By reviewing NCLEX Exam Questions, students can identify common themes and patterns in exam content, improving their chances of success.
NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 2 with Rationale
Question 1.
The unit secretary who transcribes the health care provider’s (HCP’s) prescriptions asks the nurse to interpret an illegible prescription. The nurse should clarify the prescription with the:
(a) client.
(b) pharmacist.
(c) HCP.
(d) client’s family.
Answer:
(c) HCP.
Rationale:
Illegible writing is one of the most common reasons for medication errors. The HCP [j] should be called to clarify the prescription. The previous medication record should not be used as a substitute for the exact prescription written by the HCP. The pharmacist or the client’s family cannot interpret a prescription written by an HCP.
Question 2.
A client with cholecystitis is taking propantheline bromide. What should the nurse tell the client to expect as a result of taking this drug?
(a) increased bile production
(b) decreased biliary spasm
(c) absence of infection
(d) relief from nausea
Answer:
(b) decreased biliary spasm
Rationale:
Propantheline bromide is an anticholinergic used to decrease biliary spasm. Decreasing biliary spasm helps to reduce pain in cholecystitis. Propantheline does not increase bile production or have an antiemetic effect, and it is not effective in treating infection.
Question 3.
The nurse refers the parents of a child with cystic fibrosis to an organization that helps families with children who have this disease. What does the nurse determine is the desired outcome from this referral?
(a) assistance finding tutors to educate the child at home
(b) obtaining genetic counseling to determine of having another child with cystic fibrosis
(c) meeting with other parents of children with cystic fibrosis for mutual support
(d) securing financial assistance to purchase medications for their child
Answer:
(c) meeting with other parents of children with cystic fibrosis for mutual support
Rationale:
An important function of support organizations for any health problem is to put parents of children with the condition in touch with each other. Other parents can commonly offer support and help. In some instances, organizations can offer assistance, such as providing equipment required for home care of their child with cystic fibrosis. These organizations do not obtain tutors for children, nor do they provide medications, financial assistance, or genetic counseling for parents.
Question 4.
A client tells the nurse that “the hospital food is horrible.” What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “The staff is doing the best it can to cook in such large quantities.”
(b) “I’ll report this to the health care provider (HCP).”
(c) “Would you like to speak with the dietitian about the food and meal selection?”
(d) “I don’t like the hospital cafeteria food either.”
Answer:
(c) “Would you like to speak with the dietitian about the food and meal selection?”
Rationale:
Strategies for meeting client satisfaction include involving hospital department personnel to improve service. Saying, “The staff is doing the best it can,” or, “I’ll report this to the health care provider (HCP) Q,” does not offer a practical resolution to the client’s problem. Expressing a personal dislike for the food negates the client’s problem and does not offer a solution.
Question 5.
A client had a thrombotic cerebrovascular accident and now has flaccid hemiplegia of the right side. When can the health care team begin rehabilitation for this hospitalized client?
(a) after beginning anticoagulant therapy
(b) on admission to the hospital
(c) when the client can work cooperatively with health care team
(d) as directed by the physical therapist
Answer:
(b) on admission to the hospital
Rationale:
Rehabilitation for a client who has sustained a cerebrovascular accident begins at the time the client is admitted to the hospital. The first goal of rehabilitation should be to help prevent deformities. This goal is achieved through such techniques as positioning the client properly in bed, changing the client’s position frequently, and supporting all parts of the body in proper alignment. Passive range-of-motion exercises may also be started, unless contraindicated.
Question 6.
A client has been involuntarily committed to a hospital after being assessed as being dangerous to self or others. The client has lost which right?
(a) the right to refuse medications and treatments
(b) the right to send and receive uncensored mail
(c) freedom from seclusion and restraints
(d) the right to leave the hospital against medical advice
Answer:
(d) the right to leave the hospital against medical advice
Rationale:
An involuntarily admitted client loses the right to leave the hospital until the condition is stable enough that the client no longer poses a danger to self or others. While hospitalized, the client retains all civil rights such as receiving mail, making phone calls, refusing treatment, and also receiving the least restrictive treatment. Should the involuntarily admitted client refuse treatment once admitted, he will be evaluated for the need to receive treatment against wishes in order to decrease the risk for self-harm or harm to others.
Question 7.
Which statement by a client taking valproic acid for bipolar disorder indicates that further teaching about this medication is necessary?
(a) “I need to take the pills at the same time each day.”
(b) “I can chew the pills if necessary.”
(c) “I can take the pills with food.”
(d) “I need to call my health care provider if I start bruising easily.”
Answer:
(b) “I can chew the pills if necessary.”
Rationale:
Chewing the pill or capsule form of valproic acid can cause mouth and throat irritation and is contraindicated. Taking the pills at the same time each day is important to maintain therapeutic effectiveness of the drug. Taking the pills with food is appropriate if the client is experiencing gastro-intestinal upset. Valproic acid may cause clotting problems; therefore, bruising should be reported.
Question 8.
The nurse is making rounds and observes a client who is unconscious (see figure). The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) has just turned the client from lying on her back and raised the side rail next to the bedside stand. Before raising the side rail on the opposite side, the nurse should:
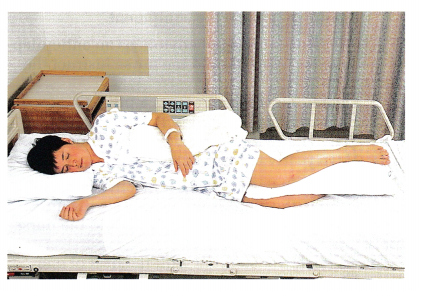
(a) Elevate the head of the bed to 30 degrees.
(b) Ask the UAP to add a pillow under the right arm.
(c) Inspect the skin at pressure points from the back-lying position.
(d) Assist the UAP to move the client closer to the head of the bed.
Answer:
(c) Inspect the skin at pressure points from the back-lying position.
Rationale:
The client is positioned correctly in the sidelying position. The pillows support the client’s joints and do not cause unnecessary pressure on the joints or skin. It is not necessary to add another pillow under the arm or to elevate the head of the bed. The nurse should assess the client’s skin for signs of breakdown, particularly at the elbows, back, hips, and heels where there were pressure points from the position in which the client was previously lying.
Question 9.
A client is having elective surgery under general anesthesia. Who is responsible for obtaining the informed consent?
(a) the nurse
(b) the surgeon
(c) the anesthesiologist
(d) the social worker
Answer:
(b) the surgeon
Rationale:
It is the role of the surgeon or the person performing the procedure to obtain the informed consent Q. This consists of informing the client about the procedure, the risks of treatment, the side effects, other types of treatments available, and the effects without the procedure. Nurses, anesthesiologists, and social workers do not obtain informed consent.
Question 10.
The family of an older adult with terminal cancer asks about having hospice services. What should the nurse tell the family?
Hospice care:
(a) focuses only on the needs of the client.
(b) can only be provided in the inpatient setting.
(c) is staffed exclusively by professional health care workers.
(d) focuses on supportive care for the client and family.
Answer:
(d) focuses on supportive care for the client and family.
Rationale:
Hospice care focuses on supportive care for the client and family. Care for the family may continue throughout the bereavement period. Hospice care involves care of the client at home as well as in an inpatient setting. Although professional care is provided in hospice, family members, volunteers, and unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) also participate in the care of the client.
Question 11.
When caring for a child who has been receiving long-term steroid therapy, the nurse should assess the child for which complication?
(a) usual behavior and temperament
(b) loss of weight from baseline
(c) development of truncal obesity
(d) demonstration of a growth spurt
Answer:
(c) development of truncal obesity
Rationale:
One of the side effects of steroid therapy is fat deposition on the trunk and face, producing classic Cushingoid signs. Therefore, the nurse should expect to find truncal obesity. Steroids also can cause altered moods or mood swings. Typically, long-term steroid use results in weight gain. Steroids may inhibit the action of growth hormone. Therefore, a growth spurt is not likely.
Question 12.
The nurse manager has assigned a nurse as the circulating nurse for a surgical abortion. The nurse has a religious objection and wishes to refuse to participate in an abortion. What should the nurse manager of the operating room do?
(a) Require the nurse to do this assignment.
(b) Change the assignment and record the behavior on the nurse’s evaluation.
(c) Change the assignment without comment.
(d) Change the assignment to circulate but have the nurse prepare the equipment.
Answer:
(c) Change the assignment without comment.
Rationale:
The nurse should not be required to participate in an abortion if it contradicts the nurse’s religious beliefs. The behavior should not be reflected negatively on the nurse’s evaluation. Preparing equipment and supplies for the case may be viewed as the same as circulating for the case. The nurse has a right not to participate in an abortion unless it is an absolute emergency and no one else is available to care for the client.
Question 13.
A client is taking phenytoin as an antiepileptic medication. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Obtain increased iron from a pill.
(b) Increased the calcium in the diet.
(c) Schedule twice-yearly dental examinations.
(d) Have yearly eye examinations.
Answer:
(c) Schedule twice-yearly dental examinations.
Rationale:
Phenytoin causes hyperplasia of the gums, and the client needs dental examinations twice a year and meticulous oral hygiene. Phenytoin therapy may contribute to a folic acid deficiency, but it is not related to iron or calcium metabolism. A need for frequent eye examinations is not related to the side effects of phenytoin, but the client should have regular eye exams as appropriate.
Question 14.
A hospitalized 5-year-old is pulseless, and after verifying the child is not breathing, the nurse begins chest compressions. Where should the nurse apply pressure?
(a) on the lower sternum with the heel of one hand
(b) midway on the sternum with the tips of two fingers
(c) over the apex of the heart with the heel of one hand
(d) on the upper sternum with the heels of both hands
Answer:
(a) on the lower sternum with the heel of one hand
Rationale:
The chest is compressed with the heel of one hand positioned on the lower sternum, two fingerbreadths above the sternal notch (at the nipple line). Fingertips are used to compress the sternum in infants, and the heels of both hands are used in adult cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Question 15.
The nurse instructs a client with coronary artery disease in the proper use of nitroglycerin.
The client has had two previous episodes of coronary artery disease. At the onset of chest pain, what should the client do?
(a) Call 911 when three nitroglycerin tablets taken every 5 minutes are not effective.
(b) Call 911 when five nitroglycerin tablets taken every 5 minutes are not effective.
(c) Take one tablet and then immediately call 911.
(d) Go to the emergency department if two nitro glycerin tablets taken 5 minutes apart are not effective.
Answer:
(a) Call 911 when three nitroglycerin tablets taken every 5 minutes are not effective.
Rationale:
Nitroglycerin tablets should be taken 5 minutes apart for three doses; if this is ineffective, 911 should be called to obtain an ambulance to take the client to the emergency department. The client should not drive or have a family member drive the client to the hospital.
Question 16.
The nurse is coaching an older adult who has been diagnosed with high serum lipids and leads a sedentary lifestyle. The goal is to increase the amount of exercise this client currently performs. After assessing the client’s interests and setting an acceptable goal with the client, which exercise will offer the client the most health benefits while being practical to implement?
(a) jogging three to five times per week for 30 to 60 minutes
(b) playing golf three times per week for 60 minutes
(c) walking three to five times per week for 30 to 60 minutes
(d) swimming once a week for 60 minutes
Answer:
(c) walking three to five times per week for 30 to 60 minutes
Rationale:
The client will obtain the most health benefits from aerobic exercises such as walking, biking, jogging, or swimming. Because the client has been sedentary, the nurse instructs the client to start the exercise program by walking slowly 10 minutes four times a day and increasing to 30 to 60 minutes three to five times per week. Jogging is not a realistic exercise at this time. Playing golf is not considered an aerobic activity; therefore, it is not beneficial in lowering serum lipids. To promote cardiovascular changes, the client would need to swim more than once a week.
Question 17.
During the health history, a client bluntly states, "I think I’m better off dead.” What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Has a family member ever committed suicide?”
(b) “When did these feelings begin?”
(c) “Do you have someone at home to help you?”
(d) “Are you thinking about suicide?”
Answer:
(d) “Are you thinking about suicide?”

Rationale:
The client who voices death wishes must be asked directly about thoughts of suicide and specific suicide plans. The other questions are important history questions but are not crucial to address the follow-up needed when the client verbalizes a death wish.
Question 18.
A client who plays football with friends is to take methotrexate orally for severe rheumatoid arthritis. What should the nurse tell the client about taking this drug? Select all that apply.
(a) “This drug will slow the progression of joint damage.”
(b) “You should avoid the chance of becoming bruised.”
(c) “Plan to increase the protein in your diet.”
(d) “Your health care provider will monitor your blood work to determine liver disease and blood count.”
(e) “Limit or avoid use of alcoholic drinks.”
(f) “Increase your fluid intake to 3,000 mL per day.”
Answer:
(a) “This drug will slow the progression of joint damage.”
(b) “You should avoid the chance of becoming bruised.”
(d) “Your health care provider will monitor your blood work to determine liver disease and blood count.”
(e) “Limit or avoid use of alcoholic drinks.”
Rationale:
Methotrexate is used for clients with rheumatoid arthritis to decrease the progression of the disease and relieve pain. Side effects of the methotrexate include decreased white blood cells and platelets and the potential for liver disease. The nurse should instruct the client to avoid infection and report signs such as fever, child or cough. The client should avoid contact sports that could cause bruising. The client should also limit the amount of alcohol use to avoid liver damage. The client will have frequent blood tests to monitor liver enzymes and complete blood count. It is not necessary for the client to increase the protein in the diet or increase fluid.
Question 19.
An older adult is constipated and tells the nurse that this has not happened before. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “Constipation is an expected problem at your age. Wait to see if this continues.”
(b) “You need to eat more fiber. I’ll tell the dietician.”
(c) “You need to drink more water. I’ll start a record so you can keep track.”
(d) “This may be a sign of a more serious problem; I’ll report this to your health care provider (HCP).”
Answer:
(d) “This may be a sign of a more serious problem; I’ll report this to your health care provider (HCP).”
Rationale:
The new onset of constipation may be a sign of a tumor or other health problems. Constipation is not an expected change of aging. Increased fiber and fluid intake is helpful with constipation, but in this case the client needs to be seen by an HCP Q to rule out a health problem.
Question 20.
The nurse should advise which client who is taking lithium to consult with the health care provider regarding a potential adjustment in lithium dosage?
A client who:
(a) continues work as a computer programmer
(b) attends college classes
(c) can now care for her children
(d) is beginning training for a tennis team
Answer:
(d) is beginning training for a tennis team
Rationale:
A client who is beginning training for a tennis team would most likely require an adjustment in lithium dosage because excessive sweating can increase the serum lithium level, possibly leading to toxicity. Adjustments in lithium dosage would also be necessary when other medications have been added, when an illness with high fever occurs, and when a new diet begins.
Question 21.
A client who has been newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes asks the nurse, “Why do I have to take two shots of insulin? One shot isn’t enough?” What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “A single shot of long-acting insulin would be preferable.”
(b) “You might be able to change to oral medications soon.”
(c) “Two shots will give you better control and decrease complications.”
(d) “I’ll ask the health care provider (HCP) to change your insulin schedule.”
Answer:
(c) “Two shots will give you better control and decrease complications.”
Rationale:
Research has shown that at least two injections daily provide improved blood glucose control and decreased incidence of target end-organ damage. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin replacement and cannot be managed with oral medications alone. It would be inappropriate to ask the HCP m to change the insulin schedule.
Question 22.
A client is receiving gentamicin sulfate intravenously. Before administering the next dose, the nurse reviews the peak and trough serum levels. The nurse uses this information to do what?
(a) Adjust the dosage to the therapeutic range.
(b) Avoid inducing an allergic reaction.
(c) Minimize side effects.
(d) Reach therapeutic levels more quickly.
Answer:
(a) Adjust the dosage to the therapeutic range.
Rationale:
Peak and trough serum levels are used to adjust the dosage within a therapeutic range. Monitoring drug levels does not prevent allergic reactions. Preventing toxicity helps decrease the risk of some side effects but will not totally prevent them. Peaks and trough levels are monitored only after a drug has been given long enough to achieve therapeutic levels
Question 23.
The nurse caring for a client with type 1 diabetes mellitus should use which report to determine how well the insulin, diet, and exercise are balanced?
(a) fasting serum glucose level
(b) 1-week dietary recall
(c) home log of blood glucose levels
(d) glycosylated hemoglobin level
Answer:
(d) glycosylated hemoglobin level
Rationale:
A glycosylated hemoglobin level gives the nurse data about the average blood glucose concentration over 2 to 3 months, providing a picture of the client’s overall glucose control. A fasting serum glucose level gives a picture of the client’s recent glucose level, not the overall effectiveness of the therapeutic regimen. A 1-week diet recall is not always accurate. Although a home log would provide some information about overall control and compliance, the log may not have all of the glucose levels recorded.
Question 24.
The nurses have instituted a falls prevention program. Which strategy will have the highest likelihood of preventing falls?
(a) putting a falls risk sign on the clients’ doors
(b) having the client wear a color-coded armband
(c) making rounds of the unit and clients’ rooms
(d) keeping all beds in low position
Answer:
(c) making rounds of the unit and clients’ rooms
Rationale:
When making rounds, nurses can note a variety of risks in the clients’ rooms, in the hallways, and other areas where clients might be at risk. Using signs and color-coded armbands and keeping the bed in a low position are also useful, but making rounds offers the opportunity for nurses to intervene immediately and teach the client, family, and staff when risks are noted.
Question 25.
A client is receiving a unit of packed red blood cells. Before the transfusion started, the client’s blood pressure was 90/50 mm Hg, pulse rate 100 bpm, respirations 20 breaths/min, and temperature 98°F (36.7°C). Fifteen minutes after the transfusion starts, the client’s blood pressure is 92/54 mm Hg, pulse 100 bpm, respirations 18 breaths/min, and temperature is 101.4°F (38.6°C). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Stop the transfusion.
(b) Raise the head of the bed.
(c) Obtain a prescription for antibiotics.
(d) Offer the client a cool washcloth.
Answer:
(a) Stop the transfusion.
Rationale:
The nurse’s first action should be to clamp off the transfusion because the client is having a transfusion reaction. It is most important that the client not receive any more blood. Other measures may be appropriate after the blood has been stopped. The nurse should raise the head of the bed if the client becomes short of breath. There is no need for antibiotic therapy for a blood transfusion related to a temperature spike. The nurse can provide a cool washcloth for a headache or fever; however, this is not a priority.
Question 26.
A client is receiving opioid epidural analgesia. The nurse should notify the health care provider (HCP) if the client has which findings? Select all that apply.
(a) blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg and baseline blood pressure of 110/60 mm Hg
(b) respiratory rate of 14 breaths/min and base line respiratory rate of 18 breaths/min
(c) report of crushing headache
(d) minimal clear drainage on the dressing
(e) pain rating of 3 on a scale of 1 to 10
Answer:
(a) blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg and baseline blood pressure of 110/60 mm Hg
(c) report of crushing headache
(d) minimal clear drainage on the dressing
Rationale:
A drop in blood pressure to 80/40 mm Hg is significant and should be reported to the HCP m Hypotension and vasodilation may occur as a result of sympathetic nerve blockage along with the pain nerve blockage. A report of a crushing headache suggests that the epidural catheter may be dislodged in the subarachnoid space rather than the epidural space.
Epidural dressings should remain dry and intact. The presence of clear fluid on the dressing could indicate a cerebral spinal fluid leak or the leakage of medication. A respiratory rate of 14 breaths/min, although somewhat decreased from baseline, is within acceptable parameters. However, if the rate drops to 10 breaths/min or less, the HCP should be notified. A pain rating of 3 out of 10 suggests that pain is being relieved with the epidural analgesia.
Question 27.
Which dietary strategy best meets the needs of a client with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)?
(a) Tell the client to eat large meals frequently.
(b) Encourage mega doses of nutritional supplements.
(c) Instruct the client to cook foods thoroughly and adhere to safe food-handling practices.
(d) Tell the client to prepare food in advance and leave it out to eat small amounts throughout the day.
Answer:
(c) Instruct the client to cook foods thoroughly and adhere to safe food-handling practices.
Rationale:
A client with AIDS is immunocompromised, and food safety is an important concern. Food-borne illnesses and infections can be devastating to the client with AIDS. Large, frequent meals are not necessary. Megadoses of vitamins can result in toxicities that may aggravate the client’s clinical condition. Leaving food out encourages growth of microorganisms.
Question 28.
The nurse examines a 6-week-old darkskinned infant. There are large spots of deep blue pigmentation across the infant’s buttocks. The nurse should identify this sign as characteristic of which finding?
(a) vascular disease
(b) telangiectatic nevi
(c) infant milia
(d) Mongolian spots
Answer:
(d) Mongolian spots
Rationale:
This finding describes Mongolian spots, which are common in newborns of African, Asian, or Latin descent. Telangiectatic nevi, or “stork bites,” are pink lesions commonly found on the back of the neck. Milia are small white papules over the nose and cheek that indicate blocked sebaceous glands.
Question 29.
A nulliparous client has been given a prescription for oral contraceptives. The nurse should instruct the client to report which sign to the health care provider (HCP) immediately?
(a) blurred vision
(b) nausea
(c) weight gain
(d) mild headache
Answer:
(a) blurred vision
Rationale:
Blurred vision is a serious adverse effect of oral contraceptives, possibly because of severe hypertension as a result of the medication. If the client experiences blurred vision, she needs to contact her HCP Q immediately. Nausea, weight gain, and mild headache are common and possibly bothersome side effects and should be noted. However, they do not need to be reported immediately unless they are severe, prolonged, or accompanied by other symptoms.
Question 30.
An older adult is admitted to the hospital with nausea and vomiting. The client has a history of heart failure and is being treated with digoxin. The client has been nauseated for a week and began vomiting 2 days ago. Laboratory values indicate hypokalemia. Because of these clinical findings, the nurse should assess the client carefully for:
(a) chronic renal failure.
(b) exacerbation of heart failure.
(c) digoxin toxicity.
(d) metabolic acidosis.
Answer:
(c) digoxin toxicity.
Rationale:
Nausea and vomiting, along with hypokalemia, are likely indicators of digoxin toxicity. Hypokalemia is a common cause of digoxin toxicity; therefore, serum potassium levels should be carefully monitored if the client is taking digoxin. The earliest clinical signs of digoxin toxicity are anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. Bradycardia, other dysrhythmias, and visual disturbances are also common signs. Chronic renal failure usually causes hyperkalemia. With persistent vomiting, the client is more likely to develop metabolic alkalosis than metabolic acidosis.
Question 31.
The nurse is instructing a female client recently diagnosed with osteoporosis about health promotion activities. The client has a 20-year history of smoking and has a sedentary life style. Which information should the nurse include in the teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Increase calcium and vitamin D intake using dietary supplements as prescribed.
(b) Begin walking for 20 to 30 minutes five times a week.
(c) Join a smoking cessation program.
(d) Add swimming to an exercise program.
(e) Enroll in a balance training program.
(f) Perform range-of-motion exercises for the joints of the hand and wrist three times a day.
Answer:
(a) Increase calcium and vitamin D intake using dietary supplements as prescribed.
(b) Begin walking for 20 to 30 minutes five times a week.
(c) Join a smoking cessation program.
(e) Enroll in a balance training program.
Rationale:
Osteoporosis involves a weakness of the bones and presents a risk for fractures. The goal of health promotion is to strengthen the bones and prevent fractures. The nurse should instruct the client to increase calcium and vitamin D intake with supplements as prescribed. The client should begin weight-bearing exercises such as walking. Swimming is not a weight-bearing exercise. The cli¬ent should stop smoking because smoking is a risk factor for osteoporosis. Balance training helps prevent falls. It is not necessary to do range-of-motion exercises; these exercises are appropriate for clients with arthritis.
Question 32.
A woman is using progestin injections for contraception. When does the nurse instruct the client to return for her next injection?
(a) 1 month
(b) 3 months
(c) 4 months
(d) 6 months
Answer:
(b) 3 months
Rationale:
At the time a client receives a Depo-Provera injection, a follow-up appointment should be made for 3 months later. The nurse should emphasize the need to adhere to the medication schedule to prevent an unplanned pregnancy. One of the most common reasons for the failure of this contraceptive is a lack of adherence to the appointment schedule for injections every 3 months.
Question 33.
While the nurse is caring for a multigravid client at 39 weeks’ gestation in active labor whose cervix is dilated to 7 cm and completely effaced at +1 station, the client says, “I need to push!” What should the nurse do next?
(a) Turn the client to her left side.
(b) Tell her to push when she has the urge.
(c) Have her pant quickly during the contraction.
(d) Tell her to focus on an object in the room to relax.
Answer:
(c) Have her pant quickly during the contraction.

Rationale:
Panting will alleviate the client’s urge to push. The client risks edema or tearing of the cervix if pushing begins before complete cervical dilation (10 cm) is achieved. Although turning the client to her left side improves uteroplacental blood flow, it will have no effect on diminishing the client’s urge to push. Although focusing on an object in the room may help the client to relax, it will have no effect on diminishing the client’s urge to push due to the pressure of a fetus at +1 station.
Question 34.
When teaching a client with chronic renal failure who is taking antibiotics about which signs and symptoms of potential nephrotoxicity to report, the nurse should encourage the client to promptly report which changes in the color of the urine? Select all that apply.
(a) straw-colored
(b) cloudy
(c) smoky
(d) pink
(e) pale yellow
Answer:
(b) cloudy
(c) smoky
(d) pink
Rationale:
The client who is taking potentially nephrotoxic antibiotics should notify the health care provider (HCP) if the urine is cloudy, smoky, or pink; early signs of nephrotoxicity are manifested by changes in urine color. Straw-colored and light yellow-colored urine is normal.
Question 35.
The nurse is coaching a client with heart failure about reducing fluid retention. Which strategy will be most effective in reducing a client’s fluid retention?
(a) low-sodium diet
(b) walking for 20 minutes three times a week
(c) restricting fluid intake
(d) elevating the feet
Answer:
(a) low-sodium diet
Rationale:
In clients with fluid retention, sodium restriction may be necessary to promote fluid loss. Increasing exercise will not reduce fluid retention. Exercise will promote circulation, but it will not manage the fluid retention. Restricting fluid intake will not reduce retained fluids; increased fluids will increase urine output and promote improved fluid balance. Elevating the client’s feet helps promote venous return and fluid reabsorption but in itself will not reduce the volume of excess fluid.
Question 36.
During a physical examination, the nurse observes a copper bracelet on a client’s wrist. The client states that she is wearing it to treat her arthritis. What should the nurse do?
(a) Recognize that the client is wearing a protective object she believes prevents illness.
(b) Inform the client that this is a not a helpful practice and ask her to remove the bracelet.
(c) Tell the client that wearing the bracelet is a form of quackery and not to use the bracelet as a treatment.
(d) Encourage the client to continue wearing the copper bracelet because this is a medically supported treatment for arthritis.
Answer:
(a) Recognize that the client is wearing a protective object she believes prevents illness.
Rationale:
The client might wear objects as a protection against specific medical disorders. Typically, these practices bring no harm to the client and should not be discouraged. The client should continue to be encouraged to follow the medical guidance of her health care provider (HCP) [Q]. If the practice is not harming the client, it is inappropriate to label it quackery and demand that the client discontinue it. There is no medical evidence to support the wearing of a copper bracelet.
Question 37.
The heart rate of a newly born term neonate is regular at 142 bpm. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the neonate’s health care provider (HCP).
(b) Check for the presence of cyanosis.
(c) Assess the heart rate again in 3 hours.
(d) Document this as a normal neonatal finding.
Answer:
(d) Document this as a normal neonatal finding.
Rationale:
Normally, a neonate’s heart rate should be between 120 and 160 bpm shortly after birth. The nurse should document this as a normal neonatal finding. The HCP Q does not need to be notified. Assessing for cyanosis is a routine assessment at birth, but with the neonate’s heart rate at 142 bpm, cyanosis should be minimal and typically located in the hands and feet. Heart rate assessments are performed routinely according to facility protocol. For example, the heart rate is assessed soon after birth, every 15 minutes for 1 hour, every 30 minutes for 1 hour, and then every 4 hours.
Question 38.
The nurse is teaching a client with diabetes insipidus about using desmopressin nasal spray.
The therapeutic effects of desmopressin nasal spray are obtained when the client no longer has which symptom?
(a) polydipsia
(b) nasal congestion
(c) headache
(d) blurred vision
Answer:
(a) polydipsia
Rationale:
The therapeutic effects of desmopressin nasal spray are relief from polydipsia and control of polyuria and nocturia in the client with diabetes insipidus. Side effects include nasal congestion and headache. Blurred vision is not related to desmopressin.
Question 39.
A client is recovering from an infected abdominal wound. Which foods should the nurse encourage the client to eat to support wound healing and recovery from the infection?
(a) chicken and orange slices
(b) cheeseburger and French fries
(c) cheese omelet and bacon
(d) gelatin salad and tea
Answer:
(a) chicken and orange slices
Rationale:
Protein and vitamin C are particularly important in promoting wound healing and recovery from infection. A diet high in carbohydrates is also essential. Because the client with an infection commonly does not feel like eating, it is important that what the client eats should be nutritious. Chicken and orange slices would help meet the client’s pro-tein and vitamin needs. A meal of a cheeseburger and fries or a cheese omelet and bacon are high in fat and low do not contain as much vitamin C as the chicken and orange slices. Gelatin salad and tea contain minimal nutrients.
Question 40.
The nurse is preparing a client for surgery. Although the client can speak English, English is the client’s second language. The client has completed high-school level education. When the nurse asks the client what type of surgery is scheduled, the client is unable to provide an answer. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Explain the procedure in detail to the client, and assess the client’s understanding.
(b) Continue to follow the preoperative procedures required to prepare the client for surgery.
(c) Notify the health care provider that the client cannot explain the scheduled surgery.
(d) Document the client’s response in the electronic medical record.
Answer:
(c) Notify the health care provider that the client cannot explain the scheduled surgery.
Rationale:
The nurse should ask the health care provider to explain the surgery to the client again and ensure the client understands the procedure and the risks. If necessary, the nurse can call an interpreter. It is the role of the health care provider to explain the surgical procedure, not the nurse. The nurse cannot continue to prepare the client until the health care provider has explained the surgery and the client agrees to proceed. The nurse should then document the client’s response and nurse’s action after notifying the health care provider of the need to reexplain the procedure to the client.
Question 41.
A toddler admitted in respiratory distress keeps pulling at the oxygen mask, trying to remove it. Which interventions are indicated? Select all that apply.
(a) Restrain the child.
(b) Have the parent read to the child.
(c) Administer a sedative.
(d) Encourage the parent to hold the child.
(e) Tell the child the mask will help him breathe better.
(f) Ask the parent to leave the child’s bedside.
Answer:
(b) Have the parent read to the child.
(d) Encourage the parent to hold the child.
Rationale:
Children in respiratory distress need to be kept as quiet as possible to decrease respiratory and heart rates. Toddlers need a parent with them for security. The best way to quiet toddlers is to read or to hold them. Restraints increase heart and respiratory rates. A sedative will mask the signs of further respiratory distress. Although you could tell toddlers that a mask will help with breathing, they cannot understand the rationale and thus fully comprehend its importance. Asking the parents to leave the bedside will most likely result in greater upset, further contributing to respiratory distress.
Question 42.
The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client who has joint stiffness due to rheumatoid arthritis. Which measure will be the most effective in relieving stiffness?
(a) a warm shower before performing activities of daily living
(b) aspirin after activity to decrease inflammation
(c) a 10-lb (4.5-kg) weight loss to limit stress on joints
(d) cold compresses to joints for 30 minutes to relieve stiffness
Answer:
(a) a warm shower before performing activities of daily living
Rationale:
Warm showers, baths, or hand soaks can help relieve joint stiffness and allow the client to more comfortably perform activities of daily living. Aspirin or other anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken before activity to help decrease inflammation and reduce joint pain and inflammation. Although weight loss may decrease stress on joints, pain and stiffness will continue to be a problem. Cold compresses are most effective for relieving joint pain, whereas moist heat is useful for decreasing pain and stiffness. When cold compresses are applied, their use should be limited to 10 to 15 minutes at a time to decrease the risk of tissue damage.
Question 43.
A client is taking large doses of aspirin daily to treat rheumatoid arthritis. The nurse should instruct the client to tell the health care provider (HCP) when having:
(a) abdominal cramps.
(b) tinnitus.
(c) rash.
(d) low blood pressure.
Answer:
(b) tinnitus.

Rationale:
Tinnitus or ringing in the ears is a sign of aspirin toxicity and should be reported. Clients should be instructed to take aspirin as prescribed and to avoid overdosage. Gastrointestinal symptoms associated with aspirin include nausea, heartburn, and epigastric discomfort caused by gastric irritation. Abdominal cramps, rash, and hypotension are not related to aspirin therapy.
Question 44.
A client is transferred from the coronary care unit to the step-down unit. Which information should be included in the transfer report? Select all that apply.
The client:
(a) needs oxygen at 2 L/min.
(b) has a “do-not-resuscitate” prescription.
(c) uses the bedpan.
(d) has four grandchildren.
(e) has been in normal sinus rhythm for 6 hours.
Answer:
(a) needs oxygen at 2 L/min.
(b) has a “do-not-resuscitate” prescription.
(c) uses the bedpan.
(e) has been in normal sinus rhythm for 6 hours.
Rationale:
The nurse should report that the client is using oxygen, has a “do-not-resuscitate” prescription, can use the bedpan, and is in normal sinus rhythm. Information about having four grandchildren is not needed to help with the client’s continuity of care.
Question 45.
A multigravid client at 26 weeks’ gestation with a history of pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) asks the nurse about traveling from North America to a village in India by airplane to visit her father, who wishes to see her before she gives birth. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “Air travel at this point in your pregnancy can lead to preterm labor.”
(b) “You can travel by airplane as long as you take frequent walks during the trip.”
(c) “You need to avoid traveling because of your history of PIH.”
(d) “You would be placing yourself and your fetus at risk for communicable diseases common in India.”
Answer:
(c) “You need to avoid traveling because of your history of PIH.”
Rationale:
Traveling is not advised because of the client’s history of PIH. The client may be in jeopardy if complications occur and medical care is not available. In some cases, insurance companies will not cover costs of medical care in foreign countries. Air travel is not associated with preterm labor, although some airlines advise clients who are at 28 weeks’ gestation or beyond not to travel by air. Any travel that causes fatigue should be avoided. Additionally, any pregnant client should get frequent exercise while traveling to avoid venous stasis from prolonged sitting. The client is not at greater risk for communicable diseases. The priority is the client’s history of PIH, which, if it occurs, could lead to complications.
Question 46.
A pregnant woman does not have funds to purchase adequate, nutritious food. She works part time at a low-wage job and has two other children. The nurse can refer the client to which type of assistance?
(a) home-delivered meals
(b) neighbors who can provide food
(c) the client’s employer
(d) food bank
Answer:
(d) food bank
Rationale:
The best option is a food bank; the nurse can guide the client to choose optimally nutritious foods. Home-delivered meals are expensive. Neighbors are unlikely to sustain in providing sufficient food. The employer is not responsible for providing food.
Question 47.
The client has various sensory impairments associated with type 1 diabetes. The nurse determines that the client needs further instruction when the client makes which statement?
I will:
(a) carefully test the temperature of my bathwater.
(b) avoid kitchen activities.
(c) avoid hot water bottles or heating pads.
(d) inspect my skin daily for pressure points and injury.
Answer:
(b) avoid kitchen activities.
Rationale:
Safety concerns are essential for a client with sensory impairment. Water temperature should be tested carefully, hot water bottles should be avoided, and the skin should be inspected regularly. Independence and self-care are also important; the client should not be instructed to avoid kitchen activities out of fear of injury.
Question 48.
The nurse is providing discharge instructions to the client with peripheral vascular disease. The nurse should include which information in the discussion with this client? Select all that apply.
(a) Avoid prolonged standing and sitting.
(b) Limit walking so as not to activate the “muscle pump.”
(c) Keep extremities elevated on pillows.
(d) Keep the legs in a dependent position.
(e) Use a heating pad to promote vasodilation.
Answer:
(a) Avoid prolonged standing and sitting.
(c) Keep extremities elevated on pillows.
Rationale:
Elevating the extremities counteracts the forces of gravity and promotes venous return and reduces venous stasis. Walking is encouraged to activate the muscle pump and promote collateral circulation. Prolonged sitting and standing lead to venous stasis and should be avoided. Although heat promotes vasodilation, use of a heating pad is to be avoided to reduce the risk of thermal injury secondary to diminished sensation.
Question 49.
A father tells the nurse that his adolescent son spends lots of time in his room, his grades are falling, and he has given away a few of his favorite video games. What is the most appropriate action for the nurse?
(a) Give the father the telephone number for the local crisis hotline.
(b) Have the father take the adolescent to the nearest mental health outpatient facility now.
(c) Make a same-day appointment for the adolescent with his usual health care provider.
(d) Obtain more history information from the distraught father before making a decision.
Answer:
(c) Make a same-day appointment for the adolescent with his usual health care provider.
Rationale:
These behaviors suggest that the adolescent is thinking of suicide. Because of these behaviors, it is imperative for the adolescent to see his health care professional as soon as possible to determine whether he has suicidal thoughts. After the nurse makes the appointment, then it would be appropriate to obtain more information. Giving the father the telephone number for the local crisis hotline is appropriate after the appointment is made, to ensure that the father has additional support should the adolescent’s behavior escalates and an emergency arises. Taking the adolescent to the nearest mental health outpatient facility now is not warranted unless the adolescent’s behavior escalates.
Question 50.
A school-age child is admitted to the hospital with acute rheumatic fever with chorea-like movements. Which eating utensil should the nurse remove from the meal tray?
(a) fork
(b) spoon
(c) plastic cup
(d) drinking straw
Answer:
(a) fork
Rationale:
For a child with chorea-like movements, safety is of prime importance. Feeding the child may be difficult. Forks should be avoided because of the danger of injury to the mouth and face with the tines. Spoons, straws, and plastic cups pose little risk.
Question 51.
A client’s catheter is removed 4 days after a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). He is experiencing urinary dribbling. What should the nurse do?
(a) Teach the client Kegel exercises.
(b) Obtain a urine culture and sensitivity analysis to screen for a urinary infection.
(c) Encourage voiding every hour to prevent dribbling.
(d) Inform the client that the dribbling will stop after a few days.
Answer:
(a) Teach the client Kegel exercises.
Rationale:
After TURP, sphincter tone is poor, resulting in dribbling or incontinence. Kegel exercises can increase sphincter tone and decrease dribbling. Voiding every hour will not prevent dribbling or improve sphincter tone. It may take up to 12 months for urinary continence to be regained. Drippling is not a sign of a urinary track infection.
Question 52.
The parent of a 2-month-old infant with colic states, “I don’t know what to do anymore. She’s up in the middle of the night crying all the time.” What should the nurse tell the parent to do?
(a) Walk the floor with the baby at night.
(b) Take the infant for a short drive in the car.
(c) Allow the infant to cry it out in her crib.
(d) Offer cereal to fill the baby’s stomach.
Answer:
(b) Take the infant for a short drive in the car.

Rationale:
Numerous things have been tried by parents with babies crying with colic. However, research has identified that the motion of a car is soothing to a baby with colic, commonly quieting the infant. The more the infant cries, the more air is swallowed, adding to the colic pain. Cereal should not be offered until the infant is age 4 to 6 months because of the increased risk of food allergies. Additionally, cereal has not been found to help with colic.
Question 53.
After the application of an arm cast, the client has pain on passive stretching of the fingers, finger swelling and tightness, and loss of function. Based on these data, the nurse anticipates that the client may be developing:
(a) delayed bone union.
(b) compartment syndrome.
(c) fat embolism.
(d) osteomyelitis.
Answer:
(b) compartment syndrome.
Rationale:
Compartment syndrome, caused by compression of blood vessels and nerves, can lead to irreversible muscle and nerve damage if not detected early. Common signs of compartment syndrome
in the arm include pain unrelieved by analgesics, pain on passive extension of fingers, loss of function, numbness and tingling, pallor, coolness of the extremity, and decreased or absent peripheral pulse. Delayed bone union does not cause symptoms of neurovascular impairment. Fat embolism is characterized primarily by confusion and respiratory symptoms. Osteomyelitis is a bone infection and is manifested by signs and symptoms of inflammation and infection.
Question 54.
The nurse is preparing a client who has just had a myocardial infarction for following an exercise program at home. Which type of exercise is most appropriate?
(a) weight lifting with increasing weight two times a week
(b) walking for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week
(c) strength training using elastic exercise bands
(d) jogging for 1 mile three times a week
Answer:
(b) walking for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week
Rationale:
The goal of exercise after a myocardial infarction is to increase cardiac strength and cardiac output. Cardiac rehabilitation programs include exercise that is individualized to the client and starts slowly. Walking is an exercise that most clients can tolerate; the goal is to be able to walk 30 minutes on most days. Weight-lifting and other strength training programs do not provide sustained exercise. The client may be able to increase tolerance for exercise and begin jogging and alternating it with walking, but not until the client has increased tolerance for walking and being able to exercise on most days.
Question 55.
While assessing a 4-day-old neonate born at 28 weeks’ gestation, the nurse cannot elicit the neonate’s Moro reflex, which was present 1 hour after birth. The nurse notifies the health care provider (HCP) because this may indicate which complication?
(a) postnatal asphyxia
(b) skull fracture
(c) intracranial hemorrhage
(d) facial nerve paralysis
Answer:
(c) intracranial hemorrhage
Rationale:
When the nurse cannot elicit the Moro reflex of a 4-day-old preterm infant and the Moro reflex was present at birth, intracranial hemorrhage or cerebral edema should be suspected. Other symptoms include lethargy, bulging fontanels, and seizure activity. Confirmation can be made by ultrasound. Postnatal asphyxia is suggested by respira-tory distress, grunting, nasal flaring, and cyanosis.
A skull fracture can be confirmed by radiography. However, it is unlikely to occur in a preterm neonate. Rather, it is more common in the large-for- gestational-age neonate. Facial nerve paralysis is indicated when there is no movement on one side of the face. This condition is more common in the large-for-gestational-age neonate.
Question 56.
The nurse teaches the client with anxiety about the appropriate use of lorazepam. Which statement indicates that the client understands the nurse’s teaching?
(a) “I can take my medicine whenever I feel anxious.”
(b) “It’s okay to double my dose if I need to.”
(c) “My medicine isn’t for the everyday stress of life.”
(d) “It’s safe to have a glass of wine while taking this medicine.”
Answer:
(c) “My medicine isn’t for the everyday stress of life.”
Rationale:
The statement. “My medicine isn’t for the everyday stress of life,” indicates an accurate understanding of the nurse’s teaching about the use of lorazepam. Antianxiety agents like the benzodiazepines are used to treat anxiety that is unmanageable by other means and beyond the client’s ability to cope. For the drug to be effective, it must be taken as prescribed. Lorazepam can cause physical and psychological dependence. Tolerance can occur, and doubling the dose of lorazepam may increase the risk of tolerance. Lorazepam is a central nervous system depressant. When it is taken in combination with alcohol, the depressant effect increases, posing a danger to the client.
Question 57.
The health care provider prescribes a maternal blood test for alpha fetoprotein for a nulligravid client at 16 weeks’ gestation. When developing the teaching plan, the nurse bases the explanations on the understanding that this test is used to detect which condition?
(a) neural tube defects
(b) Rh incompatibilities
(c) inborn errors of metabolism
(d) lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio
Answer:
(a) neural tube defects
Rationale:
A blood test for alpha fetoprotein is recommended at 15 to 20 weeks’ gestation to screen for certain chromosomal abnormalities and neural tube defects such as spina bifida. Chorionic villi sampling is used to detect chromosomal anomalies. Amniotic fluid amino acid determination is used to detect inborn errors of metabolism such as phenyl-ketonuria. An amniocentesis is used to determine the lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio for fetal lung maturity, indicated by a ratio of 2:1, or chromosomal abnormalities. Rh incompatibilities are predicted with blood type testing measured with antigen tests.
Question 58.
An unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) recorded a client’s 0600 blood glucose level as 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) instead of 216 rng/dL (12 mmol/L). The UAP did not recognize the error until 0900 but reported it to the nurse right away. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Complete an incident report.
(b) Wait and observe the client for symptoms of hyperglycemia.
(c) Reprimand the UAP for the error.
(d) Call the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(d) Call the health care provider (HCP).
Rationale:
The error should be reported to the HCI'Q promptly; the HCP may write additional prescriptions. The nurse should complete an incident report because a potentially dangerous event happened during the client’s care. The nurse should observe the client for symptoms of hyperglycemia but first must call the HCP and complete an incident report. The UAP JCQ does not need to be reassigned for this error. The nurse does not need to reprimand the UAP for the error because the UAP already knows an error was made and has reported it to the nurse.
Question 59.
A client recovering from an abdominal hys-terectomy has pain in her right calf. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Palpate the calf to note pain.
(b) Measure the circumference of both calves and note the difference.
(c) Have the client flex and extend her leg and note the presence of pain.
(d) Raise the right leg and lower it to detect changes in skin color.
Answer:
(b) Measure the circumference of both calves and note the difference.
Rationale:
After abdominal pelvic surgery, the client is especially prone to thrombophlebitis. Measuring calf circumference can help detect edema in the affected leg. The calf should not be rubbed or palpated because a clot could be loosened and travel to the lungs as a pulmonary embolism. Homan’s sign, which is calf pain on dorsiflexion of the foot when the leg is raised, is sometimes associated with thrombophlebitis. Having the client flex and extend the leg does not provide useful assessment data; the leg will not change color when raised and lowered.
Question 60.
A client recently diagnosed with lung cancer tells the nurse that she has been having difficulty sleeping and is often preoccupied with thoughts about how her life has changed. She says, “I wish my life could just go on the way it was.” Which issue should the nurse discuss with the client first?
(a) preparing a will
(b) managing insomnia
(c) understanding grief
(d) relieving anxiety
Answer:
(c) understanding grief

Rationale:
The client is grieving and is telling the nurse that she grieves for the changes occurring in her life since her cancer diagnosis. The nurse can discuss the grief process with the client and offer support at this time. While the client does have insomnia and is anxious, the priority is to help the client manage her grieving. It is premature to discuss preparing a will.
Question 61.
A 12-year-old has a fractured femur and is immobilized in traction as shown in the figure. What should the nurse do?
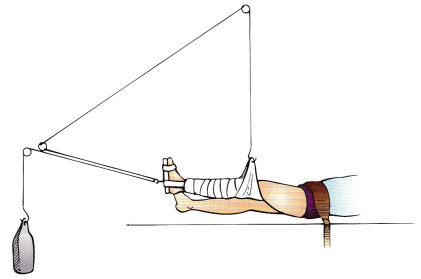
(a) Add additional weight until the foot is only 2 inches (5 cm) from the bed.
(b) Only offer foods that are easy to eat.
(c) Place a pillow under the fractured leg to provide support.
(d) Provide opportunities for age-appropriate activities.
Answer:
(d) Provide opportunities for age-appropriate activities.
Rationale:
The traction is set up correctly. Additional weights are not needed. A well-balanced diet with fiber should be offered; there is no indication that the client needs to have only easy-to-eat foods. A pillow under the leg would negate the effects of the traction. Because the adolescent is positioned this way for an extended period, the nurse can help by finding activities that interest the client.
Question 62.
The nurse is participating in a blood pressure screening event. After three separate readings taken at least 2 minutes apart, the nurse determines that a client has a blood pressure of 160/90 mm Hg. What should the nurse advise the client to do?
(a) Have blood pressure evaluated again within 1 month.
(b) Begin an exercise program.
(c) Examine lifestyle to decrease stress.
(d) Schedule a complete physical immediately.
Answer:
(a) Have blood pressure evaluated again within 1 month.
Rationale:
The client with a systolic blood pressure of 160 to 179 mm Hg should be evaluated by a health care professional within 1 month of the screening. The client with a diastolic blood pressure of 90 to 99 mm Hg should be rechecked within 2 months. Exercise and stress reduction may be desirable activities, but it is first necessary to evaluate the cause of elevated blood pressure. In the absence of other symptoms, it is not necessary to have the client evaluated immediately.
Question 63.
A client’s wife arrives on the nursing unit 6 hours after her husband’s car accident, explaining that she has been out of town. She is distraught because she was not with her husband when he was admitted. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Allow her to verbalize her feelings and concerns.
(b) Describe her husband’s medical treatment since admission.
(c) Explain the nature of the injury and reassure her that her husband’s condition is stable.
(d) Reassure her that the important fact is that she is here now.
Answer:
(a) Allow her to verbalize her feelings and concerns.
Rationale:
Verbalizing feelings and concerns helps decrease anxiety and allows the family member to move on to understanding the current situation. Describing events or explaining equipment is appropriate when the person is not distraught and is ready to learn. Reassuring the family member does not allow verbalization of feelings and discounts the person’s feelings.
Question 64.
A client is scheduled to have a graded exercise test. What should the nurse explain to the client about the purpose of this test?
The test will determine how:
(a) to set the incline gradient on a treadmill.
(b) well the body reacts to controlled exercise stress.
(c) far the client can walk.
(d) long the client can walk.
Answer:
(b) well the body reacts to controlled exercise stress.
Rationale:
Graded exercise testing is a diagnostic and prognostic tool used to determine the physiologic responses to controlled exercise stress. Information gained from a graded exercise test can achieve diagnostic, functional, and therapeutic objectives for the client. Graded exercise tests involve the use of a treadmill, stationary bicycle, or arm ergometry. The information obtained from this test is not used to set the incline on the treadmill, and measuring the distance walked and the duration of the walk is not the purpose of a graded exercise test.
Question 65.
The mother of an infant with hemophilia tells the nurse that she is planning to do home schooling when the child reaches school age. She does not want her child in school because the teacher will not watch the child as well as she would. The mother’s comments represent what common parental reaction to a child’s chronic illness?
(a) overprotection
(b) devotion
(c) mistrust
(d) insecurity
Answer:
(a) overprotection
Rationale:
Overprotection is a typical parental reaction to chronic illness in a child. Characteristics include sacrifice of self and family for the child, failure to recognize the child’s capabilities and sense of responsibility, placement of overly stringent restrictions on play and peer friendship, and a lack of confidence in other peoples’ capabilities.
Question 66.
A client with acute psychosis has been taking haloperidol for 3 days. When evaluating the client’s response to the medication, which comment reflects the greatest improvement?
(a) “I know these voices aren’t real, but I’m still scared of them.”
(b) “I’m feeling so restless, and I can’t sit still.”
(c) “Boy, do I need a shower. I think it’s been days since I’ve had one.”
(d) “I’m ready to talk about my discharge medications.”
Answer:
(a) “I know these voices aren’t real, but I’m still scared of them.”
Rationale:
Knowing that the voices are not real is a reflection that the haloperidol is effective in decreasing psychosis. Restlessness may be a side effect of haloperidol, not an indication of improvement. Awareness of need for activities of daily living is an indicator of improvement. However, recognizing that the voices are not real demonstrates a greater awareness of the client’s disorder than the need for hygiene does. Wanting to prepare for discharge before stabilization reflects denial of illness.
Question 67.
The nurse is administering an IV potassium chloride supplement to a client who has heart failure. What should the nurse consider when developing a plan of care for this client?
(a) Hyperkalemia will intensify the action of the client’s digoxin preparation.
(b) The client’s potassium levels will be unaffected by a potassium-sparing diuretic.
(c) The administration of the IV potassium chloride should not exceed 10 mEq/h or a concentration of 40 mEq/L.
(d) Metabolic alkalosis will increase the client’s serum potassium levels.
Answer:
(c) The administration of the IV potassium chloride should not exceed 10 mEq/h or a concentration of 40 mEq/L.
Rationale:
When administering IV potassium chloride, the administration should not exceed 10 or a concentration of 40 via a peripheral line. These limits are extremely important to prevent the development of hyperkalemia and the possibility of cardiac dysrhythmias. In some situations, with dangerously low serum potassium levels, the client may need cardiac monitoring and more than 10 mEq (mmol/L) of potassium per hour. Potassium-sparing diuretics may lead to hyperkalemia because they affect the kidney’s ability to excrete excess potassium. Metabolic alkalosis can cause potassium to shift into the cells, thus decreasing the client’s serum potassium levels. Hypokalemia can lead to digoxin toxicity.
Question 68.
When assessing a client who is incontinent for risk for developing a pressure ulcer, the nurse should note which factor that can most alter tissue tolerance and lead to the development of a pressure ulcer?
(a) the client’s gender
(b) exposure to moisture
(c) presence of hypertension
(d) smoking
Answer:
(b) exposure to moisture
Rationale:
Exposure to moisture can lead to maceration and the development of pressure ulcers. It is important for the client’s skin to be kept clean and dry with prompt attention to cleanliness after incidents of incontinence. The client’s gender and the presence of hypertension are not factors leading to pressure ulcers. Smoking affects the oxygen status of the client but does not directly lead to the development of pressure ulcers.
Question 69.
A nurse is teaching a parenting class about how to prevent thrush (oral candidiasis). Which statement by a parent indicates more teaching is required?
(a) "I will sterilize pacifiers.”
(b) “I should rinse my child’s mouth after using a corticosteroid.”
(c) “If my child uses a spacer with asthma medications, I need to rinse it after each use.”
(d) “I should rinse my child’s glass after each use.”
Answer:
(d) “I should rinse my child’s glass after each use.”
Rationale:
A new glass should be used each time the child wants a drink. Thrush is a fungal infection. Children who regularly use a corticosteroid inhaler, use oral corticosteroids, or have received antibiotics disturbing normal flora are at risk. It can also occur chronically in children who have an immune disorder. To prevent reinfection, parents should sterilize bottle nipples and pacifiers. Children with asthma should rinse their mouth well with water after using a corticosteroid, and if a spacer (reduces the amount of medicine in the mouth and throat) is used, it also needs to be rinsed.
Question 70.
A 10-year-old with a history of recent respiratory infection has swelling around the eyes in the morning and dark urine. What question should the nurse ask first?
(a) “Has the child had a rash and fever?”
(b) “Has the child had a sore throat?”
(c) “Does the child have any allergies?”
(d) “Does the child drink lots of liquids?”
Answer:
(b) “Has the child had a sore throat?”
Rationale:
In conjunction with the child’s history of recent respiratory infection and report of dark urine, swelling around the eyes should lead the nurse to suspect acute glomerulonephritis. Therefore, the nurse should ask about a recent sore throat because a child with glomerulonephritis typically would have had a sore throat in the past 10 days. Drinking lots of liquids is unrelated to the periorbital edema.
Question 71.
Which nursing intervention is the highest priority during the first 24 hours postoperatively for the client who had a total laryngectomy due to cancer of the larynx?
(a) Provide adequate nourishment.
(b) Prevent skin breakdown around the stoma.
(c) Maintain proper bowel elimination.
(d) Keep airway open.
Answer:
(d) Keep airway open.
Rationale:
During the first 24 hours after a total laryngectomy, maintaining a patent airway is a priority goal. After a total laryngectomy, the client will have a tracheostomy with increased secretions and will require suctioning and tracheostomy care. Providing adequate nutrition, preventing skin breakdown, and maintaining proper bowel elimination will be appropriate as the client recovers, but maintaining a patent airway is the initial priority goal.
Question 72.
It has been 5 months since a client lost his wife and child in a car-train accident. The nurse should determine that the client needs continuing counseling if he makes which statement?
(a) “I’m sleeping, eating, and working pretty well, but I still get so sad at times.”
(b) “I miss them so much, but I can tell I’m get ting better day by day.”
(c) “I wish I didn’t have to sleep. I hate the night mares about what the car looked like.”
(d) “I never thought I’d get over this, but I’m working with my legislator for train crossing safety.”
Answer:
(c) “I wish I didn’t have to sleep. I hate the night mares about what the car looked like.”
Rationale:
Not sleeping to avoid nightmares reflects inadequate grief resolution. The client is not letting go or resolving the vivid memories of the trauma as expected. Statements that the client gets sad at times but can function in daily activities or that the client still misses his family but acknowledges improvement indicate that the client is recovering and continued counseling is not necessary. Working for train crossing safety indicates motivation to help others escape what he has experienced. This action also denotes a goal for the future, indicating recovery.
Question 73.
A client is hearing voices that are telling her to kill herself. She demands a knife to use on her wrists. The nurse calls for another team member to come to the room and provide assistance. Which
is most appropriate intervention for the nurse to implement next?
(a) Put the client in restraints after giving an IM dose of PRN medication.
(b) Ask the client to talk about her anger and what is causing it.
(c) Give oral PRN doses of haloperidol and lorazepam as prescribed.
(d) Search the client’s room for potential weapons after locking the unit kitchen.
Answer:
(c) Give oral PRN doses of haloperidol and lorazepam as prescribed.
Rationale:
Haloperidol and lorazepam together decrease hallucinations and agitation, thus decreasing the risk of self-harm. Putting the client in restraints is premature because danger is not imminent. Asking the client to talk about her anger is inappropriate because the client is beyond rational conversation. A room search is appropriate only after the crisis with the client is handled.
Question 74.
Which measure is contraindicated when the nurse assists a child who has leukemia with oral hygiene?
(a) applying petroleum jelly to the lips
(b) cleaning the teeth with a toothbrush
(c) swabbing the mouth with moistened cotton swabs
(d) rinsing the mouth with a nonirritating mouthwash
Answer:
(b) cleaning the teeth with a toothbrush
Rationale:
The oral mucous membranes are easily damaged and are commonly ulcerated in the client with leukemia. It is better to provide oral hygiene without using a toothbrush, which can easily damage sensitive oral mucosa. Applying petroleum jelly to the lips, swabbing the mouth with moistened cotton swabs, and rinsing the mouth with a nonirritating mouthwash are appropriate oral care measures for a child with leukemia.
Question 75.
The nurse gave the client the wrong medication. It is 2 hours later when the nurse realizes the error. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Assess the client’s condition.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the error.
(c) Complete an incident report.
(d) Report the error to the unit manager.
Answer:
(a) Assess the client’s condition.
Rationale:
The nurse’s first response to the error is to assess the client for any untoward reactions as a result of the error. Notifying the HCP and unit manager of the error as well as completing an incident report are all appropriate later actions, but the first action is to assess the client.
Question 76.
The nurse assesses a toddler in the emergency department for burns on both feet, both lower legs, and the buttocks. The only area not burned from the waist down is the inside of the back of the knee. The parents inform the nurse that the child stepped into the bathtub and then sat down in the water when the water was too hot. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Provide fluid resuscitation and pain medications.
(b) Asses burn depth in the different areas.
(c) Document parent-child interactions.
(d) Report incident to the authorities.
Answer:
(b) Asses burn depth in the different areas.
(a) Provide fluid resuscitation and pain medications.
(c) Document parent-child interactions.
(d) Report incident to the authorities.
Rationale:
When a child steps into hot water, he or she does not sit down in it. This child was held in the scalding water and when he was held in the water, he abducted his knees (hence the areas not burned behind the knees). The nurse first assesses the extent of the burn and then assures fluid resuscitation and pain relief as needed. The nurse also documents what the parents report as well as the parent-child interaction. The burns appear to be from child abuse and must be reported to the authorities, which the nurse can do when the child is stable.
Question 77.
When planning a health promotion class with a group of women, the nurse should include which information about reducing the risk of developing osteoarthritis?
(a) Follow a high-protein diet.
(b) Exercise for 20 minutes at least twice a week.
(c) Maintain a normal weight.
(d) Take a multivitamin supplement daily.
Answer:
(c) Maintain a normal weight.
Rationale:
Obesity is a risk factor for osteoarthritis because it places increased stress on the joints. A high-protein diet, regular exercise, and vitamin supplements do not reduce a client’s risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Question 78.
A neonate circumcised with a Plastibell 1 hour ago is brought to his mother for feeding. What should the nurse instruct the mother to do?
(a) Read a pamphlet about circumcision care.
(b) Remove the petroleum jelly gauze in 24 hours.
(c) Tell the nurse when the neonate voids.
(d) Place petroleum jelly over the site every 2 hours.
Answer:
(c) Tell the nurse when the neonate voids.
Rationale:
The nurse should instruct the mother to report the first voiding after the circumcision because edema could cause a urinary obstruction. Although reading a pamphlet about circumcision care may be helpful, it may not be appropriate for all mothers. Some mothers could have difficulty reading or understanding the information. Petroleum jelly gauze is used with Gomco clamp circumcisions, not Plastibell. Petroleum jelly should not be used with Plastibell circumcision methods because the bell prevents further bleeding.
Question 79.
The nurse is assessing a client who has benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). The nurse should determine if the client has which symptom?
(a) impotence
(b) flank pain
(c) difficulty starting the urinary stream
(d) hematuria
Answer:
(c) difficulty starting the urinary stream
Rationale:
The symptoms of BPH are related to obstruction as a result of an enlarged prostate. Difficulty in starting the urinary stream is a common symptom, along with dribbling, hesitancy, and urinary retention. Impotence does not result from BPH. Flank pain is most commonly related to pyelone-phritis. Hematuria occurs in urinary tract infections, renal calculi, and bladder cancer, to name some of the most common causes.
Question 80.
Which intervention should the nurse anticipate using when caring for a term neonate diagnosed with transient tachypnea at 2 hours after birth?
(a) Monitor the neonate’s color and cry every 4 hours.
(b) Feed the neonate with a bottle every 3 hours.
(c) Obtain extracorporeal membrane oxygenation equipment.
(d) Provide warm, humidified oxygen in a warm environment.
Answer:
(d) Provide warm, humidified oxygen in a warm environment.
Rationale:
Symptoms of transient tachypnea include respirations as high as 150 breaths/min, retractions, flaring, and cyanosis. Treatment is supportive and includes provision of warm, humidified oxygen in a warm environment. The nurse should continuously monitor the neonate’s respirations, color, and behaviors to allow for early detection and prompt intervention should problems arise. Feedings are given by gavage rather than bottle to decrease respiratory stress. Obtaining extracorporeal membrane oxygenation equipment is not necessary but may be used for the neonate diagnosed with meconium aspiration syndrome.
Question 81.
The nurse is assessing a client with dark skin who has early signs of iron deficiency anemia. Which is the expected color of this client’s skin?
(a) reddish-brown
(b) yellowish-brown
(c) black-brown
(d) whitish-brown
Answer:
(b) yellowish-brown
Rationale:
One of the early signs of iron deficiency anemia in a client of Vietnamese descent with dark skin is yellowish-brown skin tones. The nurse can assess for petechiae or jaundice, which may be observed in the conjunctiva or buccal mucosa.
Question 82.
The client is having peritoneal dialysis. During the exchange, the nurse observes that the flow of dialysate stops before all the solution has drained out. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Have the client sit in a chair.
(b) Turn the client from side to side.
(c) Reposition the peritoneal catheter.
(d) Have the client walk.
Answer:
(b) Turn the client from side to side.
Rationale:
Fluid return with peritoneal dialysis is accomplished by gravity flow. Actions that enhance gravity flow include turning the client from side to side, raising the head of the bed, and gently massaging the abdomen. The client is usually confined to a recumbent position during the dialysis. The nurse should not attempt to reposition the catheter.
Question 83.
While caring for several preterm infants in the special care nursery, which action is most important for preventing nosocomial infections in these neonates?
(a) using sterile supplies for all treatments
(b) performing thorough handwashing before giving infant care
(c) donning cover gowns for nurses and visitors to the unit
(d) wearing a mask, and changing it frequently when giving care
Answer:
(b) performing thorough handwashing before giving infant care
Rationale:
The number one cause of nosocomial infections in hospital units is not washing the hands. Nosocomial infections can be significantly reduced by thorough handwashing before caring for each infant. Sterile supplies are not necessary for all treatments. Cover gowns and masks, although helpful in reducing the risk of exposure to blood and body fluids, do not decrease the risk of nosocomial infection.
Question 84.
Which type of restraints is best for the nurse to use for a child in the immediate postoperative period after cleft palate repair?
(a) safety jacket
(b) elbow restraints
(c) wrist restraints
(d) body restraints
Answer:
(b) elbow restraints
Rationale:
Recommended restraints for a child who has had palate surgery are elbow restraints. They minimize the limitation placed on the child but still prevent the child from injuring the repair with fingers and hands. A safety jacket or wrist or body restraints restrict the child unnecessarily.
Question 85.
A nulliparous client tells the nurse that during her last pelvic examination, the health care provider said that her uterus was in a severe retroverted position. The nurse determines that the client may experience which complication?
(a) frequent vaginal infections
(b) pain from endometriosis
(c) severe menstrual cramping
(d) difficulty conceiving a child
Answer:
(d) difficulty conceiving a child
Rationale:
Severe retroversion or anteversion may lead to infertility or difficulty conceiving a child because these positions can block the deposition or migration of sperm. The normal position of the uterus is tipped slightly forward. Frequent vaginal infections commonly are associated with diabetes or human immunodeficiency virus infection, not abnormal uterine positions.
Pain from endometriosis (abnormal myometrial growth outside the uterus) is not associated with abnormal uterine positions. Severe menstrual cramping or dysmenorrhea (primary) is caused by increased prostaglandin production, not abnormal uterine positions. Secondary dysmenorrhea is associated with pelvic inflammatory disease or endometriosis.
Question 86.
A client in severe respiratory distress is admitted to the hospital. When assessing the client, what should the nurse do?
(a) Obtain a brief health history.
(b) Conduct a comprehensive physical examination.
(c) Delay assessment until client’s respiratory distress is resolved.
(d) Complete a focused assessment on the respiratory system.
Answer:
(d) Complete a focused assessment on the respiratory system.
Rationale:
During an episode of acute respiratory distress, it is important that the nurse focus the assessment on the client’s respiratory system and distress to quickly address the client’s problem. Conducting a complete health history and a comprehensive physical examination can be deferred until the client’s condition is stabilized. It is not appropriate to delay all assessments until the respiratory distress is resolved because the nurse must have data to guide treatment.
Question 87.
A client has had a total hip replacement. When assessing the client, which sign most likely indicates that the hip has dislocated?
(a) abduction of the affected leg
(b) loosening of the prosthesis
(c) external rotation of the affected leg
(d) shortening of the affected leg
Answer:
(d) shortening of the affected leg
Rationale:
The most likely indication of a dislocated hip is a shortening of the affected leg. Other indications of dislocation include increasing pain, loss of function to the extremity, and deformity. Abduction of the leg after total hip replacement is a desirable position to prevent dislocation. Loosening of the prosthesis does not necessarily indicate that the hip has dislocated. External rotation of the hip can occur without the hip’s being dislocated. However, a neutral position of rotation is the desired position.
Question 88.
A client with schizophrenia is withdrawn, is suspicious of others, and projects blame. The client’s behavior reflects problems in which stage of development as identified by Erikson?
(a) trust versus mistrust
(b) autonomy versus shame and doubt
(c) initiative versus guilt
(d) intimacy versus isolation
Answer:
(a) trust versus mistrust
Rationale:
The client who is withdrawn, is suspicious, and projects blame is exhibiting problems in trust versus mistrust. Shame and doubt would be reflected as low self-esteem and suspiciousness. Guilt would be reflected in self-blame for all problems. Isolation would be reflected in a lack of longterm relationships.
Question 89.
The nurse is assessing a client who has just experienced a crisis. The nurse should first assess the client for which behavior?
(a) capability of effective problem solving
(b) increased level of anxiety
(c) shortened attention span
(d) seeks help from others
Answer:
(b) increased level of anxiety
Rationale:
During the first phase of a crisis, the client exhibits elevated levels of anxiety. If the client is able to use problem-solving capabilities, there is no crisis. A shortened attention span is a characteristic of the fourth phase of the crisis. Reaching out to others for help is indicative of the third phase of a crisis.
Question 90.
A client with a new ileal conduit asks the nurse when to wear the appliance. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “You need to wear your appliance all the time.”
(b) “You should wear your appliance after you irrigate.”
(c) “It’s only necessary to wear your appliance at night.”
(d) "The appliance must be worn after your meals.”
Answer:
(a) “You need to wear your appliance all the time.”
Rationale:
An ileal conduit is a urinary diversion that requires the client to wear an appliance, or pouch, at all times because urine drains continuously. Ileal conduits are not irrigated. The urinary drainage is affected by fluid intake, not meals.
Question 91.
A child has been exposed to varicella. Which precaution should the nurse institute for infection control?
(a) airborne precautions
(b) droplet precautions
(c) contact precautions
(d) indirect contact precautions
Answer:
(a) airborne precautions
Rationale:
Children with varicella or suspected varicella should be treated under airborne precautions in addition to standard precautions. Varicella is transmitted by airborne nuclei. Droplet precautions are indicated for conditions such as pertussis, meningococcal pneumonia, and rubella. Contact precautions are indicated for conditions such as draining major abscesses, acute viral conjunctivitis, and Clostridium difficile gastroenteritis. Indirect contact is not a method of controlling infection. Rather, it is a mode of transmission involving contamination via some intermediate object, such as an instrument, needle, or dressing, or by hands that are not washed or gloves that are not changed between clients.
Question 92.
Which nursing goal is appropriate for the nurse to make with a client who has multiple myeloma?
(a) Achieve effective management of bone pain.
(b) Recover from the disease with minimal disabilities.
(c) Decrease episodes of nausea and vomiting.
(d) Avoid hyperkalemia.
Answer:
(a) Achieve effective management of bone pain.
Rationale:
In multiple myeloma, neoplastic plasma cells invade the bone marrow and begin to destroy the bone. As a result of this skeletal destruction, pain can be significant. There is no cure for multiple myeloma. Nausea and vomiting are not characteristics of the disease, although the client may experience anorexia. The client should be monitored for signs of hypercalcemia resulting from bone destruction, not for hyperkalemia.
Question 93.
After an episode of severe pain, a client says to the nurse, “The pain really frightened me. I thought I was going to die.” Which statement is the most appropriate response from the nurse?
(a) “I understand that pain can be a frightening experience.”
(b) “Why were you frightened? You’ve had pain before.”
(c) “There’s no need to be frightened of pain.”
(d) “Pain can't cause you to die. Try to relax.”
Answer:
(a) “I understand that pain can be a frightening experience.”
Rationale:
The nurse’s most appropriate response is to acknowledge and validate the client’s concerns. Questioning the client’s fears is not a therapeutic response and can make the client feel defensive. False reassurance that the client should not be afraid disregards the client’s fears and does not promote further communication between the client and nurse. Dismissing the client’s feelings and telling the client to relax do not encourage sharing of feelings.
Question 94.
A child returns to the pediatric unit after a bowel resection. Which action has the highest priority?
(a) Administer IV fluids.
(b) Keep the child on nothing-by-mouth status.
(c) Monitor vital signs frequently.
(d) Assess the child’s pain level.
Answer:
(c) Monitor vital signs frequently.
Rationale:
In a child with abdominal surgery, it is important to check vital signs frequently to assess for internal bleeding. Administering IV fluids, assessing pain, and keeping the child on nothing-bymouth status are all important, but monitoring vital signs frequently is the priority.
Question 95.
When obtaining a health history from a client newly admitted to the hospital, which statement indicates the client’s needs for further follow-up?
(a) “I have some shortness of breath when I exercise.”
(b) “No matter how much I drink, I’m still thirsty all the time.”
(c) “I wake up early in the morning and can’t go back to sleep.”
(d) “In the past couple of weeks, I’ve been having a lot of trouble urinating.”
Answer:
(b) “No matter how much I drink, I’m still thirsty all the time.”
Rationale:
Polydipsia, or increased thirst, is a classic clinical manifestation of diabetes. The excessive loss of fluids is the result of the osmotic diuresis that occurs with glycosuria. It is unlikely that shortness of breath, early awakening, or trouble urinating are related to diabetes mellitus.
Question 96.
A young adult has been diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The nurse should further assess the client for which complication?
(a) angina
(b) fatigue and shortness of breath
(c) abdominal pain
(d) hypertension
Answer:
(b) fatigue and shortness of breath
Rationale:
Cardiomyopathy is a broad term that includes three major forms: dilated, hypertrophic, and restrictive cardiomyopathies. The underlying etiology of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is unknown; it is typically observed in young men but is not limited to them. Common symptoms are fatigue, low tolerance to activity related to the low ejection fraction, and shortness of breath. Angina may be observed if coronary artery disease is present. Abdominal pain and hypertension are not common.
Question 97.
The nurse should advise the mother of a toddler suspected of having pinworms to do the cellophane tape test at which time?
(a) before bathing
(b) after a bowel movement
(c) while the child is asleep
(d) after a meal
Answer:
(c) while the child is asleep
Rationale:
Pinworms come out of the rectum during the nighttime and early morning hours. Therefore, the best time to apply the tape to get results is while the child is asleep.
Question 98.
Which finding provides the most evidence that a fetus might have a gastrointestinal tract anomaly?
(a) meconium in the amniotic fluid
(b) low implantation of the placenta
(c) increased amount of amniotic fluid
(d) preeclampsia in the last trimester
Answer:
(c) increased amount of amniotic fluid
Rationale:
Maternal hydramnios occurs when the fetus has a congenital obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract, such as in the presence of a tracheoesophageal fistula. The fetus normally swallows amniotic fluid and absorbs the fluid from the gastrointestinal tract. Excretion then occurs through the kidneys and placenta. Most fluid absorption occurs in the colon. Absorption cannot occur when the fetus has a gastrointestinal obstruction. Meconium in the amniotic fluid, low implantation of the placenta, and preeclampsia could occur but are more specifically associated with fetal hypoxia.
Question 99.
Using the Morse Fall Risk Scale (see exhibit), the nurse should initiate highest fall risk precautions for which client?
|
Item |
Scale |
Scoring |
|
1. History of falling, immediate or within 3 months |
No 0 |
|
|
2. Secondary diagnosis |
No 0 |
|
|
3. Ambulatory aid Bed rest/nurse assist Crutches/cane/walker Furniture |
|
|
|
4. IV/heparin lock |
No 0 |
|
|
5. Gait/transferring Normal/bed rest) immobile Weak 1m paired |
|
|
|
6. Mental status Oriented to own ability Forgets limitations |
|
|
(a) an 84-year-old client with diabetes admitted with new-onset confusion who reportedly fell at home last week, is currently on bed rest, and has normal saline infusing per saline lock
(b) a 48-year-old alert and oriented client with quadriplegia admitted for wound care of a stage IV pressure ulcer, receiving IV antibiotics per a peripherally inserted central catheter
(c) a 62-year-old client with a history of Parkinson’s disease, admitted for pneumonia and receiving IV antibiotics, who has fallen at home but is able to ambulate with a cane and who during his hospitalization has gotten out of bed without calling for assistance
(d) a 27-year-old client with acute pancreatitis receiving morphine sulfate IV every 2 hours as needed for pain, no significant medical history, smokes two packs of cigarettes per day, may be up independently, and has steady gait
Answer:
(c) a 62-year-old client with a history of Parkinson’s disease, admitted for pneumonia and receiving IV antibiotics, who has fallen at home but is able to ambulate with a cane and who during his hospitalization has gotten out of bed without calling for assistance
Rationale:
Using the Morse Fall Scale, risk factors for this client include history of falling, secondary diagnosis, ambulatory aid, IV/heparin lock, weak gait/transfer, and forgetting limitations (100 points). Client no. 1 is also high risk with a secondary diagnosis, history of falling, IV access, and confusion but is on bed rest (75 points). Client no. 2 risks include IV access and secondary diagnosis (35 points). Client no. 4 is at risk due to his IV access only (20 points).
Question 100.
A 17-year-old gang member, who is living on the streets, is hospitalized after an overdose. When medically stable, the teen is admitted to the adolescent psychiatric unit of the same hospital. In what order of priority from first to last should the nurse explore the issues? All options must be used.
(a) the reason the teen is not living with parents
(b) the desire to leave or remain in the gang
(c) the current level of suicidal risk
(d) the desire to return home or go elsewhere after discharge
Answer:
(c) the current level of suicidal risk
(b) the desire to leave or remain in the gang
(d) the desire to return home or go elsewhere after discharge
(a) the reason the teen is not living with parents
Rationale:
Safety is the first priority, followed by the client’s feelings about leaving the gang. If the client chooses to remain in the gang, the other issues are moot. If the client wishes to leave the gang, the issue of living arrangements becomes significant. If the wish is to return home, it would be important to discover the reasons why the teen left the home and to explore if relationships can be repaired. If the client desires to live elsewhere, it would need to be a place safe from the gang. Foster or adoptive care is unlikely because the client is near 18 years of age.
Question 101.
How does the nurse on the obstetrics unit assure client safety? Select all that apply.
(a) reconciliation of medication prescriptions
(b) communication among staff
(c) placing culturally similar clients together
(d) use of two unique identifiers
(e) staff training
Answer:
(a) reconciliation of medication prescriptions
(b) communication among staff
(d) use of two unique identifiers
(e) staff training
Rationale:
Client care safety is enhanced by the process of reconciling all medication prescriptions at least one time each 24 hours of hospitalization. This can rule out duplication of prescriptions, missing medication prescriptions, or alerting the staff to medications that should have been terminated. Communication among all staff members enhances client safety and prevents errors in written or in verbal format.
Culturally similar clients are appreciative of being with someone who can speak their language or share thoughts and ideas, but this does not increase the safety of the clients. The use of two identifiers should be consistently used to prevent wrong client and procedure errors. Staff training is an extremely valuable tool to educate and increase communication among staff members concerning existing or potential safety situations.
Question 102.
A nurse is planning care with a family of a 4-year-old in preschool who is often disruptive in class, is difficult to engage, and rarely speaks. The child flaps his arms and screeches when he is upset. What would be the most appropriate responses for the nurse to make to the parents? Select all that apply.
(a) “Has your child received all his childhood immunizations? You know there is evidence that childhood immunizations play a role in the development of autism.”
(b) “Has your child been evaluated by a pediatrician? He seems to have some behaviors that are abnormal for a child of his age.”
(c) “How does your child behave at home? If you do not see acting out behavior at home, part of his problem may be dealing with new situations such as school.”
(d) “How do you respond if he disobeys or acts out at home? If your techniques help, stop, or prevent negative behavior, perhaps the teachers can try similar measures at school.”
(e) “Have you considered private school? This environment does not seem right for your child.”
Answer:
(b) “Has your child been evaluated by a pediatrician? He seems to have some behaviors that are abnormal for a child of his age.”
(c) “How does your child behave at home? If you do not see acting out behavior at home, part of his problem may be dealing with new situations such as school.”
(d) “How do you respond if he disobeys or acts out at home? If your techniques help, stop, or prevent negative behavior, perhaps the teachers can try similar measures at school.”
Rationale:
The child’s behavior appears to fit the criteria for autism, but suggesting the child’s immunizations are causative is inaccurate according to recent research and dangerous regarding possibly convincing the mother to forego future immunizations. A better approach would be to suggest a full evaluation by a primary care provider, especially since symptoms could result from other illnesses or conditions.
Inquiring about the child’s behavior at home and the mother’s discipline techniques would give the nurse a better idea of the home environment and could help determine whether this is a problem confined to the school setting or one that also occurs at home. Asking for the mother’s input regarding discipline demonstrates a desire to involve her in problem solving. Suggesting a different school without a full evaluation does not address the problem.
Question 103.
A client is anxious following a robbery. The client is worried about identity theft and states, “I could lose everything. I can’t stand the fears I have. I reported everything, but I still can’t eat or sleep.” Which intervention should the nurse implement first?
(a) Request a prescription for an antianxiety medication.
(b) Provide a list of free legal resources.
(c) Refer the client to a support group.
(d) Listen empathetically while the client discusses the fears.
Answer:
(d) Listen empathetically while the client discusses the fears.
Rationale:
Receiving empathy and talking about fears and feelings validate that the client is having typical reactions to a crime. A support group may help, but its effects will not be immediate. Legal resources may prove helpful, but the nurse does not yet have a clear picture if more legal resources are needed. Short-term medications for anxiety may be appropriate if other strategies are not quickly effective.
Question 104.
A client asks to read the medical record. What should the nurse do?
(a) Call the health care provider (HCP) to obtain permission.
(b) Give the client the medical record and answer the client’s questions.
(c) Tell the client to read the medical record when the HCP makes rounds.
(d) Answer any questions the client has without giving the client the medical record.
Answer:
(b) Give the client the medical record and answer the client’s questions.
Rationale:
The client should be allowed to see the medical record m. As a client advocate, the nurse should answer questions for the client. The nurse helps the client become a primary partner in the health team. The HCP Q should not need to give permission for the client to see the medical record. As a client advocate, the nurse should not make excuses to put the client off in regard to seeing the medical record.
Question 105.
A nurse is relieving the triage nurse in the labor and birth unit who is going to lunch. The report indicates that there are three clients having their vital signs assessed and a fourth client is on her way to the unit from the emergency department. In which order of priority from first to last should the nurse manage these clients? All options must be used.
(a) the client with clear vesicles and brown vaginal discharge at 16 weeks’ gestation
(b) the client with right lower quadrant pain at 10 weeks’ gestation
(c) the client who is at term and has had no fetal movement for 2 days
(d) the client from the emergency department at term and screaming loudly because of labor contractions
Answer:
(d) the client from the emergency department at term and screaming loudly because of labor contractions
(b) the client with right lower quadrant pain at 10 weeks’ gestation
(a) the client with clear vesicles and brown vaginal discharge at 16 weeks’ gestation
(c) the client who is at term and has had no fetal movement for 2 days
Rationale:
First, the nurse should assess the client from the emergency department who is screaming because she may be anywhere along the labor continuum and her status will be unknown until she has a vaginal exam to determine cervical effacement and dilation. The nurse should next assess the client with right lower quadrant pain as she may be experiencing an ectopic pregnancy or appendicitis and may need further evaluation by the health care provider (HCP) Q. The client with clear vesicles and brown vaginal discharge is experiencing a molar pregnancy and will need to have a D&C to evacuate the vesicles; this condition will not jeopardize the life of the mother if no intervention occurs within an hour.
The client who is at term without fetal movement is a priority from an emotional standpoint if there is no heart beat when she is evaluated, but the physical status of the fetus with no fetal movement for 2 days will not change if not seen within the next V2 hour, and the nurse can see this client last. The emotional care for this client will be extensive if there is a diagnosis of fetal demise, and the nurse should plan the time to be available to support this client as needed.
Question 106.
The nurse is beginning the shift and is planning care for six clients on the postpartum unit. Three of the clients have immediate needs, and three of the clients are listed as “stable.” For the best utilization of time and client safety, the nurse should make rounds on which client first?
(a) the three clients who are reported to be stable
(b) the mother with a 4-hour-old infant with initial blood glucose of 33 mg/dL (1.8 mmol/L) and now at 45 mg/dL (2.5 mmol/L) breastfeeding her infant
(c) a mother who had a spontaneous vaginal birth and received carboprost 1 hour ago for increased bleeding
(d) a mother with a 3-day-old who had a bilirubin level of 13 mg/dL (220 pmol/L) 30 minutes ago and is now in a biliblanket at the mother’s bedside
Answer:
(c) a mother who had a spontaneous vaginal birth and received carboprost 1 hour ago for increased bleeding
Rationale:
The client most in need of validating safety is the mother who has received carboprost 1 hour ago for increased bleeding. Her bleeding level needs to be documented as having been evaluated at the beginning of the shift and to determine if it has decreased to within normal limits (i.e., saturating <1 pad/h). The three stable clients will need to have an initial assessment by the oncoming nurse but can wait until the nurse can first assess the mother who is receiving carboprost. The mother with the 4-hour- old infant is able to breastfeed to maintain the blood glucose level, and the mother with the 3-day-old infant in the biliblanket is stable at this point.
Question 107.
The nurse on the postpartum unit is caring for four couplets. There will be a new admission in 30 minutes. The new client is a G4 P4, Spanishspeaking only client with an infant who is in the special care nursery (SCN) for respiratory distress. The nurse should place the new client in a room with which client?
(a) a G4 P4 who is 2 days postpartum with infant, Spanish speaking only
(b) a Gl Pi who is 1 day postpartum with an infant in the SCN
(c) a G6 P6 who gave birth 4 hours ago by cesarean section for fetal distress, infant at bedside
(d) a G1 Pi who is a non-English-speaking client with infant in SCN for fetal distress
Answer:
(a) a G4 P4 who is 2 days postpartum with infant, Spanish speaking only
Rationale:
The ability to communicate with a person of the same language would be an advantage, an opportunity for socialization and support for the new mother who speaks Spanish. If a Spanish speaking mother were placed with the client who also had a baby in SCN, she would have no com-munication opportunity, and the same would apply for rooming with the mother who has had a cesarean section. The client who is non-English speaking does not identify the language spoken, and the nurse cannot assume that it is Spanish.
Question 108.
The nurse is developing a community health education program about sexually transmitted infections. Which information about women who acquire gonorrhea should be included?
(a) Women are more reluctant than men to seek medical treatment.
(b) Gonorrhea is not easily transmitted to women who are menopausal.
(c) Women with gonorrhea are usually asymptomatic.
(d) Gonorrhea is usually a mild disease for women.
Answer:
(c) Women with gonorrhea are usually asymptomatic.
Rationale:
Many women who acquire gonorrhea are asymptomatic or experience mild symptoms that are easily ignored. They are not necessarily more reluctant than men to seek medical treatment, but they are more likely not to realize they have been affected. Gonorrhea is easily transmitted to all women and can result in serious consequences, such as pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility.
Question 109.
Which client is at greatest risk for falling?
(a) a 22-year-old man with three fractured ribs and a fractured left arm
(b) a 70-year-old woman with episodes of syncope
(c) a 50-year-old man with angina
(d) a 30-year-old woman with a fractured ankle
Answer:
(b) a 70-year-old woman with episodes of syncope
Rationale:
The 70-year-old woman with syncopal episodes is at greatest risk for falling. The nurse should assess the client’s gait and balance and the syncopal episodes. The 22-year-old man with upper body fractures and the 50-year-old man with angina are not at risk for falling. The 30-year-old woman could be at risk for falling, but she is at less risk than the 70-year-old client with syncope.
Question 110.
A child with meningococcal meningitis is being admitted to the pediatric unit. In preparation for the child's arrival, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Institute droplet precautions.
(b) Obtain the child’s vital signs.
(c) Ask the parent about medication allergies.
(d) Inquire about the health of siblings at home.
Answer:
(a) Institute droplet precautions.
Rationale:
The child with meningococcal meningitis requires droplet precautions for at least the first 24 hours after effective therapy is initiated to reduce the risk of transmission to others on the unit. After the child has been placed on droplet precautions, other actions, such as taking the child’s vital signs, asking about medication allergies, and inquiring about the health of siblings at home, can be performed.
