Some Practice NCLEX Questions incorporate multimedia elements, such as images and videos, to enhance learning and understanding.
NCLEX Cardiac Health Problems Questions
Cardiac Health Problems NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
A client returns from a left heart catheterization. The right groin was used for catheter access. In which location should the nurse palpate the distal pulse on this client?
(a) anterior to the right tibia
(b) dorsal surface of the right foot
(c) posterior to the right knee
(d) right midinguinal area
Answer:
(b) dorsal surface of the right foot
Explanation:
To best monitor that the client’s circulation remains intact, the dorsal surface of the right foot should be palpated. When the left side of the heart is catheterized, the cannula enters via an artery. In this instance, the right femoral artery was accessed. While all options assess arterial points of the right leg, the dorsal surface of the right foot (the pedal pulse) is the most distal. If this pulse point is present and unchanged from before the procedure, the other pulse points should also be intact.
Question 2.
A client is to have a treadmill stress test. Prior to the stress test, the nurse reviews the results of the laboratory reports. The nurse should report which elevated laboratory value to the health care provider (HCP) prior to the stress test?
(a) cholesterol level
(b) erythrocyte sedimentation rate
(c) prothrombin time
(d) troponin level
Answer:
(d) troponin level
Explanation:
The elevated troponin level should be reported to the HCP [T] prior to the stress test as this change indicates myocardial damage. Sending the client to walk on a treadmill for stress testing would be contraindicated with evidence of recent myocardial injury and could further extend the damage.
The other blood levels are helpful but not critical to this client’s welfare at this point in time.
Question 3.
A client has chest pain rated at 8 on a 10-point visual analog scale. The 12-lead electrocardiogram reveals ST elevation in the inferior leads, and troponin levels are elevated. What should the nurse do
first?
(a) Monitor daily weights and urine output.
(b) Limit visitation by family and friends.
(c) Provide client education on medications and diet.
(d) Reduce pain and myocardial oxygen demand.
Answer:
(d) Reduce pain and myocardial oxygen demand.
Explanation:
Nursing management for a client with a myocardial infarction should focus on pain management and decreasing myocardial oxygen demand. Fluid status should be closely monitored. Client education should begin once the client is stable and amenable to teaching. Visitation should be based on client comfort and maintaining a calm environment.
Question 4.
A client with chest pain is prescribed intravenous nitroglycerin. Which finding is of greatest concern for the nurse initiating the nitroglycerin drip?
(a) Serum potassium is 3.5 mEq/L (3.5 mmol/L).
(b) Blood pressure is 88/46 mm Hg.
(c) ST elevation is present on the electrocardiogram.
(d) Heart rate is 61 bpm.
Answer:
(b) Blood pressure is 88/46 mm Hg.
Explanation:
Nitroglycerin is a vasodilator that will lower blood pressure. The client is having chest pain, and the ST elevation indicates injury to the myocardium, which may benefit from nitroglycerin. The potassium and heart rate are within normal range.
Question 5.
The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with an anterior myocardial infarction 2 days ago. Upon assessment, the nurse identifies a systolic murmur at the apex. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Assess for changes in vital signs.
(b) Draw an arterial blood gas.
(c) Evaluate heart sounds with the client leaning forward.
(d) Obtain a 12-lead electrocardiogram.
Answer:
(a) Assess for changes in vital signs.
Explanation:
The nurse should first obtain vital signs as changes in the vital signs will reflect the severity of the sudden drop in cardiac output: decrease in blood pressure, increase in heart rate, and increase in respirations. Infarction of the papillary muscles is a potential complication of an MI causing ineffective closure of the mitral valve during systole.
Mitral regurgitation results when the left ventricle contracts and blood flows backward into the left atrium, which is heard at the fifth intercostal space, left midclavicular line. The murmur worsens during expiration and in the supine or left-side position and can best be heard when the client is in these positions, not with the client leaning forward. A 12-lead ECG views the electrical activity of the heart; an echocardiogram views valve function.
Question 6.
A client with acute chest pain is receiving IV morphine sulfate. Which is an expected effect of morphine? Select all that apply.
(a) reduces myocardial oxygen consumption
(b) promotes reduction in respiratory rate
(c) prevents ventricular remodeling
(d) reduces blood pressure and heart rate reduces anxiety and fear
(e) reduces anxiety and fear
Answer:
(a) reduces myocardial oxygen consumption
(d) reduces blood pressure and heart rate reduces anxiety and fear
(e) reduces anxiety and fear
Explanation:
(a),(d),(e). Morphine sulfate acts as an analgesic and sedative. It also reduces myocardial oxygen consumption, blood pressure, and heart rate. Morphine also reduces anxiety and fear due to its sedative effects and by slowing the heart rate. It can depress respirations; however, such an effect may lead to hypoxia, which should be avoided in the treatment of chest pain. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor drugs, not morphine, may help to prevent ventricular remodeling.
Question 7.
A client is receiving an IV infusion of heparin sodium at 1,200 units/h. The dilution is 25,000 units/500 mL. How many milliliters per hour will this client receive? Round your answer to a whole number. .................... mL/h.
Answer:
24 mL/h
First, calculate how many units are in each milliliter of the medication:
\(\frac { 25,000 units }{ 500 mL }\) = \(\frac { 50 units }{ 1 mL }\)
Next, calculate how many milliliters the client receives per hour:
Question 8.
An older adult has chest pain and shortness of breath. The health care provider (HCP) prescribes nitroglycerin tablets. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Put the tablet under the tongue until it is absorbed.
(b) Swallow the tablet with 120 mL of water.
(c) Chew the tablet until it is dissolved.
(d) Place the tablet between the cheek and gums until it disappears.
Answer:
(a) Put the tablet under the tongue until it is absorbed.
Explanation:
The client is having symptoms of a myocardial infarction. The first action is to prevent platelet formation and block prostaglandin synthesis. The client should place the tablet under the tongue and wait until it is absorbed. Nitroglycerin tablets are not effective if chewed, swallowed, or placed between the cheek and gums.
Question 9.
The nurse has completed an assessment on a client with a decreased cardiac output. Which findings should receive the highest priority?
(a) blood pressure 110/62 mm Hg, atrial fibrillation with heart rate 82, bilateral basilar crackles
(b) confusion, urine output 15 mL over the last 2 hours, orthopnea
(c) Sp02 92 on 2 L nasal cannula, respirations 20,1+ edema of lower extremities
(d) weight gain of 1 kg in 3 days, blood pressure 130/80 mm Hg, mild dyspnea with exercise
Answer:
(b) confusion, urine output 15 mL over the last 2 hours, orthopnea
Explanation:
A low urine output and confusion are signs of decreased tissue perfusion. Orthopnea is a sign of left-sided heart failure. Crackles, edema, and weight gain should be monitored closely, but the levels are not as high a priority. With atrial fibrillation, there is a loss of atrial kick, but the blood pressure and heart rate are stable.
Question 10.
The nurse notices that a client’s heart rate decreases from 63 to 50 bpm on the monitor. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer atropine 0.5 mg IV push.
(b) Auscultate for abnormal heart sounds.
(c) Prepare for transcutaneous pacing.
(d) Take the client’s blood pressure.
Answer:
(d) Take the client’s blood pressure.
Explanation:
The nurse should first assess the client’s tolerance to the drop in heart rate by checking the blood pressure and level of consciousness and determine if atropine is needed. If the client is symptomatic, atropine and transcutaneous pacing are interventions for symptomatic bradycardia. Once the client is stable, further physical assessments can be done.
Question 11.
When preparing a client for a cardiac angiogram, what actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
(a) Determine if the client has an allergy to liquid contrast material.
(b) Inform the client that an intravenous infusion will be started before the procedure.
(c) Remind the client to have nothing to eat or drink 8 hours before the procedure.
(d) Instruct the client to remain still during the procedure.
(e) Explain that the client will receive a fast-acting acting anesthetic.
Answer:
(a) Determine if the client has an allergy to liquid contrast material.
(b) Inform the client that an intravenous infusion will be started before the procedure.
(c) Remind the client to have nothing to eat or drink 8 hours before the procedure.
(d) Instruct the client to remain still during the procedure.
Explanation:
When preparing the client for a cardiac angiogram, the nurse should determine if the client has an allergy to the liquid contrast medium used in the procedure. Contrast dyes contain iodine, and the administration of a dye could lead to an anaphylactic response in clients who are allergic to the dye. An intravenous infusion will be started before the procedure to administer the contrast dye. The client should not eat or drink for 8 hours prior to the procedure. The client may experience a flushing sensation, but this is a normal response and does not indicate a life-threatening reaction. The client may receive light sedation, but not an anesthetic as the client must be awake to follow instructions. The client should be instructed to remain still during the procedure.
Question 12.
A client is admitted with a myocardial infarction and atrial fibrillation. While auscultating the heart, the nurse notes an irregular heart rate and hears an extra heart sound at the apex after the S2 that remains constant throughout the respiratory cycle. How should the nurse document these findings?
(a) heart rate irregular with S3
(b) heart rate irregular with S4
(c) heart rate irregular with aortic regurgitation
(d) heart rate irregular with mitral stenosis
Answer:
(a) heart rate irregular with S3
Explanation:
An S3 heart sound occurs early in diastole as the mitral and tricuspid valves open and blood rushes into the ventricles. To distinguish an S3from a physiologic S2 split, a split S2 occurs during inspiration, and S3 remains constant during the respiratory cycle. Its pitch is softer and best heard with the bell at the apex, and it is one of the first clinical findings in left ventricular failure. An S4 is heard in late diastole when atrial contraction pumps volume into a stiff, noncompliant ventricle. An S4 is not heard in a client with atrial fibrillation because there is no atrial contraction. Murmurs are sounds created by turbulent blood flow through an incompetent or stenotic valve.
Question 13.
An adult comes into the emergency department with crushing substernal chest pain that radiates to the shoulder and left arm. The admitting diagnosis is acute myocardial infarction. Prescriptions include oxygen by nasal cannula at 4 L/min, complete blood count, a chest radiograph, a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), and 2 mg of morphine sulfate given IV. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer the morphine.
(b) Obtain a 12-lead ECG.
(c) Obtain the blood work.
(d) Prescribe the chest radiograph.
Answer:
(a) Administer the morphine.
Explanation:
Although obtaining the ECG, chest radiograph, and blood work are all important, the nurse’s priority action should be to relieve the crushing chest pain. Therefore, administering morphine sulfate is the priority action.
Question 14.
An older adult had a myocardial infarction (MI) 4 days ago. At 0930, the client’s blood pressure is 102/64 mm Hg. After reviewing the client’s progress notes (see chart), what should the nurse do first?
|
Date |
1/10 |
|
Time |
0030 |
|
Urinary output for the last 4 hours |
90 ml |
|
Capillary refill |
> 3 seconds |
|
Blood pressure |
128/82 |
|
Extremities |
Cool |
(a) Give a fluid challenge/bolus.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Assist the client to walk.
(d) Administer furosemide as prescribed.
Answer:
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
All of the 1200 hour assessments are signs of decreased cardiac output and can be an ominous sign in a client who has recently experienced an MI; the nurse should notify the HCP Q of these changes. Cardiac output and blood pressure may continue to fall to dangerous levels, which can induce further coronary ischemia and extension of the infarct. While the client is currently hypotensive, giving a fluid challenge/bolus can precipitate increased workload on a damaged heart and extend the myocardial infarction.
Exercise or walking for this client will increase both the heart rate and stroke volume, both of which will increase cardiac output, but the increased cardiac output will increase oxygen needs especially in the heart muscle and can induce further coronary ischemia and extension of the infarct. The client is hypotensive. Although the client has decreased urinary output, this is the body’s response to a decreasing cardiac output, and it is not appropriate to administer furosemide.
Question 15.
When administering a thrombolytic drug to the client who is experiencing a myocardial infarction (MI) and who has premature ventricular contractions, which is the expected outcome of the drug?
(a) Promote hydration.
(b) Dissolve clots.
(c) Prevent kidney failure.
(d) Treat dysrhythmias.
Answer:
(b) Dissolve clots.
Explanation:
Thrombolytic drugs are administered within the first 6 hours after onset of an MI to lyse clots and reduce the extent of myocardial damage.
Question 16.
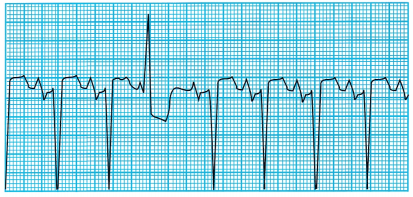
The nurse is assessing a client who has had a myocardial infarction (MI). The nurse notes the cardiac rhythm on the monitor (see the electrocardiogram strip). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Call the rapid response team.
(c) Assess the client for changes in the rhythm.
(d) Administer lidocaine as prescribed.
Answer:
(c) Assess the client for changes in the rhythm.
Explanation:
The client is experiencing a single PVC. PVCs are characterized by a QRS of longer than 0.12 second and by a wide, notched, or slurred QRS complex. There is no P wave related to the QRS complex, and the T wave is usually inverted. PVCs are potentially serious and can lead to ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest when they occur more than 6 to 10 times in an hour in clients with myocardial infarction. The nurse should continue to monitor the client and note if the PVCs are increasing. It is not necessary to notify the HCP or call the rapid response team at this point. Lidocaine is not indicated from the data on this ECG.
Question 17.
The nurse is assessing a client who has had a stent inserted in a coronary artery via the right femoral artery. The
client is receiving intravenous heparin sodium at 1,000 units per hour. During the second postprocedure check, the nurse notes that the puncture site at the groin has begun to steadily ooze blood. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Don gloves and apply direct pressure over the site.
(b) Observe and document the bleeding.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(d) Prepare protamine sulfate for intravenous administration.
Answer:
(a) Don gloves and apply direct pressure over the site.
Explanation:
The nurse should first don gloves and apply direct pressure over the site to stop blood loss from the femoral artery. While the nurse will later observe the site for further bleeding and record the extent of bleeding, this is not the first action that is needed.
If the bleeding cannot be controlled, the HCP who performed the procedure should be contacted, but first, an attempt to manually stop the bleeding with direct pressure is warranted. Protamine sulfate is the antidote for heparin sodium, but this is not an initial action to control the bleeding.
Question 18.
A client admitted for a myocardial infarction (MI) develops cardiogenic shock. An arterial line is inserted. Which prescription from the health care provider should the nurse verify before implementing?
(a) Call for urine output <30 mL/h for 2 consecutive hours.
(b) Administer metoprolol 5 mg IV push.
(c) Prepare for a pulmonary artery catheter insertion.
(d) Titrate dobutamine to keep systolic blood pressure >100 mm Hg.
Answer:
(b) Administer metoprolol 5 mg IV push.
Explanation:
Metoprolol is indicated in the treatment of hemodynamically stable clients with an acute MI to reduce cardiovascular mortality. Cardiogenic shock causes severe hemodynamic instability, and a beta-blocker will further depress myocardial contractility. The metoprolol should be discontinued. The decrease in cardiac output will impair perfusion to the kidneys. Cardiac output, hemodynamic measurements, and appropriate interventions can be determined with a PA catheter. Dobutamine will improve contractility and increase the cardiac output that is depressed in cardiogenic shock.
Question 19.
The nurse is monitoring a client admitted with a myocardial infarction (MI) who is at risk for cardiogenic shock. The nurse should report which changes noted from the client’s chart to the health care provider?
|
|
1300 |
1500 |
|
BP |
110/70 |
100/65 |
|
T |
98.7 (37.1) |
99 (37.2) |
|
HR |
70 |
75 |
|
R |
20 |
26 |
|
Urine output |
90 mL/h |
20 rnL/h |
(a) Urine output
(b) heart rate
(c) blood pressure
(d) respiratory rate
Answer:
(a) Urine output
Explanation:
Oliguria occurs during cardiogenic shock because there is reduced blood flow to the kidneys. Typical signs of cardiogenic shock include low blood pressure, rapid and weak pulse, decreased urine output, and signs of diminished blood flow to the brain, such as confusion and restlessness. Cardiogenic shock is a serious complication of MI, with a mortality rate approaching 90%. Fever is not a typical sign of cardiogenic shock. The other changes in vital signs on the client’s chart are not as significant as the decreased urinary output.
Question 20.
The health care provider prescribes continuous IV nitroglycerin infusion for the client with myocardial infarction. What should the nurse do to ensure safe administration of this drug?
(a) Use an infusion pump for the medication.
(b) Take the blood pressure every 4 hours.
(c) Monitor urine output hourly.
(d) Obtain serum potassium levels daily.
Answer:
(a) Use an infusion pump for the medication.
Explanation:
IV nitroglycerin infusion requires an infusion pump for precise control of the medication. Blood pressure monitoring would be done with a continuous system and more frequently than every 4 hours. Hourly urine outputs are not always required. Obtaining serum potassium levels is not associated with nitroglycerin infusion.
Question 21.
The client is admitted to the telemetry unit due to chest pain. The client has polysubstance abuse, and the nurse assesses that the client is anxious and irritable and has moist skin. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Obtain a history of which drugs the client has used recently.
(b) Administer the prescribed dose of morphine.
(c) Position electrodes on the chest.
(d) Take vital signs.
Answer:
(c) Position electrodes on the chest.
(d) Take vital signs.
(b) Administer the prescribed dose of morphine.
(a) Obtain a history of which drugs the client has used recently.
Explanation:
The nurse should first connect the client to the monitor by attaching the electrodes. Electrocardiography can be used to identify myocardial ischemia and infarction, rhythm and conduction disturbances, chamber enlargement, electrolyte imbalances, and the effects of drugs on the client’s heart. The nurse next obtains vital signs to establish a baseline. Next, the nurse should administer the morphine; morphine is the drug of choice in relieving myocardial infarction pain; it may cause a transient decrease in blood pressure. When the client is stable, the nurse can obtain a history of the client’s drug use.
Question 22.
A client is scheduled for insertion of a coronary stent with right groin access. Which teaching points should the nurse include in this client’s preoperative teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) “If you have a hearing aid, you will need to remove it prior to leaving for the procedure.”
(b) “If you have chest pain during this procedure, please tell the staff when or if this should occur.”
(c) “The stitches at your right groin will be able to be removed in 7 to 10 days following the procedure.”
(d) “You will be given general anesthesia and will be asleep for throughout this procedure.”
(e) “You will need to remain flat during the procedure and for 3 to 6 hours after the procedure.”
(f) “You will need to keep your right leg in a flexed position for 1 to 2 hours following the procedure.”
Answer:
(b) “If you have chest pain during this procedure, please tell the staff when or if this should occur.”
(e) “You will need to remain flat during the procedure and for 3 to 6 hours after the procedure.”
Explanation:
It is important for clients to wear hearing aids to this procedure so that they can hear the questions posed to them by the health care team. Chest pain often occurs when the balloon within the stent is inflated and deployed into the coronary artery. It is expected and brief but should still be reported by the client. During the procedure and for a prescribed amount of time after the procedure, the client will need to remain flat in bed with the right leg straight, not flexed, to prevent bleeding from the access site.
The site is not routinely stitched. It is a puncture rather than an incision requiring sutures. The client may be given intravenous medication to help with comfort, but the client is kept awake to answer questions and to hear instructions and explanations. General anesthesia is not given.
Question 23.
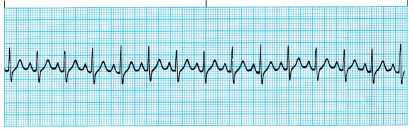
The nurse is assessing a client who has had a myocardial infarction. The nurse notes the cardiac rhythm shown on the electrocardiogram strip. How should the nurse interpret this rhythm strip?
(a) atrial fibrillation
(b) ventricular tachycardia
(c) premature ventricular contractions
(d) sinus tachycardia
Answer:
(d) sinus tachycardia
Explanation:
Sinus tachycardia is characterized by normal conduction and a regular rhythm, but with a rate exceeding 100 bpm. A P wave precedes each QRS, and the QRS is usually normal.
Question 24.
While caring for a client who has sustained a myocardial infarction (MI), the nurse notes eight premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) in 1 minute on the cardiac monitor. The client is receiving an IV infusion of 5% dextrose in water (D5W) at 125 mL/h and oxygen at 2 L/min. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Increase the IV infusion rate to 150 mL/h.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Increase the oxygen concentration to 4 L/min.
(d) Administer a prescribed analgesic.
Answer:
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
PVCs are often a precursor of life-threatening arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. An occasional PVC is not considered dangerous, but if PVCs occur at a rate greater than five or six per minute in the post- MI client, the HCP should be notified immediately. More than six PVCs per minute is considered serious and usually calls for decreasing ventricular irritability by administering medications such as lidocaine hydrochloride. Increasing the IV infusion rate would not decrease the number of PVCs. Increasing the oxygen concentration should not be the nurse’s first course of action; rather, the nurse should notify the HCP promptly. Administering a prescribed analgesic would not decrease ventricular irritability.
Question 25.
Which is an expected outcome for a client on the 2nd day of hospitalization after a myocardial infarction (MI)?
(a) The client continues to have severe chest pain.
(b) The client can identify risk factors for MI.
(c) The client participates in a cardiac rehabilitation walking program.
(d) The client can perform personal self-care activities without pain.
Answer:
(d) The client can perform personal self-care activities without pain.
Explanation:
By day 2 of hospitalization after an MI, clients are expected to be able to perform personal care without chest pain. Severe chest pain should not be present on day 2 after an MI. Day 2 of hospitalization may be too soon for clients to be able to identify risk factors for MI or to begin a walking program; however, the client may be sitting up in a chair as part of the cardiac rehabilitation program.
Question 26.
Which is an expected outcome when a client is receiving an IV administration of furosemide?
(a) increased blood pressure
(b) increased urine output
(c) decreased pain
(d) decreased premature ventricular contractions
Answer:
(b) increased urine output
Explanation:
Furosemide is a loop diuretic that acts to increase urine output. Furosemide does not increase blood pressure, decrease pain, or decrease arrhythmias.
Question 27.
The nurse is preparing to measure central venous pressure (CVP). Mark the spot on the torso indicating the location for leveling the transducer.
Answer:
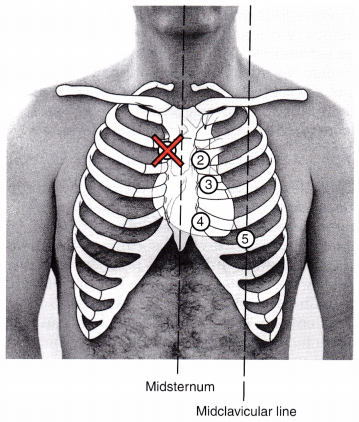
Explanation:
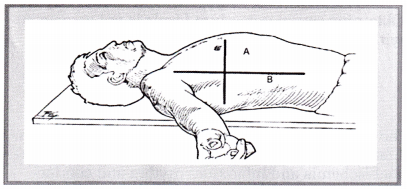
Correct location: The zero point on the CVP transducer needs to be at the level of the right atrium. The right atrium is located at the midaxillary line at the fourth intercostal space. The phlebostatic axis is determined by drawing an imaginary vertical line from the fourth intercostal space at the sternal border to the right side of the chest (A). A secondary imaginary line is drawn horizontally at the level of the midpoint between the anterior and posterior surfaces of the chest (B). The phlebostatic axis is located at the intersection of points A and B.
Question 28.
A client has had a pulmonary artery catheter inserted. In performing hemodynamic monitoring with the catheter, the nurse wedges the catheter. What information will the nurse obtain horn this procedure?
(a) cardiac output
(b) right atrial blood flow
(c) left end-diastolic pressure
(d) cardiac index
Answer:
(c) left end-diastolic pressure
Explanation:
When wedged, the catheter is “pointing” indirectly at the left end-diastolic pressure. The pulmonary artery wedge pressure is measured when the tip of the catheter is slowly inflated and allowed to wedge into a branch of the pulmonary artery. Once the balloon is wedged, the catheter reads the pressure in front of the balloon. During diastole, the mitral valve is open, reflecting left ventricular end-diastolic pressure.
Cardiac output is the amount of blood ejected by the heart in 1 minute and is determined through thermodilution and not wedge pressure. Cardiac index is calculated by dividing the client’s cardiac output by the client’s body surface area and is considered a more accurate reflection of the individual client’s cardiac output. Right atrial blood pressure is not measured with the pulmonary artery catheter.
Question 29.
After a myocardial infarction, the hospitalized client is taught to move the legs while resting in bed. What is the expected outcome of this exercise?
(a) Prepare the client for ambulation.
(b) Promote urinary and intestinal elimination.
(c) Prevent thrombophlebitis and blood clot formation.
(d) Decrease the likelihood of pressure ulcer formation.
Answer:
(c) Prevent thrombophlebitis and blood clot formation.
Explanation:
Encouraging the client to move the legs while in bed is a preventive strategy taught to all clients who are hospitalized and on bed rest to promote venous return. The muscular action aids in venous return and prevents venous stasis in the lower extremities. These exercises are not intended to prepare the client for ambulation. These exercises are not associated with promoting urinary and intestinal elimination. These exercises are not performed to decrease the risk of pressure ulcer formation.
Question 30.
Which is the most appropriate diet for a client during the acute phase of myocardial infarction (MI)?
(a) liquids as desired
(b) small, easily digested meals
(c) three regular meals per day
(d) nothing by mouth
Answer:
(b) small, easily digested meals
Explanation:
Recommended dietary principles in the acute phase of MI include avoiding large meals because small, easily digested foods are better tolerated. Fluids are given according to the client’s needs, and sodium restrictions may be prescribed, especially for clients with manifestations of heart failure. Cholesterol restrictions may be prescribed as well. Clients are not prescribed diets of liquids only or restricted to nothing by mouth unless their condition is very unstable.
Question 31.
The nurse is caring for a client who recently experienced a myocardial infarction and has been started on clopidogrel. The nurse should develop a teaching plan that includes which points? Select all that apply.
(a) The client should report unexpected bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time.
(b) The client should take clopidogrel with food.
(c) The client may bruise more easily and may experience bleeding gums.
(d) Clopidogrel works by preventing platelets from sticking together and forming a clot.
(e) The client should drink a glass of water after taking clopidogrel.
Answer:
(a) The client should report unexpected bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time.
(c) The client may bruise more easily and may experience bleeding gums.
(d) Clopidogrel works by preventing platelets from sticking together and forming a clot.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d). Clopidogrel is generally well absorbed and may be taken with or without food; it should be taken at the same time every day, and, while food may help prevent potential GI upset, food has no effect on absorption of the drug. Bleeding is the most common adverse effect of clopidogrel; the client must understand the importance of reporting any unexpected, prolonged, or excessive bleeding including blood in urine or stool.
Increased bruising and bleeding gums are possible side effects of clopidogrel; the client should be aware of this possibility. Plavix is an antiplatelet agent used to prevent clot formation in clients who have experienced or are at risk for myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, peripheral artery disease, or acute coronary syndrome. It is not necessary to drink a glass of water after taking clopidogrel.
Question 32.
Which client is at greatest risk for coronary artery disease?
(a) a 32-year-old female with mitral valve prolapse who quit smoking 10 years ago
(b) a 43-year-old male with a family history of coronary artery disease (CAD) and cholesterol level of 158 (8.8 mmol/L)
(c) a 56-year-old male with an HDL of 60 (3.3 mmol/L) who takes atorvastatin
(d) a 65-year-old female who is obese with an LDL of 188 (10.4 mmol/L)
Answer:
(d) a 65-year-old female who is obese with an LDL of 188 (10.4 mmol/L)
Explanation:
The woman who is 65 years old, is overweight, and has an elevated LDL is at greatest risk. Total cholesterol >200 (11.1 mmol/L), LDL >100 (5.5 mmol/L), HDL <40 (2.2 mmol/L) in men, HDL <50 (2.8 mmol/L) in women, men 45 years and older, women 55 years and older, smoking, and obesity increase the risk of CAD. Atorvastatin reduces LDL and decreases risk of CAD. The combination of postmenopausal, obesity, and high LDL places this client at greatest risk.
Question 33.
The client has been managing angina episodes with nitroglycerin. Which finding indicates that the therapeutic effect of the drug has been achieved?
(a) decreased chest pain
(b) increased blood pressure
(c) decreased blood pressure
(d) decreased heart rate
Answer:
(a) decreased chest pain
Explanation:
Nitroglycerin acts to decrease myocardial oxygen consumption. Vasodilation makes it easier for the heart to eject blood, resulting in decreased oxygen needs. Decreased oxygen demand reduces pain caused by heart muscle not receiving sufficient oxygen. While blood pressure may decrease ever so slightly due to the vasodilation effects of nitroglycerin, it is only secondary and not related to the angina the client is experiencing. Increased blood pressure would mean the heart would work harder, increasing oxygen demand and thus angina. Decreased heart rate is not an effect of nitroglycerin.
Question 34.
The nurse is teaching a client who has had a myocardial infarction about using nitroglycerin spray. Which information should the nurse include in the teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) “Spray the medication under your tongue as soon as you have chest pain.”
(b) “Swallow the medication as soon as you have sprayed it in your mouth.”
(c) “Store the medication in the refrigerator when not in use.”
(d) “Shake the medication container before using.”
(e) “If the chest pain continues after 2 spays of the medication, wait 5 minutes and use one more spray.”
(f) “Call 911 if chest pain continues after 10 minutes of using the third spray.”
Answer:
(a) “Spray the medication under your tongue as soon as you have chest pain.”
(e) “If the chest pain continues after 2 spays of the medication, wait 5 minutes and use one more spray.”
(f) “Call 911 if chest pain continues after 10 minutes of using the third spray.”
Explanation:
(a), (e), (f). The nurse should instruct the client to spray the nitroglycerin under the tongue at the first sign of chest pain. If pain continues after using two doses of the medication, wait 5 minutes and administer one more spray. If the chest pain continues after 10 minutes, the client should call 911 and seek emergency assistance. The client should not swallow the medication. The medication should be stored at room temperature away from heat and light, not in the refrigerator. It is not necessary to shake the medication container before use.
Question 35.
A client has risk factors for coronary artery disease, including smoking cigarettes, eating a diet high in saturated fat, and leading a sedentary lifestyle. Which coaching strategies from the nurse wall be most effective in assisting the client improve his or her health?
(a) explaining how the risk factors lead to poor health
(b) withholding praise until the client changes the risky behavior
(c) helping the client establish a wellness vision to reduce the health risks
(d) instilling mild fear into the client about the potential outcomes of the risky health behaviors
Answer:
(c) helping the client establish a wellness vision to reduce the health risks
Explanation:
In health coaching, unlike traditional client education techniques in which the nurse provides information, the goal of coaching is to encourage the client to explore the reasons for the behavior and establish a vision for health behavior and the way he or she can make changes to improve health behavior and reduce or eliminate health risks. When coaching a client, the nurse does not provide information, withhold praise, or instill fear.
Question 36.
The nurse is evaluating a client who received tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) following a myocardial infarction (MI). What is the expected outcome of this drug?
(a) Control chest pain.
(b) Reduce coronary artery vasospasm.
(c) Control the arrhythmias associated with MI.
(d) Revascularize the blocked coronary artery.
Answer:
(d) Revascularize the blocked coronary artery.
Explanation:
The thrombolytic agent t-PA, administered intravenously, lyses the clot blocking the coronary artery. The drug is most effective when administered within the first 6 hours after onset of MI. The drug does not reduce coronary artery vasospasm; nitrates are used to promote vasodilation. Arrhythmias are managed by antiar- rhythmic drugs. Surgical approaches are used to open the coronary artery and reestablish a blood supply to the area.
Question 37.
When monitoring a client who is receiving tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA), the nurse should asses the client for which changes?
(a) cardiac arrhythmias
(b) hypertension
(c) seizure
(d) hypothermia
Answer:
(a) cardiac arrhythmias
Explanation:
Cardiac arrhythmias are commonly observed with administration of t-PA. Cardiac arrhythmias are associated with reperfusion of the cardiac tissue. Hypotension is commonly observed with administration of t-PA. Seizures and hypothermia are not generally associated with reperfusion of the cardiac tissue.
Question 38.
A middle-aged client with a history of hypertension reports having “indigestion.” The nurse connects the client to a cardiac monitor, which reveals eight premature ventricular contractions per minute. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Start an intravenous infusion.
(c) Obtain a portable chest radiograph.
(d) Draw blood for laboratory studies.
Answer:
(b) Start an intravenous infusion.
Explanation:
Advanced cardiac life support recommends that at least one or two IV lines be inserted in one or both of the antecubital spaces. Calling the HCP, obtaining a portable chest radiograph, and drawing blood for the laboratory are important but secondary to starting the IV line.
Question 39.
Following diagnosis of angina pectoris, a client reports being unable to walk up two flights of stairs without pain. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Climb the steps early in the day.
(b) Rest for at least an hour before climbing the stairs.
(c) Take a nitroglycerin tablet before climbing the stairs.
(d) Lie down after climbing the stairs.
Answer:
(c) Take a nitroglycerin tablet before climbing the stairs.
Explanation:
Nitroglycerin may be used prophylacti- cally before stressful physical activities such as stair climbing to help the client remain pain free. Climbing the stairs early in the day would have no impact on decreasing pain episodes. Resting before or after an activity is not as likely to help prevent an activity-related pain episode.
Question 40.
The client who experiences angina has been told to follow a low-cholesterol diet. Which meal would be best?
(a) hamburger, salad, and milk shake
(b) baked liver, green beans, and coffee
(c) spaghetti with tomato sauce, salad, and coffee
(d) fried chicken, green beans, and skim milk
Answer:
(c) spaghetti with tomato sauce, salad, and coffee
Explanation:
Pasta, tomato sauce, salad, and coffee would be the best selection for the client following a low-cholesterol diet. Hamburgers, milk shakes, liver, and fried foods tend to be high in cholesterol.
Question 41.
Which symptom should the nurse teach the client with unstable angina to report immediately to the health care provider?
(a) a change in the pattern of the chest pain
(b) pain during sexual activity
(c) pain during an argument
(d) pain during or after a physical activity
Answer:
(a) a change in the pattern of the chest pain
Explanation:
The client should report a change in the pattern of chest pain. It may indicate increasing severity of coronary artery disease. Pain occurring during stress or sexual activity would not be unexpected, and the client may be instructed to take nitroglycerin to prevent this pain. Pain during or after an activity such as lawn mowing also would not be unexpected; the client may be instructed to take nitroglycerin to prevent this pain or may be restricted from doing such activities.
Question 42.
The nurse is caring for a client who has just returned from having a percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty with femoral artery access. In which order, from first to last, should the nurse obtain information about the client? All options must be used.
(a) vital signs and oxygen saturation
(b) pedal pulses
(c) color and sensation of extremity
(d) catheterization site
Answer:
(a) vital signs and oxygen saturation
(b) pedal pulses
(d) catheterization site
(c) color and sensation of extremity
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (c). When a client returns from having a transluminal balloon angioplasty with femoral access, the nurse should first obtain baseline vital signs and oxygen saturation to determine evidence of bleeding or decreased tissue perfusion. The nurse should next assess the pedal pulses to determine if the client has adequate peripheral tissue perfusion. Next the nurse should inspect the catheterization site and then determine color and sensation in the affected leg.
Question 43.
A client has a throbbing headache when nitroglycerin is taken for angina. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
(b) Limit the frequency of using nitroglycerin.
(c) Take the nitroglycerin with a few glasses of water.
(d) Rest in a supine position to minimize the headache.
Answer:
(a) Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Explanation:
Headache is a common side effect of nitroglycerin that can be alleviated with aspirin, acetaminophen, or ibuprofen. The sublingual nitroglycerin needs to be absorbed in the mouth, which will be disrupted with drinking. Lying flat will increase blood flow to the head and may increase pain and exacerbate other symptoms, such as shortness of breath.
Question 44.
How should the nurse instruct the client with unstable angina to use sublingual nitroglycerin tablets when chest pain occurs?
(a) “Sit down and then take one tablet every 2 to 5 minutes until the pain stops.”
(b) “Sit down and then take one tablet and rest for 15 minutes. Call the health care provider if pain persists after 15 minutes.”
(c) “Sit down and then take one tablet; then if the pain persists, take additional two tablets in 5 minutes. Call the health care provider if pain persists after 15 minutes.”
(d) “Sit down and then take one tablet. If pain persists after 5 minutes, call 911.”
Answer:
(d) “Sit down and then take one tablet. If pain persists after 5 minutes, call 911.”
Explanation:
The nurse should instruct the client that correct protocol for using sublingual nitroglycerin involves immediate administration when chest pain occurs. Sublingual nitroglycerin appears in the bloodstream within 2 to 3 minutes and is metabolized within about 10 minutes. The client should sit down and place the tablet under the tongue. If the chest pain is not relieved within 5 minutes, the client should call 911. Although some health care providers (HCPs) [3 may recommend taking a second or third tablet spaced 5 minutes apart and then calling for emergency assistance, it is not appropriate to take two tablets at once. Nitroglycerin acts within 2 to 3 minutes, and the client should not wait 15 minutes to take further action. The client should call 911 to obtain emergency help rather than calling the HCP.
Question 45.
A client with angina is taking nifedipine. What instruction should the nurse give the client?
(a) Monitor blood pressure monthly.
(b) Perform daily weights.
(c) Inspect gums daily.
(d) Limit intake of green leafy vegetables.
Answer:
(c) Inspect gums daily.
Explanation:
The client taking nifedipine should inspect the gums daily to monitor for gingival hyperplasia. This is an uncommon adverse effect but one that requires monitoring and intervention if it occurs. The client taking nifedipine might be taught to monitor blood pressure, but more often than monthly. These clients would not generally need to perform daily weights or limit intake of green leafy vegetables.
Question 46.
What instructions should the nurse give the client who will be starting a prescription for simvastatin 40 mg/day client? Select all that apply.
(a) “Take once a day in the morning.”
(b) “If you miss a dose, take it when you remember it.”
(c) “Limit greens such as lettuce in the diet to prevent bleeding.”
(d) “Be sure to take the pill with food.”
(e) “Report muscle pain or tenderness to your health care provider.”
(f) “Continue to follow a diet that is low in satu rated fats.”
Answer:
(b) “If you miss a dose, take it when you remember it.”
(e) “Report muscle pain or tenderness to your health care provider.”
(f) “Continue to follow a diet that is low in satu rated fats.”
Explanation:
(b), (e), (f). Simvastatin is used in combination with diet and exercise to decrease elevated total cholesterol. The client should take simvastatin in the evening, and the nurse should instruct the client that if a dose is missed, to take it as soon as remembered, but not to take at the same time as the next scheduled dose. It is not necessary to take the pill with food. The client does not need to limit greens (limiting greens is appropriate for clients taking warfarin), but the nurse should instruct the client to avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice, which can increase the amount of the drug in the bloodstream. A serious side effect is myopathy, and the client should report muscle pain or tenderness to the health care provider (HCP) CD.
Question 47.
Captopril, furosemide, and metoprolol are prescribed for a client with systolic heart failure.
The client’s blood pressure is 136/82 mm Hg, and the heart rate is 65 bpm. Prior to medication administration at 0900, the nurse reviews the following lab tests (see chart). What should the nurse do first?
Laboratory Results
|
Sodium |
140 mEqfL (140 mmol/L) |
|
Potassium |
6.8 mEq/L (6.8 mmol/L) |
|
BUN |
18 mg/dL (6.4 mmol/L) |
|
Creatinine |
1.0 mg/dL (76.3 imoI/L) |
|
Hemoglobin |
12 g/dL (120 g/L) |
|
Hematocrit |
37% (0.37) |
(a) Administer the medications.
(b) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Withhold the captopril.
(d) Question the metoprolol dose.
Answer:
(c) Withhold the captopril.
Explanation:
The nurse should withhold the dose of captopril; captopril is an ACE inhibitor, and a side effect of the medication is hyperkalemia. The BUN and creatinine, which are normal, should be viewed prior to administration since renal insufficiency is another potential side effect of an ACE-I. The heart rate is within normal limits. The nurse should question the dose of metoprolol if the client’s heart rate is bradycardic. The hemoglobin and hematocrit are normal for a female. The nurse should report the high potassium level and that the captopril was withheld.
Question 48.
A client was admitted with an exacerbation of heart failure breath at 0200. At 0700, which information is most important for the nurse who admitted the client to communicate during the hand-off of care report to the nurse who will next take care of the client?
(a) admission weight of 210 lb (95 kg)
(b) elevated B-type natriuretic peptide of 600 mg/mL
(c) reaching 250 mL by incentive spirometer
(d) urinary output of 120 mL
Answer:
(d) urinary output of 120 mL
Explanation:
The urinary output is less than the expected minimum of 30 mL/h, and if the urinary output does not increase, the nurse who will next care for the client should report the decreased urinary output to the health care provider. An elevated B-type natriuretic peptide level is expected with acute heart failure. The level that the client can reach with the incentive spirometer is good to know, but it is not the most essential finding to report at this time. The admission weight is helpful only if a prior or baseline weight is also provided.
Question 49.
A client with chronic heart failure has atrial fibrillation and is taking warfarin. What should the nurse tell the client about the expected outcome of this drug?
(a) “This medication will decrease the extra fluid your heart is circulating.”
(b) “This medication will improve the work of your heart.”
(c) “This medication will prevent a clot from forming.”
(d) “This medication will regulate the rhythm of your heart.”
Answer:
(c) “This medication will prevent a clot from forming.”
Explanation:
Warfarin is an anticoagulant, which is used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation and decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (<20%) to prevent thrombus formation and release of emboli into the circulation. The client may also take other medication as needed to manage the heart failure. Warfarin does not reduce circulatory load or improve myocardial workload. Warfarin does not affect cardiac rhythm.
Question 50.
A client with heart failure is taking furose- mide, digoxin, and potassium chloride. The client has nausea, blurred vision, headache, and weakness. The nurse notes that the client is confused. The telemetry strip shows first-degree atrioventricular block. What other sign should the nurse assess next?
(a) hyperkalemia
(b) digoxin toxicity
(c) fluid deficit
(d) pulmonary edema
Answer:
(b) digoxin toxicity
Explanation:
Early symptoms of digoxin toxicity include anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. Visual disturbances can also occur, including double or blurred vision and visual halos. Hypokalemia is a common cause of digoxin toxicity associated with arrhythmias because low serum potassium can enhance ectopic pacemaker activity. Although vomiting can lead to fluid deficit, given the client’s history, the vomiting is likely due to the adverse effects of digoxin toxic-ity. Pulmonary edema is manifested by dyspnea and coughing.
Question 51.
The nurse should assess the client with left sided heart failure for which findings? Select all that apply.
(a) dyspnea
(b) jugular vein distention (JVD)
(c) crackles
(d) right upper quadrant pain
(e) oliguria
(f) decreased oxygen saturation levels
Answer:
(a) dyspnea
(c) crackles
(e) oliguria
(f) decreased oxygen saturation levels
Explanation:
(a), (c), (e), (f). Dyspnea, crackles, oliguria, and decreased oxygen saturation are signs and symptoms related to pulmonary congestion and inadequate tissue perfusion associated with left-sided heart failure. JVD and right upper quadrant pain along with ascites and edema are usually associated with congestion of the peripheral tissues and viscera in right-sided heart failure.
Question 52.
Which are indications that a client with a history of left-sided heart failure is developing pulmonary edema? Select all that apply.
(a) distended jugular veins
(b) dependent edema
(c) anorexia
(d) coarse crackles
(e) tachycardia
Answer:
(d) coarse crackles
(e) tachycardia
Explanation:
(d), (e). Signs of pulmonary edema are identical to those of acute heart failure. Signs and symptoms are generally apparent in the respiratory system and include coarse crackles, severe dyspnea, and tachypnea. Severe tachycardia occurs due to sympathetic stimulation in the presence of hypoxemia. Blood pressure may be decreased or elevated, depending on the severity of the edema. Jugular vein distention, dependent edema, and anorexia are symptoms of right-sided heart failure.
Question 53.
An older adult with a history of heart failure is admitted to the emergency department with pulmonary edema. During admission, what should the nurse assess first?
(a) blood pressure
(b) skin breakdown
(c) serum potassium level
(d) urine output
Answer:
(a) blood pressure
Explanation:
It is a priority to assess blood pressure first because people with pulmonary edema typically experience severe hypertension that requires early intervention. The client probably does not have skin breakdown, but when the client is stable and when the nurse obtains a complete health history, the nurse should inspect the client’s skin for any signs of breakdown; however, when the client is stable, the nurse should inspect the skin. Potassium levels are not the first priority. The nurse should monitor urine output after the client is stable.
Question 54.
The nurse is caring for an older adult with mild dementia admitted with heart failure. What nursing care will be helpful for this client in reducing potential confusion related to hospitalization and change in routine? Select all that apply.
(a) Reorient frequently to time, place, and situation.
(b) Put the client in a quiet room furthest from the nursing station.
(c) Perform necessary procedures quickly.
(d) Arrange for familiar pictures or special items at bedside.
(e) Limit the client’s visitors.
(f) Spend time with the client, establishing a trusting relationship.
Answer:
(a) Reorient frequently to time, place, and situation.
(d) Arrange for familiar pictures or special items at bedside.
(f) Spend time with the client, establishing a trusting relationship.
Explanation:
(a), (d), (f). It is not unusual for the elderly client to become somewhat confused when “relocated” to the hospital, and this may be more difficult for those with known dementia. Frequent reorientation delivered patiently and calmly along with placing familiar items nearby so the client can see them may help decrease confusion related to hospitalization. Establishing a trusting relationship is important with every client but may be more so with this client. Putting the client in a room further from the nursing station may decrease extra noise for the client but will also make it more difficult to observe the client and maintain a safe environment. Procedures should be explained to the client prior to proceeding and should not be rushed. Visits by family and friends may help to keep the client oriented.
Question 55.
The nurse is assessing a client with chronic heart failure who is demonstrating neurohormonal compensatory mechanisms. Which are expected findings on assessment? Select all that apply.
(a) decreased cardiac output
(b) increased heart rate
(c) vasoconstriction in skin, GI tract, and kidneys
(d) decreased pulmonary perfusion
(e) fluid overload
Answer:
(a) decreased cardiac output
(b) increased heart rate
(c) vasoconstriction in skin, GI tract, and kidneys
(e) fluid overload
Explanation:
(a),(b), (c), (e). Heart failure can be a result of several cardiovascular conditions, which will affect the heart’s ability to pump effectively. The body attempts to compensate through several neuro-hormonal mechanisms. Decreased cardiac output stimulates the aortic and carotid baroreceptors, which activates the sympathetic nervous system to release norepinephrine and epinephrine. This early response increases the heart rate and contractility.
It also has some negative effects, including vasoconstriction of the skin, GI tract, and kidneys. Decreased renal perfusion (due to low CO and vasoconstriction) activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone process resulting in the release of antidiuretic hormone. This causes fluid retention in an attempt to increase blood pressure and, therefore, cardiac output. In the damaged heart, this causes fluid overload. There is no parasympathetic response. Decreased pulmonary perfusion can be a result of fluid overload or concomitant pulmonary disease.
Question 56.
Furosemide 40 mg intravenous push is prescribed. Furosemide 10 mg/mL is available. How much should the nurse administer? Round your answer to a whole number. ................... mL.
Answer:
4 mL. Desired amount (D) divided by what is available (H) times quantity (Q] = amount to administer. D = 40 mg divided by H = 10 mg/mL equals 40 divided by 10 = 4 mL.
Question 57.
Which position is best for a client with heart failure who has orthopnea?
(a) semi-sitting (low Fowler’s position) with legs elevated on pillows
(b) lying on the right side (Sims’ position) with a pillow between the legs
(c) sitting upright (high Fowler’s position) with legs resting on the mattress
(d) lying on the back with the head lowered (Trendelenburg’s position) and legs elevated
Answer:
(c) sitting upright (high Fowler’s position) with legs resting on the mattress
Explanation:
Sitting almost upright in bed with the feet and legs resting on the mattress decreases venous return to the heart, thus reducing myocardial workload. Also, the sitting position allows maximum space for lung expansion. Low Fowler’s position would be used if the client could not tolerate high Fowler’s position for some reason. Lying on the right side would not be a good position for the client in heart failure. The client in heart failure would not tolerate Trendelenburg’s position.
Question 58.
What is the major goal of nursing care for a client with heart failure and pulmonary edema?
(a) Increase cardiac output.
(b) Improve respiratory status.
(c) Decrease peripheral edema.
(d) Enhance comfort.
Answer:
(a) Increase cardiac output.
Explanation:
Increasing cardiac output is the main goal of therapy for the client with heart failure or pulmonary edema. Pulmonary edema is an acute medical emergency requiring immediate intervention. Respiratory status and comfort will be improved when cardiac output increases to an acceptable level. Peripheral edema is not typically associated with pulmonary edema.
Question 59.
Furosemide is administered intravenously to a client with heart failure. How soon after administration should the nurse begin to see evidence of the drug’s desired effect?
(a) 5 to 10 minutes
(b) 30 to 60 minutes
(c) 2 to 4 hours
(d) 6 to 8 hours
Answer:
(a) 5 to 10 minutes
Explanation:
After intravenous injection of furose- mide, diuresis normally begins in about 5 minutes and reaches its peak within about 30 minutes. Medication effects last 2 to 4 hours. When furosemide is given intramuscularly or orally, drug action begins more slowly and lasts longer than when it is given intravenously.
Question 60.
The nurse teaches a client with heart failure to take oral furosemide in the morning. What is the expected outcome for taking this drug in the morning? The client will:
(a) Avoid concentrated urine.
(b) Prevent the risk of falling.
(c) Limit the excretion of electrolytes.
(d) Obtain more sleep more.
Answer:
(d) Obtain more sleep more.
Explanation:
When diuretics are given early in the day, the client will void frequently during the daytime hours and will not need to void frequently during the night. Therefore, the client’s will be able to sleep more. The client may be at risk for falling, and the nurse should instruct all clients to rise from a sitting or lying position slowly, but the primary reason for taking the drug in the morning is to limit the number of times the client would need to void during the night if the drug were taken at bedtime. Taking furosemide in the morning has no effect on concentrating the urine or preventing electrolyte imbalances.
Question 61.
The nurse is assessing a client with a known history of chronic heart failure. Which finding indicates poor perfusion
to the tissues?
(a) blood pressure 102/64 mm Hg
(b) cool, pale extremities
(c) heart rate 104 bpm
(d) shortness of breath when supine
Answer:
(b) cool, pale extremities
Explanation:
In heart failure, the heart is unable to adequately meet the body’s metabolic demands; in an attempt to supply major organs, less blood is circulated to extremities, leaving them cool, pale and potentially cyanotic. A blood pressure of 102/64 mm Hg is lower than average, but it may be normal for this client and would not indicate poor perfusion to tissues.
It is not unusual for the client with heart failure to have a slightly elevated heart rate (unless taking medications to lower the heart rate) because the increased rate may help compensate for reduced stroke volume (and therefore, decreased cardiac output). Shortness of breath may occur with heart failure as a result of poor pumping action of the heart that allows fluid to accumulate in the lungs, however, it is not an indicator of peripheral perfusion.
Question 62.
The nurse should teach the client that signs of digoxin toxicity include:
(a) rash over the chest and back.
(b) increased appetite.
(c) visual disturbances such as seeing yellow spots.
(d) elevated blood pressure.
Answer:
(c) visual disturbances such as seeing yellow spots.
Explanation:
Colored vision and seeing yellow spots are symptoms of digoxin toxicity. Abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting are other common symptoms of digoxin toxicity. Additional signs of toxicity include arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or bradycardia. Rash, increased appetite, and elevated blood pressure are not associated with digoxin toxicity.
Question 63.
Which food should the nurse teach a client with heart failure to limit when following a 2-g sodium diet?
(a) apple
(b) canned tomato juice
(c) whole wheat bread
(d) hamburger
Answer:
(b) canned tomato juice
Explanation:
Canned foods and juices such as tomato juice are typically high in sodium and should be avoided in a sodium-restricted diet. Canned foods and juices in which sodium has been removed or limited are available. The nurse should teach the client to read labels carefully. Apples and whole wheat breads are not high in sodium. Hamburger would have less sodium than canned foods or tomato juice.
Question 64.
A client receiving a loop diuretic should be encouraged to eat which foods to prevent potassium loss? Select all that apply.
(a) angel food cake
(b) banana
(c) dried fruit
(d) orange juice
(e) peppers
Answer:
(b) banana
(c) dried fruit
(d) orange juice
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d). Hypokalemia is a side effect of loop diuretics. Bananas, dried fruit, and oranges are examples of food high in potassium. Angel food cake and peppers are low in potassium.
Question 65.
The nurse is admitting an older adult to the hospital. The echocardiogram report revealed left ventricular enlargement. The nurse notes 2+ pitting edema in the ankles when getting the client into bed. Based on this finding, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Assess respiratory status.
(b) Draw blood for laboratory studies.
(c) Insert a Foley catheter.
(d) Weigh the client.
Answer:
(a) Assess respiratory status.
Explanation:
The ankle edema suggests fluid volume overload. The nurse should assess respiratory rate, lung sounds, and Sp02 to identify any signs of respiratory symptoms of heart failure requiring immediate attention. The nurse can then draw blood for laboratory studies, insert the Foley catheter, and weigh the client.
Question 66.
What instruction should the nurse’s discharge teaching plan for the client with heart failure include?
(a) maintaining a high-fibre diet
(b) walking 2 miles (3.2 km] every day
(c) obtaining daily weights at the same time each day
(d) remaining sedentary for most of the day
Answer:
(c) obtaining daily weights at the same time each day
Explanation:
Heart failure is a complex and chronic condition. Education should focus on health promotion and preventive care in the home environment. Signs and symptoms can be monitored by the client. Instructing the client to obtain daily weights at the same time each day is very important. The client should be told to call the health care provider (HCP) HJ if there has been a weight gain of 2 lb (0.91 kg) or more.
This may indicate fluid overload, and treatment can be prescribed early and on an outpatient basis, rather than waiting until the symptoms become life threatening. Following a high-fiber diet is beneficial, but it is not relevant to the teaching needs of the client with heart failure. Prescribing an exercise program for the client, such as walking 2 miles (3.2 km) every day, would not be appro-priate at discharge.
The client’s exercise program would need to be planned in consultation with the HCP and based on the history and the physical condition of the client. The client may require exercise tolerance testing before an exercise plan is laid out. Although the nurse does not prescribe an exercise program for the client, a sedentary lifestyle should not be recommended.
Question 67.
The nurse is teaching a client with heart failure how to avoid complications and future hospitalizations. The client has understood the instruction when the client identifies which potential complications? Select all that apply.
(a) becoming increasingly short of breath at rest
(b) weight gain of 2 lb (0.9 kg) or more in 1 day
(c) high intake of sodium for breakfast
(d) having to sleep sitting up in a reclining chair
(e) weight loss of 2 lb (0.9 kg) in 1 day
Answer:
(a) becoming increasingly short of breath at rest
(b) weight gain of 2 lb (0.9 kg) or more in 1 day
(d) having to sleep sitting up in a reclining chair
Explanation:
(a),(b),(d). If the client will call the health care provider (HCP) when there is increasing shortness of breath, weight gain over 2 lb (0.9 kg) in 1 day, and need to sleep sitting up, this indicates an understanding of the teaching because these signs and symptoms suggest worsening of the client’s heart failure.
Although the client will most likely be placed on a sodium-restricted diet, the client would not need to notify the HCP if he or she had consumed a high-sodium breakfast. Instead, the client would need to be alert for possible signs and symptoms of worsening heart failure and work to reduce sodium intake for the rest of that day and in the future.

Question 68.
A client has returned from the cardiac cath-eterization laboratory after a balloon valvuloplasty for mitral stenosis. Which finding requires immediate nursing action?
(a) There is a low, grade 1 intensity mitral regurgitation murmur.
(b) Sp02 is 94% on 2 L of oxygen via nasal cannula.
(c) The client has become more somnolent.
(d) Urine output decreased from 60 mL/h to 40 mL over the last hour.
Answer:
(c) The client has become more somnolent.
Explanation:
A complication of balloon valvuloplasty is emboli resulting in a stroke. The client’s increased drowsiness should be evaluated. Some degree of mitral regurgitation is common after the procedure. The oxygen status and urine output should be monitored closely but do not warrant concern.
Question 69.
An older client with diabetes who has been maintained on metformin has been scheduled for a cardiac catheterization. The nurse should verily that the health care provider (HCP) has written which prescription for taking the metformin before the procedure?
(a) Increase the amount of protein in the diet the day before.
(b) Withhold the metformin.
(c) Administer the metformin with only a sip of water.
(d) Give the metformin before breakfast.
Answer:
(b) Withhold the metformin.
Explanation:
The nurse should verify that the HCP Q has requested to withhold the metformin prior to any procedure requiring dye such as a cardiac catheterization due to the increased risk of lactic acidosis. Additionally, the drug will usually be withheld for up to 48 hours following a procedure involving dye while it clears the client’s system. The HCP may prescribe sliding scale insulin during this time if needed. Regardless of how or when the medication is administered, the medication should be withheld. The amount of protein in the client’s diet prior to the cardiac catheterization has no correlation with the medication or the test.
Question 70.
A client with aortic stenosis has increasing dyspnea and dizziness. Identify the area where the nurse would place the stethoscope to assess a murmur from aortic stenosis.
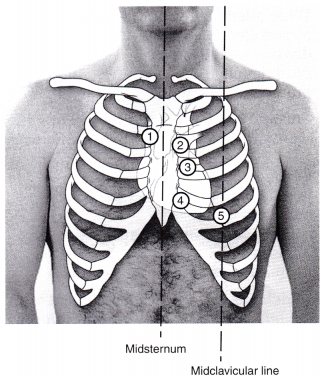
Answer:
To assess a murmur from aortic stenosis, the stethoscope is placed at the second intercostal space right of sternum; (1) location, (2) the pulmonic valve area, (3) Erb’s point, (4) tricuspid valve area, and (5) mitral valve area.
\(\frac { 50 mg }{ 250 mL }\)= \(\frac { 1 mg }{ 5 mL }\) = \(\frac { 0.2 mg }{ 1 mL }\)
Question 71.
A client is scheduled for a cardiac catheterization. The nurse should do which preprocedure tasks? Select all that apply.
(a) Verify the client has stopped taking anticoagulants if instructed by the health care provider.
(b) Check for iodine sensitivity.
(c) Verify that written consent has been obtained.
(d) Withhold food and oral fluids before the procedure.
(e) Insert a urinary drainage catheter.
Answer:
(a) Verify the client has stopped taking anticoagulants if instructed by the health care provider.
(b) Check for iodine sensitivity.
(c) Verify that written consent has been obtained.
(d) Withhold food and oral fluids before the procedure.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d). For clients scheduled for a cardiac catheterization, it is important to assess for iodine sensitivity, verily written consent and instruct the client to take nothing by mouth for 6 to 18 hours before the procedure. If the client is taking anticoagulant drugs, the nurse should ask the client if the health care provider has given instructions to withhold these medications. Oral medications are withheld unless specifically prescribed. A urinary drainage catheter is rarely required for this procedure.
Question 72.
Which is the most important initial postprocedure nursing assessment for a client who has had a cardiac catheterization?
(a) Monitor the laboratory values.
(b) Observe neurologic function every 15 minutes.
(c) Observe the puncture site for swelling and bleeding.
(d) Monitor skin warmth and turgor.
Answer:
(c) Observe the puncture site for swelling and bleeding.
Explanation:
Assessment of circulatory status, including observation of the puncture site, is of primary importance after a cardiac catheterization. Laboratory values and skin warmth and turgor are important to monitor but are not the most important initial nursing assessment. Neurologic assessment every 15 minutes is not required.
Question 73.
A client experiences initial indications of dizziness after having an IV infusion of lidocaine hydrochloride started. The nurse should further assess the client for which symptoms?
(a) palpitations
(b) tinnitus
(c) urinary frequency
(d) lethargy
Answer:
(b) tinnitus
Explanation:
Common adverse effects of lidocaine hydrochloride include dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision, tremors, numbness and tingling of extremities, excessive perspiration, hypotension, seizures, and finally coma. Cardiac effects include slowed conduction and cardiac arrest. Palpitations, urinary frequency, and lethargy are not considered typical adverse reactions to lidocaine.
Question 74.
A pulmonary artery catheter is inserted in a client with severe mitral stenosis and regurgitation. The nurse administers furosemide and nitroprusside as prescribed. The nurse notices a sudden drop in the pul-monary artery diastolic pressure and pulmonary artery wedge pressure. What should the nurse assess next?
(a) 12-lead EKG
(b) blood pressure
(c) lung sounds
(d) urine output
Answer:
(b) blood pressure
Explanation:
The nurse should immediately assess the blood pressure since nitroprusside and furosemide can cause severe hypotension from a decrease in preload and afterload. If the client is hypotensive, the nitroprusside dose should be reduced or discontinued. Urine output should then be monitored to make sure there is adequate renal perfusion. A 12-lead EKG is performed if the client experiences chest pain. A reduction in pulmonary artery pressures should improve the pulmonary congestion and lung sounds.
Question 75.
A client has mitral stenosis and will have a valve replacement. The nurse is instructing the client about health maintenance prior to surgery. Inability to follow which prescription would pose the greatest health hazard to this client at this time?
(a) medication therapy
(b) diet modification
(c) activity restrictions
(d) dental care
Answer:
(a) medication therapy
Explanation:
Preoperatively, anticoagulants maybe prescribed for the client with advanced valvular heart disease to prevent emboli. Postoperatively, all clients with mechanical valves and some clients with bioprosthesis are maintained indefinitely on anticoagulant therapy. Adhering strictly to a dosage schedule and observing specific precautions are nec-essary to prevent hemorrhage or thromboembolism.
Some clients are maintained on lifelong antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent recurrence of rheumatic fever. Episodic prophylaxis is required to prevent infective endocarditis after dental procedures or upper respiratory, gastrointestinal, or genitourinary tract surgery. Diet modification, activity restrictions, and dental care are important; however, they do not have as much significance postoperatively as medi-cation therapy does.
Question 76.
In preparing the client and the family for a postoperative stay in the intensive care unit (ICU) after open-heart surgery, what should the nurse tell the family?
(a) The client will remain in the ICU for 5 days.
(b) The client will sleep most of the time while in the ICU.
(c) Noise and activity within the ICU are minimal.
(d) The client will receive medication to relieve pain.
Answer:
(d) The client will receive medication to relieve pain.
Explanation:
Management of postoperative pain is a priority for the client after surgery, including valve replacement surgery. The client and family should be informed that pain will be assessed by the nurse and medications will be given to relieve the pain. The client will stay in the ICU as long as monitoring and intensive care are needed. Sensory deprivation and overload, high noise levels, and disrupted sleep and rest patterns are some environmental factors that affect recovery from valve replacement surgery.
Question 77.
A client who has undergone a mitral valve replacement has had a mediastinal chest tube inserted. The client has persistent bleeding from the sternal incision during the early postoperative period. What actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
(a) Administer warfarin.
(b) Check the postoperative CBC, INR, PTT, and platelet levels.
(c) Confirm availability of blood products.
(d) Monitor the mediastinal chest tube drainage.
(e) Start a dopamine drip for a systolic blood pressure <100 mm Hg.
Answer:
(b) Check the postoperative CBC, INR, PTT, and platelet levels.
(c) Confirm availability of blood products.
(d) Monitor the mediastinal chest tube drainage.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d). The hemoglobin and hematocrit should be assessed to evaluate blood loss. An elevated INR and PTT and decreased platelet count increase the risk for bleeding. The client may require blood products depending on lab values and severity of bleeding; therefore, availability of blood products should be confirmed by calling the blood bank. Close monitoring of blood loss from the mediastinal chest tubes should be done.
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that will increase bleeding. Anticoagulation should be held at this time. Information is needed on the type of valve replacement. For a mechanical heart valve, the INR is kept at 2 to 3.5. Tissue valves do not require anticoagulation. Dopamine should not be initiated if the client is hypotensive from hypovolemia. Fluid volume assessment should always be done first. Volume replacement should be initiated in a hypovolemic client prior to starting an inotrope such as dopamine.
Question 78.
What measure should the nurse take that will be most helpful in preventing wound infection when changing a client’s dressing after coronary artery bypass surgery?
(a) Wash hands before changing the dressing.
(b) Clean the incisional area with an antiseptic.
(c) Use prepackaged sterile dressings to cover the incision.
(d) Place soiled dressings a hazardous waste container.
Answer:
(a) Wash hands before changing the dressing.
Explanation:
Many factors help prevent wound infections, including washing hands carefully, using sterile prepackaged supplies and equipment, cleaning the incisional area well, and disposing of soiled dressings properly. However, most authorities say that the single most effective measure in preventing wound infections is to wash the hands carefully before and after changing dressings. Careful handwashing is also important in reducing other infections often acquired in hospitals, such as urinary tract and respiratory tract infections.
Question 79.
What information should the nurse provide to the client who is receiving warfarin?
(a) Partial thromboplastin time values determine the dosage of warfarin sodium.
(b) Protamine sulfate is used to reverse the effects of warfarin sodium.
(c) International normalized ratio (INR) is used to assess effectiveness.
(d) Warfarin sodium will facilitate clotting of the blood.
Answer:
(c) International normalized ratio (INR) is used to assess effectiveness.
Explanation:
INR is the value used to assess effectiveness of the warfarin sodium therapy. INR is the prothrombin time ratio that would be obtained if the thromboplastin reagent from the World Health Organization was used for the plasma test. It is now the recommended method to monitor effectiveness of warfarin sodium. Generally, the INR for clients administered warfarin sodium should range from 2 to 3.
In the past, prothrombin time was used to assess effectiveness of warfarin sodium and was maintained at 1.5 to 2.5 times the control value. Partial thromboplastin time is used to assess the effectiveness of heparin therapy. Fresh frozen plasma or vitamin K is used to reverse warfarin sodium’s anticoagulant effect, whereas protamine sulfate reverses the effects of heparin. Warfarin sodium will help to prevent blood clots.
Question 80.
Good dental care is an important measure in reducing the risk of endocarditis. What information about dental care should the nurse include in the teaching plan for a client with mitral stenosis? Select all that apply.
(a) Brush the teeth at least twice a day.
(b) Avoid use of an electric toothbrush.
(c) Take an antibiotic prior to oral surgery.
(d) Floss the teeth at least once a day.
(e) Have regular dental checkups.
(f) Rinse the mouth with an antibiotic mouth wash once a day.
Answer:
(a) Brush the teeth at least twice a day.
(d) Floss the teeth at least once a day.
(e) Have regular dental checkups.
Explanation:
(a),(d),(e). Daily dental care including brushing the teeth twice a day and flossing once a day and frequent checkups by a dentist who is informed about the client’s condition are required to maintain good oral health. The client can use a regular toothbrush; it is not necessary to avoid use of an electric toothbrush. Taking antibiotics prior to certain dental procedures is recommended only if the client has a prosthetic valve or a heart transplant. It is not necessary to use an antibiotic mouthwash.
Question 81.
The nurse is preparing the client for discharge after mitral valve replacement surgery. Which activity should the client avoid until after the 1-month postdischarge appointment with the surgeon?
(a) showering
(b) lifting anything heavier than 10 lb (4.5 kg)
(c) a program of gradually progressive walking
(d) light housework
Answer:
(b) lifting anything heavier than 10 lb (4.5 kg)
Explanation:
Most cardiac surgical clients have median sternotomy incisions, which take about 3 months to heal. Measures that promote healing include avoiding heavy lifting, performing muscle reconditioning exercises, and using caution when driving. Showering or bathing is allowed as long as the incision is well approximated with no open areas or drainage. Activities should be gradually resumed on discharge.
Question 82.
Three days after mitral valve replacement surgery, the client tells the nurse there is a “clicking” noise coming from the chest incision. The nurse’s response should reflect the understanding that the client may be experiencing:
(a) anxiety related to altered body image.
(b) depression related to altered health status.
(c) altered tissue perfusion.
(d) lack of knowledge regarding the postoperative course.
Answer:
(a) anxiety related to altered body image.
Explanation:
Verbalized concerns from this client may stem from anxiety over the changes in the body after open-heart surgery. Although the client may experience depression related to altered health status or may have a lack of knowledge regarding the postoperative course, the client is pointing out the changes in the body image. The client is not concerned about altered tissue perfusion.
Question 83.
Metoprolol is added to the pharmacologic therapy of a diabetic female diagnosed with stage 2 hypertension who has been initially treated with furosemide and ramipril. The nurse should evaluate the client for which expected therapeutic effect?
(a) decrease in heart rate
(b) lessening of fatigue
(c) improvement in blood sugar levels
(d) increase in urine output
Answer:
(a) decrease in heart rate
Explanation:
The effect of a beta-blocker is a decrease in heart rate, contractility, and afterload, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure. The client at first may have an increase in fatigue when starting the beta-blocker. The mechanism of action does not improve blood sugar or urine output.
Question 84.
Which set of postural vital signs in a client with hypertension should the nurse report to the health care provider (HCP)?
(a) supine 124/76 mm Hg, 88 bpm sitting 124/74 mm Hg, 92 bpm standing 122/74 mm Hg, 92 bpm
(b) supine 120/70 mm Hg, 70 bpm sitting 102/64 mm Hg, 86 bpm standing 100/60 mm Hg, 92 bpm
(c) supine 138/86 mm Hg, 74 bpm sitting 136/84 mm Hg, 80 bpm standing 134/82 mm Hg, 82 bpm
(d) supine 100/70 mm Hg, 72 bpm sitting 100/68 mm Hg, 74 bpm standing 98/68 mm Hg, 80 bpm
Answer:
(b) supine 120/70 mm Hg, 70 bpm sitting 102/64 mm Hg, 86 bpm standing 100/60 mm Hg, 92 bpm
Explanation:
There was a significant change in both blood pressure and heart rate with position change, indicating inadequate blood volume to sustain normal values. The nurse should report this change to the HCP. Normal postural changes allow for an increase in heart rate of 5 to 20 bpm, a possible slight decrease of <5 mm Hg in the systolic blood pressure, and a possible slight increase of <5 mm Hg in the diastolic blood pressure.
Question 85.
A client is taking clonidine for treatment of hypertension. The nurse should teach the client about which common adverse effects of this drug? Select all that apply.
(a) dry mouth
(b) hyperkalemia
(c) impotence
(d) pancreatitis
(e) sleep disturbance
Answer:
(a) dry mouth
(c) impotence
(e) sleep disturbance
Explanation:
(a),(c),(e). Clonidine is a central-acting adrenergic antagonist. It reduces sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system. Dry mouth, impotence, and sleep disturbances are possible adverse effects. Hyperkalemia and pancreatitis are not anticipated with use of this drug.
Question 86.
A client with hypertensive emergency is being treated with sodium nitroprusside. In a dilution of 50 mg/250 mL, how many micrograms of sodium nitroprusside are in each milliliter? Round your answer to a whole number. ...................... meg.
Answer:
First, calculate the number of milligrams per milliliter:
0.2 mg x \(\frac { 1,000 mcg }{ 1 mg }\) = 200 mcg
Next, calculate the number of micrograms in each milligram:
\(\frac { 1,200 units }{ 1 hour }\) = \(\frac { 50 units }{ 1 mL }\)
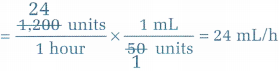
Question 87.
The nurse is discussing medications with a client with hypertension who has a prescription for furosemide daily. Which comment by the client indicates the client needs further education?
(a) “I know I shouldn’t drive after taking my furosemide.”
(b) “I should be careful not to stand up too quickly when taking furosemide.”
(c) “I should take the furosemide in the morning instead of before bed.”
(d) “I need to be sure to also take the potassium supplement that the doctor prescribed along with my furosemide.”
Answer:
(a) “I know I shouldn’t drive after taking my furosemide.”
Explanation:
Furosemide is a diuretic often prescribed for clients with hypertension or heart failure; the drug should not affect a client’s ability to drive safely. Furosemide may cause orthostatic hypotension, and clients should be instructed to be careful when changing from supine to sitting to standing position. Diuretics should be taken in the morning if possible to prevent sleep disturbance due to the need to get up to void. Furosemide is a loop diuretic that is not potassium sparing; clients should take potassium supplements as prescribed and have their serum potassium levels checked at prescribed intervals.
Question 88.
When teaching the client with hypertension to avoid orthostatic hypotension, the nurse should provide which instructions? Select all that apply.
(a) Plan regular times for taking medications.
(b) Arise slowly from bed.
(c) Avoid standing still for long periods.
(d) Avoid excessive alcohol intake.
(e) Avoid hot baths.
Answer:
(b) Arise slowly from bed.
(c) Avoid standing still for long periods.
Explanation:
(b), (c). Changing positions slowly and avoiding long periods of standing may limit the occurrence of orthostatic hypotension. Scheduling regular medication times is important for blood pressure management, but this aspect is not related to the development of orthostatic hypotension. Excessive alcohol intake and hot baths are associated with vasodilation.
Question 89.
The nurse is teaching a client with hypertension about taking atenolol. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Avoid sudden discontinuation of the drug.
(b) Monitor the blood pressure annually.
(c) Follow a 2-g sodium diet.
(d) Discontinue the medication if severe headaches develop.
Answer:
(a) Avoid sudden discontinuation of the drug.
Explanation:
Atenolol is a beta-adrenergic antagonist indicated for management of hypertension. Sudden discontinuation of this drug is dangerous because it may exacerbate symptoms. The medication should not be discontinued without a prescription. Blood pressure needs to be monitored more frequently than annually in a client who is newly diagnosed and treated for hypertension. Clients are not usually placed on a 2-g sodium diet for hypertension.
Question 90.
The nurse teaches a client who has recently been diagnosed with hypertension about following a low-calorie, low-fat, low-sodium diet. Which menu selection would best meet the client’s needs?
(a) mixed green salad with blue cheese dressing, crackers, and cold cuts
(b) ham sandwich on rye bread and an orange
(c) baked chicken, an apple, and a slice of white bread
(d) hot dogs, baked beans, and celery and carrot sticks
Answer:
(c) baked chicken, an apple, and a slice of white bread
Explanation:
Processed and cured meat products, such as cold cuts, ham, and hot dogs, are all high in both fat and sodium and should be avoided on a low-calorie, low-fat, low-salt diet. Dietary restrictions of all types are complex and difficult to implement with clients who are basically asymptomatic.
Question 91.
A client who has diabetes is taking metopro- lol for hypertension. What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Take the tablets with food at same time each day.
(b) Do not crush or chew the tablets.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP) if pulse is 82 beats/min.
(d) Have a blood glucose level drawn every 6 to 12 months during therapy.
(e) Use an appropriate decongestant if needed.
(f) Report any fainting spells to the HCP.
Answer:
(a) Take the tablets with food at same time each day.
(b) Do not crush or chew the tablets.
(d) Have a blood glucose level drawn every 6 to 12 months during therapy.
(e) Use an appropriate decongestant if needed.
Explanation:
(a), (b), 4, (d), (e). Metoprolol is a beta-adrenergic blocker indicated for hypertension, angina, and myocardial infarction. The tablets should be taken with food at same time each day; they should not be chewed or crushed. The HCP should be notified if pulse falls below 50 for several days. Blood glucose should be checked regularly during therapy since increased episodes of hypoglycemia may occur. It may mask evidence of hypoglycemia such as palpitations, tachycardia, and tremor. Use of any over-the-counter decongestants, asthma and cold remedies, and herbal preparations must be avoided. Fainting spells may occur due to exercise or stress, and the dosage of the drug may need to be reduced or discontinued.
Question 92.
A client diagnosed with primary (essential) hypertension is taking chlorothiazide. The nurse determines teaching about this medication is effective when the client makes which statement? Select all that apply.
(a) ‘I’ll weigh myself at the same time each day.”
(b) “I won’t drink alcoholic beverages while on this medication.”
(c) “I’ll reduce salt intake in my diet.”
(d) “If I have severe dizziness, I’ll reduce my dosage.”
(e) “If I have prolonged exposure to sunlight, I’ll use sunscreen.”
(f) “I’ll take the drug before I go to bed.”
Answer:
(a) ‘I’ll weigh myself at the same time each day.”
(b) “I won’t drink alcoholic beverages while on this medication.”
(c) “I’ll reduce salt intake in my diet.”
(e) “If I have prolonged exposure to sunlight, I’ll use sunscreen.”
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e). Chlorothiazide causes increased urination and decreased swelling (if there is edema) and weight loss. It is important to check and record weight two to three times per week at same time of day with similar amount of clothing. Clients should not drink alcoholic beverages or take other medications without the approval of the health care provider (HCP) Reducing sodium intake in the diet helps diuretic drugs to be more effective and allows smaller doses to be taken.
Smaller doses are less likely to cause adverse effects, and therefore, excessive table salt as well as salty foods should be avoided. Chlorothiazide is a diuretic that is prescribed for lower blood pressure and may cause dizziness and faintness when the client stands up suddenly. This can be prevented or decreased by changing positions slowly. If dizziness is severe, the HCP must be notified.
Diuretics may cause sensitivity to sunlight, hence the need to avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight, use sunscreens, and wear protective clothing. Chlorothiazide causes increased urination and must be taken early in the day to decrease nighttime trips to the bathroom. Fewer bathroom trips mean less interference with sleep and less risk of falls. The client should not change the dosage without consulting the HCP.
Question 93.
The nurse is teaching the client with hypertension about maintaining an exercise program. Which teaching strategy will be most helpful?
(a) Give the client a written exercise program to follow.
(b) Explain the exercise program to the client’s spouse.
(c) Offer reassurance that that the client can follow the exercise program.
(d) Tailor a program to meet the client’s needs and abilities.
Answer:
(d) Tailor a program to meet the client’s needs and abilities.
Explanation:
Tailoring or individualizing a program to the client’s lifestyle has been shown to be an effective strategy for changing health behaviors. Providing a written program, explaining the program to the client’s spouse, and reassuring the client that he or she can do the program may be helpful but are not as likely to promote adherence as individualizing the program.
Question 94.
Which would be most helpful when coaching a client to stop smoking?
(a) Review the negative effects of smoking on the body.
(b) Discuss the effects of passive smoking on environmental pollution.
(c) Establish the client’s daily smoking pattern.
(d) Explain how smoking worsens high blood pressure.
Answer:
(c) Establish the client’s daily smoking pattern.
Explanation:
A plan to reduce or stop smoking begins with establishing the client’s personal daily smoking pattern and activities associated with smoking. It is important that the client understands the associated health and environmental risks, but this knowledge has not been shown to help clients change their smoking behavior.
Question 95.
The nurse is making a discharge plan with an obese client with hypertension who smokes. What is the most important long-term goal for this client?
(a) Take medications as prescribed.
(b) Stop smoking.
(c) Make a commitment to long-term lifestyle changes.
(d) Lose weight.
Answer:
(c) Make a commitment to long-term lifestyle changes.
Explanation:
In most instances, clients with hypertension require lifelong treatment and their hypertension cannot be managed successfully without changes in health behavior. The client must first commit to making these long-term changes. The changes will involve taking medications, stopping smoking, and losing weight, but the client must first accept the need for a lifelong management and establish a vision and plan to control the hypertension.
Question 96.
Cardiac telemetry shows that a client who is up to the bathroom has converted from normal sinus rhythm with a rate of 72 bpm to atrial fibrillation with a ventricular response rate of 100 bpm. In what order from first to last should the nurse perform these interventions? All options must be used.
(a) Assess vital signs.
(b) Assist the client to the bed.
(c) Initiate intravenous access.
(d) Obtain a stat 12-lead electrocardiogram.
Answer:
(b) Assist the client to the bed.
(a) Assess vital signs.
(c) Initiate intravenous access.
(d) Obtain a stat 12-lead electrocardiogram.
Explanation:
(b), (a), (c), (d). To decrease myocardial workload and promote timely intervention, the client should be assisted to the bed. Assessing vital signs provides the data needed to determine client tolerance. Early initiation of an intravenous access will enable timely medication administration if it is emergently needed. While a 12-lead electrocardiogram is needed, it can be obtained after the IV is initiated.
Question 97.
A client admitted to the telemetry unit with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation has been started on warfarin. What should the nurse instruct the client to do when taking this medication? Select all that apply.
(a) Avoid injury to prevent bruising.
(b) Be careful using a razor or fingernail clippers.
(c) Report any change in color of urine or stool.
(d) Floss the teeth deep into the gums.
(e) Not take the medication if the pulse is below 60.
Answer:
(a) Avoid injury to prevent bruising.
(b) Be careful using a razor or fingernail clippers.
(c) Report any change in color of urine or stool.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c). Warfarin is an anticoagulant used in clients with atrial fibrillation to reduce the risk of stroke or systemic embolization and, therefore, will put the client at risk for bleeding. The nurse should instruct the client to watch for signs of bleeding and prevent bruising. While good oral hygiene remains important, the nurse would advise against vigorous flossing and irritating the gums as it may increase the risk of bleeding. Warfarin does not affect the heart rate.
Question 98.
When caring for a client with a newly diagnosed cardiac dysrhythmia, which laboratory values are the priority for the nurse to monitor? Select all that apply.
(a) blood urea nitrogen (BUN) of 20 mg/dL
(b) hematocrit of 40%
(c) sodium of 124 mEq/L
(d) potassium of 3.1 mEq/L
(e) hemoglobin of 14 g/dL
(f) calcium of 8.5 mEq/L
(g) prothrombin time of 12 seconds with INR of 1
Answer:
(c) sodium of 124 mEq/L
(d) potassium of 3.1 mEq/L
(f) calcium of 8.5 mEq/L
Explanation:
(c), (d), (f). Because abnormalities in electrolytes are likely to affect depolarization and repolarization of cardiac cells, it is most important for the nurse to monitor sodium, potassium, and calcium levels. The blood urea nitrogen is within normal range. Hemoglobin and hematocrit are not generally associ-ated with cardiac dysrhythmias; the hemoglobin is within normal range. The prothrombin time and INR would be monitored closely on a client taking warfarin, not necessarily a client with cardiac dysrhythmia; the PT and INR are within normal range.
Question 99.
Six hours after pacemaker insertion, a client reports sudden onset of chest pain and shortness of breath with a drop in SpO, from 98% on 2 LPM of oxygen to 90% on 2 LPM of oxygen. Which action should the nurse take first?
(a) Assess the client’s breath sounds and chest movement.
(b) Notify the health care provider to obtain a chest X-ray.
(c) Check the client’s blood pressure and heart rate.
(d) Assess the incision site for redness, pain, drainage, and/or swelling.
Answer:
(a) Assess the client’s breath sounds and chest movement.
Explanation:
The client is showing signs of pneumothorax, a potential complication of pacemaker placement. The nurse should immediately assess the client’s breath sounds and chest movement as this information will be important to share with the health care provider when notified. Assessing the insertion site and the client’s blood pressure and pulse are important, but the nurse should first perform a focused respiratory assessment.
Question 100.
A client suddenly develops paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) at a rate of 180 bpm. Current vital signs: blood pressure 90/45 mm Hg, heart rate 180 bpm, respirations 30 breaths/min, O2 saturation 90% on room air. The client is diaphoretic and reports dizziness. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Ask the client about current caffeine use.
(b) Administer atropine per agency protocol.
(c) Prepare defibrillator for synchronized cardioversion.
(d) Start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
Answer:
(c) Prepare defibrillator for synchronized cardioversion.
Explanation:
The nurse first should prepare the defibrillator for synchronized cardioversion. The client is experiencing PSVT with a heart rate of 180 bpm. PSVT with a heart rate of 180 bpm causes a decrease in cardiac output. The client’s vital signs and symptoms reveal the client is becoming hemodynamically unstable and requires an immediate intervention. Atropine is not a treatment for PSVT. CPR is not indicated for PSVT. Caffeine use can contribute to PSVT, but the client requires defibrillation now.
Question 101.
A client admitted with normal sinus rhythm converts to the following rhythm on the cardiac monitor.
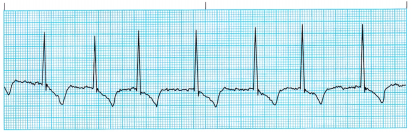
For which symptoms should the nurse assess the client? Select all that apply.
(a) carotid bruit
(b) light-headedness
(c) nausea
(d) palpitations
(e) shortness of breath
(f) systolic murmur
Answer:
(b) light-headedness
(d) palpitations
(e) shortness of breath
Explanation:
(b), (d), (e). This ECG strip indicates the client has atrial fibrillation. There is no P wave and PR interval; these are replaced with fine wavy lines. In atrial fibrillation, the ventricular rate may be normal, slow, or fast. Clients with atrial fibrillation may have palpitations secondary to a fast and irregular atrial rhythm. Because atrial fibrillation also may result in a sudden decrease in cardiac output, the client may also experience light-headedness and shortness of breath. A carotid bruit, nausea, and a systolic murmur are not manifestations of new-onset atrial fibrillation.
Question 102.
A nurse hears an irregular heart rate of 110 bpm when listening to a client’s chest. After assessing the client and noting new onset shortness of breath, which action should the nurse take next?
(a) Check the availability of medication to relieve anxiety.
(b) Recheck the pulse later in the shift.
(c) Obtain a prescription for a stat electrocardiogram.
(d) Call the radiology service to obtain a stat chest X-ray.
Answer:
(c) Obtain a prescription for a stat electrocardiogram.
Explanation:
The nurse should contact the health care provider to request a stat electrocardiogram to verify the change in rhythm. The cardiac rhythm and fast heart rate may predispose the client to decreased cardiac output. Administering an anti-anxiety medication may calm the client but does not effectively treat the problem of an irregular rhythm. Rechecking the pulse later leaves the problem unaddressed. A chest X-ray may be helpful, but it is not the priority at this time.
Question 103.
A client is admitted to the hospital for evaluation of recurrent episodes of ventricular tachycardia as observed on Holter monitoring. The client is scheduled for electrophysiology studies (EPS) the following morning. Which statement should the nurse include in a teaching plan for this client?
(a) “You’ll continue to take your medications until the morning of the test.”
(b) “You might be sedated during the procedure and won’t remember what’s happened.”
(c) “This test is a noninvasive method of determining the effectiveness of your medication regimen.”
(d) “During the procedure, the health care provider will insert a special wire to increase the heart rate and produce the irregular beats that caused your signs and symptoms.”
Answer:
(d) “During the procedure, the health care provider will insert a special wire to increase the heart rate and produce the irregular beats that caused your signs and symptoms.”
Explanation:
The purpose of EPS is to study the heart’s electrical system. During this invasive procedure, a special wire is introduced into the heart to produce dysrhythmia. To prepare for this procedure, the client should be NPO for 6 to 8 hours before the test, and all antiarrhythmics are held for at least 24 hours before the test in order to study the dysrhythmia without the influence of medications. Because the client’s verbal responses to the rhythm changes are extremely important, sedation is avoided if possible.
Question 104.
During physical assessment, the nurse should further assess the client for signs of atrial fibrillation when the nurse palpates the radial pulse and notices which signs?
(a) two regular beats followed by one irregular beat
(b) an irregular rhythm with pulse rate >100 bpm
(c) pulse rate below 60 bpm
(d) a weak, thready pulse
Answer:
(b) an irregular rhythm with pulse rate >100 bpm
Explanation:
Characteristics of atrial fibrillation include pulse rate >100 bpm, totally irregular rhythm, and no definite P waves on the ECG. During assessment, the nurse is likely to note the irregular rate and should report it to the health care provider (HCP). A weak, thready pulse is characteristic of a client in shock. Two regular beats followed by an irregular beat may indicate a premature ventricular contraction.
Question 105.
When teaching a client about self-care following placement of a new permanent pacemaker to the left upper chest, the nurse should include which information? Select all that apply.
(a) Take and record daily pulse rate.
(b) Avoid air travel because of airport security alarms.
(c) Immobilize the affected arm for 4 to 6 weeks.
(d) Avoid using a microwave oven.
(e) Avoid lifting anything heavier than 3 lb (1.36 kg).
Answer:
(a) Take and record daily pulse rate.
(e) Avoid lifting anything heavier than 3 lb (1.36 kg).
Explanation:
(a), (e). The nurse must teach the client how to take and record the pulse daily. The client should be instructed to avoid lifting the operative-side arm above shoulder level for 1 week post insertion. It takes up to 2 months for the incision site to heal and full range of motion to return. The client should avoid heavy lifting until approved by the health care provider (HCP). The pacemaker metal casing does not set off airport security alarms, so there are no travel restrictions. Prolonged immobilization is not required. Microwave ovens are safe to use and do not alter pacemaker function.
Question 106.
A client has been admitted to the coronary care unit. The nurse observes third-degree heart block at a rate of 35 bpm on the client’s cardiac monitor. The client has a blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Prepare for transcutaneous pacing.
(b) Prepare to defibrillate the client at 200 J.
(c) Administer an IV lidocaine infusion.
(d) Schedule the operating room for insertion of a permanent pacemaker.
Answer:
(a) Prepare for transcutaneous pacing.
Explanation:
Transcutaneous pacemaker therapy provides an adequate heart rate to a client in an emergency situation. Defibrillation and a lidocaine infusion are not indicated for the treatment of third- degree heart block. Transcutaneous pacing is used temporarily until a transvenous or permanent pacemaker can be inserted.
Question 107.
A client has atrial fibrillation and a heart rate of 165 bpm. In which order from first to last should the nurse implement these prescriptions? All options must be used.
(a) Administer oxygen via nasal cannula.
(b) Gather supplies for an IV insertion.
(c) Place client on a cardiac monitor (ECG).
(d) Obtain vital signs including BP, P, R, T, and O2 saturation.
Answer:
(a) Administer oxygen via nasal cannula.
(c) Place client on a cardiac monitor (ECG).
(d) Obtain vital signs including BP, P, R, T, and O2 saturation.
(b) Gather supplies for an IV insertion.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (b). Because atrial fibrillation causes a decrease in cardiac output, the heart rate increases in response to this drop. As a result of an increased heart rate, the oxygen demands of the heart increase. It is important for oxygen to be administered first to help compensate for the increased oxygen demand and cardiac workload.
Placing the client on a cardiac monitor will help confirm a diagnosis of atrial fibrillation. Performing vital signs will determine the client’s response to the abnormal rhythm and responses to treatment. If the rhythm is determined to be atrial fibrillation, it will be necessary for an IV to be inserted so medication can be administered.
Question 108.
A client is scheduled for the insertion of an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). The spouse expresses anxiety about what would happen if the device discharges during physical contact. What should the nurse tell the spouse?
(a) Physical contact should be avoided whenever possible.
(b) They will not feel the countershock.
(c) The shock would feel like a “tingle,” but it would not cause any harm.
(d) A warning device sounds before countershock, so there is time to move away.
Answer:
(c) The shock would feel like a “tingle,” but it would not cause any harm.
Explanation:
The spouse can have physical contact with the client, but if the ICD were to discharge while the spouse had contact with the client, the spouse would feel a “tingle” but would not be harmed. There is not a warning device on the ICD.
Question 109.
An older adult is admitted to the telemetry unit for placement of a permanent pacemaker because of sinus bradycardia. What is a priority goal for the client within 24 hours after insertion of a permanent pacemaker?
(a) Maintain skin integrity.
(b) Maintain cardiac conduction stability.
(c) Decrease cardiac output.
(d) Increase activity level.
Answer:
(b) Maintain cardiac conduction stability.
Explanation:
Maintaining cardiac conduction stability to prevent arrhythmias is a priority immediately after artificial pacemaker implantation. The client should have continuous electrocardiographic monitoring until proper pacemaker functioning is verified. Skin integrity, while important, is not an immediate concern. The pacemaker is used to increase heart rate and cardiac output, not decrease it. The client should limit activity for the first 24 to 48 hours after pacemaker insertion. The client should also restrict movement of the affected extremity for 24 hours.
Question 110.
The client who had a permanent pacemaker implanted 2 days earlier is being discharged from the hospital. What evidence will indicate to the nurse that the client understands the discharge plan?
(a) The client selects a low-cholesterol diet to control coronary artery disease.
(b) The client states a need for bed rest for 1 week after discharge.
(c) The client verbalizes safety precautions needed to prevent pacemaker malfunction.
(d) The client explains signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction (MI).
Answer:
(c) The client verbalizes safety precautions needed to prevent pacemaker malfunction.
Explanation:
Education is a major component of the discharge plan for a client with an artificial pacemaker. The client with a permanent pacemaker needs to be able to state specific information about safety precautions, such as to refrain from lifting more than 3 lb (1.35 kg) or stretching and bending.
The client should know how to count the pulse and do so daily or as instructed by the health care provider (HCP). The client will not necessarily be placed on a low-cholesterol diet. The client should resume activities and does not need to remain on bed rest. The client should know signs and symptoms of an MI but is not at risk because of the pacemaker.
Question 111.
An older adult is admitted to the emergency department (ED) at 2000 hours with syncope, shortness of breath, and reported palpitations (see nurse’s notes below). At 2015, the nurse places the client on the ECG monitor and identifies the following rhythm (see below). What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
|
Admitted to emergency department |
200 |
|
Pulse |
150 |
|
BP |
90/62 |
|
Oxygen saturation |
92% on room air |
|
RR |
22 |
|
Progress notes |
Clint has shortness of breath and states, "my heart is jumping out of my chest and hurts some. I am having trouble catching my breath. I don't want to faint again" |
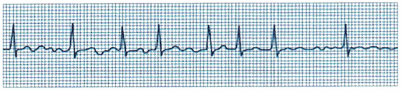
(a) Apply oxygen.
(b) Prepare to defibrillate the client.
(c) Monitor vital signs.
(d) Have the client sign consent for cardioversion as prescribed.
(e) Teach the client about warfarin treatment and the need for frequent blood testing.
(f) Draw blood for a CBC count and thyroid function study.
(g) The Client Requiring Rapid Response or Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Answer:
(a) Apply oxygen.
(c) Monitor vital signs.
(d) Have the client sign consent for cardioversion as prescribed.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d). The client has atrial fibrillation and will have an irregularly irregular pulse and will commonly be tachycardic, with rapid ventricular responses (heart rates) typically in the 110 to 140 range, but rarely over 150 to 170. The goal of treatment is the restoration of sinus rhythm. With a heart rate >150 and symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness and syncope, and chest pain, synchronized cardioversion will most likely be the treatment of choice.
With more controlled heart rates and more minor signs and symptoms, chemical conversion with drugs such as diltiazem and digoxin prior to other interventions such as synchronized cardioversion with appropriate anticoagulation may be attempted. Because of the decreased cardiac output, monitoring is essential. Obtaining consent for cardioversion requires a prescription from a health care provider (HCP), but with the current heart rate, having cardioversion is a very strong possibility for this client. Defibrillation is used for ventricular fibrillation, not atrial fibrillation.
Teaching the client about warfarin will be a possibility, but not an immediate intervention. Clients in continued atrial fibrillation usually require some form of anticoagulation. Drawing labs for CBCs to detect anemia or infection, and thyroid function studies (to determine thyrotoxicosis, a rare, but not-to-be-missed cause, especially in older adults), serum electrolytes, and BUN/creatinine (looking for electrolyte disturbances or renal failure) are commonly drawn for determining the cause of the atrial fibrillation; they are not an immediate action.
Question 112.
Upon assessment of third-degree heart block on the monitor, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Call a code.
(b) Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
(c) Place transcutaneous pacing pads on the client.
(d) Prepare for defibrillation.
Answer:
(c) Place transcutaneous pacing pads on the client.
Explanation:
Transcutaneous pads should be placed on the client with third-degree heart block. For a client who is symptomatic, transcutaneous pacing is the treatment of choice. The hemodynamic stability and pulse should be assessed prior to calling a code or initiating CPR. Defibrillation is performed for ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia with no pulse.
Question 113.
The nurse observes the cardiac rhythm (see below) for a client who is being admitted with a myocardial infarction. What should the nurse do first?
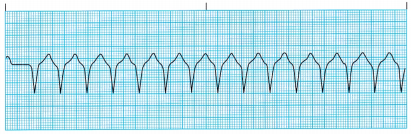
(a) Prepare for immediate cardioversion.
(b) Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
(c) Check for a pulse.
(d) Prepare for immediate defibrillation.
Answer:
(c) Check for a pulse.
Explanation:
This ECG strip indicates the client has ventricular tachycardia. The nurse should first check the client for the presence of a pulse. The presence of a pulse determines the treatment for ventricular tachycardia. It is also important to assess the client’s heart rate and level of consciousness. Cardioversion may be used to treat hemodynamically unstable tachycardias. Assessment of instability is required before cardioversion. It is not appropriate to begin CPR unless the pulse is absent. Defibrillation is used to treat ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
Question 114.
A client who has been given cardiopulmonary resuscitation is transported by ambulance to the hospital’s emergency department. What is the most effective way for the nurse to determine if this client has adequate oxygenation?
(a) There is a pulse.
(b) Pupils are reacting to light.
(c) Mucous membranes are pink.
(d) Systolic blood pressure is at least 80 mm Hg.
Answer:
(b) Pupils are reacting to light.
Explanation:
Pupillary reaction is the best indication of whether oxygenated blood has been reaching the client’s brain. Pupils that remain widely dilated and do not react to light may indicate lack of oxygenation and that serious brain damage may have occurred. The pulse rate may be normal, mucous membranes may still be pink, and systolic blood pressure may be 80 mm Hg or higher, yet there can be inadequate oxygenation to the brain.
Question 115.
A client is given amiodarone in the emergency department for a dysrhythmia. Which finding indicates the drug is having the desired effect?
(a) The ventricular rate is increasing.
(b) The absent pulse is now palpable.
(c) The number of premature ventricular contractions is decreasing.
(d) The fine ventricular fibrillation changes to coarse ventricular fibrillation.
Answer:
(c) The number of premature ventricular contractions is decreasing.
Explanation:
Amiodarone is used for the treatment of premature ventricular contractions, ventricular tachycardia with a pulse, atrial fibrillation, and atrial flutter. Amiodarone is not used as initial therapy for a pulseless dysrhythmia.
Question 116.
During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for an adult, the rescuer’s hands should be placed two fingers’ width above the lower end of the sternum. Which organ would be most likely at risk for laceration by forceful compressions over the xiphoid process?
(a) lung
(b) liver
(c) stomach
(d) diaphragm
Answer:
(b) liver
Explanation:
Because of its location near the xiphoid process, the liver is the organ most easily damaged from pressure exerted over the xiphoid process during CPR. The pressure on the victim’s chest wall should be sufficient to compress the heart but not so great as to damage internal organs. Injury may result, however, even when CPR is performed properly.
Question 117.
When performing external chest compressions on an adult during cardiopulmonary resuscitation, how deep should the rescuer depress the sternum?
(a) 0.5 inch (1 cm)
(b) 1 inch (2.5 cm)
(c) 1.5 inches (4 cm)
(d) 2 inches (5 cm)
Answer:
(d) 2 inches (5 cm)
Explanation:
An adult’s sternum must be depressed 2 inches (5 cm] with each compression to ensure adequate heart compression.
Question 118.
If a client is receiving rescue breaths, and the chest wall fails to rise during cardiopulmonary resuscitation, what should the rescuer do first?
(a) Try using a bag mask device.
(b) Decrease the rate of compressions.
(c) Intubate the client.
(d) Reposition the airway.
Answer:
(d) Reposition the airway.
Explanation:
If the chest wall is not rising with rescue breaths, the head should be repositioned first to ensure that the airway is adequately opened. A bag mask device allows for delivery of 100% oxygen but is difficult to manage if there is just one rescuer; ideally, two persons are used to operate the bag mask device, one to maintain the seal and the other to provide the ventilations. Compressions should be maintained at 100 per minute.
Question 119.
During rescue breathing in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), how will the nurse evaluate that victim is exhaling?
(a) observing normal relaxation of the chest
(b) giving gentle pressure from the rescuer’s hand on the upper chest
(c) noting the depth of pressure of cardiac compressions
(d) turning the client’s head to the side
Answer:
(a) observing normal relaxation of the chest
Explanation:
The exhalation phase of ventilation is a passive activity that occurs during CPR as part of the normal relaxation of the victim’s chest. No action by the rescuer is necessary.
Question 120.
The rapid response team has been called to manage an unwitnessed cardiac arrest in a client’s hospital room. How long should the nurse estimate the maximum time a person can be without cardiopulmonary function and still not experience permanent brain damage?
(a) 1 to 2 minutes
(b) 4 to 6 minutes
(c) 8 to 10 minutes
(d) 12 to 15 minutes
Answer:
(b) 4 to 6 minutes
Explanation:
After a person is without cardiopulmonary function for 4 to 6 minutes, permanent brain damage is almost certain. To prevent permanent brain damage, it is important to begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation promptly after a cardiopulmonary arrest.
Question 121.
A nurse is helping a suspected choking victim. When should the nurse perform the Heimlich maneuver?
(a) The victim starts to become cyanotic.
(b) The victim cannot speak due to airway obstruction.
(c) The victim can make only minimal vocal noises.
(d) The victim is coughing vigorously.
Answer:
(b) The victim cannot speak due to airway obstruction.
Explanation:
The Heimlich maneuver should be administered only to a victim who cannot make any sounds due to airway obstruction. If the victim can whisper words or cough, some air exchange is occurring, and the emergency medical system should be called instead of attempting the Heimlich maneuver. Cyanosis may accompany or follow choking; however, the Heimlich maneuver should only be initiated when the victim cannot speak.
Question 122.
When performing the Heimlich maneuver on a conscious adult victim, where should the nurse deliver the rescuer inward and upward thrusts?
(a) above the umbilicus
(b) at the level of the xiphoid process
(c) over the victim’s midabdominal area
(d) below the xiphoid process and above the umbilicus
Answer:
(d) below the xiphoid process and above the umbilicus
Explanation:
The thrusts should be delivered below the xiphoid process, but above the umbilicus, to minimize the risk of internal injuries.
Question 123.
The monitor technician informs the nurse that the client has started having premature ventricular contractions every other beat. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Activate the rapid response team.
(b) Assess the client’s orientation and vital signs.
(c) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(d) Administer a bolus of lidocaine.
Answer:
(b) Assess the client’s orientation and vital signs.
Explanation:
The priority action is to assess the client and determine whether the rhythm is life threatening. More information, including vital signs, should be obtained, and the nurse should notify the HCP. A bolus of lidocaine may be prescribed to treat this arrhythmia. This is not a code-type situation unless the client has been determined to be in a life- threatening situation.
Question 124.
A client returns to the nursing unit following successful synchronized cardioversion using transthoracic chest wall patches. What should the nurse assess when the client returns to the room? Select all that apply.
(a) vital signs
(b) skin of chest wall
(c) arterial puncture site
(d) level of consciousness
(e) cardiac rhythm
Answer:
(a) vital signs
(b) skin of chest wall
(d) level of consciousness
(e) cardiac rhythm
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e). Vital signs give an important initial assessment of this client’s status. The client may experience burns from the patches and current used for the cardioversion. Therefore, it is important to assess the skin of the chest wall for redness or burns. Because conscious sedation is used for this procedure, assessing the client’s level of consciousness also is an important initial step. Attaching the client to cardiac monitoring is also important to assess rhythm abnormalities. There is no arterial puncture associated with the procedure.
Question 125.
The nurse is preparing to defibrillate a client on a cardiac monitor who is in ventricular fibrillation (see photo). What should the nurse do?
(a) Move the paddle in the nurse’s left hand to the midline.
(b) Move the paddle in the nurse’s right hand to above the client’s nipple.
(c) Grasp the handles of the paddles to allow visibility of the black markings on the paddle.
(d) After pressing the charge button and calling “all clear,” push the shock button.
Answer:
(d) After pressing the charge button and calling “all clear,” push the shock button.
Explanation:
The paddles are in the correct position. The nurse can push the shock button to defibrillate the client.
Question 126.
The nurse is caring for a client who has become unresponsive. The blood pressure is 80/40 mm Hg, and Sp02 is 90% on 50% face mask. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Begin chest compressions.
(b) Call the rapid response team.
(c) Remove the family from the room.
(d) Ventilate the client with a bag mask device.
Answer:
(b) Call the rapid response team.
Explanation:
The rapid response team should be called immediately to evaluate and treat the client. There is no indication at this time for manual ventilations or chest compressions. If the family is not interfering in client care, it can be reassuring to the family to see that all possible care is being provided.
Question 127.
A nurse working the day shift on a cardiac unit receives the following shift report.
At the conclusion of shift report, it is 0730. Put the clients in the order from first to last in which the nurse should plan to assess them. All options must be used.
(a) Client 1: Admitted yesterday morning with hypokalemia. Awaiting repeat electrolyte lab results drawn at 0600.
(b) Client 2: Experienced chest pain at 0630. Pain resolved after two sublingual nitroglycerin tablets.
(c) Client 3: Scheduled for oral antihypertensive medications at 0900. Incontinent of urine during the night.
(d) Client 4: Scheduled for coronary artery bypass surgery at 0800. The client’s family is in the client’s room.
Answer:
(b) Client 2: Experienced chest pain at 0630. Pain resolved after two sublingual nitroglycerin tablets.
(d) Client 4: Scheduled for coronary artery bypass surgery at 0800. The client’s family is in the client’s room.
(c) Client 3: Scheduled for oral antihypertensive medications at 0900. Incontinent of urine during the night.
(a) Client 1: Admitted yesterday morning with hypokalemia. Awaiting repeat electrolyte lab results drawn at 0600.
Explanation:
(b), (d), (c), (a). Even though the chest pain experienced by Client 2 is resolved, it was recent and requires reassessment. Client 4 is scheduled to leave for major surgery very soon. The nurse should check this client and the client’s chart and make certain that everything is ready so as to not delay the surgery. Client 3 has scheduled medications for blood pressure control. While not experiencing any acute problems, this medication should be administered as scheduled. Client 1 is stable at this time and can be seen last.
Question 128.
Which activity would be appropriate for the nurse to delegate to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) for a client diagnosed with a myocardial infarction who is stable?
(a) Evaluate the lung sounds.
(b) Help the client identify risk factors for coronary artery disease.
(c) Provide teaching on a 2-g sodium diet.
(d) Record the intake and output.
Answer:
(d) Record the intake and output.
Explanation:
UAP are able to measure and record intake and output. The nurse is responsible for client teaching, physical assessments, and evaluating the information collected on the client.
Question 129.
The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) reports to the nurse that a client is “feeling short of breath.” The client’s blood pressure was 124/78 mm Hg 2 hours ago with a heart rate of 82 bpm; the unlicensed assistive personnel reports that blood pressure is now 84/44 mm Hg with a heart rate of 54 bpm, and the client stated, “I just don’t feel good. ” What actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
(a) Confirm the client’s vital signs, and complete a quick assessment.
(b) Inform the charge nurse of the change in condition, and initiate the hospital’s rapid/ emergency response team.
(c) Make a quick check on other assigned clients before spending the amount of time required to take care of this client.
(d) Position the client in semi-Fowler’s position.
(e) Stay with the client, and reassure the client.
(f) Call the health care provider (HCP), and report the situation using SBAR format.
Answer:
(a) Confirm the client’s vital signs, and complete a quick assessment.
(b) Inform the charge nurse of the change in condition, and initiate the hospital’s rapid/ emergency response team.
(d) Position the client in semi-Fowler’s position.
(e) Stay with the client, and reassure the client.
(f) Call the health care provider (HCP), and report the situation using SBAR format.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e),(f). The nurse must have assessment data and verify vital signs if necessary in order to determine the action that is required. If there is a significant change in the client’s condition, the charge nurse should be notified in order to help the nurse with both this client and the nurse’s other assigned clients if necessary; most acute care facilities have a rapid response team that can also help assess and intervene with basic standing prescriptions if necessary.
Positioning the client in semi-Fowler’s is a nursing action that may assist in breathing and relieve shortness of breath. It is important for the nurse to reassure the client by staying calm and remaining with the client. The nurse must notify the HCP. about the change in client’s condition; the nurse must have all information available and present it in a concise and accurate manner using SBAR format including a recommendation for treatment if indicated. The nurse should stay with this client and delegate checking on other assigned clients to the charge nurse or UAP.
Question 130.
The nurse is assessing a client with heart failure whose blood pressure and weight are being monitored remotely. The nurse reviews data obtained within the last 3 days.
|
Weight |
April 3 |
April 4 |
April 5 |
|
Blood |
160 (72 kg) |
162 (73 kg) |
165 (74 kg) |
|
Pressure |
120/80 |
130/88 |
140/90 |
The nurse calls the client to follow up. What should the nurse ask the client first?
(a) “How are you feeling today?”
(b) “Are you having shortness of breath?”
(c) “Did you calibrate the scales before using them?”
(d) “How much fluid did you drink during the last 24 hours?”
Answer:
(b) “Are you having shortness of breath?”
Explanation:
The client has gained 5 lb (2.3 kg) in 3 days with a steady increase in blood pressure. The client is exhibiting signs of heart failure, and if the client is short of breath, this will be another sign. Asking how the client is feeling is too general, and a more focused question will quickly determine the client’s current health status. The scales should be calibrated periodically, but a 5-lb (2.3-kg) weight gain, along with increased blood pressure, is not likely due to problems with the scale. The weight gain is likely due to fluid retention, not drinking too much fluid.
Question 131.
The nurse is tracking data on a group of clients with heart failure who have been discharged from the hospital and are being followed at a clinic. Which data are the best indicators that nursing interventions of monitoring and teaching have been effective?
(a) Ninety percent of clients have not gained weight.
(b) Seventy-five percent of the clients viewed the educational DVD.
(c) Eighty percent of the clients reported that they are taking their medications.
(d) Five percent of the clients required hospital ization in the last 90 days.
Answer:
(d) Five percent of the clients required hospital ization in the last 90 days.
Explanation:
The goals of managing clients outside of the hospital are for the clients to maintain health and prevent readmission; thus, interventions, such as monitoring and teaching, appear to have contributed to the low readmission rate in this group of clients. Although it is important that clients do not gain weight, view educational material, and continue to take their medication, the primary indicator of effectiveness of the program is the lack of rehospitalization.
Question 132.
The nurse in the intensive care unit is giving a report to the nurse in a cardiac step-down unit about a client who had coronary artery bypass surgery. Which is the most effective way to assure essential information about the client is reported?
(a) Give the report face-to-face with both nurses in a quiet room.
(b) Audiotape the report for future reference and documentation.
(c) Use a printed checklist with information individualized for the client.
(d) Document essential transfer information in the client’s medical record.
Answer:
(c) Use a printed checklist with information individualized for the client.
Explanation:
Using an individualized, printed checklist ensures that all key information is reported; the checklist can then serve as a record to which nurses can refer later. Giving a verbal report leaves room for error in memory; using an audiotape or a medical record requires nurses to spend unnecessary time retrieving information.
Question 133.
The nurse is planning care for a group of elderly clients who are affected by orthostatic hypotension. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Assist the clients to stand to help prevent falls.
(b) Teach clients how to gradually change their position.
(c) Request a prescription for antihypertensive medications for clients at high risk.
(d) Conduct “fall risk” assessments.
(e) Consider the use of sequential compression devices (SCDs) for high-risk clients.
(f) Place clients on bed rest.
Answer:
(a) Assist the clients to stand to help prevent falls.
(b) Teach clients how to gradually change their position.
(d) Conduct “fall risk” assessments.
(e) Consider the use of sequential compression devices (SCDs) for high-risk clients.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e). Orthostatic hypotension is a drop in blood pressure that occurs when changing position, usually to a more upright position. Orthostatic hypotension often occurs in elderly clients, and it is a common cause of falls. Nurses must assess clients for orthostatic hypotension and assist all clients with orthostatic hypotension in standing to help prevent falls.
Lower limb compression devices aid in preven-tion of decreased orthostatic systolic blood pressure and reduce symptoms in elderly clients with progressive orthostatic hypotension. Nurses must teach clients how to gradually change their position, and they must conduct “fall risk” assessments.
SCDs may be helpful to high-risk clients and should be considered when developing the care plan. Antihypertensive medications are not necessary for clients with orthostatic hypertension and may precipitate danger-ous drops in blood pressure. The clients should be encouraged to be ambulatory.
Question 134.
The nurse is caring for a group of clients on a medical-surgical nursing unit. Which task(s) could the nurse delegate to unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)? Select all that apply.
(a) Assess pedal pulses on a client who just returned from a cardiac angiogram.
(b) Administer oxygen via nasal cannula to a client with a saturation of 89%.
(c) Administer acetaminophen to a client with a pain level of “5” out of “10.”
(d) Perform vital signs and oxygen saturation on a client returning from the catheterization lab.
(e) Obtain intake and outputs on a client experiencing heart failure.
Answer:
(d) Perform vital signs and oxygen saturation on a client returning from the catheterization lab.
(e) Obtain intake and outputs on a client experiencing heart failure.
Explanation:
(d), (e). Performing vital signs and obtaining intake and outputs are tasks that can be delegated to UAP. Assessing pedal pulses and administering medications and oxygen are skills that require nursing judgments.
Question 135.
The nurse is caring for a group of clients. Which client should the nurse see first?
(a) a client with a history of sinus tachycardia w ho is to receive a beta-blocker
(b) a client with stable angina who took one sublingual nitroglycerine 30 minutes ago
(c) a client with a placement of a coronary artery stent 30 minutes ago
(d) a client with new onset of atrial fibrillation who has a heart rate of 95
Answer:
(c) a client with a placement of a coronary artery stent 30 minutes ago
Explanation:
The client who has just returned from having a stent placed in a coronary artery should be seen first. The nurse should assess this client to establish a baseline. Risks associated with a stent placement include a reocclusion, cardiac tamponade, dysrhythmias, bleeding, and thrombosis. While a new onset of atrial fibrillation is a concern, this client’s heart rate is <100 bpm and is not showing signs of being hemodynamically unstable.
A client with a history of sinus rhythm who will receive a beta-blocker is not a higher priority. While a client with stable angina who took a sublin-gual nitroglycerine 30 minutes ago will need to be assessed frequently, there is no evidence to suggest this client is currently experiencing chest pain.
Also Read:
