Many nursing schools incorporate NCLEX RN Practice Questions into their curriculum to familiarize students with the exam format from early on.
NCLEX Personality Disorders, Substance-Related Disorders, Anxiety Disorders Questions
Personality Disorders, Substance-Related Disorders, Anxiety Disorders NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
A client has been diagnosed with avoidant personality disorder. The client reports loneliness, but has fears about making friends. The client also reports anxiety about being rejected by others. In a long-term treatment plan, in what order, from first to last, should the nurse list interventions for the client? All options must be used.
(a) Teach the client anxiety management and social skills.
(b) Ask the client to join in a chosen activity with the nurse and two other clients.
(c) Talk with the client about self-esteem and fears activities at the center that the client would find interesting.
(d) Help the client make a list of small group activities at the center that the client would find interesting.
Answer:
(c) Talk with the client about self-esteem and fears activities at the center that the client would find interesting.
(a) Teach the client anxiety management and social skills.
(d) Help the client make a list of small group activities at the center that the client would find interesting.
(b) Ask the client to join in a chosen activity with the nurse and two other clients.
Explanation:
(c), (a), (d), (b) The client needs a stepwise plan for developing a social life. The client needs to first work on self-esteem and reduce fears of rejection before talking about how to decrease anxiety and learn new social skills. Helping the client chose interesting activities is important before suggesting an activity. Then, the client will be ready to try a structured activity with the nurse present for support and role modeling.
Question 2.
A client diagnosed with borderline personality disorder has self-inflicted cuts on the arms. The nurse is assessing the client for the risk of suicide. What should the nurse ask the client first?
(a) about medications the client has taken recently
(b) if the client is taking antidepressants
(c) if the client has a suicide plan
(d) why the client self-inflicted the cuts
Answer:
(c) if the client has a suicide plan
Explanation:
The client is at risk for suicide, and the nurse should determine how serious the client is, including if the client has a plan and the means to implement the plan. While medication history may be important, the nurse should first attempt to determine suicide risk. Asking why the client made the self-inflicted cuts will likely cause the client to respond with insufficient information to determine suicide risk.
Question 3.
When developing the plan of care for a client diagnosed with a personality disorder, the nurse plans to assist the client primarily with what factor?
(a) specific dysfunctional behaviors
(b) psychopharmacologic compliance
(c) examination of developmental conflicts
(d) manipulation of the environment
Answer:
(a) specific dysfunctional behaviors
Explanation:
The nurse should plan to assist the client who has a personality disorder primarily with specific dysfunctional behaviors that are distressing to the client or others. The client with a personality disorder has lifelong, inflexible, and dysfunctional patterns of relating and behaving. The client commonly does not view the behavior as distressful. The client becomes distressed because of others’ reactions and behaviors toward the client, which causes the client emotional pain and discomfort.
Psychopharmacologic compliance is not a primary need because medication does not cure a personality disorder. Medication is prescribed if the client has a severe symptom that interferes with functioning, such as severe anxiety or depression. Examination of developmental conflicts usually is not helpful because of the ingrained dysfunctional ways of thinking and behaving. It is more useful to help the client with changing dysfunctional behaviors. Although milieu management is a component of care, the client usually is proficient enough in the manipulation of the environment to meet personal needs.
Question 4.
A client diagnosed with paranoid personality disorder is hospitalized for physically threatening his wife because he suspects her of having an affair with a coworker. What approach should the nurse employ with this client?
(a) authoritarian
(b) parental
(c) matter of fact
(d) controlling
Answer:
(c) matter of fact
Explanation:
For this client, the nurse needs to use a calm, matter-of-fact approach to create a nonthreatening and secure environment because the client is experiencing problems with suspiciousness and trust. Use of “I” statements and responses would be therapeutic to reduce the client’s suspiciousness and increase his trust in the staff and the environment.
An authoritarian approach is nontherapeutic and inappropriate because the client may perceive this approach as an attack, subsequently responding with anger and threatening behavior. A parental or controlling approach may be perceived as authoritarian, and the client may become defensive and angry.
Question 5.
When planning care for a client diagnosed with schizotypal personality disorder, which intervention helps the client become involved with others?
(a) participating solely in group activities
(b) being involved with primarily one-to-one activities
(c) leading a sing-along in the afternoon
(d) attending an activity with the nurse
Answer:
(d) attending an activity with the nurse
Explanation:
Attending an activity with the nurse helps the client to become involved with others slowly. The client with a schizotypal personality disorder needs support, kindness, and gentle suggestion to improve social skills and interpersonal relationships. The client commonly has problems in thinking, perceiving, and communicating and appears similar to clients with schizophrenia except that psychotic episodes are infrequent and less severe.
Participation solely in group activities or leading a sing-along would be too overwhelming for the client, subsequently increasing the client’s anxiety and withdrawal. Engaging primarily in one-to-one activities would not be helpful because of the client’s difficulty with social skills and interpersonal relationships. However, activities with the nurse could be used to establish trust. Then, the client could proceed to activities with others.
Question 6.
A client is complaining to other clients about not being allowed by staff to keep food in the client’s room. What should the nurse do?
(a) Ignore the client’s behavior.
(b) Set limits on the behavior.
(c) Reprimand the client.
(d) Allow the snack to be kept in the client’s room.
Answer:
(b) Set limits on the behavior.
Explanation:
The nurse needs to set limits on the client’s manipulative behavior to help the client control dysfunctional behavior. The manipulative client bends rules to have needs met without regard for rules or the needs or rights of others.
A consistent approach by the staff is necessary to decrease manipulation. Ignoring the client’s behavior reinforces or promotes the continuation of the client’s manipulative behavior. Reprimanding the client may be perceived as a threat, resulting in aggressive behavior. Allowing the client to keep a snack in the client’s room reinforces the dysfunc-tional behavior.
Question 7.
A client with a diagnosis of antisocial personality disorder has a potential for violence and aggressive behavior. Which short-term client outcome is most appropriate for the nurse to include in the plan of care?
(a) Use humor when expressing anger.
(b) Discuss feelings of anger with staff.
(c) Ask the nurse for medication when upset.
(d) Use indirect behaviors to express anger.
Answer:
(b) Discuss feelings of anger with staff.
Explanation:
The nurse assists the client with identifying and putting feelings into words during one- to-one interactions. This helps the client express her feelings in a nonthreatening setting and avoid directing anger toward other clients. A client with an antisocial personality disorder needs to under-stand how others feel and react to her behaviors and why they react the way they do.
The client also needs to understand the consequences of her behaviors. Using humor or indirect behaviors to express anger is a passive-aggressive method that will not help the client learn how to express her anger appropriately. Asking the nurse for medication when upset is a way to avoid dealing with feelings and is not helpful. However, medication may be necessary if talking, and engaging in a physical activity has not been effective in lowering anxiety or if the client is about to lose control of her behavior.
Question 8.
A new client on the psychiatric unit has been diagnosed with depression and obsessive-compulsive personality disorder (OCPD). During visiting hours, her husband states to the nurse that he does not understand this OCPD and what can be done about it. What information should the nurse share with the client and her husband? Select all that apply.
(a) Perfectionism and overemphasis on tasks usually interfere with friendships and leisure time.
(b) It will help to interrupt her tasks and tell her you are going out for the evening.
(c) There are medicines, such as clomipramine or fluoxetine, that may help.
(d) Remind your wife that it is “OK” to be human and make mistakes.
(e) Reinforce with her that she is not allowed to expect the whole family to be perfect too.
(f) This disorder typically involves inflexibility and a need to be in control.
Answer:
(a) Perfectionism and overemphasis on tasks usually interfere with friendships and leisure time.
(c) There are medicines, such as clomipramine or fluoxetine, that may help.
(d) Remind your wife that it is “OK” to be human and make mistakes.
(f) This disorder typically involves inflexibility and a need to be in control.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (f) Inflexibility, need to be in control, perfectionism, overemphasis on work or tasks, and a fear of making mistakes are common symptoms of OCPD. Clomipramine and fluoxetine may help with the obsessive symptoms. Interrupting the client’s tasks is likely to increase her anxiety even more. Telling her that she cannot expect the family to be perfect is likely to create a power struggle.
Question 9.
A client diagnosed with paranoid personality disorder is being admitted on an involuntary 24-hour hold after a physical altercation with a police officer who was investigating the client’s threatening phone calls to his neighbors. He states that his neighbors are spying on him for the government, saying, “I want them to stop and leave me alone. Now they have you nurses and doctors involved in their conspiracy.” Which nursing approaches are most appropriate? Select all that apply.
(a) Approach the client in a professional, matter-of-fact manner.
(b) Avoid intrusive interactions with the client.
(c) Gently present reality to counteract the client’s current paranoid beliefs.
(d) Develop trust consistently with the client.
(e) Avoid pressuring the client to attend any groups.
Answer:
(a) Approach the client in a professional, matter-of-fact manner.
(b) Avoid intrusive interactions with the client.
(d) Develop trust consistently with the client.
(e) Avoid pressuring the client to attend any groups.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e) A professional, matter-of-fact approach and developing trust are the most effective with this client. A friendly approach, intrusiveness, and attempting to counteract the client’s beliefs will increase the client’s paranoia; he will present more false beliefs to prove he is right about the conspiracy. Placing the client in group settings may be counterproductive because questions and emotionality from peers, as well as confrontations with reality, will increase the client’s anxiety.
Question 10.
A young client with a diagnosis of major depression and dependent personality disorder has been living at home with very supportive parents. The client is thinking about independent living on the recommendation of the treatment team. The client states to the nurse, “I don’t know if I can make it in an apartment without my parents.” How should the nurse respond to the client?
(a) “You’re an adult now, not a child who needs to be cared for.”
(b) “Your parents will not be around forever. After all, they’re getting older.”
(c) “Your parents need a break, and you need a break from them.”
(d) “Your parents have been supportive and will continue to be even if you live apart.”
Answer:
(d) “Your parents have been supportive and will continue to be even if you live apart.”
Explaination:
Some characteristics of a client with a dependent personality are an inability to make daily decisions without advice and reassurance and the preoccupation with fear of being alone to care for oneself. The client needs others to be responsible for important areas of his life. The nurse should respond, “Your parents have been supportive of you and will continue to be supportive even if you live apart” to gently challenge the client’s fears and suggest that they may be unwarranted. Stating,
“You’re an adult now, not a child who needs to be cared for” or “Your parents need a break, and you need a break from them” is reprimanding and would diminish the client’s self-worth. Stating, “Your parents will not be around forever; after all, they’re getting older” may be true, but it is an insensitive response that may increase the client’s anxiety.
Question 11.
A client moves in with her family after her boyfriend of 4 weeks told her to leave. She is admitted to the subacute unit after reporting feeling empty and lonely, being unable to sleep, and eating very little for the last week. Her arms are scarred from frequent self-mutilation. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Monitor for suicide and self-mutilation.
(b) Discuss the issues of lonelines and emptiness.
(c) Monitor sleeping and eating behaviours.
(d) Discuss her housing options for after discharge.
Answer:
(a) Monitor for suicide and self-mutilation.
(c) Monitor sleeping and eating behaviours.
(b) Discuss the issues of lonelines and emptiness.
(d) Discuss her housing options for after discharge.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (b), (d) Safety is the priority concern, and then, eating and sleeping patterns need to be reestablished. After intervening to meet basic needs, delving into the loneliness and emptiness are important for determining underlying issues that need to be followed up in outpatient counseling. Although the client is living with her family currently, other options might be appropriate for her to consider.
Question 12.
The client approaches various staff with numerous requests and needs to the point of dis. rupting the staff’s work with other clients. The nurse meets with the staff to decide on a consistent, therapeutic approach for this client. Which approach be most effective?
(a) telling the client to stay in the client’s room until staff approach
(b) limiting the client to the dayroom qnd dining area
(c) giving the client a list of permissible requests
(d) having the client discuss needs vyph the staff person assigned
Answer:
(d) having the client discuss needs vyph the staff person assigned
Explanation:
For the client with attention-seeking behaviors, the nurse would institute a behavioral contract with the client to help decrease dysfunctional behaviors and promote self-sufficiency. Having the client approach only the assigned staff person sets limits on the attention-seeking behavior. Telling the client to stay in the client’s room until staff approach, limiting the client to a certain area, or giving the client a list of permissible requests is punitive and does nothing to help the client gain control over the dysfunctional behavior.
Question 13.
The client with diagnosed borderline personality disorder tells the nurse, “You’re the best nurse here. I can talk to you and you listen. You’re the only one here that can help me.” Which response by the nurse is most therapeutic?
(a) “Thank you; you’re a good person.”
(b) “All of the nurses here provide good care.”
(c) “Other clients have told me that too.”
(d) “Mary and Sam are good nurses too.”
Answer:
(b) “All of the nurses here provide good care.”
Explanation:
The most therapeutic response is “All of the nurses here provide good care.” This statement corrects the client’s unrealistic and exaggerated perception. “Splitting,” defined as the inability to integrate good and bad aspects of an individual and the self, is a hallmark behavior of a client with borderline personality disorder. The client sees his or her self and others as all good or all bad.
Components of “splitting” include behaviors that idealize and devalue others. It is a defense that allows the client to avoid pain and feelings associated with past abuse or a current situation involving the threat of rejection or abandonment. The other statements promote the client’s idealistic view and do nothing to help correct the client’s distortion.
Question 14.
The nurse assesses a client to be at risk for self-mutilation and implements a safety contract with the client. Which client behavior indicates that the contract is working?
(a) The client withdraws to the client’s room when feeling overwhelmed.
(b) The client notifies staff when anxiety is increasing.
(c) The client suppresses feelings when angry.
(d) The client displaces feelings onto the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(b) The client notifies staff when anxiety is increasing.
Explanation:
For the client who is at risk for self-mutilation, the nurse develops a contract to assist the client with assuming responsibility for his behavior and to help the client develop adaptive methods of coping with feelings. Self-mutilation is usually an expression of intense anxiety, anger, helplessness, or guilt or a means to block psychological pain by inducing physical pain.
A typical contract helpful to the client would have the client notify staff when anxiety is increasing. Withdrawing to the client’s room when feeling overwhelmed, suppressing feelings when angry, or displacing feelings onto the HCP J is not an adaptive method to help the client deal with feelings and could still result in self-mutilation.
Question 15.
The client diagnosed with borderline personality disorder who is to be discharged soon threatens to “do something” to herself if discharged. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Request that the client’s discharge be canceled.
(b) Ignore the client’s statement because it is a sign of manipulation.
(c) Ask a family member to stay with the client at home temporarily.
(d) Discuss the meaning of the client’s statement with her.
Answer:
(d) Discuss the meaning of the client’s statement with her.
Explanation:
Any suicidal statement must be assessed by the nurse. The nurse should discuss the client’s statement with her to determine its meaning in terms of suicide, overwhelming feelings of anxiety, abandonment, or other need that the client cannot express appropriately. It is not uncommon for a client with borderline personality disorder to make threatening comments before discharge.
Extending the hospital stay is inappropriate because it would encourage dependency and manipulation. Ignoring the client’s statement on the assumption that it is a sign of manipulation is an error in judgment. Asking a family member to stay with the client temporarily at home is not appropriate and places the responsibility for the client on the family instead of the client.
Question 16.
A young adult client is admitted to a psychiatric unit with a diagnosis of alcohol abuse and personality disorder. The client’s mother states, “He’s always in trouble, just like when he was a boy. Now he’s just a bigger prankster and out of control.” In view of the client’s history, which intervention is most important initially?
(a) letting the client know the staff has the authority to subdue him if he gets unruly
(b) keeping the client isolated from other clients until he is better known by the staff
(c) emphasizing to the client that he will have to pay for any damage he causes
(d) closely observing the client’s behavior to establish a baseline pattern of functioning
Answer:
(d) closely observing the client’s behavior to establish a baseline pattern of functioning
Explanation:
The best initial course of action when admitting a client is to observe him to establish baseline information. This assessment provides valuable information about the client’s behavior and forms the basis for the plan of care. Telling the client that the staff has authority to subdue him if he gets unruly or that he will have to pay for any damage he causes is threatening and may incite or provoke trouble. Isolating a client is not recommended unless there is a very good reason for it, such as a very active, combative client who is dangerous to himself and others.
Question 17.
The client tells the nurse at the outpatient lmc mat she does not need to attend groups because she is not a regular like these other people here.” How should the nurse respond to the client?
(a) because you’re not a regular client, sit in the a when the others are in group.”
(b) "Your family wants you to attend, and they’ll bever disappointed if you don’t.”
(c) "Ill have to mark you absent from the clinic today ‘.and speak to the health care provider about It".
(d) "You say you’re not a regular here, but you’re experiencing what others are experiencing.”
Answer:
(d) "You say you’re not a regular here, but you’re experiencing what others are experiencing.”
Explanation:
The best response is “You say you’re not a regular here, but you’re experiencing what others are experiencing.” This statement helps the client to identify factors that precipitate denial by helping her to confront that which inhibits compliance. Denial is used to help a client feel better and more secure when a situation provokes a high level of anxiety and is threatening to the client.
The statement “Because you are not a regular client, sit in the hall when the others are in group” agrees with and promotes denial in the client and interferes with treatment. The statement “Your family wants you to attend and they will be disappointed if you do not” causes the client to feel guilty and decreases her self-esteem. The statement “I’ll have to mark you absent from the clinic today and speak to the health care provider Q about it” is punitive and threatening to the client, subsequently decreasing her self-esteem.
Question 18.
The client who has a history of angry outbursts when frustrated begins to curse at the nurse during an appointment after being informed that she will have to wait to have her medication refilled. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “You’re being very childish.”
(b) “I’m sorry if you can’t wait.”
(c) “I won’t continue to talk with you if you curse.”
(d) “Come back tomorrow, and your medication will be ready.”
Answer:
(c) “I won’t continue to talk with you if you curse.”
Explanation:
Stating “I won’t continue to talk with you if you curse” sets limits on the client’s behavior and points out the negative effects of her behavior. Therefore, this response is most appropriate and therapeutic. The statement “You’re being very childish” reprimands the client, possibly causing the anger to escalate.
The statement “I’m sorry if you can’t wait” fails to provide feedback to the client about her behavior. The statement “Come back tomorrow, and your medication will be ready” ignores the client’s behavior, failing to provide feedback to the client about the behavior. It also shows poor nursing judgment because the client may need her medication before tomorrow or may not return to the clinic the following day.
Question 19.
Which behavior indicates to the nurse that the client diagnosed with avoidant personality disorder is improving?
(a) interacting with two other clients
(b) listening to music with headphones
(c) sitting at a table and painting
(d) talking on the telephone
Answer:
(a) interacting with two other clients
Explanation:
The client with avoidant personality disorder is showing signs of improvement when interacting with two other clients. A client with avoidant personality disorder is timid, socially uncomfortable, withdrawn, and hypersensitive to criticism. Social contact with others decreases isolation and withdrawal. Listening to music with headphones, sitting at a table and painting, and talking on the telephone are solitary activities and therefore do not indicate improvement, which is evidenced by social contact.
Question 20.
One evening, the client takes the nurse aside and whispers, “Don’t tell anybody, but I’m going to call in a bomb threat to this hospital tonight.” Which action is the priority?
(a) warning the client that his telephone privileges will be taken away if he abuses them
(b) offering to disregard the client’s plan if he does not go through with it
(c) notifying the proper authorities after saying nothing until the client has actually completed the call
(d) explaining to the client that this information will have to be shared immediately with the staff and the health care provider (HCP)
Answer:
(d) explaining to the client that this information will have to be shared immediately with the staff and the health care provider (HCP)
Explanation:
The priority is to explain to the client that this information has to be shared immediately with the staff and the HCP because of its serious nature. Safety of all is crucial regardless of whether the client follows through on his plan. It is possible that the client is asking to be stopped and that he is indirectly pleading for help in a dysfunctional manner.
Bargaining with the client, such as warning him that his telephone privileges will be taken away if he abuses them, or offering to disregard his plan if he does not go through with it, is inappropriate. Saying nothing to anyone until the client has actually completed the call and then notifying the proper authorities represent serious negligence on the part of the nurse.
Question 21.
The nurse orients an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) new to the mental health unit about the principles for the care of a client diagnosed with a personality disorder. What information should the nurse include?
(a) The clients are accepted, although their behavior may not be.
(b) The clients need limits on their behavior.
(c) The staff members are the primary ones left to care about these clients.
(d) The staff should use minimal humor when working with these clients.
Answer:
(a) The clients are accepted, although their behavior may not be.
Explanation:
The most basic and important idea to convey to a client is that, as a person, he or she is accepted, although his or her behavior may not be. Empathy is conveyed for emotional pain regardless of the client’s behavior. Although some clients need limits placed on their behavior, not all clients require limit setting.
That the staff members are the primary ones left to care about these clients is not necessarily true, nor is it true that the staff should use very little humor with these clients. Clients who are rigid and perfectionists and who have a restricted affect may need help with displaying humor.
Question 22.
The nurse is talking with a client who has been diagnosed with antisocial personality disorder about how to socialize during activities without being seductive. The nurse should focus the discussion on which area?
(a) explaining the negative reactions of others toward his behavior
(b) suggesting he apologize to others for his behavior
(c) asking him to explain the reasons for his seductive behavior
(d) discussing his relationship with his mother
Answer:
(a) explaining the negative reactions of others toward his behavior
Explanation:
The nurse should explain the negative reactions of others toward the client’s behaviors to make him aware of the impact of his seductive behaviors on others. Suggesting that the client apologize to others for his behavior is futile because the client cannot feel remorse for wrongdoing. Asking him to explain reasons for his seductive behavior is not helpful because this client is skillful at using projection and rationalization. Discussing his relationship with his mother is not helpful because the focus should be oriented to the present situation and managing his behavior at the present time.
Question 23.
Which approach is most appropriate to use with a client diagnosed with a narcissistic personality disorder when discrepancies exist between what the client states and what actually exists?
(a) limit setting
(b) supportive confrontation
(c) consistency
(d) rationalization
Answer:
(b) supportive confrontation
Explanation:
The nurse would specifically use supportive confrontation with the client to point out discrepancies between what the client states and what actually exists to increase responsibility for self. Limit setting and consistency also may be used. However, limit setting helps the client control unacceptable behavior, and consistency helps reduce the frequency of negative behaviors; they do not point out discrepancies. Rationalization is typically used by the client, not the nurse, to blame others, make excuses, and provide alibis for self-centered behaviors.
Question 24.
The client with histrionic personality disorder is melodramatic and responds to others and situations in an exaggerated manner. The nurse should recommend which activity for this client?
(a) party planning
(b) music group
(c) cooking class
(d) role-playing
Answer:
(d) role-playing
Explanation:
The nurse should use role-playing to teach the client appropriate responses to others in various situations. This client dramatizes events, draws attention to self, and is unaware of and does not deal with feelings. The nurse works to help the client clarify true feelings and learn to express them appropriately. Party planning, music group, and cooking class are therapeutic activities but will not help the client specifically learn how to respond appropriately to others.
Question 25.
A client has been diagnosed with dementia related to chronic and heavy alcohol consumption. In a family meeting with the client, discharge plans are being discussed. Which points should the nurse share with the family and client? Select all that apply.
(a) Even after all alcohol has been removed from the home, clients frequently find ways to get more.
(b) Without continued alcohol intake, the client will gradually get better.
(c) With the memory loss, answer the client’s question once, and then ignore that question when asked again.
(d) Safety alarms on the doors will help to keep the client from wandering off.
(e) As the need for supervision increases, it may be necessary for the client to be placed in an extended care facility.
Answer:
(a) Even after all alcohol has been removed from the home, clients frequently find ways to get more.
(d) Safety alarms on the doors will help to keep the client from wandering off.
(e) As the need for supervision increases, it may be necessary for the client to be placed in an extended care facility.
Explanation:
(a), (d), (e) As with any dementia, there is a need to protect the client from wandering off and risking harm to self. Dementia is progressive and eventually requires 24-hour supervision. The client will find a way to get more alcohol if quitting is not a personal goal. Not answering the client’s question will generally increase the client’s anger. Once the dementia is evident, lack of alcohol intake will not reverse the condition.
Question 26.
In an outpatient addiction group, a recovering client said that before her treatment, her husband drank on social occasions. “Now he drinks at home, from the time he comes home from work and drinks until he goes to bed. He says that he doesn’t like me anymore and that I expect him to do more work on the house and yard. I used to ignore that stuff. I don’t know what to do.” In which order of priority from first to last would the nurse make the comments? All options must be used.
(a) “What do you think you could do to have your husband come in for an evaluation?”
(b) "I hear how confused and frustated you are".
(c) "It can happen that as one person sobers up the spouse deterioates."
(d) "What have you tried to do about your husband's behaviours?"
Answer:
(b) "I hear how confused and frustated you are".
(c) "It can happen that as one person sobers up the spouse deterioates."
(d) "What have you tried to do about your husband's behaviours?"
(a) “What do you think you could do to have your husband come in for an evaluation?”
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d), (a) The client’s feelings and concerns need to be validated so she will open up more. She also should know that the changes in her husband are not unusual. It helps to know the client has tried with her husband to determine if they are appropriate or not. Then, there can be a discussion about getting help for her husband so that her efforts to stay sober are not compromised.
Question 27.
For the client who has difficulty falling asleep at night because of withdrawal symptoms from alcohol, which are abating, which nursing intervention is likely to be most effective?
(a) inviting the client to play a board game with the nurse
(b) allowing the client to sit in the community room until the client feels sleepy
(c) advising the client to take multiple short naps during the day until symptoms improve
(d) teaching the client relaxation exercises to use before bedtime
Answer:
(d) teaching the client relaxation exercises to use before bedtime
Explanation:
The best action by the nurse to help a client who has difficulty falling asleep would be to teach the client relaxation exercises to use before bedtime to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. This activity will also be useful for the client when out of the hospital. Inviting the client to play a board game is inappropriate because this activity can be competitive and thus stimulate the client. Allowing the client to sit in the community room until feeling sleepy is inappropriate because it does nothing to help the client relax. Taking frequent naps can worsen the ability to fall asleep at night.
Question 28.
Which symptoms are expected indications that a client has alcohol withdrawal delirium?
(a) tachycardia
(b) tachypnea
(c) dry, flushed skin
(d) thirst
(e) hypertension
(f) abdominal cramping
Answer:
(a) tachycardia
(b) tachypnea
(e) hypertension
Explanation:
(a), (b), (e) When a client is developing impending alcohol withdrawal delirium, the initial symptoms are a fast pulse and respiratory rate, and an elevated blood pressure. Red, flushed, dry skin and reports of thirst occur with diabetic ketoacidosis. Abdominal cramping and severe diarrhea are symptoms of opiate withdrawal.
Question 29.
A client known to have alcohol dependence is admitted to the emergency department with a temperature of 99°F (37.2°C), a pulse of 110 beats/min, respirations of 26 breaths/min, and blood pressure of 150/98 mm Hg. The blood alcohol level is elevated. Now, the client is becoming belligerent and uncooperative. In which order, from first to last, should the nursing and medical prescriptions be implemented? All options must be used.
(a) Administer lorazepam 2 mg IM.
(b) Draw blood for a magnesium level.
(c) Take vital signs every 15 minutes.
(d) Place the client in a quiet room the with dimmed lights.
Answer:
(d) Place the client in a quiet room the with dimmed lights.
(a) Administer lorazepam 2 mg IM.
(b) Draw blood for a magnesium level.
(c) Take vital signs every 15 minutes.
Explanation:
(d), (a), (b), (c) The nurse should first place the client in a quieter, darkened room with dimmer lights to decrease the stimuli from the busy emergency department and create a more calming environment. Next, the nurse should administer the lorazepam to help decrease agitation and reduce the risk of seizures. Drawing the blood will be easier as the client becomes less agitated.
Depending on the magnesium blood level, the client may need an IM dose of magnesium sulfate to prevent seizures. The nurse can then obtain the vital sign every 15 minutes to determine if the client is becoming stabilized and if the client needs further doses of lorazepam.
Question 30.
A client has been admitted to the emergency department with alcohol withdrawal delirium. The nurse is assessing the client for signs of withdrawal. At 0900 hours on 10/25, the nurse notes that the client is confused. Vital signs are T = 99°F (37.2°C), P = 50 bpm, R = 10 breaths/min, and BP = 100/60 mm Hg. The nurse compares these findings to the nurses’ progress notes from admission 24 hours ago (see exhibit). What should the nurse do first?
|
Date |
Time |
Progress notes |
|
10/24 |
2100 |
t = 99° F (37.2°C); p = 110 ; R = 18; BP = 140/90; client has iv D5 w keep open rates started diazpen administrated as presented client oriented × 3. |
|
10/25 |
0100 |
T = 99.2°F (33.3°C), p = 40 R = 14; BP = 130/80 client resting. |
|
10/25 |
0500 |
T = 99°F (37.2°C) , P = 70 ; R = 14; BP = 126/80; Client oriented × 3. |
(a) Contact the health care Provider (HCP).
(b) lncrease the rate of the IV infusion.
(c) Alternative to arouse the client.
(d) Administer magnesium sulfate.
Answer:
(a) Contact the health care Provider (HCP).
Explanation:
The nurse should first contact the HCP. The client’s vital signs and level of consciousness are deteriorating, indicating complications of withdrawal, which can be life threatening. Increasing the rate of the infusion may cause fluid overload and has not been prescribed by the HCP. Arousing the client will not address the underlying problems. Magnesium sulfate is used to treat seizures precipitated by alcohol withdrawal, but the client is not demonstrating signs of actual or impending seizures.
Question 31.
An intoxicated client is admitted to the hospital for alcohol withdrawal. What should the nurse do to help the client become sober?
(a) Give the client black coffee to drink.
(b) Walk the client around the unit.
(c) Have the client take a cold shower.
(d) Provide the client with a quiet room to sleep in.
Answer:
(d) Provide the client with a quiet room to sleep in.
Explanation:
The nurse should provide the client with a quiet room to sleep in. Alcohol is destroyed and oxidized in the body at a slow, steady rate. The rate of alcohol metabolism is not influenced by drinking black coffee, walking around the unit, or taking a cold shower. Therefore, it is best to have the client sleep off the effects of the alcohol.
Question 32.
The client is admitted to the hospital for alcohol detoxification. Which interventions should the nurse use? Select all that apply.
(a) taking vital signs
(b) monitoring intake and output
(c) placing the client in restraints as a safety measure
(d) reinforcing reality if the client is disoriented or hallucinating
(e) explaining to the client that the symptoms of withdrawal are temporary
Answer:
(a) taking vital signs
(b) monitoring intake and output
(d) reinforcing reality if the client is disoriented or hallucinating
(e) explaining to the client that the symptoms of withdrawal are temporary
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e) For the client experiencing symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, the nurse monitors vital signs and intake and output; reinforces reality for the client who is confused, disoriented, or hallucinating; explains that the symptoms of withdrawal are temporary; reduces stimulation; and stays with the client if he is confused or agitated. The nurse administers medications to prevent the progression of symptoms, such as seizures and delirium tre-mens, and to ensure the client’s safety. Restraints are not used as a precautionary measure. Restraints are used only as a least restrictive measure to protect the client and others when the client is a danger to himself or others.
Question 33.
The nurse is assessing a client who has fallen twice in the last 2 days. The client has been diagnosed with delirium tremens (DTs) following withdrawal from alcohol use. The nurse should further evaluate the client for which complications? Select all that apply.
(a) disorientation
(b) paralysis
(c) elevated temperature
(d) diaphoresis
(e) visual or auditory hallucinations
Answer:
(a) disorientation
(c) elevated temperature
(d) diaphoresis
(e) visual or auditory hallucinations
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (e) Two or three days after cessation of alcohol, clients may experience DTs, as evidenced by disorientation, nightmares, abdominal pain, nausea, and diaphoresis, as well as elevated temperature, pulse, and blood pressure, and visual and auditory hallucinations. If the client had a traumatic brain injury after falling, the client might have paralysis, but there is no association of paralysis from DTs.
Question 34.
A client was discharged from an alcohol rehabilitation program on clonazepam 0.5 mg three times a day. Several months later, the client reports having insomnia, shakiness, sweating, and one seizure. The nurse should first assess the client for which possible symptoms cause?
(a) drinking alcohol with the clonazepam
(b) developing tolerance to the clonazepam
(c) stopping the clonazepam suddenly
(d) increasing the clonazepam dose independently
Answer:
(c) stopping the clonazepam suddenly
Explanation:
The nurse should first confirm that the client has stopped taking the clonazepam because the client is reporting symptoms of benzodiazepine withdrawal from stopping the clonazepam abruptly. The client would report symptoms of being sedated if the client took alcohol with the clonazepam. Tolerance symptoms would be increased anxiety, not these physical symptoms. The client symptoms are consistent with clonazepam withdrawal, not excess; thus, asking about increased use is not relevant.
Question 35.
A client is entering the chemical dependency unit for treatment of alcohol dependency. Which of the client’s possessions should the nurse place in a locked area?
(a) toothpaste
(b) dental floss
(c) shaving cream
(d) antiseptic mouthwash
Answer:
(d) antiseptic mouthwash
Explanation:
Antiseptic mouthwash commonly contains alcohol and should be kept in a locked area unless labeling clearly indicates that the product does not contain alcohol. A client with an intense craving for alcohol may drink mouthwash that contains alcohol. Personal care items, such as toothpaste, dental floss, and shaving cream, do not contain alcohol, and the client would be allowed to keep them in the room.
Question 36.
A client is entering rehabilitation for alcohol dependency as an alternative to going to jail for multiple arrests for driving under the influence. While obtaining the client’s history, the nurse asks about the amount of alcohol the client consumes daily. The client responds, “I just have a few drinks with my friends after work.” Which response by the nurse is most therapeutic?
(a) “That’s what all the clients here say at first.”
(b) “Then you should have had a designated driver for yourself.”
(c) “I guess you just can’t handle a few drinks.”
(d) “You say you have a few drinks, but you have multiple arrests.”
Answer:
(d) “You say you have a few drinks, but you have multiple arrests.”
Explanation:
The best way to intervene with a client’s minimization or denial of alcohol problems is to point out the consequences of the drinking the multiple arrests. The other responses are superficial and discount the seriousness of the client’s problem.
Question 37.
While admitting a client to the alcohol treatment program, the nurse asks the client how long she has been drinking, how much she has been drinking, and when she had her last drink. The client replies that she has been drinking about a liter of vodka a day for the past week and her last drink was about an hour ago. This information helps the nurse to determine which factor?
(a) the severity of the disease
(b) the severity of withdrawal symptoms
(c) the possibility of alcoholic hallucinosis
(d) the occurrence of delirium tremens
Answer:
(b) the severity of withdrawal symptoms
Explanation:
The client’s response helps the nurse determine the severity of withdrawal symptoms because the length and extent of drinking alcohol has an effect on the severity of symptoms the client experiences during withdrawal. Decreased use of alcohol can also result in withdrawal symptoms in the client who has developed a high tolerance to alcohol and is physically dependent. The severity of the disease, the possibility of hallucinations, and the occurrence of delirium tremens are not determined by the information given.
The diagnosis of alcohol dependency is just that it is not classified as mild, moderate, or severe. Alcoholic hallucinosis is a state of auditory hallucinations that develops about 48 hours after the client has stopped drinking. The client hears voices or noises within the context of a clear sensorium, meaning that the auditory hallucination is the only symptom the client experiences.
Severe withdrawal symptoms that are not managed medically can progress to delirium tremens or a severe absti-nence syndrome. Delirium tremens occurs about 3 to 5 days after the client's last drink and is characterized by confusion, agitation, severe psychomotor activity, hallucinations, sleeplessness, tachycardia, elevated blood pressure, elevated temperature, and possibly seizures.
Question 38.
A client who is experiencing alcohol withdrawal exhibits tremors, diaphoresis, and hyperactivity. Blood pressure is 190/87 mm Hg, and pulse is 92 bpm. Which medication should the nurse expect to administer?
(a) haloperidol
(b) lorazepam
(c) benztropine
(d) naloxone
Answer:
(b) lorazepam
Explanation:
The nurse would most likely administer a benzodiazepine, such as lorazepam, to the client who is experiencing symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. The benzodiazepine substitutes for the alcohol to suppress withdrawal symptoms. The client experiences symptoms of withdrawal because of the “rebound phenomenon” when sedation of the central nervous system (CNS) from alcohol begins to decrease.
Haloperidol is an antipsychotic and is not indicated for alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Benztropine is used to treat extrapyramidal symptoms associated with antipsychotic therapy. Naloxone is used in opioid overdose to reverse the CNS depression caused by the opioid.
Question 39.
Which assessment provides the best information about the client’s physiologic response and the effectiveness of the medication prescribed specifically for alcohol withdrawal?
(a) nutritional status
(b) evidence of tremors
(c) vital signs
(d) sleep pattern
Answer:
(c) vital signs
Explanation:
Monitoring vital signs provides the best information about the client’s overall physiologic status during alcohol withdrawal and the physiologic response to the medication used. Vital signs reflect the degree of central nervous system irritability and indicate the effectiveness of the medication in easing withdrawal symptoms. Although assessment of nutritional status and sleep pattern and assessment for evidence of tremors are important, they provide only indirect information about single aspects of the client’s physiologic status.
Question 40.
A client who had been drinking heavily over the weekend could not remember specific events of where the client had been or what the client had done. The nurse interprets this information as indicating that the client experienced which condition?
(a) blackout
(b) hangover
(c) tolerance
(d) delirium tremens
Answer:
(a) blackout
Explanation:
A client is suffering from a blackout when the client cannot recall what he or she did while under the influence of alcohol. A hangover refers to symptoms experienced the day after a bout of heavy drinking. Common symptoms include headaches and gastrointestinal distress, typically after heavy alcohol consumption. Tolerance refers to the need to increase the amount of the substance or to ingest the substance more often to achieve the same effects. Delirium tremens refers to severe alcohol withdrawal or abstinence syndrome with confusion, psychomotor agitation, sleeplessness, hallucinations, and elevated vital signs.
Question 41.
A client is entering the alcohol treatment program for the fourth time in 5 years. Which statement by the nurse will be most helpful to the client?
(a) “I hope you’re serious about maintaining your sobriety this time.”
(b) “I don’t know you from past attempts, but you’ll get it right this time.”
(c) “I know someone who was successful after the fifth program.”
(d) “I’m a nurse in the program. The staff and I will help you through the program.”
Answer:
(d) “I’m a nurse in the program. The staff and I will help you through the program.”
Explanation:
Stating “I’m a nurse in the program; the staff and I will help you” is a nonjudgmental, caring approach that promotes trust and a therapeutic relationship. The statement “I hope you’re serious about maintaining your sobriety this time” blames the client, subsequently decreasing the client’s self-worth. Saying “You’ll get it right this time” is threatening to the client, possibly leading to decreased self-worth by reinforcing the client’s past failures at maintaining sobriety. The statement “I know someone who was successful after the fifth program” is impersonal and irrelevant to the client’s situation.
Question 42.
The wife of a client with alcohol dependency tells the nurse, “I’m tired of making excuses for him to his boss and coworkers when he can’t make it into work. I believe him every time he says he’s going to quit.” The nurse recognizes the wife’s statement as indicating which behavior?
(a) helpfulness
(b) self-defeat
(c) enabling
(d) masochism
Answer:
(c) enabling
Explanation:
The wife of the man with alcohol dependency is exhibiting enabling behavior when she makes excuses for her husband’s absenteeism. Enabling behavior is not helpful to the client but rescues him from adverse consequences in relation to his employment. Self-defeating behavior would be evidenced by putting oneself in a position that will lead to failure. Masochistic behavior would be evidenced by the need to experience emotional or physical pain to become sexually aroused.
Question 43.
Which statement by the nurse participating in a group confrontation of a coworker is most helpful in reducing the coworker’s denial about alcohol being a problem?
(a) “Your behavior is unprofessional.”
(b) “As a nurse, you should have sought help earlier.”
(c) “Nurses are the worst when it comes to asking for help.”
(d) “You have alcohol on your breath.”
Answer:
(d) “You have alcohol on your breath.”
Explanation:
To be most helpful, the nurse should calmly and objectively present facts by saying “You have alcohol on your breath” to help the coworker overcome denial and resistance. This statement also helps to reinforce the coworker’s awareness of the problem. The other statements blame the coworker and may reinforce denial. Blaming, nagging, and yelling diminish self-esteem in the individual with a substance abuse problem who has low frustration tolerance.
Question 44.
A nurse working in an alcohol rehabilitation program is teaching staff how to give clients constructive feedback. Which statement given as an example illustrates that the staff member understands the nurse’s teaching regarding the use of constructive feedback?
(a) “I think you’re a real con artist.”
(b) “You’re dominating the conversation.”
(c) “You interrupted twice in 4 minutes.”
(d) “You don’t give anyone a chance to finish talking.”
Answer:
(c) “You interrupted twice in 4 minutes.”
Explanation:
The statement “You interrupted twice in 4 minutes” indicates an understanding of the use of constructive feedback by describing specifically what was seen and heard in an objective manner. The other statements are judgmental and blame the client without specifying what the objectionable behavior is.
Question 45.
A client ashamedly tells the nurse that he f, his wife while intoxicated and asks the nurse if h nt wife will ever forgive him. What is the nurse’s most appropriate response?
(a) “Perhaps you could ask her and find out".
(b) “That is something you can explore in family therapy.”
(c) “It would depend on how much she really cares for you.”
(d) “You seem to have some feelings about hitting your wife.”
Answer:
(d) “You seem to have some feelings about hitting your wife.”
Explanation:
The client is feeling remorse about hitting his wife. It is best to make a comment that will help him focus on his feelings and express them. Reflecting what the client has said is a good technique to accomplish these goals. Suggesting the client ask his wife or explore the issue in family therapy is inappropriate because it gives advice and ignores the client’s underlying feelings. Saying “It would depend on how much she really cares for you” is inappropriate because it ignores the client’s feelings and reinforces the negative aspects such as the shamefulness of the behavior.
Question 46.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with an elevated blood alcohol level. The authorities state he was driving on the wrong side of the road. He is transferred to the acute care unit where he awakens the next morning. His vital signs are stable, and he has a headache. What should the nurse do first when caring for this client?
(a) Work through personal feelings related to substance use/abuse.
(b) Be persistent with the client regarding the substance use.
(c) Help to make abstinence and sobriety worthwhile for the client.
(d) Suggest a treatment program within the client’s home area.
Answer:
(a) Work through personal feelings related to substance use/abuse.
Explanation:
The nurse must work through personal feelings related to substance use. Negative feelings towards individuals with substance use problems may make the nurse prejudiced against this client. Being persistent with the client regarding the substance abuse, helping to make abstinence and sobriety worthwhile for the client, and suggesting a treatment program near the client’s home all are interventions that the nurse can accomplish after the initial approach to the client.
Question 47.
Which nursing action is contraindicated for the client who is experiencing severe symptoms of alcohol withdrawal?
(a) helping the client walk
(b) monitoring intake and output
(c) assessing vital signs
(d) using short, concrete statements
Answer:
(a) helping the client walk
Explanation:
Having the client who is experiencing severe symptoms of alcohol withdrawal walk is contraindicated because increased activity and stimulation may confuse the client and promote hallucinations. The client may also sustain an injury if the client has a seizure as part of the alcohol with-drawal process.
The nurse should monitor intake and output to ensure fluid and electrolyte balance and hydration. The nurse should assess vital signs to assess the physiologic status of the client and the response to medications. The nurse should use short, concrete statements to decrease confusion and ambiguity.
Question 48.
Which client statement indicates to the nurse that the client needs further teaching about disulfiram?
(a) “I can drink one or two beers and not get sick while on disulfiram.”
(b) “I can take disulfiram at bedtime if it makes me sleepy.”
(c) “A metallic or garlic taste in my mouth is normal when starting on disulfiram.”
(d) “I’ll read the labels on cough syrup and mouthwash for possible alcohol content.”
Answer:
(a) “I can drink one or two beers and not get sick while on disulfiram.”
Explanation:
Any amount of alcohol consumed while taking disulfiram can cause an alcohol-disulfiram reaction. The reaction experienced is in proportion to the amount of alcohol ingested. The alcohol- disulfiram reaction can begin 5 to 10 minutes after alcohol is ingested. Symptoms can be mild, as in flushing, throbbing in the head and neck, nausea, and diaphoresis. Other symptoms include vomiting, respiratory difficulty, hypotension, vertigo, syncope, and confusion. Severe reactions involve respiratory depression, convulsions, coma, and even death.
Disulfiram can be taken at bedtime if the client feels sleepy from the medication. Some clients experience a metallic or garlic taste when initiating disulfiram treatment. Anything containing alcohol, such as cough medicine, aftershave lotion, and mouthwash, can cause a reaction. Therefore, the client needs to check the labels of these items for his or her alcohol content.
Question 49.
While receiving disulfiram therapy, the client becomes nauseated and vomits severely. Which question should the nurse ask first?
(a) “How long have you been taking disulfiram?”
(b) “Do you feel like you have the flu?”
(c) “How much alcohol did you drink today?”
(d) “Have you eaten any foods cooked in wine?”
Answer:
(c) “How much alcohol did you drink today?”
Explanation:
The first question should be to ask the client how much alcohol he or she has had today because nausea with severe vomiting is a sign of an alcohol-disulfiram reaction. Asking whether the client feels flu symptoms is important after inquiring about alcohol intake. Foods cooked in an alcoholic beverage, such as wine, could also cause a reaction, but the reaction would be less severe because the alcohol dissipates with cooking. Asking how long the client has been taking disulfiram would be least important at this time.
Question 50.
The client being treated for alcohol addiction is’, receiving thiamine. What is the expected outcome foi' using thiamine with this client?
(a) Prevent the development of Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
(b) Decrease client’s withdrawal symptoms.
(c) Aid the client in regaining strength sooner.
(d) Promote elimination of alcohol from the body faster.
Answer:
(a) Prevent the development of Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
Explanation:
Thiamine specifically prevents the development of Wernicke’s encephalopathy, a reversible amnestic disorder caused by a diet deficient in thiamine secondary to poor nutritional intake that commonly accompanies chronic alcoholism. It is characterized by nystagmus, ataxia, and mental status changes. Because the client would rather drink alcohol than eat, the client is depleted of vitamins and nutrients.
Alcohol also is an irritant that causes a “malabsorption syndrome” in which vitamins and nutrients are not absorbed properly in the gastrointestinal tract. Thiamine is not associated with decreasing withdrawal symptoms, helping clients regain their strength, or promoting elimination of alcohol from the body.
Question 51.
Which client statement indicates an understanding of the risk of alcohol relapse?
(a) “I knbw I can stay dry if my wife keeps alcohol opt of the house.”
(b) “Stoppling support groups and not expressing feelings can lead to relapse.”
(c) “I’ll ha ve my support group sponsor keep the list of symptoms for me.”
(d) “If someone tells me I’m about to relapse, I’ll be sure to do something about it.”
Answer:
(b) “Stoppling support groups and not expressing feelings can lead to relapse.”
Explanation:
The statement “Stopping support groups and not expressing feelings can lead to relapse” indicates the client’s understanding of risk of relapse. The client is responsible for sobriety and must understand the risk and signs of relapse. Other antecedents to relapse include severe craving, being around users, and severe emotional crises. The other statements place the responsibility for the client’s sobriety on someone else.
Question 52.
The client sees no connection between her liver disorder and her alcohol intake. She believes that she drinks very little and that her family is making something out of nothing. The nurse interprets these behaviors as indicative of the client’s use of which defense mechanisms?
(a) denial
(b) displacement
(c) rationalization
(d) reaction formation
Answer:
(a) denial
Explanation:
The client is using denial, an unconscious defense mechanism, when she refuses to acknowledge that she has a problem with alcohol. This is further evidenced by the client’s inability to connect the liver disorder with alcohol ingestion. Displacement involves transfer of a feeling to someone else or to an object. Rationalization involves an attempt to make or prove that one’s feeling or behavior is justifiable. Reaction formation is a conscious behavior that is the exact opposite of an unconscious feeling.
Question 53.
Which food should the nurse eliminate from the diet of a client in alcohol withdrawal?
(a) milk
(b) regular coffee
(c) orange juice
(d) eggs
Answer:
(b) regular coffee
Explanation:
Regular coffee contains caffeine, which acts as a psychomotor stimulant and leads to feelings of anxiety and agitation. Serving coffee to the client may add to tremors and wakefulness. Milk, orange juice, and eggs are part of a well-balanced, high-protein diet needed by the client in alcohol withdrawal, who is nutritionally depleted.
Question 54.
A client with alcohol dependency has peripheral neuropathy. The nurse should develop a teaching plan that emphasizes which action?
(a) washing and drying the feet daily
(b) massaging the feet with lotion
(c) trimming the toenails carefully
(d) avoiding use of an electric blanket
Answer:
(d) avoiding use of an electric blanket
Explanation:
The nurse should teach the client with peripheral neuropathy to avoid using an electric blanket because the client is likely to have decreased sensitivity in the extremities owing to the damaging effects of alcohol on the nerve endings.
It is particularly important to guard against burns because the client may not be able to discern the appropriate degree of heat on the feet. Daily washing and drying, massaging with lotion, and trimming the toenails are appropriate foot care measures for any client.
Question 55.
A client experiencing alcohol withdrawal wakes up and screams, “There is something crawling under my skin! Help me!” What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Remind the client that this is a withdrawal symptom and that these symptoms will be treated.
(b) Administer a dose of loreazean depending on the severity of the withdrawl symptoms.
(c) Assess the client for other withdrawal symptoms.
(d) Take the client’s vital signs.
Answer:
(a) Remind the client that this is a withdrawal symptom and that these symptoms will be treated.
(b) Administer a dose of loreazean depending on the severity of the withdrawl symptoms.
(c) Assess the client for other withdrawal symptoms.
(d) Take the client’s vital signs.
Explanation:
(a), (d), (b), (c), After the nurse reminds the client about this withdrawal symptom, the nurse should take the client’s vital signs and then assess for other symptoms, such as visual and auditory disturbances, tremors, anxiety, nausea, and excess perspiration. The elevation of the vital signs also helps to determine the amount of lorazepam needed to control the withdrawal symptoms. The nurse should then chart the details of the episode and outcomes of the interventions.
Question 56.
Which measure should the nurse include in the plan of care for a client with alcohol withdrawal delirium?
(a) using restraints continuously
(b) touching the client before saying anything
(c) remaining with the client when the client is confused or disoriented
(d) informing the client about alcohol treatment programs
Answer:
(c) remaining with the client when the client is confused or disoriented
Explanation:
The client with alcohol withdrawal delirium should not be left unattended when confused, disoriented, or hallucinating. Injury or unintentional suicide is a possibility when the client attempts to get away from hallucinations. Restraints are used only when the client loses control and is a danger to herself or others.
Touching the client before saying anything is an additional stimulus that would most likely add to the client’s agitation. Informing the client about the alcohol treatment program while the client is delirious is inappropriate and shows poor nursing judgment. The client should be given information about alcohol treatment when the withdrawal symptoms are lessening and the client can comprehend the information.
Question 57.
A client is to be discharged from an alcohol rehabilitation program. What should the nurse emphasize in the discharge plan as a priority?
(a) supportive friends
(b) a list of goals
(c) returning to work
(d) follow-up care
Answer:
(d) follow-up care
Explanation:
Follow-up care is essential to prevent relapse. Recovery has just begun when the treatment program ends. The first few months after program completion can be difficult and dangerous for the chemically dependent client. The nurse is responsible for discharge plans that include arrangements for counseling, self-help group meetings, and other forms of aftercare. Supportive friends, a list of goals, and returning to work may be important and helpful to the client, but follow-up care is essential.
Question 58.
The client is to be discharged from the hospital after a safe, medically supervised withdrawal from alcohol. Which outcomes indicate client readiness for an outpatient alcohol treatment program? Select all that apply.
(a) The client states the need to cut down on alcohol intake.
(b) The client verbalizes the damaging effects of alcohol on the body.
(c) The client plans to attend support group meetings.
(d) The client takes naltrexone daily.
(e) The client reports feeling indestructible.
Answer:
(b) The client verbalizes the damaging effects of alcohol on the body.
(c) The client plans to attend support group meetings.
(d) The client takes naltrexone daily.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d) The client who plans to attend support group meetings, verbalizes the damaging effects of alcohol on the body, and takes naltrexone daily may be ready for alcohol rehabilitation. Other key outcomes include admitting that a problem with alcohol exists and realizing the negative effects of alcohol on his life. Stating that the client needs only to cut down on alcohol intake and that the client is indestructible are signs of denial of an alcohol problem.
Question 59.
A client diagnosed with major depression and substance dependence is being admitted to the concurrent disorder treatment unit. In explaining the focus of this program, the nurse should tell what information to the client?
(a) The addiction will be treated first, then the depression.
(b) The depression will be treated first, then the addiction.
(c) There will be simultaneous treatment of the addiction and depression.
(d) As the addiction is treated, the depression will clear up on its own.
Answer:
(c) There will be simultaneous treatment of the addiction and depression.
Explanation:
The best approach is to treat both illnesses simultaneously. Treating one and not the other is ineffective. The depression will not clear just by becoming sober or clean.
Question 60.
While caring for a client who has a bipolar disorder and alcohol dependency, which area is the priority for daily assessment?
(a) sleep pattern
(b) mental status
(c) eating habits
(d) self-care ability
Answer:
(b) mental status
Explanation:
The nurse should assess the client’s mental status daily to note changes that could occur from exacerbation of the mental illness or withdrawal from alcohol. Changes in mental status are important for treatment issues such as medication and participation in groups. Assessment of mental status takes priority because mental status affects the client’s ability to sleep, eat, and care for himself. Flexibility is necessary on the part of nurses and staff members who are working with a heterogeneous client population.
Question 61.
The nurse cares for a client admitted to the emergency department after being found lying on the bathroom floor with several empty pill bottles around her. While waiting for a psychiatric consult, the nurse discovers that the client’s boyfriend has recently broken up with her. Which response is most likely to build and maintain a therapeutic relationship within the emergency department?
(a) “You will have other boyfriends.”
(b) “I know that this hurts.”
(c) “Why did you try to kill yourself?”
(d) “What can I do to help while you are here?”
Answer:
(d) “What can I do to help while you are here?”
Explanation:
Using a client-centered approach to care will most effectively establish a therapeutic relationship. Minimizing the pain the client experiences because of the breakup does not acknowledge that at the present time, the client is in significant distress. Asking “why” suggests that the nurse is judging the appropriateness of the actions and does not demonstrate empathy.
Question 62.
A client is admitted to the hospital following an inadvertent overdose with oxycodone. He reveals that he has chronic back pain that resulted from an injury on a construction site. He states, “I know I took too much oxycodone at once, but I can’t live with this pain without them. You can’t take them away from me.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “Once you’re tapered off the oxycodone, you will find that nonaddictive pain medicines will be enough to control your pain.”
(b) “You’re going to be switched from the oxycodone to methadone for long-term pain management.
(c) “The oxycodone will be stopped tomorrow, but you’ll have lorazepam to help you with the withdrawal symptoms.”
(d) “Your pain will be controlled by tapering doses of oxycodone and with other pain management strategies and medicines.”
Answer:
(d) “Your pain will be controlled by tapering doses of oxycodone and with other pain management strategies and medicines.”
Examination:
Tapering doses of oxycodone, pain management strategies, and other pain control medicines are found to be the most helpful with opiate addictions resulting from chronic pain. Nonaddictive (over-the-counter) medicines alone are gener-ally insufficient for chronic pain management. Methadone is an addictive opioid that involves substituting one addiction with another, so now clients are being detoxed off methadone as well. Lorazepam may help with anxiety during withdrawal from opiates, but it does not control the other symptoms of opiate withdrawal.
Question 63.
A school nurse is planning a program for parents on “Drugs Commonly Abused by Teenagers.” Which information should be included about inhalants? Select all that apply.
(a) Monitor for paper bags and rags that may have been used for breathing inhalants.
(b) Brain damage is unlikely with the use of inhalants.
(c) Use of inhalants by teens is on the declin e
(d) Deaths from inhalants occur from asphyxation, suffocation, and aspiration of vomit.
(e) Inhalants usually cause depression of central nervous system.
(f) The basic groups of inhalants are hydrocarbon solvents such as glue, aerosol Propellants from spray cans, and anesthetics/gases.
Answer:
(a) Monitor for paper bags and rags that may have been used for breathing inhalants.
(d) Deaths from inhalants occur from asphyxation, suffocation, and aspiration of vomit.
(e) Inhalants usually cause depression of central nervous system.
(f) The basic groups of inhalants are hydrocarbon solvents such as glue, aerosol Propellants from spray cans, and anesthetics/gases.
Explanation:
(a), (d), (e), (f) The nurse should instruct the parents to monitor their children for use of paper bags or rags. The nurse should present information about brain damage from inhalants including damage to the frontal lobe, cerebellum, and hippocampus, and that death is possible. Rather than use being on the decline, teenagers are experimenting even more with many types of inhalants, such as Freon, ground-up candy disks, and spray cleaners for computer and TV screens.
Question 64.
The friend of a client brought to the emergency department states, “I guess she had some bad heroin today.” The client is drowsy and verbally nonresponsive. Which finding is of immediate concern to the nurse?
(a) respiratory rate of 9 breaths/min
(b) urinary retention
(c) hypotension
(d) reduced pupil size
Answer:
(a) respiratory rate of 9 breaths/min
Explanation:
A respiratory rate of < 12 breaths/min is cause for concern because it indicates central nervous system depression. Respiratory depression and arrest is the primary cause of death among clients who abuse opioids. Peripheral nervous system effects associated with opioid abuse include urinary retention, hypotension, reduced pupil size, constipation, and decreased gastric, biliary, and pancreatic secretions. Pinpoint pupils are a sign of opioid overdose. However, respiratory depression is the immediate concern.
Question 65.
A client is brought to the emergency department by a friend who states, “He was using a lot of heroin until he ran out of money about 2 days ago.” The nurse judges the client to be in opioid withdrawal if he exhibits which sign or symptom? Select all that apply.
(a) rhinorrhea
(b) diaphoresis
(c) piloerection
(d) synesthesia
(e) formication
Answer:
(a) rhinorrhea
(b) diaphoresis
(c) piloerection
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c) Symptoms of opioid withdrawal include yawning, rhinorrhea, sweating, chills, piloerection (goose bumps), tremors, restlessness, irritability, leg spasms, bone pain, diarrhea, and vomiting. Symptoms of withdrawal occur within 36 to 72 hours of usage and subside within a week. Withdrawal from heroin is seldom fatal and usually does not necessitate medical intervention. Synesthesia (a blending of senses) is associated with lysergic acid diethylamide use, and formication (feeling of bugs crawling beneath the skin) is associated with cocaine use.
Question 66.
An unconscious client in the emergency department is given IV naloxone due to an overdose of heroin. Which findings would indicate a therapeutic response to the naloxone? Select all that apply.
(a) decreased pulse rate
(b) warm moist skin
(c) dilated pupils
(d) increased respirations
(e) consciousness
Answer:
(d) increased respirations
(e) consciousness
Explanation:
(d), (e) Naloxone is an opioid antagonist used to treat an opioid overdose. Within a few minutes, the client should have an increase of respirations to near normal and become conscious. With a heroin overdose, the pulse is not significantly affected, the skin becomes warm and wet, and the pupils are dilated. With naloxone, the skin would return to a normal temperature and become dry. The pupils also would react normally, and the pulse would not be decreased.
Question 67.
Which findings should the nurse expect to assess for a client who is exhibiting late signs of heroin withdrawal?
(a) vomiting and diarrhea
(b) yawning and diaphoresis
(c) lacrimation and rhinorrheaxpl
(d) restlessness and irritability
Answer:
(a) vomiting and diarrhea
Explanation:
Vomiting and diarrhea are usually late signs of heroin withdrawal, along with muscle spasm, fever, nausea, repetitive sneezing, abdominal cramps, and backache. Early signs of heroin withdrawal include yawning, tearing (lacrimation), rhinorrhea, and sweating. Intermediate signs of heroin withdrawal are flushing, piloerection, tachycardia, tremor, restlessness, and irritability.
Question 68.
When teaching a client who is to receive methadone therapy for opioid addiction, the nurse should instruct the client that methadone is useful primarily for what reason?
(a) It is not an addictive substance.
(b) A maintenance dose is taken twice a day.
(c) The client will no longer be addicted to opioids.
(d) The client may work and live normally.
Answer:
(d) The client may work and live normally.
Explanation:
The client takes methadone primarily to be able to work, live normally, and function productively without the mental and physical deterioration caused by opioid addiction. Methadone lessens physiologic dependence on opioids and is used to prevent withdrawal symptoms. Methadone, a substance similar to morphine, is an addictive substance; the client is still considered addicted to opioids. Because methadone has a long half-life of 15 to 30 hours, it can be taken once a day on an outpatient basis.
Question 69.
A client recovering from narcotic addiction states to the nurse, “I’m not going anymore to support group meetings. I felt out of place there.” Which response by the nurse is best?
(a) “Try attending a meeting at a different location; you may feel more comfortable there.”
(b) “Maybe it just wasn’t a good day for you. Everybody has bad days now and then.”
(c) “Perhaps you weren’t paying close enough attention to what they were saying.”
(d) “Somet imes the meetings can seem like a waste of time, but you need to attend to stay clean.”
Answer:
(a) “Try attending a meeting at a different location; you may feel more comfortable there.”
Explanation:
Suggesting that the client try attending a meeting at a different location is a supportive, positive response and encourages the client to continue participating in treatment. Saying “Maybe it just wasn’t a good day for you” or “Perhaps you weren’t paying close enough attention” places blame on the client and is not helpful. The statement “Sometimes the meetings can seem like a waste of time, but you need to attend to stay clean” diminishes the importance of the self-help group and offers little support to the client.
Question 70.
Which outcome should the nurse use as the best measure to determine a client’s progress in rehabilitation?
(a) the kinds of friends the client makes
(b) the number of drug-free days the client has
(c) the way the client gets along with his or her parents
(d) the amount of responsibility the client’s job details
Answer:
(b) the number of drug-free days the client has
Explanation:
The best measure to determine a client’s progress in rehabilitation is the number of drug-free days the client has. The longer the client abstains, the better the prognosis is. Although the kinds of friends the client makes, the way the client gets along with his or her parents, and the degree of responsibility the client’s job requires could influence the client’s decision to stay clean, the number of drug-free days is the best indicator of progress.
Question 71.
Which finding would lead the nurse to suspect that a client is addicted to heroin?
(a) hilarity
(b) aggression
(c) labile mood
(d) hypoactivity
Answer:
(d) hypoactivity
Explanation:
The client who is addicted to heroin is most likely to exhibit hypoactivity. Initially, the client feels euphoric. This is followed by drowsiness, hypoactivity, anorexia, and a decreased sex drive. Hilarity, aggression, and a labile mood usually are not associated with heroin addiction.
Question 72.
A client brought by ambulance to the emergency department after taking an overdose of barbiturates is comatose. The nurse should assess the client for which complication?
(a) kidney failure
(b) cerebrovascular accident
(c) status epilepticus
(d) respiratory failure
Answer:
(d) respiratory failure
Explanation:
Because barbiturates are central nervous system depressants, the nurse should be especially alert for the possibility of respiratory failure. Respiratory failure is the most likely cause of death from barbiturate overdose. Kidney failure, cerebrovascular accident, and status epilepticus are not associated with barbiturate overdose.
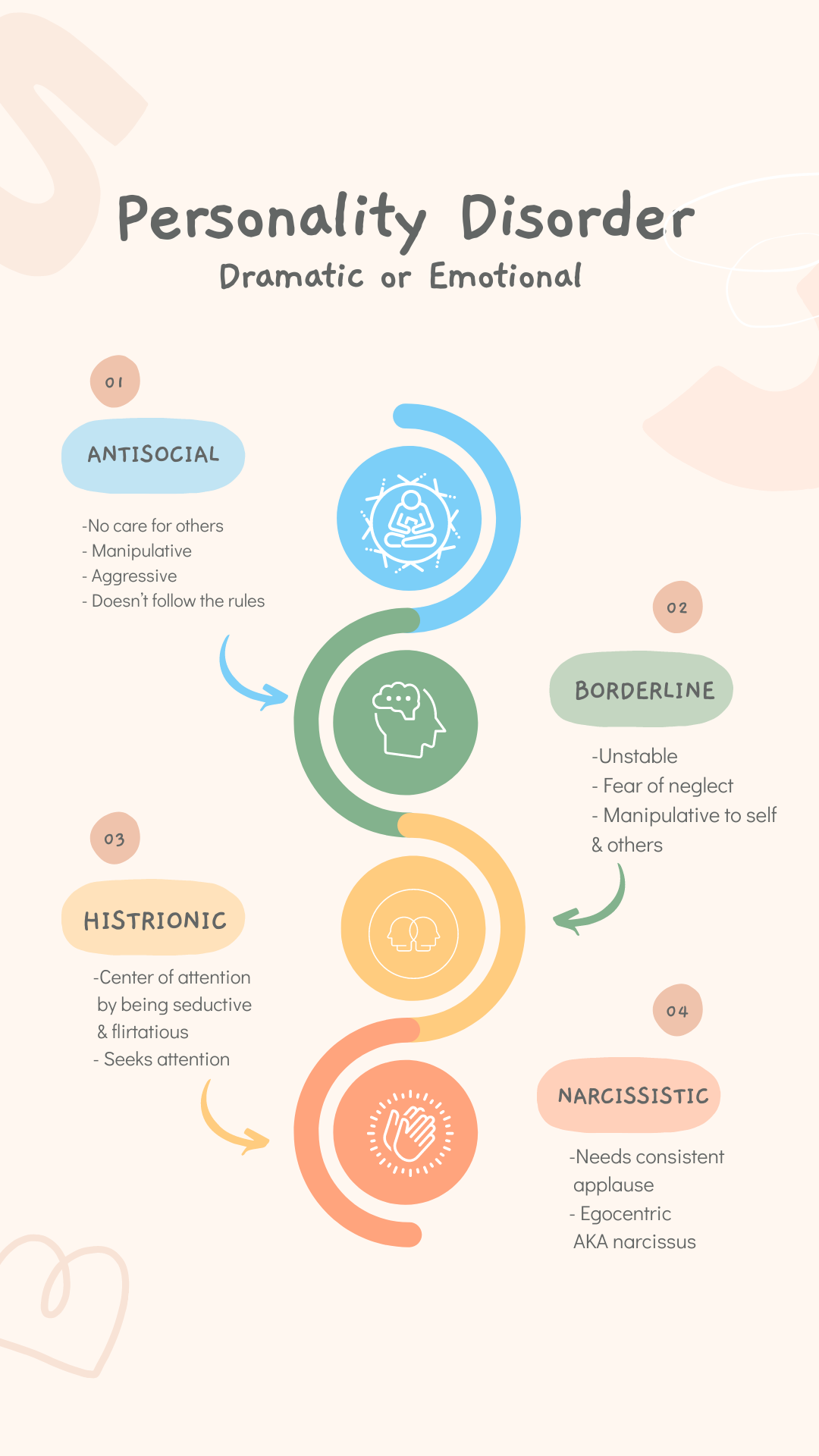
Question 73.
The client’s spouse reports that the client has been taking about 800 mg of secobarbital daily, besides drinking more alcohol than usual. The spouse asks anxiously, “Do you think she will live?” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “We can only wait and see. It’s too soon to tell.”
(b) “This must be quite a shock. How long have you been married?”
(c) “She’s very ill and may not live. Some do not pull through.”
(d) “Her condition is serious. You sound very worried about her.”
Answer:
(d) “Her condition is serious. You sound very worried about her.”
Explanation:
When a spouse asks whether a seriously ill client will live, it is best for the nurse to respond by explaining the seriousness of the client’s condition and acknowledging the spouse’s concern. This type of comment does not offer false hope. Telling the spouse to wait and see and that it is too soon to tell is a stereotypical statement that offers no support. Asking the spouse to describe the length of his or her relationship with the client ignores the spouse’s concern and does not focus on the problem. Simply saying that the client is very ill and may not live and that some do not pull through is harsh and not supportive.
Question 74.
Before hospitalization, a client needed increasingly larger doses of barbiturates to achieve the same euphoric effect the client initially realized from their use. From this information, the nurse develops a plan of care that takes into account that the client is likely suffering from what problem?
(a) tolerance
(b) addiction
(c) abuse
(d) dependence
Answer:
(a) tolerance
Explanation:
Tolerance for a drug occurs when a client requires increasingly larger doses to obtain the desired effect. Therefore, the plan of care would address the client’s state of tolerance. The term addiction refers to psychological and physiologic symptoms indicating that an individual cannot control his or her use of psychoactive substances. This term has been replaced with the term dependence.
Abuse refers to the excessive use of a substance that differs from societal norms. Drug dependence occurs when the client must take a usual or increasing amount of the drug to prevent the onset of abstinence symptoms, cannot keep drug intake under control, and continues to use even though physical, social, and emotional processes are compromised.
Question 75.
Which statement by the nurse is most appropriate when addressing a client with a barbiturate overdose who awakens in a confused state and exhibits stable vital signs?
(a) “I’m here to help you beat your drug habit. But it’s you who will need to work hard.”
(b) “It’s time to get straight and stay clean and put an end to your torture.”
(c) “I’m glad you pulled through; it was touch and go with you for a while.”
(d) “You’re in the hospital because of a drug problem; I’m one of the nurses who will help you.”
Answer:
(d) “You’re in the hospital because of a drug problem; I’m one of the nurses who will help you.”
Explanation:
For a client who is confused when awakening after taking a large dose of barbiturates, the nurse should speak in concrete terms using simple statements in a calm, nonjudgmental, gentle manner to assist the client with cognitive-perceptual impairment, enhance understanding, and decrease anxiety. The other statements contain abstract information and some slang terms that may further confuse the client and thus increase the client’s anxiety.
Question 76.
A client states that her “life has gone down the tubes” since her divorce 6 months ago. Then, after she lost her job and apartment, she took an overdose of barbiturates so she “could go to sleep and never wake up.” Which statement by the nurse should be made first?
(a) “It seems as if your self-esteem has been affected by all your losses.”
(b) “I know you took an overdose of barbiturates. Are you thinking of suicide now?”
(c) “Helplessness is common after losing a job. Are you having trouble making decisions?”
(d) “You sound hopeless about the future since your divorce.”
Answer:
(b) “I know you took an overdose of barbiturates. Are you thinking of suicide now?”
Explanation:
The highest priority is assessing for suicide risk. When the client is safe, then the self-esteem, helplessness, and hopelessness issues can be addressed.
Question 77.
A client who has experienced the loss of her husband through divorce, the loss of her job and apartment, and the development of drug dependency is suffering situational low self-esteem.
Which outcome is most appropriate initially?
(a) The client will discuss her feelings related to her losses.
(b) The client will identify two positive qualities.
(c) The client will explore her strengths.
(d) The client will prioritize problems.
Answer:
(a) The client will discuss her feelings related to her losses.
Explanation:
The most appropriate initial outcome for the client is to discuss thoughts and feelings related to her losses. The nurse should help the client identify and verbalize her feelings so that she can externalize her thoughts and emotions and begin to deal with them. This prevents the client from internalizing feelings, which leads to depression and self-harm.
The ability to identify two positive qualities, explore strengths, and prioritize problems would be appropriate after the client has explored her thoughts and feelings, gained awareness of the issues, and then can participate in the treatment plan.
Question 78.
The nurse notices that a client recovering from a barbiturate overdose spends most of his time with other young adults who have substance-related problems. This group of clients is a dominant force on the unit, keeping the nondrug users entertained with stories of their “highs.” Which method is best to use when dealing with this problem?
(a) providing additional recreation
(b) breaking up drug-oriented discussions
(c) speaking with the clients individually about their behavior
(d) discussing the behavior at the daily community meeting
Answer:
(d) discussing the behavior at the daily community meeting
Explanation:
The best method to deal with the problem is to discuss observations with clients at the daily community meeting because the problem involves all of the clients, and this provides them with the opportunity to offer their views. Peer pressure is valuable in confronting self-defeating and destructive behaviors. Providing additional recreation avoids or ignores the problem and is damaging to all clients because it decreases trust in the nurse.
Breaking up drug-oriented discussions would not be sufficient to stop the behavior. Speaking with the clients individually about their behavior is not as effective as dealing with the problem openly and directly with everyone.
Question 79.
A client recovering from a drug overdose is interacting with the nurse and recounting her exploits at numerous parties she has attended. Which action is most therapeutic?
(a) allowing the client to continue with her stories
(b) telling the client you have heard the stories before
(c) questioning the client further about her exploits
(d) directing the conversation to realistic concerns
Answer:
(d) directing the conversation to realistic concerns
Explanation:
The nurse directs the conversation to realistic concerns or issues to decrease denial and focus on rebuilding a substance-free life. Allowing the client to continue with the stories or questioning the client further about her exploits reinforces the denial. Telling the client you have heard the stories before is nondirective. Additionally, these actions do nothing to help the client focus on rebuilding a substance-free life.
Question 80.
When developing a teaching plan for a group of middle school children about the drug 3,4-methy-lenedioxymethamphetamine (Ecstasy), what information should the nurse expect to include? Select all that apply.
(a) Using Ecstasy is similar to using speed.
(b) Ecstasy is used at all-night parties.
(c) Teeth grinding is seen with cocaine, not Ecstasy use.
(d) It can cause death.
(e) It reduces self-consciousness.
Answer:
(a) Using Ecstasy is similar to using speed.
(b) Ecstasy is used at all-night parties.
(d) It can cause death.
(e) It reduces self-consciousness.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e) Ecstasy is chemically related to methamphetamine (speed) and is used at all-night parties (also known as “raves”) to enhance dancing, closeness to others, affection, and the ability to communicate. Euphoria, heightened sexuality, dis- inhibition, and diminished self-consciousness can occur.
Adverse effects include tachycardia, elevated blood pressure, anorexia, dry mouth, and teeth grinding. Pacifiers, including candy-shaped paci-fiers and lollipops, are used to ease the discomfort associated with teeth grinding and jaw clenching. Hyperthermia, dehydration, renal failure, and death can occur.
Question 81.
A young client is being admitted to the psy-chiatric unit after her obstetrician’s staff suspected she was experiencing a postpartum psychosis.
Her husband said she was doing fine for 2 weeks after the birth of the baby, except for pain from the C-section and trouble sleeping. These symptoms subsided over the next 4 weeks. Three days ago, however, the client started having anxiety, irritability, vomiting, diarrhea, and delirium, resulting in her inability to care for the baby. The husband says, “I saw that my bottles of alprazolam and oxycodone were empty even though I have not been taking them.” What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Call the health care provider for prescriptions for appropriate treatment for opiate and benzo-diazepine withdrawal.
(b) Immediately place the client on withdrawal precautions.
(c) Confirm with the client that she has in fact been using her husband’s medications.
(d) Assess the client for prior and current use of any other substances.
Answer:
(c) Confirm with the client that she has in fact been using her husband’s medications.
(d) Assess the client for prior and current use of any other substances.
(b) Immediately place the client on withdrawal precautions.
(a) Call the health care provider for prescriptions for appropriate treatment for opiate and benzo-diazepine withdrawal.
Explanation:
(c), (d), (b), (a) It is crucial to confirm that the client was taking her husband’s opiates and benzodiazepines and that her symptoms are due to the sudden withdrawal from these medications. It is also important to know if she has been using other substances (such as alcohol) that may cause other withdrawal symptoms. Even before calling for prescriptions, the nurse can initiate withdrawal precautions for client safety.
Question 82.
A 68-year-old client is admitted to the addiction unit after treatment in the emergency department for an overdose of oxycodone. Her son calls the unit and expresses intense anger that his mother is being treated as a “common street addict.” He says she has severe back pain and was given that prescription by her health care provider. “She just accidentally took a few too many pills last night. Which reply by the nurse is most therapeutic?
(a) “I understand that your mother may not have intentionally taken too many pills. Thid medication can cause one to forget how many have been taken.”
(b) “It may be appropriate for your mother to be referred to a pain management programm
(c) “Unfortunately, it’s fairly common f°r clients with pain to increase their use of jpain pills over time.”
(d) “I can hear how upset you are. You sound very concerned about your month
Answer:
(d) “I can hear how upset you are. You sound very concerned about your month
Explanation:
Acknowledging the client’s son’s feelings is the most therapeutic intervention because he is not likely to hear the nurse’s information until his anger and other feelings are addressed and subside. Then, it is important to acknowledge that oxycodone, especially in older clients, can interfere with remembering how many pills were taken.
It is common for clients with chronic pain to inadvertently overuse or become addicted to pain medications. Pain management programs help clients to withdraw from the offending medication and start on a multifaceted system for controlling the pain.
Question 83.
A client is admitted to the addiction unit for a confirmed and long-term addiction to alprazolam. She continues to strongly deny her addiction, stating she was prescribed the alprazolam to control her “panic attacks.” Which procedures would be the most important during the admission process? Select all that apply.
(a) Assess the client for suicide, escape, and aggression risks.
(b) With the client present, search the client’s clothes and belongings for contraband and restricted items.
(c) Initiate withdrawal precautions.
(d) Explain the unit routine and types of groups.
(e) Obtain a urine specimen for a urine drug screen.
Answer:
(a) Assess the client for suicide, escape, and aggression risks.
(b) With the client present, search the client’s clothes and belongings for contraband and restricted items.
(c) Initiate withdrawal precautions.
(e) Obtain a urine specimen for a urine drug screen.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e) Clients who deny an addiction and the need for treatment can be at risk for a suicide attempt, efforts to escape the unit, and aggression directed at staff. A contraband search is a safety measure to look for concealed drugs and dangerous items. Depending on the last use of the substance, withdrawal symptoms can begin quickly. A urine drug screen is crucial to determine what other substances the client may be using that may cause other withdrawal symptoms. Explaining the unit routines and groups can wait until the client is calmer and more receptive.
Question 84.
A client is returning to the health care provider’s office for follow-up on his diagnosis of coronary artery disease. After all the appropriate exams and assessments are completed, the nurse asks the client about how well he is sleeping. The client states, “Oh, that is not a problem anymore. I take a couple of my wife’s diazepam and sleep like a baby.” Which information should the nurse obtain? Select all that apply.
(a) the reason the client’s wife is taking diazepam
(b) the dose of the diazepam he is taking and how long he has been taking it
(c) exactly how much diazepam he takes at night and during the day
(d) whether he intends to stop the diazepam use
(e) what was interfering with his sleep prior to starting the diazepam
Answer:
(b) the dose of the diazepam he is taking and how long he has been taking it
(c) exactly how much diazepam he takes at night and during the day
(e) what was interfering with his sleep prior to starting the diazepam
Explanation:
(b), (c), (e) The dose, length of use, and the number of diazepam taken per day are important for assessing the severity of the substance abuse and potential withdrawal. Determining sleep interferences is necessary for treating the underlying causes of the insomnia. The reason his wife takes diazepam is confidential information and is not critical to his situation. Getting off the diazepam is essential for the client and is not an option, especially with his cardiac issues. This needs to be done safely if he has been taking diazepam for more than a week or two.
Question 85.
A client is admitted to the emergency department having just used cocaine. The nurse should assess this client for which factors? Select all that apply.
(a) mood swings
(b) feeling of euphoria
(c) constricted pupils
(d) increased blood pressure
(e) tachycardia
Answer:
(a) mood swings
(d) increased blood pressure
(b) feeling of euphoria
(e) tachycardia
Explanation:
(a), (d), (b), (e) The client who has used cocaine experiences mood swings, a feeling of euphoria, and an elevation in heart rate and blood pressure. The client with cocaine use will have dilated pupils.
Question 86.
A client who chronically snorts cocaine is brought to the emergency department due to a cocefine overdose. The client is experiencing delusions,, hallucinations, mild respiratory distress, and mild tachycardia initially. What should the nurse do? Sei’ect all that apply.
(a) Imduce vomiting.
(b) Pluce seizure pads on the bed.
(c) Adi minister PRN haloperidol as prescribed.
(d) Momitor for respiratory acidosis.
(e) Enco urage deep breathing.
(f) Moni, tor for metabolic acidosis.
Answer:
(b) Pluce seizure pads on the bed.
(c) Adi minister PRN haloperidol as prescribed.
(d) Momitor for respiratory acidosis.
(e) Enco urage deep breathing.
(f) Moni, tor for metabolic acidosis.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d), (e), (f) The cocaine was not swallowed, so inducing vomiting is not indicated. A cocaine overdose can produce seizures, paranoia, and respiratory and/or metabolic acidosis. Deep breathing will help decrease the respiratory distress and pulse rate.
Question 87.
A client walks into the clinic and tells the nurse she has run out of money for crack, has crashed, and wants something to help her feel better. Which factor is most important for the nurse to assess?
(a) suspiciousness
(b) loss of appetite
(c) drug craving
(d) suicidal ideation
Answer:
(d) suicidal ideation
Explaination:
The nurse assesses the client for feelings of depression and suicidal ideation. After experiencing an instantaneous high from crack, a crash immediately follows, and the client has an intense craving for more crack. A crash commonly leads to a cocaine-induced depression when additional crack is unavailable. At times, the depression is so severe that users attempt suicide. Although suspiciousness, loss of appetite, and drug craving are also associated with cocaine use, they are less of a priority than suicidal ideation.
Question 88.
A client in the emergency department is diagnosed as having amphetamine psychosis. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Transfer the client to the psychiatric unit.
(b) Monitor cardiac and respiratory status.
(c) Place seizure pads on the bed.
(d) Administer ¡M haloperidol as prescribed.
Answer:
(c) Place seizure pads on the bed.
(b) Monitor cardiac and respiratory status.
(d) Administer ¡M haloperidol as prescribed.
(a) Transfer the client to the psychiatric unit.
Explaination:
(c), (b), (d), (a) The risk of seizures is an immediate safety issue, and the nurse should first place seizure pads on the bed. Amphetamine overdose can produce cardiac arrhythmias and respiratory collapse; the nurse should next monitor the client. After monitoring is initiated, the haloperidol is indicated to antagonize the amphetamine affects. When the client is medically stable, the nurse can transfer the client to a psychiatric unit. Haloperidol would be stopped as the psychotic symptoms subside.
Question 89.
The client is fidgeting and has trouble sitting still. He has difficulty concentrating and is erratic. Which intervention should help decrease this client’s level of anxiety? Select all that apply.
(a) refocusing attention
(b) allowing ventilation
(c) suggesting a time-out
(d) giving intramuscular medication
(e) assisting with problem solving
Answer:
(a) refocusing attention
(b) allowing ventilation
(e) assisting with problem solving
Explanation:
(a), (b), (e) The client is exhibiting symptoms of moderate anxiety. At this level of anxiety, the nurse should help the client to decrease anxiety by allowing ventilation, crying, exercise, and relaxation techniques. The nurse would further assist the client by refocusing his attention, relating behaviors and feelings to anxiety, and then assisting with problem solving. Oral medication may be needed if the cli-ent’s anxiety is prolonged or does not decrease with the nurse’s interventions. Suggesting a time-out and giving intramuscular medication are possible interventions for a client whose anxiety level is severe.
Question 90.
When caring for a client who has overdosed on phencyclidine (PCP), the nurse should be especially cautious about which client behavior?
(a) visual hallucinations
(b) violent behavior
(c) bizarre behavior
(d) loud screaming
Answer:
(b) violent behavior
Explanation:
The nurse must be especially cautious when providing care to a client who has taken PCP because of unpredictable, violent behavior. The client can appear to be in a calm state or even in a coma, then become violent, and then return to a calm or comatose state. Visual hallucinations, bizarre behavior, and loud screaming are associated with PCP-intoxicated clients. However, the unpredictable, violent behavior presents a major issue of safety for clients and staff.
Question 91.
Which liquid should the nurse administer to a client who is intoxicated on phencyclidine (PCP) to hasten excretion of the chemical?
(a) water
(b) milk
(c) cranberry juice
(d) grape juice
Answer:
(c) cranberry juice
Explanation:
An acid environment aids in the excretion of PCP. Therefore, the nurse should give the client with PCP intoxication cranberry juice to acidify the urine to a pH of 5.5 and accelerate excretion. Water, milk, or grape juice will not acidify the urine.
Question 92.
When assessing a client with possible alcohol poisoning, the nurse should investigate the client’s use of which substance while drinking alcohol?
(a) marijuana
(b) lysergic acid diethylamide
(c) peyote
(d) psilocybin
Answer:
(a) marijuana
Explanation:
(a) Smoking marijuana while using alcohol can lead to alcohol poisoning because marijuana masks the nausea and vomiting associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Marijuana contains tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for suppressing nausea. With dangerous levels of alcohol in the body, respiratory depression, coma, and death can occur. Lysergic acid diethylamide, peyote, and psilocybin do not contain THC.
Question 93.
A client with a cocaine dependency is irritable, anxious, highly sensitive to stimuli, and overreacting to clients and staff on the unit. Which action is most therapeutic for this client?
(a) secluding and restraining the client as needed
(b) telling the client to stay in his room until he can control himself
(c) providing the client with frequent “time-outs”
(d) confronting the client about his behaviors
Answer:
(a) secluding and restraining the client as needed
Explanation:
Providing frequent “time-outs” when the client is highly anxious, sensitive, irritable, and over reactive is needed to calm the client and reduce the possibility of escalating behaviors and violence. Secluding and restraining the client is not appropriate and would only be used if the client was threatening others and other alternative actions had been unsuccessful. Telling the client to stay in his room until he can control himself is unrealistic and futile because the client cannot eliminate behaviors induced by chemicals. Confronting the client about his behaviors would most likely lead to aggression and possibly violent behavior.
Question 94.
A client with symptoms of amphetamine psychosis that are improving is anxious and still experiencing some delusions. When developing the client’s plan of care, which measure should the nurse include?
(a) Assign the client to a group meeting about the physiologic effects of drugs.
(b) Advise the client to watch television.
(c) Wait for the client to approach the nurse.
(d) Invite the client to play a game of ping-pong with the nurse.
Answer:
(d) Invite the client to play a game of ping-pong with the nurse.
Explanation:
The nurse should invite the client who is anxious to participate in an activity that involves gross motor movements. Doing so helps to direct energy toward a therapeutic activity. Appropriate activities include walking, riding a stationary bicycle, or playing volleyball. Assigning the client to an educational group is not helpful because the anxious client would be unable to sit in a group setting and concentrate on what was occurring in the group.
Watching television may be too stimulating for the client, possibly increasing anxiety. Additionally, the client may be too anxious to sit and focus. Waiting for the client to approach the nurse is not helpful or appropriate. The nurse is responsible for initiating contact with the client.
Question 95.
In consultation with his outpatient psychiatrist, a client is admitted for detoxification from methadone. He states, “I got addicted to morphine for my chronic knee pain. Methadone worked for a long time. Since I had my knee replacement surgery 3 months ago and physical therapy, I do not think I need methadone anymore.” It is important to discuss which information with this client? Select all that apply.
(a) “Detoxification will likely occur with slowly decreasing doses of methadone.”
(b) “Oxycodone will be available if needed for breakthrough pain.”
(c) “You will be monitored closely for withdrawal symptoms and treated as needed.”
(d) “Physical therapy and nonchemical pain management techniques can be prescribed if needed.”
(e) “If you have knee stiffness or pain, it is likely to be managed by nonnarcotic pain medicines.”
Answer:
(a) “Detoxification will likely occur with slowly decreasing doses of methadone.”
(c) “You will be monitored closely for withdrawal symptoms and treated as needed.”
(d) “Physical therapy and nonchemical pain management techniques can be prescribed if needed.”
(e) “If you have knee stiffness or pain, it is likely to be managed by nonnarcotic pain medicines.”
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (e) Since methadone is an addictive medication, the client will be gradually tapered off of it, while being monitored for withdrawal symptoms. Any residual pain is likely to be controlled with other pain management techniques and nonnarcotic pain medication. It is very unlikely that oxycodone would be prescribed PRN since it is a very addictive medication.
Question 96.
A client approaches the medication nurse and states, “I can’t believe you are NOT helping me with my cravings for my fentanyl patches! When I got off alcohol 2 years ago, they gave me naltrexone for my cravings, and it really helped. I can’t stand the cravings and back pain anymore, and I’m getting angry.” Which responses by the nurse would be helpful for this client? Select all that apply.
(a) “Naltrexone does help decrease the cravings for alcohol.”
(b) “Naltrexone can interfere with opiate cravings in some clients.”
(c) “Cravings are hard to deal with, especially when you are in pain too.”
(d) “I hear your frustration about how your detoxification is going.”
(e) “I’m positive naltrexone can help with your cravings for fentanyl.”
(f) “I can ask your health care provider (HCP) if he thinks naltrexone might help you.”
Answer:
(a) “Naltrexone does help decrease the cravings for alcohol.”
(b) “Naltrexone can interfere with opiate cravings in some clients.”
(d) “I hear your frustration about how your detoxification is going.”
(e) “I’m positive naltrexone can help with your cravings for fentanyl.”
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d), (e) Acknowledgment of the client’s frustration, pain, and cravings is important to decrease the client’s anger. Naltrexone can help with detoxification from alcohol and opiates. Asking the HCP about the possibility of adding naltrexone is appropriate. The nurse can never promise that a medication will help this client, since naltrexone is effective with only 20% to 30% of clients with opiate cravings.
Question 97.
An adolescent female client who has been treated for an anxiety disorder since middle school with behavioral treatment and as needed (PRN) anxiety medication is preparing to go to college. The parents are concerned that she will experience an exacerbation of symptoms if she attends college out of town and want their daughter to attend the local community college and live at home. The girl believes she can handle the challenge of leaving home for college. How should the nurse in the outpatient clinic respond to the family’s concerns?
(a) “Your parents have a point; transitions have been hard for you in the past.”
(b) “There are many pros and cons here that we all need to discuss together.”
(c) “Every high school graduate deserves the chance to take on new challenges.”
(d) “It may be premature for you to think of college at this point in time.”
Answer:
(b) “There are many pros and cons here that we all need to discuss together.”
Explanation:
The nurse cannot appear to take the side of either the student or her parent, so discussing the situation together where all points of view can be presented and evaluated is the best option. To avoid college altogether is likely to only escalate both parties’ anxiety.
Question 98.
An adolescent boy who is academically gifted is about to graduate from high school early since he has completed all courses needed to earn a diploma. Within the last 3 months, he has begun to experience panic attacks that have forced him to leave classes early and occasionally miss a day of school. He is concerned that these attacks may hinder his ability to pursue a college degree. What would be the best response by the school nurse who has been helping him deal with his panic attacks?
(a) “It’s natural to be worried about going into a new environment. I’m sure with your abilities you’ll do well once you get settled.”
(b) “You’re putting too much pressure on yourself. You just need to relax more, and things will be alright.”
(c) “It might be best for you to postpone going to college. You need to get these panic attacks controlled first.”
(d) “It sounds like you have real concern about transitioning to college. I can refer you to a health care provider (HCP) for assessment and treatment.”
Answer:
(d) “It sounds like you have real concern about transitioning to college. I can refer you to a health care provider (HCP) for assessment and treatment.”
Explanation:
The client’s concerns are real and serious enough to warrant assessment by an HCP Q rather than being dismissed as trivial. Though he is very intelligent, his intelligence cannot overcome his anxiety, and in fact, his anxiety is likely to interfere with his ability to perform in college if no assessment and treatment is received. Just postponing college is likely to increase the client’s anxiety rather than lower it since it does not address the panic he is experiencing.
Question 99.
A client takes diazepam while establishing a therapeutic dose of antidepressants for generalized anxiety disorder. Which instruction should the nurse give to this client? Select all that apply.
(a) to consult with his health care provider before he stops taking the drug
(b) to avoid eating cheese and other tyramine-rich foods
(c) to take the medication on an empty stomach
(d) not to use alcohol while taking the drug
(e) to stop taking the drug if he experiences swelling of the lips and face and difficulty breathing
Answer:
(d) not to use alcohol while taking the drug
(e) to stop taking the drug if he experiences swelling of the lips and face and difficulty breathing
Explanation:
(d), (e) The nurse should instruct the client who is taking diazepam to take the medication as prescribed; stopping the medication suddenly can cause withdrawal symptoms. This medication is used for a short term only. The drug dose can be potentiated by alcohol, and the client should not drink alcoholic beverages while taking this drug. Swelling of the lips and face and difficulty breathing are signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction.
The client should stop taking the drug and seek medical assistance immediately. The client does not need to avoid eating foods containing tyramine because it interacts with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, not benzodiazepines. The client can take the medication with food.
Question 100.
An adult client diagnosed with anxiety disorder becomes anxious when she touches fruits and vegetables. What should the nurse do?
(a) Instruct the woman to avoid touching these foods.
(b) Ask the woman why she becomes anxious in these situations.
(c) Assist the woman to make a plan for her family to do the food shopping and preparation.
(d) Teach the woman to use cognitive-behavioral approaches to manage her anxiety.
Answer:
(d) Teach the woman to use cognitive-behavioral approaches to manage her anxiety.
Explanation:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is effective in treating anxiety disorders. The nurse can assist the client in identifying the onset of the fears that cause the anxiety and develop strategies to modify the behavior associated with the fears. Avoiding touching foods, asking about reasons for the anxiety, and providing ways to work around touching the foods do not deal with the anxiety and are not interventions that will help this client.
Question 101.
A client who is pacing and wringing his hands states, “I just need to walk” when questioned by the nurse about what he is feeling. Which response by the nurse is most therapeutic?
(a) “YoU need to sit down and relax.”
(b) “Are you feeling anxious?”
(c) “Is something bothering you?”
(d) “You tnust be experiencing a problem now.”
Answer:
(b) “Are you feeling anxious?”
Explanation:
Asking, “Are you feeling anxious?” helps the client to specifically label the feeling as anxiety so that he can begin to understand and manage it. Some clients need assistance with identifying what they are feeling so they can recognize what is happening to them. Stating, “You need to sit down and relax” is not appropriate because the client needs to continue his pacing to feel better. Asking if something is bothering the client or saying that he must be experiencing a problem is vague and does not help the client identify his feelings as anxiety.
Question 102.
A client brought to the emergency department is perspiring profusely, breathing rapidly, and having dizziness and palpitations. Problems of a cardiovascular nature are ruled out, and the client’s diagnosis is tentatively listed as a panic attack. After the symptoms pass, the client states, “I thought I was going to die.” Which is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “It was very frightening for you.”
(b) “We would not have let you die.”
(c) “I would have felt the same way.”
(d) “But you are okay now.”
Answer:
(a) “It was very frightening for you.”
Explanation:
The nurse responds with the statement “It was very frightening for you” to express empathy, thus acknowledging the client’s discomfort and accepting his feelings. The nurse conveys respect and validates the client’s self-worth. The other statements do not focus on the client’s underlying feelings, convey active listening, or promote trust.
Question 103.
A client commonly jumps when spoken to and reports feeling uneasy. The client says, “It’s as though something bad is going to happen.” In which order, from first to last, should the nursing actions be done? All options must be used.
(a) Teach problem-solving strategies.
(b) Ask the client to deep breather for 2 minutes.
(c) Discuss the client feelings in more depth.
(d) Reduce environmental stimuli.
Answer:
(d) Reduce environmental stimuli.
(b) Ask the client to deep breather for 2 minutes.
(c) Discuss the client feelings in more depth.
(a) Teach problem-solving strategies.
Explaination:
(d), (b), (c), (a) Immediate anxiety-reducing strategies are decrease stimuli and perform deep breathing. Once the anxiety is lessened, the client’s feelings can be explored for triggers and underlying issues. Then, problem-solving strategies can be discussed to handle the triggers and issues appropriately.
Question 104.
A client with panic disorder is taking alprazolam 1 mg PO three times daily. The nurse understands that this medication is effective in blocking the symptoms of panic because of its specific action on which neurotransmitters?
(a) gamma-aminobutyrate
(b) serotonin
(c) dopamine
(d) norepinephrine
Answer:
(a) gamma-aminobutyrate
Explanation:
Alprazolam, a benzodiazepine used on a short-term or temporary basis to treat symptoms of anxiety, increases gamma-aminobutyrate (GABA), a major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Because GABA is increased and the reticular activating system is depressed, incoming stimuli are muted, and the effects of anxiety are blocked. Alprazolam does not directly target serotonin, dopamine, or norepinephrine.
Question 105.
A client is diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and given a prescription for venlafaxine. Which information should the nurse include in a teaching plan for this client? Select all that apply.
(a) various strategies for reducing anxiety
(b) the benefits and mechanisms of actions of venlafaxine in treating GAD
(c) how venlafaxine will eliminate his anxiety at home and work
(d) the management of the common side effects of venlafaxine
(e) substituting adaptive coping strategies for maladaptive ones
(f) the positive effects of venlafaxine being evident in 4 to 5 days.
Answer:
(a) various strategies for reducing anxiety
(b) the benefits and mechanisms of actions of venlafaxine in treating GAD
(d) the management of the common side effects of venlafaxine
(e) substituting adaptive coping strategies for maladaptive ones
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e) It is appropriate to provide education on medication mechanisms, benefits, and managing side effects. No medication will eliminate all anxiety, so teaching about anxiety reduction and adaptive coping is needed. Venlafaxine is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor antidepressant, and it will take 2 to 4 weeks to feel the effects.
Question 106.
While a client is taking alprazolam, which food should the nurse instruct the client to avoid?
(a) chocolate
(b) cheese
(c) alcohol
(d) shellfish
Answer:
(c) alcohol
Explanation:
Using alcohol or any central nervous system depressant while taking a benzodiazepine, such as alprazolam, is contraindicated because of additive depressant effects. Ingestion of chocolate, cheese, or shellfish is not problematic.
Question 107.
Which statement by a client who has been taking buspirone as prescribed for 2 days indicates the need for further teaching?
(a) “This medication will help my tight, aching muscles.”
(b) “I may not feel better for 7 to 10 days.”
(c) “The drug does not cause physical dependence.”
(d) “I can take the medication with food.”
Answer:
(a) “This medication will help my tight, aching muscles.”
Explanation:
Buspirone, a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic, is particularly effective in treating the cognitive symptoms of anxiety, such as worry, apprehension, difficulty with concentration, and irritability. Buspirone is not effective for the somatic symptoms of anxiety (muscle tension). Therapeutic effects may be experienced in 7 to 10 days, with full effects occurring in 3 to 4 weeks. This drug is not known to cause physical or psychological dependence. It can be taken with food or small meals to reduce gastrointestinal upset.
Question 108.
A week ago, a tornado destroyed the client’s home and seriously injured her husband. The client has been walking around the hospital in a daze without any outward display of emotions. She tells the nurse that she feels like she is going crazy. Which intervention should the nurse use first?
(a) Explain the effects of stress on the mind and body.
(b) Reassure the client that her feelings are typical reactions to serious trauma.
(c) Reassure the client that her symptoms are temporary.
(d) Acknowledge the unfairness of the client’s situation.
Answer:
(b) Reassure the client that her feelings are typical reactions to serious trauma.
Explanation:
The nurse initially reassures the client that her feelings and behaviors are typical reactions to serious trauma to help decrease anxiety and maintain self-esteem. Explaining the effects of stress on the body may be helpful later. Telling the client that her symptoms are temporary is less helpful. Acknowledging the unfairness of the client’s situation does not address the client’s needs at this time.
Question 109.
After being discharged from the hospital with acute stress disorder, a client is referred to the outpatient clinic for follow-up. What is most important for the client to use for continued alleviation of anxiety?
(a) recognizing when she is feeling anxious
(b) understanding reasons for her anxiety
(c) using adaptive and palliative methods to reduce anxiety
(d) describing the situations preceding her feelings of anxiety
Answer:
(c) using adaptive and palliative methods to reduce anxiety
Explanation:
The client with anxiety may be able to learn to recognize when she is feeling anxious, understand the reasons for her anxiety, and be able to describe situations that preceded her feelings of anxiety. However, she is likely to continue to experience symptoms unless she has also learned to use adaptive and palliative methods to reduce anxiety.
Question 110.
A client with acute stress disorder states to the nurse, “I keep having horrible nightmares about the car accident that killed my daughter. I should not have taken her with me to the store.” Which response by the nurse is most therapeutic?
(a) “Don’t keep torturing yourself with such horrible thoughts.”
(b) “Stop blaming yourself. It’s only hurting you.”
(c) “Let’s talk about something that’s a bit more pleasant.”
(d) “The accident just happened and couldn’t have been predicted.”
Answer:
(d) “The accident just happened and couldn’t have been predicted.”
Explanation:
Saying “ The accident just happened and couldn’t have been predicted” provides the client with an objective perception of the event instead of the client’s perceived role. This type of statement reflects active listening and helps to reduce feelings of blame and guilt. Saying “Don’t keep torturing yourself” or “Stop blaming yourself” is inappropriate because it tells the client what to do, subsequently delaying the therapeutic process. The statement “Let’s talk about something that’s a bit more pleasant” ignores the client’s feelings and changes the subject. The client needs to verbalize feelings and decrease feelings of isolation.
Question 111.
The client, who is a veteran and has posttraumatic stress disorder, tells the nurse about the horror and mass destruction of war. He states, “I killed all of those people for nothing.” Which response by the nurse is appropriate?
(a) “You did what you had to do at that time.”
(b) “Maybe you didn’t kill as many people as you think.”
(c) “How many people did you kill?”
(d) “War is a terrible thing.”
Answer:
(a) “You did what you had to do at that time.”
Explanation:
The nurse states “You did what you had to do at that time” to help the client evaluate past behavior in the context of the trauma. Clients commonly feel guilty about past behaviors when viewing them in the context of current values. The other statements are inappropriate because they do not help the client to evaluate past behavior in the context of the trauma.
Question 112.
A client with acute stress disorder has avoided feelings of anger toward her rapist and cannot verbally express them. The nurse suggests which activity to assist the client with expressing her feelings?
(a) working on a puzzle
(b) writing in a journal
(c) meditating
(d) listening to music
Answer:
(b) writing in a journal
Explanation:
Writing in a journal can help the client safely express feelings, particularly anger, when the client cannot verbalize them. Listening to music, meditating, and working on a puzzle may be relaxing, but will not help the client express their feelings. Safely externalizing anger by writing in a journal helps the client to maintain control over her feelings.
Question 113.
When developing the plan of care for a client with acute stress disorder who lost her sister in a boating accident, which intervention should the nurse initiate?
(a) helping the client to evaluate her sister’s behavior
(b) telling the client to avoid details of the accident
(c) facilitating progressive review of the accident and its consequences
(d) postponing discussion of the accident until the client brings it up
Answer:
(c) facilitating progressive review of the accident and its consequences
Explanation:
The nurse should facilitate progressive review of the accident and its consequences to help the client integrate feelings and memories and to begin the grieving process. Helping the client to evaluate her sister’s behavior, telling the client to avoid details of the accident, or postponing the discussion of the accident until the client brings it up is not therapeutic and does not facilitate the development of trust in the nurse. Such actions do not facilitate review of the accident, which is necessary to help the client integrate feelings and memories and begin the grieving process.
Question 114.
A soldier on his second tour of duty was notified of the date that he will be redeployed. As this date approaches, he is showing signs of excess anxiety and irritability and inability to sleep at night because of nightmares of explosive devices tragedies, all leading to poor work performance. His commanding officer refers him to the base hospital for an evaluation. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Remind him that any feelings and problems he is having are typical in his current situation.
(b) Ask him to talk about his upsetting experiences.
(c) Remove any weapons and dangerous items be has in his possession.
(d) Acknowledge any injustices/unfairness r elated to his experiences, and offer empathy and support.
Answer:
(c) Remove any weapons and dangerous items be has in his possession.
(a) Remind him that any feelings and problems he is having are typical in his current situation.
(d) Acknowledge any injustices/unfairness r elated to his experiences, and offer empathy and support.
(b) Ask him to talk about his upsetting experiences.
Explanation:
(c), (a), (d), (b) Safety is the first priority in clients experiencing acute stress disorder (ASD). ASD symptoms are typical reactions to an abnormal situation that are not being handled effectively. When the client believes he is “normal,” being accepted, understood, and supported, then he will be able
to discuss his thoughts and feelings related to the traumas of the war.
Question 115.
A newly admitted young adult client, diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), reluctantly reveals that she was the victim of human trafficking 2 years ago. The client says, “Nobody will ever believe the horrible things the men did to me, and no one never stopped them.” Which response is appropriate for the nurse to make?
(a) “I’ll believe anything you tell me. You can trust me.”
(b) “I can’t understand why society did not do more to protect you. It’s not right."
(c) “Tell me what the men did to you. It’s important that I understand the details.”
(d) “It must be difficult to talk about what happened. I’m willing to listen.”
Answer:
(d) “It must be difficult to talk about what happened. I’m willing to listen.”
Explanation:
Survivors of trauma/torture have a lot of difficulty with trust and do not readily talk about the horrible events. Therefore, empathy and a willingness to listen without pressuring the client are crucial. Knowing the details is not necessary to provide care and puts pressure on the client to relive painful memories. Believing everything may or may not be possible and does not convey the empathy. Saying that it was not right that society did not help diverts attention from the client.
Question 116.
An adolescent client diagnosed with post- traumatic stress disorder [PTSD) is admitted to the unit after slicing both arms with a razor blade. He says, “Maybe my mother will listen to me now. She tells me I am just crazy when I say I am screwed up because my stepdad had sex with me for years.” What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Ask the client about the stepdad possibly abusing younger children in the family.
(b) Ask the client to be specific about what he means by “screwed up.”
(c) Ask the client to state what she will do if he feels urge to hurt himself.
(d) Ask the client to talk about appropriate ways to express anger toward his mother.
Answer:
(c) Ask the client to state what she will do if he feels urge to hurt himself.
(a) Ask the client about the stepdad possibly abusing younger children in the family.
(b) Ask the client to be specific about what he means by “screwed up.”
(d) Ask the client to talk about appropriate ways to express anger toward his mother.
Explanation:
(c), (a), (b), (d) The nurse should first assure the client’s safety after the client’s self-mutilation. Another safety issue is whether the stepdad possibly may be abusing younger children; if so, a police report may need to be filed. Then, it is important to know what the client means exactly by “screwed up” to identify other emotions and behaviors that need attention. It is very common for survivors of childhood sexual abuse to have intense anger at those who did not stop or prevent the abuse, and once the other steps have been taken, the nurse can begin to help the client manage his anger.
Question 117.
A client diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder is readmitted for suicidal thoughts and continued trouble sleeping. She states that when she closes her eyes, she has vivid memories about being awakened at night. “My dad would be on top of me trying to have sex with me. I couldn’t breathe.” Which suggestions would be appropriate for the nurse to make for the insomnia? Select all that apply.
(a) trying relaxation techniques to help decrease her anxiety before bedtime
(b) taking the quetiapine 25 mg as needed as prescribed by the health care provider
(c) staying in the dayroom and trying to sleep in the recliner chair near staff
(d) listening to calming music as she tries to fall asleep
(e) processing the content of her flashbacks no less than an hour before bedtime
(f) leaving her door slightly open to decrease noise during the nightly checks
Answer:
(a) trying relaxation techniques to help decrease her anxiety before bedtime
(b) taking the quetiapine 25 mg as needed as prescribed by the health care provider
(d) listening to calming music as she tries to fall asleep
(f) leaving her door slightly open to decrease noise during the nightly checks
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (f) Relaxation techniques and listening to calming music decrease anxiety and promote sleep. Quetiapine is often effective in decreasing nightmare and flashbacks and has a beneficial side effect of drowsiness. Leaving her door slightly open will decrease the noise of making 15-minute checks at night. Staying in the dayroom in a recliner with all the noise and lights is not likely to help. Processing memories an hour or two before bedtime does not allow enough time to calm down before sleep.
Question 118.
A client with posttraumatic stress disorder needs to find new housing and wants to wait for a month before setting another appointment to see the nurse. How should the nurse interpret this action?
(a) a method of avoidance
(b) a detriment to progress
(c) the end of treatment
(d) a necessary break in treatment
Answer:
(d) a necessary break in treatment
Explanation:
The nurse judges the client’s request for an interruption in treatment as a necessary break in treatment. A “time-out” is common and necessary to enable the client to focus on pressing problems and solutions. It is not necessarily a method of avoidance, a detriment to progress, or the end of treatment. A problem like housing can be very stressful and require all of the client’s energy and attention, with none left for the emotional stress of treatment.
Question 119.
The nurse should warn a client who is taking a benzodiazepine about using which medication in combination with his current medication?
(a) antacids
(b) acetaminophen
(c) vitamins
(d) aspirin
Answer:
(a) antacids
Explanation:
Combining a benzodiazepine with an antacid impairs the absorption rate of the benzodiazepine. Acetaminophen, vitamins, and aspirin are safe to take with a benzodiazepine because no major drug interactions occur.
Question 120.
Which client statement indicates the need for additional teaching about benzodiazepines?
(a) “I can’t drink alcohol while taking diazepam.”
(b) “I can stop taking the diazepam anytime I want.”
(c) “Diazepam can make me drowsy, so I shouldn’t drive for a while.”
(d) “Diazepam will help my tight muscles feel better.”
Answer:
(b) “I can stop taking the diazepam anytime I want.”
Explanation:
Diazepam, like any benzodiazepine, cannot be stopped abruptly. The client must be slowly tapered off of the medication to decrease withdrawal symptoms, which would be similar to withdrawal from alcohol. Alcohol in combination with a benzodiazepine produces an increased central nervous system depressant effect and therefore should be avoided. Diazepam can cause drowsiness, and the client should be warned about driving until tolerance develops. Diazepam has muscle relaxant properties and will help tight, tense muscles feel better.
Question 121.
A client is diagnosed with agoraphobia without panic disorder. Which type of therapy would most the nurse expect to see included in the plan of care?
(a) insight therapy
(b) group therapy
(c) behavior therapy
(d) psychoanalysis
Answer:
(c) behavior therapy
Explanation:
The nurse should suggest behavior therapy, which is most successful for clients with phobias. Systematic desensitization, flooding, exposure, and self-exposure treatments are most therapeutic for clients with phobias. Self-exposure treatment is being increasingly used to avoid frequent therapy sessions.
Insight therapy, exploration of the dynamics of the client’s personality, is not helpful because the process of anxiety underlies the disorder. Group therapy or psychoanalysis, which deals with repressed, intrapsychic conflicts, is not helpful for the client with phobias because it does not help to manage the underlying anxiety or disorder
Question 122.
The client diagnosed with a fear of eating in public places or in front of other people has finished eating lunch in the dining area in the nurse’s presence. Which statement by the nurse should reinforce the client’s positive action?
(a) “It wasn’t so hard, now was it?”
(b) “At supper, I hope to see you eat with a group of people.”
(c) “You must have been hungry today.”
(d) “It’s progress for you to eat in the dining room with me.”
Answer:
(d) “It’s progress for you to eat in the dining room with me.”
Explanation:
Saying “ It is a sign of progress to eat in the dining area with me” conveys positive reinforcement and gives the client hope and confidence, thus reinforcing the adaptive behavior. Stating “It wasn’t so hard, now was it” decreases the client’s selfworth and minimizes his accomplishment. Stating “At supper, I hope to see you eat with a group of people” will overwhelm the client and increase anxiety. Stating “You must have been hungry today” ignores the client’s positive behavior and shows the nurse’s lack of understanding of the dynamics of the disorder.
Question 123.
The client diagnosed with agoraphobia refuses to walk down the hall to the group room. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “I know you can do it.”
(b) “Try holding onto the wall as you walk.”
(c) “You can miss group this one time.”
(d) “I will walk with you.”
Answer:
(d) “I will walk with you.”
Explanation:
The nurse should walk with the client to activate adaptive coping for the client experiencing high anxiety and decreased motivation and energy. Stating “I know you can do it,” “Try holding on to the wall,” or “You can miss group this one time” maintains the client’s avoidance, thus reinforcing the client’s behavior, and does not help the client begin to cope with the problem
Question 124.
A client diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder has been taking sertraline but would like to have more energy every day. At his monthly checkup, he reports that his massage therapist recommended he take St. John’s wort to help his depression. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “St. John’s wort is a harmless herb that might be helpful in this instance.”
(b) “Combining St. John’s wort with the sertraline can cause a serious reaction called serotonin syndrome.”
(c) “If you take St. John’s wort, we will have to decrease the dose of your sertraline.”
(d) “St. John’s wort is not very effective for depression, but we can increase your sertraline dose.”
Answer:
(b) “Combining St. John’s wort with the sertraline can cause a serious reaction called serotonin syndrome.”
Explanation:
The effectiveness of St. John’s wort with depression is unconfirmed. The critical issue is that the combination of St. John’s wort and sertraline (an SSRI antidepressant) can produce serotonin syndrome, which can be fatal. The client should not take the St. John’s wort while taking sertraline.
Question 125.
A client diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder arrives late for an appointment with the nurse at the outpatient clinic. During the interview, he fidgets restlessly, has trouble remembering what topic is being discussed, and says he thinks he is going crazy. Which statement by the nurse best deals with the client’s feelings of “going crazy?”
(a) “What do you mean when you say you think you’re going crazy?”
(b) “Most people feel that way occasionally.”
(c) “I don’t know you well enough to judge your mental state.”
(d) “I haven’t heard you make a crazy statement.”
Answer:
(a) “What do you mean when you say you think you’re going crazy?”
Explanation:
When the client says he thinks he is “going crazy,” it is best for the nurse to ask him what “crazy” means to him. The nurse must have a clear idea of what the client means by his words and actions. Using an open-ended question facilitates client description to help the nurse assess his meaning. The other statements minimize and dismiss the client’s concern and do not give him the opportunity to openly discuss his feelings, possibly leading to increased anxiety.
Question 126.
A client with obsessive-compulsive disorder reveals that he was late for his appointment “because of my dumb habit. I have to take off my socks and put them back on 41 times I can’t stop until I do it just right.” The nurse interprets the client’s behavior as most likely representing which factor?
(a) relief from anxiety
(b) control of his thoughts
(c) attention from others
(d) safe expression of hostility
Answer:
(a) relief from anxiety
Explanation:
A client who is exhibiting compulsive behavior is attempting to control his anxiety. The compulsive behavior is performed to relieve discomfort and to bind or neutralize anxiety. The client must perform the ritual to avoid an extreme increase in tension or anxiety even though the client is aware that the actions are absurd. The repetitive behavior is not an attempt to control thoughts; the obsession or thinking component cannot be controlled. It is not an attention-seeking mechanism or an attempt to express hostility.
Question 127.
A client with obsessive-compulsive disorder, who was admitted early yesterday morning, must make his bed 22 times before he can have breakfast. Because of his behavior, the client missed having breakfast yesterday with the other clients. Which action should the nurse institute to help the client be on time for breakfast?
(a) Tell the client to make his bed one time only.
(b) Wake the client an hour earlier to perform his ritual.
(c) Insist that the client stop his activity when it is time for breakfast.
(d) Advise the client to have breakfast first before making his bed.
Answer:
(b) Wake the client an hour earlier to perform his ritual.
Explanation:
The nurse should wake the client an hour earlier to perform his ritual so that he can be on time for breakfast with the other clients. The nurse provides the client with time needed to perform rituals because the client needs to keep his anxiety in check. The nurse should never take away a ritual, because panic will ensue. The nurse should work with the client later to slowly set limits on the frequency of the action.
Question 128.
The nurse notices that a client diagnosed with major depression and social phobia must get up and move to another area when someone sits next to her. Which action by the nurse is appropriate?
(a) Ignore the client’s behavior.
(b) Question the client about her avoidance of others.
(c) Convey awareness of the client’s anxiety about being around others.
(d) Have nursing staff follow the client as moves away.
Answer:
(c) Convey awareness of the client’s anxiety about being around others.
Explanation:
The nurse conveys empathy and awareness of the client’s need to reduce anxiety by showing acceptance and understanding to the client, thereby promoting trust. Ignoring the behavior, questioning the client about her avoidance of others, or telling other clients to follow her when she moves is not therapeutic or appropriate.
Question 129.
The nurse is developing a long-term care plan for an outpatient client diagnosed with dissociative identity disorder. Which interventions should be included in this plan? Select all that apply.
(a) learning how to manage feelings, especially anger and rage
(b) joining several outpatient support groups that are process oriented
(c) identifying resources to call when there is a risk of suicide or self-mutilation
(d) selecting a method for alter personalities to communicate with each other, such as journaling
(e) trying different medicines to find one that eliminates the dissociative process
(f) helping each alter accept the goal of sharing and integrating all their memories
Answer:
(a) learning how to manage feelings, especially anger and rage
(c) identifying resources to call when there is a risk of suicide or self-mutilation
(d) selecting a method for alter personalities to communicate with each other, such as journaling
(f) helping each alter accept the goal of sharing and integrating all their memories
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (f) Managing suicidal thought, urges to self-mutilate, and the intense anger are critical safety issues. Then, the focus can switch to communication methods for each alter and the integration issues. Process groups can be overwhelming when too much is revealed or when child alters are unable to understand the group content. There are no known medicines to stop the process of dissociating.
Question 130.
A client with a long history of experiencing dissociative identity disorder is admitted to the unp after the cuts on her legs were sutured in the emergency department. During the admission intervibw the client tearfully states that she does not know what happened to her legs. Then, a stronger, aper personality states that the client is useless, wear and needs to be eliminated completely. The nurse should do which action first?
(a) Explore the alter personalities’ attitudes toward the client more thoroughly.
(b) Place the client in restraints when apper personality emerges.
(c) Contract with the alter personality upper nurse when he has the urge to hcirm ppe client and the body they both share.
(d) Keep the client in a stress-free enivironment so that the stronger alter person? does not get a chance to emerge.
Answer:
(c) Contract with the alter personality upper nurse when he has the urge to hcirm ppe client and the body they both share.
Explanation:
The no-harm contract with any destructive alters is essential along with the reminder that the alters share the same body. Later, the alter’s attitudes about the client can be explored in more depth. When alter personalities emerge, their behaviors are not predictable. Restraints could not be placed on the client soon enough. There are no behaviors to justify restraints at this point. Creating a stress-free environment is not possible.
Question 131.
At 1000 hours, a client with a diagnosis of pain disorder demands that the nurse call the health care provider (HCP) for more pain medication because she is still in pain after the 0900 analgesic. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Call the HCP as the client requests.
(b) Suggest the client lie down while she is waiting for her next dose.
(c) Tell the client that the HCP will be in later to talk to her about it.
(d) Inform the client that the nurse cannot give her additional medication at this time.
Answer:
(d) Inform the client that the nurse cannot give her additional medication at this time.
Explanation:
The nurse sets limits by informing the client in a matter-of-fact manner that the nurse cannot give her additional pain medication at this time. The nurse can then invite the client to participate in another activity, such as a card game, to decrease rumination about pain by directing the client’s attention to an activity. By telling the client the nurse will call the HCP [j] as requested, the nurse is manipulated to do what the client demands. Suggesting that the client lie down because she has to wait for the next dosage or telling the client that the HCP will be in later ignores the client and her needs and is not helpful in decreasing rumination about her pain.
Question 132.
The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) tells the nurse that the client with a somatoform disorder is sick and is not coming to the dining room for lunch. The nurse should direct the UAP to do which intervention?
(a) Take the client a lunch tray, and let him eat in his room.
(b) Tell the client he will need to wait until supper to eat if he misses lunch.
(c) Invite the client to lunch and accompany him to the dining room.
(d) Inform the client that he has 10 minutes to get to the dining room for lunch.
Answer:
(c) Invite the client to lunch and accompany him to the dining room.
Explanation:
The nurse instructs the UAP to invite the client to lunch and accompany him to the dining room to decrease manipulation, secondary gain, dependency, and reinforcement of negative behavior while maintaining the client’s self-worth. Taking the client a lunch tray and allowing him to eat in his room reinforces negative behaviors and secondary gain. Telling the client he will need to wait until supper to eat if he misses lunch or informing the client that he has 10 minutes to get to the dining room challenges the client and may increase feelings of anger and the need for physical complaints.
Question 133.
The client diagnosed with conversion disorder has a paralyzed arm. A staff member states, “I would just tell the client her arm is paralyzed because she had an affair and neglected her baby’s care to the point where the baby had to be hospitalized for dehydration.” Which response by the nurse is best?
(a) “Ignore the client’s behaviors and treat her with respect.”
(b) “Pushing insight will increase the client’s anxiety and the need for physical symptoms.”
(c) “Pushing awareness will be helpful and further the client’s recovery.”
(d) “We will meet with the client and confront her with her behavior. ”
Answer:
(b) “Pushing insight will increase the client’s anxiety and the need for physical symptoms.”
Explanation:
Pushing insight or awareness into conflicts or problems increases anxiety and the need for physical symptoms to handle or take care of the anxiety. Awareness or insight must be developed slowly as the client’s need for symptoms diminishes. Saying “Ignore the client’s behavior and treat her with respect” is not helpful to the staff member or the client.
This statement fails to educate the staff member about the client’s disorder and simply dismisses the needs of both. It is not true that pushing awareness will be helpful and further the client’s recovery; this is the opposite of what is needed. Meeting with the client to confront her behavior is not therapeutic and will greatly increase the client’s anxiety and the need for the conversion symptoms.
Question 134.
The health care provider (HCP) refers a client diagnosed with somatization disorder to the outpatient clinic because of problems with nausea. The client’s past symptoms involved back pain, chest pain, and problems with urination. The client tells the nurse that the nausea began when his wife asked him for a divorce. Which intervention is most appropriate?
(a) asking the client to describe his problem with nausea
(b) directing the client to describe his feelings about his impending divorce
(c) allowing the client to talk about the HCPs he has seen and the medications he has taken
(d) informing the client about a different medication for his nausea
Answer:
(b) directing the client to describe his feelings about his impending divorce
Explanation:
The nurse helps the client to focus on his feelings about his impending divorce to decrease the client’s anxiety and decrease his focus on physical ailments. The client with a somatoform disorder typically has problems with identifying, describing, and dealing with feelings. Internalizing feelings leads to increased anxiety and the need for protective mechanisms.
Asking the client to describe his problem with nausea, allowing the client to talk about the many HCPs he has seen and the medi-cations he has taken, and informing the client about a different medication for nausea are counterproductive toward recovery because they reinforce the focus on the symptoms.
Question 135.
A client diagnosed with pain disorder has a history of ruminating on pain in his arm. The client is talking with the nurse about fishing when he suddenly reverts to talking about the pain in his arm. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Allow the client to talk about his pain.
(b) Ask the client if he needs more pain medication.
(c) Remind the client that staff are aware of his pain.
(d) Redirect the interaction back to fishing.
Answer:
(d) Redirect the interaction back to fishing.
Explanation:
The nurse should redirect the interaction back to fishing or another focus whenever the client begins to ruminate about physical symptoms or impairment. Doing so helps the client talk about topics that are more therapeutic and beneficial to recovery. Allowing the client to talk about his pain or asking if he needs additional pain medication is not therapeutic because it reinforces the client’s need for the symptom. Telling the client that staff is aware of the pain places limits but does not provide direction for a positive conversation.
Question 136.
Which statement indicates to the nurse that the client is progressing toward recovery from a somatoform disorder?
(a) “I understand my pain will feel worse when I am worried about my divorce.”
(b) "My stomach pain will go away once I get properly diagnosed.”
(c) "My headache feels better when I time my medication dose.”
(d) “I need to find a health care provider (HCP) who understands what my pain is like.”
Answer:
(a) “I understand my pain will feel worse when I am worried about my divorce.”
Explanation:
The client who states “I understand my pain will feel worse when I am worried about my divorce” recognizes the connection between his pain and the divorce and indicates developing insight into his problem. The nurse should then be able to assist the client with developing adaptive coping strategies. The other statements indicate a lack of insight into his disorder and lack of progress toward recovery. The client is still searching for the “right” diagnosis, medication, and HCP
Question 137.
A client is brought to the emergency department (ED) by a friend who states that the client recently ran out of his lorazepam and has been having a grand mal seizure for the last 10 minutes. The nurse observes that the client is still seizing. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Monitor the client’s safety, and place seizure pads on the cart rails.
(b) Record the time, duration, and nature of the seizures.
(c) Page the ED health care provider, and prepare to give diazepam intravenously.
(d) Ask the friend about the client’s medical history and current medications.
Answer:
(c) Page the ED health care provider, and prepare to give diazepam intravenously.
(b) Record the time, duration, and nature of the seizures.
(a) Monitor the client’s safety, and place seizure pads on the cart rails.
(d) Ask the friend about the client’s medical history and current medications.
Explanation:
(c), (b), (a), (d) The nurse should first obtain a prescription for and administer diazepam to stop the status epilepticus. The nurse should next prevent injury by using seizure pads. Recording the time, duration, and nature of the seizures will be important for ongoing treatment. Finally, the nurse can attempt to obtain information about medication use and abuse history from the friend until the client is able to do so for himself.
Question 138.
The client is in the emergency department with her boyfriend. She is just recovering from a temporary drug-induced psychosis from lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). She is still frightened and a little suspicious. Which nursing action is most appropriate?
(a) having an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) stay with the client to decrease her fear
(b) placing the client next to the nursing desk
(c) leaving the client alone until the “trip” is over
(d) having the boyfriend check on the client frequently
Answer:
(c) leaving the client alone until the “trip” is over
Explanation:
Having a UAP stay with the client provides for reassurance and safety. Being next to the nursing desk will increase stimuli and confusion. Being alone will increase the client’s fears and anxiety. It is inappropriate to ask the boyfriend to provide client supervision for the nurse.
Question 139.
A client on a stretcher in the emergency department begins to thrash around, slap the sheets, and yell, “Get these bugs off of me.” She is disoriented and has a blood pressure of 189/75 mm Hg and a pulse of 96 bpm. The friend who is with her says, “She was drinking a lot 3 days ago and asked me for money to get more vodka, but I didn’t have any.” What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Obtain a prescription to place the client in restraints, if needed.
(b) Implement constant observation.
(c) Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes.
(d) Administer haloperidol and lorazepam IM as prescribed.
(e) Remind the client that she is in the hospital and the nurse is with her.
(f) Chart the client’s response to the interventions.
Answer:
(e) Remind the client that she is in the hospital and the nurse is with her.
(f) Chart the client’s response to the interventions.
(a) Obtain a prescription to place the client in restraints, if needed.
(b) Implement constant observation.
(c) Monitor vital signs every 15 minutes.
(d) Administer haloperidol and lorazepam IM as prescribed.
Explanation:
(e), (f), (a), (b), (c), (d) fter orienting the client to time and place, the nurse should assure constant observation of the client to prevent the client from getting hurt. The administration of the haloperidol and lorazepam is needed to quickly decrease the symptoms of delirium tremens (DTs) and lower the vital signs. Monitoring vital signs assesses the client’s stability and need for additional medications.
The nurse can ask another staff to contact the health care provider (HCP) £3 to request a prescription for restraints in case the client becomes violent toward self or others. After the DT symptoms subside, the haloperidol would be stopped due to the decrease in the seizure threshold. Other detoxification protocols would then begin. Last, chart the client’s response.
Question 140.
The nurse is teaching unlicensed staff about caring for the client with alcohol dependency. Which statement by the staff indicates the need for additional teaching?
(a) “Alcohol dependency affects the entire family.”
(b) “The client is a weak individual and could stop if he desires.”
(c) “Alcohol is a problem when it interferes with the client’s daily life.”
(d) “The client who cannot stop drinking, even though he wants to, is alcohol dependent.”
Answer:
(b) “The client is a weak individual and could stop if he desires.”
Explanation:
The statement “The client is a weak individual and could stop if he desires” is false and indicates a lack of understanding regarding alcohol dependency. Criteria for substance dependency include the inability to stop using even when wanting to do so. The client cannot stop or control the amount used when dependent on a substance. Alcohol dependency affects individuals from every culture and socioeconomic background and has nothing to do with being a “weak” individual.
The devastating effects of alcohol dependency are felt by every member of the family and not just the individual with the alcohol problem. Family members need education about the physical, physiologic, and psychological effects of alcohol and referrals to self-help groups for support. They have felt and lived with the devastating effects of the disease. A simple and commonly held view of alcoholism is that alcohol is a problem when it interferes with life or disrupts family, work, or social relationships.
Question 141.
The nurse is serving on the hospital ethics committee that is considering the ethics of a proposal for the nursing staff to search the room of a client diagnosed with substance abuse while he is off the unit and without his knowledge. What should be considered concerning the relationship of ethical and legal standards of behavior?
(a) Ethical standards are generally higher than those required by law.
(b) Ethical standards are equal to those required by law.
(c) Ethical standards bear no relationship to legal standards for behavior.
(d) Ethical standards are irrelevant when the health of a client is at risk.
Answer:
(a) Ethical standards are generally higher than those required by law.
Explanation:
Some behavior that is legally allowed might not be considered ethically appropriate. Legal and ethical standards are often linked, such as in the commandment “Thou shalt not kill.” Ethical standards are never irrelevant, though a client’s safety or the safety of others may pose an ethical dilemma for health care personnel. Searching a client’s room when he or she is not there is a violation of privacy. Room searches can be done with an HCP’s prescription and generally are done with the client present.
Question 142.
A client with a history of cocaine abuse is receiving intravenous therapy and exits the hospital “to visit a friend.” The client returns to the nursing unit 1 hour later, agitated, aggressive, combative, and reporting “chest pain.” Place the nurse’s actions in priority order from first to last. All options must be used.
(a) Contact the security department.
(b) Obtain an ECG.
(c) Initiate a referral to obtain drug rehabilitation counseling.
(d) Obtain a urine sample
Answer:
(a) Contact the security department.
(b) Obtain an ECG.
(c) Initiate a referral to obtain drug rehabilitation counseling.
(d) Obtain a urine sample
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) The nurse should first provide for safety of the client and the staff by requesting assistance from the security department. Next, the nurse should obtain an ECG because the client reports having chest pain. The nurse should then obtain a urine sample to identify if the client has been using illegal drugs. When the client is stabilized, the nurse can develop a care plan that includes treatment goals to support the respiratory and cardiovascular functions and enhance clearance of the agent and initiate a referral for treatment where access to the drug is eliminated and drug rehabilitation is provided as part of therapeutic management of clients with substance abuse and/or a drug overdose.
Question 143.
During a unit meeting attended by clients and staff, several clients are criticizing their primary nurses. These clients have also been intimidating two other clients who have recently been admitted to the unit, and now, the new clients have stopped sharing their opinions during the meeting. What is the first action for the nurse to take?
(a) Help the new clients express the reasons they have stopped sharing their ideas.
(b) Ask the clients criticizing their nurses to suggest some possible solutions for the practices they are criticizing.
(c) Give the clients who are publicly criticizing the nurses a verbal warning that this behavior is not acceptable.
(d) Use the next unit meeting to discuss respect and the importance of collaboration with the treatment team.
Answer:
(b) Ask the clients criticizing their nurses to suggest some possible solutions for the practices they are criticizing.
Explanation:
Recognizing that the clients are part of the solution to the issues they are presenting demonstrates a client-centered approach to care. Having the new clients challenge the behaviors of other clients does not facilitate the development of a therapeutic milieu. Warning clients that behaviors are unacceptable reinforces a sense of client powerlessness and does not build a therapeutic relationship. Discussing respect and collaboration would happen after the criticisms have been acknowledged and the clients have been asked for their opinions.
Question 144.
Two nurses disagree on what is the most important information for the client with addictions to have during a discharge teaching session. How should the nurse assigned to provide the discharge teaching proceed?
(a) Share all the information that both nurses thought was important.
(b) Review the policies related to required discharge teaching.
(c) Be aware of different interpretations and personal biases held by nurses.
(d) Ask the client what is most important for her as she prepares for discharge.
Answer:
(d) Ask the client what is most important for her as she prepares for discharge.
Explanation:
The discharge teaching session will be most effective if the nurse uses a client-centered approach to better assess what the client needs and, therefore, what information to share. Sharing all the information does not respect the knowledge that the client already has. Reviewing the policies is one area to help identify important areas for teaching, but in order to ensure that client needs are met, further assessment is required. Awareness of personal biases should not be used to determine what is important for the client.
