Nursing educators often recommend integrating NCLEX Questions into daily study routines to reinforce key concepts and improve retention.
NCLEX Reproductive Health Problems Questions
Reproductive Health Problems NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
A young adult woman tells the nurse she has a slight yellow vaginal discharge. The nurse should tell the client to contact her health care provider (HCP) if she has which additional symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) vaginal discharge that has a fishy odor
(b) starting her menstrual period
(c) abdominal pain
(d) a temperature above 101°F (38.3°C)
(e) loss of appetite
Answer:
(a) vaginal discharge that has a fishy odor
(c) abdominal pain
(d) a temperature above 101°F (38.3°C)
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d). The client’s discharge may be a symptom of bacterial vaginosis, a clinical syndrome resulting from the replacement of the normal vaginal Lactobacillus species with overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria that cause a cluster of symptoms. Often the discharge disappears, but the nurse should instruct the client to seek care from her HOP if the discharge has a fishy odor, there is abdominal pain, or an elevated temperature. The client’s menstrual cycles will continue as normal. A decreased appetite is not a sign of a vaginal infection
Question 2.
A nurse is teaching a client how to prevent a vaginal infection. Which activity puts the client at risk for altering the normal pH of her vagina?
(a) consuming over four cups of coffee per day
(b) having sexual intercourse during the menstrual cycle
(c) douching unless instructed to do so by the health care provider (HCP)
(d) using tampons during the menstrual cycle
Answer:
(c) douching unless instructed to do so by the health care provider (HCP)
Explanation:
Douching may disrupt the normal flora of the vaginal lactobacilli and change the pH, which could result in overgrowth of other bacteria. Coffee, intercourse during menses, and tampons are not related to changes in vaginal pH or the incidence of bacterial vaginosis.
Question 3.
A client is prescribed oral metronidazole for treatment of bacterial vaginosis. What should the nurse instruct the client to avoid during treatment and for 24 hours thereafter?
(a) douching
(b) sexual intercourse
(c) hot tub baths
(d) alcohol consumption
Answer:
(d) alcohol consumption
Explanation:
Metronidazole interacts with alcohol and can cause a serious disulfiram-type reaction, with severe, prolonged vomiting. The client should not douche unless following a medical prescription, but douching does not interact with metronidazole. Sexual intercourse and hot tub baths are not known to affect the incidence or treatment of bacterial vaginosis.
Question 4.
A female client with which condition would be at risk for increased severity of vulvovaginal candidiasis? Select all that apply.
(a) uncontrolled diabetes
(b) immunosuppression due to cancer
(c) human immunodeficiency vims (HIV) infection
(d) hypertension
(e) asthma
Answer:
(d) hypertension
Explanation:
Metronidazole interacts with alcohol and can cause a serious disulfiram-type reaction, with severe, prolonged vomiting. The client should not douche unless following a medical prescription, but douching does not interact with metronidazole. Sexual intercourse and hot tub baths are not known to affect the incidence or treatment of bacterial vaginosis.
Question 5.
A client taking oral contraceptives is placed on a 10-day course of antibiotics for an infection. Which instruction should the nurse include in the teaching plan?
(a) “Use a barrier method of birth control for the rest of your cycle.”
(b) “You should stop taking the oral contraceptives while taking the antibiotic.”
(c) “Call your health care provider for increasedhunger or fluid retention.”
(d) “Take the antibiotics 2 hours after the oral contraceptive.”
Answer:
(a) “Use a barrier method of birth control for the rest of your cycle.”
Explanation:
Antibiotics may decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptives. The client should be instructed to continue the contraceptives and use a barrier method as a backup method of birth control until the next menstrual cycle. The client should not stop taking her oral contraceptives, and there is no indication for or benefit to taking the antibiotic 2 hours after the contraceptive. There is no incidence of the adverse effects of increased hunger and fluid retention with the interaction of antibiotic therapy and oral contraceptives.
Question 6.
A client is asking for information about using an intrauterine device (IUD). Which question when asked by the nurse would provide pertinent information on whether or not a client is a candidate for an IUD?
(a) “Do you smoke?”
(b) “Do you have hypertension?”
(c) “How often do you have sex?”
(d) “Are you in a monogamous relationship?”
Answer:
(d) “Are you in a monogamous relationship?”
Explanation:
Due to the increased risk of pelvic inflammatory disease, candidates for the IUD should be in a monogamous relationship. Smoking and hypertension are not contraindications for an IUD. The frequency of sexual relations will not affect IUD use.
Question 7.
A 39-year-old female client has been experiencing intermittent vaginal bleeding for several months. Her health care provider (HCP) tells her that she has uterine fibroids and recommends an abdominal hysterectomy. When the client expresses fear about the surgery, what should the nurse do?
(a) Reassure the client of her HCP’s competence.
(b) Give the client opportunities to express her fears.
(c) Teach the client that fear impedes recovery.
(d) Change the topic of conversation.
Answer:
(b) Give the client opportunities to express her fears.
Explanation:
The best approach for a client who is fearful about having surgery is to allow the client opportunities to express her fears. Open-ended questions should elicit the client’s individual and specific fears. This then gives the nurse the opportunity to provide clarification, information, and support and possibly to offer other resources. The other actions are not supportive and deny the client the opportu-nity to express her feelings.
Question 8.
A female with uterine fibroids has dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia. After reviewing the laboratory reports, the nurse should report which results to the health care provider? Select all that apply.
(a) hemoglobin, 9.0 g/dL (90 g/L)
(b) hematocrit, 27.1% (0.27)
(c) white blood cell count, 10,000 cells/mm3 (10 x 109/L)
(d) potassium, 4.0 mEq/L (4.0 mmol/L)
(e) normocytic red blood cells
Answer:
(a) hemoglobin, 9.0 g/dL (90 g/L)
(b) hematocrit, 27.1% (0.27)
Explanation:
(a), (b). A woman with uterine fibroids and dys-menorrhea is at risk for iron deficiency anemia. The hemoglobin and hematocrit indicate the likelihood that the fibroids causing heavy menstrual blood loss have resulted in anemia. A hemoglobin of <12 g/dL (120 g/L) in women is considered low. The white blood cell coimt and potassium levels are within normal parameters, and normocytic red blood cells are normal.
Question 9.
The client will have an abdominal hysterectomy tomorrow. Which information will be most important for the nurse to give to the client prior to admission to the hospital?
(a) what to wear to the hospital
(b) what she can eat and drink before admission
(c) the type of pain medication that will be prescribed postoperatively
(d) the amount of activity she can have after surgery
Answer:
(b) what she can eat and drink before admission
Explanation:
It is a priority that the client knows she will not be able to eat or drink for 8 hours before admission. A client who consumes food and fluid before receiving a general anesthetic is at risk for aspiration, which can lead to aspiration pneumonia, respiratory arrest, and even death. The clothing she should wear to the hospital and the type of medication she will receive are important, but not the priority. Information on exercise and resumption of normal activities can be included in the discharge teaching.
Question 10.
The nurse is witnessing the client’s signature on the informed surgical consent for an abdominal hysterectomy. The nurse should be certain the client understands that what will be the outcome of this surgery?
(a) decreased libido
(b) infertility
(c) depression
(d) weight gain
Answer:
(b) infertility
Explanation:
The client needs to understand that with removal of the uterus, she will no longer be able to bear children or have menstrual periods. The surgical procedure should not change her libido or sexual functioning. Research does not support the idea that hysterectomy contributes to depression or weight gain. Research demonstrates that women who have managed health problems for some time before the hysterectomy may actually have a more positive effect, with less worry about their health condition, contraception, or pregnancy.
Question 11.
Which is the correct order, from first to last, for proper placement of a urinary catheter? All options must be used.
(a) Lubricate the catheter adequately with a water-soluble lubricant.
(b) Ensure free flow of urine.
(c) Insert the catheter far enough into the bladder to prevent trauma to the urethral tissue.
(d) Prepare a sterile field.
Answer:
(d) Prepare a sterile field.
(a) Lubricate the catheter adequately with a water-soluble lubricant.
(c) Insert the catheter far enough into the bladder to prevent trauma to the urethral tissue.
(b) Ensure free flow of urine.
Explanation:
(d), (a), (c), (b). After gathering appropriate supplies, the nurse should prepare a sterile field. After lubricating the catheter adequately with a water- soluble lubricant to minimize trauma to the urethra, the nurse should insert the catheter fax enough into the bladder so the retention balloon does not traumatize urethral tissues. Ensuring a free flow of urine prevents infection; improper drainage occurs when tubing is kinked or twisted.
Question 12.
Which physical sensation will the client who has had an abdominal hysterectomy most likely experience if she hyperventilates while performing deep-breathing exercises?
(a) dyspnea
(b) dizziness
(c) blurred vision
(d) mental confusion
Answer:
(b) dizziness
Explanation:
Hyperventilation occurs when the client breathes so rapidly and deeply that she exhales excessive amounts of carbon dioxide. A characteristic symptom of hyperventilation is dizziness. To avoid hyperventilation, the nurse should assist the client in the practice of slow, deep breathing in a regular breathing pattern. Dyspnea, blurred vision, and mental confusion are not associated with hyperventilation.
Question 13.
Which nursing measure would most likely relieve postoperative gas pains after abdominal hysterectomy?
(a) offering the client a hot beverage
(b) providing extra warmth
(c) applying a snugly fitting abdominal binder
(d) helping the client walk
Answer:
(d) helping the client walk
Explanation:
The discomfort associated with gas pains is likely to be relieved when the client ambulates. The gas will be more easily expelled with exercise. The anesthesia, analgesics, and immobility have altered normal peristalsis. Peristalsis will be stimulated by exercise. Offering a hot beverage, providing extra warmth, and applying an abdominal binder are not recommended and could aggravate the discomfort of postoperative gas pains.
Question 14.
On the second postoperative day after an abdominal hysterectomy, the client develops a temperature of 100.4°F (38°C). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Increase the number of wound dressing changes to minimize infection.
(b) Obtain a culture and sensitivity study of the urine to determine the source of infection.
(c) Ensure that the client takes at least 10 deep breaths every hour.
(d) Change the site of the client’s IV fluid catheter to reduce the risk of infection.
Answer:
(c) Ensure that the client takes at least 10 deep breaths every hour.
Explanation:
Elevated temperature on the second postoperative day is suggestive of a respiratory tract infection. Respiratory infections most often occur during the first 48 hours after surgery. The nurse should encourage the client to take deep breaths frequently. The nurse should also monitor the client’s vital signs and report significant changes to the surgeon. Signs of infection, if present in the wound or urinary tract, are likely to occur later in the postoperative period. There is no indication that the IV catheter is the source of infection.
Question 15.
The nurse is changing the dressing of a client after an abdominal hysterectomy. If the dressing adheres to the client’s incisional area, what should the nurse do?
(a) Pull off the dressing quickly, and then apply slight pressure over the area.
(b) Lift an easily moved portion of the dressing, and then remove it slowly.
(c) Moisten the dressing with sterile normal saline solution, and then remove it.
(d) Remove part of the dressing, and then remove the remainder gradually over a period of several minutes.
Answer:
(c) Moisten the dressing with sterile normal saline solution, and then remove it.
Explanation:
When a dressing sticks to a wound, it is best to moisten the dressing with sterile normal saline solution and then remove it carefully. Trying to remove a dry dressing is likely to irritate the skin and wound. This may contribute to tension or tearing along the suture line.
Question 16.
The client with an abdominal hysterectomy is being prepared for discharge in the morning. The client has a special needs adult son whom she cares for at home. The nurse should discuss with the health care provider the need for referral to which service?
(a) home health care
(b) social work
(c) pastoral care
(d) volunteer care
Answer:
(b) social work
Explanation:
The social worker will be able to coordinate respite care for the son and other community resources for this family. Home health care would provide care for the client herself, but respite care for the son is the priority need for this family. Pastoral care provides spiritual care. The volunteer department would not be responsible for coordina-tion of care at the client’s home.
Question 17.
When planning discharge instructions with a client who has had an abdominal hysterectomy, what should the do first?
(a) Have the client watch an educational video.
(b) Assess the client’s available social supports.
(c) Call the social worker to evaluate the client.
(d) Read the discharge instructions to the client.
Answer:
(b) Assess the client’s available social supports.
Explanation:
Assessment is the first step in planning client education. Assessing social support resources is a key aspect of discharge planning that begins when the client is admitted to the hospital. It is imperative to know what assistance and support the client has at home. Assessment includes obtaining data about any family or home responsibilities the client is concerned with during the recovery period. It is within the scope of nursing practice to provide discharge instructions. A social worker is not needed at this time. The nurse should assess the client’s needs before determining whether using a video or reading instructions to the client is appropriate.
Question 18.
A client who had a hysterectomy 2 hours ago is returning to the postsurgical unit from the recovery room. The nurse is assessing the client. The vital signs are as follows: temperature 99°F (32°C), pulse 98 bmp, respirations 20 breaths/min, and blood pressure 100/65 mm Hg. The urinary catheter is draining freely, and the client wants to try voiding without the catheter. The IV is infusing at 60 gtt/min. The perineal pad is saturated with bright red blood. The nurse reviews the progress notes from the recovery room (see notes).
|
Date |
Time |
Progress Notes |
|
5/24 |
11:45 |
Client ready for transfer to room. Vital signs T = 37°C, P = 78; R = 14, BP = 114/70, O2 Sat of 95% per pulse oximetry; catherer to straight drainage; IV in left cephalic Vein infusing at keep open rate; clint awake and oriented x3. Peri pad Changed; moderately saturated. |
What should the nurse do first?
(a) Change the perineal pad.
(b) Contact the surgeon.
(c) Increase the IV fluids.
(d) Remove the urinary catheter.
Answer:
(b) Contact the surgeon.
Explanation:
The nurse’s first action is to notify the surgeon as the amount of bleeding on the perineal pad is not normal. Excessive bleeding is also indi-cated by elevated heart rate and decreased BP. Urinary catheters are not removed until the second or third postoperative day. The surgeon may pre-scribe an increase in the rate of the IV fluids. The nurse changes the perineal pad and offers comfort measures once the client is stable.
Question 19.
When preparing a client for discharge 2 days after an abdominal hysterectomy, the nurse should instruct the client to avoid which activity until recovery is complete?
(a) swimming in a pool treated with chlorine for 6 weeks after surgery
(b) walking at a leisurely pace for 30 minutes at least once a day
(c) driving until the client can push the brake pedal without pain
(d) lifting >2 lb (0.9 kg) until the abdominal incision has healed
Answer:
(c) driving until the client can push the brake pedal without pain
Explanation:
The client should be prepared for what to expect after surgery. The client should not drive until she can use the brake pedal without abdominal pain. The nurse should teach the client to avoid activities that may increase pelvic congestion, such as dancing or brisk walking, for several months, whereas activities, such as swimming and leisurely walking, may be both physically and mentally helpful. Heavy lifting should be avoided for 2 months, but the client can lift up to 10 lb (4.5 kg) as long as there is no tension on the abdomen or abdominal pain.
Question 20.
A client returned to the recovery room after a dilatation and curettage has the postoperative medication prescriptions shown in the medical record. What should the nurse do next?
Prescriptions:
Morphine sulfate 10 mg Im every 4 hours for severe pain Acetaminophen P.O. Every 4 hours for pain Ibuprofen 800 mg P.O. every 4 hour for Pain.
(a) Ask the client to rate the intensity of her pain on a scale of 1 to 10, and administer the analgesia according to the intensity of the pain.
(b) Administer the meperidine first because the client had surgery today.
(c) Administer the acetaminophen first, and if it does not relieve the pain in 2 hours, administer the morphine.
(d) Administer the ibuprofen first, and if it does not relieve the pain, administer the morphine.
Answer:
(a) Ask the client to rate the intensity of her pain on a scale of 1 to 10, and administer the analgesia according to the intensity of the pain.
Explanation:
The nurse must first assess the intensity of the client’s pain before selecting the correct analgesia. A high score would necessitate administering the meperidine. If the intensity rating is low, an oral analgesic would be appropriate. If acetaminophen is given without assessing the intensity of the client’s pain, the nurse must then wait 4 hours before administering another analgesic.
Question 21.
On the second day following an abdominal hysterectomy, a client reports she has had three brown, loose stools in moderate amount. The morning medications include a prescription for 100 mg of docusate sodium daily or as needed. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Administer the docusate sodium according to the prescription.
(b) Ask the client if she is having gas pains or hunger.
(c) Withhold the medication, and document the client’s report of loose stools.
(d) Administer the docusate sodium, and instruct the client to avoid high-fiber foods.
Answer:
(c) Withhold the medication, and document the client’s report of loose stools.
Explanation:
The nurse should withhold administering docusate sodium, a stool softener, and document that the woman has had loose stools. The nurse is responsible for assessing contraindications and adverse effects of medications, and administering the medication when the client already has loose stools is unsafe. The assessment should also include auscultation of bowel sounds and inquiry about gas pains, but the stool softener should still be withheld.
Question 22.
Which information should the nurse include when teaching a 55-year-old woman in the beginning of menopause? Select all that apply.
(a) The average age of onset for menopause is 50 to 52 years.
(b) Vaginal infections will increase.
(c) Depression is very common as a result of menopause.
(d) Hot flashes, especially at night, can occur in about 80% of women.
(e) When periods become irregular, contraception is unnecessary.
Answer:
(a) The average age of onset for menopause is 50to 52 years.
(d) Hot flashes, especially at night, can occur in about 80% of women.
Explanation:
(a), (d). The average age of menopause is 50 to 52 years, although some variation exists. Vaginal infections do not necessarily increase during menopause. Hot flashes occur in about 80% of women; they can range from mild to very debilitating with disruption of sleep patterns. Depression is not usual during menopause; if symptoms of depression do occur, the muse should refer the woman to her health care provider (HCP) CD Contraception should be used until menses has ceased for a full year.
Question 23.
A nurse is palpating a female client’s breast while assessing for breast disease. In the illustration, indicate the area of the breast in which tumors are most commonly found.
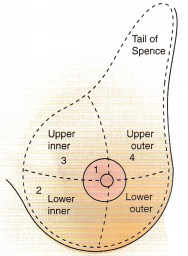
Answer:
The upper outer quadrant is the area of the breast in which most breast tumors are found. This area should be palpated thoroughly. Although breast tumors can be found in any area of the breast, including the nipple, the tumors are most often in the upper outer quadrant.
Question 24.
The client states that she has noticed that her bra fits more snugly at certain times of the month. She asks the nurse if this is a sign of breast disease. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “Benign cysts tend to cause the breasts to vary in size.”
(b) “It’s normal for the breasts to increase in size before menstruation begins.”
(c) “A change in breast size warrants further investigation.”
(d) “Differences in breast size are related to normal growth and development.”
Answer:
(b) “It’s normal for the breasts to increase in size before menstruation begins.”
Explanation:
The breasts may vary in size before menstruation because of breast engorgement caused by hormonal changes. A woman may then note that her bra fits more tightly than usual. Benign cysts do not cause variation in breast size. A change in breast size that does not follow hormonal changes could warrant further assessment. The breasts normally are about the same size, although some women have one breast slightly larger than the other.
Question 25.
A 70-year-old client asks the nurse if she needs to have a mammogram. Which is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “Having a mammogram when you are older is less painful.”
(b) “The incidence of breast cancer increases with age.”
(c) “We need to consider your family history of breast cancer first.”
(d) “It will be sufficient if you perform breast examinations monthly.”
Answer:
(b) “The incidence of breast cancer increases with age.”
Explanation:
The nurse should explain that the incidence of breast cancer increases with age and current guidelines recommend women have a mammogram every 2 years until age 74. While mammograms are less painful as breast tissue becomes softer, the nurse should advise the woman to have the mammogram. Family history is important, but only about 5% of breast cancers are genetic. Several breast cancer screening guidelines recommend against breast self-examinations for women.
Question 26.
Prior to surgery for a modified radical mas-tectomy, the client is extremely anxious and asks many questions. Which approach offers the best guide for the nurse to answer these questions?
(a) Tell the client as much as she wants to know and is able to understand.
(b) Postpone discussing the client’s questions with her until she is convalescing.
(c) Delay discussing the client’s questions with her until her apprehension subsides.
(d) Explain to the client that she should dis cuss her questions first with the health care provider.
Answer:
(a) Tell the client as much as she wants to know and is able to understand.
Explanation:
An important nursing responsibility is preoperative teaching, and the most frequently recommended guide for teaching is to tell the client as much as she wants to know and is able to understand. Delaying discussion of issues about which the client has concerns is likely to aggravate the situation and cause the client to feel distrust. As a general guide, the client would not ask the question if she were not ready to discuss her situation. The nurse is available to answer the client’s questions and concerns and should not delay discussing these with the client.
Question 27.
Following a simple mastectomy, the nurse is totaling the amount of drainage in 24 hours from a suction drain in the incision. The nurse notes there is 200 mL of serosanguineous drainage for the first 24 hours. What should the nurse do?
(a) Document the findings.
(b) Notify the surgeon.
(c) Remove the drain.
(d) Place the client’s arm in a dependent position.
Answer:
(a) Document the findings.
Explanation:
The nurse documents serosanguineous drainage of 100 to 200 mL because this is normal during the first 24 hours after surgery. The nurse notifies the surgeon only if there is excessive or very bloody drainage. The surgeon removes the drain within 24 to 48 hours. The client is instructed to keep her arm on the affected side and supported in an adducted position.
Question 28.
Atropine sulfate is included in the preoperative prescriptions for a client undergoing a modified radical mastectomy. What is the expected outcome of this drug?
(a) Promote general muscular relaxation.
(b) Decrease pulse and respiratory rates.
(c) Decrease nausea.
(d) Inhibit oral and respiratory secretions.
Answer:
(d) Inhibit oral and respiratory secretions.
Explanation:
Atropine sulfate, a cholinergic blocking agent, is given preoperatively to reduce secretions in the mouth and respiratory tract, which assists in maintaining the integrity of the respiratory system during general anesthesia. Atropine is not used to promote muscle relaxation, decrease nausea and vomiting, or decrease pulse and respiratory rates. It causes the pulse to increase.
Question 29.
During the postoperative period after a modified radical mastectomy, the client confides in the nurse that she thinks she got breast cancer because she had an abortion and she did not tell her husband. What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Cancer is not a punishment; it’s a disease.”
(b) “You might feel better if you confided in your husband.”
(c) “Tell me more about your feelings about this.”
(d) “I can have the social worker talk to you if you would like.”
Answer:
(c) “Tell me more about your feelings about this.”
Explanation:
The nurse should respond with an open- ended statement that elicits further exploration of the client’s feelings. Women with cancer may feel guilt or shame. Previous life decisions, sexuality, and religious beliefs may influence a client’s adjustment to a diagnosis of cancer. The nurse should not contradict the client’s feelings of punishment or offer advice such as confiding in the husband. A social worker referral may be beneficial in the future, but it is not the first response needed to elicit exploration of the client’s feelings.
Question 30.
Following a modified radical mastectomy, a client has an incisional drainage tube attached to Hemovac suction. The nurse determines that the suction is effective when what occurs?
(a) The intrathoracic pressure is decreased and the client breathes easier.
(b) There is an increased collateral lymphatic flow toward the operative area.
(c) Accumulated serum and blood in the opera tive area are removed.
(d) No adhesions are formed between the skin and chest wall in the operative area.
Answer:
(c) Accumulated serum and blood in the opera tive area are removed.
Explanation:
A drainage tube is placed in the wound after a modified radical mastectomy to help remove accumulated blood and fluid in the area. Removal of the drainage fluids assists in wound healing and is intended to decrease the incidence of hematoma, abscess formation, and infection. Drainage tubes placed in a wound do not decrease intrathoracic pressure, increase collateral lymphatic flow, or prevent adhesion formation.
Question 31.
Which position would be best for a client’s right arm when she returns to her room after a right modified radical mastectomy with multiple lymph node excisions?
(a) across her chest wall
(b) at her side at the same level as her body
(c) in the position that affords her the greatest comfort without placing pressure on the incision
(d) on pillows, with her hand higher than her elbow and her elbow higher than her shoulder
Answer:
(d) on pillows, with her hand higher than her elbow and her elbow higher than her shoulder
Explanation:
Lymph nodes can be removed from the axillary area when a modified radical mastectomy is done and each of the nodes is biopsied. To facilitate drainage from the arm on the affected side, the client’s arm should be elevated on pillows with her hand higher than her elbow and her elbow higher than her shoulder. A sentinel node biopsy procedure is associated with a decreased risk of lymphedema because fewer nodes are excised.
Question 32.
A client develops lymphedema after a left mastectomy with lymph node dissection. The nurse should include which points in the discharge teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Do not allow blood pressures or blood draws in the affected arm.
(b) Avoid application of sunscreen on the left arm.
(c) Use an electric razor for shaving.
(d) Immobilize the left arm.
(e) Elevate the left arm.
(f) Perform hand pump exercises.
Answer:
(a) Do not allow blood pressures or blood draws in the affected arm.
(c) Use an electric razor for shaving.
(e) Elevate the left arm.
(f) Perform hand pump exercises.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (e), (f). Blood pressures or blood draws in the affected arm, sun exposure, trauma with a sharp razor, and immobilization increase the risk of lymphedema. Elevation of the arm and hand pump exercises promote lymph flow and reduce edema.
Question 33.
The client with breast cancer is prescribed tamoxifen 20 mg daily. The client states she does not like taking medicine and asks the nurse if the tamoxifen is really worth taking. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “This drug is part of your chemotherapy program.”
(b) “This drug has been found to decrease metastatic breast cancer.”
(c) “This drug will act as an estrogen in your breast tissue.”
(d) “This drug will prevent hot flashes since you cannot take hormone replacement.”
Answer:
(b) “This drug has been found to decrease metastatic breast cancer.”
Explanation:
Tamoxifen is an antiestrogen drug that has been found to be effective against metastatic breast cancer and to improve the survival rate. The drug causes hot flashes as an adverse effect.
Question 34.
A client undergoing chemotherapy after a modified radical mastectomy asks the nurse questions about breast prosthesis and wigs. After answering the questions directly, what additional information should the nurse provide?
(a) contact information for the breast cancer support group
(b) a referral to the social worker
(c) how to contact a home health care agency
(d) when to contact a plastic surgeon
Answer:
(a) contact information for the breast cancer support group
Explanation:
Giving the client a list of community resources that could provide support and guidance assists the client to maintain her self-image and independence. The support group will include other women who have undergone similar therapies and can offer suggestions for breast products and wigs. Because the client is asking about specific resources, she does not need a referral to a social worker, home health agency, or plastic surgeon.
Question 35.
A client is to have radiation therapy after a modified radical mastectomy. What instructions should the nurse teach the client about caring for the skin at the site of the radiation therapy?
(a) Wash the area with water.
(b) Expose the area to dry heat.
(c) Apply an ointment to the area.
(d) Use talcum powder on the area.
Answer:
(a) Wash the area with water.
Explanation:
A client receiving radiation therapy should avoid lotions, ointments, and anything that may cause irritation to the skin, such as exposure to sunlight, heat, or talcum powder. The area may safely be washed with water if it is done gently and if care is taken not to injure the skin.
Question 36.
A client is to have radiation therapy following a mastectomy. What should the nurse tell the client to expect as a normal local tissue response to radiation?
(a) atrophy of the skin
(b) scattered pustule formation
(c) redness of the surface tissue
(d) sloughing of two layers of skin
Answer:
(c) redness of the surface tissue
Explanation:
The most common reaction of the skin to radiation therapy is redness of the surface tissues. Dryness, tanning, and capillary dilation are also common. Atrophy of the skin, pustules, and sloughing of two layers would not be expected and should be reported to the radiologist.
Question 37.
The nurse is providing discharge instructions about preventing infection to a client who had a modified radical mastectomy and will be pruning flowers when she returns to work. To prevent infection, what should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Wear protective gloves when gardening.
(b) Avoid crowded areas.
(c) Keep cuticles cut.
(d) Remove underarm hair with a sharp razor.
Answer:
(a) Wear protective gloves when gardening.
Explanation:
This client is at risk for lymphedema and infection. Precautions to avoid creating an entry site for infection in the affected arm include wearing protective gloves, using cuticle cream, not cutting
cuticles, using an electric razor, using a thimble when sewing, and avoiding having injections or blood drawn from that arm. She does not need to avoid crowds; she is not at high risk for respiratory infection.
Question 38.
An adult male client has been unable to void for the past 12 hours. What is the best method for the nurse to use when assessing for bladder distention in a male client?
(a) Palpate for a rounded swelling above the pubis.
(b) Percuss dullness in the lower left quadrant.
(c) Determine rebound tenderness below the symphysis.
(d) Inspect the urethral meatus for urine discharge.
Answer:
(a) Palpate for a rounded swelling above the pubis.
Explanation:
The best way to assess for a distended bladder in either a male or female client is to check for a rounded swelling above the pubis. This swelling represents the distended bladder rising above the pubis into the abdominal cavity. Dullness does not indicate a distended bladder. The client might experience tenderness or pressure above the sym-physis. No urine discharge is expected; the urine flow is blocked by the enlarged prostate.
Question 39.
When emptying the client’s bladder during a urinary catheterization, the nurse should allow the urine to drain from the bladder slowly to prevent which complication?
(a) renal failure
(b) abdominal cramping
(c) possible shock
(d) atrophy of bladder musculature
Answer:
(c) possible shock
Explanation:
Rapid emptying of an overdistended bladder may cause hypotension and shock due to the sudden change of pressure within the abdominal viscera. The nurse should empty the bladder slowly. Removal of urine from the bladder does not cause renal failure. The client may experience cramping, but the primary concern is the potential for shock. Bladder muscles will not atrophy because of a catheterization.
Question 40.
The primary reason for lubricating the urinary catheter generously before inserting the catheter into a male client is to prevent which problem?
(a) spasms at the orifice of the bladder
(b) friction along the urethra when the catheter is being inserted
(c) the number of organisms gaining entrance to the bladder
(d) the formation of encrustations that may occur at the end of the catheter
Answer:
(b) friction along the urethra when the catheter is being inserted
Explanation:
Liberal lubrication of the catheter before catheterization of a male reduces friction along the urethra and irritation and trauma to urethral tissues. Because the male urethra is tortuous, a liberal amount of lubrication is advised to ease catheter passage. The female urethra is not tortuous, and, although the catheter should be lubricated before insertion, less lubricant is necessary. Lubrication of the catheter will not decrease spasms. The nurse should use sterile technique to prevent introducing organisms. Crusts will not form immediately. Irrigating the catheter as needed will prevent clot and crust formation.
Question 41.
The nurse has inserted an indwelling catheter in a male client. Which problem is prevented if the nurse tapes the catheter laterally to the thigh?
(a) pressure at the penoscrotal angle
(b) catheter kinking in the urethra
(c) accidental catheter removal
(d) obstructing urine flow when the client turns
Answer:
(a) pressure at the penoscrotal angle
Explanation:
The primary reason for taping an indwelling catheter to the lateral aspect of the thigh of a male client is so that the penis is held in a lateral position is to prevent pressure at the penoscrotal angle. Prolonged pressure at the penoscrotal angle can cause a ureterocutaneous fistula. This position of the catheter does not prevent kinking in the urethra, accidental removal, or obstruction of the urine flow if the client turns.
Question 42.
The nurse is providing preoperative instructions to a client who is having a transurethral resection of the prostate. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “You will have a central venous access inserted just prior to the procedure.”
(b) “Plan on being in the hospital anywhere from 5 to 7 days following the procedure.”
(c) “You will be taught care of the incision and suture line prior to your discharge home.”
(d) “Expect blood in your urine in the first couple of days following the procedure.”
Answer:
(d) “Expect blood in your urine in the first couple of days following the procedure.”
Explanation:
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a common surgical procedure used to treat male clients with benign prostate enlargement. The surgery commonly results in blood from the surgery in the urine for the first few days, and the client should not be concerned; the urine will become clear within 2 to 3 days. Central venous access is not expected for this type of surgery. Peripheral IV access can be expected. Clients are instructed to anticipate hospitalization for 1 to 3 days. Because the procedure is performed transurethrally (via the urethra), there is no outward incision.
Question 43.
When providing client teaching about continuous bladder irrigation following prostate surgery, what should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “The catheter is disconnected from the drain age tubing one time per shift to enable manual irrigation of the bladder.”
(b) “The purpose of the irrigation is to keep blad der drainage clear and to prevent the formation of blood clots in the bladder.”
(c) “The fluid drips into the bladder at a slow rate to prevent the effects of overhydration and hyponatremia.”
(d) “The catheter is clamped off approximately 4 hours after returning to the nursing unit. ”
Answer:
(b) “The purpose of the irrigation is to keep blad der drainage clear and to prevent the formation of blood clots in the bladder.”
Explanation:
Continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) is performed when urinary surgery (typically prostate surgery) results in hematuria. It is accomplished using an indwelling Foley catheter with three lumens. One port is for the balloon, a second port allows irrigant inflow, and a third port enables outflow. The purpose of the irrigation is to achieve and maintain clear outflow and to prevent clot formation within the bladder. Manual irrigation is used as an intermittent type of bladder irrigation and is not the same as CBI. CBI involves irrigation of the bladder; it is not an intravascular infusion. The rate is often initially fast to achieve a clear outflow. Stopping and clamping the irrigant inflow is done only under a health care provider’s (HCP’s) direction and is typically not expected until at least 1 day following the procedure.
Question 44.
When caring for a client with a history of benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH), what should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Provide privacy and time for the client to void.
(b) Monitor intake and output.
(c) Catheterize the client for postvoid residual urine.
(d) Ask the client if he has urinary retention.
(e) Test the urine for hematuria.
Answer:
(a) Provide privacy and time for the client to void.
(b) Monitor intake and output.
(d) Ask the client if he has urinary retention.
(e) Test the urine for hematuria.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e). Because of the history of BPH, the nurse should provide privacy and time for the client to void. The nurse should also monitor intake and output, assess the client for urinary retention, and test the urine for hematuria. It is not necessary to catheterize the client.
Question 45.
A client has prostatic hypertrophy. What should the nurse assess when conducting a focused assessment of the client’s ability to urinate?
(a) voiding at less frequent intervals
(b) difficulty starting the flow of urine
(c) painful urination
(d) increased force of the urine stream
Answer:
(b) difficulty starting the flow of urine
Explanation:
Signs and symptoms of prostatic hypertrophy include difficulty starting the flow of urine, urinary frequency and hesitancy, decreased force of the urine stream, interruptions in the urine stream when voiding, and nocturia. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, and these symptoms are all attributed to obstruction of the urethra resulting from prostatic hypertrophy. Nocturia from incomplete emptying of the bladder is common. Straining and urine retention are usually the symptoms that prompt the client to seek care. Painful urination is generally not a symptom of prostatic hypertrophy.
Question 46.
A client is scheduled to undergo transurethral resection of the prostate. The procedure is to be done under spinal anesthesia. What should the nurse assess the client for after surgery?
(a) seizures
(b) cardiac arrest
(c) renal shutdown
(d) respiratory paralysis
Answer:
(d) respiratory paralysis
Explanation:
If paralysis of vasomotor nerves in the upper spinal cord occurs when spinal anesthesia is used, the client is likely to develop respiratory paralysis. Artificial ventilation is required until the effects of the anesthesia subside. Seizures, cardiac arrest, and renal shutdown are not likely results of spinal anesthesia.
Question 47.
A client with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) is being treated with terazosin 2 mg at bedtime. What should the nurse tell the client to monitor on a regular basis?
(a) glucosuria glucose
(b) restlessness
(c) blood pressure
(d) pulse
Answer:
(c) blood pressure
Explanation:
Terazosin is an antihypertensive drug that is also used in the treatment of BPH. The client should monitor his blood pressure to ensure he does not develop hypotension, syncope, or orthostatic hypotension. The client should be instructed to change positions slowly. Terazosin does not cause glycosuria, restlessness, or changes in the heart rate.
Question 48.
A client, who had a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), has a three-way indwelling urinary catheter with continuous bladder irrigation. In which circumstance should the nurse increase the flow rate of the continuous bladder irrigation? When drainage:
(a) is continuous but slow.
(b) appears cloudy and dark yellow.
(c) becomes bright red.
(d) of urine and irrigating solution stops.
Answer:
(c) becomes bright red.
Explanation:
The decision by the surgeon to insert a catheter after TURP or prostatectomy depends on the amount of bleeding that is expected after the procedure. During continuous bladder irrigation after a TURP or prostatectomy, the rate at which the solution enters the bladder should be increased when the drainage becomes brighter red. The color indicates the presence of blood. Increasing the flow of irrigating solution helps flush the catheter well so that clots do not plug it. There would be no reason to increase the flow rate when the return is continu-ous or when the return appears cloudy and dark yellow. Increasing the flow would be contraindicated when there is no return of urine and irrigating solution.
Question 49.
A client is to receive belladonna and opium suppositories, as needed, postoperatively after transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). The nurse should give the client these drugs when he demonstrates signs of which symptom?
(a) a urinary tract infection
(b) urine retention
(c) frequent urination
(d) pain from bladder spasms
Answer:
(d) pain from bladder spasms
Explanation:
Belladonna and opium suppositories are prescribed and administered to reduce bladder spasms that cause pain after TURP. Bladder spasms frequently accompany urologic procedures. Antispasmodics offer relief by eliminating or reducing spasms. Antimicrobial drugs are used to treat an infection. Belladonna and opium do not relieve urine retention or urinary frequency.
Question 50.
An unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) tells the nurse, “I think the client is confused. He keeps telling me he has to void, but that’s not possible because he has a catheter in place that is draining well.” What should the nurse tell the UAP?
(a) “His catheter is probably plugged. I will irrigate it.”
(b) “That is a common problem after prostate surgery. The client only imagines the urge to void.”
(c) “The urge to void is usually created by the large catheter, and he may be having some bladder spasms.”
(d) “I think he may be somewhat confused.”
Answer:
(c) “The urge to void is usually created by the large catheter, and he may be having some bladder spasms.”
Explanation:
The indwelling urinary catheter creates the urge to void and can also cause bladder spasms. The nurse should ensure adequate bladder emptying by monitoring urine output and characteristics. Urine output should be at least 30 to 50 mL/h. A plugged catheter, imagining the urge to void, and confusion are less likely reasons for the client’s problem.
Question 51.
A health care provider (HCP) has prescribed amoxicillin 100 PO two times a day. What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Drink 300 to 500 mL of fluids daily.
(b) Void frequently, at least every 2 to 3 hours.
(c) Take time to empty the bladder completely.
(d) Take the last dose of the antibiotic for the day at bedtime.
(e) Take the antibiotic with or without food.
Answer:
(b) Void frequently, at least every 2 to 3 hours.
(c) Take time to empty the bladder completely.
(d) Take the last dose of the antibiotic for the day at bedtime.
(e) Take the antibiotic with or without food.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d), (e). Amoxicillin may be given with or without food, but the nurse should instruct the client to obtain an adequate fluid intake (2,500 to 3,000 mL) to promote urinary output and to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. The nurse should also encourage the client to void frequently (every 2 to 3 hours) and empty the bladder completely. Taking the antibiotic at bedtime, after emptying the bladder, helps to ensure an adequate concentration of the drug during the overnight period.
Question 52.
In discussing home care with a client after transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), what should the nurse tell the male client about dribbling of urine after this surgery?
Dribbling of urine:
(a) can be a chronic problem.
(b) can persist for several months.
(c) is an abnormal sign that requires intervention.
(d) is a sign of healing within the prostate.
Answer:
(b) can persist for several months.
Explanation:
Dribbling of urine can occur for several months after TURP. The client should be informed that this is expected and is not an abnormal sign. The nurse should teach the client perineal exercises to strengthen sphincter tone. The client may need to use pads for temporary incontinence. The client should be reassured that continence will return in a few months and will not be a chronic problem. Dribbling is not a sign of healing but is related to the trauma of surgery.
Question 53.
A client is being discharged to home 3 days after transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Drink at least 3,000 mL water per day.
(b) Increase calorie intake by eating six small meals a day.
(c) Report bright red bleeding to the health care provider.
(d) Take deep breaths and cough every 2 hours.
(e) Report a temperature over 99°F (37.2°C).
Answer:
(a) Drink at least 3,000 mL water per day.
(c) Report bright red bleeding to the health care provider.
(e) Report a temperature over 99°F (37.2°C).
Explanation:
(a), (c), (e). The nurse should instruct the client to drink a large amount of fluids (about 3,000 mL/ day) to keep the urine clear. The urine should be almost without color. About 2 weeks after TURP, when desiccated tissue is sloughed out, a secondary hemorrhage could occur. The client should be instructed to call the surgeon or go to the emergency department if at any time the urine turns bright red. The nurse should also instruct the client to report signs of infection such as a temperature over 99°F (37.2°C). The client is not specifically at risk for nutritional problems after TURP and can resume a diet as tolerated. The client is not specifically at risk for airway problems because the procedure is done under spinal anesthesia and the client does not need to take deep breaths and cough.
Question 54.
A client with benign prostatic hypertrophy has an elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Instruct the client to request having a colonoscopy before coming to conclusions about the PSA results.
(b) Instruct the client that a urologist will monitor the PSA level biannually when elevated.
(c) Determine if the prostatic palpation was done before or after the blood sample was drawn.
(d) Ask the client if he emptied his bladder before the blood sample was obtained.
Answer:
(c) Determine if the prostatic palpation was done before or after the blood sample was drawn.
Explanation:
Rectal and prostate examinations can increase serum PSA levels. The prostatic palpation should be done after the blood sample is drawn. The PSA level must be monitored more often than biannually when it is elevated. Having a colonoscopy is not related to the findings of the PSA test. It is not necessary to void prior to having PSA blood levels tested.
Question 55.
What is most important information for the nurse to teach a client newly diagnosed with genital herpes?
(a) Use condoms at all times during sexual intercourse.
(b) A urologist should be seen only when lesions occur.
(c) Oral sex is permissible without a barrier.
(d) Determine if your partner has received a vaccine against herpes.
Answer:
(a) Use condoms at all times during sexual intercourse.
Explanation:
The client should be taught to abstain from sexual intercourse while lesions are present. Condoms should be used at all times as the virus can be shed without lesions present. Multiple partners would promote the spread of genital herpes. There is no vaccine available to prevent genital herpes. Although periodic examinations should be advised, a urologist does not necessarily need to be seen when lesions occur.
Question 56.
A client who is sexually active asks the nurse about using PreExposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV. The nurse should tell the client the drug, a combination of 300 mg tenofovir disoproxil fuma- rate and 200 mg emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) can be used for which group of people who are at risk for becoming infected with HIV?
(a) anyone who is in an ongoing sexual relationship with an HIV-infected partner
(b) people who do not use condoms when in a sexual relationship
(c) a person who has a sexually transmitted disease that is not being treated
(d) someone who has a compromised immune system
Answer:
(a) anyone who is in an ongoing sexual relationship with an HIV-infected partner
Explanation:
PrEP is primarily available to anyone who is in an ongoing sexual relationship with an HIV-infected partner. Others at risk, such as those who are having sex with partners who are at risk for HIV such as drug users or who are themselves sharing equipment with people who are at risk for HIV, may also receive PReP. The drug is not used for people who do not use condoms, have untreated sexually transmitted diseases, or a compromised immune system.
Question 57.
A client who is in a sexual relationship with a partner who has HIV has a prescription for PreExposure Prophylaxis (PReP) using combination of 300 mg tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and 200 mg emtricitabine (TDF/FTC). What should the nurse instruct the client about taking this drug?
(a) Renew your prescription every year.
(b) Take the medication daily.
(c) It is not necessary to use condoms.
(d) The drug is 100% effective.
Answer:
(a) Renew your prescription every year.
Explanation:
It is imperative that the client take the medication daily; the client should also use condoms. The client should have HIV testing every 3 months, and prescriptions are written for renewal every 3 months. The drug is about 92% effective, but effectiveness increases when using condoms.
Question 58.
A client with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection is taking zidovudine (AZT). What is the expected outcome of AZT for this client?
(a) Destroy the virus.
(b) Enhance the body’s antibody production.
(c) Enable slow replication of the virus.
(d) Neutralize toxins produced by the virus.
Answer:
(c) Enable slow replication of the virus.
Explanation:
Zidovudine (AZT) interferes with replication of HIV and thereby slows progression of HIV infection to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). There is no known cure for HIV infection. Today, clients are not treated with monotherapy but are usually on triple therapy due to a much- improved clinical response. Decreased viral loads with the drug combinations have improved the longevity and quality of life in clients with HIV/AIDS. AZT does not destroy the virus, enhance the body’s antibody production, or neutralize toxins produced by the virus.

Question 59.
What is a risk factor for women who have human papillomavirus (HPV)?
(a) sterility
(b) cervical cancer
(c) uterine fibroid tumors
(d) irregular menses
Answer:
(b) cervical cancer
Explanation:
Women who have HPV are much more likely to develop cervical cancer than women who have never had the disease. Cervical cancer is now considered a sexually transmitted disease. Regular examinations, including Papanicolaou tests, are recommended to detect and treat cervical cancer at an early stage. Girls and women as well as boys and men (around ages 9 to 26 depending on the vaccine) should receive a vaccine to prevent HPV. HPV does not cause sterility, uterine fibroid tumors, or irregular menses.
Question 60.
The nurse is teaching a client with HIV who has a herpes simplex virus (HSV) about the seriousness of having this virus. What should the nurse tell the client about HSV?
(a) HSV is an acquired immunodeficiency virus (AIDS)-defining illness.
(b) HSV is curable only after 1 year of antiviral therapy.
(c) HSV leads to cervical cancer.
(d) HSV causes severe electrolyte imbalances.
Answer:
(a) HSV is an acquired immunodeficiency virus (AIDS)-defining illness.
Explanation:
HSV infection is one of a group of disorders that, when diagnosed in the presence of HIV infection, are considered to be diagnostic for AIDS. Other AIDS-defining illnesses include Kaposi’s sarcoma: cytomegalovirus of the liver, spleen, or lymph nodes; and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. HSV infection is not curable and does not cause severe electrolyte imbalances. Human papillomavirus can lead to cervical cancer.
Question 61.
When teaching a client about human immu-nodeficiency virus (HIV), the nurse should take into account the fact that which strategy is the most effective way to control the spread of HIV infection?
(a) premarital serologic screening
(b) prophylactic treatment of exposed people
(c) laboratory screening of pregnant women
(d) ongoing sex education about preventive behaviors
Answer:
(d) ongoing sex education about preventive behaviors
Explanation:
Education to prevent behaviors that cause HIV transmission is the primary method of controlling HIV infection. Behaviors that place people at risk for HIV infection include unprotected sexual intercourse and sharing of needles for IV drug injection. Educating clients about using condoms during sexual relations is a priority in control-ling HIV transmission.
Question 62.
A male client with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection becomes depressed and tells the nurse: “I have nothing worth living for now.” Which statement would be the best response by the nurse?
(a) “You are a young person and have a great deal to live for.”
(b) “You should not be too depressed; we are close to finding a cure for AIDS.”
(c) “You are right; it is very depressing to have HIV.” '
(d) “Tell me more about how you are feeling about being HIV positive.”
Answer:
(d) “Tell me more about how you are feeling about being HIV positive.”
Explanation:
The nurse should respond with a statement that allows the client to express his thoughts and feelings. After sharing feelings about their diagnosis, clients will need information, support, and community resources. Statements of encouragement or agreement do not provide an opportunity for the client to express himself.
Question 63.
The nurse is obtaining a health history from a client with a sexually transmitted disease. Which description from the client indicates the likelihood of syphilis?
"In my genital area I have:
(a) tender pimples.”
(b) a wart.”
(c) a moist ulcer.”
(d) itching.”
Answer:
(c) a moist ulcer.”
Explanation:
The chancre of syphilis is characteristically a painless, moist ulcer. The serous discharge is very infectious. Because the chancre is usually painless and disappears, the client may not be aware of it or may not seek care. The chancre does not appear as pimples or warts and does not itch, thus making diagnosis difficult.
Question 64.
The nurse is interviewing a client with newly diagnosed syphilis. In order to prevent the spread of the disease, the focus of the interview should include which approach?
(a) motivating the client to undergo treatment
(b) obtaining a list of the client’s sexual contacts
(c) increasing the client’s knowledge of the disease
(d) reassuring the client that medical records are confidential
Answer:
(b) obtaining a list of the client’s sexual contacts
Explanation:
An important aspect of controlling the spread of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) is obtaining a list of the sexual contacts of an infected client. These contacts, in turn, should be encouraged to obtain immediate care. Many people with STDs are reluctant to reveal their sexual contacts, which makes controlling STDs difficult. Increasing clients’ knowledge of the disease and reassuring clients that their records are confidential can motivate them to seek treatment, which does help to control the spread of the disease, but it is not as critical as information about the client’s sexual contacts.
Question 65.
The health care provider has prescribed benzathine penicillin G, 2.4 million units IM to treat an adult with primary syphilis. In which muscle should the nurse administer the injection?
(a) deltoid
(b) ventrogluteal
(c) quadriceps lateralis
(d) dorsogluteal
Answer:
(b) ventrogluteal
Explanation:
Because of the large dose, the upper ventrogluteal is the recommended site. The deltoid, dorsogluteal, and the quadriceps lateralis muscles are not large enough for the recommended dose.
Question 66.
An 18-year-old female is to have a pelvic exam. Which response by the nurse would be best when the client says that she is nervous about the upcoming pelvic examination?
(a) “Can you tell me more about how you’re feeling?”
(b) “You’re not alone. Most women feel uncomfortable about this examination.”
(c) “Don’t worry about Dr. Smith. He is a specialist in female problems.”
(d) “We will do everything we can to avoid embarrassing you.”
Answer:
(a) “Can you tell me more about how you’re feeling?”
Explanation:
Asking the client to describe her nervousness gives her the opportunity to express her concerns. It also allows the nurse to understand her better and gives the nurse a base to respond to the client’s stated fears, questions, or need for further information. Responses that make assump-tions about the source of the concern or offer reinforcement are not supportive and block successful communication.
Question 67.
When educating a female client with gonorrhea, what should the nurse emphasize?
In women, gonorrhea:
(a) is often marked by symptoms of dysuria or vaginal bleeding.
(b) does not lead to serious complications.
(c) can be treated but not cured.
(d) may not cause symptoms until serious com plications occur.
Answer:
(d) may not cause symptoms until serious com plications occur.
Explanation:
Many women do not seek treatment because they are unaware that they have gonorrhea. They may be symptom-free or have only very mild symptoms until the disease progresses to pelvic inflammatory disease. Dysuria and vaginal bleeding are not present in gonorrhea. Gonorrhea can lead to very serious complications. It can be cured with the proper treatment.
Question 68.
Which group has experienced the greatest rise in the incidence of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) over the past two decades?
(a) teenagers
(b) divorced people
(c) young married couples
(d) older adults
Answer:
(a) teenagers
Explanation:
Statistics reveal that the incidence of STDs is rising more rapidly among teenagers than among any other age group. Many reasons have been given for this trend, including a change in societal mores and increasing sexual activity among teenagers. During this developmental stage, teenagers may engage in high-risk sexual behaviors because they often are living in the present and feel that it will not happen to them.
Question 69.
A sexually active male client has burning
on urination and a milky discharge from the urethral meatus. What documentation should be included on the client’s medical record? Select all that apply.
(a) history of unprotected sex (sex without a condom)
(b) length of time since symptoms presented
(c) history of fever or chills
(d) presence of any enlarged lymph nodes on examination
(e) names and phone numbers of all sexual contacts
(f) allergies to any medications
Answer:
(a) history of unprotected sex (sex without a condom)
(b) length of time since symptoms presented
(c) history of fever or chills
(d) presence of any enlarged lymph nodes on examination
(f) allergies to any medications
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d), (f). The client is suspected of having a sexually transmitted infection. Therefore, the client’s sexual history, assessment, and examination must be documented, including symptoms (such as fever, chills, and enlarged glands) and their onset and duration. Allergies are critical to document for every client but are especially noteworthy in this case because antibiotics will be prescribed. If a sexually transmitted infection is confirmed, sexual contacts need to be treated. To protect privacy, the names and phone numbers should never be placed in the medical record. The public health department will also assist in obtaining information and treating known sexual contacts.
Question 70.
A male client is diagnosed with a chlamydial infection. Azithromycin 1 g is prescribed. The supply of azithromycin is in 250-mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? Record your answer using a whole number.
...................... tablets.
Answer:
4 tablets
First, convert 1 g to milligrams:
1 g = 1,000 mg.
Next, divide the desired dose by the dose on hand:
1,000 mg/250 mg = 4 tablets.
Question 71.
A female client with gonorrhea informs the nurse that she has had sexual intercourse with her boyfriend and asks the nurse, “Would he have any symptoms?” The nurse can tell the client which symptoms of gonorrhea occur in men?
(a) impotence
(b) scrotal swelling
(c) urine retention
(d) dysuria
Answer:
(d) dysuria
Explanation:
Dysuria and a mucopurulent urethral discharge characterize gonorrhea in men. Gonococcal symptoms are so painful and bothersome for men that they usually seek treatment with the onset of symptoms. Impotence, scrotal swelling, and urine retention are not associated with gonorrhea.
Question 72.
The nurse assesses the mouth and oral cavity of a client with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection because the most common opportunistic infection initially presents with which symptom?
(a) herpes simplex virus (HSV) lesions on the lips
(b) oral candidiasis
(c) cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection
(d) aphthae on the gingiva
Answer:
(b) oral candidiasis
Explanation:
The most common opportunistic infection in HIV infection initially presents as oral candidiasis, or thrush. The client with HIV should always have an oral assessment. HSV and CMV are opportunistic infections that present later in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent canker sores, is not an opportunistic infection, although the sores are thought to occur more often when the client is under stress.
Question 73.
The nurse is administering didanosine to a client with HIV. Before administering this medication, the nurse should check which lab test results? Select all that apply.
(a) elevated serum creatinine
(b) elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
(c) elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
(d) elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
(e) elevated serum amylase
Answer:
(c) elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
(d) elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
(e) elevated serum amylase
Explanation:
(c), (d), (e). The nurse should withhold the medication and notify the health care provider (HCP) immediately if the client develops manifestations of pancreatitis or hepatic failure including nausea and vomiting, severe abdominal pain, elevated bilirubin, or elevated serum enzymes (e.g., amylase, AST, ALT). If both BUN and creatinine are elevated, the client may have kidney disease.
Question 74.
The nurse is caring for a client from Southeast Asia who has HIV/AIDS. The client does not speak or comprehend the English language.
What should the nurse do?
(a) Contact the hospital’s chaplain.
(b) Do an internet search for the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS.
(c) Utilize language-appropriate interpreters.
(d) Ask a family member to obtain informed consent.
Answer:
(c) Utilize language-appropriate interpreters.
Explanation:
Interpreters are essential in enabling the nurses’ communications to be understood accurately. The chaplain may not know the client’s language. The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/ AIDS has the number of reported cases of AIDS. It is not necessary for the family member to obtain informed consent.
Question 75.
The nurse is preparing a 45-year-old female for a vaginal examination. The nurse should place the client in which position?
(a) Sims’ position
(b) lithotomy position
(c) genupectoral position
(d) dorsal recumbent position
Answer:
(b) lithotomy position
Explanation:
Although other positions may be used, the preferred position for a vaginal examination is the lithotomy position. This position offers the best visualization. If the client is an older adult and frail, staff members may need to support the client’s flexed legs while the examiner conducts the examination and obtains the Papanicolaou smear. Positioning the client in the other positions will make visualization more difficult and may not be as comfortable for the client.
Question 76.
A client asks the nurse to explain the meaning of her abnormal Papanicolaou (Pap) smear result of atypical squamous cells. The nurse should tell the client that an atypical Pap smear means that what has occurred?
(a) Abnormal viral cells were found in the smear.
(b) Cancer cells were found in the smear.
(c) The Pap smear alone is not very important diagnostically because there are many false-positive results.
(d) The cells could cause various conditions and help identify a problem early.
Answer:
(d) The cells could cause various conditions and help identify a problem early.
Explanation:
The Pap smear identifies atypical cervical cells that may be present for various reasons. Cancer is the most common possible reason, but not the only one. The Pap smear does not show abnormal viral cells unless specific gene typing is done for human papillomavirus. An adequate smear provides accurate diagnostic data; the false-positive rate is only about 5%.
Question 77.
What is a risk factor for cervical cancer?
(a) sexual experiences with one partner
(b) sedentary lifestyle
(c) obesity
(d) adolescent pregnancy
Answer:
(d) adolescent pregnancy
Explanation:
Young age at first pregnancy is a risk factor for cervical cancer. Other risk factors include a family history of the disease, sexual experience with multiple partners, and a history of sexually transmitted disease (e.g., syphilis, human papillomavirus infection, gonorrhea). Cigarette smoking, promiscuous male partner, human immunodeficiency virus infection or other immunosuppression, and low socioeconomic status are other risk factors. Sexual relations with one partner, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity are not risk factors for cervical cancer.
Question 78.
A woman tells the nurse, “There has been a lot of cancer in my family.” The nurse should instruct the client to report which possible sign of cervical cancer?
(a) pain
(b) leg edema
(c) urinary and rectal symptoms
(d) light bleeding or watery vaginal discharge
Answer:
(d) light bleeding or watery vaginal discharge
Explanation:
In its early stages, cancer of the cervix is usually asymptomatic, which underscores the importance of regular Pap smears. A light bleeding or serosanguineous discharge may be apparent as the first noticeable symptom. Pain, leg edema, urinary and rectal symptoms, and weight loss are late signs of cervical cancer.
Question 79.
A 30-year-old female client asks the nurse about douching. What information should the nurse include in the teaching plan?
(a) Douching during menstruation is safe.
(b) Daily douching will decrease vaginal odor.
(c) Perfumed douches are recommended to decrease odors.
(d) Douching removes natural mucus and changes the balance of normal vaginal flora.
Answer:
(d) Douching removes natural mucus and changes the balance of normal vaginal flora.
Explanation:
The vagina naturally cleans itself, and douching is not recommended unless it is prescribed by a health care provider (HCP) [J] for a medical condition. Daily douching could destroy normal flora. Perfumed douches could trigger allergenic responses. Douching should be avoided during menses.
Question 80.
A young woman will receive 6 months of chemotherapy for cervical cancer. She is a single parent of two young children and can no longer work. The nurse contacts a social worker to help plan continuing care. The client states, “I feel overwhelmed. How can the social worker help me?” Which responses by the nurse about the role of the social worker are appropriate? Select all that apply.
(a) “The social worker is a part of a multidisciplinary team that provides care for clients with cancer.”
(b) “The social worker can assist in locating resources and programs to assist you during your treatment.”
(c) “Based on your financial situation and need to care for your children, the social worker can help you identify needed resources at this time.”
(d) “Your entire family will be included in the treatment plan. Your needs and those of your children will be assessed and determined so that referrals can be made to appropriate resources.”
(e) “The social worker can authorize temporary funds to help you with child care and to pay your bills while you are sick.”
Answer:
(a) “The social worker is a part of a multidisciplinary team that provides care for clients with cancer.”
(b) “The social worker can assist in locating resources and programs to assist you during your treatment.”
(c) “Based on your financial situation and need to care for your children, the social worker can help you identify needed resources at this time.”
(d) “Your entire family will be included in the treatment plan. Your needs and those of your children will be assessed and determined so that referrals can be made to appropriate resources.”
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d). The social worker is part of the comprehensive, holistic health care team. Because the client is now unemployed and is a single parent, the social worker can provide information about sources of financial support. The needs of the client and the family members are included in the treatment plan. The social worker cannot authorize temporary funds.
Question 81.
The husband of a client with cervical cancer says to the nurse, “The doctor told my wife that her cancer is curable. Is he just trying to make us feel better?” Which would be the nurse’s most accurate response?
(a) “When cervical cancer is detected early and treated aggressively, the cure rate is almost 100%.”
(b) “The 5-year survival rate is about 75%, which makes the odds pretty good.”
(c) “Saying a cancer is curable means that 50% of all women with the cancer survive at least 5 years.”
(d) “Cancers of the female reproductive tract tend to be slow growing and respond well to treatment.”
Answer:
(a) “When cervical cancer is detected early and treated aggressively, the cure rate is almost 100%.”
Explanation:
When cervical cancer is detected early and treated aggressively, the cure rate approaches 100%. The incidence of cervical cancer has increased among women of African descent, Native American and Aboriginal people, and Latinas, and these women often have a poorer prognosis because the cancer is not identified early. Papanicolaou smears and colposcopy have the potential to decrease mortality from invasive carcinoma when these screening and treatment programs are utilized by women.
Question 82.
A client with suspected cervical cancer had a colposcopy with conization. What information should the nurse give the client about her menstrual periods after this surgery?
(a) Her periods will return to normal after 6 months.
(b) Her next two or three periods may be heavier and more prolonged than usual.
(c) Her next two or three periods will be lighter than normal.
(d) She may skip her next two periods.
Answer:
(b) Her next two or three periods may be heavier and more prolonged than usual.
Explanation:
The client should be informed that her next two or three periods could be heavy and prolonged. The client is instructed to report any excessive bleeding. The nurse should reinforce the necessity for the follow-up check and the review of the biopsy results with the client. The client’s peri-ods will not be normal for 2 to 3 months.
Question 83.
A client with cervical cancer is undergoing internal radium implant therapy. A lead-lined container and a pair of long forceps have been placed in the client’s hospital room. What should the nurse tell the client about how these will be used?
The forceps and container will be used for:
(a) disposal of emesis or other bodily secretions.
(b) handling of a dislodged radiation source.
(c) disposal of the client’s eating utensils.
(d) storage of the radiation dose.
Answer:
(b) handling of a dislodged radiation source.
Explanation:
Dislodged radioactive materials should not be touched with bare or gloved hands. Forceps are used to place the material in the lead-lined container, which shields the radiation. Exposure to radiation can occur only by direct exposure to the encased radioactive substance; it cannot result from contact with emesis or urine or from touching the client. Disposal of eating utensils cannot lead to radiation exposure. Radioactive dose materials are kept only in the radiation department.
Question 84.
The mother of a client who has a radium implant asks why so many nurses are involved in her daughter’s care. She states, “The doctor said I can be in the room for up to 2 hours each day, but the nurses say they are restricted to being here for 30 minutes.” What should the nurse explain to the client?
Nurses:
(a) touch the client, which increases their exposure to radiation.
(b) work with many clients and could carry infection to a client receiving radiation therapy, if exposure is prolonged.
(c) work with radiation on an ongoing basis, while visitors have infrequent exposure to radiation.
(d) are at greater risk from the radiation because they are younger than the mother.
Answer:
(c) work with radiation on an ongoing basis, while visitors have infrequent exposure to radiation.
Explanation:
The three factors related to radiation safety are time, distance, and shielding. Nurses on radiation oncology units work with radiation frequently and so must limit their contact. Nurses are physically closer to clients than are visitors, who are often asked to sit 6 feet [182.9 cm) away from the client. Touching the client does not increase the amount of radiation exposure. Aseptic technique and isolation prevent the spread of infection. Age is a risk factor for people in their reproductive years.
Question 85.
A client with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is being treated by a colposcopy. The client asks the nurse if this procedure is really necessary. The nurse can tell the client that if the HPV infection is not treated which health problem is likely to occur?
(a) infertility
(b) cervical cancer
(c) pelvic inflammatory disease
(d) rectal cancer
Answer:
(b) cervical cancer
Explanation:
HPV infection, or genital warts, can lead to dysplastic changes of the cervix, referred to as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. The development of cervical cancer remains the largest threat of all condyloma-associated neoplasias. Infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and rectal cancer are not complications of genital warts.
Question 86.
Which action should be included in the nursing care for a client with cervical cancer who has an internal radium implant in place?
(a) Offer the bed pan every 2 hours.
(b) Provide perineal care twice daily.
(c) Check the position of the applicator hourly.
(d) Offer a low-residue diet.
Answer:
(d) Offer a low-residue diet.
Explanation:
Bowel movements can be difficult with the radium applicator in place. The purpose of the low-residue diet is to decrease bowel movements. The bowel is cleaned before therapy, and the woman is maintained on a low-residue diet during treatment to prevent bowel distention and defecation. To prevent dislodgment of the applicator, the client is maintained on strict bed rest and allowed only to turn from side to side. Perineal care is omitted during radium implant therapy, although any vaginal discharge should be reported to the health care provider (HCP). It is rare for the applicator to extrude, so this does not need to be checked every hour.
Question 87.
A client is being treated with internal radium implants. The nurse should assess the client for which adverse effects associated with radiation therapy to the cervix?
(a) severe vaginal itching
(b) confusion
(c) high fever in the afternoon or evening
(d) nausea and a foul vaginal discharge
Answer:
(d) nausea and a foul vaginal discharge
Explanation:
Nausea, vomiting, and a foul vaginal discharge are common adverse effects of internal radiation therapy for cervical cancer. A foul-smelling discharge may develop from the destruction and sloughing of cells. Vaginal discharge may persist for some time. General signs and symptoms of radiation syndrome include nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and malaise. Vaginal itching, confusion, and high fever are not typical adverse effects of radiation therapy for cervical cancer.
Question 88.
When teaching a client about ovarian cancer, the nurse should include which information in the teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) details about the prognosis
(b) staging and grading of ovarian cancer
(c) need for routine colonoscopy beginning at age 30
(d) procedures for diagnosis if there is a pelvic mass
(e) symptoms occurring early in the disease process
Answer:
(b) staging and grading of ovarian cancer
(d) procedures for diagnosis if there is a pelvic mass
Explanation:
(b), (d). Client teaching emphasizes the importance of regular gynecologic examinations. If a pelvic mass is found, completely explain the procedures for diagnosis. Explain presurgical and post- surgical instructions, and explain the terminology particular to staging and grading of cancer, when appropriate. Refer all questions about the prognosis to the health care provider (HCP). Routine colonoscopies are typically begun at age 50 unless family history warrants otherwise. Ovarian tumors are commonly occult until symptoms of advanced disease are present.
Question 89.
Interprofessional management of ovarian cancer includes which measures? Select all that apply.
(a) combination chemotherapy to cure the cancer
(b) bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy to remove diseased organs
(c) radiation therapy to eliminate all cancer cells
(d) referral to social services for supportive care
(e) nutrition therapy for parenteral lipids
Answer:
(b) bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy to remove diseased organs
(d) referral to social services for supportive care
Explanation:
(b), (d). Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor of the ovary. Ovarian cancer is the fourth most common gynecologic cancer, but the most lethal. It is usually found in advanced stages because it is asymptomatic in early stages. Interdisciplinary management may involve chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and supportive services. Chemotherapy may be used to achieve remission of the disease; it is not, however, curative. Surgery is the treatment of choice, usually involving total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and removal of the omentum. Radiation therapy may be performed for palliative purposes only. The nurse should provide referral to home health services, financial assistance, psychological counseling, clergy, and other social services, as appropriate. Nutrition therapy for parenteral lipids is not part of management of ovarian cancer.
Question 90.
A client with ovarian cancer asks the nurse, “What is the cause of this cancer?” Which is the most accurate response by the nurse?
(a) Use of oral contraceptives increases the risk of ovarian cancer.
(b) Women who have had at least two live births are protected from ovarian cancer.
(c) There is less chance of developing ovarian cancer when one lives in an industrialized country.
(d) The risk of developing ovarian cancer is related to environmental, endocrine, and genetic factors.
Answer:
(d) The risk of developing ovarian cancer is related to environmental, endocrine, and genetic factors.
Explanation:
A definitive cause of carcinoma of the ovary is unknown, and the disease is multifactorial. The risk of developing ovarian cancer is related to environmental, endocrine, and genetic factors. The highest incidence is in industrialized Western countries. Endocrine risk factors for ovarian cancer include women who are nulliparous. Use of oral contraceptives does not increase the risk for developing ovarian cancer but may actually be protective.
Question 91.
The nurse is planning a presentation about ovarian cancer to a group of women. Which topic should receive priority attention in the lesson plan?
(a) Ovarian cancer signs and symptoms are often vague until late in development.
(b) Ovarian cancer should be considered in any woman older than 30 years of age.
(c) A rigid board-like abdomen is the most common sign.
(d) Methods for early detection have made a dramatic reduction in the mortality rate due to ovarian cancer.
Answer:
(a) Ovarian cancer signs and symptoms are often vague until late in development.
Explanation:
varian cancer is rarely diagnosed early. Methods for mass screening and early detection have not been successful. Signs and symptoms are often vague until late in development. Ovarian cancer should be considered in any woman older than 40 years of age who has vague abdominal and/or pelvic discomfort or enlargement, a sense of bloating, or flatulence. Enlargement of the abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid is the most common sign.
Question 92.
A 28-year-old male is diagnosed with acute epididymitis. What should the nurse assess the client for when conducting a focused assessment?
(a) burning and pain on urination
(b) severe tenderness and swelling in the scrotum
(c) foul-smelling ejaculate
(d) foul-smelling urine
Answer:
(b) severe tenderness and swelling in the scrotum
Explanation:
Epididymitis causes acute tenderness and pronounced swelling of the scrotum. Gradual onset of unilateral scrotal pain, urethral discharge, and fever are other key signs. Epididymitis is occasionally, but not routinely, associated with urinary tract infection. Burning and pain on urination and foul-smelling ejaculate or urine are not classic symptoms of epididymitis.
Question 93.
A 30-year-old client is being treated for epididymitis. What information should the nurse include in the teaching plan about the likely cause of epididymitis?
(a) virus
(b) parasite
(c) sexually transmitted infection
(d) protozoon
Answer:
(c) sexually transmitted infection
Explanation:
Among men younger than age 35, epididymitis is most frequently caused by a sexually transmitted infection. Causative organisms are usually chlamydia or Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The other major form of epididymitis is bacterial, caused by the Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas organisms. The nurse should always include safe sex teaching for a client with epididymitis. The client should also be advised against anogenital intercourse because this is a mode of transmission of gram-negative rods to the epididymis.
Question 94.
When teaching a client to perform testicular self-examination, when should the nurse instruct the client to perform the exam?
(a) after intercourse
(b) at the end of the day
(c) after a warm bath or shower
(d) after exercise
Answer:
(c) after a warm bath or shower
Explanation:
After a warm bath or shower, the testes hang lower and are both relaxed and in the ideal position for manual evaluation and palpation. The testes are not relaxed or in the best position after intercourse, at the end of the day, or after exercise.
Question 95.
The nurse is assessing a client’s testes.
Which finding indicates the testes are normal?
(a) soft
(b) egg-shaped
(c) spongy
(d) lumpy
Answer:
(b) egg-shaped
Explanation:
Normal testes feel smooth, egg-shaped, and firm to the touch, without lumps. The surface should feel smooth and rubbery. The testes should not be soft or spongy to the touch. Testicular malignancies are usually nontender, nonpainful hard lumps. Lumps, swelling, nodules, or signs of inflammation should be reported to the health care pro-vider (HCP)
Question 96.
Which is a risk factor for testicular cancer?
(a) undescended testes
(b) sexual relations at an early age
(c) seminal vesiculitis
(d) epididymitis
Answer:
(a) undescended testes
Explanation:
Cryptorchidism (undescended testes) carries a greatly increased risk for testicular cancer. Undescended testes occur in about 3% of male infants, with an increased incidence in premature infants. Other possible causes of malignancy include chemical carcinogens, trauma, orchitis, and environmental factors. Testicular cancer is not associated with early sexual relations in men, even though cervical cancer is associated with early sexual relations in women. Testicular cancer is not associated with seminal vesiculitis or epididymitis.
Question 97.
A client with a testicular malignancy undergoes a radical orchiectomy. What should the nurse assess the client for during the immediate postoperative period?
(a) bladder spasms
(b) urine output
(c) pain
(d) nausea
Answer:
(c) pain
Explanation:
Because of the location of the incision in the high inguinal area, pain is a major problem during the immediate postoperative period. The incisional area and discomfort caused by movement contribute to increased pain. Bladder spasms and elimination problems are more commonly associated with prostate surgery. Nausea is not a priority problem.
Question 98.
A right orchiectomy is performed on a client with a testicular malignancy. The client expresses concerns regarding his sexuality. What information should the nurse give the client to address his concerns?
The client:
(a) is not a candidate for sperm banking.
(b) should retain normal sexual drive and function.
(c) will be impotent.
(d) will have a change in secondary sexual characteristics.
Answer:
(b) should retain normal sexual drive and function.
Explanation:
Unilateral orchiectomy alone does not result in impotence if the other testis is normal. The other testis should produce enough testosterone to maintain normal sexual drive, functioning, and characteristics. Sperm banking before treatment is commonly recommended because radiation or che-motherapy can affect fertility.
Question 99.
A client diagnosed with seminomatous testicular cancer expresses fear and questions the nurse about his prognosis. Which information should the nurse give the client about the prognosis for testicular cancer?
(a) Testicular cancer can be cured.
(b) Testicular cancer has a cure rate of 90% when diagnosed early.
(c) Surgery is the treatment of choice for testicular cancer.
(d) Testicular cancer has a 50% cure rate when diagnosed early.
Answer:
(b) Testicular cancer has a cure rate of 90% when diagnosed early.
Explanation:
When diagnosed early and treated aggressively, testicular cancer has a cure rate of about 90%. Treatment of testicular cancer is based on tumor type, and seminoma cancer has the best prognosis. Modes of treatment include combinations of orchiectomy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The chemotherapeutic regimen used currently is responsible for the successful treatment of testicular cancer. The nurse should not indicate to the client that the cancer will be cured, even though cure rates are high.
Question 100.
The nurse is developing an educational program about prostate cancer. The nurse should provide information about which topic?
(a) The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test is reliable for detecting the presence of prostate cancer.
(b) For all men, age 50 and older, the American and Canadian Cancer Societies recommend an annual rectal examination.
(c) Men over 50 should have a colonoscopy.
(d) Regular sexual activity promotes health of the prostate gland to prevent cancer.
Answer:
(b) For all men, age 50 and older, the American and Canadian Cancer Societies recommend an annual rectal examination.
Explanation:
Most cases of prostate cancer are adenocar-cinomas. An adenocarcinoma is palpable on rectal examination because it arises from the posterior portion of the gland. Although the PSA is not a perfect screening test, the American Cancer Society and the Canadian Cancer Society recommend an annual rectal examination and blood PSA level for all men age 50 years and older, or starting at age 40 years if the client is of African descent, or if there is family history of prostate cancer. A colonoscopy is performed to diagnose colon cancer, not prostate cancer. Regular sexual activity does not prevent cancer of the prostate.
Question 101.
The nurse is caring for a client who will have a bilateral orchiectomy. The client asks what is involved with this procedure. Which statement is the nurse’s most appropriate response?
“The surgery:
(a) removes the entire prostate gland, prostatic capsule, and seminal vesicles.”
(b) tends to cause urinary incontinence and impotence.”
(c) freezes prostate tissue, killing cells.”
(d) results in reduction of the major circulating androgen, testosterone.”
Answer:
(d) results in reduction of the major circulating androgen, testosterone.”
Explanation:
Bilateral orchiectomy (removal of testes) results in reduction of the major circulating androgen, testosterone, as a palliative measure to reduce symptoms and progression of prostate cancer. A radical prostatectomy (removal of entire prostate gland, prostatic capsule, and seminal vesicles) may include pelvic lymphadenectomy. Complications include urinary incontinence, impotence, and rectal injury with the radical prostatectomy. Cryosurgery freezes prostate tissue, killing tumor cells without prostatectomy.
Question 102.
The nurse is teaching a client about prostate cancer. Which points should be included in the instruction? Select all that apply.
(a) Prostate cancer is usually multifocal and slow growing.
(b) Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinoma.
(c) The incidence of prostate cancer is higher in men of African descent, and the onset is earlier.
(d) A prostate-specific antigen (PSA) lab test >4 ng/mg will need to be monitored.
(e) Cancer cells are detectable in the urine.
Answer:
(a) Prostate cancer is usually multifocal and slow growing.
(b) Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinoma.
(c) The incidence of prostate cancer is higher in men of African descent, and the onset is earlier.
Explanation:
Cancer of the prostate gland is the second leading cause of cancer death among American and Canadian men and is the most common carcinoma in men older than age 65. Incidence of prostate cancer is higher in men of African descent, and onset is earlier. Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinoma. Prostate cancer is usually multifocal and slow growing and can spread by local extension, by lymphatics, or through the bloodstream. PSA >4 ng/mg is diagnostic; a free PSA level can help stratify the risk of elevated PSA levels. Metastatic workup may include skeletal X-ray, bone scan, and computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging to detect local extension, bone, and lymph node involvement. The urine does not have prostate cancer cells.
Question 103.
What should the nurse do for a client who is receiving hormone replacement for prostate cancer? Select all that apply.
(a) Inform the client that increased libido is expected with hormone therapy.
(b) Reassure the client that erectile dysfunction will not occur as a consequence of hormone therapy.
(c) Provide the client the opportunity to communicate concerns and needs.
(d) Utilize communication strategies that enable the client to gain some feeling of control.
(e) Suggest that an appointment be made to see a psychiatrist.
Answer:
(c) Provide the client the opportunity to communicate concerns and needs.
(d) Utilize communication strategies that enable the client to gain some feeling of control.
Explanation:
(c), (d). Hormone manipulation deprives tumor cells of androgens or their by-products and, thereby, alleviates symptoms and retards disease progression. Complications of hormonal manipulation include hot flashes, nausea and vomiting, gynecomastia, and sexual dysfunction. As part of supportive care, provide explanations of diagnostic tests and treatment options and help the client gain some feeling of control over his disease and decisions related to it. To help achieve optimal sexual function, give the client the opportunity to communicate his concerns and sexual needs. Inform the client that decreased libido is expected after hormonal manipulation therapy and that impotence may result from some surgical procedures and radiation. A psychiatrist is not needed.
Question 104.
A client asks the nurse why the prostate- specific antigen (PSA) level is determined before the digital rectal examination. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “It is easier for the client.”
(b) “A prostate examination can possibly decrease the PSA.”
(c) “A prostate examination can possibly increase the PSA.”
(d) “If the PSA is normal, the client will not have to undergo the rectal examination.”
Answer:
(c) “A prostate examination can possibly increase the PSA.”
Explanation:
Manipulation of the prostate during the digital rectal examination may falsely increase the PSA levels. The PSA determination and the digital rectal examination are no longer recommended as screening tools for prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men and the second leading killer from cancer among men in the United States and Canada. Incidence increases sharply with age, and the disease is predominant in the 60- to 70-year-old age group.
Question 105.
The nurse is performing a digital rectal examination. Which finding is a key sign for prostate cancer?
(a) a hard prostate, localized or diffuse
(b) abdominal pain
(c) a boggy, tender prostate
(d) a nonindurated prostate
Answer:
(a) a hard prostate, localized or diffuse
Explanation:
On digital rectal examination, key signs of prostate cancer are a hard prostate, induration of the prostate, and an irregular, hard nodule. Accompanying symptoms of prostate cancer can include constipation, weight loss, and lymph- adenopathy. Abdominal pain usually does not accompany prostate cancer. A boggy, tender prostate is found with infection (e.g., acute or chronic prostatitis).
Question 106.
A client is undergoing a total prostatectomy for prostate cancer. The client asks questions about his sexual function. What should the nurse tell the client?
“Loss of the prostate gland means that you will:
(a) be impotent.”
(b) be infertile and there will be no ejaculation.”
(c) have no loss of sexual function and drive.”
(d) have erectile capability immediately after surgery.”
Answer:
(b) be infertile and there will be no ejaculation.”
Explanation:
Loss of the prostate gland interrupts the flow of semen, so there will be no ejaculation fluid. The sensations of orgasm remain intact. The client needs to be advised that return of erectile capability is often disrupted after surgery, but within 1 year, 95% of men have returned to normal erectile function with sexual intercourse.
Question 107.
A 65-year-old client has been told by the health care provider that his prostate cancer was graded at stage IIB. The client inquires if this means he is going to die soon. What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Prostate cancer at this stage is very slow growing.”
(b) “Prostate cancer at this stage is very fast growing.”
(c) “Prostate cancer at this stage has spread to the bone.”
(d) “Prostate cancer at this stage is difficult to predict.”
Answer:
(a) “Prostate cancer at this stage is very slow growing.”
Explanation:
Clients who have stage IA or IIB prostate cancer have an excellent survival rate. Prostate cancer is usually slow growing, and many men who have prostate cancer do not die from it. A stage I or II tumor is confined to the prostate gland and has not spread to the extrapelvic region or bone.
Question 108.
A client with prostate cancer is treated with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist and antagonist goserelin. What symptom should the nurse instruct the client to expect while receiving this treatment?
(a) tenderness of the scrotum
(b) flushing
(c) loss of pubic hair
(d) decreased blood pressure
Answer:
(b) flushing
Explanation:
Goserelin is used to decrease testosterone production in men to slow or stop the production of cancer cells. A common side effect is flushing or hot flashes. Changes in blood pressure, tenderness of the scrotum, and dramatic changes in secondary sexual characteristics should not occur.
Question 109.
The client is taking sildenafil orally for erectile dysfunction. What instruction should the nurse give the client?
(a) Sildenafil may be taken more than one time per day.
(b) The health care provider (HCP) should be notified promptly if the client experiences sudden or diminished vision.
(c) Sildenafil offers protection against some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
(d) Sildenafil does not require sexual stimulation to work.
Answer:
(b) The health care provider (HCP) should be notified promptly if the client experiences sudden or diminished vision.
Explanation:
The client should notify his HCP promptly if he experiences sudden or decreased vision loss in one or both eyes. Sildenafil should not be taken more than once per day. Sildenafil offers no protection against STDs. Sildenafil has no effect in the absence of sexual stimulation.
Question 110.
A male client reports having impotence. The nurse should teach the client that which medication is a contributing factor to impotence?
(a) aspirin
(b) antihypertensives
(c) nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(d) anticoagulants
Answer:
(b) antihypertensives
Explanation:
Antihypertensives, especially beta-blockers such as propranolol, can cause impotence. When a male client has impotence, the nurse should always examine his medication regimen as a potential contributing factor. Aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and anticoagulants do not cause erectile dysfunction.
Question 111.
A 65-year-old male client with erectile dys-function (ED) asks the nurse, “Is all this just in my head? Am I crazy?” What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “ED is believed to be psychogenic in most cases.”
(b) “More than 50% of the cases are attributed to organic causes.”
(c) “Evaluation of nocturnal erections does not help differentiate psychogenic or organic causes.”
(d) “ED is an uncommon problem among men older than age 65.”
Answer:
(b) “More than 50% of the cases are attributed to organic causes.”
Explanation:
ED is multifactorial in origin, and more than 50% of the cases can be attributed to organic causes, which include alteration in vascular supply, hormonal changes, neurologic dysfunction, medications, and associated systemic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus or alcoholism. The presence of nocturnal erections is the first evaluation to differentiate between organic and psychogenic causes. ED is a common problem among men older than age 65.
Question 112.
The nurse should teach the client with erectile dysfunction (ED) to alter his lifestyle by doing which?
(a) avoiding alcohol
(b) following a low-salt diet
(c) stopping smoking
(d) increasing attempts at sexual intercourse
Answer:
(a) avoiding alcohol
Explanation:
Avoidance of alcohol can improve the outcome of therapy. Alcohol and smoking can affect a man’s ability to have and maintain an erection. The client should be encouraged to follow a healthy diet, but no specific diet is associated with improvement of sexual function. The client should cease smoking, not just decrease smoking. Increasing attempts at intercourse without treatment will not facilitate improvement. The client should be reassured that ED is a common problem and that help is available.
Question 113.
The nurse is assigning tasks to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) for a client with an abdominal hysterectomy on the first postoperative day. Which task cannot be delegated to the UAP?
(a) taking vital signs
(b) recording intake and output
(c) giving perineal care
(d) assessing the incision site
Answer:
(d) assessing the incision site
Explanation:
The registered nurse (RN) is responsible for monitoring the surgical site for condition of the dressing, status of the incision, and signs and symptoms of complications. UAP who have been trained to report abnormalities to the RN supervising the care may take vital signs, record intake and output, and give perineal care.
Question 114.
The nurse-nranager on a gynecologic surgical unit is addressing reports from clients that they have to wait too long on the night shift for their pain medication. Which course of action should the nurse-manager take first?
(a) Change the staffing schedule on nights to include a medication nurse.
(b) Consult the nursing supervisor.
(c) Consult the nurses on the evening shift about their evaluation of the night nurses regarding these reports from the clients.
(d) Complete a quality improvement study with the night nurses to document the waiting times for pain medication and other data, including staffing and client acuity.
Answer:
(d) Complete a quality improvement study with the night nurses to document the waiting times for pain medication and other data, including staffing and client acuity.
Explanation:
To determine the cause of this problem, a quality improvement study should be conducted. Before implementing solutions to a problem, the precise issues in the hospital system must be observed and documented. Consulting with the evening nurses may result in biased observations because the evening nurses are not conducting care under the same environment as the night nurses. Including a medication nurse is not the first step in understanding the problem and may be an unrealistic or expensive solution. The supervisor is not directly involved with the problem and should only be consulted if the problem cannot be solved by those involved.
Question 115.
A nurse is reviewing the health care provider’s (HCP's) admitting prescriptions for a postmenopausal woman scheduled for a dilatation and curettage. The nurse is unable to decipher the handwriting but thinks the medication prescription reads either metoprolol or topiramate. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Ask the client if she has hypertension.
(b) Ask the client if she has migraines.
(c) Call the HCP to clarify the prescription.
(d) Ask the pharmacist to interpret the prescription.
Answer:
(c) Call the HCP to clarify the prescription.
Explanation:
The nurse must clarify this prescription with the admitting HCP QJ to ensure medication accuracy and client safety. In health care settings without computerized medical records or computer prescribing, misinterpretation of handwriting remains a leading cause of medication errors. It is not safe practice to question the client regarding a diagnosis and assume the medication is correctly prescribed. The pharmacist will need clarification of the prescription as well. It is not the role of the pharmacist to interpret the prescription.
Question 116.
The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) reports to the nurse that the client with an abdominal hysterectomy who returned from the recovery room 1 hour earlier has saturated the blue pad with bright red blood. What should the nurse do?
(a) Call the surgeon to report the bleeding.
(b) Ask the UAP to obtain vital signs while the nurse calls the surgeon.
(c) Ask the UAP to increase the flow of IV fluids to prevent shock.
(d) Assess the client again in 15 minutes before the nurse takes any further action.
Answer:
(b) Ask the UAP to obtain vital signs while the nurse calls the surgeon.
Explanation:
The surgeon should be notified when a client who has had an abdominal hysterectomy develops vaginal bleeding that saturates a blue pad in 1 hour, and care should be managed so that other personnel can obtain vital signs while the nurse contacts the surgeon. The client may need to have IV fluids increased, but the surgeon needs to be noti-fied first. Waiting 15 minutes while the client is having bright red bleeding is an unsafe nursing action; the client may lose a large amount of blood.
Question 117.
A nurse on the gynecologic surgery unit observes a respiratory therapist (RT) take a medication cup with pills that was sitting in the medication room. What course of action should the nurse take?
(a) Report the situation to the supervisor of respiratory therapy.
(b) Tell the RT that you saw her take the pills from the medication room.
(c) Report the situation to the nursing supervisor.
(d) Tell the nurse who was administering medications not to leave pills out.
Answer:
(c) Report the situation to the nursing supervisor.
Explanation:
The nurse should follow the line of authority or chain of command by reporting the observation immediately to the nursing supervisor. The nurse should not confront the person or the medication nurse because the line of authority for reporting incidents should be followed. The RT supervisor may subsequently be involved in the incident, but the nursing supervisor should initiate and follow the policy and procedure.
Read More:
