Regular practice with NCLEX PN Practice Questions enhances critical thinking skills, which are vital for making sound clinical decisions.
NCLEX Birth Experience Questions
Birth Experience NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
The nurse is managing care of a primigravida at full term who is in active labor. What should be included in the plan of care for this client?
(a) oxygen saturation monitoring every half hour
(b) supine positioning on back, if it is comfortable
(c) anesthesia/pain level assessment every 30 minutes
(d) vaginal bleeding, rupture of membrane assessment every shift
Answer:
(c) anesthesia/pain level assessment every 30 minutes
Explanation:
The nurse should monitor anesthesia/pain levels every 30 minutes during active labor to ascertain that this client is comfortable during the labor process and particularly during active labor when pain often accelerates for the client. When in active labor, oxygen saturation is not monitored unless there is a specific need, such as heart disease.
The client should not be on her back but wedged to the right or left side to take the pressure off the vena cava. When lying on the back, the fetus compresses the major blood vessels. Vaginal bleeding in active labor should be monitored every 30 minutes to 1 hour.
Question 2.
The health care provider (HCP) prescribes intermittent fetal heart rate monitoring for a 20-year- old obese primigravid client at 40 weeks’ gestation in the first stage of labor. The nurse should monitor the client’s fetal heart rate pattern at which interval?
(a) every 15 minutes during the latent phase
(b) every 30 minutes during the active phase
(c) every 60 minutes during the pushing phase
(d) every 2 hours during the transition phase
Answer:
(b) every 30 minutes during the active phase
Explanation:
The first stage of labor is categorized into three phases: latent, active, and transition. During the active stage of labor, intermittent fetal monitoring is performed every 30 minutes to detect changes in fetal heart rate such as bradycardia, tachycardia, or decelerations in low-risk labor. If complications develop, more frequent or continuous electronic fetal monitoring may be needed.
During the latent phase, intermittent monitoring is usually performed every 1 hour because contractions during this time are usually less frequent. During the transition phase, intermittent monitoring is performed every 5 minutes because the client is getting closer to the birth of the baby. Pushing occurs in stage II of labor, and monitoring continues to occur every 5 to 15 minutes.
Question 3.
The primigravid client is at +1 station and 9 cm dilated. Based on these data, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Ask the anesthesiologist to increase the epidural infusion rate.
(b) Assist the client to push if she feels the need to do so.
(c) Encourage the client to breathe through the urge to push.
(d) Support family members in providing comfort measures.
Answer:
(c) Encourage the client to breathe through the urge to push.

Explanation:
The urge to push is often present when the fetus reaches + stations. This client does not have a cervix that is completely dilated, and pushing in this situation may tear the cervix. Encouraging the client to breathe through the urge to push is the most appropriate strategy and allows the cervix to dilate before pushing.
Increasing the level of the epi-dural is inappropriate as nursing would like to have the client be able to push when she is fully dilated. Comfort measures are important for the client at this time but are not the highest priority for the nurse
Question 4.
Assessment of a primigravid client in active labor who has had no analgesia or anesthesia reveals complete cervical effacement, dilation of 8 cm, and the fetus at 0 stations. The nurse should expect the client to exhibit which behavior during this phase of labor?
(a) excitement
(b) loss of control
(c) numbness of the legs
(d) feelings of relief
Answer:
(b) loss of control
Explanation:
Assessment findings indicate that the client is in the transition phase of labor. During this phase, it is not unusual for clients to exhibit a loss of control or irritability. Leg tremors, nausea, vom-iting, and an urge to bear down also are common. Excitement is associated with the latent phase of labor.
Numbness of the legs may occur when epidural anesthesia has been given; however, it is rare when no anesthesia is given. Feelings of relief generally occur during the second stage, when the client begins bearing-down efforts.
Question 5.
The nurse is explaining to a primigravida in labor that her baby is in a breech presentation, with the baby’s presenting part in a left, sacrum, posterior (ESP) position. Which illustration should the nurse use to help the client understand how her baby is positioned?
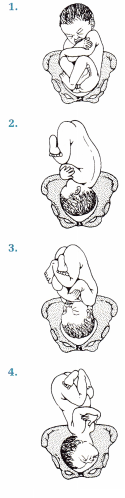
Answer:
Explanation:
This figure shows the client’s baby in a breech presentation with the baby facing the pelvis on the left, the sacrum as the presenting part, and the presenting part (sacrum) is posterior in the pelvis. Figure 2 shows a vertex presentation with the baby in a left occipitoanterior (LOA) position. Figure 3 shows a vertex presentation, left occipitoposterior (LOP). Figure 4 shows a face position with the baby in a left mentotransverse (LMT) position.
Question 6.
The nurse is discussing pain relief methods for a pregnant first-time mother. The discussion should include which labor support methods?
Select all that apply,
(a) effleurage
(b) positive reinforcement
(c) guided imagery
(d) pattern-paced breathing
(e) self-containment theory
(f) progressive relaxation
Answer:
(a) effleurage
(c) guided imagery
(d) pattern-paced breathing
(f) progressive relaxation
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (f) Effleurage is a method of light massage that can provide pain relief. Guided imagery is a relaxation technique used in birth preparation, as is pattern-paced breathing. Positive reinforcement is not a labor support method, nor is self-containment theory.
Question 7.
A primigravid client at 38 weeks’ gestation comes to the labor room because “my water broke.” The health care provider (HCP) asks the nurse to verify spontaneous rupture of membranes using nitrazine paper. The nurse observes that the nitra- zine paper turns bright blue. What action should the nurse take next?
(a) Notify the HCP that the membranes are ruptured.
(b) Perform a sterile vaginal examination to assess the cervix.
(c) Document the findings of the nitrazine test.
(d) Offer the client a sterile sanitary pad after performing perineal care.
Answer:
(a) Notify the HCP that the membranes are ruptured.

Explanation:
Nitrazine paper responds to alkaline fluids by changing blue; amniotic fluid is alkaline so the color verifies that the membranes are ruptured. The nurse notifies the provider that membranes are ruptured so that a plan of action can be developed.
Rupture of membranes in the absence of labor increases the risk of infection. Vaginal examinations are limited until labor is initiated. Wearing a sanitary pad increases potential for infection. Documentation of the nitrazine test is completed after notifying the provider.
Question 8.
The health care provider (HCP) has prescribed prostaglandin gel to be administered vaginally to a newly admitted primigravid client. Which finding indicates that the client has had a therapeutic response to the medication?
(a) resting period of 2 minutes between contractions
(b) decreasing nausea in labor
(c) softening of the cervix and beginning of effacement
(d) leaking of clear amniotic fluid in small amounts
Answer:
(c) softening of the cervix and beginning of effacement
Explanation:
Prostaglandin gel may be used for cervical ripening before the induction of labor with oxytocin. It is usually administered by catheter or suppository, or by vaginal insertion. Two to three doses are usually needed to begin the softening process. Common adverse effects include nausea, vomiting, fever, and diarrhea. Continuous fetal heart rate monitoring and close monitoring of maternal vital signs are necessary to detect subtle changes or adverse effects.
Prostaglandin gel usually does not initiate contractions; therefore, the rest period between contractions will be >2 minutes. Prostaglandins may cause nausea rather than treat it. Leaking of amniotic fluid is not caused by the use of this gel.
Question 9.
A primigravid client is admitted as an outpatient for an external cephalic version. Which factor would be a contraindication for the procedure?
(a) multiple gestations
(b) breech presentation
(c) maternal Rh-negative blood type
(d) history of gestational diabetes
Answer:
(a) multiple gestations

Explanation:
Evaluate External cephalic version is the turning of the fetus from a breech position to the vertex position to prevent the need for a cesarean birth. Gentle pressure is used to rotate the fetus in a forward direction to a cephalic lie. Contraindications to the procedure include multiple gestation because of the potential for fetal injury or uterine injury, severe oligohydramnios (decreased amniotic fluid), contraindications to a vaginal birth (e.g., cephalopelvic disproportion), and unexplained third-trimester bleeding.
If the mother has an Rh-negative blood type, the procedure can be performed, and Rh immunoglobulin should be administered in case minimal bleeding occurs. A history of gestational diabetes is not a contraindication unless the fetus is large for gestational age and the client has cephalopelvic disproportion.
Question 10.
A primigravida is admitted to the labor area with ruptured membranes and contractions occurring every 2 to 3 minutes, lasting 45 seconds. After 3 hours of labor, the client’s contractions are now every 7 to 10 minutes, lasting 30 seconds. The nurse administers oxytocin as prescribed. What is the expected outcome of this drug?
(a) The cervix will begin to dilate 2 cm/h.
(b) Contractions will occur every 2 to 3 minutes, lasting 40 to 60 seconds, with moderate intensity resting tone between contractions.
(c) The cervix will change from firm to soft, efface to 40% to 50%, and move from a posterior to an anterior position.
(d) Contractions will be every 2 minutes, lasting 60 to 90 seconds, with intrauterine pressure of 70 mm Hg.
Answer:
(b) Contractions will occur every 2 to 3 minutes, lasting 40 to 60 seconds, with moderate intensity resting tone between contractions.
Explanation:
The goal of oxytocin administration in labor augmentation is to establish an adequate contraction pattern to enhance the forces of labor. The expected outcome is a pattern of contractions occurring every 2 to 3 minutes, lasting 40 to 60 seconds, of moderate intensity with a palpable resting tone between contractions. Other contraction patterns will cause the cervix to dilate too quickly or too slowly.
Cervical changes in softening, effacement, and moving to an anterior position are associated with use of cervical ripening agents, such as prosta glandin gel. Cervical dilation of 2 cm/h is too rapid for the induction/augmentation process.
Question 11.
A primigravid client in the second stage of labor feels the urge to push. The client has had no analgesia or anesthesia. Anatomically, what would be the best position for the client to assume?
(a) dorsal recumbent
(b) lithotomy
(c) hands and knees
(d) squatting
Answer:
(d) squatting
Explanation:
Anatomically, the best position for the client to assume is the squatting position because this enhances pelvic diameters and allows gravity to assist in the expulsion stage of labor. This position also provides for natural pressure anesthesia as the fetal presenting part presses on the stretched perineum. If the client is extremely fatigued from a lengthy labor process, she may prefer the dorsal recumbent position.
However, this position is not considered the best position anatomically. The lithotomy position may be ineffective and uncomfortable for a client who is ready to push. The hands and knees position may help to alleviate some back pain. However, this position can cause discomfort to the arms and wrists and is tiring over a long period of time.
Question 12.
A 21-year-old primigravid client at 40 weeks’ gestation is admitted to the hospital in active labor. The client’s cervix is 8 cm and completely effaced at 0 station. During the transition phase of labor, which is a priority nursing problem?
(a) urinary retention
(b) hyperventilation
(c) ineffective coping
(d) pain
Answer:
(d) pain

Explanation:
During the transition, contractions are increasing in frequency, duration, and intensity. The most appropriate nursing problem is pain related to the strength and duration of the contractions. Insufficient information is provided in the scenario to support the other listed nursing diagnoses.
Urinary retention would be appropriate if the client had a full bladder and was unable to void. Hyperventilation might apply if the client was breathing too rapidly, but there is no evidence this is occurring. Ineffective coping might apply if the client said, “I can’t do this” or something similar.
Question 13.
A 24-year-old primigravid client who gives birth to a viable term neonate is prescribed oxytocin intravenously after delivery of the placenta. Which sign would indicate to the nurse that the placenta is about to be delivered?
(a) The cord lengthens outside the vagina.
(b) There is decreased vaginal bleeding.
(c) The uterus cannot be palpated.
(d) The uterus changes to a discoid shape.
Answer:
(a) The cord lengthens outside the vagina.
Explanation:
The most reliable sign that the placenta has detached from the uterine wall is the lengthening of the cord outside the vagina. Other signs include a sudden gush of (rather than a decrease in) vaginal blood. Usually, when placenta detachment occurs, the uterus becomes firmer and changes in shape from discoid to globular. This process takes about 5 minutes. If the placenta does not separate, manual removal may be necessary to prevent postpartum hemorrhage.
Question 14.
A primiparous client, who has just given birth to a healthy term neonate after 12 hours of labor, holds and looks at her neonate and begins to cry. The nurse interprets this behavior as a sign of which response?
(a) disappointment in the baby’s gender
(b) grief over the ending of the pregnancy
(c) a normal response to the birth
(d) indication of postpartum “blues”
Answer:
(c) a normal response to the birth
Explanation:
Birth is a very emotional experience. An expression of happiness with tears is a normal reaction. Cultural factors, exhaustion, and anxieties over the new role can all affect maternal responses, so the nurse must be sensitive to the client’s emotional expressions.
There is no evidence to suggest that the mother is disappointed in the baby’s gender, grieving over the end of the pregnancy, or a candidate for postpartum “blues.” However, approximately 80% of postpartum clients experience transient postpartum blues several days after birth.
Question 15.
The cervix of a 15-year-old primigravid client who has been admitted to the labor area is 2 cm dilated and 50% effaced. Her membranes are intact, and contractions are occurring every 5 to 6 minutes. Which intervention should the nurse recommend at this time?
(a) resting in the right lateral recumbent position
(b) lying in the left lateral recumbent position C
(c) walking around in the hallway
(d) sitting in a comfortable chair for a period of time
Answer:
(c) walking around in the hallway
Explanation:
Most authorities suggest that a woman in an early stage of labor should be allowed to walk if she wishes as long as no complications are present. Birthing centers and single-room maternity units allow women considerable latitude without much supervision at this stage of labor.
Gravity and walking can assist the process of labor in some clients. If the client becomes tired, she can rest in bed in the left lateral recumbent position or sit in a comfortable chair. Resting in the left lateral recumbent position improves circulation to the fetus.
Question 16.
Which technique to promote active relaxation would the nurse include in the teaching plan for a 16-year-old primigravid client in early labor?
(a) relaxing uninvolved body muscles during uterine contractions
(b) practicing being in a deep, meditative, sleep like state
(c) focusing on an object in the room during the contractions
(d) breathing rapidly and deeply between contractions
Answer:
(a) relaxing uninvolved body muscles during uterine contractions
Explanation:
Birth educators use various techniques and methods to prepare parents for labor and birth. Active relaxation involves relaxing uninvolved muscle groups while contracting a specific group and using chest breathing techniques to lift the diaphragm off the contracting uterus. A deep, meditative, sleep-like state is a form of passive relaxation. Focusing on an object in the room is part of Larnaze technique for distraction. Breathing rapidly and deeply can lead to hyperventilation and is not recommended.
Question 17.
The nurse is performing effleurage for a primigravid client in early labor. Which technique should the nurse use?
(a) deep kneading of superficial muscles
(b) secure grasping of muscular tissues
(c) light stroking of the skin surface
(d) prolonged pressure on specific sites
Answer:
(c) light stroking of the skin surface
Explanation:
Light stroking of the skin, or effleurage is commonly used with the Larnaze method of birth preparation. Light abdominal massage with just enough pressure to avoid tickling is thought to displace the pain sensation during a contraction. Deep kneading and secure grasping are typically associated with relaxation massages to relieve stress. Prolonged pressure on specific sites is associated with acupressure.
Question 18.
A 24-year-old primigravid client in active labor requests the use of the jet hydrotherapy tub to aid in pain relief. Which condition would the nurse consider to be a contraindication for hydrotherapy?
(a) ruptured membranes
(b) multifetal gestation
(c) diabetes mellitus
(d) hypotonic labor patterns
Answer:
(a) ruptured membranes

Explanation:
Some health care providers (HCPs) do not allow clients with ruptured membranes to use a hot tub or jet hydrotherapy tub during labor for fear of infections. The temperature of the water should be between 98°F and 100°F (36.7°C and 37.8°C) to prevent hyperthermia. Jet hydrotherapy is not contraindicated for clients with multifetal gestation, diabetes mellitus, or hypotonic labor patterns.
Question 19.
The health care provider (HCP) prescribes an amniocentesis for a primigravid client at 37 weeks’ gestation to determine fetal lung maturity. Which is an indicator of fetal lung maturity?
(a) amount of bilirubin present
(b) presence of red blood cells
(c) Barr body determination
(d) lecithin-sphingomyelin (L/S ratio)
Answer:
(d) lecithin-sphingomyelin (L/S ratio)

Explanation:
To determine fetal lung maturity, the sample of amniotic fluid will be tested for the L/S ratio. When fetal lungs are mature, the ratio should be 2 : 1. Bilirubin indicates hemolysis and, if present in the fluid, suggests Rh disease. Red blood cells should not appear in the amniotic fluid because their presence suggests fetal bleeding. Barr body determination is a chromosome analysis of the sex chromosomes that is sometimes used when a child is born with ambiguous genitalia
Question 20.
A 19-year-old primigravid client at 38 weeks’ gestation is 7 cm dilated, and the presenting part is at +1 station. The client tells the nurse, “I need to push!” What should the nurse do next?
(a) Use the McDonald procedure to widen the pelvic opening.
(b) Increase the rate of oxygen and intravenous fluids.
(c) Instruct the client to use a pant-blow pattern of breathing.
(d) Tell the client to push only when absolutely necessary.
Answer:
(c) Instruct the client to use a pant-blow pattern of breathing.
Explanation:
Pushing during the first stage of labor, when the urge is felt but the cervix is not completely dilated, may produce cervical swelling, making labor more difficult. The client should be encouraged to use a pant-blow (or blow-blow) pattern of breathing to help overcome the urge to push. The McDonald procedure is used for cervical cerclage for an incompetent cervix and is inappropriate here.
Increasing the rate of oxygen and intravenous fluids will not alleviate the pressure that the client is feeling. The client should not push even if she feels the urge to do so because this may result in cervical edema at 7-cm dilation.
Question 21.
What would be the priority when caring for a primigravid client whose cervix is dilated at 8 cm when the fetus is at 1+ station and the client has had no analgesia or anesthesia?
(a) giving frequent sips of water
(b) applying extra blankets for warmth
(c) providing frequent perineal cleansing
(d) offering encouragement and support
Answer:
(d) offering encouragement and support
Explanation:
The client is in the transition phase of the first stage of labor. During this phase, the client needs encouragement and support because this is a difficult and painful time, when contractions are especially strong. Usually, the client finds it difficult to maintain self-control. Everything else seems secondary to her as she progresses into the second stage of labor.
Although ice chips may be given, typically the client does not desire sips of water. Labor is hard work. Generally, the client is perspiring and does not desire additional warmth. Frequent perineal cleansing is not necessary unless there is excessive amniotic fluid leaking.
Question 22.
To determine whether a primigravid client in labor with a fetus in the left occipitoanterior (LOA) position is completely dilated, the nurse performs a vaginal examination. During the examination, the nurse should palpate which cranial sutures?
(a) sagittal
(b) lambdoidal
(c) coronal
(d) frontal
Answer:
(a) sagittal
Explanation:
The sagittal suture is the most readily felt during a vaginal examination. When the fetus is in the LOA position, the occiput faces the mother’s left. The lambdoid suture is on the side of the skull. The coronal suture is a horizontal suture across the front portion of the fetal skull that forms the anterior fontanelle. It may be felt with a brow presentation. The frontal suture may be felt with a brow or face presentation.
Question 23.
After a lengthy labor process, a primigravid client gives birth to a healthy newborn boy with a moderate amount of skull molding. What information would the nurse include when explaining to the parents about this condition?
(a) It is typically seen with breech births.
(b) It usually lasts a day or two before resolving.
(c) It is typical when the brow is the presenting part.
(d) Surgical intervention may be necessary to alleviate pressure.
Answer:
(b) It usually lasts a day or two before resolving.
Explanation:
Molding occurs with vaginal births and is commonly seen in newborns. This is especially true with primigravid clients experiencing a lengthy labor process. Parents need to be reassured that it is not permanent and that it typically lasts a day or two before resolving. Molding rarely is present if the fetus is in a breech or brow presentation. Surgical intervention is not necessary.
Question 24.
The health care provider (HCP) has informed the labor nurse that he believes the uterus has inverted in a primiparous client who has just given birth. Which findings would help to confirm this diagnosis? Select all that apply.
(a) hypotension
(b) gush of blood from the vagina
(c) intense, severe, tearing type of abdominal pain
(d) uterus is hard and in a constant state of contraction
(e) inability to palpate the uterus
(f) diaphoresis
Answer:
(a) hypotension
(b) gush of blood from the vagina
(e) inability to palpate the uterus
(f) diaphoresis
Explanation:
(a), (b), (e), (f) Uterine inversion is indicated by a sudden gush of blood from the vagina leading to decreased blood pressure, and an inability to palpate the uterus since it may be in or protruding from the vagina, and any signs of blood loss such as diaphoresis, paleness, or dizziness could be observed at this time. Intense pain and a hard, contracting uterus are not associated with uterine inversion.
Question 25.
The nurse explains to a newly admitted primigravid client in active labor that, according to the gate-control theory of pain, a closed gate means that the client should experience what type of pain?
(a) no pain
(b) sharp pain
(c) light pain
(d) moderate pain
Answer:
(a) no pain

Explanation:
According to the gate-control theory of pain, a closed gate means that the client should feel no pain. The gate-control theory of pain refers to the gate-control mechanisms in the substantia gelatinosa that are capable of halting an impulse at the level of the spinal cord so the impulse is never perceived at the brain level as pain (i.e., a process similar to keeping a gate closed).
Question 26.
The cervix of a primigravid client in active labor who received epidural anesthesia 4 hours ago is now completely dilated, and the client is ready to begin pushing. What is most important for the nurse to assess before the client begins to push?
(a) fetal heart rate variability
(b) cervical dilation again
(c) status of membranes
(d) bladder status
Answer:
(d) bladder status
Explanation:
The bladder status should be monitored throughout the labor process, but especially before the client begins pushing. A full bladder can impede the progress of labor and slow fetal descent. Because she has had an epidural anesthetic, it is most likely that the client is receiving intravenous fluids, contributing to a full bladder. The client also does not feel the urge to void because of the anesthetic.
Although it is important to monitor membrane status and fetal heart rate variability throughout labor, this does not affect the client’s ability to push. There is no need to recheck cervical dilation because increasing the frequency of examinations can increase the client’s risk for infection.
Question 27.
For the past 8 hours, a 20-year-old primigravid client in active labor with intact membranes has been experiencing regular contractions. The fetal heart rate is 136 bpm with moderate variability. After determining that the client is still in the latent phase of labor, the nurse should observe the client for which problem?
(a) exhaustion
(b) chills and fever
(c) fluid overload
(d) meconium-stained fluid
Answer:
(a) exhaustion

Explanation:
The normal length of the latent stage of labor in a primigravid client is 6 hours. If the client is having prolonged labor, the nurse should monitor the client for signs of exhaustion as well as dehydration. Hypotonic contractions, which are painful but ineffective, may be occurring. Oxytocin augmentation may be necessary. Chills and fever are manifestations of an infection and are not associated with a prolonged latent phase of labor.
Fluid overload can occur from rapid infusion of intravenous fluids administered if the client is experiencing hemorrhage or shock. It is not associated with a prolonged latent phase. The client’s membranes are intact, so it would be difficult to assess the meconium staining of the fluid. Meconium-stained fluid is associated with fetal distress, and this fetus appears to be in a healthy state, as evidenced by a fetal heart rate within normal range and good variability.
Question 28.
A primigravid client whose cervix is 7 cm dilated with the fetus at 0 stations and in a left occiput posterior (LOP) position has severe back pain. What intervention is most indicated?
(a) Provide firm pressure to the client’s sacral area.
(b) Prepare the client for a cesarean birth.
(c) Prepare the client for a precipitate birth.
(d) Maintain the client in a left-side-lying position.
Answer:
(a) Provide firm pressure to the client’s sacral area.
Explanation:
The client who has back pain during labor experiences marked discomfort because the fetus is in an LOP position. This pain is much greater than when the fetus is in the anterior position because the fetal head impinges on the sacrum in the course of rotating to the anterior position. Application of firm pressure to the sacral area can help alleviate the pain. Problems of severe back pain during labor do not typically require a cesarean birth.
The health care provider (HCP) may elect to do an episiotomy, but it is not necessarily required. It is unlikely that a primigravid client with a fetus in a LOP position will have a precipitous birth; rather, labor is usually more prolonged. A hands-and-knees position or a right-side-lying position may help to rotate the fetal head and thus alleviate some of the back pain.
Question 29.
A primigravid client in active labor has had no anesthesia. The client’s cervix is 7 cm dilated, and she is starting to feel considerable discomfort during contractions. The nurse should instruct the client to change from slow chest breathing to which breathing technique?
(a) rapid, shallow chest breathing
(b) deep chest breathing
(c) rapid pant-blow breathing
(d) slow abdominal breathing
Answer:
(a) rapid, shallow chest breathing
Explanation:
The psychoprophylaxis method of birth suggests using slow chest breathing until it becomes ineffective during labor contractions, then switching to shallow chest breathing (mostly at the sternum) during the peak of a contraction. The rate is 50 to 70 breaths/ min. Deep chest breathing is appropriate for the early phase of labor, in which the client exhibits less frequent contractions. When transition nears, a rapid pant-blow pattern of breathing is used. Slow abdominal breathing is very difficult for clients in labor.
Question 30.
Assessment of a primigravid client reveals cervical dilation at 8 cm and complete effacement. The client has severe back pain during this phase of labor. The nurse explains that the client’s severe back pain is most likely caused by the fetal occiput being in which position?
(a) breech
(b) transverse
(c) posterior
(d) anterior
Answer:
(c) posterior
Explanation:
When a client has severe back pain during labor, the fetus is most likely in an occipitoposterior position. This means that the fetal head presses against the client’s sacrum, causing marked discomfort during contractions.
These sensations may be so intense that the client requests medication for relief of the back pain rather than the contractions. Breech presentation and transverse lie are usually known prior to 8-cm dilation, and a cesarean birth is performed. The fetal occiput anterior position does not increase the pain felt during labor.

Question 31.
The nurse assesses a primiparous client with ruptured membranes in labor for 20 hours. The nurse identifies late decelerations on the monitor and initiates standard procedures for the labor client with this wave pattern. Which interventions should the nurse perform? Select all that apply.
(a) administering oxygen via mask to the client
(b) questioning the client about the effectiveness of pain relief
(c) placing the client on her side
(d) readjusting the monitor to a more comfortable position
(e) applying an internal fetal monitor
Answer:
(a) administering oxygen via mask to the client
(c) placing the client on her side
(e) applying an internal fetal monitor
Explanation:
(a), (c), (e) Decelerations alert the nurse that the fetus is experiencing decreased blood flow from the placenta. Administering oxygen will increase tissue perfusion. Placing the mother on her side will increase placental perfusion and decrease cord compression. Using an internal fetal monitor would help in identifying the possible underlying cause of the decelerations, such as metabolic acidosis. Assessing for pain relief and readjusting the monitor would have no effect on correcting the late decelerations.
Question 32.
When performing Leopold’s maneuvers on a primigravid client, the nurse is palpating the uterus as shown below. Which maneuver is the nurse performing?
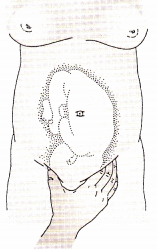
(a) first maneuver
(b) second maneuver
(c) third maneuver
(d) fourth maneuver
Answer:
(c) third maneuver
Explanation:
The third maneuver involves grasping the lower portion of the abdomen just above the symphysis pubis between the thumb and index finger. This maneuver determines whether the fetal pre-senting part is engaged. The first maneuver involves facing the woman’s head and using the tips of the fingers to palpate the uterine fundus.
This maneuver is used to identify the part of the fetus that lies over the inlet to the pelvis. The second maneuver involves placing the palms of each hand on either side of the abdomen to locate the back of the fetus. The fourth maneuver involves placing the fingers on both sides of the uterus and pressing downward and inward in the direction of the birth canal. This maneuver is done to determine fetal attitude and degree of extension and should only be done if the fetus is in the cephalic presentation.
Question 33.
Before placing the fetal monitoring device on a primigravid client’s fundus, the nurse performs Leopold’s maneuvers. The nurse explains that third maneuver is done for which reason?
(a) to determine whether the fetal presenting part is engaged
(b) to locate the fetal cephalic prominence
(c) to distinguish between a breech and a cephalic presentation
(d) to locate the position of the fetal arms and legs
Answer:
(a) to determine whether the fetal presenting part is engaged
Explanation:
Leopold’s maneuvers are performed to determine the presentation and position of the fetus. The third maneuver determines whether the fetal presenting part is engaged in the maternal pelvis. The first maneuver distinguishes between a breech and a cephalic presentation through palpation of the top of the fundus. The second maneuver locates the fetal back, arms, and legs.
The fetal heart rate monitoring device should be placed near the fetal skull and back for optimal fetal heart rate monitoring. The fourth maneuver is done to locate the fetal cephalic prominence if the fetus is in a cephalic position.
Question 34.
The nurse is caring for a G2, Tl, P0, AO, Ll client at term. The client is completely effaced, dilated to 2 cm, with contractions every 3 minutes lasting 45 seconds. The client is asking for an epidural to make her more comfortable. Indicate the appropriate response by the nurse.
(a) “We cannot give epidurals until you are 5 to 6 cm dilated. There is IV medication available if you would like it now.”
(b) “You cannot have an epidural until your membranes have ruptured.”
(c) “Your contraction pattern is slow at this point and will need to accelerate before you can have your epidural.”
(d) “It is too early in labor for the epidural, but you can have IV medication to keep you comfortable until you have dilated 1 to 2 cm more.”
Answer:
(d) “It is too early in labor for the epidural, but you can have IV medication to keep you comfortable until you have dilated 1 to 2 cm more.”
Explanation:
Epidurals are given when labor is established, usually at 3- to 4-cm dilation. The effect of the epidural should be that labor will continue and not be slowed down by the administration of the epidural. The use of an epidural is not correlated with rupture of membranes. The contraction pattern for this client is adequate, not slow, and considered normal for 2-cm dilation. Epidurals are given at 3- to 4-cm dilation, and if there is medication available, it can be given to make the client comfortable until an epidural can be given.
Question 35 .
The nurse has just received report on a labor client: a G3, Tl, PO, Abl, Ll who is 80% effaced, 3 cm dilated, 0 station. The nurse anticipates the plan of care for the shift will address what factors? Select all that apply.
(a) Birth should occur before the change of shift in 12 hours.
(b) Stage 2 should take 30 minutes or less.
(c) Contractions will remain irregular until transition.
(d) Transition will be shorter for this multiparous client.
(e) This client will withdraw into herself during transition.
Answer:
(a) Birth should occur before the change of shift in 12 hours.
(b) Stage 2 should take 30 minutes or less.
(d) Transition will be shorter for this multiparous client.
(e) This client will withdraw into herself during transition.
Explanation:
A multiparous client usually gives birth within 12 hours of the time labor began. The pushing phase statistically takes 30 minutes or less and many multiparous clients go immediately from 10-cm dilation to birth. Contractions become regular and increase in frequency, intensity, and duration as labor progresses for both primiparous and multiparous clients.
Transition will be shorter for a multiparous client than it will for a primiparous client as the entire labor process takes less time for someone who has had a baby before. This client will withdraw into herself during transition, and this is a common characteristic for those in the transition phase.
Question 36.
A multigravida in active labor is 7 cm dilated. The fetal heart rate baseline is 130 bpm with moderate variability. The client begins to have variable decelerations to 100 to 110 bpm. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Perform a vaginal examination.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the decelerations.
(c) Reposition the client and continue to evaluate fetal heart rate.
(d) Administer oxygen via mask at 2 L/min.
Answer:
(c) Reposition the client and continue to evaluate fetal heart rate.
Explanation:
The cause of variable decelerations is cord compression, which may be relieved by moving the client to one side or another. If the client is already on the left side, changing the client to the right side is appropriate. Performing a vaginal examination will let the nurse know how far dilated the client is but will not relieve the cord compression. If the decelerations are not relieved by position changes, oxygen should be initiated, but the rate should be 8 to 10 L/min. Notifying the HCP should occur if turning the client and administering oxygen does not relieve the decelerations.
Question 37.
A nurse is preparing a change-of-shift report and has been caring for a multigravid client with a normally progressing labor. Which information should be part of this report? Select all that apply.
(a) interpretation of the fetal monitor strip
(b) analgesia or anesthesia being used
(c) previous methods of birth control
(d) support persons with the client
(e) prior birth history
Answer:
(a) interpretation of the fetal monitor strip
(b) analgesia or anesthesia being used
(d) support persons with the client
(e) prior birth history
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e) Knowledge of how the fetus is tolerating contractions as well as the frequency, intensity, and duration of contractions, as indicated on the fetal monitor strip, are extremely important. The type of analgesia or anesthesia being used, the client’s response, and her pain rating should be included as well. The amount of vaginal bleeding indicates whether this labor is in the normal range.
The support persons with the client are an integral part of the labor process and greatly influence how she manages labor emotionally and, commonly, physically. A complete change-of-shift report would include the client’s name, age, gravida and parity, current and prior illnesses that may influence this hospitalization, prior labor and birth history if applicable, last vaginal examination time and findings, vaginal bleeding, support persons with the client, current IVs and other medications being used, and pertinent laboratory test results. Previous use of birth control is not important at this time.
Question 38.
A multigravid client is admitted at 4-cm dilation and is requesting pain medication. The nurse gives the client an opioid agonist-antagonist. Within 5 minutes, the client tells the nurse she feels like she needs to have a bowel movement. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Have naloxone available in the birthing room.
(b) Complete a vaginal examination.
(c) Prepare for birth.
(d) Document the client’s relief due to pain medication.
Answer:
(b) Complete a vaginal examination.

Explanation:
The feeling of needing to have a bowel movement is commonly caused by pressure on the receptors low in the perineum when the fetal head is creating pressure on them. This feeling usually indicates advances in fetal station and that the client may be close to birth. The nurse should respond initially to the client’s signs and symptoms by completing a vaginal exam to validate current effacement, dilation, and station.
If the fetus is ready to be born, having the room ready for the birth and having naloxone available are important. Naloxone completely or partially reverses the effects of natural and synthetic opioids, including respiratory depression. Documenting pain relief takes time away from the vaginal examination, preparing for birth, and
obtaining naloxone. The birth may be occurring rapidly. Being prepared for the birth is a higher priority than documentation for this client.
Question 39.
A 31-year-old multigravid client at 39 weeks’ gestation admitted to the hospital in active labor is receiving intravenous lactated Ringer’s solution and a continuous epidural anesthetic. During the first hour after administration of the anesthetic, the nurse should monitor the client for which adverse reaction?
(a) hypotension
(b) diaphoresis C
(c) headache C
(d) tremors
Answer:
(a) hypotension

Explanation:
When a client receives an epidural anesthetic, sympathetic nerves are blocked along with the pain nerves, possibly resulting in vasodilation and hypotension. Other adverse effects include bladder distention, prolonged second stage of labor, nausea and vomiting, pruritus, and delayed respiratory depression for up to 24 hours after administration. Diaphoresis and tremors are not usually associated with the administration of epidural anesthesia. Headache, a common adverse effect of many drugs, also is not associated with the administration of epidural anesthesia.
Question 40.
A 30-year-old G3, T2, Po, Ao, L2 is being monitored internally. She is being induced with IV oxytocin because she is postpartum. The nurse notes the pattern below. The client is wedged to her side while lying in bed and is approximately 6 cm dilated and 100% effaced. What should the nurse do first?
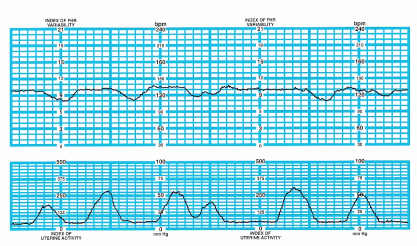
(a) Continue to observe the fetal monitor.
(b) Anticipate rupture of the membranes.
(c) Prepare for fetal oximetry.
(d) Discontinue the oxytocin infusion.
Answer:
(d) Discontinue the oxytocin infusion.
Explanation:
The fetal monitor strip shows late decelerations. The first intervention would be to turn off the oxytocin because the medication is causing the contractions. The stress caused by the contractions demonstrates that the fetus is not being perfused during the entire contraction (as shown by the late decelerations).
There is no time to continue to observe in this situation; intervention is a priority. The client is attached to an internal fetal monitor, which would be possible only if her membranes had already ruptured. If the fetus continues to experi-ence stress, fetal oximetry may be initiated.
Quesstion 41.
The nurse assists with a precipitous birth in an outpatient setting. While waiting for more advanced care, the nurse places the infant skin to skin with the mother and encourages breastfeeding. What are the desired outcomes of skin-to- skin care with early breastfeeding? Select all that apply.
(a) beginning the parental-infant bonding process
(b) preventing neonatal hypothermia
(c) providing glucose to the neonate
(d) contracting the mother’s uterus
(e) preventing maternal infection
Answer:
(a) beginning the parental-infant bonding process
(b) preventing neonatal hypothermia
(c) providing glucose to the neonate
(d) contracting the mother’s uterus
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) The nurse places the newborn skin to skin with the mother immediately following birth for many reasons. The practice facilitates transition to the extra uterine environment. Skin-to-skin contact helps to begin the parental-infant bonding process, and helps prevent neonatal hypothermia.
Early breastfeeding provides the neonate with nutrients to prevent hypoglycemia. Breastfeeding stimulates the natural production of oxytocin, which helps reduce the potential for uterine atony. Skin-to-skin care with early breastfeeding does not reduce the risk of maternal infections
Question 42.
Approximately 15 minutes after the birth of a viable term neonate, a multiparous client has chills. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Assess the client’s pulse rate.
(b) Decrease the rate of intravenous fluids.
(c) Provide the client with a warm blanket.
(d) Assess the amount of blood loss.
Answer:
(c) Provide the client with a warm blanket.
Explanation:
A chill shortly after birth is a common, normal occurrence. Warm blankets can help provide comfort for the client. It has been suggested that the shivering response is caused by a difference between internal and external body temperatures. A different theory proposes that the woman is reacting to fetal cells that have entered the maternal bloodstream through the placental site.
Assessing the client’s pulse rate will provide no further information about the chill. Decreasing the IV rate will not influence the length of time the client trembles. Assessing blood loss is a standard of care at this point postpartum but has no correlation with the chill.
Question 43.
The health care provider (HCP) plans to perform an amniotomy on a multiparous client admitted to the labor area at 41 weeks’ gestation for labor induction. After the amniotomy, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Monitor the client’s contraction pattern.
(b) Assess the fetal heart rate (FHR) for 1 full minute.
(c) Assess the client’s temperature and pulse.
(d) Document the color of the amniotic fluid.
Answer:
(b) Assess the fetal heart rate (FHR) for 1 full minute.

Explanation:
After an amniotomy, the nurse should plan to first assess the FHR for 1 full minute. One of the complications of amniotomy is cord compression and/or prolapsed cord, and an FHR of 100 bpm or less should be promptly reported to the HCP. A cord prolapse requires prompt birth by cesarean section. The client’s contraction pattern should be monitored once labor has been established.
The client’s temperature, pulse, and respirations should be assessed every 2 to 4 hours after rupture of the membranes to detect an infection. The nurse should document the color, quantity, and odor of the amniotic fluid, but this can be done after the FHR is assessed and a normal pattern is present.
Question 44.
A multigravid client who is 10 cm dilated is admitted to the labor and birth unit. In addition to supporting the client, what is the priority nursing action?
(a) turning on the infant warmer
(b) increasing IV fluids
(c) determining the client’s preferences for pain control
(d) providing client education regarding the care of the newborn
Answer:
(a) turning on the infant warmer
Explanation:
Nursing care for this client includes providing support, preparing for birth, assessing for potential complications, and providing for care of the newborn. Turning on the warmer is the best choice for providing for the care of the newborn. Oxygen and IV fluids may be indicated if variable or late decelerations are noted on the fetal heart monitor, but decelerations are not indicated in the question. It is likely too late for pharmacologic pain relief for a multigravid client. Education regarding the care of the newborn is not appropriate at this time.
Question 45.
The nurse is assessing fetal presentation in a multiparous client. The illustration below indicates which type of presentation?
(a) frank breech
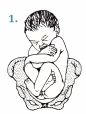
(b) complete breech
(c) footling breech
(d) vertex
Answer:
(a) frank breech
Explanation:
Breech presentations account for 5% of all births, and the most common is frank breech. In frank breech, there is flexion of the fetal thighs and extension of the knees. The feet rest at the side of the fetal head. In complete breech, there is flexion of the fetal thighs and knees; the fetus appears to be squatting. Footling breech occurs when there is an extension of the fetal knees and one or both feet protrude through the cervix. Vertex presentation occurs in 95% of births with the head engaged in the pelvis.
Question 46.
Two hours ago, a multigravid client was admitted in active labor with her cervix dilated at 5 cm and completely effaced and the fetus at 0 station. Currently, the client is experiencing nausea and vomiting, a slight chill with perspiration beads on her lip, and extreme irritability. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Warm the temperature of the room by a few degrees.
(b) Increase the rate of intravenous fluid administration.
(c) Obtain a prescription for an intramuscular antiemetic medication.
(d) Assess the client’s cervical dilation and station.
Answer:
(d) Assess the client’s cervical dilation and station.
Explanation:
The nurse should assess the client’s cervical dilation and station because the client’s symptoms are indicative of the transition phase of labor. Multiparous clients can proceed 5 to 9 cm/h during the active phase of labor. Warming the temperature of the room is not helpful because the client will soon be ready to begin expulsive pushing.
Increasing the intravenous fluid rate is not warranted unless the client is experiencing dehydration. Administration of an antiemetic at this point in labor is not warranted and may result in neonatal depression should a rapid birth occur.
Question 47.
What interval should the nurse use when assessing the frequency of contractions of a multiparous client in active labor admitted to the birthing area?
(a) acme of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction
(b) beginning of one contraction to the end of the next contraction
(c) end of one contraction to the end of the next contraction
(d) beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction
Answer:
(d) beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction
Explanation:
To assess the frequency of the client’s con¬tractions, the nurse should assess the interval from the beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction. The duration of a contraction is the interval between the beginning and the end of a contraction. The acme identifies the peak of a contraction.
Question 48.
While a client is being admitted to the birthing unit she states, “My water broke last night, but my labor started 2 hours ago.” Which findings are a concern? Select all that apply.
(a) maternal vital signs: T 99.5°F (37.5°C), HR 80, R 24, BP 130/80 mm Hg
(b) blood and mucus on perineal pad
(c) baseline fetal heart rate of 140 bpm with a range between 110 and 160 with contractions
(d) peripad stained with green fluid
(e) client stating, “This baby wants out he keeps kicking me”
Answer:
(c) baseline fetal heart rate of 140 bpm with a range between 110 and 160 with contractions
(d) peripad stained with green fluid
(e) client stating, “This baby wants out he keeps kicking me”
Explanation:
(c), (d), (e) The range of fetal heart rate fluctuating more than 25 beats per minute could indicate fetal distress. The green peripad fluid indicates meconium, which could be associated with fetal distress. Increased fetal activity during labor may also indicate distress. The maternal vital signs noted and a perineal pad with blood and mucus are normal findings.
Question 49.
While the nurse is caring for a multiparous client in active labor at 36 weeks’ gestation, the client tells the nurse, “I think my water just broke.” What should the nurse do first?
(a) Turn the client to the right side.
(b) Assess the color, amount, and odor of the fluid.
(c) Assess the fetal heart rate pattern.
(d) Check the client’s cervical dilation.
Answer:
(c) Assess the fetal heart rate pattern.
Explanation:
After spontaneous rupture of the amniotic fluid, the gushing fluid may carry the umbilical cord out of the birth canal. Sudden deceleration of the fetal heart rate commonly signifies cord com-pression and/or prolapse of the cord, which would require immediate birth. This client is particularly at risk because the fetus is preterm and the fetal head may not be engaged.
Turning the client to the right side is not a priority action. However, changing the client’s position would be appropriate if variable decelerations are present. The nurse should assess the color, amount, and odor of the fluid, but this can be done once the fetal heart rate is assessed and no problems are detected. Cervical dilation should be checked but only after the fetal heart rate pattern is assessed
Question 50.
The nurse has obtained a urine specimen from a multiparous client admitted to the labor unit. The woman asks to go to the bathroom and reports that she feels she has to move her bowels. Which actions would be appropriate? Select all that apply.
(a) assisting her to the bathroom
(b) applying an external fetal monitor to obtain fetal heart rate
(c) assessing her stage of labor
(d) asking if she had back labor pains like this with any of her other birth experiences
(e) allowing her support person to take her to the bathroom to maintain privacy
(f) checking the degree of fetal descent
Answer:
(c) assessing her stage of labor
(f) checking the degree of fetal descent
Explanation:
(c), (e) The pressure from the fetus descending into the birth canal can cause the client to feel she needs to move her bowels and could be near birth. Failure to assess the stage of labor and degree of fetal descent before allowing the client to go to the bathroom may lead to the progression of labor and could result in a birth in the bathroom.
Applying a fetal monitor may reassure the nurse that the fetus is doing well; however, it does not help to determine if the fetus is ready to be born, which is the higher priority in this situation. Regardless of the client’s prior experience with back labor pain, the fetal head moving lower into the birth canal causes pressure in the lower back area similar to the feeling of pressure with a bowel movement.
Question 51.
A multigravid client admitted to the labor area is scheduled for a cesarean birth under spinal anesthesia. Which client statement indicates that teaching about spinal anesthesia has been understood?
(a) “The medication will be administered while I am in the prone position.”
(b) “The anesthetic may cause a severe headache, which is treatable.”
(c) “My blood pressure may increase if I lie down too soon after the injection.”
(d) “I can expect immediate anesthesia that can be reversed very easily.”
Answer:
(b) “The anesthetic may cause a severe headache, which is treatable.”

Explanation:
Spinal anesthesia is used less commonly today because of the preference for epidural block anesthesia. One of the adverse effects of spinal anesthesia is a “spinal headache” caused by leakage of spinal fluid from the needle insertion. This can be treated by applying a cool cloth to the forehead, keeping the client in a flat position, or using a blood patch that can clot and seal off any further leakage of fluid.
Spinal anesthesia is administered with the client in a sitting position or side-lying. Another adverse effect of spinal anesthesia is hypotension caused by vasodilation. General anesthesia provides immediate anesthesia, whereas the full effects of spinal anesthesia may not be felt for 20 to 30 minutes. General anesthesia can be discontinued quickly when the anesthesiologist administers oxygen instead of nitrous oxide. Epidural anesthesia may take 1 to 2 hours to wear off.
Question 52.
The nurse is conducting preoperative teaching for a client with gestational diabetes scheduled for a repeat cesarean. The client tells the nurse that she has been taking ginkgo biloba to help manage her blood sugars. The nurse notifies the health care provider because this herbal supplement puts the client at risk for which complication?
(a) medication interactions
(b) hypertensive crisis
(c) oversedation
(d) prolonged bleeding
Answer:
(d) prolonged bleeding
Explanation:
Gingko biloba is an herbal supplement commonly taken to improve memory or improve glycemic control. It has known antiplatelet effects and can put surgical clients at risk for bleeding. It is not known to cause hypertension or sedation. Gingko’s primary medication interaction relates to its potential to enhance the effects of other anticoagulants and lead to prolonged bleeding.
Question 53.
The health care provider (HCP) determines that the fetus of a multiparous client in active labor is in distress, necessitating a cesarean birth with general anesthesia. Before the cesarean birth, the anesthesiologist prescribes cimetidine 300 mg PO. The nurse explains that the purpose of giving cimetidine is to decrease which factor?
(a) incidence of bronchospasm
(b) oral and respiratory secretions
(c) acid level of the stomach contents
(d) incidence of postoperative gastric ulcer
Answer:
(c) acid level of the stomach contents

Explanation:
Cimetidine is prescribed by some anesthesiologists who will be giving a general anesthetic to reduce the level of acid in the stomach contents, altering the pH to reduce the risk of complications should aspiration of vomitus occur. Aspiration of vomitus is the fifth most common cause of maternal mortality.
Most anesthesiologists insert an endotracheal tube to reduce the incidence of aspiration. Isoproterenol is used to decrease the incidence of bronchospasm. Atropine sulfate is administered to dry oral and nasal secretions. Although cimetidine is useful for gastric ulcer therapy, gastric ulcers are not a common effect associated with operative births.
Question 54.
The nurse is performing a vaginal examination on a client in labor. The nurse finds the fetal presenting part 1 cm above the ischial spines. How should the nurse document the fetal station?
(a) -1 station
(b) +1 station
(c) engaged
(d) floating
Answer:
(a) -1 station
Explanation:
If the presenting part is above the ischial spines 1 cm, the station is -1. If the presenting part is 1 cm below the ischial spines, the station is +1. Engaged and floating are not descriptive of the station.
Question 55.
The nurse is managing a pregnant client’s second stage of labor. The nurse should intervene when observing which action?
(a) closed glottis pushing
(b) open glottis pushing
(c) “rest and descent”
(d) squatting while pushing
Answer:
(a) closed glottis pushing
Explanation:
Closed glottis pushing, or when a woman is told to hold her breath when she pushes typically while the nurse typically counts to 10, creates the Valsalva maneuver and is associated with decreased perfusion. Open glottis pushing, on the other hand, encourages women to listen to their own body cues for when to breathe and when to bear down. “Rest and descent” and squatting have positive influences on the second stage of labor and birth.

Question 56.
A client in the second stage of labor who planned an unmedicated birth is in severe pain because the fetus is in the ROP position. The nurse should place the client in which position for pain relief?
(a) lithotomy
(b) right lateral position
(c) hands and knees
(d) tailor sitting
Answer:
(c) hands and knees
Explanation:
Placing the client in the hands and knees position pulls the fetal head away from the sacral promontory (relieving pain) and facilitates rotation of the fetus to the anterior position. Lithotomy is the position preferred by some health care providers (HCPs) Q for birth but does not facilitate rotation. The right lateral position will perpetuate the ROP position. Tailor sitting facilitates descent in OA positions.
Question 57.
A woman who gave birth to her last infant by caesarean birth is admitted to the hospital at term with contractions every 5 minutes. The health care provider (HCP) intends to have her undergo “a trial labor.” What does the nurse explain to the client that trial of labor means?
(a) Labor will be stimulated with exogenous oxytocin until birth.
(b) The HCP needs more information to determine the presence of true labor.
(c) Labor progress will be evaluated continually to determine appropriate progress for a vaginal birth.
(d) Labor will be arrested with tocolytic agents after a 2-hour period even if no fetal distress is noted.
Answer:
(c) Labor progress will be evaluated continually to determine appropriate progress for a vaginal birth.

Explanation:
Trial labor in this context means that the woman is allowed to go into labor, and her progress is assessed by cervical dilation and effacement as well as fetal descent to determine whether to allow the labor to progress to birth.
If there are indications that labor is not progressing, other means of birth are considered. Labor stimulation is used cautiously and may not be safe. The presence of contractions every 5 minutes indicates true labor. If fetal distress is noted and an emergency cesarean birth cannot be done immediately, tocolytic agents may be considered to stop contractions.
Question 58.
The nurse prepares a client for lumbar epidural anesthesia. Before anesthesia administration, the nurse instructs the client to assume which position.
(a) lithotomy
(b) side-lying
(c) hands and knees
(d) prone
Answer:
(b) side-lying
Explanation:
Lumbar epidural anesthesia is usually administered with the client in a sitting or a left-side-lying position with shoulders parallel and legs slightly flexed. These positions expose the vertebrae to the anesthesiologist. Paracervical and local anesthetics are usually administered with the client in the lithotomy position. The hands and knees and prone positions are not used for anesthesia administration.
Question 59.
A client in labor received an epidural for pain management. Before receiving the epidural, the client’s blood pressure was 124/76 mm Hg. Ten minutes after receiving the epidural, the client’s blood pressure is 98/56 mm Hg, and the mother is vomiting. Before calling the health care provider (HCP), what should the nurse do?
(a) Decrease the IV fluid rate.
(b) Turn the client to her side.
(c) Catheterize the client.
(d) Perform a vaginal examination.
Answer:
(b) Turn the client to her side.

Explanation:
The nurse should turn the client to the side to reduce pressure on the abdominal aorta. The IV fluid rate would be increased, not decreased. There is no information indicating the client has a full bladder or requires a vaginal examination.
Question 60.
A nurse is caring for a woman Gl, PO at 40 weeks’ gestation in active labor. Assessments include cervix 5 cm dilated; 90% effaced; station 0; cephalic presentation; FHR baseline is 135 bpm and decreases to 125 bpm shortly after the onset of five uterine contractions and returns to baseline before the uterine contraction ends.
Based on this assessment, what action should the nurse take first?
(a) Position the client on her left side and administer O2 via face mask.
(b) Document findings on the client’s chart and continue to monitor labor progress.
(c) Perform a vaginal exam to rule out umbilical cord prolapse.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) immediately, and prepare for emergency cesarean birth.
Answer:
(b) Document findings on the client’s chart and continue to monitor labor progress.
Explanation:
The nurse would document these findings as “early” decelerations. Early decelerations are thought to be the result of vagal nerve stimulation caused by compression of the fetal head during labor. They are considered normal physiologic response to labor and do not require any intervention. Early decelerations do not require position change or O2 as they are not a sign of fetal distress. Variable decelerations are thought to be due to umbilical cord compression. Early decelerations are not emergent and do not require immediate reporting to the health care provider (HCP) or preparing for caesarean birth.
Question 61.
The nurse is caring for a full-term, non-medicated, primiparous client who is in the transition stage of labor. The client is writhing in pain and saying, “Help me, help me!” Her last vaginal exam 1 hour ago showed that she was 8 cm dilated, +1 station, and in what appeared to be a comfortable position. What does the nurse anticipate as the highest priority intervention in caring for this client?
(a) Help the client through contractions until a narcotic can be given.
(b) Palpate the bladder to see if it has become distended.
(c) Ask the client for suggestions to make her more comfortable.
(d) Perform a vaginal exam to determine if the client is fully dilated.
Answer:
(d) Perform a vaginal exam to determine if the client is fully dilated.

Explanation:
Transition is the most difficult period of the labor process, and often when clients are tired, pain becomes more intensified. Clients during this stage verbalize anger and are outspoken and difficult to comfort. The most logical next step would be to determine if the client has completed transition and is ready to begin pushing. Performing a vaginal exam would provide this answer.
The use of narcotic medications is discouraged at this stage as they can lead to respiratory depression in the neonate. Palpating the bladder is an important intervention but not the highest priority as it was done less than an hour ago. Since the nurse has correctly com¬pleted the most logical steps, asking for the client’s input would certainly be in order but not the highest priority intervention.
Question 62.
A client at 33 weeks’ gestation is admitted in preterm labor. She is given betamethasone 12 mg IM every 24 hours x 2. What is the expected outcome of this drug therapy?
(a) The contractions will end within 24 hours.
(b) The client will give birth to a neonate without infection.
(c) The client will give birth to a full-term neonate.
(d) The neonate will be born with mature lungs.
Answer:
(d) The neonate will be born with mature lungs.
Explanation:
Betamethasone is a corticosteroid that induces the production of surfactant. The pulmonary maturation that results causes the fetal lungs to mature more rapidly than normal. Because the lungs are mature, the risk of respiratory distress in the neonate is lowered but not eliminated. Betamethasone also decreases the surface tension within the alveoli. Betamethasone has no influence on contractions or carrying the fetus to full term. It also does not prevent infection.
Question 63.
A full-term client is admitted for an induction of labor. The health care provider (HCP) has assigned a Bishop score of 10. Which drug would the nurse anticipate administering to this client?
(a) oxytocin 30 units in 500 mL D5W
(b) prostaglandin gel 0.5 mg
(c) misoprostol 50 meg
(d) dinoprostone 10 mg
Answer:
(a) oxytocin 30 units in 500 mL D5W

Explanation:
A Bishop score evaluates cervical readiness for labor based on five factors: cervical softness, cervical effacement, dilation, fetal position, and station. A Bishop score of 5 or greater in a multipara or a score of 8 or greater in a primipara indicates that a vaginal birth is likely to result from the induction process.
The nurse should expect that labor will be induced using oxytocin because the Bishop score indicates that the client is 60% to 70% effaced, 3 to 4 cm dilated, and in an anterior position. The cervix is soft, and the presenting part is at a -1 to 0 position. Prostaglandin gel, misoprostol, and dinoprostone are all cervical ripening agents, and the doses are accurate; however, cervical ripening has already taken place.
Question 64.
The health care provider (HCP) has performed an amniotomy on a laboring client. Which details must be included in the documentation of this procedure? Select all that apply.
(a) time of rupture
(b) color and clarity of fluid
(c) fetal heart rate (FHR) and pattern before and after the procedure
(d) size of amnio hook used during the procedure
(e) odor and amount of fluid
Answer:
(a) time of rupture
(b) color and clarity of fluid
(c) fetal heart rate (FHR) and pattern before and after the procedure
(e) odor and amount of fluid

Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e) The time of rupture; color, odor, amount, and clarity of amniotic fluid; and FHR and pattern before and after the procedure are all information that must be documented on the client’s record. There is only one size for an amnio hook.
Question 65.
Following an epidural and placement of internal monitors, a client’s labor is augmented with oxytocin. Contractions last> 90 seconds and occur every lVz minutes. The uterine resting tone is > 20 mm Hg with an abnormal fetal heart rate and pattern. Which action should the nurse take first?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Turn off the oxytocin infusion.
(c) Turn the client to her left side.
(d) Increase the maintenance of IV fluids.
Answer:
(b) Turn off the oxytocin infusion.
Explanation:
The client is experiencing uterine hyperstimulation from the oxytocin. The first intervention should be to stop the oxytocin infusion, which may be the cause of the long, frequent contractions, elevated resting tone, and abnormal fetal heart patterns. Only after turning off the oxytocin should the nurse turn the client to her left side to better perfuse the mother and fetus.
Then, she should increase the maintenance IV fluids to allow available oxygen to be carried to the mother and fetus. When all other interventions are initiated, she should notify the HCP.
Question 66.
A nurse notices repetitive late decelerations on the fetal heart monitor. What is the best initial actions by the nurse?
(a) Prepare for birth, reposition the client, and begin pushing.
(b) Perform sterile vaginal exam, increase IV fluids, and apply oxygen.
(c) Notify the provider, explain findings to the client, and begin pushing.
(d) Reposition the client, apply oxygen, and increase IV fluids.
Answer:
(d) Reposition the client, apply oxygen, and increase IV fluids.
Explanation:
Late decelerations on a fetal heart monitor indicate uteroplacental insufficiency. Interventions to improve perfusion include repositioning the client, oxygen, and IV fluids. A sterile vaginal exam is not indicated at this time. Late decelerations are not expected findings and do not indicate an imminent birth.
Question 67.
What actions does the nurse anticipate completing at the end of the second stage of labor before the delivery of the placenta in a spontaneous vaginal birth of a term newborn? Select all that apply.
(a) assigning the Apgar scores
(b) administering oxytocin
(c) assisting with perineal repairs
(d) drying the newborn
(e) initiating skin to skin care
(f) taking newborn vital signs
Answer:
(a) assigning the Apgar scores
(d) drying the newborn
(e) initiating skin to skin care
(f) taking newborn vital signs
Explanation:
(a), (d), (e), (f) The second stage of labor ends with birth. Delivery of the placenta normally happens 5 to 30 minutes after birth. It is the nurse’s responsibility to note the time of birth and complete or assist with the 1- and 5-minute Apgar scores. The infant should be dried immediately after birth to prevent heat loss from evaporation. Ideally, the infant is then placed skin to skin with the mother.
Vital signs on the infant should be taken soon after birth. Oxytocin administration is done to actively manage the fourth stage of labor after the delivery of the placenta. Perineal repairs also happen after the delivery of the placenta.
Question 68.
As a nurse begins the shift on the obstetrical unit, there are several new admissions. The client with which condition would be a candidate for induction?
(a) preeclampsia
(b) active herpes
(c) face presentation
(d) fetus with late decelerations
Answer:
(a) preeclampsia
Explanation:
The client with preeclampsia would be a candidate for the induction process because ending the pregnancy is the only way to cure preeclampsia. A client with active herpes would be a candidate for a cesarean birth to prevent the fetus from contracting the virus while passing through the birth canal. The woman with a face presentation will not be able to give birth vaginally due to the extended position of the neck.
The client whose fetus exhibits late decelerations without oxytocin would be at greater risk for fetal distress with use of this drug. Late decelerations indicate the fetus does not have enough placental reserves to remain oxygenated during the entire contraction. This client may require a cesarean birth.
Question 69.
A nurse and an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are caring for clients in a labor and birth unit. Which task should the nurse assign to the UAP?
(a) Perform a fundal check on a 2-day postpartum client.
(b) Remove a fetal monitor, and assist the client to the bathroom.
(c) Give ibuprofen 800 mg by mouth to a newly postpartum client.
(d) Teach the new mother how to bottle-feed her infant.
Answer:
(b) Remove a fetal monitor, and assist the client to the bathroom.
Explanation:
Removing a fetal monitor from a client and assisting her to the bathroom are within the realm of practice of a UAP. Performing a fundal check is an assessment, which is a responsibility of an RN. A UAP is not permitted to administer medication by any route. Education is also part of the professional nursing role. Although a UAP can assist a mother with bottle-feeding, the formal client education must be completed and validated by the nurse.
Question 70.
A laboring client smiles pleasantly at the nurse when asked simple questions. The client speaks only Mandarin, and the interpreter is busy with an emergency situation. At her last vaginal examination, the client was 5 cm dilated, 100% effaced, and at 0 station. While working with this client, which response indicates that the client may be approaching birth?
(a) The fetal monitor strip shows late decelerations.
(b) The client begins to speak to her family in her native language.
(c) The fetal monitor strip shows early decelerations.
(d) The client’s facial expressions become animated.
Answer:
(c) The fetal monitor strip shows early decelerations.
Explanation:
When the fetal head is compressed, early decelerations are seen as a vagal response, during which the fetal heart rate decelerates and inversely mirrors the contraction. This response commonly occurs when the client is 9 to 10 cm dilated or pushing. If communication cannot be facilitated, early decelerations are one indicator that birth may be approaching.
Late decelerations may occur at this time but indicate uteroplacental insufficiency rather than imminent birth. At any time during the labor process the client may communicate with her family in her native language. The client’s facial expressions may change at any point during labor and can¬not be used as an indicator of imminent birth.
Question 71.
A client is admitted with a suspected abrup- tio placentae. The nurse should assess the client for which signs and symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) bleeding that is concealed or apparent
(b) abdominal rigidity
(c) painful abdomen
(d) painless bleeding
(e) large placenta
(f) bleeding that stops spontaneously
Answer:
(a) bleeding that is concealed or apparent
(b) abdominal rigidity
(c) painful abdomen
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c) With abruptio placentae, bleeding may occur vaginally, may be obstructed by the fetal head, or it may be hidden behind a portion of the placenta. Abdominal rigidity occurs, particularly with a concealed hemorrhage because the girth and fundal height increase. Abdominal pain is one of the classic symptoms of abruption. The pain may be intermittent, as in labor contractions, or continuous. The placenta with abruption is not larger than a normal placenta, and the bleeding does not end spontaneously.
Question 72.
A 39-year-old multigravid client at 39 weeks’ gestation admitted to the hospital in active labor has been diagnosed with class II heart disease. Which measure will the nurse encourage to ensure cardiac emptying and adequate oxygenation during labor?
(a) Breathe slowly after each contraction.
(b) Avoid the use of analgesics for the labor pain.
(c) Remain in a side-lying position with the head elevated.
(d) Request local anesthesia for vaginal birth.
Answer:
(c) Remain in a side-lying position with the head elevated.
Explanation:
The multigravid client with class II heart disease has a slight limitation of physical activity and may become fatigued with ordinary physical activity. A side-lying or semi-Fowler’s position with the head elevated helps to ensure cardiac emptying and adequate oxygenation. In addition, oxygen by mask, analgesics and sedatives, diuretics, prophylactic antibiotics, and digitalis may be warranted.
Although breathing slowly during a contraction may assist with oxygenation, it would have no effect on cardiac emptying. It is essential that the laboring woman with cardiac disease be relieved of discomfort and anxiety. Effective intrapartum pain relief with analgesia and epidural anesthesia may reduce cardiac workload as much as 20%. Local anesthetics are effective only during the second stage of labor.
Question 73.
When developing the plan of care for a multigravid client with class III heart disease, the nurse should expect to assess the client frequently for which problem?
(a) dehydration
(b) nausea and vomiting
(c) iron deficiency anemia
(d) tachycardia
Answer:
(d) tachycardia

Explanation:
Assessing for signs and symptoms associated with cardiac decompensation is the priority. Class III heart disease during pregnancy has a 25% to 50% mortality. These clients are markedly compromised, with marked limitations of physical activity. They frequently experience fatigue, palpitations, dyspnea, or anginal pain. A pulse rate >100 bpm or a respiratory rate >25 breaths/min may indicate cardiac decompensation that could result in cardiac arrest. Additional symptoms include dyspnea, peripheral edema, orthopnea, tachypnea, rales, and hemoptysis.
Question 74.
A primigravid client at 39 weeks’ gestation is admitted to the hospital for induction of labor. The health care provider (HCP) has prescribed prostaglandin E2 gel for the client. Before administering prostaglandin E2 gel to the client, the nurse should perform which action first?
(a) Assess the frequency of uterine contractions.
(b) Place the client in a side-lying position.
(c) Determine whether the membranes have ruptured.
(d) Prepare the client for an amniotomy.
Answer:
(a) Assess the frequency of uterine contractions.
Explanation:
Before administering prostaglandin E2 gel, the nurse would assess the frequency and duration of any uterine contractions first because prostaglandin E2 gel is contraindicated if the client is having contractions. If there are no contractions, the client should be placed in a semi-Fowler’s position to allow for vaginal insertion of the gel.
Although determining whether the client’s membranes have ruptured is part of the assessment of any client in labor, it is not specifically related to the administration of prostaglandin E2 gel. If the membranes remain intact, an amniotomy may be performed once the client begins to dilate and the fetal head is engaged. However, it is not necessary for the nurse to prepare the client for this procedure at this time.
Question 75.
A primigravida near birth is experiencing a prolonged second stage of labor with a fetus suspected of weighing over 4 kg. Which intervention is most important?
(a) preparing for a vacuum-assisted birth
(b) administering an IV fluid bolus
(c) preparing for an emergency cesarean birth
(d) performing the McRoberts maneuver
Answer:
(d) performing the McRoberts maneuver
Explanation:
A prolonged second stage of labor with a large fetus could indicate a shoulder dystocia at birth. Immediate nursing actions for a shoulder dystocia include suprapubic pressure and the McRoberts maneuver. If after interventions for vaginal birth with a shoulder dystocia fail, an emergency cesarean birth may be needed but is not indicated at this time.
A vacuum-assisted birth would be contra indicated due to increased risk of shoulder dystocia with a macrosomic infant. An IV fluid bolus may be indicated for fetal distress, but there is not enough information to establish that they are needed at this time.
Question 76.
A multigravid client is receiving oxytocin augmentation. When the client’s cervix is dilated to 6 cm, her membranes rupture spontaneously with meconium-stained amniotic fluid. Which action should the nurse perform first?
(a) Increase the rate of the oxytocin infusion.
(b) Turn the client to a knee-to-chest position.
(c) Assess cervical dilation and effacement.
(d) Assess the fetal heart rate.
Answer:
(d) Assess the fetal heart rate.
Explanation:
Assessing the fetal heart rate is always a priority after spontaneous rupture of membranes has occurred. Meconium-stained fluid is also a common sign of fetal distress related to an inadequate transfer of oxygen to the fetus. Because the fetus has suffered hypoxia, close fetal heart rate monitoring is necessary. In addition, all clients are monitored continuously after rupture of membranes for fetal distress caused by cord prolapse.
If there are increasing signs of fetal distress (e.g., late decelerations), the health care provider (HCP) Q should be notified immediately. A cesarean birth may be performed for fetal distress. Increasing the rate of the oxytocin infusion could lead to further fetal distress. Turning the client to the left side, rather than a knee-chest position, improves placental perfusion. The HCP may wish to determine the extent of cervical dilation to make a decision about whether a cesarean birth is warranted, but continuous fetal heart rate monitoring is essential to determine fetal status.
Question 77.
A primigravid client who has had a prolonged labor but now is completely dilated has received epidural anesthesia. Which statement should the nurse include in the teaching plan about pushing?
(a) The client needs to push for at least 1 to 3 minutes.
(b) Pushing is most effective when the client holds her breath.
(c) The client should be urged to push with an open glottis.
(d) Pushing is limited to times when she feels the urge.
Answer:
(c) The client should be urged to push with an open glottis.
Explanation:
The client should be urged to push with an open glottis to prevent the Valsalva maneuver. Pushing with a closed glottis increases intrathoracic pressure, preventing venous return. Blood pressure also falls, and cardiac output decreases. Pushing for at least 1 to 3 minutes is too long; prolonged pushing can lead to reduced blood flow and fatigue.
Pushing for the duration of the contraction is sufficient. Pushing while holding the breath results in the Valsalva maneuver. Because the client has had an epidural anesthetic, she may not feel the urge to push and may need coaching during the pushing phase.
Question 78.
The health care provider (HCP) determines that outlet forceps are needed to assist in the birth of a primigravid client in active labor with a large-for- gestational-size fetus. The nurse understands that the fetus’s skull must be at what point before this procedure can take place?
(a) It is engaged past the inlet.
(b) It is at +1 station.
(c) It is visible at the perineal floor.
(d) It has reached the level of the ischial spines.
Answer:
(c) It is visible at the perineal floor.
Explanation:
When the fetal skull is on the perineum with the scalp visible at the perineal floor or vaginal opening, this is considered outlet forceps application. When the head is higher in the pelvis but engaged and its greatest diameter has passed the inlet, the operation is termed midforceps. Midforceps births are not recommended because they are extremely dangerous for the mother and fetus because of the possibility of uterine rupture.
If the head is not engaged, at -1 station, this is termed high forceps. High-forceps births also are exceedingly dangerous for both the mother and fetus because of the possibility of uterine rupture and are not recommended. Cesarean birth is preferred in these situations. The fetal head at station +2 or lower is termed low forceps.
Question 79.
The health care provider (HCP) prescribes an amnioinfusion for a primigravid client at term who is diagnosed with oligohydramnios. What does the nurse explain is the primary purpose of the procedure to the client?
(a) decreases the frequency and severity of variable decelerations
(b) minimizes the possibility of fetal metabolic alkalosis
(c) increases the fetal heart rate accelerations during a contraction
(d) raises the amniotic fluid index to more than 15 cm
Answer:
(a) decreases the frequency and severity of variable decelerations
Explanation:
Oligohydramnios, or a decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid, is associated with variable fetal heart rate decelerations due to cord compression. Maintenance of an adequate amniotic fluid volume during labor provides protective cushioning of the umbilical cord and minimizes cord compression.
Cord compression can result in fetal metabolic acidosis, not alkalosis. Amnioinfusion is used to minimize cord compression, not to increase the fetal heart rate accelerations during a contraction. The goal is to maintain the amniotic fluid index at 8 cm. This can be determined by ultrasound.
Question 80.
The nurse is admitting a primigravid client at 37 weeks’ gestation who has been diagnosed with preeclampsia to the labor and birth area. Which client care room is most appropriate for this client?
(a) a brightly lit private room at the end of the hall from the nurses’ station
(b) a semiprivate room midway down the hall from the nurses’ station
(c) a private room with many windows that is near the operating room
(d) a darkened private room as close to the nurses’ station as possible
Answer:
(d) a darkened private room as close to the nurses’ station as possible
Explanation:
A primigravid client diagnosed with preeclampsia has the potential to develop seizures (eclampsia). This client should be in a room with the least amount of stimulation possible to reduce the risk of seizures and as close to the nurses’ station as possible in case the client requires immediate assistance. Bright lighting and sunshine can be a stimulant, possibly increasing the risk of seizures, as can being in a semi-private room with roommates, visitors, conversation, and noise.
Question 81.
A multigravid client is admitted to the labor area from the emergency department. At the time of admission, the fetal head is crowning, and the client yells, “The baby is coming” To help the client remain calm and cooperative during the imminent birth, which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “You’re right; the baby is coming, so just relax.”
(b) “Please do not push because you will tear your cervix. ”
(c) “Your health care provider will be here as soon as possible.”
(d) “I’ll explain what is happening to guide you as we go along.”
Answer:
(d) “I’ll explain what is happening to guide you as we go along.”

Explanation:
The client is experiencing a precipitous birth. The nurse should remain calm during a precipitous birth. Explaining to the client what is happening as the birth progresses and how she can assist is likely to help her remain calm and cooperative. Maintaining eye contact is also beneficial. Telling the client that she is right and to just relax is inappropriate because the client may not be able to relax because of the strong urge to push the fetus out of the birth canal.
Telling the client not to push because she may tear the cervix can instill fear, not cooperation. Saying that the health care provider (HCP) will be there soon may not be an accurate statement and is not reassuring if the client is concerned about the birth.
Question 82.
The nurse is caring for a multigravid client and observes the woman squatting on the bed and the fetal head crowning. After calling for assistance and helping the client lie down, the nurse should perform which action next?
(a) Tell the client to push between contractions.
(b) Provide gentle support to the fetal head.
(c) Apply gentle upward traction on the neonate’s anterior shoulder.
(d) Massage the perineum to stretch the perineal tissues.
Answer:
(b) Provide gentle support to the fetal head.

Explanation:
During a precipitous birth, after calling for assistance and helping the client lie down, the nurse should provide support to the fetal head to prevent too rapid of emergence leading to injury. It is not appropriate to tell the client to push between contractions because this may lead to lacerations.
The shoulder should be delivered by applying downward traction until the anterior shoulder appears fully at the introitus, then upward pressure to lift out the other shoulder. Priority should be given to the safe birth of the infant over protecting the perineum by massage.
Question 83.
During the first hour after a precipitous birth, the nurse should monitor a multiparous client for signs and symptoms of which complication?
(a) postpartum “blues”
(b) uterine atony
(c) intrauterine infection
(d) urinary tract infection
Answer:
(b) uterine atony
Explanation:
Because birth occurs so rapidly and the fetus is propelled quickly through the birth canal, the major complication of a precipitous birth is a boggy fundus, or uterine atony. The neonate should be put to the breast, if the mother permits, to allow for the release of natural oxytocin. In a hospital setting, the health care provider (HCP) will probably prescribe administration of oxytocin. The nurse should gently massage the fundus to ensure that it is firm.
There is no relationship between a precipitous birth and postpartum “blues” or intrauterine infection. Postpartum "blues” usually do not occur until about 3 days postpartum, and symptoms of postpartum infection usually occur after the first 24 hours. There is no relationship between a precipitous birth and urinary tract infection even though the birth has been accomplished under clean rather than sterile technique. Symptoms of urinary tract infection typically begin on the first or second postpartum day.
Question 84.
A multigravid client in labor at 38 weeks’ gestation has been diagnosed with Rh sensitization and probable fetal hydrops and anemia. Which fetal heart rate pattern would the nurse find is most concerning?
(a) early deceleration pattern
(b) sinusoidal pattern
(c) variable deceleration pattern
(d) late deceleration pattern
Answer:
(b) sinusoidal pattern
Explanation:
A sinusoidal pattern is an ominous sign that reflects an absence of autonomic nervous control over the fetal heart rate resulting from severe hypoxia. Sinusoidal patterns, while rare, are associated with Rh sensitization, fetal hydrops, and anemia. This client will most likely require a cesarean birth to improve the fetal outcome.
Variable decelerations, associated with cord compression, and late decelerations, associated with poor placental perfusion, are concerning but may correct with appropriate interventions. Early decelerations are associated with head compression and are considered a normal variation.
Question 85.
The nurse in the labor and birth area receives a telephone call from the emergency department announcing that a multigravid client in active labor is being transferred to the labor area. The client has had no prenatal care. When the client arrives by stretcher, she says, “I think the baby is coming Help!” The fetal skull is crowning. The nurse should obtain which information first?
(a) estimated date of birth
(b) amniotic fluid status
(c) gravida and parity
(d) prenatal history
Answer:
(a) estimated date of birth
Explanation:
A priority assessment for the nurse to make is to determine the estimated date of birth or probable gestational age of the fetus. If the gestation is < 37 weeks, the neonatal team should be called to begin resuscitative efforts if needed. Amniotic fluid status is not important at this point because if the fetal skull is crowning, birth is imminent.
Determination of gravida and parity is part of the normal nursing history, but the priority is the status of the fetus and safe birth. Prenatal history is part of the nursing assessment, but this information is not especially relevant until the fetus is safely born and has been given immediate care.
Question 86.
A primigravid client at 41 weeks’ gestation is admitted to the hospital’s labor and birth unit in active labor. After 25 hours of labor with membranes ruptured for 24 hours, the client gives birth to a healthy neonate vaginally with a midline episiotomy. Which problem should the nurse identify as the priority for the client?
(a) activity intolerance
(b) sleep deprivation
(c) situational low self-esteem
(d) risk for infection
Answer:
(d) risk for infection

Explanation:
Birth trauma and prolonged ruptured membranes make risk for infection the priority problem for this client. Infection can be a serious postpartum complication. Although the client may be fatigued, she should not be experiencing activity intolerance. Clients with heart disease may experience activity intolerance due to excessive cardiac workload.
Although the client may be experiencing sleep deprivation, most clients are alert and awake after birth of a neonate. Situational low self-esteem is not a priority. Clients who undergo a cesarean birth commonly feel a sense of failure because of not having a vaginal birth experience, but this is not the case for this client.
Question 87.
The nurse is caring for a primiparous client and her neonate immediately after birth. The neonate was born at 41 weeks’ gestation and weighs 9 lb (4,082 g). Assessing for signs and symptoms of which condition should be a priority in this neonate?
(a) anemia
(b) hypoglycemia
(c) delayed meconium
(d) elevated bilirubin
Answer:
(b) hypoglycemia
Explanation:
Postmature neonates commonly have difficulty maintaining adequate glucose reserves and usually develop hypoglycemia soon after birth. Other common problems include meconium aspiration syndrome, polycythemia, congenital anomalies, seizure activity, and cold stress. These complications result primarily from a combination of advanced gestational age, placental insufficiency, and continued exposure to amniotic fluid.
Delayed meconium is not associated with postterm gestation. Hyperbilirubinemia occurs in term neonates as well as postterm neonates, but unless there is an Rh incompatibility, it does not develop until after the first 24 hours of life.
Question 88.
A multigravid client in active labor at term is diagnosed with polyhydramnios. The health care provider (HCP) has instructed the client about possible neonatal complications related to the polyhydramnios. The nurse determines that the client has understood the instructions when the client states that polyhydramnios is associated with which problem in the fetus or neonate?
(a) renal dysfunction
(b) intrauterine growth restriction
(c) pulmonary hypoplasia
(d) gastrointestinal disorders
Answer:
(d) gastrointestinal disorders
Explanation:
Polyhydramnios is an abnormally large amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus. The client has understood the instructions when the client states that polyhydramnios is associated with gastro-intestinal disorders (e.g., tracheoesophageal fistula). Polyhydramnios is also associated with maternal illnesses such as diabetes and anemia. Other fetal/ neonatal disorders associated with this condition include congenital anomalies of the central nervous system (e.g., anencephaly), upper gastrointestinal obstruction, and macrosomia.
Polyhydramnios can lead to preterm labor, premature rupture of the membranes, and cord prolapse. Renal dysfunction and intrauterine growth restriction are associated with oligohydramnios, not polyhydramnios. Pulmonary hypoplasia (poorly developed lungs) is associated with prolonged oligohydramnios.
Question 89.
A primigravid client at 39 weeks’ gestation is admitted to the hospital in active labor. On admission, the client’s cervix is 6 cm dilated. After 2 hours of active labor, the client’s cervix is still dilated at 6 cm with 100% effacement at +1 station. Contractions are 3 to 5 minutes apart, lasting 45 seconds, and of moderate intensity. The nurse determines that the client is most likely experiencing which problem?
(a) cephalopelvic disproportion
(b) prolonged latent phase
(c) prolonged transitional phase
(d) hypotonic contraction pattern
Answer:
(a) cephalopelvic disproportion
Explanation:
If a client has been in active labor and there is no change in cervical dilation after 2 hours, the nurse should suspect cephalopelvic disproportion. This may be caused by an inadequate pelvis size of the mother or by a large-for-gestational-age fetus. The health care provider (HCP) should be notified about the client’s lack of progress. If the fetus cannot descend, a cesarean birth is warranted.
The client is not experiencing a prolonged latent phase (0- to 3-cm dilation) because her cervix is dilated to 6 cm. She has not reached the transitional phase, characterized by a cervical dilation of 8 to 10 cm. With a hypotonic labor pattern, contractions are painful but far apart and not very intense. This client’s contractions are of moderate intensity.
Question 90.
The health care provider (HCP) who elects to perform a cesarean birth on a primigravid client for fetal distress has informed the client of possible risks during the procedure. When the nurse asks the client to sign the consent form, the client’s husband says, “I will sign it for her. She is too upset by what is happening to make this decision.” What should the nurse do?
(a) Ask the client if this is acceptable to her.
(b) Have the client and her husband both sign the consent form.
(c) Ask the client to sign the consent form.
(d) Ask the HCP to witness the consent form.
Answer:
(c) Ask the client to sign the consent form.

Explanation:
Preparation for cesarean birth is similar to preparation for any abdominal surgery. The client must give informed consent to UJ. Another person may not sign for the client unless the client is unable to sign the form. If this is the case, only certain designated people can do so legally. The husband does not need to sign the form unless his wife is unable to do so. In a life-threatening emergency, surgery may be performed without written consent. The HCP does not need to witness the consent.
Question 91.
A multigravid client at term is admitted to the hospital for trial labor and possible vaginal birth. She has a history of previous cesarean birth because of fetal distress. When the client is 4 cm dilated, she receives nalbuphine intravenously. While monitoring the fetal heart rate, the nurse observes minimal variability and a rate of 120 bpm. The nurse should explain to the client that the decreased variability is most likely caused by which factor?
(a) maternal fatigue
(b) fetal malposition
(c) small-for-gestational-age fetus
(d) effects of analgesic medication
Answer:
(d) effects of analgesic medication

Explanation:
Decreased variability may be seen in various conditions. However, it is most commonly caused by analgesic administration. Other factors that can cause decreased variability include anesthesia, deep fetal sleep, anencephaly, prematurity, hypoxia, tachycardia, brain damage, and arrhythmias. Maternal fatigue, fetal malposition, and small-for-gestational-age fetuses are not commonly associated with decreased variability.
Question 92.
During a scheduled cesarean birth of a primigravid client with a fetus at 39 weeks’ gestation in a breech presentation, a neonatologist is present in the operating room. The nurse explains to the client that the neonatologist is present because neonates born by cesarean birth tend to have an increased incidence of which problem?
(a) congenital anomalies
(b) pulmonary hypertension
(c) meconium aspiration syndrome
(d) respiratory distress syndrome
Answer:
(d) respiratory distress syndrome

Explanation:
Respiratory distress syndrome is more common in neonates born by cesarean section than in those born vaginally. During a vaginal birth, pressure is exerted on the fetal chest, which aids in the fetal inhalation and exhalation of air and lung expansion. This pressure is not exerted on the fetus with a cesarean birth. Congenital anomalies are not more common with cesarean birth.
Pulmonary hypertension occurs more commonly in infants with meconium aspiration syndrome, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, respiratory distress syndrome, or neonatal sepsis, not with a cesarean birth. Meconium aspiration syndrome occurs more commonly with vaginal birth, post-term neonate, and prolonged labor, not with a cesarean birth.
Question 93.
A 28-year-old multigravid client at 28 weeks’ gestation diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis is receiving intravenous fluids and antibiotics. After teaching the client about the rationale for the aggressive therapy, the nurse determines that the client needs further instruction when she says that acute pyelonephritis can lead to which complication?
(a) preterm labor
(b) maternal sepsis
(c) intrauterine growth restriction
(d) congenital fetal anomalies
Answer:
(a) preterm labor
Explanation:
Congenital anomalies are not related to maternal urinary tract infections. A multigravid client with acute pyelonephritis is susceptible to preterm labor, premature rupture of the membranes, maternal sepsis, intrauterine growth restriction, and fetal loss. The most common organism responsible for the urinary tract infection is Escherichia coli.
Question 94.
A primigravid client at 38 weeks’ gestation is admitted to the labor suite in active labor. The client’s physical assessment reveals a chlamydial infection. The nurse explains that if the infection is left untreated, the neonate may develop which problem?
(a) conjunctivitis
(b) heart disease
(c) harlequin sign
(d) brain damage
Answer:
(a) conjunctivitis

Explanation:
Conjunctivitis is a common complication of neonates who are born to mothers with untreated chlamydial infection. Neonatal pneumonia is another condition associated with chlamydial infection of the mother. Untreated chlamydial infection is not associated with heart disease or brain damage. Exposure to rubella may lead to neonatal heart defects, and brain damage may occur as a result of prolonged shoulder dystocia or difficulty delivering the fetal head during a vaginal breech birth.
Occasionally, because of immature circulation, a neonate who has been lying on his or her side appears red on one side of the body. This “harlequin sign” is transient and is of no clinical significance. Presence of a harlequin sign is unrelated to untreated chlamydial infection.
Question 95.
A 34-year-old primigravid client at 39 weeks’ gestation admitted to the hospital in active labor has type B Rh-negative blood. The nurse should instruct the client that if the neonate is Rh positive, the client will receive an Rh immune globulin injection for which reason?
(a) to prevent Rh-positive sensitization with the next pregnancy
(b) to provide active antibody protection for this pregnancy
(c) to decrease the amount of Rh-negative sensitisation for the next pregnancy
(d) to destroy fetal Rh-positive cells during the next pregnancy
Answer:
(a) to prevent Rh-positive sensitization with the next pregnancy
Explanation:
The purpose of Rh immune globulin is to provide passive antibody immunity and prevent Rh-positive sensitization with the next pregnancy. It should be given within 72 hours after birth of an Rh-positive neonate. Clients who are Rh negative and conceive an Rh-negative fetus do not need antibody protection. Rh-positive cells contribute to sensitization, not Rh-negative cells. Rh immune globulin does not cross the placenta and destroy fetal Rh-positive cells.
Question 96.
A 16-year-old primigravid client admitted at 38 weeks’ gestation with severe preeclampsia is given intravenous magnesium sulfate and lactated Ringer’s solution. The nurse should obtain which information?
(a) urinary output every 8 hours
(b) deep tendon reflexes every 4 hours
(c) respiratory rate every hour
(d) blood pressure every 6 hours
Answer:
(c) respiratory rate every hour
Explanation:
Because magnesium sulfate is a central nervous system depressant, the nurse should plan to assess the client’s respiratory rate every hour. If the respiratory rate is < 12 breaths/min, the client may be experiencing magnesium sulfate overdose. Urinary output via an indwelling catheter should be assessed hourly and should be at least 30 mL/h. Deep tendon reflexes and blood pressure should also be assessed every hour. At some institutions, continuous electronic blood pressure monitoring will be performed.

Question 97.
The nurse has received a telephone call from the emergency department indicating that a multigravid client in early labor and diagnosed with probable placenta previa will be arriving soon. What is the priority invention when the client arrives at the unit?
(a) whole blood replacement
(b) continuous blood pressure monitoring
(c) internal fetal heart rate monitoring
(d) an immediate cesarean birth
Answer:
(b) continuous blood pressure monitoring
Explanation:
For a client diagnosed with probable placenta previa, hypovolemic shock is a complication. Continuous blood pressure monitoring with an electronic cuff is the priority assessment after the client’s admission. Once the client is admitted, an ultrasound examination will be performed to determine the placement of the placenta. Whole blood replacement is not warranted at this time.
However, it may be necessary if the client demonstrates signs and symptoms of hemorrhage or shock. Internal fetal heart rate monitoring is contraindicated because the monitoring device may puncture the placenta and place both the mother and fetus in jeopardy. An immediate cesarean birth is not necessary until there has been an assessment of the amount of bleeding and the location of the placenta previa.
Question 98.
During admission, a multigravida in early active labor acts somewhat euphoric and tells the nurse that she smoked some crack cocaine before coming to the hospital. In addition to fetal heart rate assessment, the nurse should monitor the client for symptoms of which complication?
(a) placenta previa
(b) ruptured uterus
(c) maternal hypotension
(d) abruptio placentae
Answer:
(d) abruptio placentae

Explanation:
Dramatic vasoconstriction occurs as a result of smoking crack cocaine. This can lead to increased respiratory and cardiac rates and hypertension. It can severely compromise placental circulation, resulting in abruptio placentae and preterm labor and birth. Infants of these women can experience intracranial hemorrhage and withdrawal symptoms of tremulousness, irritability, and rigidity. Placenta previa, ruptured uterus, and maternal hypotension are not associated with cocaine use. Placenta previa may be associated with grand multiparity. A ruptured uterus may be associated with a large-for-gestational-age fetus.
Question 99.
A primigravid client in early labor with abruptio placentae develops disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Which agent should the nurse expect the health care provider (HCP) to prescribe?
(a) magnesium sulfate
(b) warfarin sodium
(c) fresh frozen platelets
(d) meperidine hydrochloride
Answer:
(c) fresh frozen platelets
Explanation:
To stop the process of DIC, the underlying insult that began the phenomenon must be halted. Treatment includes fresh frozen platelets or blood administration. The HCP ICQ also may prescribe heparin before the administration of blood products to restore the normal clotting mechanism. Immediate birth of the fetus is essential. Magnesium sulfate is given for pregnancy-induced hypertension or preterm labor. Heparin, not warfarin sodium, is used to treat DIC. Meperidine hydrochloride is used for pain relief.
Question 100.
A multigravid client diagnosed with chronic hypertension is now in preterm labor at 32 weeks’ gestation. The health care provider (HCP) has prescribed magnesium sulfate at 3 g/h. Which assessment finding indicates that the intended therapeutic effect has occurred?
(a) decrease in fetal heart rate accelerations
(b) decrease in the frequency and number of contractions
(c) decrease in maternal blood pressure rate
(d) decrease in maternal respiratory rate
Answer:
(b) decrease in the frequency and number of contractions

Explanation:
Magnesium sulfate may be used as an anticonvulsive or a tocolytic agent. The intended effect for this client is to decrease the number and frequency of contractions. Even though this client has chronic hypertension, the first goal is to prevent birth in a 34 weeks’ gestation client. If the blood pressure moves into the therapeutic range, that is a benefit for the client, but it is not the major goal.
Magnesium sulfate may decrease the accelerations found in this fetus as it decreases the ability of the infant to respond, acting on the infant in the same way it does on the mother. Maternal respiratory rate may also decrease, and a lower respiratory rate to 12 respirations/min indicates that this level of magnesium sulfate is becoming toxic to this client.
Question 101.
A primigravid client at 37 weeks’ gestation has been hospitalized for several days with severe preeclampsia. While caring for the client, the nurse observes that the client is beginning to have a seizure. Which action should the nurse do first?
(a) Pad the side rails of the client’s bed.
(b) Turn the client to the right side.
(c) Insert a padded tongue blade into the client’s mouth.
(d) Call for immediate assistance in the client’s room.
Answer:
(d) Call for immediate assistance in the client’s room.
Explanation:
The nurse should respond using emergency response principles. The first action by the nurse should be to call for immediate assistance in the client’s room. Throughout the seizure, the nurse should note the time and length of the seizure and continue to monitor the status of both client and fetus.
The side rails should have been padded at the time of the client’s admission to the hospital as part of seizure precautions. The client should be turned to her left side to improve placental perfu-sion. Inserting a tongue blade is not recommended because it can further obstruct the airway or cause injury to the client’s teeth.
Question 102.
While assessing a primigravid client admitted at 36 weeks’ gestation, the nurse observes multiple bruises on the client’s face, neck, and abdomen. When asked about the bruises, the client admits that her boyfriend beats her now and then and says, “I want to leave him because I am afraid he will hurt the baby.” Which action is the nurse’s most appropriate response?
(a) Tell the client to leave the boyfriend immediately.
(b) Ask the client when she last felt the baby move.
(c) Refer the client to a social worker for possible options.
(d) Report the incident to the unit nursing supervisor.
Answer:
(c) Refer the client to a social worker for possible options.
Explanation:
In an abusive situation, the client’s safety is the priority. The nurse should refer the client to a social worker who can provide the client with options such as a safe shelter. Commonly clients who are battered feel powerless and fear that the batterer will kill them. As a result, they remain in the abusive situation. Telling the client to leave the boyfriend immediately is not helpful and reflects the values of the nurse.
Although asking about fetal movement is important and is part of a routine assessment, a sonogram can be performed to confirm fetal well-being. The referral is more important at this time. Although it may be part of the unit’s policies and procedures to report any incidents such as this one to the unit supervisor, the client’s immediate need for safety must be addressed first.
Question 103.
A multigravid client in active labor at term suddenly sits up and says, “I can’t breathe! My chest hurts really bad!” The client’s skin begins to turn a dusky gray color. After calling for assistance, which action should the nurse take next?
(a) Administer oxygen by face mask.
(b) Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
(c) Administer intravenous oxytocin.
(d) Obtain a prescription for intravenous fibrinogen.
Answer:
(a) Administer oxygen by face mask.
Explanation:
The client’s symptoms are indicative of amniotic fluid embolism, which is a medical emergency. After calling for assistance, the first action should be to administer oxygen by face mask or cannula to ensure adequate oxygenation of mother and fetus. If the client needs cardiopulmonary resus-citation, this can be started once oxygen has been administered. If the client survives, disseminated intravascular coagulation will probably develop, and the client will need intravenous fibrinogen and heparin. Oxytocin, a vasoconstrictor, is not warranted for amniotic fluid embolism.
Question 104.
A newly postpartum client is asking to go to the bathroom 45 minutes after birth. She had an epidural for labor and birth and has an IV infusing, and every 15 minutes assessments are in progress. What should the nurse do to provide the safest care for this client?
(a) Ask her to remain in bed until the 15-minute assessments are complete.
(b) Assess client’s ability to stand and bear weight before going to the bathroom.
(c) Encourage the client to sit at the side of the bed before ambulating to the bathroom.
(d) Ask the client to ambulate the first time with a staff member at her side.
Answer:
(b) Assess client’s ability to stand and bear weight before going to the bathroom.
Explanation:
The nurse will need to assess the client’s ability to bear weight before taking her to the bathroom. If she cannot bear weight, she will be unable to ambulate. Asking the client to remain in bed until the assessments are complete sets the client up for increased postpartum bleeding because the bladder will displace the uterus.
Encouraging the client to sit at the bedside is an excellent strategy to prevent orthostatic hypotension, but it will not give the nurse an idea if the client can ambulate. Having a staff member with the client is also correct for the first ambulation of this client, but the ability to bear weight and walk will need to be assessed first.
Question 105.
The charge nurse is preparing for the day shift on the labor and birth unit. Which would be included in the responsibilities for this position? Select all that apply.
(a) Review the current status of each labor client with the primary nurse.
(b) Admit the new labor client sent from the triage area.
(c) Complete the work of the nurse who had to leave 30 minutes early.
(d) Follow up with the primary nurse after a birth.
(e) Complete report of unit with the oncoming charge nurse.
Answer:
(a) Review the current status of each labor client with the primary nurse.
(d) Follow up with the primary nurse after a birth.
(e) Complete report of unit with the oncoming charge nurse.
Explanation:
(a), (d), (e) In most settings, the charge nurse coordinates and directs the activities of the unit. Prior to the change of shift, the nurse will review and update the status of each of the laboring clients on the unit to include any difficulties or unusual situations that may be occurring with each of them, including following up with a primary nurse after a birth.
A change-of-shift report with the oncoming charge nurse is among the last activities completed before ending the shift. Activities such as admitting a client in labor and completing the nursing responsibilities of the nurse who had to leave 30 minutes early can be delegated to staff members. In an emergency, the charge nurse could assume responsibility for client care.
Question 106.
The labor and birth nurse is assigned to triage for the day. There are four clients already in rooms, and reports have been received about each of these clients. To provide the safest care and best manage time, the nurse should plan to see which client first?
(a) a primipara in active labor at 5 cm asking to be admitted and wanting an epidural
(b) a primipara who is 100% effaced, 8 cm dilated, +2 station with nausea
(c) a client with no prenatal care, occasional contractions, BP 148/90 mm Hg, and swollen feet
(d) a client who is at 42 weeks’ gestation with bloody show, no contractions, rupture of membranes 1 hour ago leaking green fluid
Answer:
(d) a client who is at 42 weeks’ gestation with bloody show, no contractions, rupture of membranes 1 hour ago leaking green fluid
Explanation:
The client at 42 weeks’ gestation is the greatest concern, and the nurse should make rounds on this client first based on the length of the pregnancy and the green color of the amniotic fluid. Bloody show is a normal sign of impending labor as the cervix may be beginning to dilate. Not having contractions after rupture of membranes is not unusual within a 1-hour time frame. The green amniotic fluid indicates that fetal distress has recently occurred to the point that the fetus had a bowel movement in utero.
This occurrence, along with the 42-week gestation, places this fetus at greatest risk. The nurse can see the primipara in active labor at 5-cm dilation last; this client is in pain, but nothing about her situation indicates anything but a normal labor process, and as a primipara, her labor process will be slow. The client who is completely effaced, 8 cm dilated, and at +2 station is also a primipara and thus will move through labor at a slower pace than a multiparous client.
She is experiencing nausea which is an expected situation as a laboring client enters transition. The client with no prenatal care is a cause for concern because the nurse knows nothing about her background. Her blood pressure is elevated, an indicator of mild preeclampsia, but there are no other indications of worsening preeclampsia, such as headache, visual disturbances, or epigastric pain.
Question 107.
The triage nurse is giving a telephone report to the receiving nurse in the labor and birth unit. The multigravida client is 8 cm dilated and is being transferred to the labor and birth unit. How should the labor and birth nurse manage the next 10 minutes with the client? Select all that apply.
(a) Begin fetal monitoring.
(b) Call other staff to set up the birthing table.
(c) Assess comfort needs of the client.
(d) Determine support systems for the client.
Answer:
(a) Begin fetal monitoring.
(b) Call other staff to set up the birthing table.
(c) Assess comfort needs of the client.
(d) Determine support systems for the client.

Explanation:
Assuring the safety of this client is the top priority. The nurse should begin either intermittent or continuous fetal and contraction monitor depending on the client’s risk status. Since the client is 8 cm dilated and a multigravid client, asking other staff members to set up the birthing table would be in order. This client is not a candidate for medication as this may have an influence on the baby.
This client is past the point of offering an epidural as she may have given birth by the time the medication is in effect, but comfort measures such as warm or cool clothes, back rubs, etc., may be helpful. The support system is an important aspect of the birthing process and is an easily settled situation. Preparing to give an early report to the oncoming nurse does not apply in this situation.
Question 108.
The health care provider (HCP) verbally prescribed carboprost tromethamine 0.25 mg IM stat for a client experiencing a postpartum hemorrhage. The nurse administers the medication but later finds that the HCP has written a prescription for 0.25 mg carboprost tromethamine IV stat. How should the nurse respond?
(a) Ask the charge nurse to have a discussion with the HCP about the prescription.
(b) Initiate an incident report.
(c) Call the HCP, discuss the prescription, and request revision if heard correctly.
(d) Wait until the HCP returns to the unit, and discuss the situation in person.
Answer:
(c) Call the HCP, discuss the prescription, and request revision if heard correctly.

Explanation:
In emergency situations, verbal prescriptions should be entered into the medical record y or chart and signed immediately after the emergency. The nurse taking this prescription and giving the medication needs to call the HCP D3, explain the prescription and that the medication was administered per the verbal prescription, and request that the HCP write the correct prescription.
If the nurse misunderstood the prescription and gave the medication by the wrong route, an incident report will need to be initiated. The charge nurse would become involved if an error has occurred, an incident report is needed, or there is difficulty between the nurse and HCP that cannot be remediated. Rectifying this prescription is the responsibility of the implementing nurse. Waiting until the HCP comes back to the hospital unit may not occur quickly enough to safely care for the client.
Question 109.
The nurse is asked to develop an in-service to explain documents guiding professional nursing practice on the obstetrical unit. One of the documents included is the Code of Ethics. The nurse correctly explains that the Code of Ethics asks nurses to demonstrate which behaviors? Select all that apply.
(a) Maintain the integrity of practice and shape social policy.
(b) Develop, maintain, and improve health care environments.
(c) Ask the hospital systems for fair compensation for work.
(d) Be responsible and accountable for individual practice.
(e) Increase professional competence and personal growth.
Answer:
(a) Maintain the integrity of practice and shape social policy.
(b) Develop, maintain, and improve health care environments.
(d) Be responsible and accountable for individual practice.
(e) Increase professional competence and personal growth.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) The Code of Ethics describes those actions by the nurse that guide their practice. It is the responsibility of each nurse to be active in determining policy for health care for all citizens and assuring that the way nursing is practiced is of the highest caliber. Nursing needs to participate in the development of health care of the future while caring for all members of society. In order to be productive in shaping policy, nurses need to be politically astute while growing personally and professionally to meet the needs of clients. The Code of Ethics does not address compensation for work.
Question 110.
The nurse is preparing to assist the health care provider (HCP) with a cervical check for a client whose membranes have ruptured. What equipment should the nurse have ready for the HCP? Select all that apply.
(a) sterile speculum
(b) sterile gloves
(c) sterile lubricant
(d) amnio hook
(e) cervical dilators
Answer:
(b) sterile gloves
(c) sterile lubricant

Explanation:
(b), (c) Intact membranes act as a barrier to prevent infections. Once a client’s membranes have ruptured, it is important to take precautions to limit the introduction of bacteria into the genital tract. Using sterile gloves and sterile lubricant for cervical checks helps reduce the risk of infection. A sterile speculum is only needed to diagnose if the membranes have ruptured. An amnio hook would only be indicated if the plan was to artificially rupture the membranes. Cervical dilators are not used for cervical checks in labor.
Question 111.
Which client is the best candidate for a vaginal birth after a cesarean (VBAC)?
(a) client who had an emergency cesarean birth because of fetal distress during her last birth and has a classic incision
(b) client who had a breech presentation in her last pregnancy, and this pregnancy is a vertex pregnancy
(c) client who dilated 6 cm in her last birth and failed to progress beyond this point despite 5 more hours of labor
(d) diabetic client whose last infant was over 10 lb (4.5 kg). This infant is larger, as seen on ultrasound.
Answer:
(b) client who had a breech presentation in her last pregnancy, and this pregnancy is a vertex pregnancy
Explanation:
The best candidate for a VBAC is a woman who had a cesarean section in her last birth because of a problem related to the infant that is not repeated in this pregnancy. The woman with the breech presentation in her last birth and a vertex pregnancy in this pregnancy would be the best candidate, especially if she had other vaginal births. The woman who was unable to dilate beyond 6 cm (failure to progress) may try a VBAC but is likely to experience the same problem with this birth.
The woman with the very large infant is likely to experience cephalopelvic disproportion with this birth if she experienced cephalopelvic disproportion with her last infant who was large. A classic cesarean birth scar is a contraindication for a VBAC because that type of scar may not be strong enough to withstand the stress of hours of uterine contractions and may result in a uterine disruption.
Read More:
