Many nursing schools incorporate RN Nclex Questions into their curriculum to familiarize students with the exam format from early on.
NCLEX Pressure Ulcer Questions - NCLEX Questions on Pressure Ulcer
Pressure Ulcer NCLEX Questions Test Strategies
Patient's History: A 65-year-old male patient was admitted to the hospital with a history of pressure ulcers. The patient has been bedridden for the past 3 months and has a history of immobility. The patient has stage 3 pressure ulcers on his sacral and heel regions.
Nurse's Notes:
- Patient's skin is intact and warm to touch
- Patient's sacral and heel regions have visible ulcers with a sunken appearance and some visible body fat and serum
- Patient's sacral and heel regions are painful to touch
- Patient's mobility is limited, and he requires assistance to change positions
Physician's Order:
- Administer pain medication as needed
- Clean and dress the pressure ulcers daily
- Reposition the patient every 2 hours
- Apply dressing to the sacral ulcer and calcium alginate gauze to the heel ulcer
- Monitor the patient's vital signs and wound healing progress
Lab Values:
- WBC count: 8,000/mm3 (normal range: 4,500-11,000/mm3)
- Hb: 12 g/dL (normal range: 13.5-17.5 g/dL)
- Platelet count: 200,000/mm3 (normal range: 150,000-450,000/mm3)
Question 1.
Which nursing intervention is appropriate for managing a patient with pressure ulcers as per the given nurse's notes and physician's order?
(a) Administer antibiotics as needed
(b) Apply honey dressing to the ulcers
(c) Reposition the patient every 4 hours
(d) Apply dressing to the sacral ulcer and calcium alginate gauze to the heel ulcer
Answer:
(d) Apply dressing to the sacral ulcer and calcium alginate gauze to the heel ulcer
Explanation:
Apply dressing to the sacral ulcer and calcium alginate gauze to the heel ulcer. The nurse's notes indicate that the patient has pressure ulcers on the sacral and heel regions, and the physician's order instructs to clean and dress the ulcers daily, apply dressing to the sacral ulcer, and calcium alginate gauze to the heel ulcer. These interventions are important to promote healing, prevent infection, and reduce pain. Antibiotics may be administered if there is an infection, but it is not the first-line intervention.
Honey dressing may have antimicrobial properties but is not mentioned in the physician's order. Repositioning the patient every 2 hours, as stated in the physician's order, helps to relieve pressure and prevent further damage to the skin. Therefore, option (c), repositioning every 4 hours, is not an appropriate intervention for managing pressure ulcers. Lab values show that the patient's WBC count and platelet count are within the normal range, and the Hb is slightly below the normal range. However, these values are not directly related to the management of pressure ulcers.
Question 2.
What type of dressing should be applied to the patient's stage 3 pressure ulcer on the sacral region?
(a) Nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing
(b) Composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels
(c) Hydrocolloid hydrogel with foam dressing gauze
(d) Calcium alginate gauze
Answer:
(c) Hydrocolloid hydrogel with foam dressing gauze
Explanation:
The patient's stage 3 pressure ulcer on the sacral region should be dressed with hydrocolloid hydrogel with foam dressing gauze. Option A is for stage l pressure ulcers, option B is for stage 2 pressure ulcers, and option D is for stage 4 pressure ulcers.
Question 3.
What is the purpose of repositioning immobile patients every 2 hours?
(a) To prevent pressure ulcers
(b) To help the patient sleep better
(c) To monitor the patient's breathing
(d) To check the patient’s vitals
Answer:
(a) To prevent pressure ulcers
Explanation:
Repositioning immobile patients every 2 hours helps to prevent pressure ulcers by reducing the pressure on one area of the skin for an extended period of time. This helps to maintain normal skin integrity and reduces the risk of developing pressure ulcers.
Question 4.
What is the definition of Pressure Ulcer?
(a) Any damage to normal skin due to underlying bones
(b) Any damage to skin due to external surface friction
(c) Any damage to skin due to pressure from external surface
(d) Any damage to normal skin due to internal pressure
Answer:
(a) Any damage to normal skin due to underlying bones
Explanation:
Pressure ulcer is defined as any damage to normal skin integrity due to pressures from underlying bones or frictional pressure from external surface which can restrict the blood flow and cause necrosis and ulcers.
Question 5.
What is the first stage of Pressure Ulcer?
(a) Red intact skin with no wounds
(b) Some abrasion and visibility of subcutaneous skin
(c) Dermis part is lost and forms sunken hole
(d) Full skin is lost opening underlying muscles, tendons or bones
Answer:
(a) Red intact skin with no wounds
Explanation:
The first stage of pressure ulcer is defined as red intact skin with no wounds. The skin may be warm or cool, firm or soft and does not turn white when pressed. This is a sign that a pressure ulcer may be forming.
Question 6.
What is the appropriate dressing for each stage of pressure ulcer?
(a) For stage 1: Hydrocolloid Hydrogel with foam dressing Gauze
(b) For stage 2: Nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing
(c) For stage 3: Composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels
(d) For stage 4: Calcium alginate gauze
(e) For unstageable: Hydrocolloid Hydrogel with foam dressing Gauze
(f) For deep tissue injury: Nontransport hydrocolloid dressing
(g) For stage 1: Composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels
(h) For deep tissue injury: Surgical interventions and adherent film gauze
Answer:
(b) For stage 2: Nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing
(h) For deep tissue injury: Surgical interventions and adherent film gauze
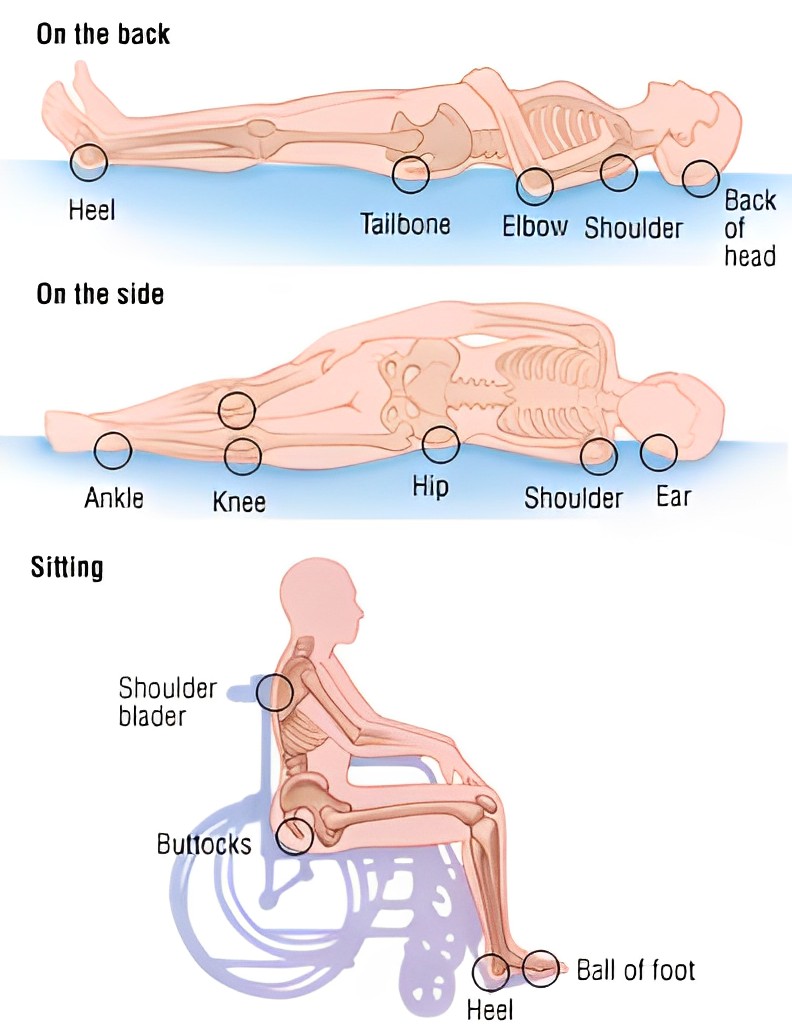
Pressure Ulcer NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
Mrs. Agrima is a 67-year-old woman who was recently hospitalized for a broken hip following a fall. She is bedridden and unable to move herself. Mrs. Agrima 's nurse attendant, Jane, noticed that Mrs. Agrima had a red area on her lower back that was painful to the touch. Upon further examination, Jane determined that Mrs. Agrima had a Stage 1 pressure ulcer.
Which of the following is the correct nursing management approach for Mrs. Agrima's Stage 1 pressure ulcer?
(a) Apply a composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels
(b) Apply a nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every day
(c) Apply a calcium alginate gauze and change the dressing 2 times a week
(d) Perform a surgical intervention and apply an adherent film gauze
Answer:
(b) Apply a nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every day
Rationale:
The correct nursing management approach for a Stage 1 pressure ulcer is to apply a nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every day. Option (a) describes the correct approach for a Stage 2 pressure ulcer. Option (c) describes the correct approach for a Stage 4 pressure ulcer, and Option (d) describes the correct approach for unstageable or deep tissue injury pressure ulcers.
Question 2.
Mrs. Agrima is a 75-year-old woman who has been bedridden for the past month due to a hip injury. She has developed a pressure ulcer on her heel. Upon assessment, the pressure ulcer is classified as a stage 2 wound.
Which of the following is the appropriate dressing for Mrs. Agrima 's pressure ulcer?
(a) Nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing
(b) Composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels
(c) Hydrocolloid hydrogel covered with foam dressing gauze
(d) Calcium alginate gauze
Answer:
(b) Composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels
Rationale:
The appropriate dressing for a stage 2 pressure ulcer is composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels. The hydrogels can stop the growth of bacteria around the affected part and the dressing should be changed every day or every 6 to 8 hours in necrotic cases.
Explanation:
Option (a) Nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing is the appropriate dressing for a stage 1 pressure ulcer, not a stage 2 pressure ulcer.
Option (c) Hydrocolloid hydrogel covered with foam dressing gauze is the appropriate dressing for a stage 3 pressure ulcer, not a stage 2 pressure ulcer.
Option (d) Calcium alginate gauze is the appropriate dressing for a stage 4 pressure ulcer, not a stage 2 pressure ulcer.
Question 3.
Mrs. Agrima is a 67-year-old patient who was recently admitted to the hospital for a hip replacement surgery. She has been bedridden for the past week and has not been able to move around much. The nurse on duty notices that Mrs. Agrima has developed a reddish patch on her lower back, which does not turn white when pressed. Upon further examination, the nurse determines that Mrs. Agrima is experiencing a stage 1 pressure ulcer.
What is the most appropriate nursing management for Mrs. Agrima 's stage 1 pressure ulcer?
(a) Apply a hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every day.
(b) Apply a hydrocolloid dressing and a composite film hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every 6-8 hours.
(c) Apply a hydrocolloid dressing, a composite film hydrocolloid dressing, and a foam dressing and clean the affected area once a week.
(d) Apply a calcium alginate gauze and clean the affected area twice a week.
Answer:
(a) Apply a hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every day.
Explanation:
Option (a) is correct because it states that the nurse should apply a hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every day, which is the appropriate nursing management for a stage 1 pressure. Hydrocolloid dressings are recommended for stage 1 pressure ulcers because they are painless to remove and are waterproof.
Option (b) is not correct because it involves the use of a composite film hydrocolloid dressing and states that the affected area should be cleaned every 6-8 hours, which is the appropriate frequency for a stage 2 pressure ulcer.
Option (c) is not correct because it involves the use of a foam dressing, which is not appropriate for a stage 1 pressure ulcer. Option D is not correct because it involves the use of a calcium alginate gauze, which is appropriate for a stage 4 pressure ulcer but not a stage 1 pressure ulcer.
Rationale:
The correct answer is A, which states that the nurse should apply a hydrocolloid dressing and clean the affected area every day. This is the appropriate nursing management for a stage 1 pressure ulcer. The other options are not appropriate for a stage 1 pressure ulcer, as they involve different types of dressings and cleaning frequencies that are specific to other stages of pressure ulcers.
Question 4.
Mrs. Agrima is a 67-year-old patient who has been hospitalized for the past week due to a severe case of pneumonia.
She has been bedridden during her stay and has developed a pressure ulcer on her right heel. Upon examination, the ulcer is determined to be a Stage 3 pressure ulcer, with visible pink tissue and body fat and the presence of serums and blisters.
What type of dressing should be applied to Mrs. Agrima's Stage 3 pressure ulcer?
(a) Nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing
(b) Composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels
(c) Hydrocolloid hydrogel with foam dressing gauze
(d) Calcium alginate gauze
Answer:
(c) Hydrocolloid hydrogel with foam dressing gauze
Explanation:
Option (a) Nontransparent hydrocolloid dressing is appropriate for a Stage 1 pressure ulcer, which is a red, intact skin with no wounds. Mrs. Agrima's pressure ulcer is a Stage 3 ulcer, which is much more severe than a Stage 1 ulcer and requires a different type of dressing.
Option (b) Composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels is appropriate for a Stage 2 pressure ulcer, which is an open sore with some abrasion and visibility of subcutaneous skin. Mrs. Agrima's pressure ulcer is a Stage 3 ulcer, which is much more severe than a Stage 2 ulcer and requires a different type of dressing.
Option (d) Calcium alginate gauze is appropriate for a Stage 4 pressure ulcer, which is a full skin loss with underlying muscle, tendon, or bone damage. Mrs. Agrima's pressure ulcer is a Stage 3 ulcer, which is not as severe as a Stage 4 ulcer and does not require the use of calcium alginate gauze.
Rationale:
The appropriate dressing for a Stage 3 pressure ulcer is a hydrocolloid hydrogel with foam dressing gauze. The advantage of the foam is that it conforms to even uneven wound surfaces, which is important for a deep wound like a Stage 3 pressure ulcer. The dressing should be changed at least once per week.
Question 5.
Mrs. Agrima is a 75-year-old patient who has been bedridden for the past month due to a hip fracture. She is at high risk for developing pressure ulcers due to her immobility. During her daily nursing assessment, you notice a red, slightly swollen area on her lower back. Upon further examination, you determine that it is a stage 1 pressure ulcer.
What is the appropriate nursing intervention for Mrs. Agrima's stage 1 pressure ulcer?
(a) Apply a composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels.
(b) Clean the affected area with a salt water (saline) rinse to remove loose, dead tissue.
(c) Wash the area gently with mild soap and water.
(d) Apply calcium alginate gauze on the affected area.
Answer:
(c) Wash the area gently with mild soap and water.
Explanation:
Option (a), "Apply a composite film hydrocolloid dressing and hydrogels," is not the correct answer because it is the appropriate nursing intervention for a stage 2 pressure ulcer. Stage 2 pressure ulcers are characterized by some abrasion and visibility of subcutaneous skin, and they form open sores.
Option (b), "Clean the affected area with a salt water (saline) rinse to remove loose, dead tissue," is not the correct answer because it is the appropriate nursing intervention for a stage 2 pressure ulcer.
Option (d), "Apply calcium alginate gauze on the affected area," is not the correct answer because it is the appropriate nursing intervention for a stage 4 pressure ulcer. Stage 4 pressure ulcers are characterized by full skin loss and damage to underlying tissues, such as muscles, tendons, or bones. Calcium alginate gauze is used as a packing material for deep wounds and helps in the development of scar tissue along with protection of the underlying parts.
Rationale:
The correct answer is option (c), "Wash the area gently with mild soap and water." This is the appropriate nursing intervention for a stage 1 pressure ulcer. Stage 1 pressure ulcers are characterized by red intact skin with no wounds. They do not turn white when pressed and may be warm or cool, firm or soft. The appropriate nursing intervention for a stage 1 pressure ulcer is to wash the area gently with mild soap and water.
Question 6.
Mrs. Agrima is a 62 year old woman who has been diagnosed with gout. Mrs. Agrima has a history of high blood pressure and diabetes, and is currently taking medication for both conditions. She is also a heavy coffee and alcohol drinker. Mrs. Agrima's healthcare provider has prescribed her a course of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage her pain and inflammation, as well as probenecid to help lower her uric acid levels.
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of gout?
(a) The formation of urate crystals in the joints
(b) The formation of chalky nodules in the hands, feet, or other body parts
(c) The development of rashes and pruritus
(d) The formation of kidney stones
Answer:
(d) The formation of kidney stones
Rationale:
Gout is characterized by the formation of urate crystals in the joints, which can lead to pain and inflammation. It is also characterized by the formation of chalky nodules, also known as tophi, on the hands, feet, or other body parts. The disease can also cause rashes and pruritus due to the deposition of urate crystals under the skin. However, while long-term gout can lead to the formation of kidney stones, it is not a characteristic of the disease itself.
Question 7.
Which of the following is NOT a recommendation for managing gout in Mrs. Agrima?
(a) Avoiding starvation
(b) Avoiding alcohol and coffee
(c) Taking a lot of water to help flush out uric acid from the body
(d) Consuming citrus fruits
Answer:
(d) Consuming citrus fruits
Rationale:
In the case study, it is recommended that Mrs. Agrima avoid starvation, alcohol, and coffee, as these activities can trigger an acute gout attack. It is also recommended that she drink at least 2-3 liters of water per day to help flush out uric acid and prevent the formation of kidney stones. However, it is not recommended that Mrs. Agrima consume citrus fruits, as they contain vitamin C which can exacerbate kidney stone formation when taken with allopurinol, a medication used to treat gout.
Question 8.
Mrs. Agrima is a 67-year-old woman who has been diagnosed with gout. She has been experiencing pain and inflammation in her toes for the past few weeks and has been prescribed NSAIDs for pain management. However, she is also taking aspirin for her heart condition and is concerned about the potential interactions between the two medications.
Which of the following statements is true regarding the use of probenecid in patients with gout?
(a) Probenecid should be avoided in patients taking aspirin
(b) Probenecid can cause visual disturbances in some patients
(c) Probenecid can increase the risk of extreme bleeding if taken with warfarin
(d) Probenecid should not be taken with citrus fruits
Answer:
(a) Probenecid should be avoided in patients taking aspirin
Explanation:
It is important for healthcare professionals to be aware of the potential interactions and side effects of medications used to treat gout in order to ensure the safe and effective management of the disease. Probenecid is a medication used to treat gout, but it should not be used in conjunction with aspirin due to the potential for salicylates to cause an elevation of uric acid levels.
Allopurinol, on the other hand, can cause visual disturbances in some patients and should not be taken with hypoglycemic agents or citrus fruits. It is also important to be aware of the potential for allopurinol to increase the effects of warfarin, which can lead to extreme bleeding.
Rationale:
Option (a) is correct because probenecid should never be used with aspirin as salicylates can cause elevation of the uric acid. Option (b) is incorrect because probenecid does not have visual side effects. Option (c) is incorrect because it refers to allopurinol, not probenecid. Option (d) is incorrect because it also refers to allopurinol, not probenecid.
Read More:
