The PN NCLEX Questions are designed to reflect the types of scenarios and patient situations encountered in real-world nursing practice.
NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 4 with Rationale
Question 1.
A primigravid client at 26 weeks’ gestation asks the nurse what causes heartburn during pregnancy. The nurse should explain to the client that heartburn during pregnancy is usually caused by which factor?
(a) increased peristaltic action during pregnancy
(b) displacement of the stomach by the diaphragm
(c) decreased secretion of hydrochloric acid
(d) backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus
Answer:
(d) backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus
Rationale:
Heartburn is caused when stomach contents enter the distal end of the esophagus, producing a burning sensation. To avoid heartburn during pregnancy, the client should avoid spicy foods, eat smaller, more frequent meals, and avoid lying down after eating. Peristalsis usually decreases during the latter half of pregnancy. Displacement of the stomach by the uterus, not the diaphragm, may contribute to heartburn. Increased, not decreased, secretion of hydrochloric acid also contributes to heartburn during pregnancy.
Question 2.
A client at a follow-up appointment after having a miscarriage 2 weeks previously yells at the nurse, “How could God do this to me? I've never done anything wrong.” Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate at this time?
(a) “God can handle your anger. It’s okay.”
(b) “I know you’re angry. It’s so hard to lose your baby.”
(c) “It’s not God’s fault. It was an accident.”
(d) “You’re a strong person. You’ll get through this.”
Answer:
(b) “I know you’re angry. It’s so hard to lose your baby.”
Rationale:
Acknowledging the anger and its source encourages communication about the client’s feelings. Although anger at God is common after a loss, the client is displacing the anger that she needs to deal with more directly. Telling the client that the miscarriage was an accident or that she is a strong person and will get through this ignores the client’s feelings of anger and loss, thereby cutting off communication.
Question 3.
A client who has been prescribed chemotherapy wants to take herbal treatments instead. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “You’re making a mistake and placing your life in jeopardy.”
(b) “Herbal treatments are not approved by the government’s regulatory agency.”
(c) “Herbal treatments have not been researched with cancer.”
(d) "Tell me about your concerns with chemotherapy.”
Answer:
(d) "Tell me about your concerns with chemotherapy.”
Rationale:
Asking the client to speak about his concerns encourages open discussion. Telling the client that he is making a mistake is judgmental of the client’s wishes and eliminates opportunities for the client to explore the situation and discuss various treatment options. Saying that herbal treatments have not been approved by the FDA or that they have not been researched is irrelevant, places a value judgment on the client’s wishes, and provides no opportunity for discussion.
Question 4.
A 4-year-old child is admitted for a cardiac catheterization. Which is most important to include as the nurse teaches this child about cardiac catheterization?
(a) a plastic model of the heart
(b) a catheter that will be inserted into the artery
(c) the child’s parents
(d) other children undergoing a catheterization
Answer:
(c) the child’s parents

Rationale:
The most important aspect of teaching a preschooler is to have the family members there for support. Preschoolers are able to understand information that is individualized to their level. Including a plastic model of the heart and a catheter as part of the preoperative preparation may be helpful. The other family members will understand the heart model and catheter better than the preschooler will.
Question 5.
A client has a reddened area over a bony prominence. The nurse finds an unlicensed nursing personnel (UAP) massaging this area. What should the nurse do?
(a) Reinforce the UAP's use of this intervention over the bony prominence.
(b) Explain to the UAP that massage is effective because it improves blood flow to the area.
(c) Inform the UAP that massage is even more effective when combined with the use of lotion.
(d) Instruct the UAP that massage is contraindicated because it decreases blood flow to the area.
Answer:
(d) Instruct the UAP that massage is contraindicated because it decreases blood flow to the area.
Rationale:
Massaging an area that is reddened due to pressure is contraindicated because it further reduces blood flow to the area. In the past, massaging reddened areas was thought to improve blood flow to the area, and some nursing personnel may still believe that massaging the area is effective in preventing pressure ulcer formation. Since massaging a reddened area is contraindicated, the nurse should not encourage the UAP Q to continue massage or explain that it is effective. The UAP should not massage the area, nor add lotion.
Question 6.
The nurse is caring for a newborn who is experiencing opioid withdrawal. To calm the infant, the nurse should include which interventions in the plan of care? Select all that apply.
(a) Swaddle the infant in a blanket.
(b) Use slow vertical rocking.
(c) Dim lighting around the crib.
(d) Provide fast tempo music.
(e) Plan care around infant cues.
Answer:
(a) Swaddle the infant in a blanket.
(b) Use slow vertical rocking.
(c) Dim lighting around the crib.
(e) Plan care around infant cues.
Rationale:
Swaddling, vertical rocking, reducing environmental stimuli like lighting, and planning care around infant cues helps drug-exposed infants to exhibit age-appropriate state modulation. Fast tempo music will be too simulating to the infant.
Question 7.
The nurse receives report on four infants (see graphic). Which infant should the nurse see first?
|
Baby |
Age |
Gestational Age |
Last Vital Signs/All Were Taken 15 Minutes Ago |
Last Feeding |
Additional Comments |
|
A |
30 minutes |
40 weeks |
T = 36.3°C Heart Rate = 120 Respiratory Rate = 56 |
Not fed yet |
No labs have been drawn |
|
B |
24 hours old |
35 weeks |
T = 36.5°C Heart Rate = 164 Respiratory Rate = 46 |
3 hours ago |
Glucose 45 mg/dL (2.5 mmol/L) 30 minutes ago |
|
C |
48 hours old |
36 weeks |
T = 36.9°C Heart Rate = 146 Respiratory Rate = 38 |
4 hours ago |
Bilirubin level of 5 mg/dL (85.5 iimol/L) 24 hours ago |
|
D |
72 hours old |
37 weeks |
T = 37.5°C Heart Rate = 110 Respiratory Rate = 40 |
5 hours ago |
Needs hearing screen before dis charge in 1 hour |
(a) A, 30 minutes 40 weeks
(b) B, 24 hours 35 weeks
(c) C, 48 hours 36 weeks
(d) D, 72 hours 37 weeks
Answer:
(a) A, 30 minutes 40 weeks
Rationale:
Of the infants the nurse received report on, infant A is the most unstable and vulnerable. The infant is only 30 minutes old and is transitioning to extra uterine life. The other three infants will need assessments and care but are currently stable.
Question 8.
A widowed client who is receiving chemotherapy tells the nurse that he does not like to cook for himself. Which community resource is appropriate for this client?
(a) a hospice/palliative care association
(b) a home care/visiting nurses group
(c) a meal delivery service
(d) an association for retirees
Answer:
(c) a meal delivery service
Rationale:
A meal delivery service would be the most helpful to this client. There are a variety of services, some of them at no cost to the client in which a volunteer brings the meal and visits with the client and is a means to check on elderly persons who live alone. Hospice care involves daily needs for the terminally ill at home, and this client does not need this type of service.
Home nursing services typically provide skilled nursing care to clients at home, and this client does not need this level of care. Associations for retired persons advocate for care and services for retirees, but they do not provide services or care.
Question 9.
After the client has a temporary pacemaker inserted, the nurse should verify documentation on the medical record about which information?
(a) the client’s cardiovascular status
(b) the client’s emotional state
(c) the type of sedation used
(d) pacemaker rate, type, and settings
Answer:
(a) the client’s cardiovascular status
Rationale:
The cardiovascular status of the client is the first information documented and will validate the effectiveness of the temporary pacemaker. The client’s emotional state and the type of sedation are important but not a high priority. The nurse will need to document the pacemaker information (settings of the pacemaker); this will be considered part of the cardiovascular information.
Question 10.
The nurse judges that the parent of a 9-month-old infant in a hip spica cast understands how to feed the child when the parent makes which statement?
(a) “I can lay my child flat and feed that way.”
(b) “I will raise my child’s head up and leave the hips and legs on a pillow.”
(c) “I can borrow a special feeding table to use.”
(d) “It will take two of us, one to hold and one to feed.”
Answer:
(c) “I can borrow a special feeding table to use.”
Rationale:
Using a special feeding table or modified high chair is the best method for an infant who is used to sitting up for feedings. The child should not be flat because of the danger of aspiration. Raising the child’s head will not work as well as using a feeding table because the child is not used to lying down to eat. Two people are not necessary.
Question 11.
The nurse is assessing home care needs for a group of clients. Which clients qualify for home care services? Select all that apply.
(a) the client requiring monitoring of prothrom bin time due to (warfarin) therapy
(b) the client needing additional instruction about preparation of food on a low-sodium diet
(c) the client who has episodes of vertigo that result in falls
(d) the client who has multiple sclerosis with an open, draining lesion on a foot
(e) the client who needs stronger lenses for glasses
Answer:
(c) the client who has episodes of vertigo that result in falls
(d) the client who has multiple sclerosis with an open, draining lesion on a foot
Rationale:
The National Association for Home Care (NAHC) defines “home care” as services for people who are recovering, disabled, or chronically ill and who are in need of treatment or support to function effectively in the home environment. The client with multiple sclerosis and an open lesion is at risk for infection and will require assistance with managing the lesion. Prothrombin monitoring is usually done at the clinic or health care provider’s (HCP’s) office.
Diet instruction can be accomplished at a health care facility or dietitian’s office. The client with vertigo should be monitored for safety in the home. Clients receiving home care services are usually under the care of an HCP with the focus of care being treatment or rehabilitation. Lenses for glasses can be evaluated at an eye clinic or an ophthalmologist’s office; a prescription for stronger lenses could be written.
Question 12.
Which type of mouth care is most appropriate when the nurse is caring for a client with dentures who has severe stomatitis?
(a) using a soft toothbrush or gauze pad to provide oral hygiene
(b) rinsing the mouth with a commercial mouth wash before and after each meal
(c) cleansing the gums and oral mucosa with an oral swab with an astringent every shift
(d) keeping dentures in place to decrease development of edema
Answer:
(a) using a soft toothbrush or gauze pad to provide oral hygiene
Rationale:
A soft toothbrush or gauze pad should be used to provide oral hygiene at least every 2 hours to promote client comfort and prevent superinfection. Commercial mouthwash is contraindicated because of high alcohol content that is irritating to inflamed mucosa. Oral swabs with an astringent should be avoided because they are drying and also can promote bacterial growth.
Leaving dentures in place will have no effect on the development of edema. Additionally, further irritation of the oral mucosa may occur if dentures are left in place. Dentures should be removed to aid in relieving the client’s discomfort or pain.
Question 13.
The nursing staff has finished restraining a combative client. In addition to determining whether anyone was injured, the staff is mandated to evaluate the incident to obtain which outcome?
(a) Coordinate documentation of the incident.
(b) Resolve negative feelings and attitudes.
(c) Improve the use of restraint procedures.
(d) Calm down before returning to the other clients.
Answer:
(c) Improve the use of restraint procedures.
Rationale:
Although coordinating documentation, resolving negative feelings, and calming down are goals of debriefing after a restraint, the ultimate outcome is to improve restraint procedures.
Question 14.
Two parents who are arguing in their infant’s room, with voices raised and getting louder, start to hit each other. The infant is crying. Which action should the staff nurse take next?
(a) Try to reason with both of the parents.
(b) Ask one of the parents to leave the room.
(c) Call security to come and break up the fight.
(d) Remove the infant from the room.
Answer:
(d) Remove the infant from the room.
Rationale:
The situation is escalating, and the nurse’s priority is to protect the infant from harm. Therefore, removal of the infant from this situation should be the first action by the nurse. Reasoning at this point or asking one of the parents to leave the room would be ineffective and may serve to further escalate the situation. Calling security is necessary, but only after the nurse has removed the infant from the room.
Question 15.
A client asks the nurse why it is necessary to complete an advance directive on admission to the hospital. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “This will provide a substitute for informed discussion with your health care provider.”
(b) “It is your chance to make your wishes known if you ever become incapable of making your own decisions.”
(c) “Your health care provider will make the best decisions for you in an emergency.”
(d) “Are you worried that extraordinary means will be taken if you are dying?”
Answer:
(b) “It is your chance to make your wishes known if you ever become incapable of making your own decisions.”
Rationale:
By federal law, all clients entering a hospital or hospice program are offered the chance to make an advance directive, so that their wishes will be known and followed in an emergency. The directive is not a substitute for informed discussion with the HCP n Worry about extraordinary means being taken can be discussed with the client later, but the client needs to be informed that the directive is a federal requirement to protect the client’s autonomy.
Question 16.
When witnessing an adult client’s signature on a consent form for a procedure, the nurse verifies that the consent was obtained in an appropriate manner. What information should the nurse verify? Select all that apply.
(a) that there was adequate disclosure of information
(b) that the client understood the information
(c) that there was voluntary consent on the client’s part
(d) that the client has full awareness of the potential complications
(e) that the client’s relative, spouse, or legal guardian was present
Answer:
(a) that there was adequate disclosure of information
(b) that the client understood the information
(c) that there was voluntary consent on the client’s part
(d) that the client has full awareness of the potential complications
Rationale:
The role of the nurse in witnessing the signing of the consent is to witness that the client is informed of the procedure, understands the information, is aware of potential complications, and is signing of his or her own free will. It is not necessary for a spouse, relative, or guardian to be present.
Question 17.
A pregnant woman at 22 weeks’ gestation is diagnosed with gonorrhea. The health care provider (HCP) prescribes doxycycline. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Instruct the client about the effects of the drug.
(b) Make sure the record notes that the baby must receive eye drops when born.
(c) Have the HCP add a single dose of ceftriaxone.
(d) Discuss with the HCP the need to change the prescription.
Answer:
(d) Discuss with the HCP the need to change the prescription.
Rationale:
Doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnancy because it can stain the teeth of the developing fetus when given during the last half of pregnancy. The nurse should withhold the drug and notify the HCP to change the prescription. All neonates are given prophylactic ophthalmic ointment for the prevention of ophthalmia neonatorum, conjunctivitis caused by gonorrhea.
Question 18.
After a client undergoes a contraction stress test that is negative, what should the nurse assess next?
(a) evidence of ruptured membranes
(b) viability status of the fetus
(c) indications that contractions have ceased
(d) fetal heart rate patterns
Answer:
(c) indications that contractions have ceased
Rationale:
The contraction stress test simulates labor and determines the fetal response to the labor process and the mother’s contractions. Therefore, determining that contractions have ceased after the test is important. Although spontaneous rupture of membranes is a possibility after a contraction stress test, it is not a typical occurrence.
The test should not affect the viability of the fetus. Fetal viability is related to gestational age. A fetus of at least 23 weeks’ gestation is considered viable or capable of extrauterine life. Stating that stress test is negative means the fetal heart rate has already been interpreted and has not been found to fall during contractions.
Question 19.
A 2-month-old infant is at risk for an ileus after surgery to correct intussusception. What should be included in a focused assessment for this complication? Select all that apply.
(a) measurement of urine specific gravity
(b) assessment of bowel sounds
(c) characteristics of the first stool
(d) measurement of gastric output
(e) bilirubin levels
Answer:
(b) assessment of bowel sounds
(c) characteristics of the first stool
(d) measurement of gastric output
Rationale:
A postoperative ileus is a functional obstruction of the bowel. Assessment of bowel sounds, the first stool, and the amount of gastric output provide information about the return of gastric function. Measurement of urine specific gravity provides information about fluid and electrolyte status; bilirubin levels provide information about liver function, and neither of these tests needs to be included in a focused assessment for ileus.
Question 20.
A client with asthma who has wheezing and shortness of breath asks the nurse if it is all right to use the salmeterol inhaler during exercise. What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “Yes, use the inhaler immediately for these symptoms.”
(b) “No, this drug is a maintenance drug, not a rescue inhaler.”
(c) “Use the inhaler 5 minutes before you exer cise to prevent the wheezing.”
(d) “This inhaler is for allergic rhinitis, not asthma.”
Answer:
(b) “No, this drug is a maintenance drug, not a rescue inhaler.”
Rationale:
Salmeterol is a beta2-agonist, a maintenance drug that the asthmatic client uses twice daily, every 12 hours. Albuterol is used as the “rescue inhaler” for bronchospasms. Salmeterol can be used to prevent exercise-induced bronchospasms, but it should be taken 30 to 60 minutes before exercise.
If the client is taking salmeterol twice daily, it should not be used in additional doses before exercise; twice daily is the maximum dosage. Indications for salmeterol include only asthma and bronchospasm induced by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Question 21.
The nurse should assess the child with nephrotic syndrome for which factors? Select all that apply.
(a) blood pressure
(b) generalized edema
(c) serum lipid levels
(d) red blood cells in the urine
(e) streptococcal antibody titers
Answer:
(a) blood pressure
(b) generalized edema
(d) red blood cells in the urine
Rationale:
Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia and normal or lower than normal blood pressure. Elevated streptococcal antibody titers are associated with poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, an immune complex disease.
Question 22.
A client is receiving spironolactone for treatment of bilateral lower extremity edema. The nurse should instruct the client to make which nutritional modification to prevent an electrolyte imbalance?
(a) Increase intake of milk and milk products.
(b) Restrict fluid intake to 1,000 mL/day.
(c) Decrease foods high in potassium.
(d) Increase foods high in sodium.
Answer:
(c) Decrease foods high in potassium.
Rationale:
Aldactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic often used to counteract potassium loss caused by other diuretics. If foods or fluids are ingested that are high in potassium, hyperkalemia may result and lead to cardiac arrhythmias. Increasing the intake of milk or milk products does not affect the potassium level.
Restricting fluid may elevate all electrolytes due to extracellular fluid volume depletion. By increasing foods high in sodium, water would tend to be retained and so would dilute all electrolytes in the extracellular fluid compartment.
Question 23.
The nurse establishes the goal of preventing the development of a stress ulcer in a burn client. Which would most likely contribute to the achievement of this goal?
(a) implementing relaxation exercises
(b) administering a sedative as needed
(c) providing a soft, bland diet
(d) administering famotidine as prescribed
Answer:
(d) administering famotidine as prescribed
Rationale:
Clients with burns are susceptible to the development of Curling’s ulcer, a gastroduodenal ulcer that is caused by a generalized stress response. The stress response results in increased gastric acid secretion and a decreased production of mucus. Prevention is the best treatment, and clients are frequently treated prophylactically with antacids and H2 histamine blockers such as famotidine.
Question 24.
A nurse is assessing a client with a history of myocardial infarction who is in the surgical unit following a gastric resection. The client has chest pains. The nurse obtains the electrocardiogram (ECG) shown (see figure). What should the nurse do first?
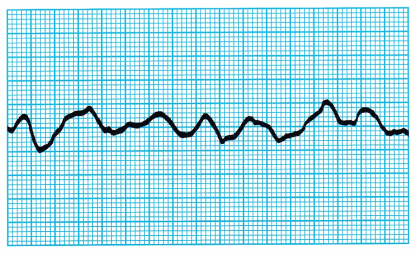
(a) Administer oxygen.
(b) Inspect the client’s incision.
(c) Call the rapid response team.
(d) Reposition the ECG electrodes.
Answer:
(c) Call the rapid response team.
Rationale:
The client has ventricular fibrillation, an arrhythmia that can lead to cardiac arrest. Given the client’s history, the nurse should call the rapid response team JJ to initiate interventions to avoid cardiac arrest. After calling the team, the nurse can administer oxygen. Taking time to inspect the incision delays the necessary intervention. This ECG strip does not show loose electrodes.
Question 25.
The nurse observes two siblings, ages 7 and 9 years, verbally arguing over a toy. The nurse has counseled the parent before about how to handle this situation. The nurse should judge that the teaching has been effective when the parent takes what action?
(a) tells the siblings to stop arguing and shake hands
(b) ignores the arguing and continues what she is doing
(c) tells the children they will be punished when they go home
(d) says they will not go out to lunch now since they have argued
Answer:
(b) ignores the arguing and continues what she is doing
Rationale:
The best approach by the mother is not to interfere. The children need to learn how to solve disagreements on their own. If the parent always intervenes, then the children do not learn how to do this. Siblings will disagree and argue as part of normal development. Punishment, including telling the children that they will not go out to lunch, is not warranted.
Question 26.
A client is diagnosed with genital herpes (herpes simplex virus type 2, or HSV-2). What information should the nurse give to the client about managing this health problem?
(a) Using occlusive ointments may decrease the pain from the lesions.
(b) Reducing stressful life events may decrease the incidence of herpetic outbreaks.
(c) There are no effective drug therapies to man age herpes symptoms.
(d) Herpes is transmitted to partners only when lesions are weeping.
Answer:
(b) Reducing stressful life events may decrease the incidence of herpetic outbreaks.
Rationale:
Managing stressful life events can decrease the incidence of outbreaks of HSV-2. Occlusive ointments should not be applied. Antiviral therapies will not cure herpes, but they can manage symptoms and decrease the incidence of outbreaks. Clients with HSV-2 should use condoms to prevent HSV transmission. Cells can be shed at other times, not only when the vesicles are weeping.
Question 27.
Following an infection, the client is having ototoxic effects of the vestibular branch of the acoustic nerve. The nurse should assess the client for which symptom? Select all that apply.
(a) vertigo
(b) tinnitus
(c) nausea
(d) ataxia
(e) hearing loss
Answer:
(a) vertigo
(c) nausea
(d) ataxia
Rationale:
The nurse should assess the client for adverse effects affecting the vestibular branch of the acoustic nerve, such as vertigo, nausea and vomiting with motion, and ataxia. Tinnitus, or a ringing in the ears, is a clinical manifestation of altered function of the auditory branch of the eighth cranial nerve, not the vestibular branch. The client will not have hearing loss.
Question 28.
A young adult has been bitten by a human, and the skin on the forearm is broken. The client’s last tetanus shot was about 8 years ago. What should the nurse tell the client about the anticipated treatment plan?
(a) “You’ll need an injection of tetanus toxoid.”
(b) “The health care provider will prescribe corticosteroid cream.”
(c) “The wound will need to be closed with sutures.”
(d) “You’ll need to be tested for rabies.”
Answer:
(a) “You’ll need an injection of tetanus toxoid.”
Rationale:
Tetanus toxoid is indicated because there has been no booster in the last 5 years. With a human bite, there is a risk of severe infection; application of a steroid cream does not prevent infection. The closure of the wound should be delayed until it is determined that there is no infection, in approximately 24 to 48 hours. Rabies is not transmitted through human bites.
Question 29.
A client 6 weeks postpartum asks the nurse about taking medroxyprogesterone injections for birth control. What should the nurse determine prior to discussing options? Select all that apply.
(a) if the client has a sexually transmitted disease
(b) how willing her husband is to have her take the drug
(c) if the woman is experiencing postpartum depression
(d) that the woman is not currently pregnant
(e) if the woman is breastfeeding
Answer:
(c) if the woman is experiencing postpartum depression
(d) that the woman is not currently pregnant
(e) if the woman is breastfeeding
Rationale:
Before discussing the use of medroxyprogesterone acetate as a birth control option, the nurse should determine if the woman is or has been depressed because medroxyprogester-one acetate can increase depression in a client with depression. The drug can be transmitted in breast milk, and the long-term effects on the baby are not known. Women who are pregnant should not take medroxyprogesterone acetate.
Medroxyprogesterone acetate does not treat or prevent sexually transmitted diseases, so this information is not essential when considering its use. Although the husband should be a part of birth control decisions, the final decision is made by the client.
Question 30.
A mother who is visibly upset tells the nurse she wants to take her child home because the child is dying. What would be the nurse’s best response?
(a) “I know how you feel, but the medication will make your child feel better.”
(b) “I can’t let you do this without calling your health care provider (HCP) first.”
(c) “Can you tell me why you want to take your child home now?”
(d) “I can imagine how hard this is for you, but it’s not what is best for the child.”
Answer:
(c) “Can you tell me why you want to take your child home now?”
Rationale:
With a parent who is visibly upset, it is best to try to determine the cause. Therefore, asking the mother about why she wants to take the child home can provide insight into the problem. The nurse cannot stop the mother from taking her child home. However, the HCP should be noti-fied about the mother’s decision, and efforts are needed to explain the ramifications of taking the child home. It is inappropriate for the nurse to say “I know how you feel” or “I can imagine how hard this is” unless the nurse has had the same experience.
Question 31.
Several clients have been admitted to the emergency department. The nurse should assess these clients in which order from first to last?
All options must be used.
(a) the client who is 12 years of age with a frac- j tured tibia
(b) the client who is 8 years of age with small lacerations to legs and arms
(c) the client who is 16 years of age with a “sore throat”
(d) the client who is 6 months of age with diarrhea and dehydration.
Answer:
(d) the client who is 6 months of age with diarrhea and dehydration.
(a) the client who is 12 years of age with a frac- j tured tibia
(b) the client who is 8 years of age with small lacerations to legs and arms
(c) the client who is 16 years of age with a “sore throat”
Rationale:
The infant who is 6 months of age with diarrhea is seen first because of risk for further dehydration; the nurse immediately starts an IV infusion. The client who is 12 years of age is seen next; this child is considered to require urgent care but can wait several hours. The client who is 8 years of age can be seen next; he is considered to require nonurgent care and will respond to assessment and first aid. The last client to receive care is the client who is 16 years of age; this client is considered nonurgent and likely will not require the services of the emergency department.
Question 32.
Which urine output indicates that a 5-month-old weighing 15 lb (6.8 kg) and being treated for dehydration has a normal urine output?
(a) 1 to 2 mL/kg/h
(b) 2. 4 to 5 mL/kg/h
(c) 6 to 8 mL/kg/h
(d) 10 to 12 mL/kg/h
Answer:
(a) 1 to 2 mL/kg/h
Rationale:
Normal urine output for an infant is 1 to 2 mL/kg/h.
Question 33.
The nurses in the neonatal intensive care unit are not identifying important clinical changes in the clients that need to be documented. What should the unit director do? Select all that apply.
(a) Identify the problem at a staff meeting with out placing blame on any individual or group.
(b) Ask the unit staff to develop a plan that they think will work for the unit members.
(c) Ask an experienced nurse to spend time reorienting newer staff members.
(d) Collaborate with the staff development educator to develop a plan.
(e) Ask the neonatologist to give a presentation about assessing newborns.
Answer:
(a) Identify the problem at a staff meeting with out placing blame on any individual or group.
(b) Ask the unit staff to develop a plan that they think will work for the unit members.
(d) Collaborate with the staff development educator to develop a plan.
Rationale:
All areas concerned with the safety and quality of care need to participate in the decision-making process and arrive at a plan that will meet the needs of the clients on the neonatal care unit. Identifying the problem at a staff meeting is an ideal forum to bring up the need for improvement and education. The staff is an integral part
of the development team.
The staff educator is an important member of the team and is responsible for orienting new nurses to the unit. Asking an experienced staff member to spend time in reorienting staff members is difficult to do as the nurses have their own clients to care for. Although the unit director can obtain additional information from the health care providers ] about the problem, the nursing staff has responsibility for assuring that they are providing safe and high-quality care.
Question 34.
A 24-year-old client, diagnosed with acute osteomyelitis in the left leg, has acute pain in the leg that intensifies on movement. The client has a temperature of 101°F (38.3°C) and a reddened, warm area in the midcalf region over the shaft of the tibia. Based on this information, what should the nurse do?
(a) Prepare the client for possible left lower leg amputation.
(b) Instruct the client to keep the leg immobile.
(c) Develop a plan for pain management.
(d) Obtain a prescription for fluid replacement.
Answer:
(c) Develop a plan for pain management.
Rationale:
Based on the data given, the nurse should develop a plan with the client to manage the pain. It is not necessary for the client to be completely immobile. There is no clinical indication that the leg will need to be amputated. A temperature of 101°F (38.3°C) would be unlikely to produce a fluid volume deficit in this client.
Question 35.
A client has undergone a vasectomy. The nurse instructs the client that he can begin having unprotected intercourse at what time following the surgery?
(a) when desired because sterilization is immediate
(b) as soon as scrotal edema and tenderness resolve
(c) when the sperm count reflects sterilization
(d) after 6 to 10 ejaculations
Answer:
(c) when the sperm count reflects sterilization
Rationale:
After vasectomy, a sperm analysis will be performed every 4 to 6 weeks. A sperm-free analysis is necessary before the man can be considered sterile. Sperms gradually disappear from the ejaculate. Clients must be informed that conception is possible in the immediate postvasectomy period.
Question 36.
The nurse is evaluating the outcome of therapy for a client with osteoarthritis. Which outcome indicates goals of therapy have been met?
(a) The client’s joint degeneration has been arrested.
(b) The client is able to self-administer gold compound safely.
(c) The client is able to tolerate pain.
(d) The client’s joint range of motion has improved.
Answer:
(d) The client’s joint range of motion has improved.
Rationale:
One outcome criterion for the client with osteoarthritis is improved joint mobility. It is realistic to expect to arrest the disease. Gold compound is administered to clients with rheumatoid arthritis, not osteoarthritis. The client can expect relief from pain with acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Question 37.
The nurse assesses an infant diagnosed with bacterial meningitis. The nurse should ask the parent if the infant has which symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) fever
(b) vomiting
(c) diarrhea
(d) poor feeding
(d) abdominal pain
Answer:
(a) fever
(b) vomiting
Rationale:
Classic signs of meningitis in an infant include fever, poor feeding, vomiting, and irritability. Abdominal pain and diarrhea are not usual signs of meningitis; they are more commonly associated with gastroenteritis.
Question 38.
What should the nurse do to help a client prevent atelectasis and pneumonia after surgery?
(a) Administer oxygen therapy as needed to maintain adequate oxygenation.
(b) Offer pain medication before having the client deep-breathe and use incentive spirometry.
(c) Instruct the client to cough, deep breathe, and turn in bed once every 8 hours.
(d) Encourage the client to drink 1,000 mL of fluids in 24 hours.
Answer:
(b) Offer pain medication before having the client deep-breathe and use incentive spirometry.
Rationale:
Deep-breathing exercises and use of incentive spirometry are more effective when pain is minimal. A client in severe pain tends to limit movement and to breathe shallowly to decrease the pain. Enough pain medication should be given to decrease pain without depressing respirations. Administration of oxygen or increasing fluids will not prevent atelectasis or pneumonia.
Deep-breathing exercises and use of incentive spirometry should be done 10 times every hour while awake. The client’s position should be changed every 1 to 2 hours to allow for full chest expansion. Ambulation, not just sitting in the chair, should be implemented as soon as approval from the health care provider Q is obtained.
Question 39.
A school-age child is admitted to the hospital with acute rheumatic fever. What intervention should the nurse teach the parents that is necessary in the child’s long-term care plan?
(a) physical therapy
(b) antibiotic therapy
(c) psychological therapy
(d) anti-inflammatory therapy
Answer:
(b) antibiotic therapy

Rationale:
A child who has had rheumatic fever is likely to develop the illness again after a future streptococcal infection. Therefore, it is advised that the child receive antibiotic prophylaxis for at least 5 years and sometimes even longer after the acute attack to prevent recurrence.
Question 40.
The nurse assesses the perineal changes of a woman in the second stage of labor. The figure below represents which perineal change?
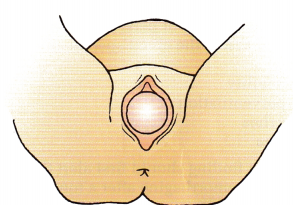
(a) anterior-posterior slit A
(b) oval opening
(c) circular shape
(d) crowning
Answer:
(d) crowning
Rationale:
Crowning occurs when the fetal head is visible. Anterior-posterior slit occurs as the perineum flattens and is followed by an oval opening. As labor progresses, the perineum takes on a circular shape, followed by crowning.
Question 41.
A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of suspected pulmonary embolism. Prescriptions include oxygen 2 to 4 L/min per nasal cannula, oximetry at all times, and IV administration of 5% dextrose in water at 100 mL/h. The client has increasing dyspnea and has a respiratory rate of 32 breaths/min. The oxygen flow rate is set at 2 L/ min. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Increase the oxygen flow rate from 2 to 4 L/min.
(b) Call the health care provider (HCP) immediately.
(c) Provide reassurance to the client.
(d) Obtain a sample for arterial blood gas analysis.
Answer:
(a) Increase the oxygen flow rate from 2 to 4 L/min.
Rationale:
The first action is to increase the oxygen flow rate from 2 to 4 L/min to help ensure adequate oxygenation for the client. Although it is important to notify the HCP Q for additional prescriptions and to obtain further assessment data, such as arterial blood gas measurements, it is a priority to support the client’s cardiopulmonary system. It would be appropriate to reassure the client while these other interventions are occurring.
Question 42.
A 10-month-old child has cold symptoms. The mother asks how she can clear the infant’s nose. What would be the nurse’s best recommendation?
(a) Use a cool air vaporizer with plain water.
(b) Use saline nose drops and then a bulb syringe.
(c) Blow into the child’s mouth to clear the infant's nose.
(d) Administer a nonprescription vasoconstrictive nose spray.
Answer:
(b) Use saline nose drops and then a bulb syringe.
Rationale:
Although a cool air vaporizer may be recommended to humidify the environment, using saline nose drops and then a bulb syringe before meals and at nap and bed times will allow the child to breathe more easily. Saline helps to loosen secretions and keep the mucous membranes moist.
The bulb syringe then gently aids in removing the loosened secretions. Blowing into the child’s mouth to clear the nose introduces more organisms to the child. A nonprescription vasoconstrictive nasal spray is not recommended for infants because if the spray is used for longer than 3 days, a rebound effect with increased inflammation occurs.
Question 43.
What should the nurse teach the client to do to prevent stress incontinence? Select all that apply,
(a) Use techniques that strengthen the sphincter and structural supports of the bladder, such as Kegel exercises.
(b) Avoid natural diuretics such as caffeine or alcoholic beverages.
(c) Carry an extra incontinence pad when away from home.
(d) Maintain a fluid intake of 500 mL/day.
(e) Refrain from coughing or laughing.
Answer:
(a) Use techniques that strengthen the sphincter and structural supports of the bladder, such as Kegel exercises.
(b) Avoid natural diuretics such as caffeine or alcoholic beverages.
Rationale:
Kegel exercises strengthen the sphincter and structural supports of the bladder, and the nurse should be sure the client knows how to do these exercises. Establishing a voiding schedule is more effective than carrying incontinence pads in preventing stress incontinence.
In nonrestricted clients, a fluid intake of at least 2 to 3 L/day is encouraged; clients with stress incontinence may reduce their fluid intake to avoid incontinence at the risk of developing dehydration and urinary tract infections. Natural diuretics, such as caffeine and alcoholic beverages, may increase stress incontinence. It is unlikely that the client can prevent laughing or coughing or other activities that might put stress on the sphincter.
Question 44.
A health care provider (HCP) is calling the pediatric unit and asking the nurse to go into the medical record for test results of a fellow pediatrician. How should the nurse respond to this request?
(a) Verify that the caller is the HCP of record or has a need to know.
(b) Access the medical record, and give the health care provider the test results.
(c) Decline to give the HCP the information requested.
(d) Determine whether the nurse can access the medical record.
Answer:
(a) Verify that the caller is the HCP of record or has a need to know.
Rationale:
The nurse should determine if the HCP m is the HCP of record and should have access to the information in the medical record Q. The medical record is not for public access. The nurse would not give client information to any HCP or refuse to give information without first determining the HCP of record and/or a legitimate need to know. As an employee, the nurse should have access to medical records, but it is not acceptable to enter a medical record without justification.
Question 45.
A client is at risk for development of metabolic alkalosis because of persistent vomiting. The nurse should assess the client specifically for which symptom?
(a) irritability
(b) hyperventilation
(c) diarrhea
(d) edema
Answer:
(a) irritability
Rationale:
A client with metabolic alkalosis may exhibit irritability or nervousness. Hyperventilation is a clinical manifestation of respiratory alkalosis. Diarrhea is a possible clinical finding in metabolic acidosis. Edema is not specifically associated with an acid-base imbalance.
Question 46.
Which finding should first alert the nurse that a child is hemorrhaging after a tonsillectomy?
(a) mouth breathing
(b) frequent swallowing
(c) requests for a drink
(d) increased pulse rate
Answer:
(b) frequent swallowing
Rationale:
An initial sign of hemorrhaging after a tonsillectomy is swallowing frequently as mucus and blood combine to increase secretions. Mouth breathing is expected after surgery because the child’s mouth is very dry and the throat is sore. Because the child has been without fluids for some time, the child usually is thirsty and asks for a drink. Increased pulse rate is a later sign of hemorrhage.
Question 47.
A nurse is caring for a client who is having an allergic reaction to a blood transfusion. In what order from first to last should the nurse provide care for this client? All options must be used.
(a) Stop the transfusion.
(b) send the blood bag and blood slip to the blood bank.
(c) keep the vein open with normal saline solution.
(d) Administer an antihistamines as directed.
Answer:
(a) Stop the transfusion.
(c) keep the vein open with normal saline solution.
(d) Administer an antihistamines as directed.
(b) send the blood bag and blood slip to the blood bank.
Rationale:
The nurse should first stop the transfusion. The nurse should next keep the IV open at the original blood transfusion site with normal saline at a keep-vein-open rate. Then, the nurse should administer an antihistamine. Last, the nurse should return the blood bag and blood slip to the blood bank for testing.
Question 48.
The nurse is to administer chloramphenicol 50 mg IV in 100 mL of dextrose 5% in water over 30 minutes. The infusion set administers 10 gtt/mL. At what flow rate (in drops per minute) should the nurse set the infusion? Round to the nearest whole number.
.......................... gtt/min.
Answer:
33 gtt/min
Rationale:
The flow rate is determined by the rate of infusion and the number of drops per milliliter of the fluid being administered: gtt/mL x mL/min = IV flow rate (gtt/min).
Therefore:
10 gtt/mL x 100 mL/30 min = 33 gtt/min.
Question 49.
A client claims to have a “special mission from God.” The nurse incorporates this religious delusion of grandeur into the client’s plan of care based on the understanding that the primary purpose of such a delusion is to provide:
(a) survival.
(b) comfort.
(c) safety.
(d) self-esteem.
Answer:
(d) self-esteem.
Rationale:
Delusions of grandeur provide the client with an exaggerated sense of self-esteem that is unrelated to the client’s actual achievements. Other, less grandiose, religious delusions may provide comfort or meaning for the client. Delusions of persecution are frequently related to safety issues. Delusions of grandeur are not about survival needs.
Question 50.
A client who has been vomiting for 2 days has a nasogastric tube inserted. The nurse notes that over the past 10 hours, the tube has drained 2 L of fluid. The nurse should further assess the client for which electrolyte imbalance?
(a) hypermagnesemia
(b) hypernatremia
(c) hypokalemia
(d) hypocalcemia
Answer:
(c) hypokalemia
Rationale:
Loss of electrolytes from the gastrointestinal tract through vomiting, diarrhea, or nasogastric suction is a common cause of potassium loss, resulting in hypokalemia. Hypermagnesemia does not result from excessive loss of gastrointestinal fluids. Common causes of hypernatremia are water loss (as in diabetes insipidus or osmotic diuresis) and excessive sodium intake. Common causes of hypocalcemia include chronic renal failure, elevated phosphorus concentration, and primary hypoparathyroidism.
Question 51.
When a client is examining her own breast, the nurse should instruct the client that which finding is normal?
(a) pronounced unilateral venous pattern
(b) peau d’orange breast tissue
(c) long-term, bilateral nipple inversion
(d) breast tissue that is darker than the areolae
Answer:
(c) long-term, bilateral nipple inversion
Rationale:
It is a normal variation for women to have long-term, bilateral nipple inversion. A woman who has a unilateral nipple inversion that is a new change is at risk for a tumor; the weight of the tumor causes pulling on the nipple. A pronounced unilateral venous pattern, peau d’orange breast tissue, and breast tissue darker than the areolae are definite warning signals for breast cancer that must be reported to the health care provider (HCP) Q immediately.
Question 52.
A child with sickle cell crisis is being discharged. As part of discharge teaching to prevent further crisis, what should the nurse advise the parent to do?
(a) Encourage the child to drink lots of liquids.
(b) Take the child’s temperature every morning.
(c) Weigh the child every day.
(d) Offer the child a high-protein diet.
Answer:
(a) Encourage the child to drink lots of liquids.
Rationale:
It is important for children with sickle cell disease to drink lots of fluids to help prevent a crisis. Dehydration precipitates sickling and a crisis. Although taking the child’s temperature may provide information about the child’s sta-tus, it will do nothing to prevent a crisis, nor will weighing the child daily. Offering the child a high-protein diet will not prevent a crisis, nor is it recommended.
Question 53.
While assessing a neonate 30 minutes after birth, the nurse observes that the child has a short neck covered with webbing. The nurse should further assess the client for which problem?
(a) genetic deviations
(b) cleft palate
(c) Potter’s syndrome
(d) neural tube defects
Answer:
(a) genetic deviations
Rationale:
The nurse notifies the pediatrician because a short, webbed neck is associated with genetic deviations or chromosomal disorders such as Turner's syndrome. Cleft palate is associated with embryonic developmental failures and an abnormal opening in the palate. Potter’s syndrome (renal agenesis) is characterized by an atypical facial appearance consisting of a flat nose, recessed chin, epicanthal folds, low-set abnormal ears, limb abnormalities, and pulmonary hypoplasia. Neural tube defects are associated with spina bifida or myelomeningocele.
Question 54.
A client has severe diarrhea that has lasted for 2 days. The nurse should now assess the client for which symptom?
(a) muscle spasms
(b) thirst
(c) irregular pulse
(d) confusion
Answer:
(c) irregular pulse
Rationale:
Diarrhea results in electrolyte loss, and the nurse should assess the client for signs of hypokalemia. Clinical manifestations of hypokalemia include an irregular pulse, fatigue, muscle weakness, flabby muscles, decreased reflexes, nausea, vomiting, and ileus. Muscle spasms are not seen in hypokalemia. Thirst is a symptom of hypernatremia.
Question 55.
The nursing staff on the antepartal unit has leuprolide acetate and medroxyprogesterone acetate in the pharmacy for their clients. The nursing staff observed that the vials are similar in size and shape and could be confused. In order to promote client safety, the nursing staff should take which actions? Select all that apply.
(a) Petition the pharmacy to relocate one drug away from the other product.
(b) Move the drugs to a new position within the medication administration system during the night shift.
(c) Communicate concerns, measures to remedy, and final decisions to all staff.
(d) Leave repositioning of drugs to pharmacy staff to resolve.
(e) Collaborate with pharmacy staff to develop a location that works well for both groups.
Answer:
(a) Petition the pharmacy to relocate one drug away from the other product.
(c) Communicate concerns, measures to remedy, and final decisions to all staff.
(e) Collaborate with pharmacy staff to develop a location that works well for both groups.
Rationale:
Notifying the pharmacy of the nursing concerns is an appropriate first action. The nursing staff should work cooperatively with the pharmacy to develop a system that works well for both nursing and pharmacy. Constant communication with all nursing staff during the quality improvement process is integral to the final approval process of both groups.
Moving the drugs to a new position within the medication system during an off shift may create errors, as medications are inserted into the system in a certain position. Leaving the decisions to the pharmacy staff eliminates the input provided by nursing, a vital link between medication and the client.
Question 56.
When assessing a client’s pain, which information is the most reliable indicator of the existence and intensity of acute pain?
(a) the client’s vital signs
(b) the client’s self-report of pain
(c) the nurse’s assessment of the client
(d) the severity of the condition causing the pain
Answer:
(b) the client’s self-report of pain
Rationale:
The client’s self-report of pain is the most reliable indicator of the existence and intensity of the pain. Client response to pain is highly individualized and subjective. The nurse must respect the client’s self-report.
Question 57.
The nurse advises a mother with a 2-year-old child to avoid encouraging excessive milk consumption by the toddler because excess milk consumption can lead to which problem?
(a) vitamin C deficiency
(b) iron deficiency
(c) biotin deficiency
(d) folate deficiency
Answer:
(b) iron deficiency
Rationale:
Excessive milk consumption can lead to the displacement of iron-rich foods in the diet. This can result in iron deficiency anemia. Drinking excess milk will not cause vitamin C, biotin, or folate deficiencies.
Question 58.
The nurse is caring for a client with a fracture of a long bone. Which symptom is the earliest indication of a fat embolism?
(a) respiratory distress
(b) confusion
(c) petechiae
(d) fever
Answer:
(b) confusion
Rationale:
Although all the symptoms listed can occur in cases of fat embolism syndrome, confusion is the earliest symptom noted. The confusion is caused by a low arterial oxygen level.
Question 59.
A client tells the nurse, “Everybody smiles at me because they know that I was chosen by God for this mission.” The nurse interprets this statement as which finding?
(a) idea of reference
(b) thought insertion
(c) visual hallucination
(d) neologism
Answer:
(a) idea of reference
Rationale:
An idea of reference is a person’s view that other people recognize that she has an important characteristic or power. Thought insertion refers to a person’s belief that others, or a specific other, can put thoughts into her mind. Visual hallucinations involve seeing objects or persons not based on reality. A neologism is a word or phrase that has meaning only to the person using it.
Question 60.
The mother of a newborn is voicing concerns about her baby’s ability to hear. What should the nurse tell the mother?
(a) Newborns cannot hear well until they are at least 6 weeks old.
(b) Her concern is unfounded because hearing problems are rare in newborns.
(c) Most American states and Canadian jurisdictions now mandate hearing tests for infants.
(d) She can test the baby’s hearing by clapping her hands 24 inches (60 cm) from the infant’s head.
Answer:
(c) Most American states and Canadian jurisdictions now mandate hearing tests for infants.
Rationale:
The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommend hearing screening for all newborns. Currently, more than 30 states mandate screening, which is done by otoacoustic emissions or auditory brainstem response.
Newborns can hear as soon as the amniotic fluid drains from the ear canal. Even though hearing problems are not common in newborns, the mother’s concerns should be addressed. Clapping to elicit a response is crude and unreliable. If done for minimal screening, the distance should be no more than 12 inches.
Question 61.
The parent asks the nurse about the causes of most brain injuries in children. What would the nurse discuss as major causes? Select all that apply.
(a) falls
(b) motor vehicle accidents
(c) bicycle accidents
(d) sports injuries
(e) violence
(f) tumors
Answer:
(a) falls
(b) motor vehicle accidents
(c) bicycle accidents
(d) sports injuries
(e) violence
Rationale:
Children tend to be impulsive, which contributes to head injuries. Also, the larger size of the heads of infants and toddlers causes them to fall more easily than do older children.
Falls account for one-third of all head injuries. Motor vehicle accidents account for about 80% of all severe head injuries in children. Children age 5 to 15 are most likely to be involved in bicycle accidents as a result of only about 50% wearing helmets.
Child abuse and tumors involve a much smaller number of children. Sports concussions are common in school-age and adolescent children. Shaken baby syndrome and physical child abuse are forms of violence that can lead to head injuries in children.
Question 62.
The nurse is planning care for a client with osteoporosis who is immobilized. What goal should the nurse include in the care plan?
(a) The client will begin weight-bearing activities.
(b) The client will increase calcium intake in the diet.
(c) The client will receive passive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises four times a day.
(d) The client will learn to perform isometric exercises.
Answer:
(a) The client will begin weight-bearing activities.
Rationale:
In order to prevent disuse osteoporosis, it is important to implement weight-bearing activities as soon as medically allowed. Increasing the client’s calcium intake will not prevent the development of osteoporosis without the inclusion of weight-bearing activity. Passive ROM exercises and isometric exercises do not provide the bone stress necessary to reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Question 63.
The mother of a toddler asks the nurse what she should do with her toddler when he has a temper tantrum. Which suggestion would be most appropriate?
(a) Move the toddler to a time-out chair.
(b) Try to talk the toddler out of the tantrum.
(c) Leave the toddler alone during the tantrum as long as he is safe.
(d) Punish the toddler for having a tempertantrum.
Answer:
(c) Leave the toddler alone during the tantrum as long as he is safe.
Rationale:
Toddlers have temper tantrums in their attempt to develop autonomy. Toddlers should be left alone as long as they are safe during a tantrum. Moving the child to a time-out chair or punishing the child reinforces the behavior and is to be avoided. Attempting to talk to the toddler also reinforces the behavior. Additionally, at this cognitive level, toddlers do not understand as well as older children do.
Question 64.
An adolescent client is hospitalized with bacterial meningitis. At 1730, the client’s mother reports her child is “burning up.” The nurse is reviewing the client’s medication administration records in the medical record. The health care provider (HCP) has prescribed ibuprofen 325 mg every 3 to 4 hours for temperature over 99°F (37.2°C). The child’s temperature at 1730 is 102.5°F (39.1°C). What should the nurse do first?
|
Medication |
Time |
Reason |
Initial |
|
Ibuprofen 200 mg Po PRN every 3 to 4 hours for fever >99CF (37.2°C) |
0910 |
T = 100°F (37.8°C) |
LM |
|
|
1315 |
T = 100°F (37.8 °C) |
LM |
|
|
1615 |
T = 101°F (38.3°C) |
LM |
(a) Notify the HCP.
(b) Initiate tepid sponge bath.
(c) Institute seizure precautions.
(d) Administer another dose of aspirin.
Answer:
(a) Notify the HCP.
Rationale:
Because the client’s temperature continues to rise in spite of recently administering ibupro- fen, the nurse notifies the HCP. After notifying the HCP m, the nurse can bathe the client with tepid water. If the temperature cannot be lowered shortly, the client is also at risk for seizures; the nurse pads the side rails and observes for seizure activity. The nurse cannot administer another dose of ibuprofen without the HCP’s orders.
Question 65.
The nurse from the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) is transferring the client to an orthopedic unit. Which is the most appropriate way for the nurse in the PACU to communicate the “hand-off-of- care” report with the nurse on the orthopedic unit?
(a) Send an email to the receiving nurse on the orthopedic unit.
(b) Give a written report to a transporter who is bringing the client to the receiving nurse.
(c) Call the nurse on the orthopedic unit and give a verbal report.
(d) Send the unit clerk from PACU to give the prescription list directly to the nurse on the orthopedic unit.
Answer:
(c) Call the nurse on the orthopedic unit and give a verbal report.
Rationale:
The Joint Commission and Health Council of Canada both mandate interactive hand- off communication fU that allows the opportunity for questioning between the giver and receiver of client information, including up-to-date information regarding the client’s care, treatment and services, current condition, and any recent or anticipated changes.
Nurses have primary responsibility and accountability for utilization of all nursing care provided to clients. The nurse retains the right and has the responsibility to refrain from delegating specific activities based on individual client care needs, caregiver expertise, and/or client care program requirements.
Question 66.
What should the nurse do to prevent pressure ulcers in an older adult?
(a) Clean the skin daily using mild soap and hot water.
(b) Perform a systematic skin assessment at least once a day.
(c) Massage bony prominences gently every shift.
(d) Encourage the client to sit in a chair as much as possible.
Answer:
(b) Perform a systematic skin assessment at least once a day.
Rationale:
Daily skin inspection is essential in preventing pressure ulcers. Hot water is irritating to the skin and should be avoided. Massaging bony prominences is contraindicated and may actually promote skin breakdown. Prolonged, uninterrupted chair sitting should be avoided; the client’s position should be adjusted at least every hour.
Question 67.
The nurse is evaluating the pin insertion site of a client’s skeletal traction. Which finding indicates a complication?
(a) presence of crusts around the pin insertion site
(b) serous drainage on the dressing
(c) slight movement of the pin at the insertion site
(d) no pain was felt by the client at the insertion site
Answer:
(c) slight movement of the pin at the insertion site
Rationale:
Skeletal pins should not be loose and able to move. Any pin loosening should be reported immediately. Slight serous drainage is normal and may crust around the insertion site or be present on the dressing. The pin insertion site should be cleaned with an aseptic technique according to facility policy. Pin insertion sites are typically not painful; pain may be indicative of an infection and should be reported.
Question 68.
On the night before a 58-year-old wife and mother is to have a lobectomy for lung cancer, she remarks to the nurse, “I’m so scared of this cancer. I should’ve quit smoking years ago. Now I’ve brought all this fear and sadness on myself and now my family.” How should the nurse respond to the client?
(a) “It’s normal to be scared. I would be, too. We’ll help you through it.”
(b) “Do you feel guilty because you smoked?”
(c) “Don’t be so hard on yourself. You don’t know if your smoking caused the cancer.”
(d) "It’s okay to be scared. What is it about cancer that you are afraid of?”
Answer:
(d) "It’s okay to be scared. What is it about cancer that you are afraid of?”

Rationale:
Acknowledging the basic feeling that the client expressed and asking an open-ended question allows the client to explain her fears. Saying, “It’s normal to be scared. We’ll help you through it,” does not focus on the client’s feelings; rather, it gives reassurance. Asking if the client feels guilty for having smoked assumes guilt, which might be present, but additional information is needed to confirm. Telling the client not to be so hard on herself does not acknowledge the client’s feelings at all.
Question 69.
The nurse is caring for an older adult who has hip pain related to rheumatoid arthritis. The client is practicing appropriate self-care activities when the client chooses to sit in which type of chair?
(a) recliner chair with arms to support wrists and hands
(b) couch with soft cushions to support thighs
(c) straight-back chair with an elevated seat
(d) curved-back rocking chair
Answer:
(c) straight-back chair with an elevated seat
Rationale:
It is important that clients with rheumatoid arthritis maintain proper posture and body alignment to support joints and decrease pain and stiffness. Clients with hip pain will be most comfortable when sitting in a straight-back chair with an elevated seat. Elevated seats avoid excessive hip flexion and place less stress on the hip joints.
A recliner chair will not provide sufficient support and likely does not have an elevated seat. A couch typically has a low seat and will cause hip flexion. A rocking chair may not provide the correct joint support and is not sufficiently stable.
Question 70.
The nurse plans discharge care with the parents of a 16-year-old boy who recently attempted suicide. The nurse should advise the parents to notify a health care provider immediately for which client finding?
(a) expressing a desire to date
(b) deciding to try out for an extracurricular activity
(c) giving away valued personal items
(d) desiring to spend more time with his friends
Answer:
(c) giving away valued personal items
Rationale:
Giving away personal items has consistently been shown to be an indicator of suicidal plans in the depressed and suicidal individual. The other behaviors indicate a return of interest in normal adolescent activities.
Question 71.
Which response would be most appropriate for the nurse when comforting a primiparous client whose critically ill neonate born at 25 weeks dies while the mother is present?
(a) “This is probably for the best because his organs were so immature.”
(b) “You should try to get pregnant again soon to get over this loss.”
(c) “You can stay with your baby as long as you want and say anything you want.”
(d) “If you want me to, I can call the chaplain to stay with you.”
Answer:
(c) “You can stay with your baby as long as you want and say anything you want.”
Rationale:
When a neonate dies, the mother should be allowed to stay with the baby as long as she wants and say anything she wants. She is grieving and needs time with the neonate. A photograph should be taken in case the mother wants a photograph at a later time. Telling the mother that this is for the best is inappropriate because such a statement discounts the mother’s feelings.
Advising the mother to get pregnant again to get over the loss is not helpful because the mother needs time to grieve and be with the neonate. The nurse should remain near the mother and not delegate this responsibility to the hospital’s chaplain. A chaplain or other religious member can be contacted if the mother desires.
Question 72.
The nurse is developing a care plan for a female child who is 12 years of age and receiving surgery to correct idiopathic scoliosis. Which postoperative problem is a priority?
(a) pain control
(b) hypotension
(c) prevention of pressure wounds
(d) infection control
Answer:
(a) pain control
Rationale:
Clients typically have considerable pain for the first few days after surgery and require frequent administration of pain medication, preferably the use of opioids administered intravenously on a regular schedule or patient-controlled analgesia (PCA). The other problems are all possible compli-cations following this type of surgery, but the priority, until noted otherwise, is to provide adequate pain control.
Question 73.
An adult recently diagnosed with Hodgkin’s disease is admitted for staging by undergoing a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. To obtain more information about the client’s nutritional status, the nurse should review the results of which test?
(a) red blood cell count
(b) direct and indirect bilirubin levels
(c) reticulocyte count
(d) albumin level
Answer:
(d) albumin level
Rationale:
Serum albumin levels help determine whether protein intake is sufficient. Proteins are broken down into amino acids during digestion. Amino acids are absorbed in the small intestine, and albumin is built from amino acids. The red blood cell count, bilirubin levels, and reticulocyte count do not indicate protein intake.
Question 74.
The nurse teaches a client taking desmopressin nasal spray about how to manage treatment. The nurse determines that the client needs additional instruction when the client makes which comment?
(a) “I should check for sores in my nose while taking this medication.”
(b) “I should use the same nostril each time I take the medicine.”
(c) “I should report nasal congestion.”
(d) “I should report any signs of respiratory infection.”
Answer:
(b) “I should use the same nostril each time I take the medicine.”
Rationale:
The client who is taking desmopressin nasal spray should not use the same naris for administration each time. The client should alternate nares every dose. The client should observe for and report promptly signs and symptoms of nasal ulceration, congestion, or respiratory infection.
Question 75.
The nurse has a prescription to administer ampicillin 250 mg IM. After reconstituting the ampicillin with sterile water for injection, the solution available is 500 mg/mL. How many milliliters should the nurse administer?
.......................... mL.
Answer:
0.5 ml
Rationale:
500 mg/mL = 250 mgIX mL X - 0.5 mL.
Question 76.
A client is a 43-year-old G2 Pi at 16 weeks’ gestation who has completed prenatal testing for chromosomal abnormalities. The results reveal the infant is a female with Down syndrome. The parents are seeking information about this syndrome. What should the nurse tell the parents? Select all that apply.
(a) Down syndrome can occur in mothers of any age.
(b) Down syndrome is correlated with autosomal dominant traits carried by the parents.
(c) Down syndrome is a result of autosomal recessive traits carried by the parents.
(d) Down syndrome depends upon maternal prenatal care since pregnancy began.
(e) Down syndrome occurs more frequently with advanced maternal age.
(f) Down syndrome results from a trisomy of chromosome 21.
Answer:
(a) Down syndrome can occur in mothers of any age.
(e) Down syndrome occurs more frequently with advanced maternal age.
(f) Down syndrome results from a trisomy of chromosome 21.
Rationale:
Down syndrome is the most common trisomal abnormality. It can occur at any maternal age with the average being 27 years. The risk of bearing a Down syndrome infant increases with advanced maternal age. The syndrome is caused by nondisjunction during the first meiotic cell division, rather than autosomal dominant or recessive traits. There is no association with timing or quality of prenatal care.
Question 77.
There has been a fire in an apartment building, and it has spread to seven apartment units. Victims have suffered burns, minor injuries, and broken bones from jumping from windows. Which persons can be safely treated at the scene and transported to a health care facility after victims with more emergent problems have been transported first? Select all that apply.
(a) female client who is 5 months pregnant with no apparent injuries
(b) male client who is 50 years of age with no injuries, rapid respirations, and coughing
(c) child client who is 10 years of age with an apparent simple fracture of the humerus
(d) female client who is 20 years of age with first-degree burns on hands and forearms
(e) male client who is 75 years of age with second-degree burns on both legs
Answer:
(a) female client who is 5 months pregnant with no apparent injuries
(c) child client who is 10 years of age with an apparent simple fracture of the humerus
(d) female client who is 20 years of age with first-degree burns on hands and forearms
Rationale:
The pregnant woman is not in imminent danger or likely to have a precipitous birth. The child who is 10 years of age is not at risk of infection and can be treated in an outpatient facility. First-degree burns are considered less urgent. The male with respiratory distress and coughing is transported first as he is likely experiencing smoke inhalation. The 75-year-old male with second-degree burns should also be also transported to a burn center or emergency department.
Question 78.
A primiparous nonbreastfeeding client at 48 hours postpartum is to be given medroxyprogesterone before discharge. What information should the nurse include in the teaching plan before administering this medication?
(a) There is an increased risk of ovarian cancer with the use of this drug.
(b) Amenorrhea is common during the first 6 months.
(c) Heavy menstrual bleeding may occur.
(d) The client may experience periods of increased energy.
Answer:
(c) Heavy menstrual bleeding may occur.

Rationale:
As with other contraceptives that are progestin-based, heavy menstrual bleeding may occur. Other adverse effects include rash, acne, alopecia, fluid retention, edema, and sudden loss of vision. Depression and weight gain have been reported. For clients taking this drug, the risk of endometrial or ovarian cancer is decreased. Amenorrhea has been reported in clients after receiving four injections 3 months apart for 1 year. Depression and loss of energy have been reported.
Question 79.
A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving clozapine. The nurse reviews the medical record. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Give the clozapine, and tell the client to lie down.
(b) Withhold the clozapine, and tell the client to go to an exercise group.
(c) Administer the clozapine, and notify the health care provider (HCP).
(d) Withhold the clozapine, and notify the HCP.
Answer:
(d) Withhold the clozapine, and notify the HCP.
Rationale:
Because clozapine can cause tachycardia, the nurse should withhold the medication if the pulse rate is >140 bpm and notify the HCP Q. Giving the drug or telling the client to exercise could be detrimental to the client.
Question 80.
The nurse is instructing the parents of a child with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) how to look for signs and symptoms of infection when the child has a cut or open wound. The nurse should tell the parents to report which finding?
(a) erythema around the area
(b) rectal temperature higher than 100.5°F (38°C)
(c) tenderness around the area
(d) increased warmth of the skin in the involved area
Answer:
(b) rectal temperature higher than 100.5°F (38°C)
Rationale:
Fever is a cardinal manifestation of infection in people with AIDS. Because the major physiologic alteration in AIDS is generalized immune system dysfunction, typical indicators of the body’s response to infection (e.g., erythema, warmth, tenderness) may be absent.
Question 81.
The nurse teaches a group of unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) about providing care to clients with depression. Which approach by one of the UAPs indicates an understanding of the most effective approach to a depressed client?
(a) cheerful
(b) empathetic
(c) serious
(d) humorous
Answer:
(b) empathetic
Rationale:
To care effectively for clients with depression, the nurse should teach the importance of demonstrating empathetic concern. Caregivers must accept clients as they are even though many will be angry and negative, acknowledge their emotional pain, and offer to help them work through their pain.
For the client who is depressed, using a cheerful demeanor or a humorous, light-hearted approach may be overwhelming because the client will be unable to meet the caregiver’s expectations, subsequently leading to decreased self-worth. A serious, business-like affect may threaten the client and inhibit the development of trust.
Question 82.
When fluids by mouth are appropriate for the infant after surgery to correct intussusception, the nurse most likely would initiate which type of feeding?
(a) cereal-thickened formula
(b) full-strength formula
(c) half-strength formula
(d) oral electrolyte solution
Answer:
(d) oral electrolyte solution
Rationale:
When a child is ready to take fluids by mouth postoperatively, clear liquids are given initially. If clear liquids are tolerated, the concentration and amount of oral feedings are gradually increased. This means advancing to half-strength and then to full-strength formula while increasing the amount given with each feeding.
Question 83.
A client is taking paroxetine 20 mg PO every morning. The nurse should monitor the client for which adverse effect?
(a) hypertensive crisis
(b) sexual problems
(c) sleep disturbance
(d) orthostatic hypotension
Answer:
(b) sexual problems
Rationale:
The nurse should monitor the client taking paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, for sexual problems, such as decreased libido, impotence, and ejaculatory disturbances, because these adverse effects can occur frequently and lead to medication noncompliance. Sleep disturbances can occur with an SSRI such as paroxetine. However, this client is taking the drug every morning, which would not affect nighttime sleep.
Hypertensive crisis is associated with the ingestion of foods rich in tyramine when a client is taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Orthostatic hypotension is a potential adverse effect of tricyclic antidepressants.
Question 84.
The nurse is assessing a client who is in shock. Which neurologic change indicates that the client is in the progressive stage of shock?
(a) restlessness
(b) confusion
(c) incoherent speech
(d) unconsciousness
Answer:
(b) confusion
Rationale:
In the progressive stage of shock, the client can display listlessness or agitation, confusion, and slowed speech. Restlessness occurs in the compensatory stage. Incoherent speech and unconsciousness are clinical manifestations of the irreversible stage.
Question 85.
A child diagnosed with osteomyelitis will be discharged on IV nafcillin. After teaching the parents about adverse effects that are important to report, which effects as stated by the parents indicate that they understand the teaching? Select all that apply.
(a) sore mouth
(b) pain with urination
(c) headache
(d) stomach upset
(e) fever
Answer:
(a) sore mouth
(d) stomach upset
(e) fever
Rationale:
Common adverse effects of nafcillin include vomiting, diarrhea, sore mouth, fever, and gastritis (stomach upset). Pain with urination and headache are not associated with this drug.
Question 86.
The rapid response team arrives in the room of a client who has had a cardiac arrest. The nurse should first apply which piece of monitoring equipment?
(a) electrocardiogram (ECG) electrodes
(b) pulse oximeter
(c) blood pressure cuff
(d) Doppler pulse detection unit
Answer:
(a) electrocardiogram (ECG) electrodes
Rationale:
The nurse should first apply the ECG electrodes to the client’s chest. If the client is found to be in ventricular fibrillation, the immediate priority is to defibrillate the client. Pulse oximetry is not an immediate priority. The client’s oxygenation is evaluated in a code situation using arterial blood gas analysis. The client’s blood pressure is evaluated after the ECG rhythm has been established. A portable Doppler ultrasound unit may be needed to check for the presence of a pulse or to check the blood pressure in a code situation.
Question 87.
A nurse counsels a client who is depressed. What nursing actions promote trust between the client and the nurse? Select all that apply.
(a) Indicate an understanding for the client’s feelings as well as for their cause.
(b) Listen and encourage the client to say more.
(c) Acknowledge hearing what the client said.
(d) Maintain eye contact with the client at all times.
(e) Stand very close to the client.
Answer:
(a) Indicate an understanding for the client’s feelings as well as for their cause.
(b) Listen and encourage the client to say more.
(c) Acknowledge hearing what the client said.
Rationale:
Active listening facilitates trust. It means that the nurse acknowledges that he or she has heard the client and indicates in his or her own words an understanding of what the client says and the emotions underlying what is said. It also involves encouraging the client to say more. Constant eye contact and standing very close to a client can be unnerving and can hamper trust building.
Question 88.
The nurse is assessing a client for heroin addiction. Which finding indicates the client has used heroin?
(a) sclera red and bloodshot
(b) pupils small and constricted
(c) pupils large and dilated
(d) drooping eyelids
Answer:
(b) pupils small and constricted
Rationale:
Heroin causes pinpoint pupils. Marijuana causes the eyes to appear red and bloodshot. Cocaine use causes pupils to dilate. Drooping of the eyelids is not typically associated with the use of any substance.
Question 89.
When performing routine health evaluations in school-age children, which finding would alert the school nurse to pediculosis capitis (head lice)?
(a) spotty baldness
(b) wheals with scalp blistering
(c) frequent scalp scratching
(d) dry, scaly patches on the skin
Answer:
(c) frequent scalp scratching
Rationale:
A typical sign of pediculosis capitis (head lice) is frequent scratching of the scalp because the condition causes severe itching. Scratch marks are usually easily visible. Because head lice are easily transmitted to others, the child’s family members and peers also should be examined for infestation. Spotty baldness, wheals, and scaly lesions are often allergic in nature.
Question 90.
When the nurse is assessing the client’s abdomen, which finding best indicates that a client’s peristaltic activity is returning to normal after surgery?
(a) The client passes flatus.
(b) The client says that she is hungry.
(c) Bowel sounds are hypoactive on auscultation.
(d) Peristalsis can be felt on abdominal palpation.
Answer:
(a) The client passes flatus.
Rationale:
Passing flatus indicates the return of peristalsis, as does active bowel sounds. Hunger is not the best indicator of peristaltic return. Hypoactive bowel sounds indicate that there is some peristaltic activity, but it is limited and not yet normal. Palpation is not an appropriate method of assessing bowel activity.
Question 91.
A client appears flushed and has shallow respirations. The arterial blood gas report shows the following: pH, 7.24; partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2), 49 mm Hg (6.5 kPa); and bicarbonate (HCO3), 24 mEq/L (24 mmol/L). These findings are indicative of which acid-base imbalance?
(a) metabolic acidosis
(b) metabolic alkalosis
(c) respiratory acidosis
(d) respiratory alkalosis
Answer:
(c) respiratory acidosis
Rationale:
The pH of 7.24 indicates that the client is acidotic. The PaCO2 value of 49 mm Hg is elevated. The HCO3 value of 24 mEq/L is normal. The client is in uncompensated respiratory acidosis. Hypoventilation and a flushed appearance are additional clinical manifestations of respiratory acidosis.
Question 92.
Which action is most important when the nurse is planning pain management for a client after a lobectomy for lung cancer?
(a) repositioning the client immediately after administering pain medication
(b) reassessing the client after administering pain medication
(c) reassuring the client after administering pain medication
(d) readjusting the pain medication dosage as needed
Answer:
(b) reassessing the client after administering pain medication
Rationale:
It is essential for the nurse to evaluate the effects of pain medication after it has had time to act. Although other interventions may be appropriate, continual reassessment is most important to determine the effectiveness and need for additional intervention, if any.
Repositioning could provide some comfort, but assessment of the client’s pain level is essential. Reassuring the client is important, but it will be of no value unless the nurse evaluates the client’s pain level. To readjust the pain dosage is appropriate only if titration is prescribed by the health care provider (HCP)
Question 93.
The nurse is evaluating a female client’s understanding of how to prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Which statement indicates that the client understands how to protect herself?
(a) “I’ll be sure my partner uses a condom.”
(b) “I need to be sure to take my birth control pills.”
(c) “I’ll always douche after sexual intercourse.”
(d) “I’ll be sure to take antibiotics to prevent an STI.”
Answer:
(a) “I’ll be sure my partner uses a condom.”
Rationale:
Barrier contraceptives must be used to protect against STIs. Birth control pills and douching are not effective for prevention of STIs. Prophylactic antibiotics are not used to prevent the acquisition of STIs.
Question 94.
While assessing a multigravid client at 10 weeks’ gestation, the nurse notes a purplish color to the vagina and cervix. The nurse documents this as what finding?
(a) Goodell’s sign
(b) Chadwick’s sign
(c) Hegar’s sign
(d) melasma
Answer:
(b) Chadwick’s sign
Rationale:
A purplish-blue discoloration of the vagina and cervix is termed Chadwick’s sign; it is caused by increased vascularity of the vagina during pregnancy and is considered a probable sign of pregnancy. Goodell’s sign, also considered a probable sign of pregnancy, refers to a softening of the cervix during pregnancy. Hegar’s sign, also a probable sign of pregnancy, refers to a softening of the lower uterine segment. Melasma, the mask of pregnancy, refers to the pigmentation of the skin on the face during pregnancy. Melasma is considered a presumptive sign of pregnancy.
Question 95.
A client with bipolar disorder, mania, has flight of ideas and grandiosity and becomes easily agitated. To prevent harmful behaviors, what should the nurse do initially?
(a) Encourage the client to stay in his room.
(b) Seclude the client at the first sign of agitation.
(c) Tell the client to seek out staff when feeling agitated.
(d) Instruct the client to ask for medication when agitated.
Answer:
(c) Tell the client to seek out staff when feeling agitated.
Rationale:
Initially, the nurse would tell the client to seek out staff when feeling agitated or upset to prevent violent episodes. Doing so helps the client to redirect negative feelings in an appropriate manner, such as talking. Encouraging the client to stay in his room is inappropriate because it does not help the client to deal with his feelings.
Secluding the client at the first sign of agitation is not indicated and may be perceived by the client as punishment. Instructing the client to ask for medication when agitated would not be the initial course of action. The nurse would interact with the client and direct the client to an activity to decrease his anxiety before intervening with any required medication.
Question 96.
The nurse is preparing written information for an older adult who is to manage intermittent self-catheterization. Which strategy will be most effective?
(a) Use charts to help convey information.
(b) Prepare information at a tenth-grade reading level.
(c) Use short words.
(d) Print the material in a condensed font.
Answer:
(c) Use short words.
Rationale:
The nurse should use short words, sentences, and paragraphs and avoid medical jargon. Correct terminology should be used when appropriate (e.g., type 1 diabetes, not “sugar diabetes”). The format should be as simple as possible; charts are not necessary and may be confusing to some clients. Information should be prepared at a fifth-grade reading level. The information should be presented in large-sized type.
Question 97.
The nurse should assess a child with newly diagnosed hyperthyroidism for which signs or symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) weight gain
(b) dry skin
(c) constipation
(d) rapid pulse
(e) heat intolerance
Answer:
(d) rapid pulse
(e) heat intolerance
Rationale:
Rapid pulse, heat intolerance, diarrhea, exophthalmos, and accelerated linear growth are more characteristic of hyperthyroidism, which is caused by an autoimmune response to thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors. Weight gain, dry skin, and constipation are characteristic of hypothyroidism, which results from a deficiency in secretion of thyroid hormone.
Question 98.
The nurse plans care for four mothers and their newborns. After reviewing the clients’ medical records, the nurse should make rounds on which client first?
(a) an 18-year-old with an uncomplicated spontaneous vaginal birth 12 hours ago who has abdominal cramps
(b) a 35-year-old with an uncomplicated vaginal birth 4 hours ago; the nurse’s notes indicated she soaked two peripads over the last 2 hours; fundus is firm
(c) a 16-year-old with a cesarean birth 4 hours ago, diagnosed with preeclampsia and receiving magnesium sulfate at 2 g/h; reflexes are 2+, and the nurse’s notes indicate she has a headache; vital signs are T 99.4°F (37.4°C), P 88, R 20, and BP 128/86 mm Hg
(d) an 18-year-old who had a caesarian birth 2 days ago and now has severe breast pain; vital signs are T 99.8°F (37.7°C), P 96, and R 22
Answer:
(b) a 35-year-old with an uncomplicated vaginal birth 4 hours ago; the nurse’s notes indicated she soaked two peripads over the last 2 hours; fundus is firm
Rationale:
The criterion for hemorrhage is saturating one pad per hour. The 35-year-old who delivered 4 hours ago had saturated a peripad per hour. Even though her fundus is firm, she may have experienced a cervical laceration, which would be the source of the bleeding. She needs to be evaluated first, based on the bleeding. The 18-year-old who has abdominal cramps is within normal limits for a G2 P2 and is experiencing afterbirth pains normally seen in a multiparous client; she will need pain medication.
The 16-year-old status post cesarean birth on magnesium sulfate is stable with adequate urinary output and normal reflexes. Her vital signs are within normal limits for a postpartum client. The headache is the one area of concern for this client. The 18-year-old who is 2 days postpartum with breast pain may be experiencing her milk coming in, although it does not indicate whether she is breast- or bottle-feeding; either situation may find a mother with milk developing within her system. The vital signs for this client are slightly elevated, but this may be from the milk coming in and would require nursing evaluation but is not emergent.
Question 99.
A nurse is evaluating the proper use of crutches by a client who has fractured the right leg. Which statement indicates the client is using the correct technique?
(a) “I move my left leg forward first as I swing forward on my crutches.”
(b) “I need to increase my arm strength because my arms tingle after I use my crutches.”
(c) “I padded the tops of my crutches so that I can lean more comfortably on my crutches.”
(d) “I feel pressure on the palms of my hands when I am walking with my crutches.”
Answer:
(d) “I feel pressure on the palms of my hands when I am walking with my crutches.”
Rationale:
It is normal for the client to feel pressure on the palms of the hands when walking with crutches. The client should move her affected (right) leg forward first as she swings forward with the crutches. Leaning on the crutches can apply pressure to the axillae, leading to neurovascular impairment. If the client’s arms are tingling after she uses her crutches, she is probably applying pressure on her axillae when walking.
Question 100.
Which factor is a priority when evaluating discharge plans for an older adult after a lower left lobectomy for lung cancer?
(a) the distance the client lives from the hospital
(b) support available for assisting the client at home
(c) the client’s ability to do home blood pressure monitoring
(d) the client’s knowledge of the causes of lung cancer
Answer:
(b) support available for assisting the client at home
Rationale:
Because clients are discharged as soon as possible from the hospital, it is essential to evaluate the support for assistance and self-care at home. If the client has support at home, the distance from the hospital may be irrelevant.
The client or support team will monitor vital signs as needed, but blood pressure monitoring is not specifically indicated. It is more important at this point for the client to understand how to manage his care at home, rather than knowing the causes of lung cancer.
Question 101.
A primiparous client planning to breastfeed her term neonate born vaginally asks, “When will my ‘real’ milk come in?” The nurse explains to the client that after birth, breasts begin to produce milk within what time period?
(a) 12 hours
(b) 24 hours
(c) 2 to 4 days
(d) 7 days
Answer:
(c) 2 to 4 days

Rationale:
If the client begins breastfeeding early and often after birth, the breasts begin to fill with milk within 48 to 96 hours, or 2 to 4 days. The breasts secrete colostrum for the first 24 to 48 hours, which is beneficial to the neonate because of the immunoglobulins contained in colostrum.
Question 102.
The nurse is caring for an older adult who has been bedridden for an extended period. Which symptom indicates that the client has hypoxia?
(a) chills
(b) productive cough
(c) confusion
(d) pleuritic chest pain
Answer:
(c) confusion
Rationale:
The predominant clinical finding in elderly or debilitated clients indicating that they have hypoxia is confusion. Fever and chills, productive cough, and pleuritic chest pain could be indicative of a respiratory tract infection.
Question 103.
A child with rheumatic fever has polyarthritis and chorea. An echocardiogram shows swelling of the cardiac tissue. Which intervention should the nurse include in the child’s plan of care?
(a) Explain that the chorea will disappear over time.
(b) Perform neurologic checks every 4 hours until the chorea subsides.
(c) Promote ambulation by administering aspirin every 4 hours.
(d) Keep the child in a slightly cool environment.
Answer:
(a) Explain that the chorea will disappear over time.
Rationale:
It is important for the child and family to understand that chorea associated with rheumatic fever is not permanent. Therefore, the nurse should explain that the chorea will disappear over time. It is not necessary to assess the child’s neurologic status because the chorea is self-limited and nonprogressive.
Because the child has cardiac involvement, ambulation is contraindicated. Aspirin is used primarily as an anti-inflammatory drug and secondarily for pain relief. A slightly cool environment is unnecessary. Environmental temperature does not affect the child’s polyarthritis and chorea.
Question 104.
A 19-year-old client who is approximately 8 weeks pregnant asks the nurse, “If I have an abortion in the next 2 or 3 weeks, how will it be done?” The nurse instructs the client that at this gestational age, an abortion is usually performed by which technique?
(a) dilatation and curettage
(b) menstrual extraction
(c) dilatation and vacuum extraction
(d) saline induction
Answer:
(a) dilatation and curettage
Rationale:
When the gestation is <13 weeks, an elective abortion is usually performed by the dilatation and curettage method. Menstrual extraction, or suction evacuation, is the easiest method, but it is used only when the client is between 5 and 7 weeks’ gestation.
Dilatation and vacuum extraction is used when clients are between 12 and 16 weeks’ gestation. Saline induction, used for clients between 16 and 24 weeks’ gestation, involves instillation of a hypertonic saline solution into the amniotic sac to initiate expulsion. Oxytocin infusion may also be used with saline induction.
Question 105.
The nurse is performing a respiratory assessment on a client who has a pleural effusion. Which breath sound is expected for this client?
(a) decreased breath sounds on the affected side
(b) normal bronchial breath sounds
(c) hyperresonance on percussion
(d) wheezing on auscultation
Answer:
(a) decreased breath sounds on the affected side
Rationale:
A pleural effusion is a collection of fluid between the pleural layers of the lung. The effusion decreases chest wall movement on the affected side. The nurse should expect the breath sounds to be decreased or diminished over the affected area. Because of the presence of fluid, percussion would elicit dullness, not hyperresonance. The nurse should not expect to hear wheezing on auscultation.
Question 106.
A nurse is caring for a child with intussusception. What is an expected outcome for a goal to relieve acute pain from abdominal cramping?
The child:
(a) exhibits no manifestations of discomfort.
(b) is very still.
(c) has a normal bowel movement.
(d) has not vomited in 3 hours.
Answer:
(a) exhibits no manifestations of discomfort.
Rationale:
An expected client outcome for a goal to reduce acute pain related to cramping is that the client exhibits no manifestations of discomfort, such as crying or drawing the legs to the abdomen. Being very still may indicate either a pain state or a state of relaxation, and the nurse would need to assess the client further. Having normal bowel movements and not vomiting are desired outcomes, but the goal here is to relieve the pain.
Question 107.
Gentamicin sulfate 25 mg IM has been prescribed every 6 hours. Gentamicin sulfate 40 mg/mL is available. Flow many milliliters (to the nearest tenth of an mL) should the nurse administer in each dose? Round to the nearest mL.
.......................... mL.
Answer:
0.6 mL
Rationale:
40 mg/mL = 25 mg/XmL X = 0.6 mL.
Question 108.
The nurse is assessing a sexually active woman who has malaise and dysuria. The client has a temperature of 100°F (37.8°C) and painful blisters on the outside of her vagina. The client tells the nurse she had intercourse with a new partner 5 days ago. What should the nurse do?
(a) Advise the client to ask her partner to use a condom.
(b) Encourage the client to increase fluid to 3,000 mL/day.
(c) Tell the client to use a lubricant jelly on the blisters.
(d) Refer the client to a health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(d) Refer the client to a health care provider (HCP).
Rationale:
The client is likely exhibiting symptoms of herpes genitalis, which include painful blisters or vesicles that appear 2 to 20 days after transmission of the disease. The client was most likely exposed from her new partner. The client should be referred to an HCP 3 for treatment. Having her partner wear a condom, increasing fluids, or using lubricant jelly will not treat the infection. While having her partner wear a condom will not cure the infection, having future partners wear condoms will help prevent its transmission.
Question 109.
A child with leukemia fails to respond to therapy. Which statement offers the nurse the best guide in making plans to assist the parents in dealing with their child’s imminent death?
(a) Knowing that the prognosis is poor helps prepare relatives for the death of children.
(b) Relatives are especially grieved when a child does well at first but then declines rapidly.
(c) Trust in health personnel is most often destroyed by a death that is considered untimely.
(d) It is more difficult for relatives to accept the death of a 10-year-old than the death of a younger child whose family membership has been short.
Answer:
(b) Relatives are especially grieved when a child does well at first but then declines rapidly.
Rationale:
It has been found that parents are more aggrieved when optimism is followed by defeat. The nurse should recognize this when planning various ways to help the parents of a dying child. It is not necessarily true that knowing about a poor prognosis for years helps prepare parents for a child’s death, that trust in health personnel is destroyed when a death is untimely, or that it is more difficult for parents to accept the death of an older child than that of a younger child.
Question 110.
The nurse cares for a child receiving a blood transfusion. The child becomes flushed and is wheezing. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Administer oxygen.
(c) Switch the transfusion to normal saline solution.
(d) Take the child’s vital signs.
Answer:
(c) Switch the transfusion to normal saline solution.
Rationale:
The child is having a reaction to the blood transfusion. The priority is to stop the blood transfusion but maintain an open venous access for medication or high fluid volume delivery. Thus, switching the transfusion to normal saline solution would be done first. Since the child is having difficulty breathing, applying oxygen would be the next action. Additionally, vital signs are taken to determine the extent of circulatory involvement. Then the HCP 3 would be notified and, if necessary, the crash cart would be obtained.
Question 111.
A client who is allergic to penicillin has a prescription to receive cefazolin. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Ask if the client has taken cefazolin before without an adverse response.
(b) Verify the prescription with the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Administer the cefazolin as prescribed.
(d) Observe the client closely for urticaria.
Answer:
(a) Ask if the client has taken cefazolin before without an adverse response.
Rationale:
A client who has an allergy to penicillin may have a cross-sensitivity to cefazolin, a first- generation cephalosporin, and the drug should be given with caution. The nurse should ask the client whether the client has taken cefazolin before. The nurse should inform the pharmacy of the client’s allergy after asking the client about prior use of cefazolin.
The medication should not be administered until the nurse first inquires about the client’s exposure to cefazolin and then consults the pharmacist or HCP 3. Observing the client for urticaria is appropriate but is not an initial response.
Question 112.
Which nursing intervention will promote successful achievement of Erikson’s stage of development for the 3-year-old toddler?
(a) Allow the toddler to choose what time to take her antibiotic.
(b) Encourage the toddler to assist in removing the dressing on her leg.
(c) Allow the toddler to work on an art project that she can complete.
(d) Encourage friends to visit the toddler in the hospital.
Answer:
(b) Encourage the toddler to assist in removing the dressing on her leg.
Rationale:
Toddlers are in Erikson’s stage of autonomy versus shame and doubt. They want to do things on their own and experience despair when they are not allowed to be independent in areas that they are capable. Allowing the toddler to participate in the dressing change promotes the toddler’s independence. Medications must be administered on a schedule to maintain therapeutic levels. Toddlers have short attention spans and would not likely complete an art project. Toddlers commonly engage in parallel play. Having another toddler visit will not aid in the achievement of Erikson’s stage of development.
Question 113.
When preparing the teaching plan for a client about lithium therapy, the nurse should provide which instruction to the client concerning sodium?
(a) Maintain an adequate sodium intake.
(b) Discontinue sodium in the diet.
(c) Buy foods labeled “low in sodium.”
(d) Increase sodium in the diet.
Answer:
(a) Maintain an adequate sodium intake.
Rationale:
The nurse would teach the client taking lithium and his family about the importance of maintaining adequate sodium intake to prevent lithium toxicity. Because lithium is a salt, reduced sodium intake could result in lithium retention with subsequent toxicity. Increasing sodium in the diet is not recommended and may be harmful. Increased sodium levels result in lower lithium levels. Therefore, the drug may not reach therapeutic effectiveness.
Question 114.
A client who is undergoing radiation therapy develops mucositis. Which action should be included in the client’s plan of care?
(a) increasing mouth care to twice per shift
(b) providing the client with hot tea to drink
(c) promoting regular flossing of teeth
(d) using half-strength hydrogen peroxide on mouth ulcers
Answer:
(c) promoting regular flossing of teeth
Rationale:
Mucositis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa caused by radiation therapy. It is important that the client with mucositis receive meticulous mouth care, including flossing, to prevent the development of an infection. Mouth care should be provided before and after each meal, at bedtime, and more frequently as needed. Extremes of temperature should be avoided in food and drink. Half-strength hydrogen peroxide is too harsh to use on irritated tissues.
Question 115.
A parent calls the Poison Control Center because her 3-year-old has eaten 10 to 12 chew- able acetaminophen tablets. What should the nurse instruct the parent to do?
(a) Give the child a large glass of milk.
(b) Induce vomiting.
(c) Take the child to the emergency department.
(d) Monitor the child’s respirations for 24 hours.
Answer:
(c) Take the child to the emergency department.
Rationale:
Acetaminophen ingestion can cause severe liver disease. The child should be evaluated in the emergency department. The child should not be offered any fluids, and the parents should not attempt to induce vomiting. Assessing the child’s respirations for 24 hours will delay needed emergency treatment.
Question 116.
The parent of a preschool-age child tells the nurse that the child is hyperactive and something needs to be done. Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate initially?
(a) “What makes you think your child is hyperactive?”
(b) “What do you think needs to be done?”
(c) “How does your child behave normally?”
(d) "Does the preschool teacher think your child is hyperactive?”
Answer:
(a) “What makes you think your child is hyperactive?”
Rationale:
The best approach by the nurse is to determine why the parent thinks the child is hyperactive. Some children are very active but do not have the necessary defining characteristics of hyperactivity. Asking what the parent thinks needs to be done, how the child behaves normally, and if the preschool teacher thinks the child is hyperactive would be an appropriate follow-up question once more information is gathered from the parent to determine whether the child indeed is hyperactive.
Question 117.
When preparing for the discharge of a newborn after surgery to correct tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF), the nurse teaches the parents about the need for long-term health care because their child has a high probability of developing which complication?
(a) recurrent mild diarrhea with dehydration
(b) esophageal stricture
(c) speech problems
(d) gastric ulcers
Answer:
(b) esophageal stricture
Rationale:
Dilatation at the anastomosis site is needed during the first years of childhood in about 50% of children who have had corrective surgery for TER Recurrent mild diarrhea with dehydration is not likely to develop with this surgery. Speech problems can occur if other abnormalities are present to produce them; the larynx and structures of speech are not affected by TEF. Dysphagia and strictures may decrease food intake, and poor weight gain may be noted, but gastric ulcers should not develop from surgery to repair TEF.
Question 118.
A young adult with Hodgkin’s disease has been readmitted to the hospital because of aggressive disease that is unresponsive to multiple therapies. Death appears imminent. Which is a priority nursing goal for this client?
(a) Reduce feelings of isolation.
(b) Reduce fear of pain.
(c) Reduce fear of more aggressive therapies.
(d) Reduce feelings of social inadequacy.
Answer:
(a) Reduce feelings of isolation.
Rationale:
Terminally ill clients most often describe feelings of isolation because they feel ignored. The terminally ill client may sense any discomfort that family and friends feel in the client’s presence. Nursing interventions include spending time with the client, encouraging discussion about feelings, and answering questions openly and honestly. Reducing fear of pain or fear of more aggressive therapies is secondary to lessening the client’s feelings of isolation. Reducing feelings of social inadequacy is not relevant to the terminally ill client.
Question 119.
A client is admitted in early active labor at 39 weeks’ gestation with intact membranes. When assessing the fetal heart rate, the nurse locates the heart sounds above the client’s umbilicus at midline. The nurse should further confirm that the fetus is lying in which position?
(a) cephalic
(b) frank breech
(c) face
(d) transverse
Answer:
(b) frank breech
Rationale:
When the fetus is in a breech position, the fetal heart rate most often is located above the umbilicus because the fetal heart is near the top of the mother’s uterus. The heart of a fetus in the cephalic position is typically located on either the left or the right side of the client’s uterus. Also, because the fetal heart typically is located in the lower portion of the mother’s uterus, the sounds would be heard below the umbilicus.
With a face presentation, fetal heart sounds are typically located on either the left or the right side of the client’s uterus; in addition, because the fetal heart typically is located in the lower portion of the mother’s uterus, the sounds would be heard below the umbilicus. When the fetus is in a transverse position, the fetal heart sounds typically would be located below the umbilicus and in the midline.
Question 120.
The nurse is caring for a client who has been diagnosed with pernicious anemia. Which statement by the client indicates an understanding of the treatment of pernicious anemia?
(a) “I’ll need to increase my dietary intake of foods that are high in vitamin B12.”
(b) “I’ll receive my first injection of vitamin B12 tomorrow, and I’ll return for a follow-up injection in 1 month.”
(c) “I understand that the oral form of vitamin B12 is preferred because it’s safer and less expensive than the injection form.”
(d) “I’ll need to take vitamin B12 replacements for the rest of my life.”
Answer:
(d) “I’ll need to take vitamin B12 replacements for the rest of my life.”
Rationale:
Clients who have been diagnosed with pernicious anemia are lacking adequate amounts of the intrinsic factor (IF) that is secreted by the gastric mucosa. IF is necessary for the absorption of cobalamin (vitamin B12) in the distal ileum. Without the presence of IF, dietary intake of vitamin Ba2 is useless because it cannot be absorbed. Treatment of pernicious anemia includes IM injections of cobalamin, at first daily for 2 weeks, then weekly until the anemia is corrected. A maintenance schedule of monthly injections is then implemented. The injections will need to be continued for the rest of the client’s life.
Question 121.
A client’s 1200 blood glucose was inaccurately documented as 310 mg/dL (17.2 mmol/L) instead of 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L). This error was not noticed until 1300. The nurse administered the sliding scale insulin for a blood glucose of 310 mg/ dL (17.2 mmol/L). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Assess the client for hypoglycemia.
(c) Consult with the clinical pharmacist.
(d) Call the charge nurse.
Answer:
(b) Assess the client for hypoglycemia.
Rationale:
The nurse should first assess the client because a hypoglycemic reaction is likely to occur. At this time, the nurse also should give the client a fast-acting simple carbohydrate. Then the nurse should notify the HCP for prescriptions to prevent or treat severe hypoglycemia. The nurse could consult the clinical pharmacist until able to contact the HCP, but the first action is to assess the client in order to have accurate information to report. When the situation has been resolved, the nurse should document the incident and report the incident to the charge nurse.
Question 122.
An older infant who has been injured in an automobile accident is to wear a splint on the injured leg. The mother reports that the infant has become mobile even while wearing the splint. What should the nurse advise the mother to do?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP) immediately to adjust the treatment plan.
(b) Confine the infant to one room in the apartment.
(c) Keep the infant in the splint at night, removing it during the day.
(d) Remove any unsafe items from the area in which the infant is mobile.
Answer:
(d) Remove any unsafe items from the area in which the infant is mobile.
Rationale:
Safety is the priority in caring for this infant. Infants adapt easily, increasing mobility even with a splint in place. Therefore, the mother needs to ensure that the area in which the infant is mobile is safe. There is no need to contact the HCP to alter the treatment plan. Confining the infant to one room may not allow the child to achieve normal development. The child needs different environments for maximum development. The infant needs to wear the splint as prescribed by the HCP to ensure optimal healing.
Question 123.
While preparing a client for surgery, the nurse assesses for psychosocial problems that may cause preoperative anxiety. Which is believed to be the most distressing fear a preoperative client is likely to experience?
fear of:
(a) the unknown
(b) changes in body image
(c) the effects of anesthesia
(d) being in pain
Answer:
(a) the unknown
Rationale:
Anxiety in a preoperative client may be caused by many different fears, such as fear of the effects of anesthesia, the effects of surgery on body image, separation from family and friends, job loss, disability, pain, or death. However, fear of the unknown is most likely to be the greatest fear because the client feels helpless. Therefore, an important part of preoperative nursing care is to assess the client for anxieties and explore possible causes. Emotional support can then be offered so that the client is in the best possible psychological condition for surgery.
Question 124.
A 56-year-old woman is admitted for a modified radical mastectomy. The client appears anxious and asks many questions. How should the nurse respond to this client?
(a) Tell the client as much as she wants to know and is able to understand.
(b) Delay discussing the client’s questions with her until the convalescent phase of her care.
(c) Delay discussing the client’s questions with her until her apprehension subsides.
(d) Explain to the client that she should discuss her questions with her health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(a) Tell the client as much as she wants to know and is able to understand.
Rationale:
An important nursing responsibility is preoperative teaching. The recommended guide for teaching is to tell the client as much as she wants to know and is able to understand. Delaying discussion of issues or concerns will most likely increase the client’s anxiety. Telling the client to discuss questions with the HCP avoids acknowledging the client’s concerns.
Question 125.
One hour before surgery, the client asks the nurse about the risks of the surgical procedure. Which statement by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “What are your concerns? I can answer any questions that you have.”
(b) “There are several risks. Did the surgeon tell you about them?”
(c) “It’s important that your questions are answered and you understand the risks before you have surgery. I'll contact the surgeon.”
(d) “Actually, the risks associated with this procedure are minimal. The surgeon has performed this surgery many times.”
Answer:
(c) “It’s important that your questions are answered and you understand the risks before you have surgery. I'll contact the surgeon.”
Rationale:
The client must have adequate disclosure of the risks associated with the surgery before signing the consent form. It is the health care provider’s (HCP’s) responsibility to explain the risks of any procedures and to obtain the client’s informed consent. If the nurse suspects that the client has not been truly informed, it is the responsibility of the nurse to act as a client advocate and contact the surgeon to provide additional information to the client. It is not appropriate to have the client go to surgery without understanding the risks. The nurse should not minimize the procedure or dismiss the client’s concerns.
Question 126.
The nurse is assessing fetal position in a 32-year-old woman in her 8th month of pregnancy. From the figure, how would the nurse document the fetal position?
(a) left occipital transverse
(b) left occipital anterior
(c) right occipital transverse
(d) right occipital anterior
Answer:
(d) right occipital anterior
Rationale:
In right occipital anterior lie, the occiput faces the right anterior segment of the woman’s pelvis. In left occipital transverse lie, the occiput faces the woman’s left hip. In left occipital anterior lie, the occiput faces the left anterior segment of the woman’s pelvis. In right occipital transverse lie, the occiput faces the woman’s right hip.
Question 127.
A child has a urinary tract infection and is being treated with antibiotics. The nurse should instruct the parents to report which symptom?
(a) increased urine output
(b) loss of appetite
(c) jaundice
(d) fever
Answer:
(d) fever
Rationale:
The nurse should advise the parents to report an increasing fever, which would indicate the infection is not resolving. Increased urine output may occur, but it would be very difficult for the parent to actually determine this and it is not a cardinal sign of increasing infection. The child may have a loss of appetite related to the infection or the medication, but is not indicative of an infection that is becoming worse. The child should not have jaundice from a urinary tract infection that is being treated.
Question 128.
After teaching a mother about the neonate’s positive Babinski’s reflex, the nurse determines that the mother understands the instructions when she says that a positive Babinski’s reflex indicates which factor?
(a) possible partial paralysis
(b) possible lower limb defect
(c) immature central nervous system
(d) possible injury to nerves that innervate the legs
Answer:
(c) immature central nervous system
Rationale:
A positive Babinski’s reflex in a neonate is a normal finding demonstrating the immaturity of the central nervous system in corticospinal pathways. A neonate’s muscle coordination is immature, but the Babinski’s reflex does not help determine this immaturity. A positive Babinski’s reflex does not indicate a defect in the spinal cord or an injury to nerves that innervate the legs. There is no evidence to suggest partial paralysis. A positive Babinski’s reflex in an adult indicates disease.
Question 129.
The nurse should instruct a client who is taking dexamethasone and furosemide to report which symptom?
(a) excitability
(b) muscle weakness
(c) diarrhea
(d) increased thirst
Answer:
(b) muscle weakness
Rationale:
The nurse should instruct the client who is taking dexamethasone and furosemide to observe for signs and symptoms of hypokalemia, such as malaise, muscle weakness, vomiting, and a paralytic ileus, because both dexamethasone and furosemide deplete serum potassium. This combination of drugs does not cause the client to become excitable or have diarrhea or thirst.
Question 130.
A client with a suspected diagnosis of lung cancer has a bronchoscopy with biopsy. Following the procedure, what nurse should the nurse do?
(a) Encourage the client to gargle with oral lido-caine to decrease throat irritation.
(b) Monitor the client for signs of pneumothorax.
(c) Administer pain medication as needed to relieve mediastinal discomfort.
(d) Advise the client not to talk until the gag reflex returns.
Answer:
(b) Monitor the client for signs of pneumothorax.
Rationale:
After a bronchoscopy with a biopsy, the nurse should monitor the client for signs of pneumothorax as well as hemorrhage. The client should not gargle with oral lidocaine; this will not allow the gag reflex to return. The client should not have any mediastinal discomfort after a bronchoscopy; if pain does occur, it should be reported promptly to the health care provider (HCP) It is not necessary to tell the client not to talk until the gag reflex returns.
Question 131.
A nurse is preparing to administer 500 mL of an IV solution to a child over 12 hours via tubing that delivers microdrips at 60 gtt/mL. At what rate should the nurse infuse the solution?
......................... gtt/min.
Answer:
42 gtt/min
Rationale:
The number of drops the client should receive each minute is determined as follows:
500 mL/12 hours = between 41 and 42 mL to be infused each hour
42 mL x 60 (drop factor) = 2,520 drops to be infused each hour
2,520 drops/60 minutes = 42 drops to be infused every minute
Question 132.
Which technique is correct when the nurse administers a subcutaneous injection?
(a) Use a 1-inch (2.5-cm) needle for injection.
(b) Insert the needle at a 45-degree angle to the skin.
(c) Spread the skin tightly at the injection site.
(d) Draw 0.2 mL of air into the syringe before administration.
Answer:
(b) Insert the needle at a 45-degree angle to the skin.
Rationale:
Subcutaneous injections are administered at an angle of 45 to 90 degrees, depending on the size of the client. Subcutaneous needles are typically % to Vs inches in length. The skin should be pinched up at the injection site to elevate the subcutaneous tissue. Air is not drawn into the syringe for a subcutaneous injection.
Question 133.
An older adult client hospitalized 4 days ago for treatment of acute respiratory distress has become confused and disoriented. The client has been picking invisible items off blankets and has been yelling at the daughter who is not in the room. The family tells the nurse that the client has been treated for anxiety with alprazolam for years, but alprazolam is not on the current medication list. Which safety measures should be implemented? Select all that apply.
(a) The client should be placed on withdrawal precautions and treatment should start immediately.
(b) The client should be placed in soft restraints.
(c) A prescription should be obtained to help with the hallucinations.
(d) The daughter should not visit until the client is better.
(e) The client’s medical and mental status should be evaluated frequently and treated as needed.
Answer:
(a) The client should be placed on withdrawal precautions and treatment should start immediately.
(c) A prescription should be obtained to help with the hallucinations.
(e) The client’s medical and mental status should be evaluated frequently and treated as needed.

Rationale:
Especially in the elderly, alprazolam withdrawal requires immediate and aggressive treatment. Hallucinations are frightening for the client and family. Changes in medical and mental status can occur quickly in the elderly, and the client must be monitored closely. Restraints are not indicated for the client and would likely aggravate the confusion and agitation. There is no need to restrict the daughter from visiting at this point.
Question 134.
The mother of a toddler tells the nurse her child is “fussy” and not as “easygoing” as her other children. She is having difficulty feeding the child because he fusses and cries when she serves a meal. What instructions should the nurse should give the mother?
(a) Allow the child to determine when feeding should occur.
(b) Do not feed the child if he cries.
(c) Provide structured feeding times and routines.
(d) Give the child finger foods and let him eat when he wants.
Answer:
(c) Provide structured feeding times and routines.
Rationale:
Each child has unique temperaments and energy levels, and parents must adapt parenting strategies for each child. Children who are easily upset do better in structured environments where they can learn what to expect. Easygoing children can manage flexible feeding times.
Not feeding the child when he cries will not promote nutrition and does not provide the structure that will help the child learn appropriate eating behaviors. Children who are very active and always “on the go” respond well to eating food that can be carried in their hand, and eating more frequently.
Question 135.
When giving a client a tube feeding, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Warm the feeding solution before administration.
(b) Place the client in a left side-lying position.
(c) Aspirate residual gastric contents before the feeding and discard.
(d) Verify position of the tube before beginning feeding.
Answer:
(d) Verify position of the tube before beginning feeding.
Rationale:
The position of the tube should be verified before the feeding is implemented. Warming the solution is not necessary or desirable because it can encourage bacterial growth; however, if the solution has been refrigerated, the nurse can bring the solution to room temperature. The client should be lying down with the head elevated or sitting upright during the administration of the feeding. Gastric residuals should be aspirated and then reinstalled to prevent electrolyte losses.
Question 136.
A multiparous client 48 hours postpartum who is breastfeeding tells the nurse, “I’m having a lot of cramping. This didn’t happen when I nursed my first baby.” Which would be the nurse’s best response?
(a) “I’ll notify your health care provider (HCP). It’s possible there are some placental fragments remaining.”
(b) “I need to check your lochial flow. You may have a clot that is being dislodged.”
(c) “You must have gotten a heavy dose of oxytocin. It should wear off soon.”
(d) “The cramping is normal and is caused by your baby’s sucking, which stimulates the release of oxytocin.”
Answer:
(d) “The cramping is normal and is caused by your baby’s sucking, which stimulates the release of oxytocin.”

Rationale:
The cramping is caused by the baby’s sucking and subsequent stimulation for the release of oxytocin. This cramping is normal. With each subsequent pregnancy, the uterus becomes “stretched” and the release of oxytocin causes the uterus to contract, resulting in the feeling of cramping that can become more severe with each birth. Continued moderate to large amounts of lochia rubra are indicative of retained placental fragments.
Cramping indicates that the uterus is contracting and most likely firm. A boggy uterus, continued moderate to heavy lochia, mild vasoconstriction, and restlessness and anxiety suggest delayed postpartum hemorrhage due to subinvolution of the placental site, retained placental tissue, or infection. Most clients receive a standard dose of oxytocin after birth. Oxytocin has a duration of action of 60 minutes. Therefore the effects of the drug would have worn off by 24 hours postpartum.
Question 137.
The mother of a child with moderate diarrhea asks how to manage her child’s illness. What should the nurse suggest?
(a) Begin clear liquids for 24 hours.
(b) Feed the child bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast.
(c) Offer foods that are low in fat.
(d) Continue the child’s regular diet.
Answer:
(b) Feed the child bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast.
Rationale:
When performing tracheostomy care, it is important that the tracheostomy ties be securely tied to prevent dislodgment of the tube. It is not necessary to remove the inner cannula every 2 hours for cleaning. Routine cleaning is usually performed every 8 hours. The nurse should use precut tracheostomy dressings under the neck plate to protect the skin surrounding the stoma. Cutting and using a gauze dressing can cause loose gauze fibers to enter the airway. The inner cannula should be suctioned before cleaning, not afterward.
Question 138.
Prior to discharge from the hospital, the nurse is instructing a client about performing tracheostomy care at home Which information should the nurse include in the instructions?
(a) Remove the inner cannula every 2 hours for cleaning.
(b) Secure the tracheostomy ties with a square knot.
(c) Use cut gauze under the neck plate to protect the skin.
(d) Suction the inner cannula on completion of the procedure.
Answer:
(b) Secure the tracheostomy ties with a square knot.
Rationale:
The nurse should send the unopened bag of IV 50% dextrose found in the sink to the pharmacy. A concentrated medication such as 50% dextrose could be lethal if inadvertently administered and should not be stored outside the pharmacy. An incident report is not necessary in this situation. The sharps container is not the appropriate method for disposal of this medication.
Question 139.
The nurse finds an unopened bag of IV 50% dextrose in a sink on the nursing unit. What should the nurse do with the IV bag?
(a) Leave it where found and notify the charge nurse.
(b) Send it to the pharmacy.
(c) File an incident report.
(d) Discard it in a sharps container.
Answer:
(c) File an incident report.
Rationale:
The client who is wheelchair-bound with a spinal cord injury should be taught to make small weight shifts, lifting off the sacral area every 15 minutes. This decreases the risk of pressure ulcer formation. Bathing daily promotes skin cleanliness, but by itself will not prevent pressure ulcer formation. Eating a well-balanced diet that includes proteins and carbohydrates promotes good skin integrity. Moving from the bed to the wheelchair every 2 hours is not desirable because the client should not spend excessive amounts of time in bed. Pressure sores can develop in < 2 hours.
Question 140.
To reduce the risk of pressure ulcer formation, which activity should the nurse teach the client who is wheelchair-bound as a result of a spinal cord injury?
(a) Bathe daily.
(b) Eat a high-carbohydrate diet.
(c) Shift your weight every 15 minutes.
(d) Move from the bed to the wheelchair every 2 hours.
Answer:
(a) Bathe daily.
Rationale:
Anatomically, the squatting position enlarges the pelvic outlet and uses the force of gravity during pushing. The mother should curve her body into a C shape for the greatest effectiveness. The side-lying, knee-chest, and squatting with arched back positions do not enlarge the pelvic outlet.
Question 141.
A client in the second stage of labor has had no anesthesia or analgesia. The nurse should assist the client into which position so the client can begin pushing?
(a) squatting with the body curved in a C shape
(b) side-lying while keeping the head elevated
(c) in the knee-chest position while keeping the head down
(d) squatting with the back arched
Answer:
(b) side-lying while keeping the head elevated
Rationale:
Saying “ If you punch people out, you’ll get into trouble” helps the client by pointing out the negative consequences of his behavior. Clients with antisocial personality disorder are aggressive, impulsive, and reckless; engage in illegal activities; and lack guilt or remorse.
The nurse teaches the client that there are consequences to his irresponsible behavior and that the way to stay out of trouble is to change his behavior. Saying, “It’s wrong to punch others,” is not helpful since the client does not feel guilt or remorse. Saying, “I wouldn’t do that again if I were you” or “Don’t ever do that again,” is authoritative and scolds the client without helping him.
Question 142.
A client with antisocial personality disorder tells the nurse, “I punched the guy out because he deserved it, and then the cops arrested me.” Which response would be most helpful to the client?
(a) “It’s wrong to punch others.”
(b) “If you punch people out, you’ll get into trouble.”
(c) “I wouldn’t do that again if I were you.”
(d) “Don’t ever do that again; you’re an adult.”
Answer:
(c) “I wouldn’t do that again if I were you.”
Rationale:
Self-mutilation is a way to express anger and rage, commonly seen in clients with borderline personality disorder. It typically is a cry for help, an expression of intense anger, helplessness, or guilt. When a client is experiencing numbness or feelings of unreality, self-mutilation induces physical pain that validates the person’s being alive because of the ability to feel the physical pain.
Self-mutilation is not a means of getting what the person wants. It is not used as a form of manipulation, although it is often misinterpreted as such. Self-mutilation is a serious behavior that is harmful to the self and cannot be ignored.
Question 143.
The nurse is teaching an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) about the care of clients with selfmutilation. Which statement by the UAP would indicate teaching about self-mutilation has been effective?
(a) “It’s a means of getting what the person wants.”
(b) “It’s a nonserious event that can be ignored.”
(c) “It’s a way to express anger and rage.”
(d) “It’s a form of manipulation.”
Answer:
(c) “It’s a way to express anger and rage.”
Rationale:
Hepatitis C is transferred by percutaneous exposure, such as tattooing. Hepatitis A is acquired through contaminated water, exposure in underdeveloped countries, or shellfish in contaminated waters.
Question 144.
The nurse is obtaining a nursing history of a client suspected of having hepatitis C. What information should the nurse obtain from the client? Has the client:
(a) drunk contaminated water?
(b) traveled to India?
(c) had a tattoo?
(d) eaten shellfish?
Answer:
(a) drunk contaminated water?
Rationale:
Lorazepam, a benzodiazepine, is commonly used to decrease the symptoms of central nervous system irritability in the client who is experiencing early symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. An antihypertensive will not treat the underlying CNS irritability. If the lorazepam is effective, it will not be necessary to have someone sit with the client. At this point, it is not necessary to notify the health care provider
Question 145.
A client is experiencing symptoms of early alcohol withdrawal. The client’s blood pressure is 150/85 mm Hg, and the pulse is 98 bpm. What should the nurse do?
(a) Administer lorazepam.
(b) Administer an antihypertensive.
(c) Assign an unlicensed assistive personnel to sit with the client.
(d) Notify the health care provider.
Answer:
(b) Administer an antihypertensive.
(c) Assign an unlicensed assistive personnel to sit with the client.
Rationale:
Appropriate diet instructions for the client in the early stages of cirrhosis include ensuring an adequate intake of protein and eating small, frequent meals. There is no need to limit protein intake unless the client has evidence of hepatic encephalopathy. Additionally, fluid intake is not restricted unless the client has significant ascites or edema (these typically occur later in the disease). Because of gastrointestinal dysfunction, small, frequent meals are frequently better tolerated than three regular meals. Clients with cirrhosis should be encouraged to increase their caloric intake instead of restricting it. Alcohol intake in any amount is discouraged.
Question 146.
Which diet instructions are appropriate when teaching a client in the early stages of cirrhosis about nutritional needs? Select all that apply.
(a) “Limit your caloric intake so that you don’t become overweight.”
(b) “An adequate intake of protein is important to your health.”
(c) “I encourage you to eat small, frequent meals.”
(d) “Restrict your fluid intake to 1,000 mL/day.”
(e) “Limit your alcohol intake to one glass of wine daily.”
Answer:
(c) “I encourage you to eat small, frequent meals.”
Rationale:
After surgery, the nurse’s initial assessment is the surgical site dressing to determine whether there is any bleeding or drainage. Once this assessment is completed, then the nurse would assess the other areas such as the IV access site, pain, and nasogastric tube function.
Question 147.
After a child returns from the postanesthesia care unit after surgery, what should the nurse assess first?
(a) the IV fluid access site
(b) the child’s level of pain
(c) the surgical site dressing
(d) the functioning of the nasogastric tube
Answer:
(a) the IV fluid access site
Rationale:
The nurse should use the radial artery to obtain blood gas samples because it is easier to maintain firm pressure there than on the femoral artery. Nursing interventions to protect the client who has received t-PA or alteplase recombinant therapy include maintaining arterial pressure for 30 seconds because it takes longer for coagulation to occur with the thrombolytic agent on board. IM injections are contraindicated during thrombolytic therapy. The nurse should prevent physical manipulation of the client, which can cause bruising.
Question 148.
To protect a client who has received tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) or alteplase recombinant therapy, what should the nurse do?
(a) Use the radial artery to obtain blood gas samples.
(b) Maintain arterial pressure for 10 seconds.
(c) Administer IM injections.
(d) Encourage physical activity.
Answer:
(d) Encourage physical activity.
Rationale:
Serum amylase and lipase are increased in pancreatitis, as is urine amylase. Other abnormal laboratory values include decreased calcium level and increased glucose and lipid levels.
Question 149.
A client is admitted with acute pancreatitis. The nurse should monitor which laboratory values?
(a) decreased urine amylase level
(b) increased calcium level
(c) decreased glucose level
(d) increased serum amylase and lipase levels
Answer:
(b) increased calcium level
Rationale:
For the client with an alcohol or drug problem, group sessions are helpful in dealing with emotions and concerns about alcohol and drugs. Clients with substance abuse problems identify with each other’s similar experiences and can best help each other deal with these feelings and emotions. Additionally, the members of the group are able to support and confront each other.
Individual therapy is not as helpful as group sessions because group members offer peer support and confrontation when needed. Solitary activities and recreation lead to increased avoidance of the issues that must be faced and dealt with by the client. These are often areas that the client must learn to develop and manage while in recovery.
Question 150.
For the client with a substance abuse problem, which intervention would be most helpful to aid the client in dealing with feelings and concerns related to alcohol and drugs?
(a) individual therapy
(b) group sessions
(c) solitary activities
(d) recreation
Answer:
(d) recreation
Rationale:
Foul-smelling urine is indicative of cystitis. Other symptoms include dysuria and urinary frequency and urgency. Flank pain, nausea, and vomiting indicate pyelonephritis.
Question 151.
A client has cystitis. The nurse should ask the client about experiencing which symptom?
(a) flank pain
(b) oliguria
(c) nausea and vomiting
(d) foul-smelling urine
Answer:
(d) foul-smelling urine
Rationale:
By saying “You couldn’t have prevented the tornado; it just happened’’ the nurse helps the client to develop an objective perspective and promotes a better understanding of the event. The other statements tell the client how to feel, possibly causing resistance, and thus delay therapeutic healing. Guilt and self-blame will not be decreased.
Question 152.
A client with acute stress disorder is telling the nurse about the tornado that leveled his house and killed his wife and baby while he was out of town on business. He states, “If only I had been
at home, I could’ve saved them.” Which response would be most appropriate?
(a) “Don’t blame yourself; you’ll only feel worse.”
(b) “It’s not your fault, so stop feeling so guilty.”
(c) “You might not have been at home.”
(d) “You couldn’t have prevented the tornado; it just happened.”
Answer:
(c) “You might not have been at home.”
Rationale:
In many Asian cultures, the 30 days after the birth of the neonate is a time for the mother to heal from the birth. The appropriate action by the nurse is to determine whether this is a cultural practice for this client and her family. If so, the client is behaving within her cultural practices. Teaching should be provided to both the mother and her mother-in-law. There is no indication that bonding is not taking place.
Lack of bonding might be indicated if the client did not show any interest in the neonate. Documenting the client’s maternal behavior in her medical record jylj is a routine task. However, the nurse should not assume that this behavior is unusual because it may be reflective of the client’s cultural framework. A home visit is not warranted unless there is evidence of infant neglect or the family needs additional follow-up or teaching.
Question 153.
On the first postpartum day, the nurse is caring for a primiparous client who has recently emigrated from Asia and speaks only a little English. The nurse observes that the client has been bottle-feeding her neonate on occasion, but most of the neonatal care is being performed by the client’s mother-in-law. Which action would be most appropriate?
(a) Notify the social worker because bonding may be affected.
(b) Document the unusual maternal behavior in the client’s medical record.
(c) Determine whether this is a cultural practice for the client and her family.
(d) Obtain a prescription to make a home visit after the client’s discharge.
Answer:
(a) Notify the social worker because bonding may be affected.
Rationale:
A creatinine clearance test is a 24-hour urine test that measures the degree of protein breakdown in the body. The collection is not maintained in a sterile container. There is no need to insert an indwelling urinary catheter as long as the client is able to control urination. It is not necessary to increase fluids to 3,000 mL.
Question 154.
A client is scheduled for a creatinine clearance test. What should the nurse do to prepare the client?
(a) Instruct the client about the need to collect urine for 24 hours.
(b) Insert an indwelling urethral catheter.
(c) Provide the client with a sterile urine collection container.
(d) Tell the client to obtain 3,000 mL fluids the day before the test.
Answer:
(d) Tell the client to obtain 3,000 mL fluids the day before the test.
Rationale:
The statement, “Your eyes look dark,” is the least sensitive statement because it points out an obvious difference for no real purpose. The nurse has a reason to ask the client about favorite foods and needs to know about past health problems. Also, it is appropriate for the nurse to ask the client how he or she wishes to be addressed.
Question 155.
When the nurse is assessing a client’s cultural adaptation, which statement is least sensitive to the client’s needs?
(a) “What are some of your favorite foods?”
(b) “Describe any health problems in your past.”
(c) “Please tell me how you would like to be addressed.”
(d) “Your eyes look dark; is this normal for you?”
Answer:
(b) “Describe any health problems in your past.”
Rationale:
Insight into the illness is demonstrated when the client recognizes the relationship between the chemical imbalance and his illness and symptoms. Stating that the olanzapine is the best medicine or that the client’s mother is proud of him for staying on his medicines reflects awareness about the effect of medications and the need for compliance. Stating that he may be able to get a part-time job indicates an awareness of his increased capacity for work.
Question 156.
After several months of taking olanzapine, the client reports that he is no longer hearing voices of any kind. Which statement would confirm that the client is developing insight into his illness?
(a) “That olanzapine is the best medicine I have ever had.”
(b) “I didn’t realize how sick I could get from a chemical brain imbalance.”
(c) “My mom is proud of me for staying on my medicines.”
(d) “I think I may be able to get a little part-time job soon.”
Answer:
(c) “My mom is proud of me for staying on my medicines.”
Rationale:
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in which the median nerve becomes compressed in the wrist. The brachial nerve is not affected. Carpal tunnel syndrome may be the result of a systemic disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes mellitus, or it may be an occupational hazard for people whose jobs require repetitive hand movements such as someone who works long hours on a computer. It is not a condition resulting from disuse. The wrists do not develop flexion contractures with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Question 157.
A client whose job requires extensive use of a computer has developed carpal tunnel syndrome. The nurse should instruct the client to prevent which situation?
(a) decreased circulation to the brachial nerve
(b) muscle atrophy resulting from disuse
(c) median nerve compression
(d) progressive flexion contracture of the wrist
Answer:
(a) decreased circulation to the brachial nerve
Rationale:
Barbiturates can cause significant respiratory depression. The nurse’s first action is to immediately assess the respiratory status and assist in bag-mask-valve ventilation as needed. Monitoring the vital signs is important, but respiratory care takes precedence over the blood pressure. Without other injury, blood products are not necessary. Placing the client in the Trendelenburg position will put pressure from the abdominal contents onto the diaphragm and further impair breathing.
Question 158.
A client is admitted to the emergency department following an overdose of barbiturates. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Assess ventilation and assist ventilation as needed.
(b) Monitor the blood pressure.
(c) Prepare to administer blood products.
(d) Place the client in the Trendelenburg position.
Answer:
(c) Prepare to administer blood products.
Rationale:
Clients who have undergone TURP need to be instructed to maintain an adequate fluid intake despite urinary dribbling or incontinence. The client should be advised to drink at least eight glasses of water a day to dilute the urine and help prevent urinary tract infections. Maintaining a voiding schedule of every 2 hours can help decrease incidents of incontinence. Teaching the client Kegel exercises is also beneficial for strengthening sphincter tone.
The nurse should not encourage the client to decrease fluids. It is not necessarily true that a decreased intake will cause renal calculi. Threatening the client with a catheter is not beneficial, and it is not the treatment of choice for a client who is experiencing incontinence from TURP.
Question 159.
A client who is recovering from transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) experiences urinary incontinence and has decreased the fluid intake because of the incontinence. What is the nurse’s best response to the client?
(a) “Yes, limiting your fluids can decrease your incontinence.”
(b) “Limiting your fluids will cause kidney stones.”
(c) “Drink eight glasses of water a day, and urinate every 2 hours.”
(d) “If your incontinence continues, we will reinsert your catheter.”
Answer:
(d) “If your incontinence continues, we will reinsert your catheter.”
Rationale:
Risk factors for TSS include the use of tampons at night, when the tampon would be in place for 7 to 9 hours. TSS can occur in other situations, but it is commonly associated with women during menses, particularly women who use tampons. The longer the tampon is left in place, the greater the risk for TSS. Changing tampons every 3 hours or more frequently, avoiding use of deodorized tampons, and alternating tampons with sanitary pads are actions that decrease the risk of TSS.
Question 160.
The nurse is teaching a client about preventing toxic shock syndrome (TSS). Which action is a risk factor for toxic shock syndrome?
(a) changing tampons every 3 hours
(b) avoiding use of deodorized tampons
(c) alternating tampons with sanitary pads
(d) using only tampons at night
Answer:
(d) using only tampons at night
Rationale:
Costovertebral tenderness occurs on the side of the affected kidney in pyelonephritis. Dysuria, suprapubic pain, and urine retention may occur in pyelonephritis but do not specifically support a diagnosis of pyelonephritis. Dysuria, suprapubic pain, and urine retention are symptoms of cystitis, which can lead to pyelonephritis if not treated.
Question 161.
A client with a history of cystitis is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of pyelonephritis. The nurse should assess the client for which symptom?
(a) suprapubic pain
(b) dysuria
(c) urine retention
(d) costovertebral tenderness
Answer:
(b) dysuria
Rationale:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics can cause decreased efficacy of oral contraceptives, placing the client at risk for an unplanned pregnancy. When a client is prescribed a course of antibiotics, a backup method of contraception should be used. Antihypertensives, diuretics, and antihistamines do not interfere with oral contraceptive efficacy.
Question 162.
A woman is taking oral contraceptives. The nurse teaches the client that which medications may interfere with oral contraceptive efficacy?
(a) antihypertensives
(b) antibiotics
(c) diuretics
(d) antihistamines
Answer:
(a) antihypertensives
Rationale:
Adverse effects of danazol include headaches, dizziness, irritability, and decreased libido. Masculinization effects, such as deepened voice, facial hair, and weight gain, also may occur.
Question 163.
A 28-year-old female client is prescribed dan- azol for endometriosis. The nurse should instruct the client to report which symptoms to the health care provider?
(a) headaches
(b) weight loss
(c) increased libido
(d) hair loss
Answer:
(b) weight loss
Rationale:
The nurse should assign the Muslim male client who needs complete morning care to Joe. Muslim men cannot be cared for by female nurses. The nurse must also consider workload, and Joe has the lightest assignment.
Question 164.
To which unlicensed assistive personnel should the nurse assign a male orthodox Muslim client who needs complete morning care?
(a) Judy, who has two other clients requiring complete morning care
(b) Joe, who has one client requiring complete morning care
(c) Jill, who has four clients requiring partial morning care
(d) Jim, who has five clients requiring partial morning care
Answer:
(c) Jill, who has four clients requiring partial morning care
Rationale:
Central nervous system changes include such symptoms as apathy, lethargy, and decreased concentration. Seizures and coma can also occur. The nurse should assess the client’s level of consciousness at regular intervals and maintain client safety. Allowing the client to express feelings related to body image changes and restricting foods high in potassium and fluid intake are all appropriate activities, but they are not related to the central nervous system changes.
Question 165.
A client with chronic renal failure is experiencing central nervous system (CNS) changes caused by uremic toxins. Which nursing approach would be most appropriate for addressing these CNS changes?
(a) Allow the client to grieve for body image changes.
(b) Restrict foods that are high in potassium.
(c) Restrict fluid intake to 1,000 mL/day.
(d) Assess the client’s mental status regularly.
Answer:
(c) Restrict fluid intake to 1,000 mL/day.
Rationale:
Elderly individuals have less subcutaneous tissue. An elderly, emaciated client will require a short needle and a shallow angle to avoid hitting an underlying bone. The nurse should choose the shortest subcutaneous needle available and use the least angle.
Question 166.
The nurse is preparing to give a subcutaneous injection to an older adult who is emaciated. Which needle length and angle should the nurse plan to use to administer the injection safely?
(a) a V2-inch (1.3-cm) needle at a 90-degree angle
(b) a %-inch (1.6-cm) needle at a 45-degree angle
(c) a %-inch (0.95-cm) needle at a 15-degree angle
(d) a 5/8-inch (1.6-cm) needle at a 90-degree angle
Answer:
(c) a %-inch (0.95-cm) needle at a 15-degree angle
Rationale:
Elderly individuals have less subcutaneous tissue. An elderly, emaciated client will require a short needle and a shallow angle to avoid hitting an underlying bone. The nurse should choose the shortest subcutaneous needle available and use the least angle.
Question 167.
A female client is treated for trichomoniasis with metronidazole. What should the nurse tell the client about this medication?
(a) The medication should not alter the color of the urine.
(b) She should discontinue oral contraceptive use during this treatment.
(c) She should avoid alcohol during treatment and for 24 hours after completion of the drug.
(d) Her partner does not need treatment.
Answer:
(c) She should avoid alcohol during treatment and for 24 hours after completion of the drug.
Rationale:
Metronidazole can cause a disulfiram-like reaction if it is taken with alcohol. Tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, and other serious interaction effects can occur. Flagyl will make the urine a darker color. Oral contraceptives should never be discontinued with trichomoniasis. The partner also requires treatment to prevent retransmission of infection.
Question 168.
A client is in the advanced stages of osteoarthritis. Which statement best describes the pain that occurs in the advanced stage of the disease?
(a) Pain occurs with minimal activity.
(b) Crepitation develops and intensifies pain.
(c) Joints are symmetrically affected by pain.
(d) Fatigue accompanies pain.
Answer:
(a) Pain occurs with minimal activity.
Rationale:
In the advanced stages of osteoarthritis, pain can occur with minimal activity or even when the client is at rest. Crepitation can be present at any stage of the disease and does not exacerbate pain. Joints are not symmetrically affected by the disease. Symmetric joint involvement and fatigue are characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis.
Question 169.
A family has requested to have a client who is Vietnamese transferred to die at home. Which traditional belief of some Vietnamese guides this request from the family?
(a) It is disloyal to leave their loved one in the hospital.
(b) The hospital cannot be trusted.
(c) The family can provide more comfort at home.
(d) Reincarnation will not occur in the hospital.
Answer:
(c) The family can provide more comfort at home.
Rationale:
The traditional belief of Vietnamese Americans is that the family can provide more comfort for their loved one at home. It is not seen as being disloyal if their loved one dies in the hospital. The request is not based on a feeling that the hospital cannot be trusted. Vietnamese Americans accept death as a part of life and do not think that reincar-nation is prevented in the hospital.
Question 170.
A client has just been admitted with acute delirium of unknown etiology. The client’s daughter states that she is worried about her mom because she has never been this sick before. Which would be the most helpful statement to make to the daughter?
(a) “Please don’t worry. We’ll take good care of your mother.”
(b) “The health care provider will prescribe tests to find out what’s causing her condition.”
(c) “We can help you learn how to take care of her after she’s discharged.”
(d) “It helps if you avoid arguing when she talks about seeing people who aren’t there.”
Answer:
(b) “The health care provider will prescribe tests to find out what’s causing her condition.”
Rationale:
It is important for the daughter to know that there is an underlying cause for what her mother is experiencing and that it is treatable. Telling her not to worry is a useless cliche and does nothing to inform the daughter. Talking about care after discharge implies that the delirium is irreversible. Delirium is a reversible condition. Although not arguing with hallucinations is valid, this response ignores the daughter’s concern.
Question 171.
A client with Alzheimer’s disease is going to live with his daughter who does not work outside of the home. The nurse determines that the daughter needs further education when she makes which statement?
(a) “I’ve put special locks on all the doors that Dad will not be able to unlock.”
(b) “Dad said that what he missed most while he was here was using his aftershave.”
(c) “Dad will be in a bedroom that has nothing for him to trip over getting to the bathroom.”
(d) “I’ve taken the knobs off of the stove so he won’t be able to turn it on.”
Answer:
(b) “Dad said that what he missed most while he was here was using his aftershave.”
Rationale:
The client with Alzheimer’s dementia should not have access to toiletries that could be swallowed (such as aftershave) unless closely supervised. Putting special locks on all the doors is appropriate to prevent wandering, thus maintaining the client’s safety. Placing the client in a room that has nothing to trip over is appropriate to reduce the client’s risk of falling. Taking the knobs off of the stove is appropriate to prevent possible bums.
Question 172.
Allopurinol is prescribed for a client who has chronic gout. Which comment indicates that the client understands how to take the allopurinol?
(a) “I’ll take the medication whenever my joints hurt.”
(b) “I must take this drug on an empty stomach.”
(c) “I should drink plenty of fluids when taking allopurinol.”
(d) “I shouldn’t take aspirin when taking allopurinol.”
Answer:
(c) “I should drink plenty of fluids when taking allopurinol.”
Rationale:
It is important that the client force fluids to 3,000 mL/day to avoid the development of renal calculi when taking allopurinol. Allopurinol must be taken consistently to be effective in the treatment of gout. The drug should be taken after meals to avoid gastrointestinal distress. Although the client can take aspirin when taking allopurinol, both drugs can cause gastrointestinal irritation, and the practice is not recommended if the client is sensitive to the medications.
Question 173.
The mother calls the nurse to report that her toddler has just been burned on the arm. What should the nurse should advise the mother to first?
(a) Pack the arm in ice, and then take the child to the closest emergency department.
(b) Rub the burned area with an antibacterial ointment, and then call the child’s health care provider (HCP).
(c) Run cool water over the burned area, and then wrap it in a clean cloth.
(d) Call the child’s HCP immediately, and then wrap the arm in a clean cloth.
Answer:
(c) Run cool water over the burned area, and then wrap it in a clean cloth.
Rationale:
The best advice for the nurse to give the child’s mother is to run cool water over the burned area to stop the burning process. Then the area should be wrapped in a clean cloth. Once these initial actions are completed, the mother can call the child’s HCP 3. Packing the arm in ice may cause more damage to the burned area because cold can cause burns just as heat can. For most burns, it is not advised to apply ointment until the area has been evaluated.
Question 174.
A client with osteomyelitis of the left great toe has pain with partial weight bearing, unsteady gait, and general weakness. Based on these data, the nurse should institute which safety measures?
(a) bed rest
(b) airborne precautions
(c) referral to physical therapy
(d) falls precautions
Answer:
(d) falls precautions
Rationale:
The client is at risk for falling, and the nurse should initiate falls precaution. The client does not require airborne precautions. There is no indication the client needs a referral to physical therapy. The client should be encouraged to maintain mobility.
Question 175.
A client receiving a blood transfusion begins to have chills and headache within the first 15 minutes of the transfusion. What should the nurse do
first?
(a) Administer acetaminophen.
(b) Take the client’s blood pressure.
(c) Discontinue the transfusion.
(d) Check the infusion rate of the blood.
Answer:
(c) Discontinue the transfusion.
Rationale:
Chills and headache are signs of a febrile, nonhemolytic blood transfusion reaction, and the nurse’s first action should be to discontinue the transfusion as soon as possible and then notify the health care provider (HCP) CD. Antipyretics and antihistamines may be prescribed. The nurse would not administer acetaminophen without a prescription from the HCP. The client’s blood pressure should be taken after the transfusion is stopped. Checking the infusion rate of the blood is not a pertinent action; the infusion needs to be stopped regardless of the rate.
Question 176.
The family of an older adult wants their mother to have counseling for depression. During the initial nursing assessment, the client denies the need for counseling. Which statement by the client supports the fact that the client may not need counseling?
(a) “My primary care provider just put me on an antidepressant, and I’ll be fine in a week or so.”
(b) “My daughter sent me here. She’s mad because I don’t have the energy to take care of my grandkids.”
(c) “Since I’ve gotten over the death of my husband, I’ve had more energy and been more active than before he died.”
(d) “My son got worried because I made this silly comment about wanting to be with my husband in heaven.”
Answer:
(c) “Since I’ve gotten over the death of my husband, I’ve had more energy and been more active than before he died.”
Rationale:
Resolving grief and having increased energy and activity convey good mental health, indicating that counseling is not necessary at this time. Taking an antidepressant or having less energy and involvement with grandchildren reflects possible depression and the need for counseling. Wanting to be with her dead husband suggests possible suicidal ideation that warrants serious further assessment and counseling.
Question 177.
A client takes isosorbide dinitrate as an antianginal medication. Which statement indicates that the client understands the adverse effects of the drug?
(a) “I should take my pulse before taking the medication.”
(b) “I should take isosorbide dinitrate with food.”
(c) “I’ll need to change positions slowly so I won’t get dizzy.”
(d) “It’s important that I report any swelling in my ankles.”
Answer:
(c) “I’ll need to change positions slowly so I won’t get dizzy.”
Rationale:
Common adverse effects of isosorbide are light-headedness, dizziness, and orthostatic hypotension. Clients should be instructed to change positions slowly to prevent these adverse effects and to avoid fainting. Ankle swelling is not related to isosorbide administration. The client does not need to take his pulse before taking the medication. The client does not need to take the medication with food.
Question 178.
The nurse plans discharge with a client who is diagnosed with intermittent explosive disorder, characterized by sudden angry outbursts. The nurse determines that the client is ready for discharge when the client makes which comment?
(a) “I’m just not going to let myself get angry anymore.”
(b) “Drinking doesn’t help, but I like being with my buddies at the bar.”
(c) “I'll be taking valproic acid and propranolol to help stay in control.”
(d) “It would help if my mom would stop getting on my case all the time.”
Answer:
(c) “I'll be taking valproic acid and propranolol to help stay in control.”
Rationale:
Valproic acid and propranolol are often prescribed to help manage explosive anger. Recognizing the need for medications indicates readiness for discharge. Not ever getting angry is difficult, impractical, and unrealistic without specific anger management strategies. Drinking does not address anger control and suggests a risk of continued drinking. Blaming others, such as the client’s mother, does not address anger control and indicates a lack of responsibility for the client’s own behavior.
Question 179.
The nurse walks into a client’s room to administer the 0900 medications and notices that the client is in an awkward position in bed. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Ask the client to state his or her name.
(b) Check the client’s name band.
(c) Straighten the client’s pillow behind the back.
(d) Give the client his medications.
Answer:
(c) Straighten the client’s pillow behind the back.
Rationale:
The nurse should first help the client into a position of comfort even though the primary purpose for entering the room was to administer medication. After attending to the client’s basic care needs, the nurse can proceed with the proper identification of the client, such as asking the client his name and checking his armband, so that the medication can be administered.
Question 180.
The nurse is performing the initial assessment on a middle-aged woman recently diagnosed with Cushing’s syndrome. The nurse reviews the history and physical (see chart). The nurse should develop
a plan with the client to manage which effect? Select all that apply.
|
History and Physical |
||
|
A recent ground-level fall resulting in multiple bruises on_both arms and left shoukier |
||
|
A slow-healing laceration on the right hand from a fall 2 weeks_prior |
||
|
Muscle weakness |
||
|
Unable to sleep more than 2 to 3 hours at a time |
||
|
Moon-faced appearance |
||
|
Oily skin |
||
|
Recent 20-lb (9.1-kg) weight gain |
||
|
Vitalsigns |
BP: |
148/94 |
|
|
Heart rate: |
96/strong! regular |
|
|
Respirations: |
20/regular! unlabored |
|
|
Pain: |
Denies |
(a) low blood volume
(b) risk for injury
(c) slow healing
(d) changes in physical appearance
(e) risk for infection
Answer:
(b) risk for injury
(c) slow healing
(d) changes in physical appearance
(e) risk for infection
Rationale:
Cushing’s syndrome results from excessive levels of cortisol. Some effects of excessive adrenocortical activity include musculoskeletal changes, and the client may be at risk for injury and falls. There is excessive protein catabolism causing muscle wasting, decreased inflammatory response, and potential for delayed healing and infection.
The increased cortisol levels cause a moon-faced appearance to which clients must adjust. The skin becomes thin and fragile, and the client is also at risk for infection. Increased cortisol levels do not cause deficient fluid volume.
Question 181.
A “read-back” procedure has been implemented on a nursing unit to prevent discrepancies in telephone prescriptions and reports. When should this procedure be implemented?
(a) When the float nurse gives a written report to the oncoming nurse.
(b) When the nurse receives a critical lab value via phone or in person from the lab.
(c) When the lab report shows up on the computerized medical record.
(d) When the unit clerk takes a telephone prescription for a stat lab test.
Answer:
(b) When the nurse receives a critical lab value via phone or in person from the lab.
Rationale:
For any verbal or telephone prescription or result, it is important to read back the information to assure its accuracy. It is also important to document that it was read back according to facility policy. It is not necessary to use “read-back” procedures when data are entered on the computerized medical record GJ. The unit clerk is not a licensed health care worker and should not take telephone prescriptions. When giving a written report, it is not necessary to “read back,” but the nurse should always clarify if there is any question.
Question 182.
Four clients in a critical care unit have been diagnosed with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The Infection Prevention and Control Department has determined that this is probably a nosocomial infection. What should the nurse do to prevent spread of the disease?
(a) Wear an N-95 mask when caring for these clients.
(b) Initiate transmission-based precautions.
(c) Use contact precautions.
(d) Ensure that staff does not have artificial fingernails.
Answer:
(d) Ensure that staff does not have artificial fingernails.
Rationale:
It is well documented that the subungual areas of the hand harbor bacteria that can be transmitted to others despite aggressive handwashing procedures, and therefore, it is important that the staff on this unit do not have artificial fingernails that could be the source of the infection on this unit. There is no need to institute transmission-based or contact precautions. It is not necessary to wear a mask when caring for these clients.
Question 183.
The nurse is instructing the spouse of a client who had an incision and drainage procedure for an abscess how to care for the wound at home. What information should the nurse give the spouse about cleaning the wound?
(a) Clean the incision and drainage sites simultaneously.
(b) Clean from the incision site to the drainage site.
(c) Clean from the drainage site to the incision site.
(d) Clean each site independently.
Answer:
(d) Clean each site independently.
Rationale:
The sites should be treated as separate sites to avoid cross-contamination. This adheres to the principle of cleaning from the least contaminated area to the most contaminated area. Each site is considered a separate area for wound care.
Question 184.
After completing initial assessment rounds, which client should the nurse discuss with the health care provider (HCP) first?
(a) a client who was admitted from the emergency department last evening after a blow to the head who is now vomiting and confused as to time and place
(b) a client who returned from abdominal surgery last evening and now has a dime-sized bright red spot on the dressing
(c) a client who had a right total knee replacement 2 days ago and now is reporting constipation and abdominal discomfort
(d) a client admitted for lower extremity vasculitis and wound care who is requesting more pain medication before the next dressing change in 2 hours
Answer:
(a) a client who was admitted from the emergency department last evening after a blow to the head who is now vomiting and confused as to time and place
Rationale:
Any change in level of consciousness (vomiting, severe headache that is not improving or is getting worse, memory changes, confusion, irritability, change in pupils) should be immediately reported to the HCP and further evaluated, especially in a client with head trauma.
The nurse should mark a circle around the amount of drainage on a dressing after surgery so it can be monitored and reported to the HCP if it grows in size, but a dime-sized spot is not an immediate priority. Constipation and abdominal discomfort after sur-gery require attention but are not priority. Obtaining proper pain medication in order to promote wound care and healing must be addressed with the HCP, but it is not the first priority.
Question 185.
Which is the correct knot used to secure a restraint to the bedframe?
Answer:
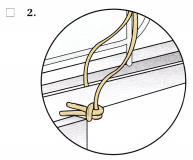
Rationale:
In order to prevent injury to a client, restraints must be secured to the bed frame using a slipknot in order to ensure quick release if necessary. A square knot would be secure but would not be easily released in an emergency. A restraint tied in a bow at the client’s side would not be easily released in an emergency. A hitch, although secure, is not easily released in an emergency.
Question 186.
The obstetrical triage nurse assesses a client with a term pregnancy. There has not been any change in the cervix for the past 2 hours despite irregular contractions. When discharging the client to her home, the nurse should tell the client to return to the hospital when which conditions occur? Select all that apply.
(a) She feels more than three contractions an hour.
(b) Contractions become more intense and closer together.
(c) She notices vaginal bleeding.
(d) She thinks the membranes have ruptured.
(e) She notices an absence of fetal movement.
(f) She feels the urge to push
Answer:
(b) Contractions become more intense and closer together.
(c) She notices vaginal bleeding.
(d) She thinks the membranes have ruptured.
(e) She notices an absence of fetal movement.
(f) She feels the urge to push
Rationale:
Because there have been no cervical changes, the client is not in labor. The client should understand to return to the hospital if the contractions become more intense and regular, if she has vaginal bleeding, if she thinks her membranes rupture, if the baby is not moving, or if she has an urge to push. Three contractions an hour would be too infrequent to indicate active labor.
Question 187.
The parents of a newborn with Down syndrome are tearful when they tell the nurse that the diagnosis was a surprise to them. Which statement by the parents indicates that they have some understanding of Down syndrome?
(a) “Children with Down syndrome are often fearful of strangers and have difficulty making friends.”
(b) “At some point during their life span, children with Down syndrome will need to be institutionalized."
(c) “Children with Down syndrome often become violent when they experience hormonal changes during puberty.”
(d) “There's a broad spectrum of mental capabilities and physical characteristics of children with Down syndrome.”
Answer:
(d) “There's a broad spectrum of mental capabilities and physical characteristics of children with Down syndrome.”
Rationale:
The mental abilities of Down syndrome children range from severe intellectual disabilities to low average intelligence. They also exhibit a wide range of physical features including almond-shaped eyes, a small, flat nose, a small mouth with a protruding tongue, and small ears. Many also have a single crease across the palms of their hands, short stubby fingers, and straight hair that is fine and thin.
Children with Down syndrome are socially 2 to 3 years behind their peers. Many children with Down syndrome will be capable of living in group homes. They may also continue living with their parents or other family members. Children with Down syn-drome are well tempered and very friendly.
Question 188.
A toddler is brought to the emergency department after experiencing a seizure. The child currently has the flu and has had fevers for the last 3 days. The father asks what caused the seizure to occur. What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “Your child’s seizure was likely caused by the rapid elevation of her temperature.”
(b) “The seizure likely occurred because your child’s temperature rose beyond a personal threshold.”
(c) “Your child’s seizure was likely caused by the prolonged duration of her fevers.”
(d) “The seizure likely occurred because your child’s immune system is not developed.”
Answer:
(b) “The seizure likely occurred because your child’s temperature rose beyond a personal threshold.”
Rationale:
Febrile seizures usually occur during the rise in temperature and are related to the peak of the temperature rather than the rapidity or duration of elevation. When children experience febrile seizures, fevers usually exceed 38.0°C (100.4°F). Febrile seizures are not related to the rapidity or duration of elevation. Febrile seizures are most common among children 18 months to 3 years but are not related to the maturity of their immune system.
Question 189.
Thirty minutes ago, a term multigravida was 5 cm dilated, 100% effaced, and -1 station. She is now visibly uncomfortable and states that she needs to get up for a bowel movement. What is the best nursing intervention?
(a) Assist the client up to the bathroom.
(b) Reassure the client that the sensation she is feeling is due to pressure from the fetal head.
(c) Perform another sterile vaginal exam on the client.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the client’s pain.
Answer:
(a) Assist the client up to the bathroom.
Rationale:
This client could have progressed rapidly and is now ready to deliver her infant. A sterile vaginal exam is indicated prior to getting her up to the bathroom to determine if she is fully dilated. If she is ready to deliver, she could be reassured that the sensation she is feeling is due to pressure from the fetal head. If her cervix exam is unchanged, she may need pain control interventions. The nurses’ assessment findings then should be discussed with the client and the HCP.
