary focus should be on covering the wound with a moist, sterile covering.
Question 93.
On the fourth day after surgery, a client’s incision is red and inflamed. There is moderate drainage from the incision. The client has a temperature of 102°F (38.9°C). The total white blood count (WBC) 10,000/mm3 (10 x 109/L). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Encourage the client to increase the fluid intake.
(b) Cleanse the incision site with soap and water.
(c) Place an absorbent dressing over the incision.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
The findings (WBC count above normal; inflammation and drainage at the incision site; and an elevated temperature) indicate that the client has an infection. The nurse should first notify the HCP Encouraging fluids will be helpful, but it is not the first action. The nurse should not cleanse the site or place a dressing over the incision until the HCP writes a prescription to do so.
Question 94.
The nurse is making rounds and observes the client receiving oxygen (see figure). What should the nurse do next?
(a) Position the mask tower on the client’s nose.
(b) Verify that the reservoir bag remains deflate
(c) Confirm that the flow rate is set to deliver oxygen at 6 to 10 L/min.
(d) Loosen the elastic hand on the clients face.
Answer:
(c) Confirm that the flow rate is set to deliver oxygen at 6 to 10 L/min.
Explanation:
The client is receiving oxygen using a partial rebreathing mask, which is positioned correctly. The correct flow rate for this type of oxygen mask is 6 to 10 L of oxygen per minute. To be effective, the mask must cover the client’s face. The elastic band must be tight enough to secure the mask. When used correctly, the reservoir bag should inflate during the inspiratory phase.
Question 95.
When changing a wet-to-dry dressing covering a surgical wound, what should the nurse do?
(a) Place a dry dressing in the wound.
(b) Use an aqueous solution of aluminum acetate (Burow's solution) to wet the dressing.
(c) Pack the wet dressing tightly into the wound.
(d) Cover the wet packing with a dry sterile dressing.
Answer:
(d) Cover the wet packing with a dry sterile dressing.
Explanation:
A wet-to-dry dressing should be able to dry out between dressing changes. Thus, the dressing should be moist, not dry, when applied. As the moist dressing dries, the wound will be debrided of necrotic tissue and exudate. Normal saline is most commonly used to moisten the sponge; Burow’s solu-tion will irritate the wound. The sponge should not be packed into the wound tightly because the circulation to the site could be impaired.
The moist sponge should be placed so that all surfaces of the wound are in contact with the dressing. Then the sponge is covered and protected by a dry sterile dressing to prevent contamination from the external environment.
Question 96.
Two days following abdominal surgery, a client is refusing to take a narcotic pain medication, even though the pain rating is an 8 on a 0 to 10 scale. The client tells the nurse, “I don’t want to get dependent on that stuff.” Which response from the nurse is the most appropriate?
(a) “You will recover more quickly and more effectively if you take pain medication now. ”
(b) “Newer pain medications don’t cause dependence or addiction.”
(c) “It’s your right to not take pain medication.”
(d) “You don’t need to worry about becoming addicted so soon.”
Answer:
(a) “You will recover more quickly and more effectively if you take pain medication now. ”
Explanation:
Common client misconceptions regarding pain and pain medication administration include a concern that taking pain medication regularly will lead to addiction. However, this misconception overstates the risk of addiction and greatly understates the risk of immobility due to poor pain control, including atelectasis, decubitus formation, and delayed healing.
The nurse should assist the client to understand the importance of adequate pain medication to support and promote client mobilization following surgery and client/family satisfaction with care. There is a potential for dependence and addiction with all narcotic drugs, although this is not likely during the postoperative period.
Question 97.
The nurse empties a Jackson-Pratt drainage bulb. Which nursing action ensures correct functioning of the drain?
(a) irrigating it with normal saline
(b) connecting it to low intermittent suction
(c) compressing it and then plugging it to establish suction
(d) connecting it to a drainage bag and clamping it off
Answer:
(c) compressing it and then plugging it to establish suction
Explanation:
After emptying a Jackson-Pratt drainage bulb, the nurse should compress the bulb, plug it to establish suction, and then document the amount and type of drainage emptied. Irrigating a Jackson- Pratt drain is inappropriate because it could contaminate the wound. The Jackson-Pratt drain is not usually connected to wall suction. The purpose of the Jackson-Pratt drain is to remove bloody drainage from the deep tissues of the incision; clamping the drain would be counterproductive.
Question 98.
To prevent pulmonary emboli in a client who has had abdominal surgery, what should the nurse do?
(a) Have the client perform leg exercises every hour while awake.
(b) Encourage the client to cough and deep breathe.
(C) Massage the client’s calves.
(d) Have the client wear antiembolism stockings when out of bed.
Answer:
(a) Have the client perform leg exercises every hour while awake.
Explanation:
Performing leg exercises, including ankle pumping, ankle rotation, and quadriceps setting exercises, will help prevent stasis of blood in the lower extremities, which can lead to blood clot formation. Encouraging the client to cough and deep breathe is an important postoperative intervention; however, it is directed at preventing pneumonia, not pulmonary emboli. The nurse should not massage the calves because a deep vein thrombus could dislodge and travel to the pulmonary vasculature. Antiembolism stockings should be worn continuously during the postoperative period.
Question 99.
The nurse assesses a client who has just received morphine sulfate. The client’s blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg; pulse rate, 58 bpm; and respiration rate, 4 breaths/min. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Call the rapid response team.
(b) Administer naloxone hydrochloride.
(c) Start oxygen at 2 liters/min per nasal cannula.
(d) Obtain a stat ECG.
Answer:
(b) Administer naloxone hydrochloride.
Explanation:
The nurse should first administer naloxone hydrochloride, which is the antidote for morphine sulfate. The signs of overdose on morphine sulfate are a respiration rate of 2 to 4 breaths/min, bradycardia, and hypotension. If the client does not respond, the nurse can call the rapid response team D The client’s respirations should improve after receiving the naloxone. Obtaining an ECG is not the first priority for reversing the effects of the morphine.
Question 100.
The nurse observes the client with an intermittent compression device in place after abdominal surgery (see figure). What should the nurse do next?
(a) Elevate the client’s legs.
(b) Apply thromboembolic stockings to be worn under the device.
(c) Instruct the client not to move while the device is inflated.
(d) Make sure the client is comfortable.
Answer:
(d) Make sure the client is comfortable.
Explanation:
The device is applied correctly, and the nurse should ensure the client’s comfort. The client’s legs should remain extended as shown while using the device; legs may be elevated, but it is not necessary to elevate the client’s legs. The device should be placed directly on the client’s legs; it is not necessary to apply antiembolic stockings under them. The client may move in bed as needed; active and isometric movement is encouraged to promote blood flow.
Question 101.
A client is being discharged from same-day surgery. Which statement indicates that the client does not understand postoperative instructions about transportation to home?
(a) “My husband is taking the day off from work to drive me home.”
(b) “I can drive myself home after surgery.”
(c) “I am taking a taxi home, and my daughter will meet me at home.”
(d) “My son will be here at noon to take me home.”
Answer:
(b) “I can drive myself home after surgery.”
Explanation:
The client admitted for same-day surgery should not drive home after the surgical procedure because it is unsafe. Even without an anesthetic, the surgical event can be more stressful than anticipated. It is acceptable to have someone arrive after the surgery has started to take the client home. A taxi is permissible but not desirable.
Question 102.
The initial postoperative assessment is completed on a client who had an arthroscopy of the knee. Which information is not necessary to obtain every 15 minutes during the first postoperative hour?
(a) vital signs including pulse oximeter
(b) pain rating of the operative site
(c) urine output
(d) neurovascular check distal to the operative site
Answer:
(c) urine output
Explanation:
The urine output does not have to be checked every 15 minutes for a client who has had an arthroscopy because this client probably does not have a catheter in place. If the client voids, the output would be recorded. Assessments every 15 minutes during the first hour would include vital signs, pulse oximeter values, and pain to monitor the client’s comfort level and check for compartment syndrome.
Neurovascular checks distal to the operative site are especially vital because a tourniquet was used proximal to the operative site during the surgical procedure and because edema may develop during the postoperative period.
Question 103.
After surgery, a client was treated for postoperative nausea and vomiting and now is experiencing hypotension and tachycardia. The nurse should review the medication record to determine if the client has received which medication?
(a) ondansetron hydrochloride
(b) droperidol
(c) prochlorperazine
(d) promethazine
Answer:
(b) droperidol
Explanation:
Hypotension and tachycardia are common adverse effects of droperidol and should be monitored closely by the nurse. Hypotension and tachycardia are not common adverse effects of ondansetron hydrochloride, prochlorperazine, or promethazine.
Question 104.
When an epidural catheter is used for postoperative pain management, what should the nurse do?
(a) Assess but not disturb the epidural dressing.
(b) Change the epidural dressing daily.
(c) Change the epidural dressing daily only if it is wet.
(d) Use strict aseptic technique when handling the epidural catheter.
Answer:
(a) Assess but not disturb the epidural dressing.
Explanation:
The nurse should assess but not disturb the epidural dressing because the catheter can be easily dislodged and organisms can easily be transmitted into the central nervous system. The nurse should not have to change the dressing at all if a waterproof dressing is applied over the epidural site.
Even with strict aseptic technique, a drain into a sterile cavity is a direct route for transmission of organisms and places a client at increased risk of infection, and the nurse should not handle the dressing or the catheter.
Question 105.
After surgery, the client is receiving epidural pain management. The client wants to get out of bed and walk to the bathroom. The nurse should base the decision to ambulate on which information?
(a) The analgesia is periodically administered through the epidural catheter.
(b) A low concentration of analgesia is used with the catheter.
(c) The analgesia from the epidural catheter bathes the spinal fluid.
(d) The epidural medication affects the sympathetic and motor function.
Answer:
(b) A low concentration of analgesia is used with the catheter.
Explanation:
The client who has epidural pain management postoperatively can ambulate because a low concentration of local analgesia causes sensory blockage only. The catheter is placed so that constant pain management plus patient-controlled administration of an analgesic dose can block sensory innervation. Motor function should not be affected since the catheter is placed above the dura lining the spinal fluid. If the catheter would move through the dura sac, spinal analgesia would occur, affecting motor function as well as sympathetic nervous system function.
Question 106.
The nurse is caring for a client who is using a portable wound suction unit (see figure). Six hours following surgery, the drainage unit is full. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Remove the drain from the incision.
(b) Notify the surgeon.
(c) Empty drainage.
(d) Record the amount in the unit as output on the client’s medical record.
Answer:
(c) Empty drainage.
Explanation:
Portable wound suction units can be emptied and drained. The nurse should compress the unit after emptying to create suction before reinserting the plug. It is normal for the suction unit to be full 6 hours after surgery, and the nurse does not need to notify the surgeon.
The drainage unit should be emptied when full or every 8 hours. The drain in the incision should remain in place until the surgeon removes it. While all drainage should be noted as output on the medical record recording the amount without emptying the drainage unit is not accurate, nor is it safe practice.
Question 107.
Three days after surgery, a client continues to take hydrocodone 7.5 mg and acetaminophen 500 mg for postoperative pain. What should the nurse ask the client before administering the pain medication?
(a) “When did you last have a bowel movement?”
(b) “Have you emptied your bladder?”
(c) “How long has it been since your last dose?”
(d) “Is your pain better than before you had surgery?”
Answer:
(a) “When did you last have a bowel movement?”
Explanation:
The nurse should ask the client about having a bowel movement because acetaminophen with hydrocodone is an opioid, which can be constipating. By the 3rd day, many clients become constipated and are feeling distended, with sharp, cramping pain due to gas, which is treated with ambulation, not more opioids. The client’s emptying the bladder should not affect the pain level.
The nurse should look at the client’s medical record Q to determine when the client’s last dose of pain medication was administered, rather than asking the client. The client’s statement regarding the pain level before the surgery is not relevant to whether the nurse should administer the acetaminophen and hydrocodone.
Question 108.
Upon waking up in the postanesthesia care unit and seeing a drain with bright red fluid in it exiting from his total hip incision, a client asks the nurse, “Is this the way it’s supposed to be?” What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “The drainage is blood and fluid that must be drained out for healing.”
(b) “Don’t worry about it. I’ll explain it when you are more awake.”
(c) “This blood is being kept sterile and will be given back to you.”
(d) “I’ll give you something to make you sleep so you won’t worry.”
Answer:
(a) “The drainage is blood and fluid that must be drained out for healing.”
Explanation:
Blood and serous fluid is drained from the operative site to prevent hematoma formation or a collection of fluid that could become a site for infection. This also minimizes postoperative swelling, which can be painful. A simple explanation such as this is appropriate because the client is just waking up from surgery. Blood from the operative site can be collected through an autotransfusion system so that it can be transfused to the client during or immediately after surgery.
However, strict guidelines about volume of blood lost, how quickly the device fills, and how long the blood has been out of the client’s bod govern whether the blood can be transfused. Therefore, although it is possible that the drainage system to which the client refers is an autotransfusion system, it is more likely that the client has a simple Hemovac drain. It is incorrect to tell a client not to worry about something even if he or she is in the drowsy state of awakening from anesthesia. It is inappropriate to ignore the client and give the client something to make him or her drowsy instead of addressing his or her concerns.
Question 109.
A client has a Jackson-Pratt drainage tube in place the first day after surgical repair of a ruptured diverticulum. The client asks the nurse the purpose of the drain. What should the nurse tell the client?
“The drainage tube is used to prevent:
(a) infection in the peritoneal cavity.”
(b) bleeding into the peritoneal cavity.”
(c) pressure on the bladder.”
(d) pressure on the gallbladder.”
Answer:
(a) infection in the peritoneal cavity.”
Explanation:
The purpose of the Jackson-Pratt drainage tube is to drain off the purulent drainage from the sterile peritoneal cavity and prevent peritonitis. A Jackson-Pratt drain cannot prevent bleeding. The Jackson-Pratt drain has no effect on pressure on the bladder. There is no reason to be concerned about pressure on the gallbladder.
Question 110.
A client who had a cholecystectomy has a biliary drainage tube in place. What color of the drainage is expected?
(a) pinkish red
(b) dark yellow-orange
(c) clear
(d) green
Answer:
(b) dark yellow-orange
Explanation:
Biliary drainage tubes (T tubes) are placed in the common bile duct and drain bile, which is dark yellow-orange. Serosanguineous drainage is thin and pinkish red. Bile is not clear and is not green unless it comes in contact with gastric fluid.
Question 111.
A client is to be discharged from same-day surgery 7 hours after his inguinal hernia repair. Which nursing observation indicates this client is ready to be discharged?
The client:
(a) voids 500 mL of urine.
(b) tolerates eating a hamburger.
(c) is pain free.
(d) walks in the hallway unassisted.
Answer:
(a) voids 500 mL of urine.
Explanation:
Urinary elimination in the first 8 hours postoperatively is a requirement before the client who has had an inguinal hernia repair can be discharged from same-day surgery. Ingestion of fluids without nausea and vomiting is important, but eating solid foods is not a requirement for discharge from same-day surgery.
Being completely pain free is an unrealistic expectation for the time frame and is not a requirement for leaving same-day surgery. However, the client should be comfortable, and his pain should be controlled. It is not a requirement for the client to ambulate in the hallway, but the client should be able to sit up and go to the bathroom without assistance.

Question 112.
A client has requested to have patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) after surgery? When is it appropriate for a client to receive PCA?
(a) A family member is able to assist with self-dosing.
(b) There are advanced directives in place.
(c) The client has the ability to self-administer.
(d) There is a nurse to assist with self-administration.
Answer:
(c) The client has the ability to self-administer.
Explanation:
The ability to self-administer the drug is a requirement for the client to use PCA. Having a family member or advance directives is not a requirement for initiating PCA. The nurse teaches the client about how to use PCA and monitors effectiveness of the pain medication; however, it is not necessary for the nurse to assist with the administration of the drug.
Question 113.
How often should the client’s temperature be assessed during the first 24 hours after surgery?
(a) every 2 hours
(b) every 4 hours
(c) every 6 hours
(d) every 8 hours
Answer:
(b) every 4 hours
Explanation:
The client’s body temperature should be assessed every 4 hours during the first 24 hours because the client is still at risk for hypothermia or malignant hyperthermia. The client does not need to be checked every 2 hours unless indicated by an abnormal finding.
Question 114.
A nurse is assessing a client’s blood pressure 8 hours after surgery. The client’s blood pressure before surgery was 120/80 mm Hg, and on admission to the postsurgical nursing unit it was 110/80 mm Hg. The client’s blood pressure is now 90/70 mm Hg. After determining that other vital signs are normal, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Elevate the head of the bed.
(c) Administer pain medication.
(d) Call the rapid response team.
Answer:
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
The client’s systolic blood pressure is dropping, and the pulse pressure is narrowing, indicating impending shock. The nurse should immediately notify the HCP Elevating the head of the bed will not increase the blood pressure. Administering pain medication could cause the blood pressure to drop further. It is not necessary to activate the rapid response team unless the client’s vital signs change before the HCP evaluates the client.
Question 115.
A client has been positioned in the lithotomy position under general anesthesia for a pelvic procedure. In which anatomic area may the client expect to experience postoperative discomfort?
(a) shoulders
(b) thighs
(c) legs
(d) feet
Answer:
(a) shoulders
Explanation:
The client who has been positioned in the lithotomy position under general anesthesia may experience discomfort in the shoulders postoperatively because the client is placed in the Trendelenburg position to expose the perineal area. The client’s weight is then shifted toward the shoulders, and the client experiences muscle soreness postoperatively. Although there may be pressure on the nerves in the thighs, legs, or feet from pressure from the stirrups, there should be no discomfort if the stirrups are well padded.
Question 116.
Which nursing action does not aid in meeting the goal of clear breath sounds?
(a) offering pain relief before having the client cough
(b) providing a minimum of 1,000 mL of fluid per day
(c) using an incentive spirometer
(d) assisting with early ambulation
Answer:
(b) providing a minimum of 1,000 mL of fluid per day
Explanation:
After surgery, the client should drink a minimum of 2,500 mL of fluid per day (not 1,000 mL) to keep secretions liquefied and easier to cough up and eliminate from the upper respiratory tract. The client should use pain medication before coughing. The client should use the incentive spirometer every 2 to 4 hours. The nurse should monitor the client’s breath sounds and temperature to detect early signs of infection. The nurse should assist with early ambulation.
Question 117.
The nurse is teaching the client about deepbreathing techniques. Which statement from the client indicates the need for additional education?
(a) “I will use my incentive spirometer every hour while I am awake.”
(b) “I should place my hands lightly over my lower ribs and upper abdomen.”
(c) “I should get into a comfortable position before doing my breathing exercises.”
(d) “I should take four deep breaths and then cough deeply from the lungs.”
Answer:
(c) “I should get into a comfortable position before doing my breathing exercises.”
Explanation:
The client should sit in an upright position when doing breathing exercises to allow for full chest expansion of both lungs and all fields and bases. Using an incentive spirometer every hour while awake is appropriate and allows the client visual feedback. Placing his hands lightly over the lower ribs and upper abdomen allows the client to see muscles of inspiration and expiration and is appropriate. Coughing deeply from the lungs after four deep breaths allows the client to effectively cough up secretions.
Question 118.
A client has had a nasogastric tube connected to low intermittent suction. What is the client at risk for?
(a) confusion
(b) muscle cramping
(c) edema
(d) tremors
Answer:
(b) muscle cramping
Explanation:
Muscle cramping is a sign of hypokalemia. Potassium is an electrolyte lost with nasogastric suctioning. Confusion is seen with hypercalcemia. Edema is seen with protein deficit or fluid volume overload. Tremors are seen with hypomagnesemia.
Question 119.
On admission to same-day surgery, the nurse reviews the medical record to verify the client’s identification documentation. Which information is most important?
(a) admitting record
(b) preprinted labels
(c) identification bracelet
(d) location of family
Answer:
(c) identification bracelet
Explanation:
The most critical piece of information is the client identification bracelet. Misidentification of clients can result in serious harm to the client. The nurse also needs the admitting records and any preprinted labels as part of verifying the client’s identification. The location of the family is not included in verifying identification.
Question 120.
A 12-year-old client needs lifesaving emergency surgery, but the relatives live an hour away from the hospital and cannot sign the consent form. What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) Send the client to surgery without the consent.
(b) Call the family for a consent over the telephone, and have another nurse listen as a witness.
(c) No action is necessary in this case because consent is not needed.
(d) Have the family sign the consent form as soon as they arrive.
Answer:
(b) Call the family for a consent over the telephone, and have another nurse listen as a witness.
Explanation:
While laws in states and provinces may vary, generally, when the client cannot sign the operative consent and it is a true lifesaving emergency, consent may be obtained over the telephone from the client’s next of kin or guardian. The surgeon must obtain the telephone consent, but if it is a true lifesaving emergency, the surgeon often is already in surgery, so the nurse makes the telephone call and another nurse witnesses the call.
Some institutions have a special consent form for emergency surgery. Consent can be waived in situations in which no family is available; however, if the family can be reached by telephone before surgery, verbal consent is legally required.
Question 121.
A client who has type 1 diabetes is being prepared to have a craniotomy. The nurse is evaluating the client’s understanding of the informed consent before witnessing the client’s signature on the operative consent form. Which statement from the client indicates that the nurse needs to contact the surgeon for further communication with the client?
(a) “We talked about the effect of my diabetes on healing. ”
(b) “The surgeon explained how the craniotomy was done.”
(c) “There are no major risks from this surgery.”
(d) “I will die if the tumor is not removed from my brain.”
Answer:
(c) “There are no major risks from this surgery.”
Explanation:
There are risks with both the surgical procedure and the general anesthesia required for a craniotomy. The risks involved in the procedure are a part of the informed consent Other information that is part of an informed consent includes potential complications, expected benefits, inability of the surgeon to predict results, irreversibility of the procedure (if applicable), and other available treatments. Talking about the effects of the diabetes on healing, explaining how the craniotomy is performed, and explaining the consequences of declining treatment (e.g., death if the tumor is not removed) represent appropriate actions to provide information to the client.
Question 122.
The nurse is helping to prepare a client for nonemergency surgery. What should the nurse do?
(a) Obtain informed consent from the client.
(b) Explain the surgical procedure in detail.
(c) Verify that the client understands the informed consent form.
(d) Inform the client about the risks of the surgery to be performed.
Answer:
(c) Verify that the client understands the informed consent form.
Explanation:
The surgeon is responsible for explaining the surgical procedure to be performed and the risks of the procedure, as well as for obtaining the informed consent from the client. A nurse may be responsible for obtaining and witnessing a client’s signature on the consent form. The nurse is the client’s advocate, verifying that a client (or family member) understands the consent form and its implications and that consent for the surgery is truly voluntary.
Question 123.
When a client cannot read or write but is of sound mind, the nurse should read the informed consent to the client in the presence of two witnesses and do what next?
(a) Have the client’s next of kin sign the informed consent.
(b) Have the client put an “X” on the signature line.
(c) Have a court appoint a guardian for the client.
(d) Have a hospital quality management coordinator sign for the client.
Answer:
(b) Have the client put an “X” on the signature line.
Explanation:
When the client cannot read or write, the consent can be read to the client, and the client can sign in the presence of two witnesses. The client (not the next of kin) should always sign for self unless he or she is a minor or not of sound mind. The court does not appoint a guardian for a person of sound mind just because he or she cannot read or write. Hospital personnel would not and could not sign a consent form for a client.
Question 124.
The nurse should review the glucose level of which clients who are going to surgery today? Select all that apply.
(a) a client with diabetes mellitus controlled by diet
(b) a client with a high stress response to surgery
(c) a client receiving corticosteroids for the past 3 months
(d) a client with a family history of diabetes receiving dextrose 5% in lactated Ringer’s solution (D5LR) IV fluids
(e) a client who consumes a high-carbohydrate diet
Answer:
(a) a client with diabetes mellitus controlled by diet
(b) a client with a high stress response to surgery
(c) a client receiving corticosteroids for the past 3 months
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c) Clients who have diabetes mellitus controlled by diet, those with a high stress response to surgery, or those who have been on steroid treatment for the last 3 months should have their serum glucose level assessed. A client with a family history of diabetes receiving D5LR IV fluids does not need to have the serum glucose level checked unless other clinical manifestations are present. The client who has a high-carbohydrate diet should be able to metabolize the glucose unless there are other health problems.
Question 125.
Which client has the greatest risk for latex allergies?
(a) a woman who is admitted for her seventh surgery
(b) a man who works as a sales clerk
(c) a man with well-controlled type 2 diabetes
(d) a woman who is having laser surgery
Answer:
(a) a woman who is admitted for her seventh surgery
Explanation:
Clients who have had long-term multiple exposures to latex products, such as would occur with six previous surgeries and recoveries, are at increased risk for latex allergies. The nurse should explore what types of surgeries these were, how involved the client’s recoveries were, and whether signs of latex allergies have occurred in the past. Working as a sales clerk, having type 2 diabetes, and undergoing laser surgery do not expose a client to latex or increase the risk of latex allergy.
Question 126.
A client is admitted on the day of surgery for an arthroscopy of the left knee. Which nursing activities should be completed prior to administering anesthesia to the client to avoid wrong-site surgery? Select all that apply.
(a) Verify that the surgeon has marked with a permanent marker the correct knee for the surgical site.
(b) Verbally ask the client to state his or her name, surgical site, and procedure.
(c) Verify the correct client with the correct operative site from medical records and diagnostic reports.
(d) Call a “time-out” in the operating room to have the surgeon verify the correct knee before making the incision.
(e) Show the client an anatomic model of the surgery site.
Answer:
(a) Verify that the surgeon has marked with a permanent marker the correct knee for the surgical site.
(b) Verbally ask the client to state his or her name, surgical site, and procedure.
(c) Verify the correct client with the correct operative site from medical records and diagnostic reports.
(d) Call a “time-out” in the operating room to have the surgeon verify the correct knee before making the incision.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) The root cause of wrong-site surgery involves a breakdown in communication between the client and family and the health care team. Information retrieved from the client in the preoperative assessment, such as the client’s name, surgical site, and procedure, should be verbally assessed and verified with medical records and radiographic diagnostic reports. This information should be compiled in a checklist that the intraoperative team can recheck, thus avoiding unnecessary distraction and delay in the operating room.
The nurse in the operating room is responsible for calling a “time-out” so that every surgical team member can doublecheck the correct site of surgery, verify the site using the operative consent fXI form, and verify that the surgeon has marked the operative site on the client. Showing the client an anatomic model will assist the client in understanding the location of the surgery, but it will not prevent anyone from identifying the wrong site on the client,
Question 127.
The nurse is planning care for a client with severe postoperative pain. There is a prescription for morphine written as “10 mg MSO4” on the medical record. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Obtain an intravenous infusion system.
(b) Prepare the medication for administration.
(c) Contact the pharmacy department.
(d) Contact the health care provider (HCP) who prescribed the medication.
Answer:
(d) Contact the health care provider (HCP) who prescribed the medication.
Explanation:
The nurse should first contact the HCP Q because the prescription for the morphine is not complete. The Joint Commission of the United States and the Institute for Safe Medication Practices Canada recommend not to use MSO4 because it can apply to morphine as well as to magnesium sulfate.
There is no mention of an IV system being needed. The morphine should not be in the medication cabinet because the prescription is not complete. Although pharmacy may offer a suggestion as to what the medication prescribed is, the best means to confirm the intent of the prescription is to contact the HCP who wrote the prescription.
Question 128.
The client has returned to the surgery unit from the postanesthesia care unit (PACU). The client’s respirations are rapid and shallow, the pulse is 120 bpm, and the blood pressure is 88/52 mm Hg. The client’s level of consciousness is declining. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Call the PACU.
(b) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Call the respiratory therapist.
(d) Call the rapid response team (RRT)/medical emergency team.
Answer:
(d) Call the rapid response team (RRT)/medical emergency team.
Explanation:
The nurse should first call the rapid response team (RRT) or medical emergency team that provides a team approach to evaluate and treat immediately clients with alterations in vital signs or neurological deterioration. The client’s vital signs have changed since the client was in the PACU, and immediate action is required to manage the changes; the staff in PACU are not responsible for managing care once the client is transferred to the surgical unit. The respiratory therapist may be a part of the RRT but should not be called first.
Question 129.
When completing the preoperative checklist on the nursing unit, the nurse discovers an allergy that the client has not reported. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer the prescribed preanesthetic medication.
(b) Note this new allergy prominently on the medical record.
(c) Contact the scrub nurse in the operating room.
(d) Inform the anesthesiologist.
Answer:
(d) Inform the anesthesiologist.
Explanation:
The anesthesiologist who administers the anesthetic agent and monitors the client's physical status throughout the surgery must have knowledge of all known allergies for client safety. The completed record (with the preoperative checklist) must be available to all members of the surgical team, and any unusual last-minute observations that may have a bearing on anesthesia or surgery are noted promi-nently at the front of the medical record CD. The preanesthetic medication can cause lightheadedness or drowsiness. The nurse in the scrub role provides sterile instruments and supplies to the surgeon during the procedure.
Question 130.
Which activities should the nurse encourage the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) to assist with in the care of postoperative clients? Select all that apply.
(a) Empty and measure indwelling urinary catheter collection bags.
(b) Reposition clients for pain relief.
(c) Teach clients the proper use of the incentive spirometer.
(d) Tell the nurse if clients report they are having pain.
(e) Assess IV insertion site for redness.
Answer:
(a) Empty and measure indwelling urinary catheter collection bags.
(b) Reposition clients for pain relief.
(d) Tell the nurse if clients report they are having pain.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d) Nurses can delegate to the UAP to observe clients and promote their comfort following surgery and to empty and measure urinary catheter drainage bags. UAPs cannot teach clients; that is the responsibility of the registered nurse (RN) or respiratory therapist. UAPs cannot assess IV insertion sites, which is the responsibility of an RN.
Question 131.
The client’s identification armband was cut and removed to start an IV line as a part of the preoperative preparation. The transport team has arrived to transport the client to the operating room. The nurse notices that the client’s identification band is not on either wrist. What should the nurse do?
(a) Send the removed armband with the medical record and the client to the operating room.
(b) Place a new identification armband on the client’s wrist before transport.
(c) Tape the cut armband back onto the client's wrist.
(d) Send the client without an armband because the client is alert and can respond to questions about his or her identity.
Answer:
(b) Place a new identification armband on the client’s wrist before transport.
Explanation:
The client must have an identification bracelet properly secured on the wrist before being transported to the operating room to ensure correct identification. It is incorrect to send the client without a properly secured identification bracelet. The perioperative nurse must verify the client’s identification by checking for the same name on the medical record, armband, and schedule and by the client’s statement. The preoperative nurse may be asked to physically identify the client and obtain a new armband.
Question 132.
On the 2nd day after surgery, the nurse assesses an older adult client. The nurse finds:
(a) blood pressure is 148/92 mm Hg; heart rate is 98 bpm; respirations are 32 breaths/min.
(b) O2 saturation is 88% on 4 L/min of oxygen administered by nasal cannula.
(c) breath sounds are coarse and wet bilaterally with a loose, productive cough
(d) The client has voided 100 mL very dark, concentrated urine during the last 4 hours.
(e) bilateral pitting pedal edema.
Answer:
(c) breath sounds are coarse and wet bilaterally with a loose, productive cough
Explanation:
The client is experiencing a fluid overload and has vital signs that are outside of normal limits. The provider must be notified of the client’s current status. It would be appropriate to recommend the provider administer a diuretic to correct the fluid overload. It is not appropriate to administer an anti-hypertensive medication or administer more fluids. It may be appropriate to administer additional oxygen, but because of the fluid volume excess the client exhibits, diuretic administration is most important.
Or
Using the SBAR (Situation-Background-Assessment- Recommendation) method to notify the health care provider of current assessment findings, the nurse should recommend which prescription?
(a) antihypertensive medication
(b) additional fluid intake
(c) diuretic medication
(d) increased oxygen liter flow rate
Answer:
(c) diuretic medication
Explanation:
The client is experiencing a fluid overload and has vital signs that are outside of normal limits. The provider must be notified of the client’s current status. It would be appropriate to recommend the provider administer a diuretic to correct the fluid overload. It is not appropriate to administer an anti-hypertensive medication or administer more fluids. It may be appropriate to administer additional oxygen, but because of the fluid volume excess the client exhibits, diuretic administration is most important.
Question 133.
Which prescription is entered correctly on the medical record?
(a) fentanyl 50 mg given IV every 2 hours as needed for pain greater than 6/10
(b) give 4 U regular insulin IV now
(c) 0.5 mg MS given IM for c/o pain
(d) 60.0 mg ketorolac tromethamine given IM for c/o pain
Answer:
(a) fentanyl 50 meg given IV every 2 hours as needed for pain greater than 6/10
Explanation:
Prescriptions should be written clearly to avoid confusion or misinterpretation. Clearly written prescriptions do not use a “trailing” zero (a zero following a decimal point) and do use a “leading” zero (a zero preceding a decimal point). Additionally, the prescribed medication should be written in full and avoid abbreviations of the drug and the dosage, for example, “morphine sulfate” (avoiding use of “MS”), “mL” instead of “cc,” and “micrograms” instead of “meg.”
Question 134.
The nurse has just received morning change- of-shift report on four clients. In what order from first to last should the nurse perform the actions? All options must be used.
(a) Discuss the plan for the day with the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP), delegating duties as appropriate. (b) Assess the client who has been vomiting according to the report from the night nurse.
(c) Begin discharge paperwork for a client who is jeager to go home.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) about a client who has a serum potassium level of 6.2 mEq/L.
Answer:
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) about a client who has a serum potassium level of 6.2 mEq/L.
(a) Discuss the plan for the day with the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP), delegating duties as appropriate. (b) Assess the client who has been vomiting according to the report from the night nurse.
(c) Begin discharge paperwork for a client who is jeager to go home.
Explanation:
(d), (a), (b), (c) The nurse should first notify the HCPQ of the high serum potassium level. Normal serum potassium level is 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L; a level of 6.2 mEq/L must be called to the HCP immediately because hyperkalemia may cause serious cardiac arrhythmias, potentially leading to death if left untreated.
The nurse should next assess the client who has been vomiting and if necessary contact the HCP for a prescription for an antiemetic if none has been prescribed. After assessing all clients, the nurse should discuss the plan for the day, with the UAP delegating duties as appropriate. Though the client is eager to go home, the discharge paper work must wait until all clients have been assessed and immediate needs met.
Question 135.
While making rounds, the nurse observes that a client’s primary bag of IV solution is light yellow. The label on the IV bag says the solution is D5W. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Continue to monitor the bag of IV solution.
(b) Ask another nurse to look at the solution.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(d) Hang a new bag of D5W, and complete an incident report.
Answer:
(d) Hang a new bag of D5W, and complete an incident report.
Explanation:
Maintenance of IV sites and systems includes regular assessment and rotation of the site and periodic changes of the dressing, solution, and tubing; these measures help prevent complications. The nurse should also observe the solution for discoloration, turbidity, and particulates. An IV solution is changed every 24 hours or as needed, and because the nurse noted an abnormal color, the nurse should change the bag of D5W and note this on an incident report.
It is not necessary to verify this action with another nurse. Paging the HCP is not necessary; maintaining the IV and using the correct solutions is a nursing responsibility. Although the first action is to hang a new bag, hospital policy should be followed if there is a question as to whether there could have been an unknown substance in the bag that caused it to change color.
Question 136.
A client informs the nurse that the venipuncture site “hurts.” The nurse should assess the site for which findings? Select all that apply.
(a) redness
(b) pain
(c) coolness
(d) blanching
(e) firmness
(f) edema
Answer:
(a) redness
(b) pain
(c) coolness
(d) blanching
(e) firmness
(f) edema
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) (e), (f) The venipuncture site must be assessed for signs of infection (redness and pain at the puncture site), infiltration (coolness, blanching,
and edema at the site), and thrombophlebitis (redness, firmness, pain along the path of the vein, and edema).
Question 137.
A client has accidentally received twice the normal dose of a medication that was administered on the previous shift. What should the nurse who discovers the error do first?
(a) Call the person who made the error, and request that an incident report be completed.
(b) Assess the client, and note any changes in condition.
(c) Call the health care provider (HCP) to obtain a prescription for additional IV fluids to dilute the drug.
(d) Administer a drug antidote per standing prescription.
Answer:
(b) Assess the client, and note any changes in condition.
Explanation:
In any situation that involves a medication error, the nurse first assesses the client immediately to determine any changes in condition and the need for urgent interventions. Calling the HCP and/or administering an antidote is not done until the client is assessed and the necessary data are gathered. The nurse finding the error can complete an inci-dent report after the client’s safety is established and any emergency treatments are completed.
Question 138.
A client is in the operating room having surgery to replace a hip. Prior to starting the surgery, there is confusion about the view of the hip on the X-ray. The surgical team requests a “time-out” and stops the surgery. When can surgery continue? Select all that apply.
(a) The surgeon verifies the correct procedure.
(b) The surgeon verifies correct surgical site.
(c) The nurse reestablishes the sterile field.
(d) The surgical team identifies the client using two sources of identification.
(e) Another X-ray is obtained.
Answer:
(a) The surgeon verifies the correct procedure.
(b) The surgeon verifies correct surgical site.
(d) The surgical team identifies the client using two sources of identification.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d) When a “time-out” is called prior to surgery, the surgical team must read back all prescriptions, verify the correct site, identify the client again, and double-check the echocardiogram. The sterile field has not been disrupted and does not need to be set up again. It is not necessary to obtain another X-ray as long as the confusion is clarified and the surgical team is satisfied that all are ready to begin the surgery.
Question 139.
A client is being transferred from the recovery room to the medical-surgical nursing unit. The nurse from the recovery room should report which information to the nurse in the medical-surgical unit? Select all that apply.
(a) type of surgery
(b) name of insurance provider
(c) current vital signs
(d) names of all surgeons participating in the surgery
(e) amount of blood loss
(f) fluids infusing including rate and type of fluid.
Answer:
(a) type of surgery
(c) current vital signs
(e) amount of blood loss
(f) fluids infusing including rate and type of fluid.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (e), (f) Transfer reports must include information about the client’s surgery; all current treatments and medications; vital signs, including pain level; fluid status, including blood loss; and current IV infusions. It is not necessary to identify the surgeons who were present during the surgery or report the name of the insurance provider.
Question 140.
A client with a history of myocardial infarction 3 years ago was admitted at 0700 for a cholecystectomy scheduled at 0900. The client has been NPO since midnight. At 0830, the client reports having chest pains. At 0700, the client’s vital signs were pulse, 80 bpm; respirations, 14 breaths/min; and blood pressure, 110/70 mm Hg. At 0830 the nurse takes the vital signs again: pulse is 110 bpm; respirations, 20 breaths/min; and blood pressure, 90/60 mm Hg. The nurse calls the surgeon and, using the SBAR (Situation-Background-Assessment- Recommendation) communication protocol, should discuss which information with the surgeon? Select all that apply.
(a) that the client has remained NPO
(b) history of myocardial infarction and current report of chest pains
(c) the change in vital signs
(d) the type of surgery scheduled
(e) request for ECG
(f) request to administer nitroglycerin
Answer:
(b) history of myocardial infarction and current report of chest pains
(c) the change in vital signs
(e) request for ECG
(f) request to administer nitroglycerin
Explanation:
(b), (c), (e), (f) Using SBAR (Situation-Background- Assessment-Recommendation), the nurse informs the surgeon of the current situation (chest pains), the background (history of myocardial infarction), and assessment (chest pains, vital signs changes, likelihood of having a myocardial infarction). The nurse should also discuss recommendations and suggestions for prescriptions such as the ECG and nitroglycerin. The nurse is focusing on the chest pain and change in vital signs and communicating recommendations for managing the chest pain; it is not necessary to report at this time that the client has been NPO or the type of surgery the client will have.
Question 141.
When taking a client’s vital signs on the first postoperative day, the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) reports to the nurse that the oral temperature is 100°F (37.8°C). After encouraging the client to use the incentive spirometer, the nurse should delegate which activity to the UAP?
(a) Apply an ice cap to a client’s forehead.
(b) Bathe the client with cool water.
(c) Place a hyperthermia blanket on the client’s bed.
(d) Continue to monitor the client’s temperature.
Answer:
(d) Continue to monitor the client’s temperature.
Explanation:
Temperature variation in the postoperative period provides valuable information about a client’s status. Fever may occur at any time during the postoperative period. A mild elevation (up to 100.4°F [38°C]) during the first 48 hours usually reflects the surgical stress response. After the first 48 hours, a moderate to marked elevation (higher than 99.9°F [37°C]) is usually caused by infection. It is not appropriate to do any of the other options to lower a client’s temperature at this time.
Question 142.
A nurse is working with an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which clients should the nurse assign to the UAP? Select all that apply.
(a) adult client newly diagnosed with diabetes who is learning to administer insulin
(b) older adult client who had hip replacement surgery and needs to walk in the hall with a walker
(c) adult client who had abdominal surgery yesterday and requires a dressing change
(d) young adult client who requires tube feedings
(e) adult client who had a hysterectomy 3 days ago and requires vital sign checks every 4 hours.
Answer:
(b) older adult client who had hip replacement surgery and needs to walk in the hall with a walker
(e) adult client who had a hysterectomy 3 days ago and requires vital sign checks every 4 hours.
Explanation:
(b), (e) The UAP m can assist clients ambulate and take vital signs. It is within the RN scope of practice to teach the client to administer insulin, change dressings, and administer tube feedings.
Question 143.
A nurse is caring for a postsurgical client with two types of drains. Which activities can the nurse delegate to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)? Select all that apply.
(a) Assess the drainage of an open drainage system, such as a Penrose drain.
(b) Document drain site and surrounding tissue status.
(c) Stabilize an open drainage system, such as a Penrose drain.
(d) Empty a closed drainage system, such as a Jackson-Pratt drain or Hemovac drain.
(e) Record the output from a closed-drainage system, such as a Jackson-Pratt drain or Hemovac drain.
Answer:
(d) Empty a closed drainage system, such as a Jackson-Pratt drain or Hemovac drain.
(e) Record the output from a closed-drainage system, such as a Jackson-Pratt drain or Hemovac drain.
Explanation:
(d), (e) The nurse may delegate to the UAP emptying the closed drainage system and recording the output to the unlicensed assistive personnel. A closed drainage system, such as a Jackson-Pratt drain or Hemovac drain is anchored to the skin with one or more sutures. However, open-drainage systems, such as the Penrose drain, are not anchored to the skin. For this type of drain, it is important for the nurse to care for the drain so as to prevent inadvertent dislodgment. Assessing and documenting the drain site is a nursing responsibility.
Question 144.
The nurse is giving a 40-year-old client with limited English language skills printed information about postoperative dressing care. The nurse is using the interpreter to explain the printed information. What should the nurse do to determine that the client understands the procedure?
(a) Question the client to determine the highest level of education achieved.
(b) Administer a pre-test/post-test about how to change a dressing.
(c) Have the client demonstrate how to change the dressing.
(d) Allow the client sufficient time to read the printed information and ask questions.
Answer:
(c) Have the client demonstrate how to change the dressing.
Explanation:
The client will demonstrate understanding through a “teach back” approach. The nurse is also available to answer questions that may arise. The level of education achieved is not an indicator of ability to read a second language. Administering a pre-test or post-test of knowledge is inappropriate if the client cannot read the document printed in English. Having the client review the materials and ask questions is not appropriate if the client cannot read the information.
Question 145.
A client who does not speak English is to be discharged from the hospital following outpatient surgery. Using an interpreter, the nurse reviewed all postoperative instructions, including the need to come in for the follow-up appointment in 2 weeks. The nurse also explained the reconciled medication list, including when to resume taking each medication and the signs and symptoms that would require a call to the physician. In order to ensure the client will continue ongoing care management, what should the nurse do next?
(a) Schedule follow-up visits and inform client of dates/times.
(b) Provide the reconciled client medication list.
(c) Obtain the client’s signature following receipt of discharge materials.
(d) Provide a copy of the discharge materials to the interpreter.
Answer:
(a) Schedule follow-up visits and inform client of dates/times.
Explanation:
Making appointments and navigating the health care system is a major obstacle for non- English speaking clients. In order to support ongoing care management, the nurse can help the client by making the appointment for the follow-up visit, providing dates and times. Providing the reconciled medication list and obtaining the client’s signature are part of the discharge process. Providing a copy of the discharge materials to the interpreter is not part of the discharge process and would be a violation of HIPAA.
Question 146.
A nurse is caring for a group of clients. After receiving shift report, the nurse should make rounds on the clients in which order? Place in order of the highest to lowest priority. All options must be used.
(a) female client who is 34 years of age and just returning from the recovery room following an abdominal hysterectomy; IV running at 50 drops per minute with 100 mL remaining
(b) client who is 50 years of age and diagonsed with diabetes mellitus 3 days ago who is learning to administration insulin
(c) client who is 75 years of age with a fractured hip of 4 days who needs to be turned frequently
(d) client who is 79 years of age 2 days post surgery for removal of cancer of the colon who has had a trachetomy for 4 years
Answer:
(a) female client who is 34 years of age and just returning from the recovery room following an abdominal hysterectomy; IV running at 50 drops per minute with 100 mL remaining
(d) client who is 79 years of age 2 days post surgery for removal of cancer of the colon who has had a trachetomy for 4 years
(c) client who is 75 years of age with a fractured hip of 4 days who needs to be turned frequently
(b) client who is 50 years of age and diagonsed with diabetes mellitus 3 days ago who is learning to administration insulin
Explanation:
(a), (d), (c), (b) The nurse establishes priorities based on airway, breathing, circulation, and disability as well as immediacy of client needs. The client who is just returning from surgery needs to be assessed; the nurse will also need to check the IV. The client with cancer of the colon also needs to have vital signs, pain, and dressings checked; the tracheotomy is established, and in the report, there was no mention of distress. The client with the fractured hip is at risk for pressure ulcers and should be seen next. The nurse should then make rounds on the client with diabetes and schedule the time to continue teaching injection technique at that time.
Question 147.
A client scheduled for surgery is confused and shows signs of dementia. The nurse should ask which person to sign the consent for the client?
(a) minister
(b) nursing supervisor
(c) attorney
(d) spouse
Answer:
(d) spouse
Explanation:
Although practices for signing informed consent O3 documents may vary across practice jurisdictions, generally, the spouse, or other responsible family member, may sign the consent form for a client with dementia. The minister, supervisor, and attorney cannot provide legal consent for surgery for this client.
Question 148.
A client who has an abdominal dressing has asked to use the urinal. A nurse drops a clean glove on the floor while attempting to don gloves. In which order, from first to last, should the nurse proceed?
(a) Apply new, clean gloves.
(b) Assess the client’s surgical dressing.
(c) Dispose of the glove on the floor.
(d) Reposition the client’s urinal.
Answer:
(a) Apply new, clean gloves.
(b) Assess the client’s surgical dressing.
(d) Reposition the client’s urinal.
(c) Dispose of the glove on the floor.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (c) The nurse should always work from least contaminated to most contaminated area. If the nurse picks up and disposes of the glove on the floor, the hands are contaminated and the nurse will need to repeat hand hygiene before caring for the client. The nurse should first put on a new pair of clean gloves and then assess the client’s surgical dressing.
The nurse can next assist the client with using the urinal, and last, the nurse can pick up and dispose of the glove on the floor. It is more time efficient to dispose of fallen objects when all client care is complete unless the fallen object is required to proceed with client care.
