Time management is a key aspect of the NCLEX exam, and practicing with timed NCLEX Study Guide can help students improve their pacing.
NCLEX Vascular Disease Questions - NCLEX Questions on Vascular Disease
Vascular Disease NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
What instructions should the nurse give a client experiencing signs and symptoms related to decreased arterial insufficiency? Select all that apply.
(a) Avoid smoking and exposure to the cold.
(b) Take acetaminophen if experiencing pain at night.
(c) Take aspirin or clopidogrel as prescribed.
(d) Use additional bed clothes at night.
(e) Wear tight socks to keep feet warm.
Answer:
(a) Avoid smoking and exposure to the cold.
(c) Take aspirin or clopidogrel as prescribed.
(d) Use additional bed clothes at night.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d). Smoking and exposure to the cold cause vasoconstriction and should be avoided. Aspirin and clopidogrel should be taken as prescribed for the antiplatelet properties. Using extra bed clothes at night provides warmth, which increases vasodilation. The presence of pain should be investigated as it could indicate increasing arterial insufficiency. Tight socks should be avoided as they could impair circulation.
Question 2.
A client is admitted for a revascularization procedure for arteriosclerosis in the left iliac artery. What should the nurse do to promote circulation in the extremities?
(a) Position the client on a firm mattress.
(b) Keep the involved extremity warm with blankets.
(c) Position the left leg at or below the body’s horizontal plane.
(d) Encourage the client to raise and lower the leg four times every hour.
Answer:
(c) Position the left leg at or below the body’s horizontal plane.
Explanation:
Keeping the involved extremity at or below the body’s horizontal plane will facilitate tissue perfusion and prevent tissue damage. The nurse should avoid placing the affected extremity on a hard surface, such as a firm mattress, to avoid pressure ulcers. In addition, the involved extremity should be free from heavy overlying bed linens. The nurse should handle the involved extremity in a gentle fashion to prevent friction or pressure. Raising the leg would cause occlusion to the iliac artery, which is contrary to the goal to promote arterial circulation.
Question 3.
A sedentary, obese, middle-aged client is recovering from surgery to remove an embolus in the right iliac artery. The nurse should develop a discharge plan with the client that will focus on participating in which activities? Select all that apply.
(a) aerobic activity
(b) strength training
(c) weight control
(d) stress management
(e) wearing supportive athletic shoes
Answer:
(a) aerobic activity
(c) weight control
Explanation:
(a), (c). Discharge teaching begins when the client enters the hospital. One of the risk factors for clot formation is a sedentary lifestyle, and the client should engage in daily aerobic activity, such as biking or swimming (non-eight-bearing). The client is also overweight and should plan to control the weight through dietary counselling or attending weight management programs in the community.
Strength training is beneficial by increasing strength and lean body mass, but not helpful in preventing vascular disease. Stress management is not a focus based on the client’s needs at this time. It is not necessary to wear special supportive shoes; comfortable shoes for walking are adequate.
Question 4.
The nurse is assessing the pulse in a client with aortoiliac disease. On the illustration below, indicate the pulse site that will give the nurse the most useful data.
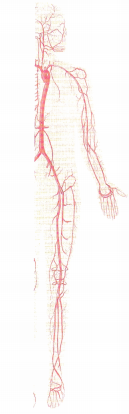
Answer:
The nurse should assess the femoral artery. Weak or absent femoral pulses are symptomatic of aortoiliac disease.
Question 5.
The nurse is assessing a 48-year-old client with a history of smoking during a routine clinic visit. The client, who exercises regularly, reports having pain in the calf during exercise that disappears at rest. Which finding requires further evaluation?
(a) heart rate 57 bpm
(b) Sp02 of 94% on room air
(c) blood pressure 134/82 mm Hg
(d) ankle-brachial index of 0.65
Answer:
(d) ankle-brachial index of 0.65
Explanation:
An ankle-brachial index of 0.65 suggests moderate arterial vascular disease in a client who is experiencing intermittent claudication. A Doppler ultrasound is indicated for further evaluation. The bradycardic heart rate is acceptable in an athletic client with normal blood pressure. The Sp02 is acceptable; the client has a smoking history.
Question 6.
A client with peripheral artery disease has undergone a right femoral-popliteal bypass graft. The blood pressure has decreased from 124/80 mm Hg to 88/62 mm Hg. What should the nurse assess first?
(a) IV fluid infusion rate
(b) pedal pulses
(c) nasal cannula flow rate
(d) capillary refill
Answer:
(b) pedal pulses

Explanation:
With each set of vital signs, the nurse should assess the dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses. The nurse needs to ensure adequate perfusion to the lower extremity with the drop in blood pressure. IV fluids, nasal cannula setting, and capillary refill are important to assess; however, the priority is to determine the cause of the drop in blood pressure and that adequate perfusion through the new graft is maintained.
Question 7.
An obese client taking warfarin has dry skin due to decreased arterial blood flow. What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Apply lanolin or petroleum jelly to intact skin.
(b) Follow a reduced-calorie, reduced-fat diet.
(c) Inspect the involved areas daily for new ulcerations.
(d) Limit activities of daily living (ADLs).
(e) Use an electric razor to shave.
Answer:
(a) Apply lanolin or petroleum jelly to intact skin.
(b) Follow a reduced-calorie, reduced-fat diet.
(c) Inspect the involved areas daily for new ulcerations.
(e) Use an electric razor to shave.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e). Maintaining skin integrity is important in preventing chronic ulcers and infections. The client should be taught to inspect the skin on a daily basis. The client should reduce weight to promote circulation; a diet lower in calories and fat is appropriate. Because the client is receiving warfarin, the client is at risk for bleeding from cuts.
To decrease the risk of cuts, the nurse should suggest that the client use an electric razor. The client with decreased arterial blood flow should be encouraged to participate in ADLs. In fact, the client should be encouraged to consult an exercise physiologist for an exercise program that enhances the aerobic capacity of the body.
Question 8.
The nurse is caring for a client with peripheral artery disease who has recently been prescribed clopidogrel. Which statement by the client indicates that the nurse should continue giving information to the client about this medication?
(a) “I should not be surprised if I bruise easier or if my gums bleed a little when brushing my teeth.”
(b) “It does not really matter if I take this medicine with or without food, whatever works best for my stomach.”
(c) “I should stop taking my medicine if it makes me feel weak and dizzy.”
(d) “The doctor prescribed this medicine to make my platelets less likely to stick together and help prevent clots from forming.”
Answer:
(c) “I should stop taking my medicine if it makes me feel weak and dizzy.”
Explanation:
Weakness, dizziness, and headache are common adverse effects of clopidogrel, and the client should report these to the health care provider (HCP) if they are problematic; in order to decrease the risk of clot formation, the drug must be taken regularly, and should not be stopped or taken intermittently. The main adverse effect of clopidogrel is bleeding, which often occurs as increased bruising or bleeding when brushing teeth.
Clopidogrel is well absorbed, and while food may help decrease potential gastrointestinal upset, the drug may be taken with or without food. Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet agent used to prevent clot formation in clients who have experienced or are at risk for myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, peripheral artery disease, or acute coronary syndrome.
Question 9.
A client is receiving cilostazol for peripheral artery disease causing intermittent claudication. Which statement by the client indicates to the nurse that this medication is effective?
(a) “I am having fewer aches and pains.”
(b) “I do not have headaches anymore.”
(c) “I am able to walk further without leg pain.”
(d) “My toes are turning grayish black in color.”
Answer:
(c) “I am able to walk further without leg pain.”

Explanation:
Cilostazol is indicated for the management of intermittent claudication. Symptoms usually improve within 2 to 4 weeks of therapy. Intermittent claudication prevents clients from walking for long periods of time. Cilostazol inhibits platelet aggregation induced by various stimuli and improves blood flow to the muscles allowing the client to walk long distances without pain.
Peripheral artery disease causes pain mainly in the leg muscles. “Aches and pains” does not specify exactly where the pain is occurring. Headaches may occur as a side effect of this drug, and the client should report this information to the health care provider (HCP). Peripheral artery disease causes a decreased blood supply to the peripheral tissues and may cause gangrene of the toes; the drug is effective when the toes are warm to the touch and the color of the toes is similar to the color of the body.
Question 10.
The client with peripheral artery disease reports both legs hurt when walking. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Avoid walking when the pain occurs.
(b) Rest frequently with the legs elevated.
(c) Wear support stockings.
(d) Enroll in a supervised exercise training program.
Answer:
(d) Enroll in a supervised exercise training program.

Explanation:
Decreased blood flow is a common characteristic of all peripheral artery disease. When the demand for oxygen to the working muscles becomes greater than the supply, pain is the outcome. The nurse should suggest that the client enroll in a supervised exercise training program that will assist the client in gradually increasing walking distances without pain. Not walking and resting will not increase blood flow to the legs. Support stockings may be prescribed, but the client should improve their capacity to walk and exercise.
Question 11.
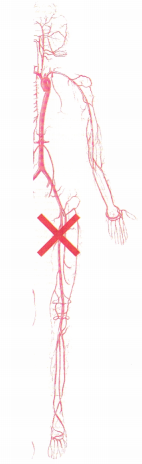
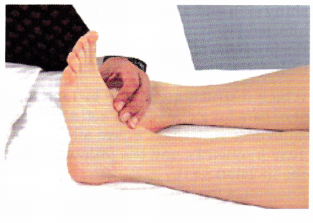
The nurse is assessing a client with peripheral artery insufficiency. In the illustration below, where should the nurse palpate the client’s pulse to identify tibioperoneal artery involvement on the right side of the body?
Answer:
The nurse palpates the dorsalis pedis; if the pulse is obtained in that artery, the tibioperoneal artery is patent.
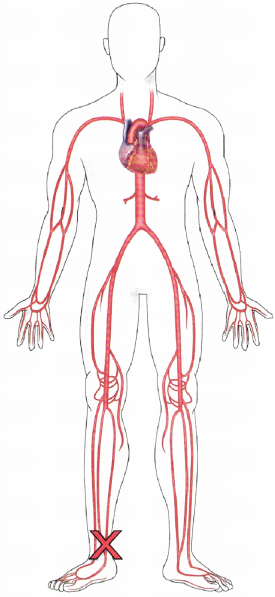
Question 12.
The nurse is obtaining the pulse of a client who has had a femoral-popliteal bypass surgery 6 hours ago (see below). Which assessment provides the most accurate information about the client’s postoperative status?
(a)
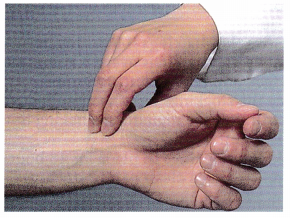
(b)
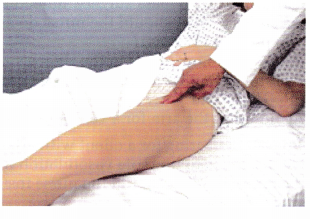
(c)
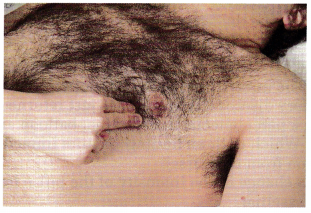
(d)
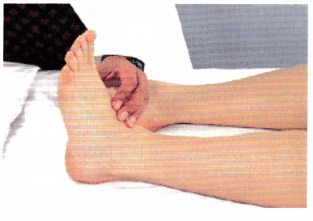
Answer:
(d)
Explanation:
The presence of a strong dorsalis pedis pulse indicates that there is circulation to the extremity distal to the surgery indicating that the graft between the femoral and popliteal artery is allowing blood to circulate effectively. Answer 1 shows the nurse obtaining the radial pulse; answer 2 shows the femoral pulse, which is proximal to the surgery site and will not indicate circulation distal to the surgery site. Answer 3 shows the nurse obtaining an apical pulse.
Question 13.
The nurse is assessing the lower extremities of the client with peripheral artery disease. Which findings are expected? Select all that apply.
(a) hairy legs
(b) mottled skin
(c) pink skin
(d) coolness
(e) moist skin
Answer:
(b) mottled skin
(d) coolness
Explanation:
(b), (d). Reduction of blood flow to a specific area results in decreased oxygen and nutrients. As a result, the skin may appear mottled. The skin will also be cool to the touch. Loss of hair and dry skin are other signs that the nurse may observe in a client with peripheral artery disease of the lower extremities.
Question 14.
The nurse is unable to palpate the client’s left pedal pulses. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Auscultate the pulses with a stethoscope.
(b) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Use a Doppler ultrasound device.
(d) Inspect the lower left extremity.
Answer:
(c) Use a Doppler ultrasound device.
Explanation:
When pedal pulses are not palpable, the nurse should obtain a Doppler ultrasound device. Auscultation is not likely to be helpful if the pulse is not palpable. Inspection of the lower extremity can be done simultaneously when palpating, but the nurse should first try to locate a pulse by Doppler. Calling the HCP may be necessary if there is a change in the client’s condition.
Question 15.
When the nurse is assessing an individual with peripheral artery disease, which clinical manifestation would indicate complete arterial obstruction in the lower left leg?
(a) aching pain in the left calf
(b) burning pain in the left calf
(c) numbness and tingling in the left leg
(d) coldness of the left foot and ankle
Answer:
(d) coldness of the left foot and ankle
Explanation:
Coldness in the left foot and ankle is consistent with complete arterial obstruction. Other expected findings would include paralysis and pallor. Aching pain, a burning sensation, or numbness and tingling are earlier signs of tissue hypoxia and ischemia and are commonly associated with incomplete obstruction.
Question 16.
A client has returned to the surgical care unit after having femoral-popliteal bypass grafting. Indicate in which order from first to last the nurse should conduct assessment of this client. All options must be used.
(a) postoperative pain
(b) peripheral pulses
(c) urine output
(d) incision site
Answer:
(b) peripheral pulses
(d) incision site
(c) urine output
(a) postoperative pain
Explanation:
(b), (d), (c), (a). Because assessment of the presence and quality of the pedal pulses in the affected extremity is essential after surgery to make sure that the bypass graft is functioning, this step should be done first. The nurse should next ensure that the dressing is intact and then that the client has adequate urine output. Lastly, the nurse should determine the client’s level of pain.
Question 17.
A client with heart failure has bilateral +4 edema of the right ankle that extends up to midcalf. The client is sitting in a chair in no evident distress with the legs in a dependent position. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Assist the client to the bed.
(b) Request a prescription for support stockings.
(c) Elevate the client’s legs on a foot stool.
(d) Take the client’s blood pressure.
Answer:
(c) Elevate the client’s legs on a foot stool.
Explanation:
Decreasing venous congestion in the extremities is a desired outcome for clients with heart failure. The nurse should elevate the client’s legs. It is not necessary for the client to return to bed. Support stockings are not indicated at this time. The client is not having difficulty breathing or other signs of distress; it is not necessary to take the vital signs.
Question 18.
The nurse is assessing a client who has a history of peripheral artery disease. The nurse observes that the left great toe is black. The nurse determines that the black color is caused by which factor?
(a) atrophy
(b) contraction
(c) gangrene
(d) rubor
Answer:
(c) gangrene
Explanation:
The term gangrene refers to blackened, decomposing tissue that is devoid of circulation. Chronic ischemia and death of the tissue can lead to gangrene in the affected extremity. Injury, edema, and decreased circulation lead to infection, gangrene, and tissue death. Atrophy is the shrinking of tissue, and contraction is joint stiffening secondary to disuse. The term rubor denotes a reddish color of the skin.
Question 19.
A client has peripheral artery disease of both lower extremities. The client tells the nurse, “I’ve really tried to manage my condition well.” Which example indicates the client is using appropriate care management strategies?
(a) The client rests with the legs elevated above the level of the heart.
(b) The client walks slowly but steadily for 30 minutes twice a day.
(c) The client limits activity to walking around the house.
(d) The client wears antiembolism stockings at all times when out of bed.
Answer:
(b) The client walks slowly but steadily for 30 minutes twice a day.
Explanation:
Slow, steady walking is a recommended activity for clients with peripheral vascular disease because it stimulates the development of collateral circulation. The client with PVD should not remain inactive. Elevating the legs above the heart or wearing antiembolism stockings is a strategy for alleviating venous congestion and may worsen peripheral artery disease.
Question 20.
A client is scheduled to have an arteriogram. During the arteriogram, the client reports having nausea, tingling, and dyspnea. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer epinephrine.
(b) Inform the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Administer oxygen.
(d) Inform the client that the procedure is almost over.
Answer:
(b) Inform the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
Clients may have an immediate or a delayed reaction to the radiopaque dye. The HCP should be notified immediately because the symptoms suggest an allergic reaction. Treatment may involve administering oxygen and epinephrine. Explaining that the procedure is over does not address the current symptoms.
Question 21.
A client with peripheral artery disease has chronic, severe bilateral pretibial and ankle edema; the client is on complete bed rest. To maintain skin integrity, what should the nurse do?
(a) Administer pain medication.
(b) Ensure fluid intake of 3,000 mL per 24 hours.
(c) Turn the client every 1 to 2 hours.
(d) Maintain hygiene.
Answer:
(c) Turn the client every 1 to 2 hours.
Explanation:
The client is at greater risk for skin breakdown in the lower extremities related to the edema and to remaining in one position, which increases capillary pressure. Turning the client every 1 to 2 hours promotes vasodilation and prevents vascular compression. Administering pain medication will not have an effect on skin integrity. Encouraging fluids is not a direct intervention for maintaining skin integrity, although being well hydrated is a goal for most clients. Maintaining hygiene does influence skin integrity but is secondary in this situation.
Question 22.
A client who has been diagnosed with peripheral artery disease (PVD) is being discharged. What statement by the client indicates the client needs further instruction?
(a) “I don’t use a heating pad.
(b) “I’ll sit in a chair with both of my legs on the floor.”
(c) “I wear leather shoes when I’m out of bed.
(d) “I should wipe any injury with iodine on acotton ball.”
Answer:
(d) “I should wipe any injury with iodine on acotton ball.”
Explanation:
The client should avoid using iodine or over-the-counter medications. Iodine is a highly toxic solution. An individual who has known PVD should be seen by a health care provider (HCP) for treatment to avoid infection. The client with PVD should avoid heating pads and crossing the legs, and should wear leather shoes. A heating pad can cause injury, which, because of the decreased blood supply, can be difficult to heal. Crossing the legs can further impede blood flow. Leather shoes provide better protection.
Question 23.
A client with peripheral artery disease has femoral-popliteal bypass surgery. What goal should the nurse establish with the client immediately after surgery?
(a) Maintain circulation.
(b) Prevent infection.
(c) Relieve pain.
(d) Provide education.
Answer:
(a) Maintain circulation.
Explanation:
Maintaining circulation in the affected extremity after surgery is the focus of care. The graft can become occluded, and the client must be assessed frequently to determine whether the graft is patent. Preventing infection and relieving pain are important but are secondary to maintaining graft patency. Education should have taken place in the preoperative phase and then continued during the recovery phase.
Question 24.
The nurse is instructing a client who is at risk for peripheral artery disease how to use knee-length elastic stockings (support hose). What instructions should the nurse include in the teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Apply the elastic stockings before getting out of bed.
(b) Remove the stockings if swelling occurs.
(c) Remove the stockings every 8 hours, elevate the feet, and reapply in 15 minutes.
(d) Once the stockings have been pulled over the calf, roll the remaining stocking down to make a cuff.
(e) Keep the stockings in place for 48 hours, and reapply using a clean pair of stockings.
Answer:
(a) Apply the elastic stockings before getting out of bed.
(c) Remove the stockings every 8 hours, elevate the feet, and reapply in 15 minutes.
Explanation:
(a), (c). Elastic stockings (support hose) are used to promote circulation by preventing pooling of blood in the feet and legs. The stockings should be applied in the morning before the client gets out of bed. The stockings should be applied smoothly to avoid wrinkles, but the top should not be rolled down to avoid constriction of circulation. The stockings should be removed every 8 hours, and the client should elevate the legs for 15 minutes and reapply the stockings. Clean stockings should be applied daily or as needed.
Question 25.
A client is scheduled to undergo right axillary-to-axillary artery bypass surgery. Immediately following surgery, what should the nurse do as a priority to prevent infection?
(a) Assess the temperature in the right arm.
(b) Monitor the radial pulse in the right arm.
(c) Protect the extremity from the cold.
(d) Avoid using the arm for venipuncture.
Answer:
(d) Avoid using the arm for venipuncture.
Explanation:
If surgery is scheduled, the nurse should avoid venipunctures in the affected extremity. The goal should be to prevent unnecessary trauma and possible infection in the affected arm. Disruptions in skin integrity and even minor skin irritations can cause the surgery to be canceled. The nurse can continue to monitor the temperature and radial pulse in the affected arm; however, doing so is not the priority Keeping the client warm is important but is not the priority at this time.
Question 26.
One goal in caring for a client with arterial occlusive disease is to promote vasodilation in the affected extremity. What should the nurse instruct the client to do to achieve this goal?
(a) Avoid eating low-fat foods.
(b) Elevate the legs above the heart.
(c) Stop smoking.
(d) Jog daily.
Answer:
(c) Stop smoking

Explanation:
Nicotine causes vasospasm and impedes blood flow. Stopping smoking is the most significant lifestyle change the client can make. The client should eat low-fat foods as part of a balanced diet. The legs should not be elevated above the heart because this will impede arterial flow. The legs should be in a slightly dependent position. Jogging is not necessary and probably is not possible for many clients with arterial occlusive disease. A rehabilitation program that includes daily walking is suggested.
Question 27.
The nurse is caring for a client with peripheral artery disease (PAD) who has just returned from having a percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty. Which of these findings require immediate attention from the nurse?
(a) a change in the intensity of the pulse from the baseline
(b) pain “2 out of 10” at the catheterization site
(c) shiny skin and a hairless appearance on the affected leg
(d) the presence of an ulcer on the limb of the catheterization site
Answer:
(a) a change in the intensity of the pulse from the baseline
Explanation:
A change in the intensity of a pulse may be indicative of arterial closure and warrants immediate attention; the nurse should notify the health care provider (HCP) jjT] immediately. A pain level of 2 out of 10 is not uncommon from the catheter insertion site especially after the placement of a stent. Shiny and hairless skin is expected in clients with PAD. A client undergoing a catheterization may experience pain at the catheterization site as large-bore sheaths are placed in the femoral artery. Because people with PAD have poor circulation in their lower extremities, it is possible for them to develop leg ulcers. However, it is unlikely that the percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty caused this.
Question 28.
Which instructions should be included in the plan of care for a client who had a left femoral- popliteal bypass yesterday? Select all that apply.
(a) Turn frequently, and use pillows to support the incision.
(b) Encourage the client to change positions frequently to prevent atelectasis.
(c) Place the left leg in a knee-flexed position to promote oxygenation.
(d) Place the client in supine position, and elevate the leg above the heart to prevent edema.
(e) Encourage the client to walk short distances to promote circulation.
(f) Encourage the client to maintain bed rest to prevent stress on the suture line.
Answer:
(a) Turn frequently, and use pillows to support the incision.
(b) Encourage the client to change positions frequently to prevent atelectasis.
(e) Encourage the client to walk short distances to promote circulation.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (e). Turning frequently promotes circulation while using pillows for support will prevent stress to the suture line. Short periods of different leg/body positions will not impair postoperative oxygen levels. The client should only be in a knee-flexed position when walking and not at rest. Prolonged sitting is discouraged, and it may cause pain and edema. It is not recommended that the leg be placed in a dependent position as this promotes edema. Placing a client in a supine position with the leg elevated above the heart is recommended only if the client develops edema.
Question 29.
The client with peripheral artery disease has been prescribed diltiazem. To determine the effectiveness of this medication, the nurse should assess the client for which intended outcome?
(a) decreased anxiety
(b) prolonged sleep
(c) cooler extremities
(d) improved blood flow
Answer:
(d) improved blood flow

Explanation:
Diltiazem is a calcium channel blocker that blocks the influx of calcium into the cell. The primary use of diltiazem for this client is to promote vasodilation and prevent spasms of the arteries so blood, oxygen, and nutrients can reach the muscles and tissues. Diltiazem is not an antianxiety agent and does not promote sleep. It also does not cause vasoconstriction, which would cause coolness in the extremities, and is contraindicated for the client with peripheral vascular disease.
Question 30.
A client is receiving cilostazol for intermittent claudication. What should the nurse ask the client to determine the effectiveness of the drug?
(a) “Do you have less pain in the legs?”
(b) “Can you wiggle your toes?”
(c) “Are you urinating more frequently?”
(d) “Do you experience less dizziness?”
Answer:
(a) “Do you have less pain in the legs?”

Explanation:
Cilostazol improves blood flow, and the client should have improved circulation in the legs as evidenced by less pain. The client does not have nerve impairment and should be able to wiggle the toes. Urination is not improved by taking cilostazol. Dizziness is a side effect of the drug, not an intended outcome.
Question 31.
A client with peripheral artery disease is recovering from surgery to insert an aortofemoral-popliteal bypass graft. When developing a postoperative education plan, which question by the nurse will provide the most helpful information?
(a) “How did you manage your health before admission?”
(b) “How far could you walk without pain before surgery?”
(c) “What is your home environment like?”
(d) “Do you have problems with urine retention?”
Answer:
(a) “How did you manage your health before admission?”
Explanation:
Assessing the individual’s health behavior before surgery will help the nurse and client develop strategies to manage the postoperative course. Asking open-ended questions will elicit the most helpful information. The client’s ability to walk will be improved after surgery. The client should report any changes in urination, but urinary retention is not expected before or after surgery.
Question 32.
The client with peripheral artery disease and a history of hypertension is to be discharged on a low-fat, low-cholesterol, low-sodium diet. Which should be the nurse’s first step in planning the dietary instructions?
(a) Determine the client’s knowledge level about cholesterol.
(b) Ask the client to name foods high in fat, cholesterol, and salt.
(c) Explain the importance of complying with the diet.
(d) Assess the family’s food preferences.
Answer:
(d) Assess the family’s food preferences.
Explanation:
Before beginning dietary interventions, the nurse must assess the client’s pattern of food intake, lifestyle, food preferences, and ethnic, cultural, and financial influences. With this information, the nurse can then discuss the client’s knowledge about cholesterol, foods high in fat, cholesterol and sodium, and coach the client about the importance of following the diet plan.
Question 33.
While the nurse is providing preoperative teaching for a client with peripheral vascular disease who is to have a below-the-knee amputation, the client says, “I hate the idea of being an invalid after they cut off my leg.” What would be the nurse’s most therapeutic response?
(a) “Focusing on using your one good leg will make your recovery easier.”
(b) “Tell me more about how you are feeling.”
(c) “We will talk more about this after your surgery. ”
(d) “You are fortunate to have a wife who can take care of you.”
Answer:
(b) “Tell me more about how you are feeling.”
Explanation:
Encouraging the client who is undergoing amputation to verbalize feelings is the most therapeutic nursing intervention. By eliciting concerns, the nurse may be able to provide information to help the client cope. The nurse should avoid value-laden responses, such as “You will still have one good leg,” that may make the client feel guilty or hostile and block further communication. The nurse should not ignore the client’s expressed concerns, nor should the nurse reinforce the client’s concern about invalidism and dependency or assume that his wife is willing to care for him.
Question 34.
The client asks the nurse, “Why can’t the doctor tell me exactly how much of my leg they’re going to take off? Don’t you think I should know that?” What information should the nurse use to answer the client’s question?
The decision about the level of the amputation depends on:
(a) the need to remove as much of the leg as possible.
(b) the adequacy of the blood supply to the tissues.
(c) the ease with which a prosthesis can be fitted.
(d) considering how to fit a prosthesis.
Answer:
(b) the adequacy of the blood supply to the tissues.
Explanation:
The level of amputation commonly cannot be accurately determined until surgery, when the surgeon can directly assess the adequacy of the circulation of the residual limb. A longer residual limb facilitates prosthesis fitting and will make it easier for the client to walk. However, although these aspects will be considered in the final decision, they are not the primary factors influencing the decision.
Question 35.
A client has undergone an amputation of three toes and a femoral-popliteal bypass. The nurse should teach the client that after surgery, which leg position is contraindicated while sitting in a chair?
(a) crossing the legs
(b) elevating the legs
(c) flexing the ankles
(d) extending the knees
Answer:
(a) crossing the legs
Explanation:
Leg crossing is contraindicated because it causes adduction of the hips and decreases the flow of blood into the lower extremities. This may result in increased pressure in the graft in the affected leg. Elevating the legs, flexing the ankles, and extending the knees are not necessarily contraindicated.
Question 36.
The nurse is assessing a client after an above- the-knee amputation and notes that blood has saturated through the distal part of the dressing. What should the nurse do immediately?
(a) Apply a tourniquet.
(b) Assess vital signs.
(c) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(d) Elevate the involved extremity with a large pillow.
Answer:
(b) Assess vital signs.
Explanation:
The client should be evaluated for hemodynamic stability and extent of bleeding prior to calling the HCP Direct pressure can be used prior to applying a tourniquet if there is significant bleeding. To avoid flexion contractures, which can delay rehabilitation, elevation of the surgical limb is contraindicated.
Question 37.
The client has had a below-the-knee amputation secondary to arterial occlusive disease. The nurse is instructing the client about residual limb care. Which statement by the client indicates that the client understands how to implement the plan of care?
(a) “I should inspect the incision carefully when I change the dressing every other day.”
(b) “I should wash the incision, dry it, and apply moisturizing lotion daily.”
(c) “I should rewrap the stump as often as needed.”
(d) “I should elevate the stump on pillows to decrease swelling.”
Answer:
(c) “I should rewrap the stump as often as needed.”
Explanation:
The purpose of wrapping the residual limb is to shape the residual limb to accept a prosthesis and bear weight. The compression bandaging should be worn at all times for many weeks after surgery and should be reapplied as needed to keep it free of wrinkles and snug. The dressing should be changed daily to allow for inspection of the stump incision. No lotions should be applied to the stump unless specifically prescribed by the health care provider (HCP). The stump should not be elevated on pillows because this will contribute to the formation of flexion contractures. Contractures will prevent the client from wearing a prosthesis and ambulating.
Question 38.
The nurse is developing a discharge teaching plan for a client who had a graft insertion for an abdominal aortic aneurysm 4 days ago. The nurse reviews the client’s chart for information about the client’s history. See the chart below.
- Smokes four cigars a month.
- Vital signs: blood pressure, ranges from 150/76-170/98 mm Hg; Heart rate, 90-100 bpm; respirations, 12-18 bpm; temperature, 99.9°F (97.8°C).
- +1 bilateral ankle edema.
Based on the data and expected outcomes, which area should the nurse emphasize in the teaching plan?
(a) food intake
(b) fluid volume
(c) skin integrity
(d) tissue perfusion
Answer:
(d) tissue perfusion
Explanation:
The underlying pathophysiology in this client is atherosclerosis. The findings from the assessment indicate the risk factors of smoking and high blood pressure. Therefore, tissue perfusion is a priority for health-promoting education. The data do not support education that focuses on food or fluid intake. Although edema is a potential problem and could contribute to poor skin integrity, the edema will likely be resolved by the aneurysm repair.
Question 39.
A client is admitted with a 6.5 cm thoracic aneurysm. The nurse records findings from the initial assessment in the client’s chart, as shown below.
|
Date |
05/07 |
|
Time |
1000 |
|
Blood pressure |
1 60/90 mm Hg |
|
Heart rate |
74 bpw |
At 1030, the client has sharp mid-chest pain after having a bowel movement. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Assess the client’s vital signs.
(b) Administer pain medication as prescribed.
(c) Assess the client’s neurologic status.
(d) Contact the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(a) Assess the client’s vital signs.

Explanation:
The size of the thoracic aneurysm is rather large, so the nurse should anticipate rupture. A sudden incidence of pain may indicate leakage or rupture. The blood pressure and heart rate will provide useful information in assessing for hypovolemic shock. The nurse needs more data before initiating other interventions. After assessment of vital signs, neurologic status, and pain, the nurse can then contact the HCP
Question 40.
A client with an enlarged abdominal aorta admitted to the emergency department has severe back pain, nausea, blood pressure of 90/40 mm Hg, heart rate 128 bpm, and respirations 28/min.
In which order from first to last should the nurse implement these prescriptions? All options must be used.
(a) Monitor intake and output.
(b) Establish an intravenous infusion.
(c) Administer pain medication.
(d) Insert a nasogastric tube.
Answer:
(b) Establish an intravenous infusion.
(d) Insert a nasogastric tube.
(c) Administer pain medication.
(a) Monitor intake and output.
Explanation:
(b), (d), (c), (a). The data suggest an abdominal aortic aneurysm that is leaking or rupturing. When implementing the prescriptions, the nurse should first establish an intravenous infusion with a large- bore needle for immediate volume replacement. Next, the nurse should insert the nasogastric tube to relieve the nausea and vomiting and decompress the stomach. The nurse next should administer pain medication. Last, the nurse should monitor intake and output; with hypovolemia, the urine output will be diminished.
Question 41.
An immigrant from Korea with a ruptured aneurysm is to have surgery to insert a graft. The surgeon has explained the procedure, but the client is not ready to sign the surgical consent form. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the surgeon
(b) Refer the client to the chaplain.
(c) Cancel the surgery.
(d) Ask if the client wants to speak with someone else about the surgery.
Answer:
(d) Ask if the client wants to speak with someone else about the surgery.
Explanation:
There may be many reasons why the client has doubts about the surgery and is not ready to sign the surgical consent. The nurse should assist the client in obtaining information that will help the client make the decision to have surgery by offering to have the client talk with family members or others who can offer support to the client. The nurse should not contact the surgeon or cancel the surgery until the client has had time to consider the decision. Unless the client requests to speak with a religious advisor or the chaplain, it is not necessary at this time to refer the client to the chaplain.
Question 42.
A client had a repair of a thoracoabdominal aneurysm 2 days ago. Which findings should the nurse consider unexpected and report to the health care provider immediately?
(a) abdominal pain at 5 on a scale of 0 to 10 for the last 2 days
(b) heart rate of 100 bpm after ambulating 200 feet (0.06 km)
(c) urine output of 2,000 mL in 24 hours
(d) weakness and numbness in the lower extremities
Answer:
(d) weakness and numbness in the lower extremities

Explanation:
One of the complications of a thoracoabdominal aneurysm repair is spinal cord injury. Therefore, it is important for the nurse to assess for signs and symptoms of neurologic changes at and below the site where the aneurysm was repaired. The client is expected to have moderate pain following surgery. An elevated heart rate is expected after physical exertion. It is important to monitor urine output following aneurysm surgery, but a urine output of 2,000 rnL in 24 hours is adequate following surgery.
Question 43.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with severe abdominal pain. A radiograph reveals a large abdominal aortic aneurysm. What is the nurse’s primary goal at this time?
(a) Maintain circulation.
(b) Manage pain.
(c) Prepare the client for emergency surgery.
(d) Teach postoperative breathing exercises.
Answer:
(c) Prepare the client for emergency surgery.
Explanation:
The primary goal is to prepare the client for emergency surgery. The goal would be to prevent rupture of the aneurysm and potential death. Circulation is maintained, unless the aneurysm ruptures. When the client is prepared for surgery, the nurse should place the client in a recumbent position to promote circulation, teach the client about postoperative breathing exercises, and administer pain medication if prescribed.
Question 44.
A client has sudden, severe pain in the back and chest, accompanied by shortness of breath. The client describes the pain as a “tearing” sensation. The healthcare provider suspects the client is experiencing a dissecting aortic aneurysm. The nurse should assess the client for which potential complication of a dissecting aneurysm?
(a) cardiac tamponade
(b) stroke
(c) pulmonary edema
(d) myocardial infarction
Answer:
(a) cardiac tamponade
Explanation:
Cardiac tamponade is a life-threatening complication of a dissecting thoracic aneurysm. The sudden, painful “tearing” sensation is typically associated with the sudden release of blood, and the client may experience cardiac arrest. Stroke, pulmonary edema, and myocardial infarction are not common complications of a dissecting aneurysm.
Question 45.
The nurse is planning care for a client who has just returned to the medical-surgical unit following repair of an aortic aneurysm. What is a priority assessment for this client?
(a) decreased urinary output
(b) electrolyte imbalance
(c) anxiety
(d) wound infection
Answer:
(a) decreased urinary output
Explanation:
Following surgical repair of an aortic aneurysm, there is a potential for an alteration in renal perfusion, manifested by decreased urine output. The altered renal perfusion may be related to renal artery embolism, prolonged hypotension, or prolonged aortic cross-clamping during surgery. Electrolyte imbalance and anxiety do not present an imminent risk for this client; signs of wound infection are generally not evident immediately following surgery, but the nurse should monitor the incision on an ongoing basis.
Question 46.
A client underwent surgery to repair an abdominal aortic aneurysm. The surgeon made an incision that extends from the xiphoid process to the pubis. At 1200 hours 2 days after surgery, the client has abdominal distention. The nurse checks the progress notes in the client’s medical record, as shown below.
|
Date |
Time |
Progress Notes |
|
07/07 |
2200 |
The client is receiving D5 Q, 1,000 mL every 8h. The NG tube is attached to low suction and draining well. The client has been NPO except ice chips. The client has had 10 mg morphine for pain at 6 AM |
What is most likely contributing to the client’s abdominal distention?
(a) nasogastric (NG) tube
(b) ice chips
(c) IV fluid intake
(d) morphine
Answer:
(d) morphine
Explanation:
The client is experiencing a paralytic ileus. One of the adverse effects of morphine used to manage pain is decreased GI motility. Bowel manipulation and immobility also contribute to postoperative ileus. Insertion of an NG tube generally prevents a postoperative ileus. The ice chips and IV fluids will not affect the ileus.
Question 47.
A client is discharged after an aortic aneurysm repair with a synthetic graft to replace part of the aorta. The nurse should instruct the client to notify the health care provider (HCP) before having which procedure?
(a) blood drawn
(b) an IV line inserted
(c) tooth extraction
(d) an X-ray examination
Answer:
(c) tooth extraction

Explanation:
The client with a synthetic graft may need to be treated with prophylactic antibiotics before undergoing major dental work and should notify the HCP before any such procedure. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment reduces the danger of systemic infection caused by bacteria from the oral cavity. Venous access for drawing blood, IV line insertion, and X-rays do not contribute to the risk of infection.

Question 48.
The nurse is assessing a client who had an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair 2 hours ago. Which finding warrants further evaluation?
(a) absent bowel sounds and mild abdominal distension
(b) a blood urea nitrogen (BUN) of 26 mg/dL (26mmol/L) and creatinine of 1.2 mg/dL (1.2 pmol/L)
(c) an arterial blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg
(d) +1 pedal pulses in bilateral lower extremities
Answer:
(c) an arterial blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg
Explanation:
A blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg in a client who has just had surgical repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm warrants further evaluation as this indicates decreased perfusion to the brain, heart, and kidneys. A BUN of 26 and a creatinine of 1.2 are normal findings. While +1 pedal pulses may be an abnormal finding, it is not uncommon, and it is important to compare this finding to previous assessments and note if this is a change of the strength of the pedal pulses. Absent bowel sounds and mild abdominal distension are expected for a client immediately following surgery. However, this finding should be monitored as it could indicate a paralytic ileus.
Question 49.
The nurse is planning care for a client who had an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair 3 days ago. The nurse is reviewing the progress notes below.
|
Date |
Time |
Progress Notes |
|
2/20 |
0900 |
Temperattire os 36.8°C; pulse is 138; BP is 86/44 mm Hg; CVP is 2 mm Hg |
|
2/20 |
1100 |
Urine ouput is 20 mL/hr for the last 2 hours; Hgb is 708 g/dL, IV of D5 1/2 normal salline is infusing at 7t CC/hr |
Two units of packed red blood cells (PRBCs) have been prescribed for transfusion. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer furosemide.
(b) Increase the drip rate of IV fluids.
(c) Initiate a dopamine drip.
(d) Transfuse PRBCs.
Answer:
(d) Transfuse PRBCs.
Explanation:
A blood transfusion is required postoperatively with significant blood loss from surgery or bleeding. Data from the progress notes indicate the client is hypovolemic and has a low hemoglobin level, which warrants transfusion at this time rather than IV fluids. The nurse must continue to assess the client for signs of bleeding. Correction of hypovolemia precedes a dopamine infusion. The transfusion should improve the hemodynamics, and the hemoglobin and hematocrit are reassessed after the transfusion. The client has fluid volume deficit, so furosemide is not needed at this time.
Question 50.
A client has been diagnosed with Raynaud’s phenomenon on the tip of the nose and fingertips. The health care provider has prescribed reserpine to determine if the client will obtain relief. The client often works outside in cold weather and also smokes two packs of cigarettes per day. The nurse should include which instructions in the discharge plan for this client? Select all that apply.
(a) Stop smoking.
(b) Wear a face covering and gloves in the winter.
(c) Place fingertips in cool water to rewarm them.
(d) Find employment that can be done in a warm environment.
(e) Report signs of orthostatic hypotension.
Answer:
(a) Stop smoking.
(b) Wear a face covering and gloves in the winter.
(d) Find employment that can be done in a warm environment.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d). Vasospastic disorder (Raynaud’s disease) is a form of intermittent arteriolar vasoconstriction that results in coldness, pain, and pallor of the fingertips, toes, or tip of the nose, and a rebound circulation with redness and pain. The nurse should instruct the client to stop smoking because nicotine is a vasoconstrictor. An adverse effect of reserpine is orthostatic hypotension.
The client should report dizziness and low blood pressure as it may be necessary to consider stopping the drug. The client should prevent vasoconstriction by covering affected parts when in cold environments. The nurse can teach the client to rewarm exposed extremities by using warm water or placing them next to the body, such as under the axilla. It is not realistic to ask this client to change jobs at this time.
Question 51.
A nurse assesses a 40-year-old female client with Raynaud’s phenomenon involving her right hand. The nurse records the information in the progress notes, as shown below. From these findings, what should the nurse first instruct the client how to manage?
|
Date |
Time |
Progress Notes |
|
06/10 |
1500 |
The client has a palpable but faint right radial pulse. Capillary refill on all five digits < 8 S. No Observable swelling. The client is reporting numbness in the tips of all five digits. The skin is warm, dry, and red. |
(a) acute pain
(b) numbness
(c) lack of circulation
(d) potential for skin breakdown
Answer:
(b) numbness
Explanation:
The client has numbness in the fingertips, and the nurse should first help the client regain sensory perception and discuss strategies for the prevention of injury. The client does not have acute pain. The client does have adequate circulation and is not at risk for skin breakdown at this time.
Question 52.
A client has Raynaud’s phenomenon. What information should the nurse include in a teaching plan about managing an attack? Select all that apply.
(a) Go to a warm room.
(b) Move the fingers and toes.
(c) Place hands under hot, running water.
(d) Massage the fingers and toes.
(e) Place hands under the armpits.
Answer:
(a) Go to a warm room.
(b) Move the fingers and toes.
(d) Massage the fingers and toes.
(e) Place hands under the armpits.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e). When the client with Raynaud’s disease is having a vasospastic attack the nurse can teach the client to go to a warmer room, move the fingers and toes to improve circulation, massage the extremities to promote circulation and put the hands under the armpits to take advantage of body heat. The client should not put the hands or fingers under hot water as there is a risk of burns. If necessary, the client can warm the hands and fingers under slightly warm water.
Question 53.
The client with Raynaud’s phenomenon has a skin ulcer on the forearm. The skin surrounding the ulcer is dry. The health care provider prescribed nitroglycerine cream. What should the nurse instruct the client about the purpose of nitroglycerine?
(a) It treats pain.
(b) It prevents an infection.
(c) It promotes healing.
(d) It softens the surrounding skin.
Answer:
(c) It promotes healing.
Explanation:
The nurse should instruct the client that with Raynaud’s disease that the nitroglycerine cream is used to promote healing by promoting vasodilation. The drug is not used in this instance to treat pain. The drug does not have properties to treat infection or soften the skin.
Question 54.
What should the nurse instruct a client who has been diagnosed with Raynaud’s phenomenon to do to prevent a vasospastic attack? Select all that apply.
(a) Avoid sudden changes in temperatures.
(b) Wear hand splints to limit constricting movements of the fingers.
(c) Wear warm clothing when the temperature gets below 50°F (10°C).
(d) Use gloves when handling ice or frozen foods.
(e) Limit stressful situations.
Answer:
(a) Avoid sudden changes in temperatures.
(c) Wear warm clothing when the temperature gets below 50°F (10°C).
(d) Use gloves when handling ice or frozen foods.
(e) Limit stressful situations.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (e). The nurse should instruct the client to prevent vasospastic attacks by avoiding extreme changes in temperature; using gloves when handling frozen foods or ice; wearing clothing that will keep the client warm; and avoiding stressful situations. The client does not need to wear hand splints.
Question 55.
A client with Raynaud’s phenomenon is prescribed diltiazem. The nurse should assess the client for which intended outcome of this drug?
(a) increased heart rate
(b) less pain in extremities
(c) fewer episodes of numbness in the fingers
(d) lower serum calcium levels
Answer:
(c) fewer episodes of numbness in the fingers

Explanation:
Calcium channel blockers are first-line drug therapy for the treatment of vasospasms with Raynaud’s phenomenon when other therapies are ineffective. Diltiazem relaxes smooth muscles and improves peripheral perfusion, thereby reducing finger numbness. Diltiazem reduces the heart rate; it does not increase it. Diltiazem does not directly reduce pain, but it does improve circulation. The intended outcome of diltiazem is not to decrease calcium levels.
Question 56.
A client with Raynaud’s phenomenon is considering having a sympathectomy. What information should the nurse give the client about this surgery? A sympathectomy is performed:
(a) in the early stages of the disease to prevent further circulatory disturbances.
(b) when the disease is controlled by medication.
(c) when the client is unable to control stress-related vasospasm.
(d) when other treatment alternatives have not been effective.
Answer:
(d) when other treatment alternatives have not been effective.

Explanation:
Sympathectomy is scheduled only after other treatment alternatives have been explored and have failed. Medication and stress management are beneficial strategies to prevent the advancement of the disease process. If the disease is controlled by medication, there is no reason for surgery.
Question 57.
The nurse reviews the morning laboratory results from a client admitted with a deep vein thrombosis. The client is receiving intravenous heparin. Based on the client’s current laboratory values, what should the nurse do?
|
Test |
Result |
|
Hgb |
12 g/dL (120 g/L) |
|
Hct |
37 g/dL |
|
Plt |
165,000 mm3 (165 x 109/L) |
|
aPTT |
65 sec (control 26) |
|
PT |
11.0 sec |
|
INR |
1.1 |
|
BUN |
19 mg/dL |
|
Cr |
1.0 mg/dL (76.3 µmol/L) |
|
AST |
25 lU/L (0.42 µkat/L) |
|
ALT |
30 lU/L (0.5 µkat/L) |
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP) about the increased liver enzymes.
(b) Encourage the client to drink 3,500 mL of fluids daily.
(c) Monitor oxygen saturation levels every 4 hours.
(d) Maintain the current rate of the heparin infusion.
Answer:
(d) Maintain the current rate of the heparin infusion.
Explanation:
An aPTT of 65 seconds is considered therapeutic with a control of 30. Therapeutic levels for heparin are 1.5 to 2.5 times the control, which would make therapeutic level between 45 seconds and 75 seconds. The nurse should continue the infusion at the current rate and continue to monitor the client. The liver enzymes (AST, ALT) are within normal range; it is not necessary to notify the HCP. The BUN and creatinine are within normal limits; the client does not need to increase fluid intake beyond 3,000 mL. The hemoglobin and hematocrit are within normal limits; it is not necessary to obtain frequent oxygen saturation levels.
Question 58.
A client is being treated for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the left femoral artery. The health care provider (HCP) has prescribed 60 mg of enoxa- parin subcutaneously. Before administering the drug, the nurse checks the client’s laboratory results, noted below.
|
Test |
Result |
|
Prothrombin time |
12.5 s |
|
INR |
2.0 s |
|
Platelet count |
50,000/jiL (50 X 109/L) |
Based on these results, what should the nurse do?
(a) Contact the pharmacist for a lower dose of the medication.
(b) Administer the medication as prescribed.
(c) Assess the client for signs of bruising on the extremities.
(d) Withhold the dose of the medication and contact the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(d) Withhold the dose of the medication and contact the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
Based on the laboratory findings, prothrombin time and INR are at acceptable anticoagulation levels for the treatment of DVT. However, the platelets are below the acceptable level. Clients taking enoxaparin are at risk for thrombocytopenia. Because of the low platelet level, the nurse should withhold the enoxaparin and contact the HCP. The nurse should not administer the drug until the HCP has been contacted. The HCP, not the pharmacist, will make the decision about the dose of the enoxaparin. The decision about administering the drug will be based on laboratory results, not evidence of bruising or bleeding.
Question 59.
A client with deep vein thrombosis suddenly develops d3^spnea, tachypnea, and chest discomfort. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Elevate the head of the bed 30 to 45 degrees.
(b) Encourage the client to cough and deep breathe.
(c) Auscultate the lungs to detect abnormal breath sounds.
(d) Contact the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(a) Elevate the head of the bed 30 to 45 degrees.
Explanation:
Elevating the head of the bed facilitates breathing because the lungs are able to expand as the diaphragm descends. Coughing and deep breathing do not alleviate the symptoms of a pulmonary embolus, nor does lung auscultation. The HCP must be kept informed of changes in a client’s status, but the priority in this case is alleviating the symptoms.
Question 60.
A client with a recent diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) has sudden onset of shortness of breath and chest pain that increases with a deep breath. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Assess the oxygen saturation.
(b) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Administer morphine sulfate, 2 mg IV.
(d) Perform range-of-motion exercises in the involved leg.
Answer:
(a) Assess the oxygen saturation.
Explanation:
A client with DVT is at high risk for a pulmonary embolism from an embolus traveling to the lung. Sudden onset of symptoms and worsening of chest pain with a deep breath suggest a pulmonary embolism. The nurse assesses the client and obtains oxygen saturation levels prior to calling the HCP and administering morphine. Range of motion is a preventive measure for DVT and is not appropriate that this time.
Question 61.
The nurse is caring for a client with venous thrombosis of the left lower extremity. To prevent further tissue damage, it is important for the nurse to observe for which finding?
(a) blood pressure and heart rate changes
(b) gradual or acute loss of sensory and motor function
(c) metabolic acidosis
(d) swelling in the left lower extremity
Answer:
(b) gradual or acute loss of sensory and motor function
Explanation:
Acute arterial occlusion is a sudden interruption of blood flow. The interruption can be the result of complete or partial obstruction. Acute pain, loss of sensory and motor function, and a pale, mottled, numb extremity are the most dramatic and observable changes that indicate a life-threatening interruption of tissue perfusion. Blood pressure and heart rate changes may be associated with the acute pain episode. Metabolic acidosis is a complication of irreversible ischemia. Swelling may result but may also indicate venous stasis or arterial insufficiency.
Question 62.
The nurse is instructing a client who had knee surgery 2 days ago about taking rivaroxaban to prevent deep vein thrombosis. Which information should the nurse include in the teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) “You may bleed more easily.”
(b) “You should not play contact sports.”
(c) “You will need to have prothrombin levels checked regularly.”
(d) “Tell your health care provider (HCP) if you have increased urination.”
(e) “Continue to take your medication until the HCP tells you otherwise.”
Answer:
(a) “You may bleed more easily.”
(b) “You should not play contact sports.”
(d) “Tell your health care provider (HCP) if you have increased urination.”
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d). The nurse should instruct the client who is taking oral rivaroxaban that the client will bleed more easily, should avoid contact sports that could cause bruising or injury, and to continue to take the medication until the HCP indicates otherwise. It is not necessary for the client to have prothrombin time checks as rivaroxaban does not act on the clotting process in this way. The client should report a decrease in urination as this may be a sign of kidney disease, which can be a side effect of rivaroxaban.
Question 63.
A client with venous thrombus reports having pain in the legs. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Elevate the foot of the bed.
(b) Elevate the legs by using a pillow under the knees.
(c) Encourage adequate fluid intake.
(d) Massage the lower legs.
Answer:
(a) Elevate the foot of the bed.
Explanation:
Venous stasis can increase pain. Therefore, proper positioning in bed with the foot of the bed elevated or when sitting up in a chair can help promote venous drainage, reduce swelling, and reduce the amount of pain the client might experience. Placing a pillow under the knees causes flexion of the joint, resulting in a dependent position of the lower leg and causing a decrease in blood flow. Fluids are encouraged to maintain normal fluid and electrolyte balance but do little to relieve pain. Therapeutic massage to the legs is discouraged because of the danger of breaking up the clot.
Question 64.
A 45-year-old client had a complete abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorec- tomy 2 days ago. The client’s abdominal dressing is dry and intact. While sitting up in the chair, the client has severe pain and numbness in her left leg. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer pain medication.
(b) Assess edema in the left leg.
(c) Assess color and temperature of the left leg.
(d) Encourage the client to change her position.
Answer:
(c) Assess color and temperature of the left leg.
Explanation:
The client is likely suffering from an embolus as a result of abdominal surgery. The nurse should inspect the left leg for color and temperature changes associated with tissue perfusion. Administering pain medication without gathering more information about the pain can mask important signs and symptoms. Although assessing for edema is important, it is not critical to this situation. Encouraging the client to change her position does not adequately address the need for gathering more data.
Question 65.
A client who is being discharged after a hospitalization for thrombophlebitis will be riding home in a car. During the 2-hour ride, what should the nurse advise the client to do?
(a) Perform arm circles.
(b) Do ankle pumps.
(c) Elevate the legs.
(d) Take an ambulance.
Answer:
(b) Do ankle pumps.

Explanation:
Performing active ankle and foot range-of-motion exercises periodically during the ride home will promote muscular contraction and provide support to the venous system. It is the muscular action that facilitates return of the blood from the lower extremities, especially when in the dependent position. Arm circle exercises will not promote circulation in the leg. It is not necessary for the client to elevate the legs as long as the client does not occlude blood flow to the legs and does the leg exercises. It is not necessary to take an ambulance because the client is able to sit in the car safely.
Question 66.
A client with a cerebral embolus is receiving IV recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA). The nurse should evaluate the client for which expected therapeutic outcomes of this drug therapy?
(a) improved cerebral perfusion
(b) decreased vascular permeability
(c) dissolved emboli
(d) prevention of cerebral hemorrhage
Answer:
(c) dissolved emboli
Explanation:
Thrombolytic agents such as streptokinase are used for clients with a history of thrombus formation, cerebrovascular accidents, and chronic atrial fibrillation. The thrombolytic agents act by dissolving emboli. Thrombolytic agents do not directly improve perfusion or increase vascular permeability, nor do they prevent cerebral hemorrhage.
Question 67.
A client who weighs 187 lb (85 kg) has a prescription to receive enoxaparin 1 mg/kg. This drug is available in a concentration of 30 mg/0.3 mL. What dose would the nurse administer in milliliters? Record your answer to two decimal points. .............................. mL.
Answer:
0.85 mL. The prescription is for the client to receive enoxaparin 1 mg/kg. Therefore, the client is to receive 85 mg. The desired dose in milliliters then can be calculated by using the formula of desired dose (D) divided by dose or strength of dose on hand (H) times volume (V).
85(mg) x0.3mL = 25.5 mg / mL
25.5 mg 30 = 0.85 mL
Question 68.
A client is on complete bed rest. The nurse should initiate measures to prevent which complication of bed rest?
(a) air embolus
(b) fat embolus
(c) stress fractures
(d) thrombophlebitis
Answer:
(d) thrombophlebitis
Explanation:
Thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of a vein. The underlying etiology involves stasis of blood, increased blood coagulability, and vessel wall injury. The symptoms of thrombophlebitis are pain, swelling, and deep muscle tenderness. Air embolus is a result of air entering the vascular system. Fat embolus is associated with the presence of intracellular fat globules in the lung parenchyma and peripheral circulation after long-bone fractures. Stress fractures are associated with the musculoskeletal system.
Question 69.
The health care provider (HCP) prescribed knee-high sequential compression devices. The client reports new pain localized in the right calf area. The nurse notes the area is reddened and warm to touch. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Offer analgesics as prescribed, and apply the compression devices.
(b) Leave the compression devices off, and contact the health care provider (HCP) to report the assessment findings.
(c) Massage the area of discomfort before apply ing the compression devices.
(d) Leave the compression devices off, and report assessment findings to the oncoming shift.
Answer:
(b) Leave the compression devices off, and contact the health care provider (HCP) to report the assessment findings.
Explanation:
Localized pain, tenderness, redness, and warmth may be symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), information the nurse should report to the HCP the compression devices should not be applied until further evaluation is completed as intermittent compression may dislodge a thrombus. Massaging the area may dislodge a thrombus and is not recommended. The nurse may offer PRN analgesics if the client requires pain management, but the compression devices should not be applied until further evaluation is completed. Diagnosis and treatment of DVT should be discussed with the HCP as soon as possible; the nurse should not wait until the next shift to report findings as a DVT can become life-threatening if a thrombus travels to the lung and becomes a pulmonary embolus.
Question 70.
A client is receiving an IV infusion of 5% dextrose in water (D5W). The skin around the IV insertion site is red, warm to touch, and painful. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer acetaminophen.
(b) Change the D5W to normal saline.
(c) Discontinue the IV.
(d) Place a warm compress on the area.
Answer:
(c) Discontinue the IV.
Explanation:
The nurse’s first action should be to discontinue the IV. The nurse should restart the IV elsewhere and then apply a warm compress to the affected area. The nurse should administer acetaminophen or an anti-inflammatory agent only if prescribed by the health care provider (HCP). The type of infusion cannot be changed without an HCP’s prescription, and such a change would not help in this case.
Question 71.
The nurse is planning care for a client on complete bed rest. To prevent venous thrombosis, what should the nurse include in the plan of care? Select all that apply.
(a) turning every 2 hours
(b) passive and active range-of-motion exercises
(c) use of thromboembolic disease (TED) support hose
(d) maintaining the client in the supine position
(e) increasing fluid intake to 3,500 mL/day
Answer:
(a) turning every 2 hours
(b) passive and active range-of-motion exercises
(c) use of thromboembolic disease (TED) support hose
(e) increasing fluid intake to 3,500 mL/day
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e). Bed rest and immobilization are associated with decreased blood flow and venous pooling in the lower extremities. The nurse should turn the client every 1 to 2 hours, use passive and active range-of-motion exercises, and apply TED hose to help prevent venous stasis in the lower extremities. The client should increase fluid intake to prevent hypercoagulability of the blood. Keeping the client in the supine position would contribute to venous stasis.
Question 72.
The client is admitted with left lower leg pain, a positive Homans’ sign, and a temperature of 100.4°F (38°C). What additional signs should the nurse assess?
(a) aortic aneurysm
(b) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the left leg
(c) IV drug abuse
(d) intermittent claudication
Answer:
(b) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the left leg
Explanation:
The client demonstrates classic symptoms of DVT, and the nurse should continue to assess the client. Signs and symptoms of an aortic aneurysm include abdominal pain and a pulsating abdominal mass. Clients with drug abuse demonstrate confusion and decreased levels of consciousness. Claudication is an intermittent pain in the leg.
Question 73.
A client is admitted with a diagnosis of thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis of the right leg. A loading dose of heparin has been given in the emergency department, and IV heparin will be continued for the next several days. What should the nurse include in the plan of care for this client?
(a) administering aspirin as prescribed
(b) encouraging green leafy vegetables in the diet
(c) monitoring the client’s prothrombin time (PT)
(d) monitoring the client’s activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and international normalized ratio (INR)
Answer:
(d) monitoring the client’s activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and international normalized ratio (INR)
Explanation:
Heparin dosage is usually determined by the health care provider (HCP) based on the client’s aPTT and INR laboratory values. Therefore, the nurse monitors these values to prevent complications. Administering aspirin when the client is on heparin is contraindicated. Green leafy vegetables are high in vitamin K and therefore are not recommended for clients receiving heparin. Monitoring of the client’s PT is done when the client is receiving warfarin sodium.
Question 74.
A client has had abdominal surgery. What should the nurse do to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? '
(a) Limit fluids to 1,000 mL in 24 hours.
(b) Encourage deep breathing.
(c) Assist the client to remain sedentary.
(d) Use pneumatic compression stockings.
Answer:
(d) Use pneumatic compression stockings.
Explanation:
The use of pneumatic compression stockings is an intervention used to prevent DVT. Other strategies include early ambulation, leg exercises if the client is confined to bed, adequate fluid intake, and administering anticoagulant medication as prescribed. Deep breathing would be encouraged postoperatively, but it does not prevent DVT.
Question 75.
A client diagnosed with a deep vein thrombosis has heparin sodium infusing at 1,500 units/h. The concentration of heparin is 25,000 units/500 mL. If the infusion remains at the same rate for a full 12-hour shift, how many milliliters of fluid will infuse? Round your answer to a whole number................... mL.
Answer:
360 mL
25,000 U / 500 mL = 50 U / mL
1 mL/50 Uxl500 U/h =30mL/hxl2h
= 360 mL
Question 76.
A client weighs 300 lb (136 kg) and has a history of deep vein thrombosis and thrombophlebitis. When coaching a client about behaviors to maintain health, the nurse determines that the client has understood the nurse’s instructions when the client makes which statement?
(a) “I’ll limit exercise that involves walking.”
(b) “I’ll try to lose weight by following a reduced- calorie, balanced diet.”
(c) “I’ll perform leg lifts every 4 hours to strengthen hamstring muscles.”
(d) “I’ll wear knee-high stockings, rolled at the top to hold the stockings up.”
Answer:
(b) “I’ll try to lose weight by following a reduced- calorie, balanced diet.”
Explanation:
The client is at risk for development of varicose veins. Therefore, prevention is key in the treatment plan. Maintaining ideal body weight is the goal. In order to achieve this, the client should consume a balanced diet and participate in a regular exercise program. Performing leg lifts improves muscle strength, but it is more important for the client to increase exercise by walking. Wearing support stockings is helpful to promote circulation, but the client should not roll the stockings at the top to hold the stockings up as this will decrease circulation at the knees.
Question 77.
Which instructions should the nurse include when developing a teaching plan for a client being discharged from the hospital on anticoagulant therapy after having deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? Select all that apply.
(a) Check urine for bright blood and a dark smoky color.
(b) Walk daily as a good exercise.
(c) Use garlic and ginger, which may decrease bleeding time.
(d) Perform foot/leg exercises and walk around the airplane cabin when on long flights.
(e) Prevent DVT because of the risk of pulmonary emboli.
(f) Avoid surface bumps because the skin is prone to injury.
Answer:
(a) Check urine for bright blood and a dark smoky color.
(b) Walk daily as a good exercise.
(d) Perform foot/leg exercises and walk around the airplane cabin when on long flights.
(e) Prevent DVT because of the risk of pulmonary emboli.
(f) Avoid surface bumps because the skin is prone to injury.

Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e),(f). Clients with resolving DVT being sent home on anticoagulant therapy need instructions about assessing and preventing bleeding episodes and preventing a recurrence of DVT. Blood in the urine (hematuria) is often one of the first symptoms of anticoagulant overdose. Fresh blood in the urine is red; however, blood in the urine may also be a dark smoky color.
Daily ambulation is an excellent activity to keep the venous blood circulating and thus to prevent blood clots from forming in the lower extremities. Garlic and ginger increase the bleeding time and should not be used when a client is on anticoagulant therapy. Clients who have had previous DVTs should avoid activities that cause stagnation and pooling of venous blood.
Prolonged sitting coupled with a change of air pressure without foot or leg exercises or ambulation in the cabin are activities that prevent venous return. Instructing the client about prevention measures is important because clients with DVT are at high risk for pulmonary emboli (PE), which can be fatal.
The client can be taught risk factors for DVT and PE. In addition, recommendations for the prevention of these events also are standard protocol in practice and should be shared with the client for home care purposes. Older adults should be monitored closely for bleeding because the skin becomes thinner and the capillaries become more fragile with the aging process.
Question 78.
A client has an emergency embolectomy for an embolus in the femoral artery. After the client returns from the recovery room, in what order, from first to last, should the nurse provide care? All options must be used.
(a) Administer pain medication.
(b) Draw blood for laboratory studies.
(c) Regulate the IV infusion.
(d) Monitor the pulses.
(e) Inspect the dressing.
Answer:
(d) Monitor the pulses.
(e) Inspect the dressing.
(c) Regulate the IV infusion.
(a) Administer pain medication.
(b) Draw blood for laboratory studies.
Explanation:
(d), (e), (c), (a), (b). The nurse should first monitor the popliteal and the pedal pulses in the affected extremity after arterial embolectomy. Monitoring peripheral pulses below the site of occlusion checks the arterial circulation in the involved extremity.
The nurse should next inspect the dressing to be sure that the client is not bleeding at the surgical site. The nurse should next regulate the IV infusion to prevent fluid overload. Then the nurse should assess pain and administer pain medications as prescribed. Last, the nurse can obtain blood for laboratory studies.
Question 79.
A client with deep vein thrombosis has been receiving warfarin for 2 months. The client is to go to an anticoagulant monitoring laboratory every 3 weeks. The last visit to the laboratory was 2 weeks ago. The client reports bleeding gums, increased bruising, and dark stools. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Decrease the dose of the warfarin.
(b) Return to laboratory for analysis of prothrombin times.
(c) Decrease the amount of vitamin K in the diet.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) about the bleeding.
Answer:
(b) Return to laboratory for analysis of prothrombin times.
Explanation:
These symptoms suggest that the client is receiving too much warfarin; the client should return to the laboratory and have a blood sample drawn to determine the prothrombin levels and have the dosage of warfarin adjusted. The diet can influence clotting, but the client needs to first have the prothrombin levels checked. It is not necessary to contact the HCP the client should return to the laboratory first, and the results of the prothrombin time will be reported to the HCP.
Question 80.
A client is talking with the nurse about unsightly varicose veins and their discomfort. What information should the nurse provide to the client?
(a) Avoid walking to reduce the discomfort.
(b) Keep the legs elevated when sitting or lying down.
(c) Sclerotherapy can be used for cosmetic improvement.
(d) Contact a surgeon to perform a femoral-popliteal bypass graft.
Answer:
(b) Keep the legs elevated when sitting or lying down.
Explanation:
The nurse instructs the client to elevate the legs to improve venous return and alleviate discomfort. Walking is encouraged to increase venous return. Sclerotherapy or laser treatment is done for cosmetic reasons, but it does not improve circulation. Surgery may be performed. For severe venous insufficiency or recurrent thrombophlebitis in the varicosities. Femoral-popliteal bypass graft is a surgical intervention for arterial disease.
Question 81.
The nurse is teaching a group of women about risk for varicose veins. Which client is at risk for varicose veins?
(a) a client who has had a cerebrovascular accident
(b) a client who has had anemia
(c) a client who has had thrombophlebitis
(d) a client who has had transient ischemic attacks
Answer:
(c) a client who has had thrombophlebitis
Explanation:
Secondary varicosities can result from previous thrombophlebitis of the deep femoral veins, with subsequent valvular incompetence. Cerebrovascular accident, anemia, and transient ischemic attacks are not associated with an increased risk of varicose veins.
Question 82.
A client is to have sclerotherapy to treat varicose veins. What information about the procedure should the nurse include in the teaching plan for this client?
(a) It causes the veins to fade and disappear.
(b) It ensures that varicosities will not occur again.
(c) It requires a short hospitalization for complete recovery.
(d) It results in bruising lasting for 2 weeks.
Answer:
(a) It causes the veins to fade and disappear.
Explanation:
Sclerotherapy involves injecting small- and medium-sized varicose veins with a solution that scars and closes those veins. In a few weeks, the veins should fade and disappear. This procedure does not require anesthesia and can be done in a health care provider’s (HCP’s) office. Varicose veins can reoccur regardless of the procedure. Bruising is more likely following vein stripping or catheter-assisted procedures.
Question 83.
A clinically obese client with moderately painful varicose veins chooses self-care options for managing the varicosities. The nurse should coach the client to follow which health care practices? Select all that apply.
(a) Lose weight.
(b) Wear compression stockings.
(c) Apply lotion to the veins.
(d) Elevate the legs.
(e) Sleep with pillows under the knees.
Answer:
(a) Lose weight.
(b) Wear compression stockings.
(d) Elevate the legs.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d). To manage varicose veins, the nurse should coach the client to lose weight to relieve pressure on the veins, wear compression stockings to promote circulation, and elevate the legs when sitting or lying down. Applying lotion to the veins will keep the skin moist, but does not promote venous circulation. Pillows under the knees will obstruct circulation.
Question 84.
A well-nourished client is admitted with a stasis ulcer. The nurse assesses the ulcer and finds excavation of the skin surface as a result of sloughing of inflammatory necrotic tissue. The health care provider has prescribed the ulcer to be flushed with a fibrinolytic agent. Which goals are appropriate for this client? Select all that apply.
(a) Increase oxygen to the tissues.
(b) Prevent direct trauma to the ulcer.
(c) Improve nutrition.
(d) Prevent infection.
(e) Reduce pain.
Answer:
(a) Increase oxygen to the tissues.
(b) Prevent direct trauma to the ulcer.
(d) Prevent infection.
(e) Reduce pain.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e). The underlying pathophysiology in stasis ulcers of the skin surface is a result of inadequate oxygen and other nutrients to the tissues because of edema and decreased circulation. The nurse should first initiate care that will increase oxygen and improve tissue integrity. It is also important to prevent trauma to the tissues and prevent infections, which result from decreased microcirculation that limits the body’s response to infection. Stasis ulcers are painful. The nurse can administer prescribed analgesics 30 minutes before changing the dressing. There is no indication that the client’s overall nutrition needs to be improved.
Question 85.
A client has had a stasis ulcer of the left ankle with 2+ pitting edema for 2 years. The client is taking chlorothiazide. What should the nurse evaluate to determine the effectiveness of this drug?
(a) improved capillary circulation
(b) decreased blood pressure
(c) wound healing
(d) absence of infection
Answer:
(a) improved capillary circulation
Explanation:
The result of chronic venous stasis is swelling and edema and superficial varicose veins. Diuretics will help reduce the swelling, thus improving capillary circulation. Although diuretics may decrease blood pressure, that is not the intended outcome of this drug. The nurse should teach the client to prevent infection and monitor wound healing, but these are not the primary outcomes of chlorothiazide.
Question 86.
The nurse assesses a client with a 5 inch x 2 inch (12.7 cm x 5 cm) stasis ulcer just above the left malleolus. The wound is open with irregular, reddened, swollen edges, and there is a moderate amount of yellowish tan drainage coming from the wound. The client verbalizes pressure-type pain and rates the discomfort at 7 on a scale of 0 to 10. What is the primary nursing goal for this client?
(a) administering prescribed analgesics.
(b) applying lanolin lotions to the left ankle stasis ulcer.
(c) encouraging the client to sit up in a chair four times per day.
(d) keeping pressure of bed linens off the area.
Answer:
(d) keeping pressure of bed linens off the area.

Explanation:
The nurse should keep bed linens off of the stasis ulcer to decrease the amount of pressure that the linens exert upon the lower extremity and prevent further tissue breakdown. Administering prescribed analgesics would be an intervention for reducing the pain. Applying lanolin lotions to the left ankle ulcer will not promote healing. Encouraging the client to sit up in a chair four times per day is an intervention to promote activity. The nurse would elevate the involved extremity while the client is sitting up to reduce venous stasis and capillary pressure.
Question 87.
In preparation for being discharged to home, the nurse is teaching a client with a chronic right ankle stasis ulcer about wound care. What statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
(a) “I’ll make an appointment with a physical therapist.”
(b) “I’ll apply a home herb mixture to the wound to promote healing.”
(c) “I’ll be patient with the healing process.”
(d) “I’ll eat a balanced diet.”
Answer:
(b) “I’ll apply a home herb mixture to the wound to promote healing.”

Explanation:
The nurse should first determine how the client will apply an herb mixture to the ulcer. The nurse should then encourage the client to consult the health care provider (HCP) because home remedies may be beneficial or may interfere with the medical treatment plan. In many cultures, home remedies are commonly used and may be helpful. The nurse must be sensitive to these traditions and cultural beliefs. The other statements demonstrate that the client understands the plan of care for the ulcer.
Question 88.
The nurse has received a change of shift report about clients. Which client should the nurse assess first?
(a) a client with chronic heart failure with right upper quadrant fullness
(b) a client in atrial fibrillation with a heart rate of 90 with a “fluttering” feeling
(c) a client with peripheral artery disease (PAD) just returning from an angiogram
(d) a client who had coronary artery bypass surgery 2 days ago who reports having incisional pain of “3” out of “10”
Answer:
(c) a client with peripheral artery disease (PAD) just returning from an angiogram
Explanation:
It is important for the nurse to assess the client with PAD returning from an angiogram. It will be important to make baseline assessments on this client. A client with atrial fibrillation with a heart rate of 90 bpm is not an abnormal finding. A “fluttering feeling” is expected in a client with atrial fibrillation. A client with heart failure experiencing right upper quadrant fullness does not require urgent attention; the client might be experiencing signs and symptoms of hepatomegaly.
Question 89.
A client with a history of hypertension and peripheral vascular disease underwent an aortic-bifemoral bypass graft. Preoperative medications included pentoxifylline, metoprolol, and furosemide. On postoperative day 1, the 1200 vital signs are as follows: temperature 98.9°F (37.2°C), heart rate 132 bpm, respiratory rate 20 breaths/min, and blood pressure 126/78 mm Hg. Urine output is 50 to 70 mL/h. The hemoglobin and the hematocrit are stable. The medications have not been prescribed for administration after surgery. Using the SBAR (Situation- Background-Assessment-Recommendation) technique for communication, the nurse contacts the health care provider (HCP) and recommends to:
(a) continue the pentoxifylline.
(b) increase the IV fluids.
(c) restart the metoprolol.
(d) resume the furosemide.
Answer:
(c) restart the metoprolol.

Explanation:
The client is experiencing rebound tachycardia from the abrupt withdrawal of the beta-blocker. The beta-blocker should be restarted due to the tachycardia, history of hypertension, and the desire to reduce the risk of postoperative myocardial morbidity. The bypass surgery should correct the claudication and the need for pentoxifylline. The furosemide and increase in fluids are not indicated since the client’s urine output and blood pressure are satisfactory and there is no indication of bleeding. The nurse should also determine the potassium level before starting the furosemide.
Question 90.
The nurse is planning care for a client who had surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair 2 days ago. The pain medication and the use of relaxation and imagery techniques are not relieving the client’s pain, and the client refuses to get out of bed to ambulate as prescribed. The nurse contacts the health care provider (HCP), explains the situation, and provides information about drug dose, frequency of administration, the client’s vital signs, and the client’s score on the pain scale. The nurse requests a prescription for a different, or stronger, pain medication. The HCP tells the nurse that the current prescription for pain medication is sufficient for this client and that the client will feel better in several days. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Explain to the HCP that the current pain medication and other strategies are not helping the client and it is making it difficult for the client to ambulate as prescribed.
(b) Ask the surgical resident to write a prescrip tion for a stronger pain medication.
(c) Wait until the next shift and ask the nurse on that shift to contact the HCP.
(d) Report the incident to the team leader.
Answer:
(a) Explain to the HCP that the current pain medication and other strategies are not helping the client and it is making it difficult for the client to ambulate as prescribed.

Explanation:
The nurse is the client’s advocate in planning for pain relief. When presented with a communication conflict, the nurse should first restate the concern, providing as much information as needed. If the HCP m still does not offer an acceptable solution for pain management, the nurse can then discuss the situation with the hospitalist on the team and report the incident to the team leader. Waiting until the next shift to handle the problem does not contribute to the goal of managing the client’s pain.
Question 91.
The nurse is making the client assignment for a group of clients. The personnel include the registered nurse (RN), a licensed practical/vocational nurse (LPN/VN), and an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which client would the nurse assign to the LPN/VN?
(a) a client who is undergoing femoropopliteal bypass graft surgery this morning and needs the preoperative checklist completed
(b) a stable client with thrombophlebitis of the lower left extremity with limited mobility and requiring a complete bed bath
(c) a client with a palpable abdominal mass, painful lower extremities, and decreasing blood pressure
(d) a client with intermittent claudication who needs frequent assistance with getting out of bed and ambulating
Answer:
(a) a client who is undergoing femoropopliteal bypass graft surgery this morning and needs the preoperative checklist completed
Explanation:
The LPN/VN Q can complete the assessment sheet and care for the client before surgery. Clients who are stable and require complete care or frequent assistance with basic care needs along with vital signs and intake and output recordings can be assigned to a UAP An unstable client requiring critical assessments receives care from the RN
Question 92.
The nurse is obtaining a blood sample for a partial thromboplastin time test prescribed for a client who is taking heparin. It is 0500 when drawing the blood. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Awaken the client.
(b) Check the armband for the client identification number and compare it with the prescription.
(c) Label the sample vial in front of the client.
(d) Verily the room number with the room assignment.
(e) Ask the client to state his/her name.
Answer:
(a) Awaken the client.
(b) Check the armband for the client identification number and compare it with the prescription.
(c) Label the sample vial in front of the client.
(e) Ask the client to state his/her name.

Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e). When obtaining blood samples, the nurse must use two acceptable sources of identification (the client states his/her name; the nurse verifies the client’s name and identification number of the armband); verifying a room number is not acceptable as clients can be easily reassigned to other rooms. The client must be awake to state his/ her name. Blood samples must be labeled in front of the client.
Question 93.
A client has acute arterial occlusion. The healthcare provider has prescribed IV heparin.
What should the nurse do before starting the medication?
(a) Review the blood coagulation laboratory values.
(b) Test the client’s stools for occult blood.
(c) Count the client’s apical pulse for 1 minute.
(d) Check the 24-hour urine output record.
Answer:
(a) Review the blood coagulation laboratory values.
Explanation:
Before starting a heparin infusion, it is essential for the nurse to know the client’s baseline blood coagulation values (hematocrit, hemoglobin, and red blood cell and platelet counts). In addition, the partial thromboplastin time should be monitored closely during the process.
The client’s stools would be tested only if internal bleeding is suspected. Although monitoring vital signs such as apical pulse is important in assessing potential signs and symptoms of hemorrhage or potential adverse reactions to the medication, vital signs are not the most important data to collect before administering the heparin. Intake and output are not important assessments for heparin administration unless the client has fluid and volume problems or kidney disease.
Question 94.
The nurse is caring for a client who has a below-the-knee amputation. The client has been somewhat confused since returning from surgery last evening but has no history of falls. The client is receiving intravenous antibiotics intermittently through a peripheral IV and has prescriptions to be up with physical therapy only. Using the Morse Fall Risk Scale (see scale), what is this client’s total score and risk level?
|
Item |
Scale |
Scoring |
|
1. History of falling; immediate or within 3 months |
No 0 Yes 25 |
|
|
2. Secondary diagnosis |
No 0 Yes 15 |
|
|
3 Ambulatory aid Bed rest/nurse assist Crutches/cane/walker Furniture |
0 15 30 |
|
|
4. IV/Heparin Lock |
No 0 Yes 20 |
|
|
5. Gait/Transferring Normal/bedrest/ immobile Weak Impaired |
0 10 20 |
|
|
6. Mental status Oriented to own ability Forgets limitations |
0 15 |
|
(a) 20, low risk
(b)30, medium risk
(c) 40, medium risk
(d) 50, high risk
Answer:
(d) 50, high risk
Explanation:
Several variables make this client a high fall risk including secondary diagnosis of diabetes (15); intermittent IV antibiotics (20); and mental status changes (15) possibly due to anesthesia, pain, or recent limb loss. This client’s assessment may clearly change as the effects of anesthesia wear off, pain is controlled, and the client becomes accus-tomed to ambulating with a prosthesis. Because assessments may be continually changing, in most acute care facilities, a fall risk is completed every 24 hours and, sometimes, every shift.
