NCLEX PN Practice Questions often incorporate scenarios involving ethical dilemmas, requiring students to apply ethical principles in their decision-making process.
NCLEX Respiratory System Questions - NCLEX Questions on Respiratory System
Respiratory System NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
Which breath sound is characterized by a high pitched whistling sound due to the narrowing of the bronchial tubes?
(a) Rhonchi
(b) Crackles
(c) Wheezing
(d) Stridor
Answer:
(c) Wheezing
Explanation:
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound heard during expiration and sonìclirnes during inspiration. it occurs due to the narrowing of the bronchial tubes. which can be caused by a tiumber of conditions such as asthma. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or bronchitis.
Rhonchi on the other hand, are low-pitched breath sounds that resemble snoring or rattling. They are usually caused by secretions or obstructions in the larger airways. such as in patients with chronic bronchitis or pneumonia.
Crackles also known as raies, are high-pitched sounds that resemble popping or snapping. They are caused by the movement of air through huid in the alveoli, and can he indicative of conditions such as pulmonary fibrosis or heart failure.
Stridor is a harsh. ibratory sound that is heard most prominently during inspiration. It is caused by narrowing or obstruction of the upper airway, and can be a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention. Stridor is often associated with croup, epiglottitis, or anaphylaxis.
Overall, the assessment of breath sounds is an important component of respiratory assessment, and can provide valuable information about the condition of the lungs and airways. Proper identification and inteipretation of breath sounds can assist in the diagnosis and management of various respiratory conditions.
Question 2.
A nurse is conducting an assessment of a patient's respiratory system. During auscultation, the nurse hears breath sounds that are louder and higher in pitch with a short pause between inspiration and expiration. The sounds are present over the large airways in the anterior chest near the second and third intercostal spaces. Which of the following breath sounds is the nurse likely hearing?
(a) Tracheal breath sounds
(b) Bronchial breath sounds
(c) Bronchovesicular breath sounds
(d) Vesicular breath sounds
(e) Wheezing
(f) Crackles
Answer:
(b) Bronchial breath sounds and (c) Bronchovesicular breath sounds.
Explanation:
Bronchial breath sounds are heard over the large airways in the anterior chest near the second and third intercostal spaces. These sounds are more tubular and hollow-sounding than vesicular sounds, but not as harsh as tracheal breath sounds. Bronchial sounds are loud and high in pitch with a short pause between inspiration and expiration; expiratory sounds last longer than inspiratory sounds.
Bronchovesicular sounds are heard in the posterior chest between the scapulae and in the center part of the anterior chest. These sounds are softer than bronchial sounds, but have a tubular quality. Bronchovesicular sounds are about equal during inspiration and expiration; differences in pitch and intensity are often more easily detected during expiration.
Tracheal breath sounds are heard over the trachea. These sounds are harsh and sound like air is being blown through a pipe. Vesicular sounds are soft, blowing, or rustling sounds normally heard throughout most of the lung fields. Vesicular sounds are normally heard throughout inspiration, continue without pause through expiration, and then fade away about one third of the way through expiration.
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that is heard during breathing when air passages are narrowed or constricted.

Crackles are heard when there is fluid in the airways. They are typically heard during inspiration and may be fine or coarse. In this case, the breath sounds heard are loud and high in pitch with a short pause between inspiration and expiration, which indicates bronchial breath sounds. Bronchovesicular breath sounds are also a possibility since they are softer than bronchial sounds but have a tubular quality and are about equal during inspiration and expiration.
Question 3.
A patient has been experiencing symptoms of asthma, including coughing and wheezing. The patient's healthcare provider has diagnosed the patient with asthma and prescribed inhaled albuterol and corticosteroids.
Question 3 What position should the nurse place the patient in during the treatment of asthma?
(a) Lying on their back with their head elevated
(b) Lying on their stomach with their head turned to the side
(c) Seated in a semi-sitting position with their knees bent
(d) Lying on their side with their head turned to the side
Answer:
(c) Seated in a semi-sitting position with their knees bent
Rationale:
The correct answer is (c) because the patient should be placed in Fowler's position, which is a semi-sitting position with the knees either bent or straight. This position can help to open the airways and make breathing easier for the patient.
Explanation:
Option (a) is incorrect because lying on the back with the head elevated does not mention anything about the position of the knees. Option (b) is incorrect because lying on the stomach is not a position typically used for the treatment of asthma. Option (d) is incorrect because lying on the side does not mention anything about the position of the knees.
Correct answer is (c) (Fowler's position with bent or straight knees) as it opens airways for easier breathing. (a) and (d) are incorrect as they don't mention knee position. (b) is incorrect as lying on stomach isn't used for asthma treatment. Case (a) patient with asthma is experiencing an acute attack and needs a bronchodilator to help improve their breathing. The healthcare provider recommends using a beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilator.
Question 4.
Which of the following is a beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilator?
(a) Albuterol
(b) Levalbuterol
(c) Salmeterol
(d) Formoterol
Answer:
(a) Albuterol
(b) Levalbuterol
(c) Salmeterol
(d) Formoterol
Explanation:
To identify a beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilator, the drugs ending with 'terol' or 'of should be considered. All four options end with 'terol'. indicating that they are all beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilators.
Explanation of Why Options are Right or Wrong: Option (a) is correct because Albuterol is a beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilator. Option (b) is correct because Levalbuterol is a beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilator. Option (c) is correct because Salmeterol is a beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilator. Option (d) is correct because Formoterol is a beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilator.
Rationale:
All four options, Albuterol, Lcvalbutcrol, Salmeterol, and Formoterol, are beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilators. Albuterol and Levalbuterol are short acting bronchodilators that work within 15 minutes and are an efficient choice for new asthma conditions. Salmeterol and Formoterol are long acting bronchodilators that are available in dry powder inhaler and nebulizer form and act for as long as 12 hours.
Question 5.
What are the two short acting bronchodilators that are Beta 2 adrenergic agonists?
(a) Albuterol and Salmeterol
(b) Formoterol and Levalbuterol
(c) Albuterol and Levalbuterol
(d) Salmeterol and Formoterol
Answer:
(c) Albuterol and Levalbuterol
Rationale:
Option (c) Albuterol and Levalbuterol is the correct answer because both of these drugs are Beta 2 adrenergic agonists and are short acting bronchodilators. Albuterol and Levalbuterol both work within 15 minutes and are efficient choice for new asthma conditions.
Explanation:
Option (a) Albuterol and Salmeterol is incorrect because while Albuterol is a Beta 2 adrenergic agonist and a short acting bronchodilator, Salmeterol is a Beta 2 adrenergic agonist but is a long acting bronchodilator. Option (b) Formoterol and Levalbuterol is incorrect because while Levalbuterol is a Beta 2 adrenergic agonist and a short acting bronchodilator, Formoterol is a Beta 2 adrenergic agonist but is a long acting bronchodilator. Option (d) Salmeterol and Formoterol is incorrect because both of these drugs are Beta 2 adrenergic agonists but are long acting bronchodilators.
Question 6.
What are the side effects of Beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilators?
(a) Nervous or shaky feeling
(b) Mouth dryness
(c) Overexcitement or hyperactivity and hypertension
(d) Increased heart rate or tachycardia and dysrhythmias
(e) Hyperglycemia
(f) All of the above
Answer:
(f) All of the above
Explanation:
To solve this question, the reader should be able to identify the sympathomimetic side effects of Beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilators.
Rationale:
Beta 2 adrenergic agonist bronchodilators show sympathomimitics property and the sympathomimetic side effects include nervous or shaky feeling, mouth dryness, overexcitement or hyperactivity and hypertension, increased heart rate or tachycardia and dysrhythmias, and hyperglycemia. Therefore, the right answer is (f) All of the above.
Question 7.
A patient with asthma is prescribed theophylline to manage their symptoms. The patient is experiencing gastric irritation as a side effect of the medication.
What is the nursing management approach to address the patient's gastric imitation?
(a) Administer the medication via IV
(b) Crush or break the medication
(c) Administer the medication with food and educate the patient not to take it on an empty stomach
(d) Administer the medication at irregular intervals
Answer:
(c) Administer the medication with food and educate the patient not to take it on an empty stomach
Explanation:
The ophylline is a bronchodilator that relaxes the smooth muscles in the bronchial airways and pulmonary blood vessels. It is used to treat symptoms of lung conditions that block the airways, such as emphysema or chronic bronchitis, and is taken orally. The drug can cause side effects such as gastric irritation, tachycardia, insomnia, restlessness, confusion, and dysrhythmias.
To minimize the risk of gastric irritation, it is important to administer the medication with food and educate the patient not to take it on an empty stomach. The enteric coated tablet form of the medication is also designed to protect it from the acidic environment of the stomach and should not be crushed or broken while administered to the patient.
The drug should also be given at regular intervals to achieve a normal therapeutic level, and patients taking the drug should avoid cigarettes, tea, coffee, and chocolate as they can worsen respiratory conditions. It is important to monitor for drug interactions, as theophylline should not be given with antibiotics like ciprofloxacin or cimetidine as they can disturb the absorption of the drug and increase the risk of toxicity. If theophylline is administered via IV, it should be done slowly via an infusion pump.
Rationale:
Administering the medication with food and educating the patient not to take it on an empty stomach helps to protect the drug from the acidic environment of the stomach and minimizes the risk of gastric imitation.
Question 8.
What are some nursing management principles for administering theophylline to a patient with asthma?
(a) Give the medication with food and educate the patient not to take it on an empty stomach to avoid gastric irritation.
(b) Educate the patient that tachycardia, insomnia, and restlessness are normal side effects of the medication.
(c) Administer the drug slowly via an infusion pump if given intravenously.
(d) Advise the patient to avoid cigarettes, tea, coffee, and chocolate while taking the medication.
(e) All the above
Answer:
(e) All the above
Explanation:
Option (a) is correct because theophylline can cause gastric irritation and should be given with food to avoid this side effect. Option (b) is correct because theophylline can cause sympathomimetic side effects such as tachycardia, insomnia, and restlessness. Option (c) is correct because the theophylline should be administered slowly via an infusion pump if given intravenously. Option (d) is correct because the patient should avoid cigarettes, tea, coffee, and chocolate while taking the medication to prevent worsening of respiratory conditions.
Rationale:
(a) is correct because the theophylline can cause gastric irritation and should be given with food to avoid this side effect. (b) is correct as theophylline can cause sympathomimetic side effects such as tachycardia, insomnia, and restlessness. (c) is correct because theophylline should be administered slowly via an infusion pump if given intravenously. (d) is correct because the patient should avoid cigarettes, tea, coffee, and chocolate while taking the medication to prevent worsening of respiratory conditions.
Question 9.
Which of the following is NOT a side effect of glucocorticoids, a class of drugs used to treat restrictive airway disorders such as asthma and COPD?
(a) Palpitations and tachycardia
(b) Constipation
(c) Blurred vision
(d) Dry mouth
(e) Weight gain
Answer:
(e) Weight gain
Explanation:
(a) Palpitations and tachycardia: This is a correct answer because palpitations and tachycardia are listed as side effects of glucocorticoids.
(b) Constipation: This is a correct answer because constipation is listed as a side effect of glucocorticoids.
(c) Blurred vision: This is a correct answer because blurred vision is listed as a side effect of glucocorticoids.
(d) Dry mouth: This is a correct answer because dry mouth is listed as a side effect of glucocorticoids.
(e) Weight gain: This is the correct answer because weight gain is not taken as a side effect of glucocorticoids.
Question 10.
A patient is diagnosed with severe asthma and is prescribed a glucocorticoid drug to manage the condition. The patient is given the following options to choose from:
(a) Beclomethasone
(b) Prednisone
(c) Fluticasone
(d) Momentasone furoate
(e) Budesonide
The patient wants to know which option is the best choice for long term treatment of their asthma.
Answer:
All options are glucocorticoids and can be used for long term treatment of asthma.
To determine the best option for the patient, it is important to understand the properties of glucocorticoids and their potential side effects. All options listed (A-E) are glucocorticoids that are used for long term treatment of asthma and other restrictive airway disorders. Therefore, any of the options could be a suitable choice for the patient.
Rationale:
All options listed in the question (a-e) are examples of drags that belong to the class of glucocorticoids. These drags are used to treat restrictive airway disorders such as asthma and COPD, and are not typically used for short term or emergency treatment. They work by blocking muscarinic receptors in the bronchioles, causing bronchodilation and relieving symptoms of air restriction.
However, they also have sympathomimetic properties, which can cause side effects such as palpitations, tachycardia, hypertension, constipation, blurred vision, diy mouth, urinary retention, and drying of body secretions. One of the most significant side effects of glucocorticoids is immunosuppression, which can increase the risk of infections, particularly in the mouth. Therefore, it is important for patients taking these drags to take good care of their oral health.
All options (a-e) are correct because they are all examples of drags that belong to the class of glucocorticoids. These drags are used for long term treatment of restrictive airway disorders such as asthma and COPD, and can be effective in relieving symptoms and improving quality of life for patients with these conditions.
However, they also have potential side effects, including immunosuppression, which can increase the risk of infections. Therefore, it is important for patients taking these drags to be aware of the potential risks and to follow their healthcare provider's instructions for use.
Question 11.
A patient presents with symptoms of a common cold, including nasal congestion and increased mucus production. The nurse practitioner decides to prescribe an antihistamine to help relieve these symptoms.
Which of the following is NOT a common side effect of antihistamines?
(a) Palpitations
(b) Tachycardia
(c) Hypertension
(d) Diarrhea
Answer:
(d) Diarrhea
Rationale:
Option (a) is correct because palpitations are listed as a common side effect of antihistamines. Option (b) is correct because tachycardia is listed as a common side effect of antihistamines. Option (c) is incorrect because while it is possible for antihistamines to cause hypertension due to their sympathomimetic effects, it is not specifically listed as a common side effect.
Option (d) is correct because diarrhea is not side effect of antihistamines. Option (a) and (b) are correct as palpitations and tachycardia are listed as side effects, Option (c) is incorrect as this is not listed as a common side effect, and Option (d) is correct as it is not taken as a side effect.
Question 12.
Mr. Saigrace is a 50-year-old man who suffers from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and is experiencing symptoms of a common cold, including sneezing, runny nose, and congestion. His doctor prescribed him an antihistamine to help relieve these symptoms.
Which of the following is a nursing intervention for Mr. Saigrace taking an antihistamine?
(a) Instruct the patient to take the drug with alcohols, opioids, or tranquilizers
(b) Use the drug cimetidine or loratidine to treat motion sickness
(c) Use diphenhydramine to treat glaucoma
(d) Advise the patient not to use the drug as it may dry out mucus membranes and body secretions
Answer:
(d) Advise the patient not to use the drug as it may dry out mucus membranes and body secretions
Explanation:
It is important for nurses to be aware of the potential side effects and contraindications of medications, as well as any potential interactions with other drugs. In this case, Mr. Saigrace's COPD may make it more difficult for him to tolerate the drying effects of an antihistamine. Therefore, it is important for the nurse to advise Mr. Saigrace not to use the drug in order to prevent any potential negative effects on his respiratory system.
Option (a). (b) and (c) are wrong. Antihistamines shouldn't be taken with alcohol, opioids, or tranquilizers. Cimetidine and loratidine not for motion sickness. Diphenhydramine has anticholinergic effects and not suitable for glaucoma. Nurses need to be aware of side effects and interactions to prevent respiratory complications for patients with COPD
Rationale:
Option (a) is incorrect because the antihistamines should not be taken with alcohols, opioids, or tranquilizers as they can cause CNS depression. Option (b) is incorrect because cimetidine and loratidine are not frequently used to treat motion sickness. Option (c) is incorrect because diphenhydramine has anticholinergic effects and is contraindicated for glaucoma.
Question 13.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of leukotriene modifiers?
(a) They are used to treat chronic asthma conditions.
(b) They are cleared through the liver.
(c) They can cause cyanosis as a side effect.
(d) They can be used by pregnant and breastfeeding mothers.
Answer:
(d) They can be used by pregnant and breastfeeding mothers.
Explanation:
Leukotriene modifiers are a class of drugs used to treat chronic asthma conditions. They work by relaxing the smooth muscles of the bronchioles and respiratory track, similar to other respiratory medicines used to treat asthma. These drugs are cleared through the liver, so caution should be taken with clients with hepatic disorders and liver function tests should be done to assess liver enzymes such as AST and ALT. Leukotriene modifiers can cause cyanosis as a side effect, and the therapeutic dose should be maintained and the drug should not be discontinued unless advised by a healthcare worker.
These drugs should not be used by pregnant and breastfeeding mothers or hypersensitive individuals, and they can cause immunosuppression if used for a long time, so blood profile or WBC profile checks should be done. It is also important to avoid administering glucocorticoids such as prednisone or beclomethasone with leukotriene modifiers, as they can increase the risk of upper respiratory track infections.
Rationale:
Option (a) is correct, leukotriene modifiers are used to treat chronic asthma conditions.
Option (b) is also correct, drug is cleared through the liver, and caution should be taken with clients with hepatic disorders.
Option (c) is also correct, leukotriene modifiers can cause cyanosis as a side effect.
Option (d) is incorrect, leukotriene modifiers should not be used by-pregnant and breastfeeding mothers.
Question 14.
Saigrace, a 45 year old male with a history of hypertension and diabetes mellitus, presents with symptoms of hay fever.
What is the appropriate nasal decongestant to prescribe for Saigrace?
(a) naphazoline
(b) xylometazoline
(c) oxymetazoline
(d) tetrahydrozoline
(e) phenylephrine hydrochloride
(f) pseudoehedrine hydrochloride
Answer:
(e) phenylephrine hydrochloride
Explanation:
In this case, it is important to consider the patient's medical history and potential contraindications for certain nasal decongestants. Since Saigrace has a history of hypertension and diabetes mellitus, we need to choose a nasal decongestant that does not have sympathomimetic activity-’ and is safe for use in these conditions. Based on the given information, only option (e) (phenylephrine hydrochloride) meets these criteria.
Rationale:
Option (a) (naphazoline), option (b) (xylometazoline), option (c) (oxymetazoline). and option (d) (tetrahydrozoline) are all nasal decongestants with sympathomimetic activity and should be avoided in patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus due to the potential for increased blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
Option (f) (pseudoehedrine hydrochloride) is also a nasal decongestant with sympathomimetic activity and should be avoided in patients with hypertension due to the potential for increased blood pressure. Option (e) (phenylephrine hydrochloride) is a safe alternative for patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus because it does not have sympathomimetic activity.
Option (e) (phenylephrine hydrochloride) is the only safe option for Saigrace as it lacks sympathomimetic activity and won't increase blood pressure or blood sugar levels. Options (a-d) (naphazoline, xylometazoline, oxymetazoline, tetrahydrozoline) and (f) (pseudoehedrine hydrochloride) should be avoided due to their sympathomimetic activity which is harmful for hypertension and diabetes patients.
Question 15.
A patient presents to the clinic with symptoms of hay fever and is prescribed a nasal decongestant. The nurse is responsible for educating the patient on the proper use and potential side effects of the medication.
What are the potential side effects of nasal decongestants?
(a) Hypertension and hyperglycemia
(b) Rebound nasal congestion
(c) Dysrhythmia
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation:
Option (a) Hypertension and hyperglycemia is correct because nasal decongestants can cause both of these side effects due to their sympathomimetic activity.
Option (b) Rebound nasal congestion is correct because if these drugs are used for more than 2 days, they can cause irritation of the nasal mucosa and lead to rebound congestion.
Option (c) Dysrhythmia is correct because nasal decongestants can cause abnormal heart rhythms.
Option (d) All of the above is the correct answer because it includes all of the potential side effects listed in the case study.
Rationale:
Nasal decongestants have sympathomimetic activity, which can cause symptoms such as hypertension, hyperglycemia, palpitations, restlessness, and insomnia. If used for more than 2 days, they can also cause rebound nasal congestion due to irritation of the nasal mucosa. In addition, these drugs can cause dysrhythmia and should be avoided in patients with hypertension or other cardiac diseases. They can also cause hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) All of the above.
Question 16.
A patient presents to the emergency department with respiratory depression after taking a large dose of hydrocodone. The physician decides to administer naloxone, an opioid antagonist, to reverse the respiratory depression.
What are the potential side effects of naloxone?
(a) Tachycardia and palpitations
(b) Hypertension
(c) Restlessness
(d) Vomiting and sweating
(e) All of the above
Answer:
(e) All of the above
Explanation:
Option (a) Tachycardia and palpitations is correct -ssside effects of these types of drugs include tachycardia and palpitations.
Option (b) Elypertension is correct - side effects of these types of drags include hypertension.
Option (c) Restlessness is correct -side effects of these types of drags include restlessness.
Option (d) Vomiting and sweating is correct -side effects of these types of drags include vomiting and sweating.
Rationale:
Naloxone is an opioid antagonist that can reverse respiratory depression in cases of opioid overdose. Sside effects of these types of drugs include tachycardia and palpitations, hypertension, restlessness, tremor, vomiting and sweating. Therefore, the correct answer is (e) All of the above.
Question 17.
A patient in the emergency department has esophageal trauma. Subcutaneous emphysema in the mediastinal area up to the lower part of the neck is palpated by the nurse. What is the priority action the nurse should take?
(a) Assess the patient’s oxygenation status
(b) Obtain a STAT chest X-ray
(c) Prepare for immediate surgery
(d) Start two large-bore IVs
Answer:
(a) Assess the patient’s oxygenation status
Explanation:
Subcutaneous emphysema occurs when air or another gas such as CO2 gets into the tissues under the subcutaneous tissue. The nursing assessment reveals a crackling sensation under the skin during palpation. This is a potential complication of a ruptured esophagus.
Airway is the priority in care because the patency of the patient’s airway may be compromised. Thus, the priority in this option is to assess the patient’s oxygenation status and observe for respiratory distress: tachypnea, dyspnea, shortness of breath, tachycardia, and abnormal or absent lung sounds.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because immediate airway assessment at the bedside is the priority over diagnostic procedures.
(c) is incorrect because the airway must be assessed and maintained before a surgical procedure.
(d) is incorrect because IV access is important and will help the nurse infuse fluids and medications, but the airway is initially more important than circulatory volume or IV medications.
Question 18.
A patient with hepatopulmonary syndrome is experiencing dyspnea, and his oxygen saturation level is 92%. He says he doesn't want to wear oxygen because it causes nosebleeds. He insists the nurse leave his room and leave him alone. Which action should the nurse take?
(a) Instruct the patient to sit as upright as possible
(b) Add humidity to the oxygen and encourage the patient to wear it
(c) Document the patient’s refusal and notify the healthcare provider
(d) Contact the healthcare provider to request an additional dose of the patient’s diuretic
Answer:
(a) Instruct the patient to sit as upright as possible
Explanation:
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is an uncommon condition that affects the lungs of people with advanced liver disease. Symptoms include hypoxemia as a result of dilation of blood vessels. This makes it hard for the lungs to deliver adequate amounts of oxygen to the body, causing dyspnea. This patient’s oxygenation status is low, so sitting upright should be the first intervention.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because the first intervention should be sitting the patient upright. The higher the head of the bed, the easier it is to breathe. Then the nurse can add humidity to the oxygen.
(c) is incorrect because documentation and notification of the healthcare provider should occur, but this is not priority. The nurse must immediately address the dyspnea and low oxygen saturation.
(d) is incorrect because an additional dose of diuretic could risk hypovolemia and electrolyte imbalance. This will not correct the condition. Hepatopulmonary syndrome is ultimately only correctable with a liver transplant.
Question 19.
A nurse is preparing a patient for paracentesis. Which intervention is appropriate for the nurse delegate to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)?
(a) Have the patient sign the informed consent
(b) Assist the patient to void before the procedure
(c) Help the patient lay flat in bed on the right side
(d) Get the patient into a chair after the procedure
Answer:
(b) Assist the patient to void before the procedure
Explanation:
Paracentesis is accessing a body cavity with a needle to remove a fluid collection or gas where it does not belong. The procedure is done to remove fluid from around the lungs or the abdominal cavity to improve breathing ability and oxygenation status. Voiding should occur just before a paracentesis procedure to prevent bladder puncture. Other appropriate nursing actions include checking baseline weight and vital signs before the paracentesis, monitoring BP during the procedure, and assessing dressing for drainage after the procedure.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the healthcare provider is responsible for obtaining the signed informed consent. The nurse may act as the witness.
(c) is incorrect because the correct position for paracentesis is sitting upright in bed or on the side of the bed leaning over bedside table.
(d) is incorrect because the patient should be on bed rest after paracentesis.
Question 20.
A patient is in the emergency room after being stung by a bee. The patient is experiencing anxiety and difficulty breathing. What priority action should the nurse perform?
(a) Have the patient lie down
(b) Assess the patient’s airway
(c) Administer high-flow oxygen
(d) Remove the stinger from the site
Answer:
(b) Assess the patient’s airway With any patient experiencing difficulty breathing, the initial action is to assess and maintain airway.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because lying down would not help the patient’s breathing. The correct position for a patient with breathing difficulties is head of bed elevated.
(c) is incorrect because the nurse should elevate the head of bed and then start low-flow oxygen and reassess for improvement.
(d) is incorrect because removing the stinger may be appropriate, but it is not priority. After oxygenation has been addressed, the nurse can then proceed to remove the stinger with a flat edge such as a credit card. (Tweezers should not be used, because they can release additional venom into the patient as the stinger is squeezed for removal.)
Question 21.
A patient admitted for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia reports activity-related shortness of breath and extreme fatigue. The nurse will promote comfort with which of the following interventions?
(a) Administer sleeping medication
(b) Perform most activities for the patient
(c) Increase the patient’s oxygen during activity
(d) Pace activities, allowing for adequate rest
Answer:
(d) Pace activities, allowing for adequate rest
Explanation:
In patients with pneumonia, decreased oxygenation status and infection cause fatigue and shortness of breath. The nurse should encourage patients to participate in as much of their care as they possibly can, keeping them independent. The nurse should pace activities, allowing for adequate rest in between.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because sleeping medication may be indicated, but not as a first step. The nurse should try non-pharmacologic measures to promote rest before adding a sleep aid.
(b) is incorrect because the patient should be allowed to do as much as they can for themselves, promoting independence.
(c) is incorrect because increased oxygen is only required if the patient’s saturation drops while active.
Question 22.
The nursing instructor is supervising several nursing students on the medical surgical floor. When a student asks why chronic obstructive pulmonary disease leads to polycythemia, what is the best response by the nursing instructor?
(a) It is due to side effects of medications for bronchodilation
(b) It is from overactive bone marrow in response to chronic disease
(c) It combats the anemia caused by an increased metabolic rate
(d) It compensates for tissue hypoxia caused by lung disease
Answer:
(d) It compensates for tissue hypoxia caused by lung disease
Explanation:
Polycythemia is increase in red blood cell numbers in response to the lung disease. Red blood cells are produced in a response to hypoxia, which leads to more oxygen carrying capacity and ability to deliver oxygen to tissues.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because polycythemia is not a side effect of a bronchodilator medications. Note: anabolic steroids used by athletes can cause polycythemia.
(b) is incorrect because polycythemia can be an effect of overactive bone marrow, but patients with COPD do not often have overactive bone marrow.
(c) is incorrect because polycythemia is not a response to anemia.
Question 23.
While in triage in a busy emergency room, the nurse assesses a patient who has symptoms of tuberculosis. Which is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Place a mask on the patient and the nurse
(b) Administer intravenous 0.9% saline solution
(c) Transfer the patient to a negative pressure room
(d) Obtain a sputum culture and sensitivity
Answer:
(a) Place a mask on the patient and the nurse
Explanation:
Tuberculosis is a highly contagious respiratory infection that is spread through airborne means. When TB is suspected, the nurse must first place a mask on their own face and then the patient’s.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because the greatest priority is prevention of the spread of this highly contagious disease, not fluid infusion.
(c) is incorrect because the patient must be wearing a mask before they are transferred within the hospital. Patients who exhibit signs and symptoms of tuberculosis must be placed in a negative pressure room in order to prevent staff, patients, and family members from possibly being infected.
However, the transfer cannot occur until the nurse ensures the safety of those who may come into contact with the patient during the transfer. (d) is incorrect because while a sputum culture and sensitivity are indicated, they are not the first action.
Question 24.
A person in the public park is stung by a bee and encountered by a nurse. The person's lips are swollen and wheezes are easily heard. What is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Elevate the site and notify the person’s next of kin
(b) Remove the stinger with tweezers and encourage rest
(c) Administer topical diphenhydramine, apply ice, and call 911
(d) Administer an EpiPen from the first aid kit
Answer:
(d) Administer an EpiPen from the first aid kit
Explanation:
Swollen lips indicate anaphylaxis, and this is a true medical emergency. The EpiPen should be administered at the first sign of anaphylaxis, if available. Then the patient should be transported to the closest emergency room, and the nurse should frequently assess the airway while in transport.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because elevating this site is not a treatment for airway obstruction from anaphylaxis.
(b) is incorrect because removing the stinger will not treat airway obstruction from anaphylaxis. Tweezers are not the best method for removing the stinger because they can release additional venom into the patient as the stinger is squeezed for removal. The stinger should be removed with a flat edge such as a credit card.
(c) is incorrect because topical diphenhydramine will not treat airway obstruction from anaphylaxis. Ice will reduce swelling at the site of the sting but not treat the airway. Calling 911 is not an inappropriate nursing action, but the EpiPen should be administered first.
Question 25.
A patient arrives in the emergency room with full-thickness burns to the lower extremities from a structure fire. The patient is occasionally disoriented, has a headache, and has 0.9 normal saline running at too ml/hr through a peripheral IV. Which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse?
(a) Increase the patient’s oxygen and obtain arterial blood gases
(b) Draw a blood sample for a carboxyhemoglobin level
(c) Change the fluid to Lactated Ringers and increase the infusion rate
(d) Perform a thorough Mini-Mental State Examination
Answer:
(c) Change the fluid to Lactated Ringers and increase the infusion rate
Explanation:
The emergent phase following a burn is the first 24-48 hours. The patient is likely to exhibit hypotension from fluid loss (from open wounds or extravasation into deeper tissues.) LR or plasma is infused rapidly over the first eight hours, and more slowly over the next 16 hours.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because fluids are priority. The disorientation and headache are signs of carbon monoxide poisoning, which will not be revealed with an ABG.
(b) is incorrect because fluids are priority. Being in a fire in an enclosed space increases risk for carbon monoxide poisoning. Carboxyhemoglobin blood levels should be drawn after fluids have been addressed.
(d) is incorrect because a Mini-Mental State Examination will not address the fluids needs or give information related to carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 26.
A patient rescued from a house fire has burns on the arms, legs, and chest. Eight hours after admission, the patient has become restless and agitated. What is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Remain at the bedside and comfort the patient
(b) Administer morphine IV
(c) Assess the patient’s orientation and level of consciousness
(d) Check pulse oximetry for oxygenation status
Answer:
(d) Check pulse oximetry for oxygenation status
Explanation:
The patient may have experienced smoke inhalation injury. Agitation is an indication of hypoxia. Pulse oximetry is the priority assessment as it gives here-and-now information about the patient’s current respiratory status.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because comforting the patient will not help with agitation in the hypoxemic patient. The nurse must treat physical problems first.
(b) is incorrect because morphine will treat pain but does not address potential hypoxia.
(c) is incorrect because the nurse does not need further LOC assessment at this time. Airway assessment is priority.
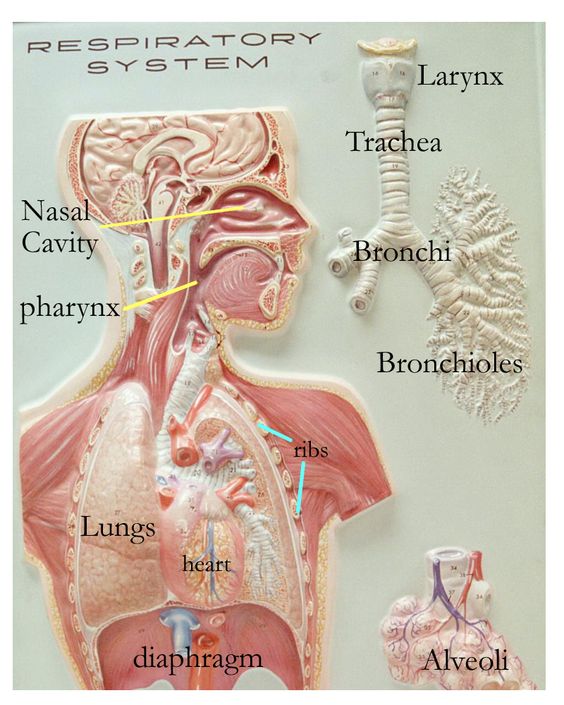
Question 27.
A patient rescued from a house fire has sustained burns to the face and upper chest. As the patient arrives by ambulance, the nurse notes the patient has a bolus of LR infusing and 4L/min 02 by face mask applied. Which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse first?
(a) Auscultate lung sounds
(b) Determine depth and extent of burns
(c) Infuse TPN with high-protein concentration
(d) Administer hydromorphone
Answer:
(a) Auscultate lung sounds
Explanation:
The patient with burns to the head, neck, upper back, chest or upper extremities is at high risk for inhalation injury or burns to the structures of the airway. The nurse should not assume that a thorough airway assessment has been made or that the oxygen face mask is effective for meeting oxygen needs. Assessment of the airway and breathing is the first action the nurse should take.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because determining the depth and extent of burns is an important nursing assessment after airway has been addressed.
(c) is incorrect because protein is needed for wound healing, but LR is infused for the first 24-48 hours. Nutritional needs do not take priority over airway assessment, initially. Note: a high-calorie, high-carbohydrate, high-protein diet is needed for optimal healing of burns. Tube feeding or TPN may be indicated if the patient is not able to take in enough nutrition PO.
(d) is incorrect because administration of analgesics is important due to the extreme severe pain experienced by burn patients, but airway is priority.
Question 28.
A patient with lung cancer informs the nurse he has a 50-pack/year smoking history. Which of the following nursing actions is best?
(a) Encourage the patient to quit smoking to stop further cancer development
(b) Encourage the patient to be completely honest about both tobacco and marijuana use
(c) Maintain a nonjudgmental attitude to avoid causing the patient to feel guilty
(d) Educate the patient about cancer treatment options and prognosis
Answer:
(c) Maintain a nonjudgmental attitude to avoid causing the patient to feel guilty
Explanation:
Cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco, and marijuana are all part of smoking history. The patient may have guilt or denial related to this, so a nonjudgmental attitude should be assumed by the nurse during the interview to encourage the patient to be honest.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because quitting may not stop the cancer from spreading.
(b) is incorrect because this may suggest distrust and is non-therapeutic.
(d) is incorrect because the nurse is not responsible for initially educating the patient about his treatment options. That is the role of the healthcare provider. The nurse must remain focused on the nurse-patient relationship and maintain a nonjudgmental attitude.
Question 29.
The nurse is caring for a patient recovering after an open lung biopsy procedure. Which expected nursing assessment is matched with the correct nursing intervention?
(a) Patient has leaking fluid from needle site, so nurse applies a new, sterile dressing
(b) Patient’s heart rate is 55 beats/min, so nurse withholds pain medication
(c) Patient has reduced breath sounds, so nurse calls physician immediately
(d) Patient’s respiratory rate is 18 breaths/min, so nurse decreases oxygen flow rate
Answer:
(c) Patient has reduced breath sounds, so nurse calls physician immediately
Explanation:
Lung biopsy can be performed using an open (surgical) or closed (through skin or trachea) procedure. Samples of lung tissue are removed to determine if cancer or lung disease is present. The risk for pneumothorax (lung collapse) is greater with an open procedure.
Pneumothorax is a serious complication which requires chest tube insertion for lung re-expansion. If the nurse notes decreased breath sounds (a sign of pneumothorax), the healthcare provider must be notified immediately. Other signs of pneumothorax include shortness of breath, tachycardia, and bluish discoloration of skin (late sign).
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because a needle is not used during an open biopsy procedure. If any leaking is noted from the needle insertion site after a closed biopsy procedure, the nurse should reinforce the sterile dressing and call the healthcare provider.
(b) is incorrect because bradycardia is not an indication for withholding pain medication.
(d) is incorrect because a respiratory rate of 18 is normal and does not necessitate a decreased oxygen flow rate.
Question 30.
The nurse is assessing the health history of a patient. Which of the following data is highest priority for the nurse to collect when determining risks for respiratory disease?
(a) Daily fluid intake
(b) Neck circumference
(c) Height and weight
(d) Occupation and hobbies
Answer:
(d) Occupation and hobbies
Explanation:
Occupation and hobbies can be a source of chronic exposure to inhaled irritants and respiratory problems. Occupations at high risk for respiratory disease include welding, mining, furnace repair/installation, and work in plants with poor ventilation (chemical, plastic, or rubber plants).
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because fluid intake is not directly linked to risk to respiratory disease.
(b) is incorrect because neck circumference is not important for assessment of respiratory risks. Neck circumference is used to determine obesity, complications with endotracheal tube placement, and sleep apnea, which is not a disease process.
(c) is incorrect because height and weight are important but aren’t directly linked to respiratory disease.
Question 31.
The nurse is caring for a 68-year-old patient admitted for pulmonary infection. Which of the following actions should be taken by the nurse first?
(a) Encourage fluid intake
(b) Assess level of consciousness
(c) Raise head of bed to 60 degrees
(d) Provide humidified oxygen
Answer:
(b) Assess level of consciousness
Explanation:
Assessing level of consciousness is important in a patient with pulmonary infection because this helps the nurse determine if oxygen should be applied. Pulmonary infection affects oxygenation status and gas exchange which can limit cerebral oxygenation, leading to disorientation and drowsiness.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because fluid intake is important but not the first action.
(c) is incorrect because raising the head of the bed will facilitate breathing, but the nurse should gather assessment data before implementing.
(d) is incorrect because humidified oxygen will not be applied until the nurse has assessed the respiratory system. Not all patients with pulmonary infection necessarily need humidified oxygen.
Question 32.
The nurse has just auscultated the patient's breath sounds. Which finding is matched correctly with the nurse's intervention?
(a) Hollow sounds heard over the trachea, so the nurse increases the oxygen flow rate
(b) Crackles are heard in bases, so the nurse administers beclomethasone inhaler
(c) Wheezes are heard in central areas, so the nurse administers bronchodilator inhaler
(d) Vesicular sounds are heard over the periphery, so the nurse has the patient breathe deeply
Answer:
(c) Wheezes are heard in central areas, so the nurse administers bronchodilator inhaler
Explanation:
Wheezes in the lungs indicate narrowed airways, which can be treated with bronchodilators to open airways.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because hollow sounds are normal in the trachea and no intervention is necessary.
(b) is incorrect because crackles in lung bases are an indication of fluid in the interstitial spaces of the lungs. The patient should be encouraged to cough. Crackles that don’t clear with coughing may indicate pulmonary edema. Beclomethasone is a corticosteroid (generally used twice a day) to prevent asthma symptoms such as chest tightness, difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing. This is not a rescue inhaler and will not help clear crackles.
(d) is incorrect because vesicular sounds in the periphery are normal and no intervention is necessary.
Question 33.
A 55-year-old male patient has measurements of the anteroposterior (AP) and lateral chest diameter that are equal. Which question should be asked by the nurse?
(a) “Do you take any medications or herbal supplements?”
(b) “Do you have chronic breathing problems?”
(c) “How often do you exercise?”
(d) “Have you been exposed to any allergens lately?
Answer:
(b) “Do you have chronic breathing problems?”
Explanation:
In a normal chest, the lateral diameter should be two times the AP diameter (1:1 until the age of six). This patient has a 1:1 AP to Lateral diameter, known as a ‘barrel chest,’ which can be a result of long-term chronic breathing problems such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because medications and herbal supplements are not associated with barrel chest.
(c) is incorrect because exercise is not associated with barrel chest.
(d) is incorrect because allergies do not cause barrel chest. The nurse should assess for the presence of chronic respiratory issues as well as occupation and hobbies that may expose the patient to irritants that lead to chronic respiratory problems.
Question 34.
A patient is scheduled for a thoracentesis this morning. Before the procedure, which intervention should be completed by the nurse?
(a) Measure oxygen saturation before and after a 12-minute walk
(b) Verify that the patient understands all possible complications
(c) Explain the procedure in detail to the patient and the family
(d) Validate that informed consent has been signed by the patient
Answer:
(d) Validate that informed consent has been signed by the patient
Explanation:
Thoracentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the pleural space between the lungs and the chest wall. This procedure is performed to remove excess fluid (pleural effusion) from the pleural space to facilitate easier breathing or send for biopsy. Informed consent is required before any invasive procedure. Complications may include pneumothorax, bleeding, bruising, infection, and, in rare cases, liver or spleen injuries.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because oxygen saturation before and after a 12-minute walk is not required before a thoracentesis.
(b) is incorrect because understanding of complications is verified by the healthcare provider.
(c) is incorrect because explanation of the procedure is performed by the healthcare provider.
Question 35.
The nurse cares for a patient following a thoracentesis procedure. The dressing is on the left side of the posterior thorax. Which finding requires immediate action?
(a) The patient rates pain as a 5/10 at the site of the procedure
(b) Serosanguinous drainage on dressing
(c) Pulse oximetry is 93% on 2 liters of oxygen
(d) The trachea is deviated toward the right side of the neck
Answer:
(d) The trachea is deviated toward the right side of the neck
Explanation:
Tracheal deviation is a sign of tension pneumothorax a medical emergency. Tension pneumothorax is collection of air or fluid in the pleural cavity that causes the affected lung to shift in the opposite direction, which also shifts the trachea.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because pain is expected after thoracentesis and does not require immediate action.
(b) is incorrect because although this is not an expected finding, tracheal deviation is the greatest concern.
(c) is incorrect because although this is a low pulse-ox reading, this may be expected after a thoracentesis depending on whether lung disease is present. This should be investigated by the nurse, but tracheal deviation is the priority.
Question 36.
The nurse is caring for a patient recovering from bronchoscopy two hours ago. When the patient asks for ice cream to soothe their sore throat, what is the next action the nurse should take?
(a) Notify the healthcare provider and request a diet order
(b) Give the patient ice chips
(c) Assess gag reflex before giving water
(d) Give the patient a sip to assess swallowing ability
Answer:
(c) Assess gag reflex before giving water
Explanation:
During a bronchoscopy, a flexible tube is inserted into the trachea. This procedure can be used for visualization of the lower airways, removal of a foreign object from the trachea/lungs, or sputum/tissue sample collection. A topical anesthetic is sprayed in the patient’s throat, and the patient may be sedated for the procedure, which affects the patient’s ability to swallow. The gag reflex should be checked before giving the patient anything by mouth.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because notifying the healthcare provider is not necessary. Standard procedure following a bronchoscopy is to keep the patient NPO until drowsiness subsides. When alert and oriented, the nurse must assess for a positive gag reflex before allowing the patient to take anything by mouth. Then clear liquids are acceptable, progressing to a regular diet.
(b) is incorrect because the patient may aspirate if the gag reflex has not returned.
(d) is incorrect because the gag reflex should be assessed first, and then the nurse can offer a sip of water to assess swallowing ability.
Question 37.
A patient experiences dyspnea and has to stop several times when climbing stairs. When planning care for this patient, which intervention should be included by the nurse?
(a) Assistance with activities of daily living
(b) Physical therapy activities every day
(c) Oxygen therapy at 2 liters per nasal cannula
(d) Complete bedrest with frequent repositioning
Answer:
(a) Assistance with activities of daily living
Explanation:
This patient has class III dyspnea, which is characterized by dyspnea upon completing activities. Assistance should be provided with activities, but the patient should be encouraged to remain as independent as possible.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because help with ADLs addresses the safety issue. Safety is priority over physical therapy daily.
(c) is incorrect because oxygen is only necessary if the patient is hypoxic.
(d) is incorrect because the patient does not require complete bedrest. The nurse should encourage the patient to stay active and address safety needs.
Question 38.
A patient was administered benzocaine spray by the nurse before bronchoscopy earlier today. The patient now has low oxygen saturation levels and cyanosis, despite oxygen administration via non-rebreather. What is the next action the nurse should take?
(a) Administer an albuterol treatment
(b) Notify the rapid response team
(c) Assess the patient’s peripheral pulses
(d) Increase the oxygen flow rate
Answer:
(b) Notify the rapid response team
Explanation:
This patient has manifestations of methemoglobinemia, an adverse effect of the benzocaine spray. Increased levels of methemoglobin in the blood prevent hemoglobin from releasing oxygen throughout the body. This is a medical emergency and can lead to shock, seizures, and death.
Symptoms include bluish coloring of the skin, headache, fatigue, shortness of breath, and lack of energy. Methemoglobinemia can also be caused by other medications such as are dapsone (an antibiotic used to treat leprosy), chloroquine (used to treat malaria), and nitrites (used to preserve meat.)
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because albuterol is a bronchodilator and will not reverse the effects of the benzocaine spray. Bronchodilator inhalers are used to open airways when wheezing is present.
(c) is incorrect because assessment of pulses does not provide information related to the problem. The nurse does not need any more assessment at this time.
(d) is incorrect because the condition this patient is experiencing cannot be corrected with increased oxygen. Treatment includes methylene blue, ascorbic acid, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or red blood cell transfusion.
Question 39.
A nurse admits a new patient to the medical surgical unit. While assessing lung sounds, the nurse places the stethoscope over the trachea and larynx and hears a harsh, hollow sound. What is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Document the findings
(b) Administer oxygen therapy
(c) Position the patient in high-Fowler’s position
(d) Administer albuterol
Answer:
(a) Document the findings
Explanation:
Harsh, hollow sounds over the trachea and larynx are bronchial breath sounds and are a normal finding. This should be documented in the patient’s chart. Documentation is appropriate when no other intervention is necessary and when no other direct patient care options are available as answer choices.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because oxygen therapy is not indicated.
(c) is incorrect because position changes are not indicated.
(d) is incorrect because albuterol is not indicated with normal breath sounds.
Question 40.
A patient is on 2 liters per minute of oxygen via nasal cannula. The nursing student removes the oxygen according to the healthcare provider’s order. The patient says, “I need that still, or I won’t be getting any oxygen.” What is the correct response by the student nurse?
(a) “If you desaturate or show signs of hypoxia, we will reapply the nasal cannula.”
(b) “The room air is actually 21% oxygen. We will monitor you closely and make sure you are able to breathe without difficulty.”
(c) “I think you will be ok without it.”
(d) “The doctor ordered for the oxygen to be removed.”
Answer:
(b) “The room air is actually 21% oxygen. We will monitor you closely and make sure you are able to breathe without difficulty.”
Explanation:
This answer choice provides information, responds to the patient’s concern, and offers reassurance. After removing oxygen, the student nurse (and the nurse) will monitor for pulse-ox desaturation, shortness of breath, disorientation, and other signs of hypoxia. Oxygen will be reapplied if these assessments are made.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the student nurse should not assume that the patient will understand medical terms such as “desaturate” or “hypoxia.” The student nurse must communicate in a way that the patient will understand.
(c) is incorrect because it dismisses the patient’s concern, and it focuses on the student nurse.
(d) is incorrect because it does not focus on the patient’s concern or provide enough information to reassure the patient.
Question 41.
The nurse prepares a patient for a tracheostomy procedure scheduled in one hour. What is the priority action by the nurse?
(a) Administer anxiolytic medication
(b) Obtain verbal consent for the procedure
(c) Reinforce pre-op teaching
(d) Start preoperative antibiotic infusion
Answer:
(c) Reinforce pre-op teaching
Explanation:
Tracheostomy is an invasive surgical procedure in which a new opening is created into the trachea for an artificial airway to be inserted. After the healthcare provider explains the procedure and obtains signed consent, the nurse is responsible for reinforcing teaching about the procedure and what to expect afterwards.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because anxiolytics are indicated, but the patient should be NPO. IV anxiolytics will be administered but not a full hour before the procedure. (IV meds will have effect more quickly; PO anxiolytics may take an hour to reach full effect.)
(b) is incorrect because written consent is obtained by the healthcare provider for a tracheostomy. The nurse signs as a witness but cannot obtain the consent.
(d) is incorrect because antibiotics are not often given prophylactically before tracheostomy placement.
Question 42.
A patient underwent surgical tracheostomy placement three days ago. While assessing the patient, the nurse discovers the face and eyelids are puffy and swollen. What is the priority action by the nurse?
(a) Assess the patient’s oxygen saturation
(b) Notify the rapid response team
(c) Oxygenate the patient with a bag-valve-mask
(d) Palpate the skin of the upper chest
Answer:
(a) Assess the patient’s oxygen saturation
Explanation:
This patient has signs and symptoms of subcutaneous emphysema, air that leaks into tissues around the tracheostomy. Oxygenation status should be assessed by the nurse as priority.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because the rapid response team is notified if the patient is unstable. The nurse must first assess for hypoxia before determining whether the rapid response team needs to be called.
(c) is incorrect because oxygenation with a bag-valve-mask may not be indicated.
(d) is incorrect because the skin of the upper chest may be palpated to further assess the extent of the subcutaneous emphysema but not as priority.
Question 43.
The nurse discovers food particles when suctioning a patient's tracheostomy tube. What is the best action by the nurse?
(a) Elevate head of the patient’s bed
(b) Measure and compare cuff pressures
(c) Place the patient on NPO status
(d) Request a swallow study
Answer:
(b) Measure and compare cuff pressures
Explanation:
The patient may be suffering from tracheomalacia, a softening of the tracheal tissue and supporting tracheal cartilage. This can be a result of tissue necrosis caused by abnormally high tracheostomy cuff pressure. Tracheomalacia is often manifested by food in secretions. The nurse may also notice that greater pressure is needed to inflate the tracheostomy cuff than usual.
The nurse should measure the current cuff pressure and compare it to previous pressures documented to determine if cuff pressure is high and how long it has been high. Normal cuff pressure is less than 25cm H20 (14-20 mmHg) and should generally be checked every eight hours.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because elevating the head of bed will not alleviate the situation or help determine the cause.
(c) is incorrect because NPO status will not alleviate the situation or help determine the cause.
(d) is incorrect because a swallow study will not alleviate or confirm tracheomalacia. A chest X-ray is the diagnostic tool needed to verify tracheomalacia.
Question 44.
A patient who had a tracheostomy placed four days ago is fed lunch by an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). That evening, the UAP tells the nurse the patient coughed frequently during lunch. What is the priority action by the nurse?
(a) Immediately assess the patient’s lung sounds
(b) Assign a different patient to the UAP
(c) Report the UAP to the nursing supervisor
(d) Request thicker liquids for meals
Answer:
(a) Immediately assess the patient’s lung sounds
Explanation:
Assessment of lung sounds and oxygenation is priority because this patient may have possibly aspirated.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because assigning the UAP a different patient does not address the safety of the initial tracheostomy patient. The nurse must provide adequate teaching to the UAP before any further patient care activities are performed on any patients.
(c) is incorrect because reporting the UAP to the supervisor should be done after the nurse assesses the patient and then reminds the UAP that abnormal findings (such as frequent coughing while feeding a patient) should always be reported to the RN immediately.
(d) is incorrect because thickening liquids is not priority and does not give any further information about the current status of the lungs.
Question 45.
Tracheostomy care for a patient is provided by the student nurse. During the procedure, which student action would require the instructor to intervene?
(a) Holding the device securely when changing ties
(b) Suctioning the patient prior to tracheostomy care
(c) Tying a square knot at the back of the neck
(d) Using half-strength hydrogen peroxide for cleansing
Answer:
(c) Tying a square knot at the back of the neck
Explanation:
For patient safety, the knot should be placed at the side of the neck for easy access. This can also prevent pressure ulcers from forming at the back of the neck when the patient is laying supine.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because holding the device when changing ties is appropriate. This prevents the tracheostomy from becoming displaced, so no intervention is required.
(b) is incorrect because suctioning the patient for secretions is appropriate, so no intervention is required.
(d) is incorrect because half-strength hydrogen peroxide is appropriate for cleaning during trach care and rinsing the inner cannula. No intervention is necessary.
Question 46.
Tracheostomy skills are being practiced by a nursing student in the simulation lab. Which of the following student actions is an indication that additional teaching is necessary?
(a) Applying suction while inserting the catheter
(b) Preoxygenating the client prior to suctioning
(c) Suctioning for a total of three times, if needed
(d) Suctioning for only 10 to 15 seconds each time
Answer:
(a) Applying suction while inserting the catheter
Explanation:
When suctioning a patient, suction is only applied during withdrawal of the suction catheter. The nursing student should apply suction intermittently and slowly rotate the catheter between the dominant thumb and forefinger as the catheter is withdrawn. This will prevent causing hypoxia.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because preoxygenation is appropriate prior to suctioning. During the suctioning process, the patient will not be able to breathe as effectively through the tracheostomy tube, so it is important to hyperoxygenate before beginning the process. Thus, no additional teaching is necessary.
(c) is incorrect because suctioning should be limited to three times total. The patient should be hyperoxygenated between suction passes. No additional teaching is necessary.
(d) is incorrect because suctioning for 10-15 seconds is appropriate.
Question 47.
A patient is placed on oxygen via nasal cannula in the hospital. When the nurse assesses the patient, which finding indicates the patient is meeting goals for a priority diagnosis?
(a) 100% of meals being eaten by the patient
(b) Intact skin behind the ears
(c) The patient understanding the need for oxygen
(d) Unchanged weight for the past three days
Answer:
(b) Intact skin behind the ears
Explanation:
Anything that applies pressure to the skin, such as oxygen tubing, can cause pressure ulcers. If the skin behind the patient’ ears is intact, this indicates a goal for the nursing diagnosis “risk for impaired skin integrity” is met.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because although this is a good outcome, nutrition is not related to oxygenation.
(c) is incorrect because understanding the need for oxygen is important, but patient education is psychosocial. Physical needs are a greater priority7.
(d) is incorrect because weight consistence is not related to oxygenation.
Question 48.
While assessing a patient, the nurse notes pulsation of the tracheostomy tube corresponding with the pulse rate. The nurse finds no other abnormal assessments. What is the most appropriate action by the nurse?
(a) Call the operating room to inform them of a pending emergency case
(b) No action is needed at this time; this is a normal finding
(c) Remove the tracheostomy tube and ventilate the patient with a bag-valve-mask
(d) Stay with the patient and have someone else call the provider immediately
Answer:
(d) Stay with the patient and have someone else call the provider immediately
Explanation:
A trachea-innominate artery fistula may have formed, which is life-threatening. This is an abnormal connection between the patient’s trachea and a nearby artery. Through this connection, blood from within the artery may pass into the trachea or alternatively, air from within the trachea may cross into the artery.
This is a complication from prolonged endotracheal intubation, cuff over-inflation, or poorly-placed endotracheal tube. Primary threats are respiratory compromise or hemorrhage. The nurse should stay with the patient (provide respiratory support, assess for hemorrhage). The nurse can delegate another member of the nursing team to call the healthcare provider immediately.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the patient will need surgery, but the nurse does not schedule the OR. Bedside care of the deteriorating patient is priority.
(b) is incorrect because this is not a normal finding.
(c) is incorrect because the tube should only be removed if the patient starts hemorrhaging.
Question 49.
The nurse in the oncology clinic cares for a patient diagnosed with throat cancer. The patient had a tracheostomy placed one week ago. Which assessment finding indicates that goals for the nursing diagnosis related to self-esteem are being met?
(a) The patient demonstrates good understanding of stoma care
(b) The patient has joined a book club that meets weekly at the library
(c) Family members take turns assisting with stoma care
(d) Skin around the stoma is intact without signs of infection
Answer:
(b) The patient has joined a book club that meets weekly at the library
Explanation:
An activity that requires the patient to be active in public with other individuals is the best sign for goals related to impaired self-esteem.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because stoma care is important for infection prevention and skin integrity but is not a direct indication of self-esteem.
(c) is incorrect because family members assisting with stoma care are unrelated to the nursing diagnosis.
(d) is incorrect because intact stoma skin is a good outcome, but is unrelated to the nursing diagnosis.
Question 50.
A patient is receiving oxygen via nasal cannula. What task may be performed by the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)?
(a) Applying water-soluble ointment to nares and lips
(b) Increasing the oxygen flow rate if the patient starts to decompensate
(c) Removing the tubing from the patient’s nose
(d) Checking for reddened areas behind the ears where the cannula rests
Answer:
(a) Applying water-soluble ointment to nares and lips
Explanation:
Water-soluble ointment helps with preventing the drying that occurs with oxygen administration. This task is within the scope of practice for the UAP.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because the UAP is not able to make a judgment about whether or not the patient is deteriorating. The UAP can count breaths per minute and can read the pulse-oximetry, but abnormal findings must be reported to the nurse immediately. The nurse will then make the nursing judgment to increase the oxygen flow rate. The UAP cannot adjust oxygen flow.
(c) is incorrect because it is not within the UAP’s scope of practice to remove oxygen.
(d) is incorrect because skin assessment is the responsibility of the RN, and this cannot be delegated.
Question 51.
Lunch has been delivered to a patient receiving oxygen via Venturi mask. What is the best action by the nurse?
(a) Assess the patient’s oxygen saturation and, if normal, turn off the oxygen
(b) Determine if the patient can switch to a nasal cannula during the meal
(c) Have the patient replace the mask back on the face between bites of food
(d) Turn the oxygen off while the patient eats the meal and then restart it
Answer:
(b) Determine if the patient can switch to a nasal cannula during the meal
Explanation:
Oxygen should be delivered constantly, and the nurse should check the patient’s chart to see if switching this patient to a nasal cannula during meals has been approved. Otherwise, the nurse should contact the healthcare provider to discuss the issue.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the oxygen should not be turned off.
(c) is incorrect because removing the oxygen supply to take bites will not meet the patient’s oxygen needs.
(d) is incorrect because the oxygen should not be turned off.
Question 52.
A patient is receiving 50% oxygen via Venturi mask. The nurse assesses the oxygen adjunct and notes the mask fits appropriately and oxygen is flowing at 3 L/min. What is the best action by the nurse?
(a) Assess the patient’s oxygen saturation
(b) Document these findings in the chart
(c) Immediately increase the flow rate
(d) Turn the flow rate down to 2 L/min
Answer:
(c) Immediately increase the flow rate
Explanation:
A Venturi mask is used to deliver a high flow of oxygen between 4 and 12 L/min. This type of oxygen delivery is used most often for critically ill patients who require a specific amount of oxygen administered. This patient’s flow rate is low and should be increased by the nurse.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because oxygen saturation is assessed after flow rate adjusted.
(b) is incorrect because the flow rate is too low.
(d) is incorrect because the flow rate is too low.
Question 53.
A patient is admitted to the emergency room with a nasal fracture. What is the first assessment the nurse should perform?
(a) Facial pain
(b) Vital signs
(c) Bone displacement
(d) Airway patency
Answer:
(d) Airway patency
Explanation:
Maxillofacial fractures can potentially cause airway impairment. Assessing airway is more important than any other assessment answer choice. Other fractures that can impact airway include the clavicles, scapulae, ribs, and sternum.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because pain assessment is not priority over airway.
(b) is incorrect because vital signs are important but not priority. The nurse must assess for a patent airway, good oxygenation, and the presence of bilateral lung sounds. Once airway assessment is completed, vital signs should be measured.
(c) is incorrect because bone displacement will be assessed after the patient is determined to be stable.
Question 54.
A patient tells the nurse they are always tired upon waking, despite getting eight hours of sleep. What is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Contact the provider for a prescription for sleep medication.
(b) Tell the patient not to drink beverages with caffeine before bed.
(c) Educate the patient to sleep upright in a reclining chair.
(d) Ask the patient if they have ever been evaluated for sleep apnea.
Answer:
(d) Ask the patient if they have ever been evaluated for sleep apnea.
Explanation:
Sleep apnea interrupts normal breathing patterns during sleep, preventing the patient from getting a full night’s rest, despite being in bed for eight hours. Many times, patients are not even aware of having sleep apnea. Persistently awaking tired is one of the classic symptoms of sleep apnea. Other conditions to evaluate for include depression, restless leg syndrome, and narcolepsy.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the cause should be identified first.
(b) is incorrect because the nurse should not assume that the patient drinks caffeine before bed.
(c) is incorrect because sleeping in a chair is priority for someone with difficulty breathing while sleeping. This has not been identified in this patient.
Question 55.
A patient with a paralyzed vocal cord is educated by the nurse. For aspiration prevention, what technique does the nurse teach?
(a) Tilt the head back as far as possible when swallowing
(b) Tuck the chin down when swallowing
(c) Breathe slowly and deeply while swallowing
(d) Keep the head very still and straight while swallowing
Answer:
(b) Tuck the chin down when swallowing
Explanation:
Patients who have paralyzed vocal cords in the open position are at risk for aspiration. Tucking in the chin when swallowing will prevent aspiration.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because tilting the head back increases risk of aspiration.
(c) is incorrect because breathing slowly does not decrease risk of aspiration.
(d) is incorrect because limiting movement does not decrease risk of aspiration.
Question 56.
The nurse is assessing four patients on the medical-surgical unit. Which of the following patients does the nurse place at greatest risk for obstructive sleep apnea?
(a) 19-year-old who is eight months pregnant
(b) 65-year-old with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
(c) 42-year-old who is 60 pounds overweight
(d) 75-year-old with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Answer:
(c) 42-year-old who is 60 pounds overweight
Explanation:
Obstructive sleep apnea is closure of the airway when sleeping due to excess weight and tissue. The patient at highest risk is overweight. The risk for sleep apnea is also higher in men with a neck circumference of 17 inches or more (16 inches or more for women) because a large neck has more soft tissue that can block the airway during sleep. Sleep apnea is more common between young adulthood and middle age and more common in men than women. Women’s risk for sleep apnea increases with menopause.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because pregnancy is not a risk for obstructive sleep apnea.
(b) is incorrect because GERD is not a risk for obstructive sleep apnea.
(d) is incorrect because diabetes is not a risk for obstructive sleep apnea.
