Free NCLEX Questions cover various areas, such as pharmacology, medical-surgical nursing, pediatric care, and mental health.
NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 3 with Rationale
Question 1.
A client asks why she feels so much variability in fetal activity each day. The nurse explains that fetal movement is affected by which factors? Select all that apply.
(a) fetal sleep
(b) barometric pressure
(c) blood glucose
(d) time of day
(e) cigarette smoking
Answer:
(a) fetal sleep
(c) blood glucose
(d) time of day
(e) cigarette smoking
Rationale:
The fetus does go through sleep cycles, rendering it less likely to move while it is asleep. Blood glucose does cross the placenta and can affect fetal movement. Cigarette smoking causes carbon monoxide to cross the placenta, which reduces fetal oxygen. Pregnant women are more likely to notice fetal movement while they are sitting or lying down, and time of day often determines this. Most pregnant women notice fetal movement in the evening. Barometric pressure does not affect fetal activity in utero.
Question 2.
The parent of a 2-week-old infant brings the child to the clinic for a checkup. The parent expresses concern about the baby’s breathing because the infant breathes quickly for a while and then breathes slowly. The nurse interprets this finding as an indication of what factor?
(a) a normal pattern in infants of this age
(b) the need for an apnea monitor
(c) a need for close monitoring for the parent
(d) the need for a chest radiograph
Answer:
(a) a normal pattern in infants of this age
Rationale:
The infant is exhibiting periodic breathing, which is normal in infants of this age. The infant typically alternates short periods of rapid, louder respirations with periods of slower, quieter respirations.
Question 3.
The client is Asian and does not speak English. The nurse arranges for the interpreter who can speak the client’s dialect and begins the health assessment. The client is describing symptoms as numbness, feeling “hot under the skin,” and thinking too much. The nurse should next ask specific questions about which symptom?
(a) depression
(b) constipation
(c) pain
(d) hunger
Answer:
(c) pain
Rationale:
The client may be describing symptoms of pain. Culture specific symptoms for “feeling bad” include numbness, thinking too much, feeling hot under the skin. Asian clients may describe pain in terms of Yin and Yang (hot and cold). Nurse’s knowledge of pain associated with health problems is necessary to assist this client manage pain. Clients from some cultures may associate mental health symptoms with evil spirits and will not report them as being unusual. Clients from Asian cultures may not describe symptoms locally but in a diffuse fashion.
Question 4.
When conducting the preoperative preparations, the nurse determines that the client does not speak English, and the nurse does not speak the client’s language. The surgeon needs to obtain the client’s informed consent. What is the best way for the nurse to obtain the client’s informed consent?
(a) Have the client call a family member to act as interpreter.
(b) Have the client sign the Spanish surgical consent form.
(c) Call the Spanish interpreter to translate the surgeon’s explanation of the procedure, risks, and alternatives to obtain the client’s consent and to answer the client’s questions.
(d) Notify the surgical charge nurse of the situation.
Answer:
(d) Notify the surgical charge nurse of the situation.
Rationale:
The surgeon is required to give the client explanations and have questions answered. The nurse has no way of assessing the client’s understanding without the interpreter. The client should sign the Spanish consent Q form only after receiving an explanation of the procedure, its risks, and alternatives. A family member cannot be relied on to translate the surgeon’s instructions.
The nurse is commonly asked to witness the explanation and to obtain the client’s signature on the informed consent form. Informed consent is the provision of information concerning the procedure and its risks, not obtaining the client’s signature on the form. The surgical charge nurse does not need to be notified.
Question 5.
The nurse is discharging a client who has been hospitalized for preterm labor. Which client statement indicates the need for further instruction?
(a) “If I think I have a bladder infection, I need to see my obstetrician.”
(b) “If I have contractions, I should contact my health care provider (HCP).”
(c) “Drinking water may help prevent early labor for me.”
(d) “If I travel on long trips, I need to get out of the car every 4 hours.”
Answer:
(d) “If I travel on long trips, I need to get out of the car every 4 hours.”
Rationale:
Traveling is usually discouraged if preterm labor has been a problem, as it restricts normal movement. A client should be able to walk around frequently to prevent blood clots and to empty her bladder at least every 1 to 2 hours. Bladder infections often stimulate preterm labor, and preventing them is of great importance to this client. Contractions that recur indicate the return of preterm labor, and the HCP Q3 needs to be notified. Dehydration is known to stimulate preterm labor, and encouraging the client to drink adequate amounts of water helps to prevent this problem.
Question 6.
A client who has glaucoma has been prescribed timolol eye drops. The nurse should give which instructions about the administration of the eye drops?
(a) Instill the eye drops whenever the eyes feel irritated.
(b) The medication may cause some transient eye discomfort.
(c) Keep the medication refrigerated between doses.
(d) The need to use the eye drops will be reevaluated after 1 month.
Answer:
(b) The medication may cause some transient eye discomfort.
Rationale:
Timolol can cause some eye discomfort when administered. It is important for the client to continue to take the drug. Glaucoma eye drops should be administered as prescribed, not whenever the client desires. The client with glaucoma needs to take eye medication on an ongoing basis to control the disorder and prevent vision damage. There is no need to refrigerate the drug.
Question 7.
A client newly diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) of the left lower left extremity is on bed rest. What should the nurse instruct the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) providing routine morning care for the client to do?
(a) Check that the legs are in a low, dependent position.
(b) Ensure that the lower extremity is elevated.
(c) Massage the leg and foot with lotion.
(d) Place one or two pillows under the client’s left knee.
Answer:
(b) Ensure that the lower extremity is elevated.
Rationale:
DVT causes edema; therefore, the UAP Q should elevate the extremity to promote venous return. Dependent positioning is appropriate for a client with arterial insufficiency. Placing a pillow under the knee would position the foot in a low position, and pressure behind the knee may obstruct venous flow. Massaging the extremity could dislodge the thrombus.
Question 8.
The nurse observes a darkish blue pigment on the buttocks and back of an infant of African descent. Which action is most appropriate?
(a) Ask the obstetrician to assess the child.
(b) Assess the child for other areas of cyanosis.
(c) Document this observation in the child’s medical record.
(d) Advise the mother that the bruising will fade in a few days.
Answer:
(c) Document this observation in the child’s medical record.
Rationale:
The bluish pigment on the buttocks and back of an infant of African descent is a common finding and should be documented as Mongolian spots in the child’s medical record Q, These spots typically fade by the time the child is 5 or 6 years. Additional assessment by the care provider is not indicated. The marks are not bruises.
Question 9.
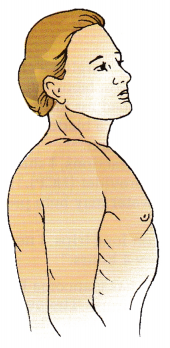
The nurse is assessing a client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The client weighs 200 lb (90.7 kg] and is 6 feet (183 cm) tall. Using the diagram shown here, how should the nurse describe the client’s chest in the record in the health history?
(a) barrel shaped
(b) indicative of lifting weights
(c) normal for the client’s age, height, and weight
(d) showing the effects of long-term use of bronchodilators
Answer:
(a) barrel shaped
Rationale:
This client has a barrel chest. The anterior-posterior diameter of the chest is larger than the transverse diameter, as is characteristic of the client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Although the client may be muscular from lifting weights, the barrel chest is not associated with the client’s age, height, or weight. Use of bronchodila- tors will not change the shape of the client’s chest.
Question 10.
A primigravid client with diabetes at 38 weeks’ gestation asks the nurse why she had a fetal acoustic stimulation during her last nonstress test. Which should the nurse include as the rationale for this test?
(a) to listen to the fetal heart rate
(b) to startle and awaken the fetus
(c) to stimulate mild contractions
(d) to confirm amniotic fluid amount
Answer:
(b) to startle and awaken the fetus
Rationale:
Fetal acoustic stimulation involves the use of an instrument that emits sound levels of approximately 80 dB at a frequency of 80 Hz. The sharp sound startles and awakens the fetus and is used with nonstress testing as a method to evaluate fetal well-being. A fetoscope or Doppler stethoscope is used to listen to the fetal heart rate. Nipple stimulation or intravenous oxytocin is used to stimulate contractions. Ultrasound testing is used to determine amniotic fluid volume.
Question 11.
When creating an educational program about safety, what information should the nurse include about sexual predators? Select all that apply.
(a) Child molesters pick children or teens over whom they have some authority, making it easier for them to manipulate the child with special favors or attention.
(b) Child molesters resort to molestation because they have bad childhoods, so understanding that can help them decrease their molesting.
(c) Child molesters gain the child’s trust before making sexual advances so the child feels obligated to comply with sex.
(d) Child molesters often choose children whose parents must work long hours, making the extra attention initially welcomed by the child.
(e) Child molesters maintain the secrecy of their actions by making threats if offering attention and favors fail or if the child is close to revealing the secret.
Answer:
(a) Child molesters pick children or teens over whom they have some authority, making it easier for them to manipulate the child with special favors or attention.
(c) Child molesters gain the child’s trust before making sexual advances so the child feels obligated to comply with sex.
(d) Child molesters often choose children whose parents must work long hours, making the extra attention initially welcomed by the child.
(e) Child molesters maintain the secrecy of their actions by making threats if offering attention and favors fail or if the child is close to revealing the secret.
Rationale:
Child molesters prey on lonely children or those who spend a lot of time at home alone due to a working parent. They initially show interest and assist the child and family such as by providing rides, money, and homework help.
Once trust is established, molesters push for a more sexual relationship, which they justify by pointing out what they have done to help the child. If the child tries to stop the sexual interaction or appears ready to tell someone, molesters will use threats to maintain the secret. Though some child molesters have had difficult childhoods in which they may have been molested, having them recognize that is not enough to keep them from offending again.
Question 12.
A client with severe depression states, “My heart has stopped, and my blood is black ash.” The nurse interprets this statement to be evidence of which problem?
(a) hallucination
(b) illusion
(c) delusion
(d) paranoia
Answer:
(c) delusion
Rationale:
A client with severe depression may experience symptoms of psychosis such as hallucinations and delusions that are typically mood congruent. The statement “My heart has stopped, and my blood is black ash” is a mood-congruent somatic delusion. A delusion is a firm, false, fixed belief that is resistant to reason or fact. A hallucination
is a false sensory perception unrelated to external stimuli. An illusion is a misinterpretation of a real.
Question 13.
The mother of an older infant reports stopping the prescribed iron supplements after 2 weeks of treatment. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “Bring the child in so that we can retest him.”
(b) “You need to continue the iron for several more weeks.”
(c) “Let’s start a diet that is high in iron.”
(d) “No more medication is needed at this time.”
Answer:
(b) “You need to continue the iron for several more weeks.”
Rationale:
Typ ically, iron supplements are needed for at least 1 month. By the end of this time, there should be a significant rise in the hemoglobin and hematocrit. Therefore, the mother needs to continue the iron supplements for several more weeks. Testing the child after only 2 weeks of treatment may not be beneficial.
A significant rise in hemoglobin and hematocrit usually requires approximately 1 month of therapy. An iron-rich diet should have been started when the diagnosis was made and continued for at least the duration of iron supplement therapy.
Question 14.
The parents of a child with cystic fibrosis express concern about how the disease was transmitted to their child. What information should the nurse give to the clients?
(a) A disease carrier also has the disease.
(b) Two parents who are carriers may produce a child who has the disease.
(c) A disease carrier and an affected person will never have children with the disease.
(d) A disease carrier and an affected person will have a child with the disease.
Answer:
(b) Two parents who are carriers may produce a child who has the disease.
Rationale:
Cystic fibrosis is the most common inherited disease in children. It is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, meaning that the child inherits the defective gene from both parents. The chances are one in four for each of this couple’s pregnancies.
Question 15.
A Jewish client requests an orthodox diet while hospitalized. The nurse should refer this request to which team member?
(a) dietitian
(b) health care provider (HCP)
(c) unit case manager
(d) rabbi in pastoral care
Answer:
(a) dietitian
Rationale:
The dietary department should meet with the client to ensure that the foods are available and prepared according to religious beliefs. On admission, the client should be asked whether there are special dietary needs. The dietary department should be notified of these special needs, and a dietary representative should meet with the client and family when possible. The HCP should be consulted if a requested food is contrary to a prescribed diet restriction. The unit case manager does not need to be contacted regarding a dietary request. The rabbi is not involved in dietary requests.
Question 16.
Which interventions should the nurse use to assist the client with grandiose delusions? Select all that apply.
(a) Accept the client while not arguing with the delusion.
(b) Focus on the feelings or meaning of the delusion.
(c) Focus on events and topics based in reality.
(d) Confront the client’s beliefs.
(e) Interact with the client only when the client is based in reality.
Answer:
(a) Accept the client while not arguing with the delusion.
(b) Focus on the feelings or meaning of the delusion.
(c) Focus on events and topics based in reality.
Rationale:
For the client with grandiose delusions, the nurse should accept the client but not argue with the delusion to build trust and the client’s self-esteem. Focusing on the underlying feeling or meaning of the delusion helps to meet the client’s needs. Focusing on events and topics based in reality distracts the client from the delusional thinking.
confronting the client’s delusions or beliefs can lead to agitation in the client and the need to cling to the grandiose delusion to preserve self-esteem. Interacting with the client only when based in reality ignores the client’s needs and therapeutic nursing intervention.
Question 17.
A mother reports she cannot afford the antibiotic azithromycin, which was prescribed by the health care provider (HCP) for her toddler’s otitis media. What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) Instruct the mother on the importance of the medication.
(b) Ask the mother if she has considered using any medical assistance programs in her community.
(c) Confer with the HCP about whether a less expensive drug could be prescribed.
(d) Consult with the social worker.
Answer:
(c) Confer with the HCP about whether a less expensive drug could be prescribed.
Rationale:
The nurse must act as an advocate for the client when the client cannot afford treatment. It may be possible to substitute a less expensive antibiotic. Correct procedure includes contacting the HCP m to explain the mother’s economic situation and request a substitution. For example, amoxicillin is more economical than azithromycin. If it is not possible to use another antibiotic, then the nurse can explore other avenues with the mother and/or social worker.
Question 18.
Which response is most helpful for a client who is euphoric, intrusive, and interrupts other clients engaged in conversations to the point where they get up and leave or walk away?
(a) “When you interrupt others, they leave the area.”
(b) “You’re being rude and uncaring.”
(c) “You should remember to use your manners.”
(d) “You know better than to interrupt someone.”
Answer:
(a) “When you interrupt others, they leave the area.”
Rationale:
Saying “When you interrupt others, they leave the area” is most helpful because it serves to increase the client’s awareness of others’ perceptions of the behavior by giving specific feedback about the behavior. The other statements are punitive and authoritative, possibly threatening to the client, and likely to increase defensiveness, decrease self-worth, and increase feelings of guilt.
Question 19.
The nurse transfers a multigravid client who is at 25 weeks’ gestation with preeclampsia from the obstetrical intensive care unit to the antenatal unit. What should the nurse include in the transfer report to safely manage his client? Select all that apply.
(a) record of blood pressure trends
(b) record of urine protein
(c) edema characteristics
(d) client use of dietary sodium
(e) fetal position
(f) fetal heart rate pattern
Answer:
(a) record of blood pressure trends
(b) record of urine protein
(c) edema characteristics
(f) fetal heart rate pattern
Rationale:
The important information to be given with a preeclamptic client should include blood pressure trends while being monitored and the protein that is and has been present in the urine as these are indicators of increasing eclampsia. Edema of the face, a history of headache, blurred vision, and epigastric pain are important as these also indicate worsening preeclampsia.
The fetal position at 25 weeks is of minor importance as the fetus is constantly changing positions at this point in the pregnancy. The use of dietary sodium does not have an impact on preeclampsia. Glycosuria is an important consideration if this client has gestational diabetes but is not significant for the client with preeclampsia.
Question 20.
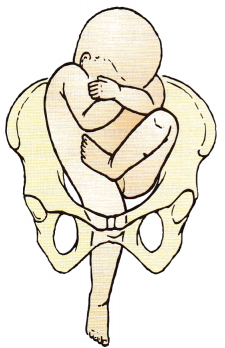
The nurse is assessing fetal presentation in a multiparous client. The figure here indicates which presentation?
(a) frank breech
(b) complete breech
(c) footling breech
(d) vertex
Answer:
(c) footling breech
Rationale:
Although breech presentations are rare, footling breech occurs when there is an extension of the fetal knees and one or both feet protrude through the pelvis. In frank breech, there is flexion of the fetal thighs and extension of the knees. The feet rest at the sides of the fetal head. In complete breech, there is flexion of the fetal thighs and knees; the fetus appears to be squatting. Vertex position occurs in 95% of births; in such cases, the head is engaged in the pelvis.
Question 21.
A client believes she is experiencing premenstrual syndrome (PMS). The nurse should next ask the client about what symptom?
(a) menstrual cycle irregularity with increased menstrual flow
(b) mood swings immediately after menses
(c) tension and fatigue before menses and through the second day of the menstrual cycle
(d) midcycle spotting and abdominal pain at the time of ovulation
Answer:
(c) tension and fatigue before menses and through the second day of the menstrual cycle
Rationale:
The timing of symptoms is important to the diagnosis of PMS. The client should keep a 3-month log of symptoms and menses. With PMS, the symptoms begin 3 to 7 days before menses and resolve 1 to 2 days after the menstrual cycle has started. Menstrual cycle irregularity and mood swings after menses are not related to PMS, and other causes
should be investigated. Midcycle spotting and pain are related to ovulation.
Question 22.
Which sign should the nurse closely assess in a client who is reversing from general anesthesia and receiving clindamycin?
(a) tachycardia
(b) respiratory depression
(c) hypotension
(d) decreased urinary output
Answer:
(b) respiratory depression
Rationale:
The client who has received general anesthesia with neuromuscular blocking agents must be carefully monitored when given clindamycin. A serious interaction could be enhanced, neuromuscular blockage, skeletal muscle weakness, or respiratory depression, if this combination is used during or immediately after surgery. Concurrent use should be avoided.
The combined effect of the medications places the client at increased risk, and the nurse should assess the client closely for respiratory depression or paralysis. The nurse will be monitoring the client’s heart rate, blood pressure, and urinary output but not specifically because of potential drug interactions and adverse effects of clindamycin.
Question 23.
A client with delirium becomes very anxious and says, “I can’t stop what’s happening to me. Make it stop, please!” What is the nurse’s most appropriate response?
(a) “Take some deep breaths. The more you worry, the worse it will get.”
(b) “As soon as we know what’s causing this, we can try to stop it. I’ll get you some medicine to help you relax.”
(c) "I wish I could do something to make it stop, but unfortunately I can’t.”
(d) “I’ll sit with you until you calm down a little.”
Answer:
(b) “As soon as we know what’s causing this, we can try to stop it. I’ll get you some medicine to help you relax.”
Rationale:
The client needs to know that there is a cause for the delirium, that there is hope for treatment, and that medications can help decrease anxiety. Saying that the more the client worries, the worse the delirium will get is inappropriate and most likely would add to the client’s anxiety. Telling the client that noting can be done is not true or therapeutic. The nurse can sit quietly with the client after providing an explanation and medication.
Question 24.
A 16-year-old client is in the emergency department for treatment of minor injuries from a car accident. A crisis nurse is with the client because the client became hysterical and was saying, “It’s my fault. My Mom is going to kill me. I don’t even have a way home.” What should be the nurse’s initial intervention?
(a) Hold her hands and say, “Slow down. Take a deep breath.”
(b) Say, “Calm down. The police can take you home.”
(c) Put a hand on her shoulder and say, “It wasn’t your fault. ”
(d) Say, “Your mother is not going to kill you. Stop worrying.”
Answer:
(a) Hold her hands and say, “Slow down. Take a deep breath.”
Rationale:
The client is in a crisis and has a high anxiety level. Holding the client’s hands and encouraging the client to slow down and take a deep breath conveys caring and helps decrease anxiety. Telling the client to calm down or stop worrying offers no concrete directions for accomplishing this task. It is unknown from the data who was at fault in the accident. Therefore, it is inappropriate for the nurse to state that it was not the client’s fault.
Question 25.
A hospitalized adolescent with type 1 diabetes mellitus is weak and nauseated with poor skin turgor. The nurse notes a fruity odor to the client’s breath. The client uses lispro insulin. The last meal was lunch, 2 hours ago. Place the nursing actions in the order in which the nurse should perform them. All options must be used.
(a) Obtain a fingerstick test for blood glucose.
(b) Start an IV infusion with normal saline solution.
(c) Administer insulin lispro.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(a) Obtain a fingerstick test for blood glucose.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Start an IV infusion with normal saline solution.
(c) Administer insulin lispro.
Rationale:
The client is experiencing ketoacidosis. The nurse should first obtain the blood glucose level and then notify the HCP who will then prescribe the appropriate dose of insulin. Prior to administering the insulin, the nurse will start the IV infusion.
Question 26.
A nurse is planning care for a hospitalized school-age child and is delegating care to a pediatric care assistant. When a nurse delegates a task to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP), which factor is most important?
(a) The nurse has observed the UAP perform the task.
(b) The child and UAP have established a positive relationship.
(c) The task is appropriate for that individual's preparation.
(d) The UAP has previously performed the task.
Answer:
(c) The task is appropriate for that individual's preparation.
Rationale:
Tasks that the UAP GJ can undertake vary greatly. The nurse must be aware of the scope of the UAP’s preparation and the policies of the health care agency. The important consideration is that the task is appropriate for that individual and is within the guidelines for practice at the health care agency. The UAP can perform complicated tasks within the scope of the preparation.
Although the nurse observes the UAP and evaluates the UAP on his or her ability to perform the task, the most important aspect of delegation is to delegate within the UAP’s educational preparation. A positive relationship with clients, while desirable, is not essential to delegation. Delegation involves giving clear directions and following up after the task has been delegated.
Question 27.
The nurse is assessing a client with superficial thrombophlebitis in the greater saphenous vein of the left leg. The client has “aching” in the leg. Which finding indicates the nurse should contact the health care provider (HCP) to request a prescription to improve the client’s comfort?
(a) brown discoloration of the skin with edema in the lower left leg
(b) dark, protruding veins of both legs that are uncomfortable when standing
(c) absence of pain or swelling when the client dorsiflexes the left foot
(d) red, warm, palpable linear cord along the vein that is painful on palpation
Answer:
(d) red, warm, palpable linear cord along the vein that is painful on palpation
Rationale:
Superficial thrombophlebitis is associated with pain, warmth, and erythema. The nurse can request a prescription for warm packs to relieve the pain. Venous insufficiency causes edema and a brown discoloration of the lower leg. Varicose veins are dark, protruding veins, and symptoms of discomfort increase with standing. Pain on dorsiflexion of the foot indicates deep vein thrombosis; the client does not indicate having this pain.
Question 28.
A client who has been recently diagnosed with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) inquires about hospice services. What should the nurse tell the client about these services?
Hospice services are appropriate:
(a) for clients with an inevitable death within weeks to months.
(b) for all clients with AIDS at any stage.
(c) only when the client has written advance directives.
(d) when the client is ready to discuss the prognosis.
Answer:
(a) for clients with an inevitable death within weeks to months.
Rationale:
Hospice programs are appropriate programs for clients with any type of terminal illness when death is imminent within weeks up to 6 months. Clients may discuss their prognosis of a terminal illness before it progresses to the terminal stage when a referral to hospice care is indicated. Clients are not required to have advance directives to be admitted to hospice services, but they will be asked to complete them upon admission.
Question 29.
While assessing a neonate at age 24 hours, the nurse observes several irregularly shaped, red, flat patches on the back of the neonate’s neck. The nurse interprets this as which finding?
(a) stork bite
(b) port-wine stain
(c) newborn rash
(d) cafe au lait spot
Answer:
(a) stork bite
Rationale:
Several irregularly shaped red patches, common skin variations in neonates, are termed stork bites. They eventually fade away as the neonate grows older. Port-wine stains are disfiguring darkish red or purplish skin discolorations on the scalp and face that may need laser therapy for removal.
Newborn rash is typically generalized over the body, not localized to one body area, and is commonly raised. Cafe au lait spots are brown and typically found anywhere on the body. More than six spots or spots larger than 1.5 cm are associated with neurofibromatosis, a genetic condition of neural tissue.
Question 30.
A mother brings her 2-month-old son to the emergency department with a high fever and possible sepsis. The health care provider has prescribed a lumbar puncture, but the mother will not sign the consent until the father arrives to give permission. What should the nurse do?
(a) Report this to the social worker.
(b) Call the regional protective services for children.
(c) Wait until the father arrives.
(d) Inform the health care provider (HCP) that the mother has refused to have the procedure.
Answer:
(c) Wait until the father arrives.
Rationale:
In the traditional Mexican household, the man is the head of the family and makes the major decisions. Efforts should be made to reach the father as soon as possible to acquire his permission. It is not necessary to contact the social worker at this point. The client has not refused the procedure, so it is premature to contact the HCP Q. This is not a situation of suspected child abuse.
Question 31.
What action is most appropriate when dealing with a client who is expressing anger verbally, is pacing, and is irritable?
(a) Convey empathy and encouraging ventilation.
(b) Use calm, firm directions to get the client to a quiet room.
(c) Put the client in restraints.
(d) Discuss alternative strategies for when the client is angry in the future.
Answer:
(a) Convey empathy and encouraging ventilation.
Rationale:
At this time, the client’s anger is not out of control, so empathy and talking are appropriate to diffuse the anger. Using time-out Q is appropriate when the client’s anger is escalating and the client can no longer talk about the anger rationally. Restraints are appropriate only when there is imminent risk of harm to the client or others. Future strategies are discussed after the initial incident is resolved.
Question 32.
A client with Alzheimer’s disease is started on a low dose of lorazepam because of agitation and a sleep disturbance. The nurse should assess the client for which complication?
(a) nighttime agitation
(b) extrapyramidal side effects
(c) vomiting
(d) anticholinergic side effects
Answer:
(a) nighttime agitation
Rationale:
In the cognitively impaired client, benzodiazepines, such as lorazepam, can increase confusion and nighttime agitation. Extrapyramidal side effects are more common with antipsychotics. Vomiting and sweating are signs of benzodiazepine withdrawal. Anticholinergic side effects are more likely with antipsychotics and tricyclic antidepressants.
Question 33.
The nurse is conducting a counseling session with a client experiencing posttraumatic stress disorder (PSTD) using a two-way video telehealth system from the hospital to the client’s home, which is 2 hours away from the nearest mental health facility. What are expected outcomes of using telehealth as a venue to provide health care to this client? Select all that apply. The client will:
(a) save travel time from the house to the health care facility.
(b) avoid reliving a traumatic event that might be precipitated by visiting a health care facility.
(c) experience a shorter recovery time than being treated on-site at a health care facility.
(d) receive health care for this mental health problem.
(e) obtain group support from others with a similar health problem.
Answer:
(a) save travel time from the house to the health care facility.
(b) avoid reliving a traumatic event that might be precipitated by visiting a health care facility.
(d) receive health care for this mental health problem.
Rationale:
Telehealth is becoming an increasingly available way for nurses to conduct counseling sessions with clients who are at a distance from a health care provider (HCP) Q or health care facility. The client saves travel time and can avoid precipitating symptoms associated with the stress disorder that might occur as a result of a visit to a health care facility.
The client also can access care that might not otherwise be easily available. Treatment for PSTD is long term, and there is no evidence to suggest that telehealth versus face-to- face counseling shortens recovery time. Counseling sessions using telehealth technology are conducted on an individual basis between one client and an HCP, but group support may be available if required as a part of a treatment plan.
Question 34.
A nurse who is not assigned to care for a client may access the client’s electronic health record in which circumstance?
(a) The client is the nurse’s son in the emergency department and has pending lab results.
(b) The nurse had previously provided care to the client during past hospitalization.
(c) The nurse is reporting lab results to the Code Blue team during resuscitation.
(d) The client is the nurse’s neighbor who asks the nurse to review the chart.
Answer:
(c) The nurse is reporting lab results to the Code Blue team during resuscitation.
Rationale:
Although not directly assigned to the client's care, the nurse is participating on the team providing emergency resuscitative care when relaying information from the client’s health record. In order to gain access to the client’s health informa-tion, regardless of employment at the hospital where the client was receiving care, the nurse would need to sign the HIPPA releases, just as any parent would need to do. While the nurse may have provided care to a client in the past, the nurse does not have permission to access the client’s records on the current admission if not assigned to provide care. Although the neighbor gave verbal permission to access the records, the permission is not in writing and therefore would be unauthorized access by the nurse.
Question 35.
A child who is of preschool age is diagnosed as having severe autism. The most effective therapy involves which intervention?
(a) antipsychotic medications
(b) group psychotherapy
(c) one-on-one play therapy
(d) social skills group
Answer:
(c) one-on-one play therapy
Rationale:
The preschool-age child with severe autism will benefit from one-on-one play therapy. The therapist can develop a rapport with this child with nonverbal play. Antipsychotic medications are not indicated for the autism client. The child has difficulty with interpersonal relationships; therefore, group psychotherapy and social skills groups would not be effective.
Question 36.
The nurse on the antenatal unit is planning care for four clients. The nurse should assess which client first?
(a) a 29-year-old client carrying twins, being treated for preterm labor at 29 weeks’ gestation and receiving magnesium sulfate at 2 g/h, with stable fetal heart rates and no contractions for the past 2 hours
(b) a 19-year-old 18 weeks intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) who is now 12 hours post motor vehicle accident with bright red vaginal bleeding
(c) a client at 38 weeks’ gestation hospitalized frequently during this pregnancy for placenta previa and who 2 days ago was admitted with severe bright red vaginal bleeding that has tapered off now
(d) a 9-week IUP hospitalized for hyperemesis gravidarum who has not vomited for the last 12 hours
Answer:
(b) a 19-year-old 18 weeks intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) who is now 12 hours post motor vehicle accident with bright red vaginal bleeding
Rationale:
The client who is 18 weeks with an intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) is not stable with bright red vaginal bleeding. Even with a nonviable fetus, the mother is in jeopardy with continued bleeding. The client who is 9 weeks IUP and has not vomited for 12 hours appears stable at this point with a nonviable fetus. The G8 also appears stable as her bleeding has tapered off since admission. The 29-week gestation client carrying twins has no information indicating that she is in jeopardy, with no contractions in the past 2 hours, and is becoming more stable.
Question 37.
The nurse is planning care for a client with a spinal injury who is to remain on complete bed rest. What should the nurse do to prevent the development of pressure ulcers? Select all that apply.
(a) Turn the client every 2 hours.
(b) Insert an indwelling urinary catheter.
(c) Monitor the serum albumin.
(d) Monitor the white blood cell count.
(e) Request a prescription for a pressure mattress.
(f) Inspect the skin for redness.
Answer:
(a) Turn the client every 2 hours.
(c) Monitor the serum albumin.
(e) Request a prescription for a pressure mattress.
(f) Inspect the skin for redness.
Rationale:
The nurse should establish a schedule to turn the client every 2 hours. The nurse should also monitor the client’s serum albumin; a decreased serum albumin indicates malnutrition and is considered a risk factor in the development of pressure ulcers. An alternating air pressure mattress prevents pressure on the skin, which is a risk factor for pressure ulcers. The nurse should assess the client’s skin for redness, an early sign of pressure. Inserting an indwelling catheter requires a health care provider’s (HCP’s) Qj prescription and is not necessary at this time. The nurse monitors the white blood cell count only if an infection is present.
Question 38.
A client hospitalized with heart failure is receiving digoxin and furosemide intravenously and now has continuous ringing in the ears. What is the appropriate action for the nurse to take at this time?
(a) Obtain a digoxin level to check for toxicity.
(b) Note the observation in the medical record, and plan to reassess in 2 hours.
(c) Ask the client about taking aspirin in addition to other medications.
(d) Discontinue the furosemide, and notify the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(d) Discontinue the furosemide, and notify the health care provider (HCP).
Rationale:
The nurse should recognize the ringing in the ears, or tinnitus, as a sign of ototoxicity probably caused by the furosemide. The appropriate action is for the nurse to stop the furosemide and notify the HCP. If the drug is stopped soon enough, permanent hearing loss can be avoided, and the tinnitus should subside.
The nurse should note the observation in the medical record Q but should not delay action. Tinnitus is not a symptom of digoxin toxicity. Aspirin can cause tinnitus, but the nurse should first investigate the obvious cause of tinnitus, which in this case is the furosemide.
Question 39.
A woman who speaks Chinese only and is very upset brings her child to the clinic with bleeding from the mouth. Which is the appropriate first action by the nurse who does not speak Chinese?
(a) Call for the interpreter.
(b) Grab the child, and take the child to the treatment room.
(c) Immediately apply ice to the child’s mouth.
(d) Give the ice to the mother and demonstrate what to do.
Answer:
(d) Give the ice to the mother and demonstrate what to do.
Rationale:
Any injury to the mouth results in copious amounts of blood because the mouth is a highly vascular area. Because the nurse does not know the mother and does not speak Chinese, the most appropriate action is to give the mother the ice and demonstrate what she is to do. The child will be less fearful if the ice is applied by the mother. Calling for an interpreter is appropriate after caring for the immediate need of the child. Grabbing the child away will probably upset the mother more, further adding to the stress experienced by the child.
Question 40.
The nurse should give which discharge instructions about thermal injury to a client with peripheral vascular disease? Select all that apply.
(a) “Warm the fingers or toes by using an electric heating pad.”
(b) “Avoid sunburn during the summer.”
(c) “Wear extra socks in the winter.”
(d) “Choose loose, soft, cotton socks.”
(e) “Use an electric blanket when you’re sleeping.”
Answer:
(b) “Avoid sunburn during the summer.”
(c) “Wear extra socks in the winter.”
(d) “Choose loose, soft, cotton socks.”
Rationale:
The client should recognize the signs of potential thermal dangers to prevent skin breakdown and wear clean, loose, soft cotton socks so that the feet are comfortable, air can circulate, and moisture is absorbed. In the winter or if the client has cold feet, the client should be encouraged to wear an extra pair of socks and a larger shoe size. Getting a sunburn during the summer puts the client at risk for tissue injury and skin breakdown. Using a heating pad to warm the feet or using an electric blanket places the client at risk for injury and should be avoided.
Question 41.
Which is most critical for the nurse to communicate to the health care provider (HCP) prior to placing an epidural analgesia catheter? The client:
(a) consumed 240 mL of beef broth 4 hours prior.
(b) has had an indwelling urinary catheter in place for 2 days.
(c) received enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneously 1 hour ago.
(d) has an albumin level of 3.5 g/dL.
Answer:
(c) received enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneously 1 hour ago.
Rationale:
Clients receiving anticoagulation are at high risk for an epidermal hematoma. If the client is taking any anticoagulants, this should be immediately relayed to the HCP X3 scheduled to perform the procedure. Clear liquids may be limited 2 hours prior to the procedure, but this varies by HCP and institutional guidelines. The albumen level is on the lower end of normal and is not a concern. The indwelling urinary catheter is not a concern at this time.
Question 42.
An older adult has few health problems, performs self-care, plays cards, and talks about “the good old days.” The client wants to make “final” arrangements, such as completing an advance directive and planning and paying for a funeral and burial. What interpretation does the nurse make about the client?
(a) The client is depressed and should be watched for further signs of depression.
(b) The request is age-appropriate and should be honored.
(c) The client should be placed on suicide precautions and seen by a psychiatrist.
(d) The request suggests that the client has a premonition about dying soon and needs to talk about it.
Answer:
(b) The request is age-appropriate and should be honored.
Rationale:
Given the client’s age, making final plans is age appropriate. The absence of any signs of ill health, depression, or suicidal ideation makes the other options inappropriate.
Question 43.
A client with hydrocephalus reports having had a headache in the morning on arising for the last 3 days, but it disappears later in the day. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Tell the client that this is normal because intracranial pressure (ICP) fluctuates throughout the day.
(c) Instruct the client to increase fluid intake prior to going to bed to prevent a headache in the morning.
(d) Advise the client to request pain medication from the HCP.
Answer:
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Rationale:
ICP is highest in the early morning, and the client with hydrocephalus may be experiencing signs of increased ICP that need to be treated. The increased ICP is not related to fluid levels, and the nurse should not advise the client to increase fluid intake. While ICP does fluctuate during the day, it is highest in the morning, and the nurse should notify the HCP. Pain medication will not treat the potentially increasing ICP and may mask important signs of increasing ICP.
Question 44.
A primigravid client visits the clinic for a routine examination at 35 weeks’ gestation. The client’s blood pressure is near the baseline of 120/74 mm Hg with no proteinuria or evidence of facial edema. The client asks the nurse, “What should I take if I get an occasional headache after looking at my computer at work all day?” Which over-the- counter medicine does the nurse consider to be safest for occasional use by a pregnant client with no known risks?
(a) acetaminophen
(b) aspirin
(c) ibuprofen
(d) naproxen
Answer:
(a) acetaminophen
Rationale:
The nurse should instruct the client that symptoms from an occasional headache due to eye strain or continuous work at a computer can be relieved by acetaminophen. Although this drug causes prostaglandin inhibition, this effect is rapidly reversed and cleared with no apparent harmful effects in pregnancy. If the headaches become more frequent or severe, the client should be instructed to contact her health care provider [HCP) 2 immediately. Aspirin should be avoided during pregnancy because it inhibits prostaglandin synthesis.
It also decreases uterine contractility and may delay the onset of labor or prolong pregnancy and labor. Aspirin decreases platelet aggregation, possibly increasing the risk of bleeding. Ibuprofen and naproxen can lead to premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus and decreased amniotic fluid with prolonged use. They may also prolong pregnancy or labor because of their antiprostaglandin effects.
Question 45.
A client is experiencing a flashback from the use of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). What should the nurse do?
(a) Confront the client’s misperceptions.
(b) Reassure the client while presenting reality.
(c) Seclude the client until the flashback ends.
(d) Challenge the client’s unrealistic statements.
Answer:
(b) Reassure the client while presenting reality.
Rationale:
When a client is experiencing a flashback, the nurse should stay with the client, offer reassurance, and present reality in a nonthreatening manner to minimize the client’s anxiety and agitation. The client needs to be told that he or she is expe-riencing an effect from lysergic acid diethylamide and that he or she is safe and the flashback will end. Confronting the client’s misperceptions or challenging unrealistic statements could increase anxiety and agitation, possibly leading to aggressive behavior. Secluding the client until the flashback ends usually is not necessary or appropriate unless the client threatens or demonstrates aggression toward self or others.
Question 46.
A an adolescent client has undergone an exam-ination and had evidence collected after being sexually assaulted. Her father is overheard yelling at his daughter, “You’re going to tell me who did this to you. What’s his name?” Which is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “Please come with me, sir. I need some important information.”
(b) “Stop yelling. You’re being inappropriate.”
(c) “Please be quiet. You’re not helping your daughter this way.”
(d) “If you don’t stop yelling, I’ll have to call Security.”
Answer:
(a) “Please come with me, sir. I need some important information.”
Rationale:
With this level of anger in a crisis, the father needs simple but firm directions to leave the room, calm down, and then to talk. Doing so relieves the daughter of any pressure from her father. Telling the father to stop yelling or be quiet provides no concrete directions to the father and may embarrass him in front of his daughter. Telling the father that if he does not stop yelling, the nurse will call Security is a threat, possibly leading to an escalation of the situation.
Question 47.
The nurse is in the process of assessing a non-English-speaking client, communicating through an interpreter. To facilitate communication, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Direct all questions to the interpreter.
(b) Request all family members leave the room.
(c) Ask client how the client wishes to be addressed.
(d) Offer the client a cold drink.
Answer:
(c) Ask client how the client wishes to be addressed.
Rationale:
Some cultures have no first or last names, and it is a sign of respect to ask the client how they wish to be addressed. Directing questions to the interpreter is culturally incongruent behavior. The interpreter will coach the nurse to direct questions to the client. The family should stay with the client so the nurse can determine who is the decision maker in the family.
In some cultures, the matriarch or patriarch may be the designated decision maker and should be involved in decisions about the client’s care. Some cultures believe health is a holistic balance between hot and cold. Therefore, before providing hot drinks or cold drinks, the nurse should determine the client’s preferences.
Question 48.
A nurse is establishing priorities for home visits to a group of clients. Which client can be seen later on in the week?
(a) a client recently diagnosed with terminal cancer with metastasis to the brain
(b) a female client recently diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
(c) a client who is to demonstrate the ability to perform an insulin injection
(d) a client with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) with CD4 < 200 cells/mm2
Answer:
(b) a female client recently diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Rationale:
Female clients with HIV are at risk for acquiring the papillomavirus, which predisposes them to cancer. This client needs to have regular Pap smears. Visiting this client could be delayed. Because of the safety risks and the need for pain management, the nurse visits the client with brain metastasis as soon as possible. A client with diabetes who may not inject insulin properly will be at great risk, and the nurse should plan to visit this client early as well. Because the client with CD4 is at great risk for a fulminating infection, the nurse does not postpone the appointment.
Question 49.
During a neonate’s assessment shortly after birth, the nurse observes a large pad of fat at the back of the neck, widely set eyes, simian hand creases, and epicanthal folds. Which action is most appropriate?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP) immediately.
(b) Ask the mother to consent to genetic studies.
(c) Explain these deviations to the newborn’s mother.
(d) Document these findings as minor deviations.
Answer:
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP) immediately.
Rationale:
A large pad of fat at the back of the neck, widely set eyes, a simian crease in the hands, and epicanthal folds are typically associated with Down syndrome. The nurse should notify the HCP immediately. The HCP should obtain consent Qfor genetic studies and is responsible for explaining these deviations to the parents. However, the nurse may need to provide additional teaching to the mother and to answer any questions that may arise.
Question 50.
To help prevent hip flexion deformities associated with rheumatoid arthritis, the nurse should help the client assume which position in bed several times a day?
(a) prone
(b) very low Fowler’s
(c) modified Trendelenburg
(d) side lying
Answer:
(a) prone
Rationale:
To help prevent flexion deformities, a client with rheumatoid arthritis should lie in a prone position in bed for about Vz hour several times a day. This positioning helps keep the hips and knees in an extended position and prevents joint flexion. Low Fowler’s, modified Trendelenburg, and side- lying positions do not prevent hip flexion.
Question 51.
A client with severe arthritis has been receiving maintenance therapy of prednisone 10 mg/ day for the past 6 weeks. The nurse should instruct the client to immediately report which symptom?
(a) respiratory infection
(b) joint pain
(c) constipation
(d) joint swelling
Answer:
(a) respiratory infection
Rationale:
Clients receiving chronic steroid therapy can become immunosuppressed and are prone to infections. Signs of infection can also be masked with prednisone. Signs and symptoms of infection should be reported immediately. Joint pain, constipation, and joint swelling are not related to the adverse effects of steroid therapy.
Question 52.
A nurse hears a client state, “I’ve had it with this marriage. It would be so much easier to just hire someone to kill my husband!" What action should the nurse take?
(a) Since the client is still admitted to the hospital, the nurse must hold the statement in confidence.
(b) The nurse must start the process to warn the client’s husband.
(c) An assessment of the client’s response to treatment must be performed.
(d) The comment must be held in confidence because the client did not report the statement directly to the nurse.
Answer:
(b) The nurse must start the process to warn the client’s husband.
Rationale:
Confidentiality must be broken if there are credible threats made against another person’s safety. Confidentiality does not override the safety of other persons.
Question 53.
When teaching unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) about the importance of handwashing in preventing disease, what should the nurse tell the UAP?
(a) “It's not necessary to wash your hands as long as you use gloves.”
(b) “Handwashing is the best method for preventing cross-contamination.”
(c) “Waterless commercial products are not effective for killing organisms.”
(d) “The hands do not serve as a source of infection.”
Answer:
(b) “Handwashing is the best method for preventing cross-contamination.”
Rationale:
Handwashing with the correct technique is the best method for preventing cross-contamination. The hands serve as a source of infection. Waterless commercial products containing at least 60% alcohol are as effective at killing organisms as handwashing.
Question 54.
A 7-year-old child is admitted to the hospital with acute rheumatic fever. During the acute phase of the illness, which diversional activity would the nurse most discourage?
(a) reading a book with the father
(b) playing with a doll with the nurse
(c) watching the television with a sibling
(d) playing checkers with a roommate
Answer:
(d) playing checkers with a roommate
Rationale:
School-age children enjoy board games and are commonly intense about following rules. Their play can become emotional. Adequate rest is of utmost importance during the acute stage of rheumatic fever. Therefore, playing a game with another child probably would be too strenuous. Such diversional activities as reading a book, playing with a doll, and watching television would be more satisfactory.
Question 55.
Before discharge from the hospital after a myo-cardial infarction, the nurse teaches the client to exercise by gradually increasing the distance walked. What should the nurse teach the client to do to determine whether to increase or decrease the exercise level?
(a) Obtain the heart rate for 1 minute at the end of the walk.
(b) Count the number of steps taken before becoming tired.
(c) Determine how many minutes it takes to walk a mile.
(d) Count the number of breaths per minute at the middle of the walk.
Answer:
(a) Obtain the heart rate for 1 minute at the end of the walk.
Rationale:
The client who is on a progressive exercise program at home after a myocardial infarction should be taught to monitor the heart rate and take the pulse at the end of each walk. The heart rate can be expected to increase with exercise, but the client should not increase the exercise if the heart rate increases more than about 25 bpm from baseline
or exceeds 100 to 125 bpm. The nurse should also teach the client to discontinue exercise if chest pain occurs. The number of steps and the time to walk a mile are not determining factors for increasing the amount of exercise as long as the heart rate remains within range. The respirations may increase, but do not determine the ability to increase the exercise unless the client becomes short of breath.
Question 56.
A woman is taking oral contraceptives. The nurse teaches the client to report which complication?
(a) breakthrough bleeding
(b) severe calf pain
(c) mild headache
(d) weight gain of 3 lb (1.4 kg)
Answer:
(b) severe calf pain
Rationale:
Women who take oral contraceptives are at increased risk for thromboembolic conditions. Severe calf pain needs to be investigated as a potential sign of deep vein thrombosis. Breakthrough bleeding, mild headache, or weight gain may be common benign side effects that accompany oral contraceptive use. Clients may be monitored for these side effects without a change in treatment.
Question 57.
The nurse is planning care for a client 1 day after having surgery to create a tracheostomy. Which nursing action is the priority goal for the client at this time?
(a) Keep the secretions moist with saline.
(b) Teach the client about tracheostomy care.
(c) Relieve anxiety about breathing.
(d) Maintain a patent airway.
Answer:
(d) Maintain a patent airway.
Rationale:
The priority for a client with a new tracheostomy is to maintain a patent airway. A new tracheostomy commonly causes bleeding and excess secretions, and the client may require frequent suctioning to maintain a patent airway. The nurse can keep the secretions moist as a part of the suctioning procedure. The nurse can help the client manage anxiety while maintaining the priority of a patent airway. While the nurse will begin teaching the client about self-care, this is not the priority at this time.
Question 58.
The nurse walks into the room of a client who has a “do-not-resuscitate” prescription and finds the client without a pulse, respirations, or blood pressure. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Stay in the room, and call the nursing team for assistance.
(b) Push the emergency alarm to call a code.
(c) Page the client’s health care provider (HCP).
(d) Pull the curtain and leave the room.
Answer:
(a) Stay in the room, and call the nursing team for assistance.
Rationale:
The nurse should call to the nursing station to ask the nursing team for assistance. It is not necessary to page the HCP because this is not an emergency, but the nurse will need to notify the provider of the client’s death and then also notify the family. A “code” should not be called because the client and family have designated a “do-not- resuscitate” status. Nursing personnel should begin postmortem care so that the family does not walk in unannounced to find their loved one deceased and looking disarrayed.
Question 59.
When developing a nutritional plan for a child who needs to increase protein intake, the nurse should suggest which foods? Select all that apply.
(a) potatoes
(b) cooked dry beans
(c) peanut butter
(d) yogurt
(e) apples
Answer:
(b) cooked dry beans
(c) peanut butter
(d) yogurt
Rationale:
Yogurt, dry beans, and peanut butter all contain protein in amounts that make them good sources of protein for the child. Potatoes and apples are carbohydrates and do not provide a sufficient source of protein.
Question 60.
Immediately after receiving an injection of bupivacaine, the client becomes restless and nervous and reports a feeling of impending doom. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Ask the client to explain these feelings.
(b) Reassure the client that it is normal to feel restless before a procedure.
(c) Assess the client’s vital signs.
(d) Administer epinephrine.
Answer:
(c) Assess the client’s vital signs.
Rationale:
The nurse should assess the client’s vital signs because there is a likelihood of having a reaction to the bupivacaine. If the client’s vital signs are abnormal, immediate intervention may be necessary. Although the nurse may ask the client to continue to describe feelings, this is not likely to be a psycho-social reaction. Simple reassurance is inappropriate in most clinical situations and can be dangerous if physiologic causes of restlessness are overlooked. The nurse should not administer epinephrine until vital signs have been assessed.
Question 61.
The nurse has just received report on four clients. Which client should be seen first?
(a) a client who had a cardiac catheterization 8 hours ago whose vital signs have been stable for the last 2 hours
(b) a client diagnosed with asthma who just received a respiratory therapy treatment
(c) a client feeling sweaty and requesting antacid for stomach upset
(d) a client with diabetes whose fingerstick blood glucose was 90 mg/dL 1 hour ago
Answer:
(c) a client feeling sweaty and requesting antacid for stomach upset
Rationale:
Signs of indigestion and sweating can be signs of impending myocardial infarction that should be carefully assessed by the nurse. The client who had the cardiac catheterization has stable vital signs and should be reassessed after assessing the client with a potential impending myocardial infarction. The client who had respiratory therapy does not require immediate attention. The client with diabetes has a normal finger stick glucose level and does not require immediate attention.
Question 62.
A menopausal woman is taking hormone replacement therapy. What warning sign of endometrial cancer should the nurse instruct the client to report to her health care provider?
(a) hot flashes
(b) irregular vaginal bleeding
(c) urinary urgency
(d) dyspareunia
Answer:
(b) irregular vaginal bleeding
Rationale:
Endometrial cancer has very few warning signals; irregular bleeding may be the only sign. Any irregular bleeding in a menopausal woman should be investigated, and an endometrial biopsy may be prescribed. Hot flashes result from the decreased estrogen levels that accompany menopause. Urinary urgency should be monitored and treated as a separate problem. Dyspareunia is the occurrence of pain in the labial, vaginal, or pelvic areas during or after sexual intercourse. It may be caused by inadequate vaginal lubrication in the menopausal woman.
Question 63.
A client tells the nurse that she has had sexual contact with someone whom she suspects has genital herpes. What information should the nurse give to the client?
(a) Anticipate lesions within 25 to 30 days.
(b) Continue sexual activity unless lesions are present.
(c) Report any difficulty urinating.
(d) Drink extra fluids to prevent lesions from forming.
Answer:
(c) Report any difficulty urinating.
Rationale:
The client should be encouraged to report painful urination or urinary retention. Lesions may appear 2 to 12 days after exposure. The client is capable of transmitting the infection even when asymptomatic, so a barrier contraceptive should be used. Drinking extra fluids will not stop the lesions from forming.
Question 64.
As part of a preconception visit, a couple ask the nurse about their risk for having a child with a genetic disorder. What information should the nurse tell the clients about the risk of having a child with sickle cell disease?
(a) If both parents have sickle cell trait, the chance is 25% of having a child with sickle cell anemia.
(b) If one parent has sickle cell anemia, there is a 50% chance the child will have sickle cell anemia.
(c) If one parent has sickle cell trait, there is a 25% chance that the child will have sickle cell trait.
(d) If both parents have sickle cell anemia, there is a 50% chance that the child will have sickle cell trait
Answer:
(a) If both parents have sickle cell trait, the chance is 25% of having a child with sickle cell anemia.
Rationale:
Sickle cell disease is recessive genetic disorder. Carriers with only one recessive sickle cell gene have sickle cell trait. If both parents have sickle cell trait there is a one-in-four chance with each pregnancy that the child will have sickle cell anemia. If one parent has sickle cell anemia and the other is not a carrier, the child will have sickle cell trait only. If one parent has sickle cell trait, the chance is 50% that the child will also have sickle cell trait. If both parents have sickle cell anemia, there is a 100% chance that the child will have the same disease.
Question 65.
The nurse is assessing a client with peripheral arterial disease who had a femoral-popliteal bypass. Which finding indicates improved arterial blood supply to the lower extremity?
(a) decrease in muscle pain when walking
(b) dependent rubor
(c) absence of pulse using a Doppler ultrasound
(d) reduction in pitting edema
Answer:
(a) decrease in muscle pain when walking
Rationale:
With increased blood supply to the leg, there should be less or absent claudication (cramping pain in leg with walking). Pulses should be palpable with improved blood supply. Edema is associated with venous disease. Pallor with eleva-tion and dependent rubor are symptoms of peripheral arterial disease.
Question 66.
The nurse is caring for a client who had an open cholecystectomy 24 hours ago. The client’s vital signs have been stable for the last 24 hours, but the client now has a temperature of 38.4°C (101.1°F), a heart rate of 116 bpm, and a respiratory rate of 26 breaths/min. The client has an IV infusion running at a keep-open rate. The nurse contacts health care provider (HCP) and receives several prescriptions (see chart). Which prescription should the nurse implement first?
Prescriptions:
- Continue to check vital signs every 2 hours.
- Draw stat blood cultures x 2.
- CT of abdomen.
- Start broad-spectrum IV antibiotic 4 hours after blood cultures are drawn.
- Draw CBC, CRP, ESR, and UA with culture and sensitivity if indicated.
- Ensure patent IV access for fluid bolus.
(a) Obtain blood cultures.
(b) Increase the rate of the intravenous infusion.
(c) Obtain a computed tomography scan of the abdomen.
(d) Chart vital signs.
Answer:
(a) Obtain blood cultures.
Rationale:
The nurse should first obtain the blood culture because subsequent treatment will be dependent on the results. The client has an intravenous infusion; the HCP did not write a prescription to increase the infusion rate. Unless indicated otherwise, the nurse can take the client’s vital signs after completing scheduling the computed tomography scan and other laboratory work.
Question 67.
A client was talking with her husband by telephone, and then she began swearing at him. The nurse interrupts the call and offers to talk with the client. She says, “I can’t talk about that bastard right now. I just need to destroy something.” What should the nurse do next?
(a) Tell her to write her feelings in her journal.
(b) Urge her to talk with the nurse now.
(c) Ask her to calm down or she will be restrained.
(d) Offer her a phone book to “destroy” while staying with her.
Answer:
(d) Offer her a phone book to “destroy” while staying with her.
Rationale:
At this level of aggression, the client needs an appropriate physical outlet for the anger. She is beyond writing in a journal. Urging the client to talk to the nurse now or making threats, such as telling her that she will be restrained, is inappropriate and could lead to an escalation of her anger.
Question 68.
A man of Chinese descent is admitted to the hospital with multiple injuries after a motor vehicle accident. His pain is not under control.
The client states, “If I could be with my people, I could receive acupuncture for this pain.” The nurse should respond to the client by understanding that in the Asian culture which is the intended outcome of acupuncture?
Acupuncture:
(a) purges evil spirits.
(b) promotes tranquility.
(c) restores the balance of energy.
(d) blocks nerve pathways to the brain.
Answer:
(c) restores the balance of energy.
Rationale:
Acupuncture, like acumassage and acupressure, is performed in certain Asian cultures to restore the energy balance within the body. Pressure, massage, and fine needles are applied to energy pathways to help restore the body’s balance. Acupuncture is not based on a belief in purging evil spirits. Although pain relief through acupuncture can promote tranquility, acupuncture is performed to restore energy balance. In the Western world, many researchers think that the gate-control theory of pain may explain the success of acupuncture, acumassage, and acupressure.
Question 69.
The nurse is caring for a multigravid client in active labor when the nurse detects variable fetal heart rate decelerations on the electronic monitor. The nurse interprets this as the compression of which structure?
(a) head
(b) chest
(c) umbilical cord
(d) placenta
Answer:
(c) umbilical cord
Rationale:
Variable decelerations are associated with compression of the umbilical cord. The nurse should alter the client’s position and increase the IV fluid rate. Fetal head compression is associated with early decelerations. Severe compression of the fetal chest, such as during the process of vaginal birth, may result in transient bradycardia. Compression
or damage to the placenta, typically from abruptio placentae, results in severe, late decelerations.
Question 70.
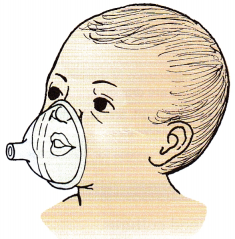
A neonate is experiencing respiratory distress and is using a neonatal oxygen mask. An unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) has positioned the oxygen mask as shown. The nurse is assessing the neonate and determines that the mask:
(a) is appropriate
(b) is too large.
(c) is too small
(d) is positioned too low
Answer:
(a) is appropriate
Rationale:
The mask is appropriate because it covers the nose and mouth and fits snugly against the cheeks and chin. The mask is not too low. Masks that are too large may cover the eyes. Masks that are too small obstruct the nose.
Question 71.
Which findings should lead the nurse to suspect that a client who had a cesarean birth 8 hours earlier is developing disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and report to the health care provider (HCP)? Select all that apply.
(a) petechiae on the arm where the blood pressure was taken
(b) heart rate of 126 bpm
(c) abdominal incision dressing with bright red drainage
(d) platelet count of 80,000/mm3 (80 x 109/L)
(e) urine output of 350 mL in the past 8 hours
(f) temperature of 98.4°F (36.9°C)
Answer:
(a) petechiae on the arm where the blood pressure was taken
(b) heart rate of 126 bpm
(c) abdominal incision dressing with bright red drainage
(d) platelet count of 80,000/mm3 (80 x 109/L)
Rationale:
DIC is diagnosed based on clinical symptoms and laboratory findings. Findings such as excessive and unusual bruising or bleeding over areas of tissue trauma, such as IV insertion or incision sites, or application of a blood pressure cuff should be reported to the HCP. Tachycardia and diaphoresis also may be noted. Laboratory results reveal low platelet, fibrinogen, proaccelerin, antihemophilic factor, and prothrombin levels. Bleeding time is normal, and partial thromboplastin time is increased. A urine output of 350 mL in 8 hours indicates adequate renal function. Temperature is not an indication of DIC.
Question 72.
A client has a plural chest tube following removal of the lower lobe of the lung. Two days after surgery, the tube is accidentally pulled out of the chest wall. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Immerse the tube in sterile water.
(b) Apply an occlusive dressing such as petroleum jelly gauze.
(c) Instruct the client to cough to expand the lung.
(d) Auscultate the lung to determine whether it collapsed.
Answer:
(b) Apply an occlusive dressing such as petroleum jelly gauze.
Rationale:
If the chest tube is accidentally pulled out (a rare occurrence), a petroleum jelly gauze and sterile 4- x 4-inch dressing should be applied over the chest wall insertion site immediately. The dressing should be covered with adhesive tape and be occlusive, and the surgeon should be notified.
The lungs can be auscultated, and vital signs can be taken after the dressing is in place and the surgeon has been called. Placing the tube in sterile water will not reestablish a seal to prevent air entering the insertion site of the chest tube.
Question 73.
Three victims with gunshot wounds are brought to the emergency department. The nurse should take which action to preserve forensic evidence on the clients’ clothing?
(a) Cut around blood stains to remove clothing.
(b) Place each item of clothing in a separate paper bag.
(c) Place all wet clothing in a plastic bag.
(d) Request that a police officer observe the removal of clothing.
Answer:
(b) Place each item of clothing in a separate paper bag.
Rationale:
Preserving forensic evidence is essential for investigative purposes following injuries that may be suspected as having criminal intent. The nurse places each item of clothing in a separate paper bag and labels it; wet clothing is hung to dry. The nurse does not cut or otherwise unnecessarily handle clothing, particularly clothing with evidence such as blood or body fluids.
It is not necessary to have police present at this time, but the nurse should document all nursing care and use quotes around the clients’ exact words where possible; documentation will become a part of the clients’ medical records ED and can be subpoenaed for subsequent investigation.
Question 74.
An 18-year-old female takes birth control pills and is sexually active with her boyfriend. She has a purulent vaginal discharge that is sometimes frothy. What nursing judgment should the nurse make about this finding?
The client has a:
(a) sexually transmitted infection.
(b) normal variation in vaginal discharge.
(c) need for vaginal douching.
(d) side effect of using birth control pills.
Answer:
(a) sexually transmitted infection.
Rationale:
A frothy, purulent vaginal discharge in a sexually active female client is typically caused by a sexually transmitted organism such as trichomonas. Other diseases, such as chlamydia, may also be present. Both the client and the boyfriend need treatment after the disease is determined.
Normal variations in female vaginal discharge should be clear to white, not frothy or purulent. The client should be instructed to wear cotton underwear and avoid pantyhose, wet gym clothes, and tight-fitting garments, such as jeans, so that air can circulate.
Question 75.
A client is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of a pulmonary embolism. Which nursing problem should the nurse address first?
(a) productive cough
(b) activity intolerance
(c) difficulty breathing
(d) impaired gas exchange
Answer:
(d) impaired gas exchange
Rationale:
Emboli obstruct blood flow, leading to a decreased perfusion of the lung tissue. Because of the decreased perfusion, a ventilation-perfusion mismatch occurs, causing hypoxemia to develop. Arterial blood gas analysis typically will indicate hypoxemia and hypocapnia. A priority objective in the treatment of pulmonary emboli is maintaining adequate oxygenation.
A productive cough and activity intolerance do not indicate impaired gas exchange. The client does not demonstrate an ineffective breathing pattern; rather, the problem of impaired gas exchange is caused by the inability of blood to flow through the lung tissue.
Question 76.
A client is receiving morphine sulfate by a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) system after a left lower lobectomy 4 hours ago. The client reports moderately severe pain in the left thorax that worsens when coughing. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Reassure the client that the PCA system is working and will relieve pain.
(b) Request a prescription for a cough suppressant.
(c) Assess the pain using a pain scale and compare to the previous assessment.
(d) Encourage the client to take deep breaths and expectorate the mucous that is stimulating the cough.
Answer:
(c) Assess the pain using a pain scale and compare to the previous assessment.
Rationale:
Immediately following surgery, the nurse should assess the client for pain frequently and note changes on the pain scale as a guide to pain management. Reassuring the client is not sufficient when the client is reporting pain. The nurse should encourage the client to cough and take deep breaths; cough suppression is contraindicated because
the client must raise and expectorate retained secretions.
Question 77.
The nurse is receiving a change of shift report on a group of clients. Which client should the nurse see first?
A client with:
(a) wheezing and who has a PaO2 of 79 and an oxygen saturation of 90% on room air.
(b) heart failure who has a PaO2 of 75 and an oxygen saturation is 90% on a nonrebreather mask.
(c) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who has a PaO2 of 65 and an oxygen saturation of 91% on 2 L nasal cannula.
(d) a PaO2 of 80 and an oxygen saturation of 93% on room air after being transferred from the operating room 30 minutes ago after having cardiac surgery.
Answer:
(b) heart failure who has a PaO2 of 75 and an oxygen saturation is 90% on a nonrebreather mask.
Rationale:
The nurse should first see the client with heart failure who is on a nonrebreather mask and only has an oxygen saturation of 90% and a PaCb of 75. This client is not responding appropriately to oxygen therapy and warrants further assessment. This client is most likely experiencing an exacerbation of heart failure, and gas exchange is not occur-ring at the capillary-membrane level in the lungs.
The client with wheezing has an oxygen saturation of 90% on room with a PaO2, of 79 indicating that gas exchange is impaired but not severely. The client with COPD can have PaO2 of 65 if damage to the lungs is underway. A client with COPD can be considered adequately oxygenated with oxygen saturation of 91% on 2L nasal cannula.
The client who is 30 minutes post-op from cardiac surgery and has a PaO2 of 80, which is within the normal range, and an oxygen saturation of 93% is considered normal. This client is not experiencing poor oxygenation because of the surgery.
Question 78.
A loading dose of digoxin is given to a client newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation. The nurse instructs the client about side effects of the medication to monitor. Which response indicates the client has understood the instruction?
The client can:
(a) count the radial pulse.
(b) demonstrate how to take the medication.
(c) explain the cause of atrial fibrillation.
(d) verbalize the action of the medication.
Answer:
(a) count the radial pulse.
Rationale:
The most serious side effect of digoxin is slow heart rate; the nurse should instruct the client to take the pulse and observe that the client can accurately locate and count the radial pulse. While the nurse can ask the client to explain how to take the medication, why it is necessary to do so, and its actions, the most important outcome is to be sure the client can take the pulse and recognize an abnormally slow heart rate.
Question 79.
Which are culturally appropriate actions on the part of the nurse when caring for a non-English- speaking client? Select all that apply.
(a) Look the client directly in the eye when asking questions.
(b) Ask the client specific and direct questions.
(c) Direct questions to the culturally appropriate decision maker.
(d) Arrange for an interpreter who speaks the client’s dialect.
(e) Point at the client using an index finger to show the client where to sit.
Answer:
(b) Ask the client specific and direct questions.
(c) Direct questions to the culturally appropriate decision maker.
(d) Arrange for an interpreter who speaks the client’s dialect.
Rationale:
Miscommunication is a common cause for error and a risk to safety. Use of interpreters is the most important first step to ensure client understanding and support self-determination related to decision-making. Asking specific and direct ques-tions and directing the questions to the culturally appropriate decision maker are culturally congruent behaviors. Direct eye contact is disrespectful in some cultures. Calling or directing someone with an index finger is considered disrespectful in some cultures and may be interpreted as an invitation to fight.
Question 80.
The nurse administers a tap water enema to a client. While the solution is being infused, the client has abdominal cramping. What should the nurse
do first?
(a) Clamp the tubing, and carefully withdraw the tube.
(b) Temporarily stop the infusion, and have the client take deep breaths.
(c) Raise the height of the enema container.
(d) Rub the client’s abdomen gently until the cramps subside.
Answer:
(b) Temporarily stop the infusion, and have the client take deep breaths.
Rationale:
If the client begins to experience abdominal cramping during administration of the enema fluid, the nurse’s first action is to temporarily stop the infusion and have the client take a few deep breaths. After the cramping subsides, the nurse can continue with the enema solution. If the cramping does not subside, the nurse should clamp the tubing and remove it. Raising the height of the container will increase the flow of fluid and cause the cramping to increase. Rubbing the abdomen while infusing the enema fluid will not stop the cramping.
Question 81.
The mother of a 7-month-old child born 6 weeks early asks the nurse what play activities and toys are appropriate for her child. What should the nurse suggest?
(a) picture books
(b) peekaboo
(c) rattle
(d) colored blocks
Answer:
(c) rattle
Rationale:
Although chronologically the infant is 7 months old, because of being born 6 weeks early, the child is only 5Vz months old developmentally. Appropriate activities for a 5- to 5V2-month-old infant include placing a rattle or ball in the infant’s hand. Picture books are an appropriate choice for an infant older than 9 months. Playing peekaboo is appropriate for a 9- to 12-month-old infant. Colored blocks are appropriate for a toddler approximately age 15 to 18 months.
Question 82.
The client has heart failure and is taking a diuretic to promote fluid loss. Which is the most accurate method of determining the extent of a client’s fluid loss?
(a) measuring intake and output
(b) assessing vital signs
(c) weighing the client
(d) assessing skin turgor
Answer:
(c) weighing the client
Rationale:
Accurate daily weight measurement provides the best measure of a client’s fluid status: 1 kg (2.2 lb) is equal to 1,000 mL of fluid. To be accurate, weight should be obtained at the same time every day, with the same scale, and with minimal clothing on.
Question 83.
A client had abdominal surgery 2 days ago and has copious drainage. The nurse uses Montgomery straps when changing the dressing. Which is the expected outcome of using these straps?
(a) Maintain pressure on the suture line.
(b) Prevent dehiscence.
(c) Avoid skin breakdown.
(d) Keep the client from touching the incision.
Answer:
(c) Avoid skin breakdown.
Rationale:
While the client has copious drainage and requires frequent dressing changes, the nurse uses Montgomery straps to avoid removing the tape that is holding the dressing in place and thus preventing skin breakdown. The straps are not used to provide pressure on the incision and will not help prevent dehiscence. The straps are secured on the abdomen and would not prevent the client from touching the incision.
Question 84.
The nurse is counseling a client regarding treatment of the client’s newly diagnosed depression. The nurse emphasizes that full benefit from antidepressant therapy usually takes how long?
(a) 1 week
(b) 2 to 4 weeks
(c) 5 to 7 weeks
(d) 8 weeks
Answer:
(b) 2 to 4 weeks
Rationale:
Full benefit from an antidepressant medication usually takes about 2 to 4 weeks on an adequate dose.
Question 85.
A multigravid client is scheduled for a percutaneous umbilical blood sampling procedure. The nurse instructs the client that this procedure is useful for diagnosing which condition?
(a) twin pregnancies
(b) fetal lung maturation
(c) Rh disease
(d) alpha fetoprotein level
Answer:
(c) Rh disease
Rationale:
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling is a useful procedure for diagnosing Rh disease, obtaining fetal complete blood count, and karyotyping chromosomes to evaluate for genetic disorders. Ultrasound commonly is used to detect twins. A lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio is the procedure of choice to diagnose fetal lung maturation. A maternal blood test is used to determine the alpha fetoprotein level.
Question 86.
An older adult who has been previously well asks the nurse, “I notice I have tremors. Is this just normal for my age?” What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “I would not be worried because this is common with aging.”
(b) “You should report this to the health care provider (HCP) because it may indicate a problem.”
(c) “You should drink orange juice when this occurs.”
(d) “You should have your blood pressure checked when this occurs.”
Answer:
(b) “You should report this to the health care provider (HCP) because it may indicate a problem.”
Rationale:
Fine tremors are the first symptom reported in 70% of clients with Parkinson’s disease. A new onset of tremors needs to be investigated by the HCP. Tremors are not an expected change with aging.
Question 87.
A client is to receive atropine 0.4 mg intramus-cularly. The atropine vial is labeled 0.5 mg/mL. How many milliliters should the nurse plan to administer? Record your answer using one decimal place.
....................... mL.
Answer:
8mb
Rationale:
imm
0.4 = 0.5X
imm
0.8 mL = X.
Question 88.
A school-age child diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is prescribed meth- ylphenidate. What finding should alert the school nurse to the possibility that the child is experiencing a common side effect of the drug?
(a) loss of appetite
(b) vomiting
(c) photosensitivity
(d) weight gain
Answer:
(a) loss of appetite
Rationale:
Loss of appetite is one of the more common adverse effects associated with methylphenidate. Although nausea is associated with this drug, vomiting is not. Photosensitivity is not associated with this drug. Because of decreased appetite, the client will not gain more weight.
Question 89.
A nurse is planning to implement nonphar- macological pain management strategies as part of a multimodal approach for managing the client’s pain. For which strategy does the nurse seek a prescription from the health care provider?
(a) massage
(b) application of an ice bag
(c) distraction
(d) deep breathing
Answer:
(b) application of an ice bag
Rationale:
Application of cold or heat requires a health care provider’s [3 prescription. The nurse can initiate massage, distraction, and deep breathing as pain management strategies.
Question 90.
Which meal would be appropriate for the child with osteomyelitis to choose?
(a) beef and bean burrito with cheese, carrot and celery sticks, and a glass of milk
(b) fries, beef hot dog, and an apple
(c) potato soup, jelly sandwich, and a peach
(d) tomato soup made with water, grilled cheese sandwich, and a banana
Answer:
(a) beef and bean burrito with cheese, carrot and celery sticks, and a glass of milk
Rationale:
Children with osteomyelitis need a diet that is high in protein and calories. Milk, eggs, cheese, meat, fish, and beans are the best sources of these nutrients.
Question 91.
The nurse is planning a continuous quality improvement (CQI) process to decrease the infection rate on the nursing unit. The nurse should consider which factors when planning the process? Select all that apply.
(a) CQI processes are required by accrediting agencies.
(b) The approach to CQI can be retrospective or concurrent.
(c) Institutional review board (IRB) approval is required.
(d) CQI is conducted by people who are not part of the process.
(e) The CQI process has a fixed end point.
Answer:
(a) CQI processes are required by accrediting agencies.
(b) The approach to CQI can be retrospective or concurrent.
Rationale:
The purpose of CQI is to improve a local process to benefit clients and providers; it is required by the institution, regulatory, or accrediting agencies. The approach to the problem can be retrospective or concurrent; institutional review board (IRB approval) is not required unless the results will be made avail¬able to external parties, and specific clients could be identified. CQI is performed by clinicians and managers who are part of the process being studied; the timeframe is continuous or cyclical.
Question 92.
The nurse is conducting a health assessment of an older adult. The client tells the nurse about cramping leg pain that occurs when walking for 15 minutes; the pain is relieved with rest. The lower extremities are slightly cool to touch, and pedal pulses are palpable +1. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Increase the length of time for walking.
(b) Include more potassium in the diet.
(c) Perform leg circles and ankle pumps.
(d) Seek consultation from the health care provider.
Answer:
(d) Seek consultation from the health care provider.
Rationale:
This client has indications of peripheral artery disease and needs additional follow-up. Increasing walking or exercising the legs and feet likely will not be sufficient to improve periph-eral circulation. Muscle cramping is a result of inadequate arterial circulation. Increasing potassium will not decrease the cramping.
Question 93.
A client has a newly placed tracheostomy tube. The nurse should assess the client for which possible complication?
(a) decreased cardiac output
(b) damage to the laryngeal nerve
(c) pneumothorax
(d) acute respiratory distress syndrome
Answer:
(b) damage to the laryngeal nerve
Rationale:
Tracheostomy tubes are associated with several potential complications, including laryngeal nerve damage, bleeding, and infection. Tracheostomy tubes do not cause decreased cardiac output, pneumothorax, or acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Question 94.
Which comment from a client indicates a need for further instruction after being taught about taking ciprofloxacin?
(a) “I must drink 500 to 1,500 mL of water a day.”
(b) “I shouldn’t take an antacid before taking the ciprofloxacin.”
(c) “I should let the health care provider (HCP) know if I start vomiting from the ciprofloxacin.”
(d) “I may get light-headed from the ciprofloxacin.”
Answer:
(a) “I must drink 500 to 1,500 mL of water a day.”
Rationale:
To reduce the risk of crystalluria, the client should drink 2,000 to 3,000 mL of water a day, not 1,000 to 1,500 mL. The client should not take an antacid before taking ciprofloxacin. An antacid decreases the absorption of the drug. The client should let the HCP know if vomiting occurs from the medication. The client may get light-headed from the ciprofloxacin. If so, the client should not drive a motor vehicle and should contact the HCP.
Question 95.
A multiparous client tells the nurse that she is using medroxyprogesterone injections for contraception. The nurse should instruct the client to increase her intake of which nutrient?
(a) folic acid
(b) vitamin C
(c) magnesium
(d) calcium
Answer:
(d) calcium
Rationale:
The nurse should instruct the client to increase her intake of calcium because there is a slight increase in the risk of osteoporosis with this medication. Weight-bearing exercises are also advised. The drug may also impair glucose tolerance in women who are at risk for diabetes.
Question 96.
When reviewing the plan of care for a client with Alzheimer’s disease, which intervention would the nurse question?
(a) reminiscence group
(b) walking
(c) pet therapy
(d) stress management
Answer:
(d) stress management
Rationale:
Stress management is not beneficial to the client with Alzheimer’s disease because of cognitive impairment, confusion, and short-term memory loss. Reminiscence group, walking, and pet therapy are beneficial.
Question 97.
Before an incisional cholecystectomy is performed, the nurse instructs the client in the correct use of an incentive spirometer. Why is incentive spirometry essential after surgery in the upper abdominal area?
(a) The client will be maintained on bed rest for several days.
(b) Ambulation is restricted by the presence of drainage tubes.
(c) The operative incision is near the diaphragm.
(d) The presence of a nasogastric tube inhibits deep breathing.
Answer:
(c) The operative incision is near the diaphragm.
Rationale:
The incisions made for upper abdominal surgeries, such as cholecystectomies, are near the diaphragm and make deep breathing painful. Incentive spirometry, which encourages deep breathing, is essential to prevent atelectasis after surgery.
The client is not maintained on bed rest for several days. The client is encouraged to ambulate by the first postoperative day, even with drainage tubes in place. Nasogastric tubes do not inhibit deep breathing and coughing.
Question 98.
The nurse should instruct the parents of a school-age child with hemophilia to implement which interventions when the child develops bleeding into a joint? Select all that apply.
(a) Have the child rest.
(b) Apply heat to the joint area.
(c) Begin factor VIII therapy.
(d) Start physical therapy.
(e) Apply a topical antifibrinolytic.
Answer:
(a) Have the child rest.
(c) Begin factor VIII therapy.
Rationale:
When a child with hemophilia develops bleeding into a joint, the parents should have the child rest and begin factor VIII therapy. If therapy is started immediately, usually other interventions such as ice are not necessary. Heat causes vasodilation and promotes bleeding. Starting factor VIII immediately helps prevent chronic joint disease. Starting physical therapy further traumatizes the joint, possibly increasing the bleeding. Applying a topical agent does not control internal bleeding.
Question 99.
When cleaning the skin around an incision and drain site, what should the nurse do?
(a) Clean the incision and drain site separately.
(b) Clean from the incision to the drain site.
(c) Clean from the drain site to the incision.
(d) Clean the incision and drain site simultaneously.
Answer:
(a) Clean the incision and drain site separately.
Rationale:
When cleaning the skin around an incision and drain, the nurse should clean the incision and drain separately to avoid contaminating either wound. This is applying the principle of working from the least contaminated area to the most con-taminated area. In this case, both areas are fresh wounds and should be kept separate.
Question 100.
The nurse is teaching a client about using topical gentamicin sulfate. Which comment by the client indicates the need for additional teaching?
(a) “I will avoid being out in the sun for long periods.”
(b) “I should stop applying when the redness is gone.”
(c) “I will call the health care provider (HCP) if the condition worsens.”
(d) “I should apply it to large open areas.”
Answer:
(d) “I should apply it to large open areas.”
Rationale:
The aminoglycoside antibiotic gentamicin sulfate should not be applied to large denuded areas because toxicity and systemic absorption are possible. The nurse should instruct the client to avoid excessive sun exposure because gentamicin sulfate can cause photosensitivity. The client should be instructed to apply the cream or ointment for only the length of time prescribed because a superinfection can occur from overuse. The client should contact the HCP El if the condition worsens after use.
Question 101.
Which goal is most important when developing a long-term care plan for a child with hemophilia?
(a) Increase the parent’s and child’s knowledge about hemophilia.
(b) Prevent injury during each stage of development.
(c) Improve the child’s self-esteem during bleeding episodes.
(d) Manage acute pain when there is bleeding into joints.
Answer:
(b) Prevent injury during each stage of development.
Rationale:
The priority for ongoing care for this child is to prevent injury while maintaining normal growth and interests. As with all chronic illnesses, there is a potential for self-esteem problems, but no data are presented to support this as a priority for care planning. The parents should have a good understanding of the disease process and realize the importance of obtaining regular health care for their child. The client may have episodes of acute pain, for the child who has bleeding into a joint, but this is a transient situation.
Question 102.
The nurse prepares a 3-year-old child to have blood specimens drawn for laboratory testing. What should the nurse do to prepare the child?
(a) Explain the procedure in advance.
(b) Explain why the blood needs to be drawn.
(c) Use distraction techniques during the procedure.
(d) Provide verbal explanations about what will occur.
Answer:
(c) Use distraction techniques during the procedure.
Rationale:
A 3-year-old child responds best to distraction during a procedure because of the typical level of cognitive development of a 3-year-old and the fear of painful events. Preparation for the procedure should be done immediately beforehand so that the child will not become too frightened. A 3-year-old is not concerned about the why of the procedure but about whether the procedure will hurt. This child is too young for verbal explanations alone because of the limited verbal abilities at this age and the fear of a painful event.
Question 103.
The client has been prescribed lisinopril to treat hypertension. The nurse should assess the client for which electrolyte imbalance?
(a) hyponatremia
(b) hypocalcemia
(c) hyperkalemia
(d) hypermagnesemia
Answer:
(c) hyperkalemia
Rationale:
Lisinopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Hyperkalemia can be a side effect of ACE inhibitors. Because of this side effect, ACE inhibitors should not be administered with potassium-sparing diuretics.
Question 104.
A usually reliable interpreter called by the nurse to help communicate with a mother of a child who does not speak English and has brought her child in for a routine visit has yet to arrive in the clinic. The nurse has paged the interpreter several times. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Continue with the examination.
(b) Reschedule the infant’s appointment for later in the week.
(c) Ask the mother to stay longer in the hope that the interpreter arrives.
(d) Page the interpreter one more time.
Answer:
(b) Reschedule the infant’s appointment for later in the week.
Rationale:
The interpreter may have been delayed. Therefore, the nurse’s best action would be to reschedule the child’s appointment when the interpreter can be scheduled as well. Because the mother does not speak English, there is no point in examining the infant because history information is needed and most likely would be too difficult to obtain. Asking the mother to stay longer is rude to her. Also, doing so would probably be difficult because of the communication gap. If the interpreter is delayed, paging one more time will not help.
Question 105.
A client with angina shows the nurse the nitroglycerin tablets that the client carries in a plastic bag in a pocket. Where should the nurse teach the client to keep the nitroglycerin tablets?
(a) in the refrigerator
(b) in a cool, moist place
(c) in a dark container to shield from light
(d) in a plastic pill container where it is readily available
Answer:
(c) in a dark container to shield from light
Rationale:
Nitroglycerin in all dosage forms (sublingual, transdermal, or intravenous) should be shielded from light to prevent deterioration. The client should be instructed to keep the nitroglycerin in the dark container that is supplied by the pharmacy, and it should not be removed or placed in another container.
Question 106.
A client with a chronic mental illness who does not always take her medications is separated from her husband and receives public assistance funds. She lives with her mother and older sister and manages her own medication. The client’s mother is in poor health and also receives public assistance benefits. The client’s sister works outside the home, and the client’s father is dead. Which issue should the nurse address first?
(a) family support
(b) marital communication
(c) financial concerns
(d) medication compliance
Answer:
(d) medication compliance
Rationale:
Medication noncompliance is a primary cause of exacerbation in chronic mental illnesses. Of the issues listed, medications should be addressed first. Other issues, such as family, marriage, and finances, can be addressed as client stabilization is maintained.
Question 107.
A client is receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN). The nurse notices that the bag of TPN solution has been infusing for 24 hours but has 300 mL of solution left. What should the nurse do?
(a) Continue the infusion until the remaining 300 mL is infused.
(b) Change the filter on the tubing, and continue with the infusion.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP), and obtain prescriptions to alter the flow rate of the solution.
(d) Discontinue the current solution, change the tubing, and hang a new bag of TPN solution.
Answer:
(d) Discontinue the current solution, change the tubing, and hang a new bag of TPN solution.
Rationale:
IV fluids should not be infused for longer than 24 hours because of the risk of bacterial growth in the solution. The appropriate action for the nurse to take is to discontinue the current TPN solution, change the tubing, and hang a new bag of solution. Changing the filter does not decrease the risk of contamination. Notifying the HCP El fr a change in flow rate is not an acceptable solution.
Question 108.
The nurse should suspect that the client taking disulfiram has ingested alcohol when the client exhibits which symptom?
(a) sore throat and muscle aches
(b) nausea and flushing of the face and neck
(c) fever and muscle soreness
(d) bradycardia and vertigo
Answer:
(b) nausea and flushing of the face and neck
Rationale:
The client who drinks alcohol while taking disulfiram experiences sweating, flushing of the neck and face, tachycardia, hypotension, a throbbing headache, nausea and vomiting, palpitations, dyspnea, tremor, and weakness.
Question 109.
A client with a history of cardiac problems is having severe chest pain. What should be the nurse’s first response?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Administer an analgesic to control the pain.
(c) Assess the client’s pain.
(d) Start oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula.
Answer:
(c) Assess the client’s pain.
Rationale:
The nurse’s first response is to further assess the client’s pain. After a thorough assessment, additional appropriate actions may be to notify the HCP, administer an analgesic, and administer oxygen.
Question 110.
Which common characteristics should the nurse include in the teaching plan for a multiparous client after giving birth to a neonate diagnosed with Down Syndrome? Select all that apply.
(a) webbed neck
(b) small testes
(c) congenital heart defects
(d) polydactyly
(e) epicanthal folds
(f) hypotonia
Answer:
(a) webbed neck
(c) congenital heart defects
(e) epicanthal folds
(f) hypotonia
Rationale:
Down syndrome (trisomy 21) is an autosomal disorder. Characteristics include hypotonia, tongue protrusions, and epicanthal folds on the inner eye corner. Congenital heart defects occur in 40% to 60% of clients with Down syndrome. Other common characteristics include short stature, small head with flat profile, low set ears, Brushfield spots, excessive skin on the neck, broad hands with short fingers, and single palmar crease on the palm. Small testes and absence of sperm are associated with Klinefelter’s syndrome (47 chromosomes). Polydactyly is associated with trisomy.
Question 111.
A client calls the clinic and tells the nurse that she forgot to take her oral contraceptive this morning. What should the nurse tell the client to do?
(a) Take the medication immediately.
(b) Restart the medication in the morning.
(c) Use another form of contraception for 2 weeks.
(d) Take two pills tonight before bedtime.
Answer:
(a) Take the medication immediately.
Rationale:
The nurse should instruct the client to take the medication immediately or as soon as she remembers that she missed the medication. There is only a slight risk that the client will become pregnant when only one pill has been missed, so there is no need to use another form of contraception. However, if the client wishes to increase the chances of not getting pregnant, a condom can be used by the male partner. The client should not omit the missed pill and then restart the medication in the morning because there is a possibility that ovulation can occur, after which intercourse could result in pregnancy. Taking two pills is not necessary and also will result in putting the client off her schedule.
Question 112.
A client is being treated for acute low back pain. The nurse should report which of these clinical manifestations to the health care provider (HCP)
immediately?
(a) diffuse, aching sensation in the L4 to L5 area
(b) new onset of footdrop
(c) pain in the lower back when the leg is lifted
(d) pain in the lower back that radiates to the hip
Answer:
(b) new onset of footdrop
Rationale:
Neurologic symptoms, such as footdrop or bowel or bladder changes, should be reported to the HCP Q3 immediately. When musculoskeletal strain causes back pain, these symptoms may take 4 to 6 weeks to resolve. As an accompanying symptom of acute low back pain, the client may have a diffuse, aching sensation in the L4 to L5 area, pain in the lower back when the leg is lifted, or pain that radiates to the hip.
Question 113.
A client with type 1 diabetes mellitus asks the nurse about taking ginseng at home. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “There are no therapeutic benefits of ginseng.”
(b) “Taking ginseng will increase the risk of hypoglycemia.”
(c) “You can take the ginseng to help improve your memory.”
(d) “It’s ok to take ginseng if you take it with a carbohydrate.”
Answer:
(b) “Taking ginseng will increase the risk of hypoglycemia.”
Rationale:
Taking ginseng when on insulin is not encouraged because ginseng increases the risk of hypoglycemia. Ginseng can be therapeutic in certain situations but is potentially harmful for clients taking insulin. Taking ginseng with a carbohydrate will not offset the effect of the ginseng.
Question 114.
A client has had a central venous pressure line inserted. The nurse should immediately report which sign to the health care provider?
(a) sharp pain on the affected side
(b) urinary output of 50 mL/h
(c) heart rate of 88 bpm
(d) discomfort at the insertion site
Answer:
(a) sharp pain on the affected side
Rationale:
Sudden, sharp pain with breathing or coughing on the affected side, tachypnea, dyspnea, diminished or absent breath sounds on the affected side, tachycardia, anxiety, and restlessness indicate a pneumothorax, which can be a complication of inserting a central venous pressure line. The other findings are within normal limits.
Question 115.
The nurse is teaching the client with cirrhosis about taking lactulose. The nurse should tell the client that which type of bowel movement is an expected outcome of taking this drug?
(a) one regular bowel movement a day
(b) two to three soft stools per day
(c) four to five loose stools per day
(d) five to six loose stools per day
Answer:
(b) two to three soft stools per day
Rationale:
The expected effect of lactulose is for the client to have two to three soft stools a day to help reduce the pH and serum ammonia levels, which will prevent hepatic encephalopathy.
Question 116.
The nurse is evaluating the laboratory results of a client who was recently admitted to the hospital. Which result indicates the presence of inflammation?
(a) decreased sedimentation rate
(b) thrombocytopenia
(c) leukocytosis
(d) erythrocytosis
Answer:
(c) leukocytosis
Rationale:
Leukocytosis, an increased white blood cell count, indicates the presence of inflammation, infection, or a leukemia process. In inflammation and infection, the client's sedimentation rate is increased. Thrombocytopenia, a platelet deficiency, occurs in the client with leukemia, immunocompromised client, client with aplastic anemia, or client with other conditions. Erythrocytosis, an elevation of the red blood cell count, occurs in polycythemia vera.
Question 117.
The client sustained an open fracture of the femur from an automobile accident. The nurse should assess the client for which type of shock?
(a) cardiogenic
(b) hypovolemic
(c) neurogenic
(d) anaphylactic
Answer:
(b) hypovolemic
Rationale:
A fractured femur, especially an open fracture, can cause much soft tissue damage and lead to significant blood loss. Hypovolemic shock can develop. Cardiogenic shock occurs when cardiac output is decreased as a result of ineffective pumping. Neurogenic shock occurs as a result of an impaired autonomic nervous system function. Anaphylactic shock is the result of an allergic reaction.
Question 118.
The nurse assesses a teenage girl’s musculoskeletal system (see figure). What finding should the nurse document?

(a) normal posture
(b) kyphosis
(c) scoliosis
(d) lordosis
Answer:
(d) lordosis
Rationale:
This girl has an exaggeration of the lumbar spine, swayback, or lordosis. Kyphosis is an increased convexity or roundness of the curve of the thoracic spine. Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine.
Question 119.
A client with a broken ulna reports having pain in the casted arm that is unrelieved by pain medication. The nurse assesses the arm and notes that the fingers are swollen and difficult to separate. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer morphine 2 mg intravenously.
(b) Apply an ice bag to the fingers to relieve pain.
(c) Elevate the arm on two pillows and reassess in 30 minutes.
(d) Call the health care provider (HCP) to report swelling and pain.
Answer:
(d) Call the health care provider (HCP) to report swelling and pain.
Rationale:
The most appropriate action is to report the swelling, loss of mobility, and unrelieved pain to the HCP. These symptoms are indicators of neurovascular impairment. Administering opioids will not eliminate the cause of the problem, which is unrelieved pressure on nerves and blood supply. If prompt action (cutting the cast) is not taken to relieve the pressure, permanent muscular and neurologic injury may result.
Applying the ice bag would have been appropriate earlier to decrease or prevent swelling, but applying it at this time could actually lead to further decreased circulation. The arm should be elevated, but the nurse cannot wait 30 minutes to reassess the client without risking permanent damage.
Question 120.
A primiparous client develops uterine atony and postpartum hemorrhage 1 hour after a vaginal birth. The health care provider has prescribed IM dinoprost. After administration of the medication, the nurse should observe the client for which complication?
(a) tachycardia
(b) hypotension
(c) constipation
(d) abdominal distention
Answer:
(a) tachycardia
Rationale:
Dinoprost promotes uterine contractions, thereby minimizing uterine atony and subsequent hemorrhage. Possible side effects include nausea, tachycardia, hypertension, and diarrhea. Abdominal distention is not associated with the use of dinoprost.
Question 121.
A client is receiving morphine for postoperative pain. What should the nurse assess before administering the drug? Select all that apply.
(a) apical-radial heart rate
(b) urinary output
(c) mental status
(d) swelling in the feet
(e) pain level
Answer:
(b) urinary output
(c) mental status
(e) pain level
Rationale:
Prior to administering morphine the nurse should check the client’s pain level using a pain scale and assess the client for side effects of the drug. Morphine can cause a variety of side effects, including urinary retention and changes in mental status. The nurse should assess the client for urinary hesitancy or retention and note the urinary output. The nurse should also assess the client’s mental status because morphine can cause such effects as sedation, delirium, and disorientation. It is not necessary to assess the client for a change in the apical- radial heart rate or for pedal edema.
Question 122.
While caring for a mother and her 1-day-old neonate bom vaginally at 30 weeks’ gestation, the nurse explains about the neonate’s need for gavage feeding at this time instead of the mother’s plan for bottle-feeding. What should the nurse include as the rationale for this feeding plan?
(a) The neonate has difficulty coordinating sucking, swallowing, and breathing.
(b) A high-calorie formula, presently needed at this time, is more easily delivered via gavage.
(c) Gavage feedings can minimize the neonate’s increased risk of developing hypoglycemia.
(d) This type of feeding, easily given in the iso-lette, decreases the neonate’s risk of cold stress.
Answer:
(a) The neonate has difficulty coordinating sucking, swallowing, and breathing.
Rationale:
Before 32 weeks’ gestation, most neonates have difficulty coordinating sucking and swallowing reflexes along with breathing. Increased respiratory distress may occur with bottle-feeding. Bottle-feedings can be given after the neonate shows sucking and swallowing behaviors.
High-calorie for-mulas can be given by bottle or by gavage feeding. Although frequent feeding prevents hypoglycemia, the feeding does not have to be given via a gavage tube. Although these neonates can be stressed by cold, they can be kept warm with blankets while being bottle-fed or fed while in the warm isolette environment.
Question 123.
The nurse is giving preoperative instructions to a client who will have a reversal of a colostomy. What should the nurse prepare the client to expect during the immediate postoperative period? Select all that apply.
(a) nasogastric (NG) tube attached to low inter mittent suction
(b) administration of IV fluids
(c) daily measurement of abdominal girth
(d) calculation of intake and output every 8 hours
(e) assessment of vital signs every 6 hours
Answer:
(a) nasogastric (NG) tube attached to low inter mittent suction
(b) administration of IV fluids
(d) calculation of intake and output every 8 hours
Rationale:
After bowel surgery, an NG tube attached to low intermittent suction is used to remove gastric fluids. The amount of fluid from the NG tube suction is important because it contributes to the client’s overall fluid and electrolyte balance. IV fluids are used to maintain hydration, and intake and output is measured to determine hydration status. Postoperative vital signs are assessed more frequently than every 6 hours. Bowel sounds will be auscultated to determine when they return. Measuring abdominal girth is not necessary following colostomy reversal.
Question 124.
The nurse is teaching a client with rheumatoid arthritis about how to manage the fatigue associated with this disease. Which statement indicates the client understands how to manage the fatigue?
(a) “I sleep for 8 to 10 hours every night so that I’ll have the energy to care for my children during the day.”
(b) “I schedule afternoon rest periods for myself in addition to sleeping 10 hours every night.”
(c) “I spend one weekend day a week resting in bed while my husband cares for the children.”
(d) “I get up early in the morning and get all my household chores completed before my children wake up.”
Answer:
(b) “I schedule afternoon rest periods for myself in addition to sleeping 10 hours every night.”
Rationale:
Regularly scheduled rest periods during the day along with 8 to 10 hours of sleep at night helps relieve the fatigue, pain, and stiffness associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Even
with mild rheumatoid arthritis, the client may find it difficult to perform activities of daily living without some rest periods. Spending 1 day a week in bed to relieve fatigue does not adequately manage the disease.
The client must recognize the need for rest before feeling exhausted because overexertion can cause exacerbations. In addition, prolonged periods of inactivity can increase joint stiffness and pain. Getting up early to do household chores before the children are awake does not allow for adequate rest.
Question 125.
The nurse is caring for a child with hemophilia who is actively bleeding from the leg. What should the nurse apply to the site?
(a) direct pressure, checking every few minutes to see if the bleeding has stopped
(b) ice to the injured leg area several times a day
(c) direct pressure to the injured area continuously for 10 minutes
(d) ice bag with elevation of the leg twice a day
Answer:
(c) direct pressure to the injured area continuously for 10 minutes
Rationale:
For the child with hemophilia who is actively bleeding, the nurse should apply direct pressure to the injured area for 10 minutes continuously along with elevating the leg. The continuous application of direct pressure aids in stopping the bleeding. Elevating the leg reduces blood flow to the area, thereby minimizing the extent of blood loss. Although ice will cause local vasoconstriction and slow the bleeding, applying continuous direct pressure is essential.
Question 126.
When assessing for signs of a blood transfusion reaction in a client with dark skin, what sign should the nurse assess?
(a) hypertension
(b) diaphoresis
(c) polyuria
(d) warm skin
Answer:
(b) diaphoresis
Rationale:
The nurse should assess for signs of impending shock such as diaphoresis. The client would have hypotension, dysuria, and cool skin.
Question 127.
The nurse can assign an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) to which client? A client who:
(a) is 1 day postoperative following cranial surgery.
(b) has prostate cancer undergoing radiation implant seeding.
(c) had a newly created urinary diversion 3 days ago.
(d) was admitted to the hospital showing signs of progressive confusion.
Answer:
(c) had a newly created urinary diversion 3 days ago.
Rationale:
When delegating care, the nurse should consider the skill level of the UAP QJ and the needs of the client. The UAP is able to assist with activities of daily living and basic care activities. The client who had surgery to establish a urinary diversion 3 days ago is the most stable of the clients and can be assigned to the UAP for basic care.
The client with cranial surgery is 1 day postoperative and will require frequent neurological assessment; this client should be assigned to a registered nurse ty. The client with a radiation seeding is on radiation precautions and should be assigned to a registered nurse. The client showing signs of progressive confusion is the least stable and requires direct care by a nurse.
Question 128.
A client suspected of being a victim of abuse returns to the emergency department and, sobbing, tells the nurse, “I guess you really know that my husband beats me and that’s why I have bruises all over my body. I don’t know what to do. I am afraid he’ll kill me one of these times.” Which response best demonstrates that the nurse recognizes the client’s needs at this time?
(a) “The fear that your husband will kill you is unfounded.”
(b) “We can begin by discussing various options open to you.”
(c) “You can legally leave your husband because he has no right to hurt you.”
(d) “We can begin by listing ways to avoid making your husband angry with you.”
Answer:
(b) “We can begin by discussing various options open to you.”
Rationale:
The client’s return to the emergency department and her statement about not knowing what to do about being abused by her husband indicate that the client is asking for help. The nurse’s best course of action is to explain the various options available to her. This helps the client make decisions based on appropriate knowledge. Research reveals that women are more likely to be killed by partners than by strangers. Although the client can legally leave her husband, this answer provides the client with no safety options. Listing ways to avoid making the husband angry ignores the dynamics of abuse and blames the victim.
Question 129.
A client has been receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN) for the last 5 days. Before discontinuing the infusion, the infusion rate is slowed. What complication of TPN infusion should the nurse assess the client for as the infusion is discontinued?
(a) essential fatty acid deficiency
(b) dehydration
(c) rebound hypoglycemia
(d) malnutrition
Answer:
(a) essential fatty acid deficiency
Rationale:
When dextrose is abruptly discontinued, rebound hypoglycemia can occur. The nurse should assess the client for symptoms of hypoglycemia. Essential fatty acid deficiency is very unlikely to occur because some of these fatty acids are stored. Preventing dehydration or malnutrition is not the reason for tapering the infusion rate; the client’s hydration and nutritional status and ability to maintain adequate intake must be established before TPN is discontinued.
Question 130.
A client has just returned from surgery for a gastrectomy. The nurse should position the client in which position?
(a) prone
(b) supine
(c) low Fowler’s
(d) right or left Sims’
Answer:
(c) low Fowler’s
Rationale:
The nurse places a postoperative client who has had abdominal surgery in low Fowler’s position. This position relaxes abdominal muscles and promotes maximum respiratory and cardiovascular function.
Question 131.
A child with heart disease starts on oral digoxin. When preparing to administer the medication, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Check the last serum electrolyte results for the child.
(b) Verify the dosage with the pharmacist.
(c) Ask the mother if she is willing to administer the medication.
(d) Teach the mother how to measure the child’s heart rate.
Answer:
(a) Check the last serum electrolyte results for the child.
Rationale:
It is most important to know the child’s serum potassium level when administering digoxin. Digoxin increases contractility of the heart and increases renal perfusion, resulting in a diuretic effect with increased loss of potassium and sodium. Hypokalemia increases the risk of digoxin toxicity. Verifying the dosage is specified by facility policy and varies among facilities.
Although the child may take the medication better from the mother than from the nurse, asking the mother to give the medication is not necessary. In addition, this would be done after the nurse has checked the electrolyte levels. Teaching the parent how to measure the child’s heart rate can be done at any time, not necessarily when preparing to give digoxin.
Question 132.
A client with diabetes has been diagnosed with hypertension, and the health care provider has prescribed atenolol, a beta-blocker. When teaching the client about the drug, what should the nurse tell the client about how it may interact with the client’s diabetes?
Atenolol may cause:
(a) a decrease in the hypoglycemic effects of insulin.
(b) an increase in the hypoglycemic effects of insulin.
(c) an increase in the incidence of ketoacidosis.
(d) a decrease in the incidence of ketoacidosis.
Answer:
(b) an increase in the hypoglycemic effects of insulin.
Rationale:
There is a direct interaction between the effects of insulin and those of beta-blockers. The nurse must be aware that there is a potential for increased hypoglycemic effects of insulin when a beta-blocker is added to the client’s medication regimen. The client’s blood sugar should be monitored. Ketoacidosis occurs in hyperglycemia. Although a decrease in the incidence of ketoacidosis could occur when a beta-blocker is added, the direct result is an increase in the hypoglycemic effect of insulin.
Question 133.
The nurse is caring for a client who has deep partial-thickness and full-thickness burns. During the emergent (resuscitative) phase of burn management, the nurse should assess the client for a fluid shift from the:
(a) intracellular to extracellular compartment.
(b) extracellular to intravascular compartment.
(c) interstitial to the intracellular compartment.
(d) intravascular to the interstitial compartment.
Answer:
(d) intravascular to the interstitial compartment.
Rationale:
During the emergent phase of burn management, there is a massive shift of fluid from the blood vessels (intravascular compartment) into the tissues (interstitial compartment). The result of this shift is hypovolemic shock and edema formation. The fluid shift is caused by increased capillary per-meability that allows water, sodium, and protein to shift to the tissues. As the emergent period ends and capillary permeability returns to normal, the fluid in the interstitial compartment will return to the intravascular compartment.
Question 134.
The nurse is caring for an elderly client who has experienced a sensorineural hearing loss. The nurse anticipates that the client will exhibit which symptom?
(a) difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds
(b) problems with speaking clearly
(c) inability to assign meaning to sound
(d) vertigo when changing positions
Answer:
(a) difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds
Rationale:
The client with sensorineural hearing loss has difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds. Aging and ototoxicity are two causes of sensorineural hearing loss. The client’s ability to speak is not affected. The client who cannot assign meaning to sound has central hearing loss. Vertigo is commonly an indication of an inner ear problem
Question 135.
The nurse is evaluating the effectiveness of fluid resuscitation during the emergency period of burn management. Which finding indicates that adequate fluid replacement has been achieved?
(a) The body weight has increased.
(b) The fluid intake is less than urinary output.
(c) The urine output is >35 mL/h.
(d) The blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg.
Answer:
(c) The urine output is >35 mL/h.
Rationale:
A urine output of 30 to 50 mL/h indicates adequate fluid replacement in the client with burns. An increase in body weight may indicate fluid retention. A urine output greater than fluid intake does not represent a fluid balance. Depending on the client, blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg could indicate the presence of a hypovolemic state; by itself, it does not indicate adequate fluid replacement.
Question 136.
The parent of a child who is taking an antibiotic for bilateral otitis media tells the nurse that he has stopped the medicine since the child is better and is saving the rest of the medication to use the next time the child gets sick. What should the nurse tell the parent?
(a) “It’s important to give the medicine as prescribed.”
(b) “How do you know your child’s ears are cured?”
(c) “Your child needs all of the medicine so that the infection clears.”
(d) “Stopping the medicine will make the next ear infection harder to treat.”
Answer:
(c) “Your child needs all of the medicine so that the infection clears.”
Rationale:
Commonly, when a child appears better, the parents stop the medication. Unfortunately, the infection remains. Therefore, the nurse needs to explain that all of the medication must be administered to clear up the infection. Explaining why the medicine should be continued is more helpful to parents than saying it needs to be given. Telling the parent that stopping the medication will make the next ear infection harder to treat does not focus on the present issue.
Question 137.
A client who comes to the emergency department with multiple bruises on her face and arms, a black eye, and a broken nose says that these injuries occurred when she fell down the stairs. The nurse suspects that the client may have been physically assaulted. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Ask the client directly about the possibility of physical abuse.
(b) Tell the client that it is difficult to believe that such injuries resulted from a fall.
(c) Ask the client what she did to make someone beat her so badly.
(d) Discuss with the client what she can do to deescalate the situation next time.
Answer:
(a) Ask the client directly about the possibility of physical abuse.
Rationale:
Many clients who experience abuse are hesitant to talk about it and need help to do so. The nurse should ask the client directly about abuse when it is suspected, using a sensitive, empathetic, and compassionate approach. In this way, the client can feel comfortable revealing information about the abuse. Telling the client that it is difficult to believe her injuries resulted from a fall is not helpful because it is blameful and puts the client on the defensive. Asking the client what she did to make someone hit her or discussing what she can do the next time blames and alienates the client.
Question 138.
A client has blood loss following an automobile accident. The blood pressure on admission to the emergency department is 80/40 mm Hg. What is the primary goal for the care of the client at this time?
(a) Achieve adequate tissue perfusion.
(b) Preserve renal function.
(c) Prevent hypostatic pneumonia.
(d) Maintain adequate vascular tone.
Answer:
(a) Achieve adequate tissue perfusion.
Rationale:
A primary outcome for the care of the client in shock is to achieve adequate tissue perfusion, thus avoiding multiple organ dysfunction. The lungs are susceptible to injury, especially acute respiratory distress syndrome. Vasoconstriction occurs as a compensatory mechanism until the client enters the irreversible stage of shock.
Question 139.
A client with emphysema has been admitted to the hospital. The nurse should assess the client further for which symptom?
(a) frequent coughing
(b) bronchospasms
(c) underweight appearance
(d) copious sputum
Answer:
(c) underweight appearance
Rationale:
The client with emphysema is commonly underweight in appearance. The weight loss may be caused by the increased energy required to support the work of breathing. Frequent coughing, broncho- spasms, and copious sputum are clinical manifestations of chronic bronchitis.
Question 140.
The parent of a young child diagnosed with low-dose lead exposure asks about long-term effects. Which conditions should the nurse mention as possible long-term effects to this parent? Select all that apply.
(a) seizures
(b) depression
(c) hyperactivity
(d) aggression
(e) impulsiveness
Answer:
(c) hyperactivity
(d) aggression
(e) impulsiveness
Rationale:
The neurologic system can be affected and cause long-term consequences in a young child exposed to lead. Common behavioral effects include hyperactivity, impulsivity, and aggression. Seizures may occur in a child with high-dose lead exposure. Depression is not usually associated with lead exposure.
Question 141.
A nurse has made a medication error. Which information is appropriate to include in the incident report?
(a) an interpretation of the likely cause of the incident
(b) what the nurse saw and did
(c) the client’s statement about the incident that occurred
(d) the extenuating circumstances involved in the situation
Answer:
(b) what the nurse saw and did
Rationale:
The incident report includes only what the nurse saw and did the objective data. The nurse does not try to interpret the likely cause of the incident, include statements from the client about the incident, or comment on extenuating circumstances.
Question 142.
The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for a client who is being discharged after being admitted for chest pain. The client has had one previous myocardial infarction 2 years ago and has been taking simvastatin 40 mg for the last 2 years. After reviewing the lab results for the client’s cholesterol levels (see chart), what should the nurse do?
|
Test |
Result |
Units |
Refrence Range |
|
Cholestrol total |
19.5(5.05) |
Mg/Dl(mmol/L) |
< 200 (<5.18) |
|
Triglycerides |
106(1.20) |
Mg/Dl(mmoL) |
<150 (<1.69) |
|
HDL-cholestrol |
69(1.79) |
Mg/Dl(mmoL) |
>39(<1.03) |
(a) Ask if the client is taking the simvastatin regularly.
(b) Tell the client that the cholesterol levels are within normal limits.
(c) Instruct the client to lower the saturated fat in the diet.
(d) Review the chart for lab reports of hemoglobin and hematocrit.
Answer:
(b) Tell the client that the cholesterol levels are within normal limits.
Rationale:
The serum cholesterol is within normal range for this client, indicating the medication is effective. Since the cholesterol levels are within normal limits, it is likely that the client is taking the medication, and asking may indicate the nurse has doubts or mistrusts that the client is taking the medication. The client does not need to change the diet at this point. Hemoglobin and hematocrit are not affected by simvastatin; since liver damage is a side effect of simvastatin, the nurse could review the liver function studies.
Question 143.
The client is to have a gastrectomy. The surgeon will use a transverse incision. Prior to surgery, the nurse is checking to be sure the correct site has been marked. Identify the site the client should have marked.
Answer:
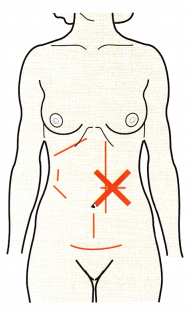
Rationale:
The area on the abdomen where the transverse incision will be made should be marked by the surgeon.
Question 144.
A homeless client is brought to the emergency department by the police after being found unconscious on the street. Following examination and evaluation of laboratory test results, a diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis is confirmed. Which information is most crucial to document on the client’s medical record? Select all that apply.
(a) size of pupils and reaction of pupils to light
(b) response to verbal and painful stimuli
(c) skin condition and presence of any rashes, lesions, or ulcers
(d) blood pressure
(e) length of time the client has had diabetes
(f) hourly urine output
Answer:
(a) size of pupils and reaction of pupils to light
(b) response to verbal and painful stimuli
(c) skin condition and presence of any rashes, lesions, or ulcers
(d) blood pressure
(f) hourly urine output
Rationale:
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a potentially life-threatening problem. The state of unconsciousness requires very astute monitoring of the neurologic condition. Frequent assessments of neurologic status (including the client’s ability to respond to stimuli), blood pressure, and urinary output need to be documented. Assessment of skin condition for the presence of lesions, bruises, ulcers, or bumps is documented to assess for possible injuries, such as falls associated with head injury or internal injuries. Although it would be helpful to know how long the client has had diabetes, this information is not essential to document.
Question 145.
The nurse is reconciling the medications with a client who is being discharged. Which information indicates there is a “discrepancy”?
(a) There is agreement between the client’s home medication list and current medication prescriptions.
(b) There is justification for a difference in the medication prescriptions.
(c) There is lack of congruence between a client’s home medication list and current medication prescriptions.
(d) Sample medications have been included in the medication list.
Answer:
(c) There is lack of congruence between a client’s home medication list and current medication prescriptions.
Rationale:
The medications prescribed for, administered to, or dispensed to the client while under the care of a health care organization are compared to those on the list, and any discrepancies (e.g., omissions, duplications, potential interactions) are resolved. A complete list of the client’s medications is communicated to the next provider of service when a client is referred or transferred to another setting, service, practitioner, or level of care within or outside the organization.
The complete, accurate list of medications is also provided to the client on discharge from the organization. The next provider of service checks the Medication Reconciliation List again to make sure it is accurate and in concert with any new medications to be prescribed.
Question 146.
The health care provider (HCP) has determined that a primigravid client in active labor requires a cesarean birth because of cephalopelvic disproportion. After the birth of a healthy neonate, which assessment should the nurse make first?
(a) nasopharyngeal secretions
(b) high-pitched cry
(c) skull fracture
(d) decreased muscle tone
Answer:
(a) nasopharyngeal secretions
Rationale:
A neonate born by cesarean birth has not had the benefit of the chest-squeezing action of a vaginal birth, which helps remove some of the nasopharyngeal secretions. The nurse should place the neonate under the radiant warmer and suction the mouth and nares with a bulb syringe to remove nasopharyngeal secretions. A high-pitched cry is associated with neurologic involvement or neonatal drug withdrawal and is unrelated to cesarean birth. Skull fractures may occur with difficult vaginal births and are not typically seen with cesarean births. Decreased muscle tone is associated with oversedation, neurologic impairment, or use of general anesthesia.
Question 147.
An older adult’s daughter is asking about the follow-up evaluation for her father after his pneumonectomy for primary lung cancer. What should the nurse tell the daughter?
(a) “The usual follow-up is chest X-ray and liver function tests every 3 months.”
(b) “The follow-up for your father will be a chest X-ray and a computed tomography scan of the abdomen every year.”
(c) “No follow-up is needed at this time.”
(d) “The follow-up for your father will be a chest X-ray every 6 months.”
Answer:
(d) “The follow-up for your father will be a chest X-ray every 6 months.”
Rationale:
Follow-up generally involves semiannual chest radiographs. Recurrence usually occurs locally in the lungs and may be identified on chest radiographs. Follow-up after cancer treatment is an important component of the treatment plan. Serum markers (liver function tests) have not been shown to detect recurrence of lung cancer. There are no data to support the need for an abdominal computed tomography scan.
Question 148.
A parent of a toddler brings the child to the emergency department because the child has accidentally been scalded by hot water spilling from the stove. In order to differentiate the burn from potential abuse, the nurse should first assess the child:
(a) on the back of the body.
(b) on the front of the body.
(c) for circular patterns.
(d) on the buttocks.
Answer:
(b) on the front of the body.
Rationale:
Accidental scaldings are usually splash related and occur on the front of the body. Any burns on the back of the body or in a well-defined circular or glove pattern may indicate physical abuse. Immersion burns on the buttocks are also suspicious injuries.
Question 149.
A 17-year-old client visits the clinic at 36 weeks’ gestation. The client’s blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg. On previous visits, her blood pressure ranged from 100 to 110 mm Hg systolic and 70 to 80 mm Hg diastolic. Further assess-ment reveals slight edema of her hands and 1 + proteinuria. The nurse anticipates that the health care provider will most likely prescribe which treatment?
(a) IV magnesium sulfate
(b) labetalol
(c) bed rest with bathroom privileges
(d) hourly blood pressure checks
Answer:
(c) bed rest with bathroom privileges
Rationale:
A client exhibiting mild preeclampsia is initially treated with activity restriction. Bed rest, or lying on the left side, decreases pressure on the vena cava and improves circulatory blood flow. Restriction of visitors and a quiet environment are also necessary. IV magnesium sulfate, a central nervous system depressant, is usually prescribed for the client with severe preeclampsia.
Labetalol is used for the client with severe preeclampsia. Frequent monitoring of the client’s blood pressure is important. However, hourly blood pressure checks are more routinely prescribed for the client with severe preeclampsia. Additionally, the client needs to rest, and checking her blood pressure hourly could interfere with her ability to rest.
Question 150.
A female client who is 32 years of age has been diagnosed with stage 1 hypertension. The client’s height is 5 feet 5 inches (165 cm), and her weight is recorded as 125 pounds (56.6 kg); she reports that she frequently eats at “fast-food” restaurants and enjoys a glass of wine to relax on week-ends. In developing a teaching plan for this client, the nurse should address which topic?
(a) potential use of nitroprusside
(b) adverse effects of alcohol
(c) decreasing dietary caloric intake
(d) low-sodium food choices
Answer:
(d) low-sodium food choices
Rationale:
Lifestyle modification to lower blood pressure includes weight reduction in clients who are overweight, reducing the intake of dietary sodium, and an increase in physical activity. Client teaching involves instruction on low-sodium diet and foods because of the propensity for high-sodium foods at fast-food restaurants. The client is of a normal weight, and alcohol intake is in moderation. Nitroprusside is a treatment for hypertensive crisis.
Question 151.
The nurse observes that an area in the mouth of a child with leukemia is bleeding. Which item should the nurse use to promote homeostasis over the lesion?
(a) karaya gum
(b) a cotton ball imbedded with petroleum jelly
(c) a nonsticking gauze sponge
(d) a dry tea bag
Answer:
(d) a dry tea bag
Rationale:
A dry tea bag placed on the bleeding area can be effective to control bleeding from lesions on the oral mucosa. The tannic acid in the tea apparently helps control bleeding.
Question 152.
A client with a fractured leg has been instructed to ambulate without weight bearing on the affected leg. The nurse evaluates that the client is ambulating correctly if the client uses which crutch-walking gait?
(a) two-point gait
(b) four-point gait
(c) three-point gait
(d) swing-to gait
Answer:
(c) three-point gait
Rationale:
The three-point gait, in which the client advances the crutches and the affected leg at the same time while weight is supported on the unaffected extremity, is the appropriate gait of choice. This allows for non-weight bearing on the affected extremity. The two-point, four-point, and swing- to gaits require some weight bearing on both legs, which is contraindicated for this client.
Question 153.
Which is appropriate for the nurse to include in a plan for the prevention of pressure ulcers?
(a) daily skin cleaning with soap and hot water
(b) gentle massage of bony prominences every shift
(c) encouraging the client to sit up as much as possible
(d) systematic skin assessment at least once per shift
Answer:
(d) systematic skin assessment at least once per shift
Rationale:
The best treatment for a pressure ulcer is prevention. If a client has been determined to be at risk for developing a pressure ulcer, a systematic skin assessment should be conducted at least once per shift. Other preventive measures include daily gentle cleaning of the skin and avoiding harsh soaps and hot water, which are damaging to the skin. Massage of bony prominences is not done because it can increase damage to the underlying tissue. The client should be encouraged to change position at least every 2 hours to avoid pressure on any one area for a prolonged period.
Question 154.
A client at 36 weeks’ gestation tells the nurse, “I’ve been having a lot of backaches lately.” After giving instructions about how to decrease the backaches, the nurse determines that the client needs further instruction when she makes which statement?
(a) “I should walk with my pelvis tilted backward.”
(b) “I may need to put a board under my mattress.”
(c) “I should squat and not bend to pick up objects.”
(d) “I should wear flat or low-heeled shoes.”
Answer:
(a) “I should walk with my pelvis tilted backward.”
Rationale:
The client needs further instructions when she says “I should walk with my pelvis tilted backward.” Walking in this position puts greater strain on the back. The client should walk with her pelvis tilted forward. Pelvic tilt exercises can also help the client with backaches.
Putting a board under the mattress makes the mattress firmer and provides more support. Squatting and not bending to pick up objects helps decrease back strain. Squatting involves the use of the large thigh muscles rather than those of the back. Flat or low-heeled shoes provide better balance and greater support and can help decrease backaches.
Question 155.
The nurse is assessing a young adult who thinks he has a sexually transmitted disease. When obtaining a health history, the nurse should ask the client if he is experiencing which symptom?
(a) impotence
(b) scrotal pain
(c) penile lesion
(d) urethral discharge
Answer:
(d) urethral discharge
Rationale:
Urethritis is usually the initial clinical manifestation of gonorrhea in men. The symptoms include a profuse, purulent discharge and dysuria. Complications are uncommon, but they include prostatitis and sterility. Impotence, scrotal pain, and penile lesions are not associated with gonorrhea.
Question 156.
A client’s blood pressure is elevated at 160/90 mm Hg. The health care provider prescribed “cloni- dine 1 mg by mouth now.” The nurse sent the prescription to pharmacy at 0710, but the medication still has not arrived at 0800. What should the nurse do next? Select all that apply.
(a) Check all appropriate places on the unit to which the drug could have been delivered.
(b) Check the client’s blood pressure.
(c) Call the pharmacy.
(d) Go to the pharmacy to obtain the drug.
(e) Use a pill from another client’s box who is taking the same medication.
Answer:
(a) Check all appropriate places on the unit to which the drug could have been delivered.
(b) Check the client’s blood pressure.
(c) Call the pharmacy.
Rationale:
The nurse should first check to see if the medication has been misplaced, check the client’s blood pressure to determine the immediacy of administering the drug, and then call the phar-macy to check that the medication was delivered. Although the nurse needs to obtain and administer the medication as soon as possible, it is inappropriate for the nurse to go to the pharmacy and request the drug without first calling the pharmacy. The nurse should not use another client’s medication.
Question 157.
The client with major depression states, “I’m too tired to get out of bed to go to group therapy. I just want to rest.” What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “Perhaps you’ll feel better later on.”
(b) “I’ll let you rest for as long as you need.”
(c) “Attending group therapy is an important part of your treatment plan.”
(d) “You’ve been in bed long enough and need to get up.”
Answer:
(c) “Attending group therapy is an important part of your treatment plan.”
Rationale:
The client with major depression suffers from lack of energy and withdrawal. The nurse should emphasize the importance of group involvement for the client to gain support from others and to see that others have similar problems and con-cerns. Attendance at group sessions and activities decreases social isolation and destructive rumination. The other statements are not therapeutic and interfere with increasing the client’s involvement with others.
Question 158.
After teaching the mother of a 7-month-old diagnosed with bronchiolitis, the nurse determines that the teaching has been effective when the mother states she will immediately report which sign or symptom?
(a) seven wet diapers a day
(b) temperature of 100°F (37.8°C) for 2 days
(c) clear nasal discharge for longer than 2 days
(d) longer periods of sleep than usual
Answer:
(d) longer periods of sleep than usual
Rationale:
An infant’s sleeping longer than usual can indicate that the child is expending too much energy to breathe and is tiring, suggesting that the child’s condition is getting worse. This should be reported to the health care provider (HCP).
Question 159.
A 4-year-old who weighs 40 lbs (18 kg] is brought to the emergency department with sudden onset of a temperature of 103°F (39.4°C), sore throat, and refusal to drink. The child will not lie down and prefers to lean forward while sitting up. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Give 600 mg of acetaminophen rectally, as prescribed.
(b) Inspect the child’s throat for redness and swelling.
(c) Have equipment to secure the airway available.
(d) Obtain a specimen for a throat culture.
Answer:
(c) Have equipment to secure the airway available.
Rationale:
The child is exhibiting signs and symptoms of possible epiglottitis. As a result, the child is at high risk for laryngospasm and airway occlusion. Therefore, the nurse should have intubation equipment and tracheostomy tube and setup readily available should the child experience an airway occlusion. Although acetaminophen is an antipyretic, the dosage of 600 mg to be administered rectally is too high.
A typical 4-year-old weighs approximately 40 lb (18 kg). The recommended dose is 125 mg. When any type of respiratory illness, and especially epiglottitis, is suspected, putting any object, including a tongue depressor for inspection or a cotton-tipped applicator to obtain a throat culture, in the back of the mouth or throat or having the child open the mouth is inappropriate because doing so may predispose the child to laryngospasm or occlusion of the airway by a swollen epiglottis.
Question 160.
Which client would benefit from the application of warm moist heat?
(a) a client with appendicitis
(b) a client with a recently sprained joint
(c) a client with a suspected malignancy
(d) a client with low back pain
Answer:
(d) a client with low back pain
Rationale:
Direct application of warm moist heat would benefit a client with low back pain because the heat relaxes muscle spasms. Heat should not be applied to a client who has appendicitis because it can lead to rupture of the appendix and peritonitis. Ice is applied to recently sprained joints to help decrease edema. Applying heat to the area of a suspected malignancy can increase blood flow to the tumor and promote nourishment of the cancer cells.
Question 161.
A client is newly diagnosed with pernicious anemia. The nurse is teaching the client to increase the vitamin B12 intake. Which is the most effective way for this client to increase vitamin B12 intake?
(a) increasing dietary intake of vitamin B12
(b) taking an oral vitamin B12 replacement
(c) taking vitamin B12 injections or nasal spray replacement
(d) using chelation therapy
Answer:
(c) taking vitamin B12 injections or nasal spray replacement
Rationale:
The client with pernicious anemia will require lifelong supplementation of vitamin B12, available through injection or nasal spray administration. It must be given in these forms to ensure absorption. Oral vitamin B12, would not be absorbed because the client lacks the intrinsic factor in the stomach necessary for absorption. Chelation therapy is used to extract metals at toxic levels such as in lead poisoning.
Question 162.
The nurse has received a prescription to add 20 mEq of potassium chloride to a 1,000-mL bottle of IV fluid. The nurse has a 30-mL, multiple-dose vial of potassium chloride. The label reads 2 mEq/ mL. How many milliliters should the nurse add to the IV fluid? Record your answer using a whole number.
................................ mL.
Answer:
10mL
Rationale:
10mL, To administer 20 mEq of potassium chloride, the nurse needs to administer 10 mL. The following formula is used to calculate the correct dosage:
20 mEq / X mL = 2 mEq / lmL X = lOnL
Question 163.
A client with major depression and suicidal ideation is suddenly calmer and more energetic. Which conclusion should the nurse reach?
(a) The client is improving.
(b) The client’s medication dosage is too high.
(c) The client is overstimulated.
(d) The client is suicidal.
Answer:
(d) The client is suicidal.
Rationale:
When a client with major depression and suicidal ideation displays a sudden elevation in mood, seems calmer, has more energy, and is more peaceful, the nurse should judge these behaviors as an indication that a suicide attempt is imminent. These symptoms may indicate relief from ambivalent thoughts about suicide and that the client has an immediate plan for killing himself.
Question 164.
A multigravid client at 38 weeks’ gestation is scheduled to undergo a contraction stress test. What should the nurse include in the explanation as the purpose of this test?
(a) evaluation of fetal lung maturity
(b) determination of the fetal biophysical profile
(c) assessment of fetal ability to tolerate labor
(d) determination of fetal response during movements
Answer:
(c) assessment of fetal ability to tolerate labor
Rationale:
The purpose of a contraction stress test is to determine fetal response during labor. If late decelerations are noted with the contractions, the test is considered positive or abnormal. Fetal lung maturity is evaluated through amniocentesis to obtain the lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio. The nonstress test is part of the biophysical profile. Determining fetal response during movements is evaluated as part of the nonstress test.
Question 165.
The nurse is caring for a client who has been diagnosed with atypical pneumonia. The nurse should assess this client carefully for which symptom?
(a) high fever
(b) tachypnea
(c) dry cough
(d) severe chills
Answer:
(c) dry cough
Rationale:
Atypical pneumonia is characterized by a gradual onset of symptoms, such as dry cough, headache, sore throat, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. Typical pneumonia is characterized by tachypnea, fever, chills, and productive cough with purulent sputum.
Question 166.
The nurse is teaching a client with emphysema how to do pursed-lip breathing. What is the expected outcome of using pursed-lip breathing?
(a) increased oxygenation
(b) prolonged exhalation
(c) increase exercise tolerance
(d) relief from shortness of breath
Answer:
(b) prolonged exhalation
Rationale:
The primary reason for instructing the client with emphysema about how to pursed-lip breathe is to prolong exhalation. Prolonging exhalation helps to prevent bronchiolar collapse and the trapping of air. It does not directly prevent respiratory infection. Because pursed-lip breathing affects the expiratory phase of the respiratory cycle, it does not affect oxygenation. It may decrease shortness of breath, but this is not the primary reason for the technique.
Question 167.
A nursing unit is using an automated medication dispensing system to track dispensing narcotics. What is the advantage of using an automated medication dispensing system?
(a) It facilitates the change-of-shift count of narcotics.
(b) It keeps a record of narcotic usage.
(c) It allows nurses unmonitored access to narcotics.
(d) It cancels the charges for narcotics.
Answer:
(b) It keeps a record of narcotic usage.
Rationale:
The primary purpose of the automated dispensing machine for nurses is to keep an up-to-date record of the narcotic usage and count. The automated dispensing machine has eliminated the need for change-of-shift counts for narcotics. It does not include unmonitored access by nurses to narcotics, which would not be considered an advantage. The pharmacy has direct information about the narcotics being used on the client at what intervals and by whom, and it automatically records the charges of narcotics used. Not recording the charges would not be an advantage.
Question 168.
Immediately following an automobile accident, a 21-year-old client has severe pain in the right chest from hitting the steering wheel and a compound fracture of the right tibia and fibula and multiple lacerations and contusions. What is the priority nursing goal for this client?
(a) Reduce the client’s anxiety.
(b) Maintain adequate oxygenation.
(c) Decrease chest pain.
(d) Maintain adequate circulating volume.
Answer:
(b) Maintain adequate oxygenation.
Rationale:
Blunt chest trauma can lead to respiratory failure. Maintenance of adequate oxygenation is the priority for the client. Decreasing the client’s anxiety is related to maintaining effective respirations and oxygenation. Although pain is distressing to the client and can increase anxiety and decrease respiratory effectiveness, pain control is secondary to maintaining oxygenation, as is maintaining adequate circulatory volume.
Question 169.
While assessing a primiparous client 8 hours after birth, the nurse inspects the episiotomy site, finding it edematous and slightly reddened. Which interpretation by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) The client needs application of an ice pack.
(b) The episiotomy site is infected.
(c) A hematoma will likely develop.
(d) The client has had a repair of a vaginal laceration.
Answer:
(a) The client needs application of an ice pack.
Rationale:
An episiotomy that is edematous and slightly reddened 8 hours after birth is normal. Therefore, the nurse should offer the client an ice pack to provide some relief from the perineal pain for the first 24 hours. An infection is present if greenish, purulent drainage is observed from the site. The edema and discoloration of the episiotomy at this time after birth are normal and do not indicate that a hematoma is likely to develop. A laceration when repaired should appear intact with edges well approximated, clean, and dry.
Question 170.
When administering an IM injection, when should the nurse use the Z-track technique? when the medication:
(a) has a long absorption time
(b) takes effect very quickly
(c) is irritating to tissues
(d) has a viscous consistency
Answer:
(c) is irritating to tissues
Rationale:
The Z-track technique is used with medications that are irritating to tissues. It allows the medication to be trapped in the muscle and prevents it from leaking back through the tissues.
Question 171.
The mental health unit provides a unit landline for clients to use for telephone calls. A client with bipolar disorder is monopolizing the use of the telephone by making several calls each day, interfering with the ability of other clients to use the telephone. What should the nurse do?
(a) Allow the client to use a personal cell phone for calls.
(b) Limit the amount of calls the client can make each day.
(c) Remind the client that others need to use the telephone.
(d) Take away the client’s telephone privileges.
Answer:
(b) Limit the amount of calls the client can make each day.
Rationale:
The nurse should limit the amount of telephone calls the client can make. Setting limits for a client with bipolar disorder, mania, helps to control the hyperactive client who has excessive goal- directed activity, especially when it interferes with the rights of other clients. Giving the client access to his cell phone rewards the behavior.
Reminding the client that others need to use the telephone will probably be futile because the client with mania is experiencing cognitive impairment and needs to be active. Taking away the client’s telephone privileges is not the best action because the client has a right to use the telephone. The nurse is responsible for helping the client manage behavior by setting constructive limits.
Question 172.
When preparing a 20-month-old for removal of a foreign body in the nasal passage by die health care provider, the nurse should use which method of restraint?
(a) jacket restraint
(b) elbow restraint
(c) use of father to hold
(d) papoose board
Answer:
(d) papoose board
Rationale:
Because a toddler is strong and moves frequently, the child needs to be restrained during the removal procedure by a total body restraint. To protect the child, the papoose board is best because the arms, legs, chest, and head can be fully restrained. A jacket restraint would immobilize only the child’s upper body. Elbow restraints would immobilize only the child’s arms. The father should be available to provide comfort before and after the procedure but not to hold the child down during the procedure.
Question 173.
The nurse auscultates the lungs of a client who has been diagnosed with a tumor in the lung and notes wheezing over one lung. What additional assessment should the nurse make?
(a) the presence of exudate in the airways
(b) the client’s history of smoking
(c) an indication of pleural effusion
(d) obstruction of the airway
Answer:
(d) obstruction of the airway
Rationale:
Wheezing over one lung in the presence of a lung tumor is most likely caused by obstruction of the airway by a tumor. Exudate would be more likely to cause crackles. The client’s history of smoking would not cause unilateral wheezing. Pleural effusion would produce diminished or absent breath sounds.
Question 174.
A client is to have an insertion of a peripheral venous access device (VADj. After explaining the procedure to the client, the nurse will perform the steps from first to last in which order?
(a) Apply the tourniquet and select a vein for inserting the VAD.
(b) Apply clean gloves and cleanse the insertion site with an antiseptic swab.
(c) Insert the VAD with the bevel up at a 10- to 30-degree angle.
(d) Observe for blood return in the flashback chamber.
Answer:
(a) Apply the tourniquet and select a vein for inserting the VAD.
(b) Apply clean gloves and cleanse the insertion site with an antiseptic swab.
(c) Insert the VAD with the bevel up at a 10- to 30-degree angle.
(d) Observe for blood return in the flashback chamber.
Rationale:
The nurse should first apply the tourniquet and then select a vein for inserting the VAD. The tourniquet slows the venous return and allows the nurse to identify an appropriate vein. The nurse should then put on clean gloves and cleanse the insertion site with antiseptic swab.
The nurse may wear gloves while applying a tourniquet, but the insertion site must be cleansed immediately prior to the insertion of the VAD. Next, the nurse should insert the VAD with the bevel up at a 10- to 30-degree angle. These steps must be performed in order to ensure proper placement and prevent infection and are completed prior to observing for blood return or securing the device with a clear adhesive dressing.
Question 175.
A nurse receives a report of a subtherapeutic lithium level on a client who has previously had normal drug levels. What hypothesis does the nurse make about the lithium level?
(a) Lithium levels are often low in clients with recent gastrointestinal illnesses.
(b) Doses may need to be increased as clients develop tolerance to lithium.
(c) Nonadherence to lithium therapy is a major problem when treating bipolar disorder.
(d) The client’s disease has significantly worsened, requiring higher lithium doses.
Answer:
(c) Nonadherence to lithium therapy is a major problem when treating bipolar disorder.
Rationale:
One of the most serious problems in mental health is nonadherance with medication therapy. In clients with a previous history of therapeutic lithium levels, the nurse should assess if the client is taking the medication as prescribed. Loss of sodium during gastrointestinal illnesses can lead to lithium toxicity. Tolerance is not a complication of lithium. While a client would manifest increased bipolar symptoms with low lithium levels, worsening of the disease would not cause the levels to drop.
Question 176.
A child with 20% second- and third-degree burns is admitted to the burn center. The child weighs 44 lbs (20 kg). The nurse has started an IV infusion of lactated Ringer solution and inserted an indwelling catheter. Which of the findings indicate that the child is going into shock? Select all that apply.
(a) Urinary output is 25 mL/h.
(b) Specific gravity is within normal limits.
(c) Pain is 7 on a pain scale of 1 to 10.
(d) Heart rate is elevated.
(e) Blood pressure is dropping.
Answer:
(d) Heart rate is elevated.
(e) Blood pressure is dropping.
Rationale:
The child is observed for shock that can occur following a severe burn. Shock is noted by the increasing heart rate and dropping blood pressure. This child has an adequate urine output (more than 1 rnL/kg body weight), and the specific gravity is within normal range. Pain is expected and is not an indicator of shock.
Question 177.
A client has been receiving radiation therapy for 3 weeks to treat cancer and has fatigue. The nurse should consider which factor when planning to help the client cope with the fatigue?
(a) Fatigue is a temporary problem that requires no active intervention.
(b) The cause of the fatigue should be determined.
(c) Fatigue indicates that the client’s cancer is not under control.
(d) A balance of activity and rest will help man age the fatigue.
Answer:
(d) A balance of activity and rest will help man age the fatigue.
Rationale:
The plan of care to treat fatigue associated with radiation therapy should include encouraging the client to remain active and to plan scheduled rest periods as necessary before activity. Engaging in activities, such as walking, has been shown to decrease the cycle of fatigue, anxiety, and depres-sion that can occur during treatment.
Fatigue is a very common side effect of radiation therapy that typically begins during the 3rd or 4th week of treatment and persists until after treatment ends. The presence of fatigue does not mean that the cancer is not responding to treatment or that the client has developed another health problem.
Question 178.
When educating unlicensed nursing personnel (UAP) about how to prevent the development of pressure ulcers, the nurse should emphasize that which nursing action is most important?
(a) close adherence to a turning schedule
(b) keeping the skin clean and dry
(c) proper positioning
(d) use of skin lubricants
Answer:
(c) proper positioning
Rationale:
Shearing forces occur because of improper movement and positioning, which causes the underlying tissues and capillary blood supply to be pulled and disrupted. This leads to tissue trauma and the potential beginning of skin breakdown. To prevent shearing, clients should be moved with the use of lift sheets and other devices, thus preventing dragging of the skin across the mattress and linens. Clients should also be positioned and supported to prevent pulling or tension of the skin across bony prominences. Turning clients, if not done properly, can cause shearing injuries. Keeping the skin clean, dry, and moisturized is an important aspect of care, but care must be used to decrease the amount of pulling forces exerted on the tissues.
Question 179.
The nurse should instruct a client who is using crutches to bear weight primarily on which part of the body?
(a) axillae
(b) elbows
(c) upper arms
(d) hands
Answer:
(d) hands
Rationale:
The proper use of crutches requires supporting the body weight primarily on the hands. Improper use of crutches can cause nerve damage from excess pressure on the axillary nerve.
Question 180.
A child with aggressive and impulsive behaviors is admitted to the child psychiatric unit with a diagnosis of a conduct disorder. Which intervention is appropriate?
(a) Allow autonomy.
(b) Elicit descriptions of feelings.
(c) Set limits.
(d) Teach assertiveness.
Answer:
(c) Set limits.
Rationale:
The nurse promotes consistent limit setting for the client with the aggressive and impulsive behaviors of a conduct disorder. It is not appropriate for the nurse to allow autonomy or elicit a description of feelings; assertiveness classes are also inappropriate.
Question 181.
What should the nurse do first when admitting a toddler with croup?
(a) Monitor vital signs.
(b) Assess respiratory status.
(c) Ensure adequate fluid intake.
(d) Place a tracheostomy set at the bedside.
Answer:
(b) Assess respiratory status.
Rationale:
For the child with croup, assessing the child’s respiratory status is the priority. It is especially important to assess airway patency because laryngeal spasms can occur suddenly. After the nurse has assessed the toddler’s respiratory status, having a tracheostomy set at the bedside would be the next priority. Monitoring vital signs is important, as is ensuring adequate fluid intake to keep secretions loose, but assessing respiratory status is key.
Question 182.
When administering IV replacement of 5% dextrose in water with potassium chloride, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Add potassium chloride to the bag at the bedside.
(b) Evaluate laboratory results for electrolytes.
(c) Prime tubing using sterile technique.
(d) Check the rate for IV push administration.
Answer:
(b) Evaluate laboratory results for electrolytes.
Rationale:
solutions are prescribed based upon the fluid and electrolyte status of the client, so laboratory results should be monitored first. Safety recommendations are for standard premixed solutions. If solutions are not premixed, additives are completed by the pharmacy, not at the bedside. Potassium chloride is never given by IV push because this could be fatal. Administration guidelines require no more than 10 mEq (10 mmol/L) of potassium chloride be infused per hour on a general medical-surgical unit. An infusion device or pump is required for safe administration.
Question 183.
A 45-year-old client diagnosed with colon cancer states, “I don’t want any treatment. I haven’t seen any family members in 25 years. I’m a loner. Besides, I’ll decide when and how I want to die.” In which order of priority from first to last should the nurse perform the actions? All options must be used.
(a) Ask the client what methods for suicide are available.
(b) Tell the client that the primary care provider will ask for a psychiatric consult.
(c) Ask the client about thoughts of sucide.
(d) Express concern for the client’s feelings and safety.
Answer:
(c) Ask the client about thoughts of sucide.
(a) Ask the client what methods for suicide are available.
(d) Express concern for the client’s feelings and safety.
(b) Tell the client that the primary care provider will ask for a psychiatric consult.
Rationale:
Even with such a blatant suicide clue, it is still important to confirm that he is truly suicidal. Then, it is crucial to know what methods of suicide are available to him. Before asking for a psychiatric consult, the client needs to understand that the nurse cares, is empathetic, and will take actions to protect him from harm.
Question 184.
Which sign is an early indication that a client has developed hypocalcemia?
(a) tingling in the fingers
(b) depressed reflexes
(c) ventricular dysrhythmias
(d) memory changes
Answer:
(a) tingling in the fingers
Rationale:
Neuromuscular irritability is usually the first indication that a client has developed a low serum calcium level. Numbness and tingling around the mouth as well as in the extremities is an early sign of neuromuscular irritability. Depressed reflexes, decreased memory, and ventricular dysrhythmias are indications of hypercalcemia.
Question 185.
The nurse is auscultating the lung sounds of a client with long-standing emphysema. Which lung sounds are expected for this client?
(a) fine crackles
(b) diminished breath sounds
(c) stridor
(d) pleural friction rub
Answer:
(b) diminished breath sounds
Rationale:
In emphysema, the anteroposterior diameter of the chest wall is increased. As a result, the client's breath sounds may be diminished. Fine crackles are present when there is fluid in the lungs. Stridor occurs as a result of a partially obstructed larynx or trachea; stridor can be heard without auscultation. A pleural friction rub is present when pleural surfaces are inflamed and rub together.
Question 186.
A client with a paranoid personality disorder sees some clients laughing during a group activity and asks the nurse, “Why are they laughing at me?
I bet they’re making fun of me.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “You shouldn’t let yourself get so upset.”
(b) “Don’t worry about them. They don’t mean any harm.”
(c) “Look. They seem to be having fun.”
(d) “They’re laughing at a joke John told. They’re not laughing at you.”
Answer:
(d) “They’re laughing at a joke John told. They’re not laughing at you.”
Rationale:
The client with paranoid personality disorder interprets the actions of others as personal threats, feels vulnerable, and is overly sensitive to others’ motives. Saying “They’re laughing at a joke John told. They’re not laughing at you” is a simple explanation of others’ behavior, which helps to decrease the client’s suspiciousness and promote trust. The other statements do not help the client to realistically interpret situations and the behavior of others and are not helpful in reducing the client’s suspicions or mistrust.
Question 187.
The parent of a school-age child with pinworms calls the nurse to ask a question about using over-the-counter pyrantel pamoate. The child has a 24-month-old brother and a 4-year-old sister. The nurse should be sure that the parents are also treating which family members with this drug?
(a) both of the siblings
(b) the parents and brother
(c) everyone who lives in the household
(d) the parents and sister
Answer:
(c) everyone who lives in the household
Rationale:
Pyrantel pamoate should be used to treat everyone in the home. Children age 2 and older can be dosed according to package information. Parents should consult a health care provider 23 for instructions on use in children In general, infants who are not yet mobile are at lower risk for pinworms and probably do not need treatment.
Question 188.
When planning a presentation on the topic of osteoporosis to a group of middle-aged women, the nurse should include which information in the presentation?
(a) An early symptom of osteoporosis is the dowager’s hump.
(b) Women of African and Latin descent are at greater risk.
(c) Loss of height is an early symptom of the disease.
(d) Conventional radiographs are usually used to confirm the disease.
Answer:
(c) Loss of height is an early symptom of the disease.
Rationale:
Loss of height and back pain are early indications of the disease that are caused by collapse of the vertebrae. Later signs include the dowager’s hump and loss of the waistline. The dowager’s hump is a later sign of osteoporosis that occurs when the vertebrae can no longer support the upper body in an upright position. Fair-skinned, smallboned, White, and Asian women are at greater risk for osteoporosis. Conventional radiographs are little help because more than 30% of the bone mass must be lost before the disease is detected. High-density bone scans can detect the disease earlier.
Question 189.
The nurse is to administer an enteral feeding to an adult client. Prior to initiating the feeding, the nurse evaluates the gastric residual. What should the nurse determine from evaluating the gastric residual?
(a) how well nutrients are being absorbed
(b) if the client is receiving enough feeding
(c) extent of overdistention of the stomach
(d) presence of undigested formula
Answer:
(c) extent of overdistention of the stomach
Rationale:
The primary reason for evaluating gastric residual is to determine whether gastric emptying has been delayed and the stomach is becoming overdistended from the feeding. With delayed gastric emptying, the possibility of aspiration of the feeding into the lungs is increased. It is not possible to determine how well the client’s body is absorbing nutrients or whether the client is receiving enough feeding by checking the gastric residual. It is not necessary to keep partially digested formula separate from undigested formula.
Question 190.
The nurse is teaching a client who is a refugee from Burma (Myanmar) about taking medication. Which responses by the client indicates a need for further education? Select all that apply.
The client:
(a) stops taking prescribed medications when the symptoms are relieved.
(b) takes a long time to respond to the nurses’ questions.
(c) nods the head in agreement to the medical plan advised by the health care provider.
(d) continues to utilize traditional practices to relieve symptoms. takes nonprescribed medications purchased from a neighborhood Burmese grocery store.
Answer:
(a) stops taking prescribed medications when the symptoms are relieved.
Rationale:
The concept of prevention of disease is not common in all cultures and some clients will take medicine when the symptoms are present and stop when symptoms are resolved. Clients highly respect educated professionals. Clients from a collectivist culture may also favor the collective perspective over individualism and prefer the health care provider 23 direct medical decision-making.
In support of client autonomy and self-determination additional time may be required to determine the client wishes. It is important to educate clients related to taking medications/ointments received locally from health care systems that are less regulated; lead and arsenic are common in products from some Asian countries. The client focuses on listening to the information and questions asked and take longer to respond, and the nurse should allow extra time when caring for a non-English-speaking client.
Some compromise in the medical plan may be required to gain client agreement to the suggested medical plan of care that includes continuance of traditional practices. Clients from different cultures may believe traditional practices release evil spirits causing illness, and some of these traditional practices are not a health risk.
Question 191.
When planning the care for a client diagnosed with hepatitis A, the nurse should include which interventions? Select all that apply.
(a) Implement an exercise program.
(b) Provide relief from nausea and vomiting.
(c) Administer pain medication.
(d) Encourage multiple small meals daily.
(e) Plan frequent rest periods.
Answer:
(b) Provide relief from nausea and vomiting.
(d) Encourage multiple small meals daily.
(e) Plan frequent rest periods.
Rationale:
Clients with hepatitis A commonly experience fatigue and altered nutrition due to anorexia and nausea. Because of the severe fatigue associated with hepatitis, clients are encouraged to rest and restrict activity during the active phase of the disease. It is important that frequent rest periods be planned throughout the day. Clients may experience nausea and vomiting; thus, providing relief is important.
Small, frequent meals help clients manage the anorexia associated with hepatitis. An exercise program is not appropriate due to the need for rest. Clients with hepatitis do not experience pain. All medications administered to clients with hepatitis need to be evaluated for their potential for hepatotoxicity.
Question 192.
The nurse is assessing a client who has had a myocardial infarction. The nurse notes the cardiac rhythm shown. The nurse identifies that this rhythm is:
(a) atrial fibrillation.
(b) ventricular tachycardia.
(c) premature ventricular contractions.
(d) third-degree heart block.
Answer:
(d) third-degree heart block.
Rationale:
Third-degree heart block occurs when atrial stimuli are blocked at the atrioventricular junction. Impulses from the atria and ventricles are conducted independently of each other. The atrial rate is 60 to 100 bpm; the ventricular rate is usually 10 to 60 bpm.
Question 193.
The client with borderline personality disorder spends much time around the nurse’s station, making numerous minor requests. The nurse interprets these behaviors as indicating which factor?
(a) fears of abandonment and attention seeking
(b) enjoyment of bothering the staff
(c) boredom suggesting the need for something to do
(d) lack of desire for involvement in milieu activities
Answer:
(a) fears of abandonment and attention seeking
Rationale:
Clients with borderline personality disorder have fears of abandonment and seek attention. Clients are dependent and fear being alone; this stems from disapproval, feelings of being abandoned, and not having needs met earlier in their life. The nurse intervenes by reducing attention-seeking behaviors and abandonment fears to help with intense feelings and emotions.
Question 194.
A client has soft wrist restraints to prevent the client from pulling out the nasogastric tube. Which nursing intervention should be implemented while the restraints are on the client?
(a) Instruct the client not to move while the restraints are in place.
(b) Remove the restraints every 4 hours to provide skin care.
(c) Secure the restraints to side rails of the bed.
(d) Check on the client every 30 minutes while the restraints are on.
Answer:
(d) Check on the client every 30 minutes while the restraints are on.
Rationale:
The application of restraints places the client in a vulnerable, confined position. The nurse should check on the client every 30 minutes while restrained to make sure that the client is safe. The client should be able to move while the restraints are in place. The restraints should be removed every 2 hours to provide skin care and exercise the extremities. Restraints should not be secured to the side rails; they should be secured to the movable bed frame so that when the bed is adjusted, the restraints will not be pulled too tightly.
Question 195.
A client with alcohol dependence states, “I feel so bad because of what I’ve done to my wife and kids. I’m just no good.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “Why do you think you’re no good?”
(b) “They’ve stayed with you so far.”
(c) “Alcohol dependence is a disease that can be treated.”
(d) “Alcoholism is painful for everyone involved.”
Answer:
(c) “Alcohol dependence is a disease that can be treated.”
Rationale:
The most appropriate response is “Alcohol dependence is a disease that can be treated” because it conveys hope. It also emphasizes that the client has a treatable illness, which is helpful in reducing denial and guilt and encouraging the client to seek and comply with treatment. Clients often cannot answer “why” questions. While saying that the family has stayed with the client so far may be true, there is no guarantee that they will continue to do so especially if the client does not enter into treatment. Saying alcoholism is painful for everyone is guilt producing, possibly leading to denial and furthering the need for alcohol.
Question 196.
Which statement by a parent indicates the best understanding of why raisins should be limited as a snack food in toddlers?
(a) “Raisins are low in nutritional value.”
(b) “Raisins can increase tooth decay.”
(c) “Raisins are easy to choke on.”
(d) “Raisins are hard to digest entirely.”
Answer:
(b) “Raisins can increase tooth decay.”
Rationale:
Raisins are high in nutritional value but are sticky and have a high sugar content. The raisin can stick to the teeth and act like high-sugar foods in promoting tooth decay. Although anything can be aspirated, round, hard, smooth foods are more easily aspirated than raisins, which are soft and chewy. Raisins need to be chewed thoroughly for maximum nutritional value.
Question 197.
A client has been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation. The health care provider prescribed warfarin to be taken on a daily basis. The nurse instructs the client to avoid using which over-the-counter medication while taking warfarin?
(a) aspirin
(b) diphenhydramine
(c) digoxin
(d) pseudoephedrine
Answer:
(a) aspirin
Rationale:
Aspirin is an antiplatelet medication. The use of aspirin is contraindicated while taking warfarin because it will potentiate the drug’s effects. Diphenhydramine and pseudoephedrine do not affect blood coagulation. Digoxin is not an over-the- counter medication; it requires a prescription.
Question 198.
The nurse should inform a client taking car- bamazepine that it can affect other medications in which way?
(a) It decreases the effects of oral anticoagulants.
(b) It decreases the serum concentration of verapamil.
(c) It increases the serum concentration of other anticonvulsants.
(d) It increases the effects of oral contraceptives.
Answer:
(a) It decreases the effects of oral anticoagulants.
Rationale:
The nurse should inform the client that carbamazepine can decrease the effects of oral anticoagulants. Carbamazepine can increase the serum concentration of verapamil and can decrease the serum concentration of other anticonvulsants and the effects of oral contraceptives.
Question 199.
A client has been diagnosed with hepatitis A. Which nursing goal is most appropriate for the client?
(a) Achieve control of abdominal pains.
(b) Increase activity levels gradually.
(c) Be able to breathe without difficulty.
(d) Experience relief from edema.
Answer:
(b) Increase activity levels gradually.
Rationale:
Viral hepatitis causes fatigue. It is important for the client to rest to allow the liver to recover. Activity levels are resumed gradually as the client begins to recover. Abdominal pain is not a common manifestation of hepatitis. The client typically does not have difficulty breathing or experience edema.
Question 200.
Which activity by the mother offers the most support to the child during the first few days after surgery to repair a cleft lip?
(a) holding and cuddling the child
(b) helping the child play with some toys
(c) reading some of the child’s favorite stories
(d) staying at the bedside and holding the child’s hand
Answer:
(a) holding and cuddling the child
Rationale:
The mother should be encouraged to hold and cuddle her child to provide needed emotional support. Such activities as helping the child play with toys, reading stories, and staying with the child would not be contraindicated, but these activities do not offer as much emotional support as holding and cuddling.
Question 201.
Which strategy is the most effective for a nurse to use to reduce the number of children involved in automobile accidents who were not wearing seat belts?
(a) Contact the local government representative to discuss new legislation about child seat belts.
(b) Attend a school board meeting to advocate for classes teaching children seat belt safety.
(c) Call the town mayor’s office with this information so that the mayor can discuss it with the media.
(d) Start a letter-writing campaign to the school superintendent about seat belt importance.
Answer:
(b) Attend a school board meeting to advocate for classes teaching children seat belt safety.
Rationale:
The best strategy to affect child seat belt safety is to attend the school board meeting and advocate for educational programming. The programming could be simple and done quickly. This action also targets the best audience.
Question 202.
The nurse is developing a discharge plan for a client who has had a myocardial infarction and been in the cardiac care unit for 2 days. The client will be transferred to a telemetry unit tomorrow. When can the client begin cardiac rehabilitation?
(a) today, with a gradual increase of daily activities
(b) when transferred to the telemetry unit
(c) after an EKG shows 2 days of normal sinus rhythm
(d) when discharged from the hospital
Answer:
(c) after an EKG shows 2 days of normal sinus rhythm
Rationale:
A basic principle of rehabilitation, including cardiac rehabilitation, is that rehabilitation begins on hospital admission and the client should increase activities as tolerated each day. It is not necessary to wait until the client is moved to a telemetry unit as the client will have EKG monitoring in both units. It is not necessary for the client to have normal sinus rhythm to increase activity; monitoring will detect potentially dangerous dysrhythmias. Delaying rehabilitation activities is associated with poorer client outcomes.
Question 203.
A child is admitted to the emergency department with dyspnea related to bronchospasms. The nurse should place the client in which position?
(a) high Fowler’s
(b) side lying
(c) prone
(d) supine
Answer:
(a) high Fowler’s
Rationale:
The goal of the intervention is to decrease the child’s work of breathing by decreasing pressure on the diaphragm and increase chest expansion by increasing the pull of gravity on the diaphragm. Placing the client in high Fowler’s position accomplishes this. Side-lying positions make it more difficult to expand the side of the lung closest to the bed. The prone or supine position does not decrease the work of breathing unless the head of the bed is raised.
Question 204.
A nurse has inserted a peripheral intravenous catheter. Which type of dressing is most appropriate to use to cover the insertion site?
(a) transparent
(b) adhesive
(c) hydrocolloid
(d) gauze
Answer:
(a) transparent
Rationale:
A transparent dressing is optimal since it allows assessment of the insertion site. A sterile gauze dressing must be changed every 48 hours or more often if needed according to agency protocol. Adhesive bandages are not occlusive, cover a small surface area, and often irritate the skin. Hydrocolloid and foam dressings are used on pressure ulcers and not peripheral intravenous sites.
Question 205.
The nurse is preparing to administer IM morphine sulfate to a client who is in pain. On checking the health care provider’s (HCP’s) prescription, the nurse notes that the prescription states “morphine sulfate 60 mg IM every 4 hours as needed for pain.” The usual dose of morphine is 10 to 15 mg. What is the most appropriate action for the nurse to take?
(a) Administer the medication as prescribed.
(b) Administer 15 mg of the drug.
(c) Contact the HCP to verify the prescription.
(d) Ask another nurse to review the prescription.
Answer:
(c) Contact the HCP to verify the prescription.
Rationale:
The most appropriate action is to contact the HCP f”J to verify that the prescription is correct. Although 60 mg of morphine is a significant dose, the amount of morphine administered to a client can vary widely, especially if a client has been taking morphine for an extended period and has developed a tolerance to the medication. The safest approach is for the nurse to verify prescriptions that do not appear to fall within the norm.
Administering the medication without verification is unsafe. The nurse cannot decide to reduce the amount of a prescribed medication without a prescription. Asking another nurse to review the prescription is not inappropriate; however, checking with the HCP to verify the prescription should be done.
Question 206.
Following surgery for removal of a brain tumor, a client is coughing and short of breath and has a “bad” feeling. The nurse obtains the following vital signs: blood pressure of 80/60 mm Hg, pulse rate of 120 bpm, and respiratory rate of 30 shallow breaths/min. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Call the neurosurgeon.
(b) Place the client in the Trendelenburg position.
(c) Consult the neurologic clinical nurse specialist (CNS).
(d) Activate the rapid response team (RRT).
Answer:
(d) Activate the rapid response team (RRT).
Rationale:
RRTs 23, or medical emergency teams, provide a team approach to evaluate and treat immediately clients with alterations in vital signs or neurological deterioration. Calling the neurosurgeon or consulting the CNS may not result in a rapid response. The Trendelenburg position is usually used in treating shock, but because the client has had brain surgery, the head should not be lower than the trunk.
Question 207.
The nurse is preparing a client for paracentesis. What should the nurse do?
(a) Have the client void before the procedure.
(b) Scrub the client’s abdomen with an antiseptic skin cleanser.
(c) Position the client supine.
(d) Put the client on nothing-by-mouth (NPO) status 4 hours before the procedure.
Answer:
(a) Have the client void before the procedure.
Rationale:
Before paracentesis, the client is asked to void. This is done to collapse the bladder and decrease the risk of accidental bladder perforation. The abdomen is not prepared with an antiseptic cleansing solution. The client is placed in a Fowler’s position. The client does not need to be put on NPO status before the procedure.
Question 208.
Which behavior in a 20-month-old would lead the nurse to suspect that the child is being abused?
(a) absence of crying during the examination
(b) clinging to the parent during the examination
(c) playing with toys on the examination room floor
(d) talking easily with the nurse
Answer:
(a) absence of crying during the examination
Rationale:
Children who are being abused may demonstrate behaviors such as withdrawal, apparent fear of parents, and lack of an appropriate reaction, such as crying and attempting to get away when faced with a frightening event (an examination or procedure).
Question 209.
What information should the nurse plan to include when teaching the client and family about a substance abuse problem?
(a) the role of the family in perpetuating the problem
(b) the family’s responsibility for the client
(c) the physical, physiologic, and psychological effects of substances
(d) the reasons that could have led the client to use the substance
Answer:
(c) the physical, physiologic, and psychological effects of substances
Rationale:
The nurse should include teaching the client and family about the physical, physiologic, and psychological effects of substances to educate them about the potential injury, illness, and disability that can result from substance use. Teaching about the role of the family in perpetuating the problem, the family’s responsibility for the client, or the reasons that could have led the client to use the substance is inappropriate and based on an erroneous assumption. Including these topics blames the family for the problem and attempts to rationalize the use of the substance.
Question 210.
The nurse is giving discharge instructions to a client who has had a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Which statement indicates that the client has understood the instructions?
(a) “I need to maintain a low-fat diet for the next 6 months.”
(b) “I can remove the dressing from my incision tomorrow and take a shower.”
(c) “I can anticipate some nausea for several days after surgery.”
(d) “I can return to work in 4 to 6 weeks.”
Answer:
(b) “I can remove the dressing from my incision tomorrow and take a shower.”
Rationale:
Postoperative care after a laparoscopic cholecystectomy includes removal of the dressing from the incisional site the day after surgery and allowing the client to bathe or shower. The client can resume a normal diet but may wish to follow a low-fat diet for a few weeks after surgery. Nausea is not expected to last for several days after surgery. The client usu-ally can return to work within 1 week.
Question 211.
The nurse is planning staffing assignments for a group of clients. Which client is most appropriate for the nurse to assign to a nurse who normally works on the maternity unit?
(a) a client in a halo traction brace following surgery for a cervical spine injury
(b) a client who had an open appendectomy yesterday
(c) a client with cancer who requires ventilator support
(d) a client with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis showing signs of progression
Answer:
(b) a client who had an open appendectomy yesterday
Rationale:
The nurse who usually works on a maternity unit has more experience with clients who have had abdominal surgery similar to a cesarean birth and should be assigned to a client who will closely match the nurse’s experience level. The nurse should assign the client in halo traction to a nurse who has experience with the traction equipment.
The client with cancer requiring ventilation and the client with progressing amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
require care from a nurse who has more experience with clients with these needs.
Question 212.
A client has extreme fatigue and is malnourished, and laboratory tests reveal a hemoglobin level of 8.5 g/dL (85 g/L). The nurse should specifically ask the client about the intake of food high in which nutrients?
(a) vitamins A, E, and C
(b) vitamins B6 and B12, folate, iron, and copper
(c) thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin
(d) vitamins A and B
Answer:
(b) vitamins B6 and B12, folate, iron, and copper
Rationale:
Many vitamin and mineral deficiencies can result in anemia. All of these vitamins and minerals need to be assessed, preferably through a nutrition assessment. Deficiencies of vitamins A, B6, and C result in a small cell, microcytic anemia. Folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies result in a large cell, macrocytic anemia. Iron, copper, and vitamin E deficiencies can also result in anemia.
Question 213.
The nurse is assessing a neonate born to a mother with type 1 diabetes. Which finding is expected?
(a) hypertonia
(b) hyperactivity
(c) large size
(d) scaly skin
Answer:
(c) large size
Rationale:
Women with diabetes mellitus generally have neonates who are large but physically immature. Other common findings in these infants are hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, hyperbilirubinemia, polycythemia, renal thrombosis, and congestive anomalies. The neonates do not exhibit hypertonia, hyperactivity, or scaly skin.
Question 214.
A client who had transurethral resection of the prostate has dribbling urine after his Foley catheter is removed on the second postoperative day.
The nurse notes that the client had 200 mL of urine output in the last 8 hours with a 1,000-mL intake. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Apply a condom catheter.
(b) Assess for bladder distention.
(c) Obtain a urine specimen for culture.
(d) Teach the client Kegel exercises.
Answer:
(b) Assess for bladder distention.
Rationale:
The imbalance between the client’s intake and output indicates that the client may be retaining urine since the removal of his Foley catheter. The nurse’s first action is to validate this assumption by assessing for bladder distention. Applying a condom catheter will not relieve urinary retention; condom catheters are meant to be used for incontinence. A urine specimen for a culture is obtained if a urinary infection is suspected, but this is not a priority at this point. Kegel exercises are helpful in controlling urinary dribbling but do not treat retention.
Question 215.
A client has atrial fibrillation. The nurse should monitor the client for which condition?
(a) cardiac arrest
(b) cerebrovascular accident
(c) heart block
(d) ventricular fibrillation
Answer:
(b) cerebrovascular accident
Rationale:
Because of the poor emptying of blood from the atrial chambers, there is an increased risk for clot formation around the valves. The clots become dislodged and travel through the circulatory system. As a result, cerebrovascular accident is a common complication of atrial fibrillation.
Question 216.
A child diagnosed with tinea is being treated with griseofulvin. What instructions should the nurse give the parents?
(a) Give the medication before a meal.
(b) Have the child avoid intense sunlight.
(c) Give the medication for 10 days.
(d) Encourage increased fluid intake.
Answer:
(b) Have the child avoid intense sunlight.
Rationale:
Griseofulvin is associated with photosensitivity reactions. Therefore, the nurse should instruct the parents to have the child avoid intense sunlight. Griseofulvin is best absorbed when administered after a high-fat meal. Treatment with gris-eofulvin typically lasts for at least 1 month. There are no indications that increased fluid intake affects absorption.
Question 217.
The nurse develops a care plan for a client with a diagnosis of a borderline personality disorder. Which interventions would be effective to help the client cope and control emotions? Select all that apply.
(a) Assist client with identifying his/her emotions.
(b) Decrease impulsivity.
(c) Have client keep a journal of emotions and coping techniques.
(d) Encourage the client to delay gratification.
(e) Use confrontation techniques.
Answer:
(a) Assist client with identifying his/her emotions.
(b) Decrease impulsivity.
(c) Have client keep a journal of emotions and coping techniques.
(d) Encourage the client to delay gratification.
Rationale:
To help the client with a borderline personality cope with and control emotions, the nurse assists the client to identify which emotions he or she is experiencing, plans to decrease the number of impulsive acts the client completes, and promotes client use of a journal in which emotions and coping techniques can be recorded. The nurse also encourages the client to delay immediate gratification of impulses. The nurse may use confrontation, but this is a component of the development of a therapeutic relationship and does not help the client cope and control emotions.
Question 218.
A client undergoes cystoscopy with bladder biopsy. After the procedure, which assessment is most appropriate for the nurse to make?
(a) Assess the patency of the Foley catheter.
(b) Assess urine for excessive bleeding.
(c) Percuss the bladder for distention.
(d) Obtain a urine specimen for culture.
Answer:
(b) Assess urine for excessive bleeding.
Rationale:
After cystoscopy with biopsy, the nurse would assess for excessive hematuria, which might indicate hemorrhage caused by the biopsy. Catheters are not routinely inserted after cystoscopy. The nurse would not assess for bladder distention unless the client was having difficulty voiding. Urine cultures are not routinely prescribed after cystoscopy.
Question 219.
The nurse is assessing an infant who is 6 months of age and has a black eye; the infant is brought by his mother to the quick-care clinic. The mother reports that the daycare provider told her the child “fell down the steps with his walker.” What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Report the incident to the social services department.
(b) Document findings accurately.
(c) Ask the mother for details about the incident and the daycare center.
(d) Place an ice bag on the infant’s eye.
Answer:
(d) Place an ice bag on the infant’s eye.
(c) Ask the mother for details about the incident and the daycare center.
(b) Document findings accurately.
(a) Report the incident to the social services department.
Rationale:
The nurse first assesses and manages the physical effects of the eye injury by placing an ice pack on the eye to reduce swelling. Next, the nurse obtains as much information about the situation and the daycare center as possible. The nurse documents all physical assessment findings and information provided by the mother.
Because an infant who is 6 months of age should not be in a walker unattended and black eyes do not occur from falls with walkers, this is a potential child abuse incident; therefore, the nurse reports the incident as such using the agency’s reporting structure (usually, social services department reports the incidents to the authorities).
Question 220.
A client from Mexico has bacterial pneumonia and has a temperature of 102°F (39°C). The client has been treating the infection by drinking milk. How should the nurse interpret the client’s method of self-treatment?
The client:
(a) has confusion from the fever.
(b) is using the hot disease concept.
(c) is taking the milk as a laxative.
(d) needs a referral to a dietitian.
Answer:
(b) is using the hot disease concept.
Rationale:
The nurse interprets the client’s statement as use of the hot disease concept in the Mexican culture, where the belief of a hot and cold balance of the body exists. A hot disease such as an infection is treated with the opposite, a cold food such as milk. The nurse should focus on the cultural differences and be sensitive to the cultural diversity.
Question 221.
A female client with paranoid schizophrenia has been hearing negative voices and “getting special messages from various sources.” Which intervention is most appropriate for the client’s symptoms?
(a) Ask her to make simple decisions.
(b) Be matter-of-fact with her.
(c) Monitor her reactions to television programs.
(d) Reinforce appropriate dress and hygiene.
Answer:
(c) Monitor her reactions to television programs.
Rationale:
A client who is “getting special messages” (ideas of reference) commonly misinterprets content presented on television as containing messages for the client. Therefore, it is important for the nurse to monitor the client’s reactions to television programs.
Question 222.
The nurse is talking with a client who was diagnosed with bulimia 3 months ago. The client needs more education about the illness if she makes which comments? Select all that apply.
(a) “I know that this illness is chronic and intermittent. I’ll always have to control it.”
(b) “If I start severely restricting my eating, I may be building up to a bingeing episode.”
(c) “When I’m not bingeing and purging, I can skip that eating disorder support group.”
(d) “I’ve made a real effort to be more social and involved in activities.”
(e) “My depression is gone, so I don’t need my antidepressant any longer.”
Answer:
(c) “When I’m not bingeing and purging, I can skip that eating disorder support group.”
(e) “My depression is gone, so I don’t need my antidepressant any longer.”
Rationale:
Not attending the support group consistently and not taking the antidepressant may lead to a relapse, and the client needs this information. Bulimia is chronic and intermittent and involves cycles of bingeing, purging, and restrictive eating. Increased socialization and activities promote healthy relationships.
Question 223.
The nurse suspects that a newborn has an imperforate anus. Which assessment findings support the nurse’s hypothesis? Select all that apply.
(a) failure to pass a first stool within 48 hours after birth
(b) curdled vomitus
(c) missing or moved opening to the anus
(d) stool passes out of the vagina, base of penis, scrotum, or urethra
(e) distended abdomen
Answer:
(a) failure to pass a first stool within 48 hours after birth
(c) missing or moved opening to the anus
(d) stool passes out of the vagina, base of penis, scrotum, or urethra
(e) distended abdomen
Rationale:
An imperforate anus is an anorectal anomaly involving the absence of an anus, or the opening in the wrong position Classic symptoms include failure to pass meconium in the first 48 hours of life, abdominal distention, passing stool from an opening other than the anus, and a missing or moved anal opening. Curdled vomiting is associated with digestive rather than obstructive disorders.
Question 224.
An older adult is receiving morphine to manage pain after abdominal surgery. The nurse should observe the client for which side effect of this drug?
(a) respiratory depression
(b) dysrhythmias
(c) constipation
(d) seizures
Answer:
(a) respiratory depression
Rationale:
It is especially important for the nurse to carefully assess the elderly client for respiratory depression after administering a dose of meperidine. It may be necessary to reduce the dosage to prevent respiratory depression. Dysrhythmias, constipation, and seizures are all potential adverse effects of meperidine, but respiratory depression is most significant in the elderly.
Question 225.
The mother of a child with bronchial asthma tells the nurse that the child wants a pet. Which pet is most appropriate?
(a) cat
(b) fish
(c) gerbil
(d) canary
Answer:
(b) fish
Rationale:
Pets are discouraged when parents are trying to allergy proof a home for a child with bronchial asthma, unless the pets are kept outside. Pets with hair or feathers are especially likely to trigger asthma attacks. A fish is a satisfactory pet for this child, but the parents should be taught to keep the fish tank clean to prevent it from harboring mold.
Question 226.
A client with iron deficiency anemia is taking iron supplements. What nutrient should the nurse instruct the client to take the supplements with in order to increase the absorption of iron?
(a) milk
(b) orange juice
(c) food
(d) beta-carotene
Answer:
(b) orange juice
Rationale:
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) increases iron absorption. Taking iron with a food rich in ascorbic acid, such as orange juice, increases absorption. Milk delays iron absorption. It is best to give iron on an empty stomach to increase absorption. Beta-carotene does not affect iron absorption.
Question 227.
When obtaining the nursing history of a client who has type 1 diabetes mellitus, the nurse should assess the client for which early symptom of renal insufficiency?
(a) polyuria
(b) dysuria
(c) hematuria
(d) oliguria
Answer:
(a) polyuria
Rationale:
In early renal insufficiency, the kidneys lose the ability to concentrate urine, resulting in polyuria. Oliguria occurs later. Dysuria and hematuria are not associated with renal insufficiency.
Question 228.
When an infant resumes taking oral feedings after surgery to correct intussusception, the parents comment that the child seems to suck on the pacifier more since the surgery. The nurse explains that sucking on a pacifier:
(a) provides an outlet for emotional tension.
(b) indicates readiness to take solid foods.
(c) indicates intestinal motility.
(d) is an attempt to get attention from the parents.
Answer:
(a) provides an outlet for emotional tension.
Rationale:
Sucking provides the infant with a sense of security and comfort. It also is an outlet for releasing tension. The infant should not be discouraged from sucking on the pacifier. Fussiness after feeding may indicate that the infant’s appetite is not satisfied. Sucking is not manipulative in the sense of seeking parental attention.
Question 229.
Parents of a neonate who is 32 weeks of age ask the nurse, “Why does he have a feeding tube in his nose?” What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) The sucking, swallowing, and breathing are not coordinated.
(b) There is no sucking reflex at this gestational age.
(c) The stomach cannot digest formula or breast milk at this time.
(d) The infant needs extra fluids to prevent dehydration.
Answer:
(a) The sucking, swallowing, and breathing are not coordinated.
Rationale:
At 32 weeks’ gestation, a neonate has limited ability to coordinate sucking, swallowing, and breathing. The sucking reflex is present at 32 weeks’ gestation, but the neonate cannot coordinate the reflex with swallowing and breathing. The stomach has the capacity for digestion at this gestational age. There are no indications that this neonate is dehydrated.
Question 230.
The nurse is assessing for oxygenation in a client with dark skin. Where will oxygenation be most evident on this client?
(a) skin
(b) buccal mucosa
(c) nape of the neck
(d) forehead
Answer:
(b) buccal mucosa
Rationale:
The nurse should examine the buccal mucosa, along with the conjunctiva and sclera, nail beds, palms, soles, lips, and tongue to assess for oxygenation in a client with dark skin.
Question 231.
To prevent shoulder ankyloses following chest surgery, what should the nurse teach the client to do?
(a) Turn from side to side.
(b) Raise and lower the head.
(c) Raise the arm on the affected side over the head.
(d) Flex and extend the elbow on the affected side.
Answer:
(c) Raise the arm on the affected side over the head.
Rationale:
The nurse should teach a client who has undergone chest surgery to raise the arm on the affected side over the head to help prevent shoulder ankylosis. This exercise helps restore normal shoulder movement, prevents stiffening of the shoulder joint, and improves muscle tone and power.
Question 232.
A client with a tracheostomy tube coughs and dislodges the tracheostomy tube. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Call for emergency assistance.
(b) Attempt reinsertion of tracheostomy tube.
(c) Position the client in semi-Fowler’s position with the neck hyperextended.
(d) Insert the obturator into the stoma to reestab lish the airway.
Answer:
(b) Attempt reinsertion of tracheostomy tube.
Rationale:
The nurse’s first action should be to attempt to replace the tracheostomy tube immediately so that the client’s airway is reestablished. Although the nurse may also call for assistance, there should be no delay before attempting reinsertion of the tube. The client is placed in a supine position with the neck hvperextended to facilitate reentry of the tube. The obturator is inserted into the replacement tracheostomy tube to guide insertion and is then removed to allow passage of air through the tube.
Question 233.
The experienced licensed practical/vocational nurse (LPN/VN) under the supervision of the registered nurse (RN) team leader is providing nursing care for an infant with respiratory syncytial virus. Which tasks are appropriate for the RN to delegate to the LPN/VN? Select all that apply.
(a) Auscultate breath sounds.
(b) Administer prescribed aerosolized medications.
(c) Initiate the nursing care plan.
(d) Check oxygen saturation using pulse oximetry.
(e) Complete an in-depth admission assessment.
(f) Evaluate the parent’s ability to administer aerosolized medications.
Answer:
(b) Administer prescribed aerosolized medications.
(d) Check oxygen saturation using pulse oximetry.
Rationale:
LPN/VNs work collaboratively with colleagues in health care to assess, plan, and deliver quality nursing services. The experienced LPN/VN is capable of gathering data and observations, including breath sounds and pulse oximetry. Administering medications, such as aerosolized medications, is within the scope of practice for the LPN/LVN.
The actions that are within the scope of practice for the professional RN Q include independently completing the admission assessment, initiating the nursing care plan, and evaluating a parent’s abilities, as these activities require additional education and skills.
Question 234.
A first-time mother is concerned that her 6-month-old infant is not gaining enough weight. What should the nurse tell the mother?
(a) “Birth weight doubles by 6 months of age.”
(b) “Using a body mass index (BMI] for age growth chart is the best way to assess proper weight gain.”
(c) “The baby will eat what he needs.”
(d) “You need to make sure the baby finishes each bottle.”
Answer:
(a) “Birth weight doubles by 6 months of age.”
Rationale:
A general growth parameter is that the birth weight doubles in 6 months and triples in a year. A child must be at least 2 years of age before they can be assessed with a BMI for age growth chart. Telling the mother that the baby will eat what he needs is not appropriate. The nurse needs to investigate whether the baby’s weight is within the normal parameters of infant weight gain. A bottle- fed baby should not be forced to complete the bottle because this may contribute to obesity.
Question 235.
When the nurse is assessing a client who reports a back injury, what should the nurse ask the client about first?
(a) family history of back problems
(b) previous hospitalizations
(c) personal history of illness
(d) mechanism of injury
Answer:
(d) mechanism of injury
Rationale:
The mechanism of injury is always the most critical information to obtain from a client with a musculoskeletal injury. In the event of a back injury, the mechanism of injury provides the greatest clue as to the extent of injury and the proper treatment plan. The other questions are important but will not give the critical information needed related to this specific problem and injury.
Question 236.
A client is taking metoprolol and hydrochlo-rothiazide. Which finding indicates the medications are having the desired effect?
The client:
(a) has lower blood pressure.
(b) has an increased heart rate.
(c) has improved circulation in the extremities.
(d) has decreased dyspnea.
Answer:
(a) has lower blood pressure.
Rationale:
Antihypertensive medications such as metoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide work to lower the blood pressure by reducing peripheral resistance or decreasing cardiac output; the effectiveness of these drugs is noted by a lowering of the blood pressure. Vasodilators are used to improve peripheral circulation. Cardiac stimulants and antiarrhythmic drugs are used to increase heart rate. Although cardiac problems can cause dyspnea, the use of drugs to manage dyspnea depends on the underlying cause.
Question 237.
A client in cardiac rehabilitation would like to eat the right foods to ensure adequate endurance on the treadmill. Which nutrient is most helpful for promoting endurance during sustained activity?
(a) protein
(b) carbohydrate
(c) fat
(d) water
Answer:
(b) carbohydrate
Rationale:
The stored glucose of muscle glycogen is the major fuel during sustained activity. Glucose production slows as the body begins to depend on fat stores for glucose and fatty acids. Protein is not the body’s preferred energy source. Fat is a secondary source of energy. Water is not an energy source, although sufficient water is required to engage in aerobic activity without causing dehydration.
Question 238.
The nurse is examining an older adult woman with possible rheumatoid arthritis. The nurse should ask the client if she is having which symptom?
(a) nausea
(b) dizziness
(c) fatigue
(d) limitation of movement
Answer:
(c) fatigue
Rationale:
Typical early signs of rheumatoid arthritis are nonspecific and not necessarily related to specific joint pain. Common early symptoms include fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, and generalized feelings of stiffness. Joint swelling and limitation of movement usually occur later as joint involvement becomes more specific. Dizziness is not a sign of rheumatoid arthritis. Nausea is not typically associated with the disease process but can be related to medications prescribed to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Question 239.
The nurse instructs the client in mixing and administering regular and NPH insulin. Which statement indicates that the client needs additional instruction?
(a) “I draw up the regular insulin first.”
(b) “I shake the bottle of NPH insulin before drawing it up.”
(c) “I store the insulin in a cool place.”
(d) “I insert the needle at a 90-degree angle.”
Answer:
(b) “I shake the bottle of NPH insulin before drawing it up.”
Rationale:
NPH insulin should be rolled between the palms to mix it before drawing it up; shaking it will introduce air bubbles into the solution, which can cause inaccurate dosing. The client should draw up the insulin first, store the insulin in a cool place, and inject the insulin at a 90-degree angle.
Question 240.
The mother of a child with newly diagnosed Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy asks how her child developed the disease. The nurse gives a response incorporating which statement about its transmission?
(a) “It’s an autosomal recessive genetic disorder.”
(b) “It’s a genetic disorder carried by males and transmitted to male children.”
(c) “It’s a disorder primarily transmitted by males in the family.”
(d) “It’s a disorder usually carried by females and transmitted to male children.”
Answer:
(d) “It’s a disorder usually carried by females and transmitted to male children.”
Rationale:
The gene for Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy is carried by women and transmitted to their male children. It involves an X-linked inheritance pattern. About one-third of new cases involve mutations.
Question 241.
What is a priority nursing goal for an infant with intussusception?
(a) Restore fluids.
(b) Control diarrhea.
(c) Protect the skin.
(d) Manage acute pain.
Answer:
(d) Manage acute pain.
Rationale:
Infants with intussusception have coliclike abdominal pain caused by the telescoping of the bowel. The nursing priority is to relieve this pain. There are no data to indicate a skin problem or dehydration. Diarrhea or constipation may precede the appearance of currant jelly stools.
Question 242.
A client is trying to lose weight at a moderate pace. If the client eliminates 1,000 cal/day from the usual food intake, how many pounds/kilograms would the client lose in 1 week?
........................... lb/kg.
Answer:
2 lb or 0.9 kg.
Rationale:
One pound or 0.45 kg of weight is approximately equivalent to 3,500 cal. Removing 1,000 cal/day results in a 2-lb (0.9-kg) weight loss per week (7,000 cal divided by 7 days). A client who wanted to lose 1 lb (0.45 kg) in a 7-day period would need to cut out 500 cal/day (3,500 cal divided by 7 days). It is unsafe to try to lose more than 2 lb (0.9 kg)/week.
Question 243.
The health care provider (HCP) prescribes IV cefazolin 1 g for a client. In preparing to administer the cefazolin, the nurse notes that the client is allergic to penicillin. Based on this information, what is an appropriate action for the nurse to take?
(a) Continue to prepare to administer the cefazo lin as prescribed.
(b) Notify the HCP of the client’s allergy to penicillin.
(c) Administer the cefazolin, staying at the client’s bedside during the infusion.
(d) Call the pharmacist to verify that the cefazolin should be administered as prescribed.
Answer:
(b) Notify the HCP of the client’s allergy to penicillin.
Rationale:
The nurse should notify the HCP that the client is allergic to penicillin before giving the cefazolin. Cephalosporins are contraindicated in clients who are allergic to penicillin. Clients who are allergic to penicillin may have a cross-allergy to cephalosporins.
Question 244.
A client is prescribed buspirone 5 mg two times a day. Which statements indicate that the client has understood the nurse’s teaching about this drug? Select all that apply.
(a) “This medicine will make me sleepy.”
(b) “Buspirone will relax my muscles.”
(c) “My anxiety will be gone in about 2 weeks.”
(d) “Buspirone will help me not to worry so much.”
(e) “I’ll be able to focus better.”
Answer:
(d) “Buspirone will help me not to worry so much.”
(e) “I’ll be able to focus better.”
Rationale:
Buspirone is not a benzodiazepine but acts as a serotonin agonist. Serotonin is the neurotransmitter implicated in depression. Buspirone reduces symptoms of worry, apprehension, difficulty with concentration, and irritability. Buspirone takes 1 to 6 weeks to be effective with full therapeutics benefits taking 3 to 6 weeks to occur. It does not cause muscle relaxation, or produce dependence, withdrawal, or tolerance.
Question 245.
The nurse has delegated providing postmortem care of an Asian adult man to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). The family does not wish to have an autopsy but is considering organ donation. Which instructions should the nurse give to the UAP who will provide postmortem care for this client? Select all that apply.
(a) The family may remain with the client for 8 hours after death.
(b) Ask the client’s family if they have any requests for how to prepare the body.
(c) Elevate the head of the bed as soon as possible.
(d) Check two identifiers before starting postmortem care.
(e) Inquire about the family’s preference for shaving the client’s beard.
(f) Remove all indwelling lines and catheters.
Answer:
(a) The family may remain with the client for 8 hours after death.
(b) Ask the client’s family if they have any requests for how to prepare the body.
(c) Elevate the head of the bed as soon as possible.
(d) Check two identifiers before starting postmortem care.
(e) Inquire about the family’s preference for shaving the client’s beard.
Rationale:
In the Asian culture, family may wish to remain with the body for 8 hours after a family member’s death. Before shaving a client’s beard, the nurse should always check with the family or in the chart for the client and family’s preference and verify the hospital’s policy about shaving the head. The nurse should consult with the family about any preparation requests such as wearing special clothing or jewelry.
The nurse should always use two identifiers before providing care. It is impor-tant to elevate the head of the bed to prevent pooling of blood and discoloration from pooling blood. In the case of a potential organ donation, indwelling lines should not be removed.
Question 246.
A client with schizophrenia is responding well to risperidone and is no longer psychotic. After the nurse teaches the client about managing the illness, which statement by the client reflects a need for further intervention?
(a) “I just don’t know if I can remember to keep taking medicines every day.”
(b) “When my thoughts start racing, I know I need to relax more.”
(c) “I can name the side effects of risperidone, but I’m not having any.”
(d) “I don’t listen to my mom’s religious beliefs about not using medicines.”
Answer:
(a) “I just don’t know if I can remember to keep taking medicines every day.”
Rationale:
The major cause of relapse is nonadherence to the medication treatment plan. If the client is worried about remembering to take the medicines on a regular basis, it is a warning sign to the nurse that the client may be at risk for noncompliance.
The nurse needs to discuss strategies to help the client establish a new routine such as using digital reminders, integrating medications into a daily routine, and utilizing family support systems when available. Understanding when to relax and the side effects of medicines are positive findings. Choosing not to listen to a family member’s negative beliefs about medication is also a positive finding.
Question 247.
While a mother is feeding her full-term neonate 1 hour after birth, she asks the nurse, “What are these white dots in my baby’s mouth? I tried to wash them out, but they’re still there.” After assessing the neonate’s mouth, the nurse explains that these spots indicate which condition?
(a) Koplik’s spots
(b) Epstein’s pearls
(c) precocious teeth
(d) thrush curds
Answer:
(b) Epstein’s pearls
Rationale:
Epstein’s pearls are tiny, hard, white nodules found in the mouth of some neonates. They are considered normal and usually disappear without treatment. Koplik’s spots, associated with measles in children, are patchy and bright red with a bluish-white speck in the middle. Precocious teeth are actual teeth that some neonates have at birth. Usually, only one or two teeth are present. Candida albicans, or thrush, is not apparent in the mouth immediately after birth but may appear a day or 2 later. This infection is manifested by yellowish- white spots or lesions that resemble milk curds and bleed when attempts are made to wipe them away.
Question 248.
A nurse is assessing a client with hepatitis A. The client reports having a poor appetite and the presence of food causes nausea. What should the nurse encourage the client to eat?
(a) high-fat foods at each meal
(b) foods high in protein
(c) the majority of the calories in the morning during small frequent snacks
(d) a low-calorie diet with numerous snacks
Answer:
(c) the majority of the calories in the morning during small frequent snacks
Rationale:
It is important to explain to the client who is having nausea that the majority of calories should be eaten in the morning because nausea most often occurs in the afternoon and evening. Small, frequent portions are best. Clients with viral hepatitis should select a diet high in calories because energy is required for healing. An intake of adequate carbohydrates can spare the protein because protein places an increased workload on the liver. Changes in bilirubin interfere with fat absorption, so low-fat diets are better tolerated.
Question 249.
A client had a cast applied to the left femur to stabilize a fracture. To promote early rehabilitation, what should the nurse do?
(a) Call physical therapy to provide passive exercise of the affected limb.
(b) Teach the client how to do isometric exercises of the quadriceps.
(c) Show the family how to do active range-of-motion exercises of the unaffected limb.
(d) Obtain weights so the client can exercise the upper extremities.
Answer:
(b) Teach the client how to do isometric exercises of the quadriceps.
Rationale:
The nurse should teach the client how to do isometric exercise, contraction of the quadriceps muscle without movement of joint, to maintain muscle strength. Physical therapy may assist the client later and will then teach the client how to do active exercises and crutch walking if prescribed. The client will be able to move the unaffected limb; the family will not need to assist. If the client will be using crutches, building upper extremity strength will be helpful, but the immediate need is to maintain and develop strength in the quadriceps.
Question 250.
The client arrives in the emergency department following a bicycle accident in which the client’s forehead hit the pavement. The client is diagnosed as having a hyphema. The nurse should place the client in which position?
(a) supine
(b) semi-Fowler’s
(c) side lying on the affected side
(d) side lying on the unaffected side
Answer:
(b) semi-Fowler’s
Rationale:
A hyphema is the presence of blood in the anterior chamber of the brain. Hyphema is produced when a force is sufficient to break the integrity of the blood vessels in the eye and can be caused by direct injury, such as penetrating injury from a small bullet or pellet, or indirectly, such as from striking the forehead on the pavement during an accident. The client is treated by bed rest in a semi-Fowler’s position to assist gravity in keeping the hyphema away from the optical center of the cornea.
Question 251.
The nurse has just received change-of-shift report for four clients. Based on this report, the nurse should assess which client first?
(a) a 38-year-old who is 2 days postmastectomy due to breast cancer, having difficulty coping with the diagnosis
(b) a 52-year-old with pneumonia and chronic back pain who is requesting pain medication
(c) a 35-year-old admitted after motor vehicle accident whose urine output has totaled 30 mL over the last 2 hours
(d) an 84-year-old with resolving left-sided weakness who is slightly confused and has been awake most of the night
Answer:
(c) a 35-year-old admitted after motor vehicle accident whose urine output has totaled 30 mL over the last 2 hours
Rationale:
Urine output should be at least 500 mL in 24 hours (20 mL/h); this client’s output has been just 15 mL/h for the past 2 hours requiring further assessment by the nurse. The nurse should first assess all clients and address physiological needs including pain control and safety measures; the nurse should then take time with the client having difficulty coping in order to listen and further determine her needs.
Question 252.
An obese diabetic client who has bilateral leg aching is to start a cardiac rehabilitation with an exercise program. Using which exercise equipment will be most helpful to the client?
(a) stationary bicycle
(b) treadmill
(c) elliptical trainer
(d) stair climber
Answer:
(a) stationary bicycle
Rationale:
The stationary bicycle is the most appropriate training modality because it is a non-weightbearing exercise. The time that the individual exercises on the stationary bicycle is increased with improved functional capacity. The other exercise equipment requires exercising while standing.
Question 253.
The nurse has received a change-of-shift report. The nurse should assess which client first?
(a) a 72-year-old admitted 2 days ago with a blood alcohol level of 0.08
(b) a 36-year-old with chest tube due to spontaneous pneumothorax with current respiratory rate 18 breaths/min and oxygen saturation 95% on oxygen at 2 L per nasal cannula
(c) a 28-year-old who is 2 days post appendectomy with discharge prescriptions written and whose husband is waiting to take her home
(d) a 62-year-old admitted with a recent gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding whose hemoglobin is 13.8 g/dL (138 g/L)
Answer:
(a) a 72-year-old admitted 2 days ago with a blood alcohol level of 0.08
Rationale:
The nurse should closely monitor the client admitted with an elevated blood alcohol level for several hours for signs and symptoms of withdrawal, administering sedation as needed; delirium tremens, the most severe form of withdrawal, usually peaks at 48 to 72 hours following the last drink.
The client with the chest tube is not in any distress and has no pressing needs. For an older client who has had GI bleeding, a hemoglobin of 13.8 g/dL (138 g/L) is within normal limits. After assessing all clients’ needs, the nurse will prepare the client who had an appendectomy for discharge as soon as possible.
Question 254.
A small-for-gestational-age infant is born with facial abnormalities and vision abnormalities. These abnormalities are likely caused by which maternal factor?
(a) alcohol consumption
(b) rubella exposure
(c) tetracycline use
(d) folic acid deficiency
Answer:
(a) alcohol consumption
Rationale:
Fetal alcohol syndrome is characterized by central nervous system damage, poor growth, and specific facial stigmata. As many as 90% of children with fetal alcohol syndrome have eye abnormalities. Congenital syphilis is more frequently associated with preterm birth, and tetracycline use is associ-ated with dental abnormalities. Folic acid deficiency contributes to neural tube defects.
Question 255.
An adolescent with cystic fibrosis has been placed on ciprofloxacin for a lung infection. Which statement from the client indicates the need for more teaching?
(a) “I won’t take this drug with any dairy products.”
(b) “I’ll need to have drug levels drawn while I’m on this medication.”
(c) "I should immediately report any muscle or joint pain.”
(d) “If I miss a dose, I should take it as soon as I remember.”
Answer:
(b) “I’ll need to have drug levels drawn while I’m on this medication.”
Rationale:
Therapeutic serum drug monitoring is not routinely done with ciprofloxacin. This medicine should not be taken with dairy products or other significant sources of calcium such as collard greens, calcium supplements, calcium carbonate antacids, or calcium-fortified juice. Clients may take a missed dose as soon as they remember. If it is very close to the time of the next dose, the missed dose should be omitted. The client should not take a double dose.
Question 256.
A client whose condition remains stable after a myocardial infarction is to gradually increase activity. Which sign best indicates that the activity is appropriate for the client?
(a) edema
(b) skin color
(c) respiratory rate
(d) weight
Answer:
(c) respiratory rate
Rationale:
Physical activity is gradually increased after a myocardial infarction while the client is still hospitalized and through a period of rehabilitation. The client is progressing too rapidly if activity significantly changes respirations, causing dyspnea, chest pain, a rapid heartbeat, or fatigue. When any of these symptoms appears, the client should reduce activity and progress more slowly.
Edema suggests a circulatory problem that must be addressed but does not necessarily indicate overexertion. Cyanosis indicates reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of red blood cells and indicates a severe pathology. It is not appropriate to use cyanosis as an indicator for overexertion. Weight loss indicates several factors but not overexertion.
Question 257.
The parents of a 7-year-old child with glo-merulonephritis ask what they can do to ensure that their other children do not develop the disease. The nurse should respond with which statement?
(a) “If you suspect your child has a urinary tract infection, see your primary health care provider (HCP) right away.”
(b) “I’m afraid there’s nothing you can do; glomerulonephritis is a genetic disorder.”
(c) “Glomerulonephritis isn’t contagious, so your other children won’t get the disease.”
(d) “If your child has a streptococcal infection, complete the course of prescribed antibiotics.”
Answer:
(d) “If your child has a streptococcal infection, complete the course of prescribed antibiotics.”
Rationale:
The most common noninfectious renal disease in children is acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Ensuring that children diagnosed with streptococcal infections complete a full course of antibiotics will decrease their risk of developing acute glomerulonephritis. Parents should contact the primary HCP tyj if they suspect a UTI; however, glomerulonephritis is not caused by a UTI. Glomerulonephritis is not a genetic disease, and it is not contagious.
Question 258.
A client admitted for alcohol detoxification is taking disulfiram. The nurse should instruct the client to avoid ingestion of which foods and/or liquids? Select all that apply.
(a) aged cheeses
(b) beer
(c) communal wine at church
(d) chocolates
(e) cough syrup
Answer:
(b) beer
(c) communal wine at church
(e) cough syrup
Rationale:
The client who is taking disulfiram is advised to avoid all forms of alcohol, including beer, communal wine at church, and cough syrup; these can trigger a serious physical reaction. Aged cheeses and chocolate are to be avoided by the client taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Question 259.
The nurse is evaluating an infant for auditory ability. What is the expected response in an infant with normal hearing?
(a) blinking and stopping body movements when sound is introduced
(b) evidence of shy and withdrawn behaviors
(c) saying “da-da” by age 5 months
(d) absence of squealing by age 4 months
Answer:
(a) blinking and stopping body movements when sound is introduced
Rationale:
In response to hearing a noise, normally hearing infants blink or startle and stop body movements. Shy and withdrawn behaviors are characteristics of older children with hearing impairment. Squealing occurs in 90% of infants by age 4 months. Most infants can say “da-da” by age 9 months.
Question 260.
When admitting a neonate whose mother received magnesium sulfate, the nurse should assess the baby for which complication? Select all that apply.
(a) increased Moro reflex
(b) decreased muscle tone
(c) increased respirations
(d) decreased respirations
(e) increased temperature
Answer:
(b) decreased muscle tone
(d) decreased respirations
Rationale:
Magnesium sulfate decreases muscle contractility and crosses the placenta. Because of this, a neonate who has been exposed to this drug may have decreased muscle tone and decreased respirations. The Moro reflex will be decreased because of the decreased muscle tone. There are no findings that show magnesium sulfate has a direct effect on temperature.
Question 261.
The neonate has a prescribed IV rate of 8 mL/h. Fluid totals are recorded every 2 hours on the even hours. There is a new prescription written at 1030 to decrease the IV rate to 6 mL/h. What is the fluid total to be infused and recorded at 1200?
........................... mL.
Answer:
13 mL.
Rationale:
1000 to 1030 = 4 mL (hourly rate 8), 1030 to 1100 = 3 mL (hourly rate 6 mL), 1100 to 1200 = 6 mL (hourly rate 6 mL). 4 + 3 + 6 = 13.
Question 262.
The nurse is auscultating Sj and S2 in a client. Identify the area where the nurse should hear S2 the loudest.
Answer:
Rationale:
S1 is loudest at the mitral area.
Question 263.
While assessing the psychosocial aspects of a primigravid client at 30 weeks’ gestation, the nurse expects which feelings?
(a) vulnerability
(b) confirmation
(c) ambivalence
(d) body image disturbance
Answer:
(a) vulnerability
Rationale:
During the third trimester, particularly in the 9th month of pregnancy, the client typically exhibits feelings of vulnerability and fear that the baby will be lost. Confirmation that the fetus is real occurs during the second trimester. Ambivalence is typically seen and resolved during the first trimester. Body image disturbance commonly occurs during the second trimester because of the profound changes that occur to the body during this time.
Question 264.
An older adult is taking eight medications to manage hypertension, diabetes, and arthritis and reports having nausea, diarrhea, tremors, and unusual thoughts. When investigating the cause of these symptoms, the nurse should consider which reason for underestimating adverse drug reactions in older adults?
(a) Adverse reactions rarely have an atypical presentation.
(b) Cognitive impairment is an expected finding in the older adult.
(c) Physical or psychological symptoms are attributed to the effects of aging.
(d) Excess sedation is difficult to assess in the older adult.
Answer:
(c) Physical or psychological symptoms are attributed to the effects of aging.
Rationale:
The elderly client commonly has vague or atypical responses to medications and diseases that are erroneously attributed to aging. A new cognitive change needs to be investigated and is not an expected change with aging. Changes in a client’s behavior should be investigated to see whether there is a relation to excessive sedation. The nurse can interview the family members to obtain information.
Question 265.
A parent tells the nurse that their 8-month- old infant is anxious. Which suggestion by the nurse is most appropriate to help the parent lessen anxiety in the infant?
(a) Limit holding the infant to feeding times.
(b) Talk quietly to the infant while awake.
(c) Play music in his room for most of the day and night.
(d) Have a close friend keep the infant for a few days.
Answer:
(b) Talk quietly to the infant while awake.
Rationale:
Infants are sensitive to stress in their caretakers. The best way to handle an anxious infant is to talk quietly, thereby soothing the infant. Limiting holding of the infant to feeding periods interferes with meeting the infant’s needs for close contact, possibly compromising his ability to develop trust.
Also Read: NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 2 with Rationale
Playing music in the room for most of the day and night will make it difficult for the infant to differentiate days from nights. Having a friend take the infant for several days will not necessarily take care of the problem because when the infant returns to the parents, the same behaviors will recur unless the parents make some changes.
