Some Practice NCLEX Questions present ethical dilemmas, requiring students to analyze moral principles and make ethically responsible choices.
NCLEX Pediatric: Neurology Questions
Pediatric: Neurology NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
The nurse in the pediatric intensive care unit (ICU) is caring for an infant with a congenital myelomeningocele. The nurse knows this condition is commonly associated with which of the following?
(a) Hydrocephalus
(b) Microencephaly
(c) Cranial suture overlap
(d) Absence of cranial vault
Answer:
(a) Hydrocephalus
Explanation:
Congenital myelomeningocele is a defect of the neural tube that develops in utero and causes the fetal spinal bones to incompletely form and thus fail to completely cover the spinal cord. The spinal cord and meninges protrude from the child's back. The condition is commonly associated with hydrocephalus, or excessive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cranial vault.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because microencephaly is associated with maternal exposure to rubella or cytomegalovirus (CMV).
(c) is incorrect because cranial suture overlap may occur with a vaginal „ birth but is not associated with myelomeningocele.
(d) is incorrect because absence of cranial vault or anencephaly is an unrelated neural tube defect.
Question 2.
An infant is brought to the emergency room for unusual behavior. The pediatric nurse assesses for which of the following manifestations that could indicate increased intracranial pressure?
(a) Overflow voiding
(b) Bulging fontanel with crying
(c) High-pitched cry
(d) Minimal movement of lower extremities
Answer:
(c) High-pitched cry
Explanation:
Intracranial pressure is the pressure within the skull. Increased intracranial pressure can cause brain injury or be the result of brain injury (most commonly caused by shaken baby syndrome). Increased intracranial pressure in an infant is usually indicated by a high-pitched cry, most notably with Chiari malformation obstructing CSF flow. Nausea, vomiting, decreased level of consciousness, and sluggish or nonreactive pupils are other signs of increased ICP.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because overflow voiding is associated with neurogenic bladder.
(b) is incorrect because a bulging fontanel when the infant cries is a normal finding and not indicating of increased ICP.
(d) is incorrect because minimal movement of lower extremities is associated with damage to the spinal cord.
Question 3.
The nurse in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is caring for a newborn with open spinal defect. When the parents arrive to meet their infant for the first time, which of the following is a priority nursing action?
(a) Encourage the parents to feed the newborn
(b) Discuss parental fears and concerns
(c) Provide educational pamphlets
(d) Emphasize normal and positive features of the newborn
Answer:
(d) Emphasize normal and positive features of the newborn
Explanation:
An open spinal defect is a defect of the neural tube that develops in utero and causes the fetus’ spinal bones to form incompletely. The spinal bones and meninges fail to completely cover the spinal cord, which requires surgical intervention. Parents of children with disability or defect need to hear positive comments and emphasis on the normal and beautiful aspects of their child. The nurse must teach the parents how to hold the child, if possible, and encourage bonding and positive interaction.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because feeding of the infant must wait until after the defect is repaired.
(b) is incorrect because discussion of fears and concerns is not priority during the first visit.
(c) is incorrect because educational material is not priority for the first visit.
Question 4.
The nurse in the clinic is speaking with the parents of a newborn male with Down syndrome. Which of the following would be the most appropriate statement for the nurse to make when teaching the parents about the baby’s diagnosis?
(a) “Plan to teach the child something new daily as he grows up, so he" can be as independent as possible.”
(b) “The life expectancy for children with Down syndrome is significantly longer than it used to be.”
(c) “Large ears and long fingers are common with Down syndrome.”
(d) “If your child doesn’t learn to read by the age of 6, he will probably never read.”
Answer:
(b) “The life expectancy for children with Down syndrome is significantly longer than it used to be.”
Explanation:
Down syndrome is a genetic defect that occurs when an extra chromosome is inherited. Down syndrome causes decreased muscle tone, large forehead, flattened facial features, congenital heart defects, and intellectual disability. When Down syndrome was first discovered, children often did not live beyond age 15. In the 1980s, the life expectancy was 25 years. The current life expectancy is age 60.
No cure is available for Down’s syndrome, but many treatments are available to enhance quality of life and promote healthy, active and more independent lives. Many people with Down syndrome can still learn the physical, mental, and social skills that most other people acquire; they just do it at a different pace.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because learning new things daily may not be possible for a child with Down syndrome.
(c) is incorrect because small ears and short fingers are characteristic with Down syndrome.
(d) is incorrect because all children with Down’s syndrome will have some degree of learning disability. The ability to communicate or to read may develop later than other children the same age. It is important for the nurse to provide factual information to prepare the parents for life with a child with Down syndrome.
Question 5.
The nurse is walking a 6-year-old child with a seizure disorder back from the restroom in his hospital room. When the child starts exhibiting tonic- clonic movements, what is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Note the time
(b) Ease the child to the floor
(c) Clear the area of objects and pad the child’s head
(d) Roll child to the side-lying position for airway protection
Answer:
(a) Note the time
Explanation:
A tonic-clonic seizure is characterized by stiffened muscles, jerking movements, and loss of consciousness. The time should be noted quickly for the nurse to be able to calculate how long the seizure lasts. After noting the time, the nurse’s greatest priority is to stay with the patient and provide for safety, while monitoring the airway.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because easing the child to the floor is the first action after noting the start time.
(c) is incorrect because clearing the area and padding the child’s head is important but not the first action. Risk for injury is increased during a tonic-clonic seizure, and safety is the greatest priority after noting the start time of the seizure.
(d) is incorrect because rolling the child to a side-lying position to protect the airway is important during a tonic-clonic seizure but should not be done until after the start time is noted, the patient has been eased to the floor, and the head has been padded.
Question 6.
The nurse in the pediatric emergency room is assessing a child who sustained a moderate brain injury after a fall. Which assessment gives
the earliest indication of potential increasing intracranial pressure (ICP) „ in this child?
(a) Bilateral pupil response to light
(b) Vital signs
(c) Level of consciousness
(d) Gross motor strength
Answer:
(c) Level of consciousness
Explanation:
Brain injury is caused by several actions including violent shaking, a direct blow, whiplash, or a fall and results in shaking of the brain and trauma. Changes in level of consciousness are the earliest indicator of increasing ICP in a child because brain cells responsible for cognition are extremely sensitive to decreased circulating oxygen in cerebral blood flow.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because changes in level of consciousness (disorientation, restlessness) are the earliest indicator of increasing ICP and may be seen before changes in pupillary response are assessed.
(b) is incorrect because changes in vital signs are a later sign of increasing ICP. Vital sign changes that correlate with increasing ICP include decreased pulse and respiratory rate, increase in blood pressure and temperature, widened pulse pressure, and Cheyne-stokes breathing (rhythmic waxing and waning of rate and depth of respirations alternating with brief periods of apnea).
(d) is incorrect because gross motor strength (weakness on one extremity or on one side of the body) usually occurs after changes in level of consciousness.
Question 7.
A child in the pediatric neurological intensive care unit (NICU) has mannitol prescribed by the healthcare provider for head injury. Which of the following best indicates the medication is effective?
(a) Increased urine output
(b) Improved level of consciousness (LOC)
(c) Decreased facial swelling
(d) Intracranial pressure (ICP) 22 mm Hg
Answer:
(b) Improved level of consciousness (LOC)
Explanation:
Increased ICP is manifested by altered level of consciousness (LOC), headache, nausea and vomiting, pupillary changes, diplopia, increased systolic blood pressure, slow respirations, slow and bounding pulse, widening pulse pressure, and hyper/hypothermia. Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic that decreases intracranial pressure. LOC would be the best indicator of the medication being an effective treatment.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because increased urine output is expected with an osmotic diuretic, but the effectiveness is best assessed by improved LOC.
(c) is incorrect because although an osmotic diuretic may decrease facial swelling, the medication is not primarily given for the purpose of reducing edema.
(d) is incorrect because normal ICP is 10-20 mm Hg. Increased ICP is not a sign that mannitol is effective, as this is a high reading.
Question 8.
The nurse on the pediatric intensive care unit (ICU) is admitting a 10- year-old girl for a suspected infratentorial brain tumor. Which action is the nurse’s greatest priority?
(a) Implement seizure precautions
(b) Introduce the child to other patients of the same age
(c) Prepare the child and her parents for the ordered diagnostic procedures
(d) Use distraction techniques to eliminate the child’s anxiety
Answer:
(c) Prepare the child and her parents for the ordered diagnostic procedures
Explanation:
Infratentorial brain tumors, including glial tumors and medulloblastomas, are located in the cerebellum or brain stem and affect movement coordination, problem solving, judgement, personality, and reasoning. The diagnosis of suspected an infratentorial brain tumor requires diagnostic procedures to confirm, so the nurse should prepare the family.
It is the ordering healthcare provider’s responsibility to explain the diagnostic procedure and obtain consent, but the nurse must be available to answer questions and perform the pre-procedure preparations for the client. These preparations may include switching the child to a gown without snaps (if going for an MRI), administering pre-procedure medications, initiating IV access, performing a neurological assessment, documenting vital signs, and reinforcing the teaching provided by the ordering healthcare provider.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because infratentorial brain tumors do not commonly cause seizure activity.
(b) is incorrect because promoting social interaction with other children of the same age meets the child’s psychosocial needs. The greater nursing priority is to prepare the child and family for diagnostic procedures, which are a greater physical need at this time.
(d) is incorrect because anxiety may be reduced with distraction, but diagnostic procedures are the greatest priority.
Question 9.
The nurse in the clinic is assessing an 8-year-old boy who complains of a sore throat, generally not feeling well, muscle tenderness, bilateral leg weakness, and recent tingling in the fingertips. Which assessment is most important for the nurse to assess?
(a) 24-hour previous dietary intake
(b) Exposure to contagious illnesses
(c) Urination difficulty
(d) Swallowing ability
Answer:
(d) Swallowing ability
Explanation:
The child has symptoms of Guillain-Barre (GB) syndrome, a progressive inflammatory autoimmune response occurring in the peripheral nervous system, in which paralysis ascends from the lower extremities upward. With GB syndrome, nerve roots are compressed, and demyelination occurs. A sore throat commonly precedes paralysis related to this condition. Swallowing ability should be evaluated to determine if immediate action is needed.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because 24-hour dietary intake will not elicit useful information related to the symptoms. Assessment of the airway (right- here-and-now) is a greater priority than previous food intake.
(b) is incorrect because the child is showing signs of GB, which is not contagious.
(c) is incorrect because difficulty with urination will not elicit useful information related to the symptoms, and the urinary system does not take priority over the airway.
Question 10.
A 13-year-old male patient in the pediatric intensive care unit (ICU) was admitted the previous day following a motor vehicle accident. When
assessing the adolescent, which finding indicates spinal shock is , resolving?
(a) Widening pulse pressure
(b) Hyperactive reflexes
(c) Atonic urinary bladder
(d) Flaccid paralysis
Answer:
(b) Hyperactive reflexes
Explanation:
Spinal shock is manifested by bradycardia, decreased pulses, hypotension, complete loss of sensation, and vasodilation with warm skin. After spinal cord injury and spinal shock, nerve reflex return usually results in hyperactivity and spasticity of limbs and bladder. Abnormally strong reflexes can be produced with minimal stimulation.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because widened pulse pressure is unrelated to resolution of spinal shock and may be an indication of increasing intracranial pressure.
(c) is incorrect because atonic urinary bladder is an indication of continuing spinal shock.
(d) is incorrect because flaccid paralysis of skeletal muscles is an effect of spinal shock, indicating it is not yet resolving.
Question 11.
The nurse in the pediatric emergency room is caring for a 9-year-old girl with suspected Guillain-Barre (GB) syndrome. Which of the following is not a symptom associated with this syndrome?
(a) Weakening or tingling sensation in legs
(b) Weakness in arms and upper body
(c) Nearly complete paralysis
(d) Altered mental status
Answer:
(d) Altered mental status
Explanation:
Guillain-Barre syndrome is a progressive inflammatory autoimmune disorder occurring in the peripheral nervous system, in which paralysis ascends from the lower extremities upward. With GB syndrome, nerve roots are compressed, and demyelination occurs. Complete paralysis can occur over time. Physical movement and sensation are affected, but altered mental status is not a symptom associated with Guillain-Barre.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because weakening or tingling sensation in the legs is a symptom of Guillain-Barre.
(b) is incorrect because weakness in arms and upper body is a symptom of Guillain-Barre.
(c) is incorrect because nearly complete paralysis is a symptom of Guillain-Barre.
Question 12.
The nurse in the family practice clinic is teaching the parents of a 4-year- old about epilepsy. Which of the following is NOT a test that can diagnose epilepsy?
(a) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan
(b) Electroencephalogram (EEG)
(c) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain
(d) Wadatest
Answer:
(d) Wadatest
Explanation:
Epilepsy is a disorder of the neurological system characterized by loss of consciousness, convulsions, and recurrent episodes of disturbance of sensory functions due to abnormal brain electrical activity. A Wada test itself does not diagnose epilepsy. After epilepsy is diagnosed, a Wada test can be used to determine which hemisphere controls language and helps the neurosurgeon plan the surgical intervention for epilepsy.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because a PET scan can diagnose epilepsy.
(b) is incorrect because an electroencephalogram (EEG) charts and records the electrical activity in the brain. Certain abnormal patterns, such as spike and sharp wave activities on an EEG, can help support or confirm a clinical diagnosis of epilepsy.
(c) is incorrect because MRI of the brain can be used to diagnose epilepsy.
Question 13.
The family of a 6-year-old girl diagnosed with epilepsy asks the nurse how epilepsy can be treated to eliminate or reduce seizure frequency. Which of the following does the nurse NOT inform the parents of?
(a) Cognitive-behavioral therapy
(b) Narrow spectrum and broad-spectrum antiepileptic medications
(c) Vagus nerve stimulation
(d) Surgery
Answer:
(a) Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Explanation:
Epilepsy is a disorder of the neurological system characterized by loss of consciousness, convulsions, and recurrent episodes of disturbance of sensory functions due to abnormal brain electrical activity. Behavioral or emotional difficulty may develop in response to stigmatization, so cognitive-behavioral therapy is not usually considered to eliminate or reduce seizure frequency; however, it may be used as adjunctive therapy.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because narrow- and broad-spectrum antiepileptic medications are used for treatment of epilepsy.
(c) is incorrect because vagus nerve stimulation is used for treatment of epilepsy.
(d) is incorrect because surgery is used for treatment of epilepsy.
Question 14.
The nurse in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) is caring for an infant diagnosed with hydrocephalus. When teaching the parents about treatments for hydrocephalus, which of the following does the nurse inform the parents of as a possibility?
(a) Lumbar puncture
(b) Osmotic diuretics
(c) Shunt placement
(d) Monitoring intracranial pressure
Answer:
(c) Shunt placement
Explanation:
Hydrocephalus is accumulation of the spinal fluid within the brain due to abnormal production or recycling of the fluid in the neurological system. This leads to rapid enlargement of the head and neurological disruption. A shunt can be placed in the brain or the abdomen to create a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) reservoir and prevent the fluid from flowing back to the brain, decreasing the pressure and fluid level in the brain to normal levels.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because lumbar puncture is not a treatment for hydrocephalus. A lumbar puncture is used to collect a sterile sample of CSF for laboratory testing, relieve pressure, inject dye, or inject medication.
(b) is incorrect because osmotic diuretics are not a treatment for hydrocephalus.
(d) is incorrect because monitoring intracranial pressure is an important . nursing assessment but is not a treatment for hydrocephalus.
Question 15.
A 6-month-old infant is admitted to the neurological unit for hydrocephalus. Which of the following does the nurse expect to find when assessing the infant?
(a) Normal growth and development
(b) Enlarged head circumference
(c) Infant is able to sit upright unassisted
(d) Unresponsiveness
Answer:
(b) Enlarged head circumference
Explanation:
Hydrocephalus is accumulation of the spinal fluid within the brain due to abnormal production or recycling of the fluid in the neurological system. This leads to rapid enlargement of the head and neurological disruption. Symptoms of hydrocephalus include enlargement of head circumference, nystagmus, convulsions, vomiting, irritability, delay of growth and meeting developmental milestones, and failure to thrive. Other common findings with hydrocephalus include a prominent forehead, dilated scalp veins, and widened, tense fontanelles.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because children with hydrocephalus tend to have delayed growth and development.
(c) is incorrect because the 6-month-old infant with hydrocephalus is usually unable to sit upright unassisted due to developmental delay.
(d) is incorrect because hydrocephalus may cause somnolence but does not cause unresponsiveness.
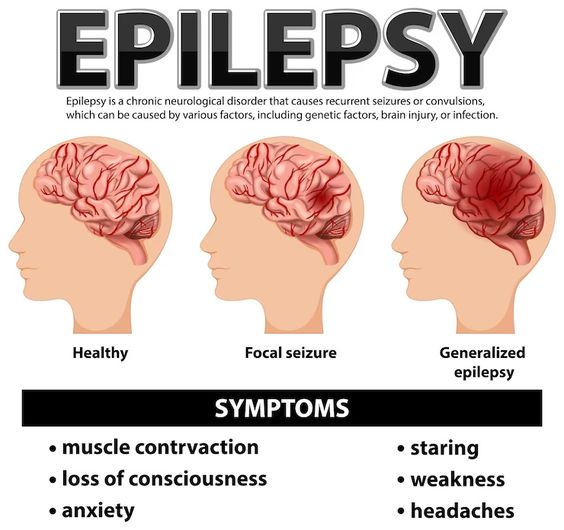
Question 16.
The mother of an infant admitted with cerebral palsy is upset about the child’s diagnosis. She explains that she experienced a normal pregnancy and delivery. When the mother asks what she did to cause this, what is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Your child’s cerebral palsy may be due to your ingestion of sushi during pregnancy.”
(b) “The cerebral palsy is due to complications during delivery.”
(c) “It’s not always known why cerebral palsy occurs, but it happens during development of the baby’s brain.”
(d) “Cerebral palsy is usually due to jaundice at birth.”
Answer:
(c) “It’s not always known why cerebral palsy occurs, but it happens during development of the baby’s brain.”
Explanation:
Cerebral palsy affects function of the brain and nervous system and includes several different types. The etiology of cerebral palsy is not always clear, but is possibly due to brain bleed, encephalitis or meningitis, head injury, or rubella infection in the mother during pregnancy.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because ingestion of sushi during pregnancy is not linked to increased incidences of cerebral palsy. Brain damage and hearing and vision problems have been linked to maternal ingestion of sushi and other mercury-containing foods during the prenatal period.
(b) is incorrect because some cases of cerebral palsy are related to a traumatic delivery, anoxia during birth, or infection at the time of delivery, but the mother already indicated that the pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated. The nurse should use caution making definitive, accusatory, presumptive statements.
(d) is incorrect because jaundice develops after birth and would have to be severe in order to increase the risk of cerebral palsy.
Question 17.
The nurse on the pediatric ward is caring for a 4-year-old female patient with spastic cerebral palsy. When observing the child ambulating, which of the following does the nurse expect to see?
(a) Tight muscles and abnormal gait
(b) Seizure activity
(c) Muscle weakness and hypermobile joints
(d) Increased muscle mass in lower extremities
Answer:
(c) Muscle weakness and hypermobile joints
Explanation:
Cerebral palsy is a group of permanent disorders that affect function of the brain and development of the child’s nervous system. Movement and posture are affected, causing activity limitation due to disturbances that occurred in the developing fetal or infant brain. Spastic cerebral palsy, the most common type of cerebral palsy, is characterized by symptoms including tight muscles and abnormal gait, joint contracture, and paralysis in groups of muscles.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because although the risk for seizures is increased with cerebral palsy in general, seizure activity is not expected when assessing the gait of a child with spastic cerebral palsy.
(c) is incorrect because although muscles weakness may be seen, hypermobility of joints is not expected with spastic cerebral palsy. Joint contractures are more common.
(d) is incorrect because children with cerebral palsy often have decreased muscle mass.
Question 18.
The parents of a 9-year-old girl diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) ask the nurse what they can do to help their child. Which of the following suggestions does the nurse make?
(a) Speak with her teacher about putting her in a large class with other children the same age
(b) Provide lenient rules and be patient
(c) Praise her for good behavior and give rewards
(d) Avoid schedules and routines to decrease the child’s frustration
Answer:
(c) Praise her for good behavior and give rewards
Explanation:
ADHD is a collection of one or more symptoms related to focus, activity, and control of behavior. Children with ADHD will be inattentive, hyperactive, or impulsive, or any combination of the three symptoms. Helping the child with ADHD consists of regularly speaking with the teacher, small class size, setting consistent rules, praising good behavior, maintaining normal schedules and routines, providing for sufficient sleep, and limiting distractions.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because, although children with ADHD can often thrive in a classroom with others of the same age group and developmental stage, they benefit from a small class size.
(b) is incorrect because the parent of a child with ADHD should be encouraged to use both consistency and patience when enforcing rules.
(d) is incorrect because the child with ADHD benefits from regular schedules and routines.
Question 19.
The nurse in the family practice clinic is teaching the parents of an 8- year-old boy with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) regarding a new prescription for dextroamphetamine. When the parents ask how the medication works, what is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “The medication will increase your child’s mental alertness to help him focus in school.”
(b) “The medication will help your child sleep better at night.”
(c) “Monitor your child’s heart rate when starting this medication, as it can cause the heart to beat more slowly.”
(d) “This medication will decrease motor activity, so your child won’t fidget as much.”
Answer:
(a) “The medication will increase your child’s mental alertness to help him focus in school.”
Explanation:
ADHD is a collection of one or more symptoms related to focus, activity, and control of behavior. Dextroamphetamine is a CNS stimulant that facilitates the release of catecholamines which increases motor activity, enhances mental alertness, and decreases drowsiness to help the child focus.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because the medication is a stimulant which can cause insomnia, so it should be given in the morning.
(c) is incorrect because the medication is a stimulant which can cause tachycardia and palpations.
(d) is incorrect because the medication stimulates the nervous system and increases motor activity. Fidgeting is a common side effect with administration of this type of drug.
Question 20.
The parents of a 4-year-old girl have brought their child to the family practice clinic to be evaluated for changes in mobility. The parents report that she has started tripping and falling, has become very clumsy, complains of leg pain, and is no longer able to climb stairs at home. Which of the following does the nurse suspect?
(a) Hydrocephaly
(b) Myelomeningocele
(c) Cerebral palsy
(d) Muscular dystrophy
Answer:
(d) Muscular dystrophy
Explanation:
Muscular dystrophy is an inherited, terminal muscular disorder that causes progressive muscle weakness, atrophy, and replacement with fatty tissue over time. The nerves are not affected. Symptoms include clumsy movements, difficulty with stair climbing, tripping and falling frequently, leg pain, and weakness. Diagnosis usually occurs between the ages of 3 and 6 years. Treatment includes intense physical therapy, frequent range of motion, and often, the use of leg braces to help with ambulation.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the symptoms are not characteristic of hydrocephaly. Hydrocephaly is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, and common symptoms in a pre-school-aged child are high- pitched cry, changes in personality, crossed eyes, difficulty feeding, sleepiness, headache, and irritability.
(b) is incorrect because myelomeningocele is a type of spina bifida in which the unfused portion of the spinal column allows the spinal cord to protrude through an opening. This diagnosis is either made while the fetus is in utero, or shortly after birth, not at age 4.
(c) is incorrect because cerebral palsy symptoms are present at birth, and do not suddenly worsen at the age of 4.
Question 21.
A 12-year-old girl is admitted to the emergency room following a fall off of a horse. She is disoriented and restless and determined to have sustained a concussion. Which of the following nursing diagnoses is the highest priority?
(a) Disturbed visual sensory perception
(b) Self-care deficit
(c) Impaired verbal communication
(d) Risk for injury
Answer:
(d) Risk for injury
Explanation:
A concussion is a traumatic injury of the brain that jars the brain within the skull. There are usually no visible signs of brain injury with a concussion, and symptoms include losing consciousness, inability to remember what happened, repetitive questions, confusion, disorientation, and restlessness. The patient is at risk for injury due to disorientation and restlessness. The nurse should keep the patient’s bed in the lowest position, raise side rails to prevent falling from the bed, and monitor the patient closely.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because disturbed visual sensory perception may be present with a concussion but is not a greater priority than physical safety.
(b) is incorrect because no information is provided to indicate that the child is experiencing a self-care deficit.
(c) is incorrect because the information given about the patient does not indicate that the child is having difficulty with verbal communication and this is not a greater priority than physical safety from injury.
Question 22.
The nurse is caring for a 15-year-old patient with paraplegia at the T4 level due to a history of a skateboarding accident which occurred nine months ago. Which of the following interventions should the nurse perform to prevent autonomic dysreflexia in this patient?
(a) Support a high-protein diet
(b) Discuss sexuality and fertility options
(c) Plan a bowel program
(d) Teach quad coughing
Answer:
(c) Plan a bowel program
Explanation:
Autonomic dysreflexia is uncontrolled hypertension with acute onset that can develop in patients with spinal cord injury at the level of T6 and above. It can lead to seizures, pulmonary edema, myocardial infarction, hemorrhage, and death. A common stimulus is fecal impaction (due to the patient’s inability to sense the need to have a bowel movement), so a bowel program should be planned to prevent impaction from developing.
Other causes of autonomic dysreflexia include bladder distention, pain, and tactile stimulation. Nursing priorities include emptying the urinary bladder frequently (patient self-catheterization or straight-catheterization by the nurse) and that linens are not creased underneath the patient.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because a high-protein diet will not prevent fecal impaction or autonomic dysreflexia. The diet should contain adequate fiber and liquids to keep stool soft and minimize the likelihood of constipation or impaction.
(b) is incorrect because discussion of sexuality and fertility options is not appropriate for a 15-year-old and will not prevent autonomic dysreflexia.
(d) is incorrect because, although teaching coughing and incentive spirometry exercises are important for respiratory health, these will not prevent autonomic dysreflexia.
Question 23.
A 5-year-old girl is scheduled for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Which of the following actions should be implemented by the nurse before the test?
(a) NPO status for 12 hours prior to the MRI
(b) Withhold all daily medications until after the MRI is completed
(c) Administer morphine for prevention of claustrophobia
(d) Place the patient in gown with cloth ties
Answer:
(d) Place the patient in gown with cloth ties
Explanation:
MRI has a magnetic field, and metal objects are a hazard around the MRI. A gown with cloth ties should be placed on the patient to prevent injury to the patient. If a gown with metal snaps is used, this can cause burning to the skin.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because if a child requires sedation for an MRI, NPO status is generally required for eight hours prior to the procedure.
(b) is incorrect because withholding daily medications may not be necessary for an MRI.
(c) is incorrect because morphine is an opiate pain medication which is not used to prevent claustrophobia during an MRI. If the child has a history of claustrophobia or experiences claustrophobia during the procedure, anxiolytic medications maybe administered.
Question 24.
The nurse is caring for a 6-year-old patient with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Which of the following actions is most important?
(a) Treatment of peripheral pain with acetaminophen
(b) Encourage the child to participate in activities of daily living
(c) Determine if the child has recently been ill
(d) Assessment of progression of muscle weakness
Answer:
(d) Assessment of progression of muscle weakness
Explanation:
Guillain-Barre is an autoimmune disorder which leads to the immune system attacking nerves, which causes patients to be temporarily paralyzed over time. Early symptoms include sensation changes with pain and muscle weakness beginning in the feet and hands and progressing up the legs and arms. This weakness can spread to respiratory muscles and may require mechanical ventilation. Assessing the progression of muscle weakness and respiratory effort is the greatest priority.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because Guillain-Barre can cause pain, but assessment of muscle weakness is the greater physical priority.
(b) is incorrect because it is beneficial to the child to participate in ADLs as tolerated, but assessment of respiratory status and muscle weakness is the greater concern.
(c) is incorrect because Guillain-Barre can be triggered by recent infection, but determining the cause is not more important than current physical assessment.
Question 25.
A nurse on the pediatric neurological unit performs a neurological assessment on an unresponsive 11-year-old boy. When painful stimuli are introduced, the boy’s arms are drawn up to the middle of the chest with the elbows bent and backs of the hands together, and the toes are pointed inward. How does the nurse document the finding?
(a) Decorticate posturing
(b) Decerebrate posturing
(c) Atypical hyperreflexia
(d) Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) motor response score : 4
Answer:
(a) Decorticate posturing
Explanation:
Decorticate posturing occurs when there is an interruption of the corticospinal pathway. The arms are flexed with the backs of the hands pressed together in the middle of the chest, and toes are pointed toward the midline. This is an abnormal finding and is indicative of brain damage. The healthcare provider must be notified immediately when this occurs.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because decerebrate posturing is external rotation and extension of extremities, and this type of posturing is indicative of more severe brain damage, often involving the brainstem.
(c) is incorrect because hyperreflexia is increased reflex response.
(d) is incorrect because a GCS motor response score of 4 is documented if the child withdraws to painful stimuli. Decorticate posturing scores a motor response score of 3.
