NCLEX RN Practice Questions provide an opportunity to reinforce knowledge of nursing fundamentals, including anatomy and physiology.
NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 7 with Rationale
Question 1.
Rho (D) immune globulin is prescribed for a client before she is discharged after a spontaneous abortion. The nurse instructs the client that this drug is used to prevent which condition?
(a) development of a future Rh-positive fetus
(b) an antibody response to Rh-negative blood
(c) a future pregnancy resulting in abortion
(d) development of Rh-positive antibodies
Answer:
(d) development of Rh-positive antibodies
Rationale:
Rh sensitization can be prevented by Rho(D) immune globulin, which clears the maternal circulation of Rh-positive cells before sensitization can occur, thereby blocking maternal antibody production to Rh-positive cells. Administration of this drug will not prevent future Rh-positive fetuses, nor will it prevent future abortions. An antibody response will not occur to Rh-negative cells. Rh-negative mothers do not develop sensitivities if the fetus is also Rh negative.
Question 2.
The primary health care provider prescribes intravenous magnesium sulfate for a primigravid client at 38 weeks’ gestation diagnosed with severe preeclampsia. Which medication would be most important for the nurse to have readily available?
(a) diazepam
(b) hydralazine
(c) calcium gluconate
(d) phenytoin
Answer:
(c) calcium gluconate
Rationale:
The client receiving magnesium sulfate intravenously is at risk for possible toxicity. The antidote for magnesium sulfate toxicity is calcium gluconate, which should be readily available at the client’s bedside. Diazepam is used to treat anxiety, and usually it is not given to pregnant women. Hydralazine would be used to treat hypertension, and phenytoin would be used to treat seizures.
Question 3.
The primary health care provider prescribes whole blood replacement for a multigravid client with abruptio placentae. What should the nurse do first before administering the intravenous blood product?
(a) Validate client information and the blood product with another nurse.
(b) Check the vital signs before transfusing over 5 to 6 hours.
(c) Ask the client if she has ever had any allergies.
(d) Administer 100 mL of 5% dextrose solution intravenously.
Answer:
(a) Validate client information and the blood product with another nurse.
Rationale:
When administering blood replacement therapy, extreme caution is needed. Before administering any blood product, the nurse should validate the client information and the blood product with another nurse to prevent administration of the wrong blood transfusion. Although baseline vital signs are necessary, she should initiate the infusion of blood slowly for the first 10 to 15 minutes.
Then, if there is no evidence of a reaction, she should adjust the rate of infusion to ensure that the blood product is infused over 2 to 4 hours. The nurse can ask the client if she has ever had a reaction to a blood product, but a general question about allergies may not elicit the most complete response about any reactions to blood product administration. Blood transfusions are typically given with intravenous normal saline solution, not dextrose solutions.
Question 4.
The primary health care provider (HCP) prescribes betamethasone for a 34-year-old multigravid client at 32 weeks’ gestation who is experiencing preterm labor. Previously, the client has experienced one infant death due to preterm birth at 28 weeks’ gestation. The nurse explains that this drug is given for which reason?
(a) to enhance fetal lung maturity
(b) to counter the effects of tocolytic therapy
(c) to treat chorioamnionitis
(d) to decrease neonatal production of surfactant
Answer:
(a) to enhance fetal lung maturity
Rationale:
Betamethasone therapy is indicated when the fetal lungs are immature. The fetus must be between 28 and 34 weeks’ gestation, and birth must be delayed for 24 to 48 hours for the drug to achieve a therapeutic effect. Antibiotics would be used to treat chorioamnionitis. Betamethasone is not an antagonist for tocolytic therapy. It increases, not decreases, the production of neonatal surfactant.
Question 5.
A multigravid laboring client has an extensive documented history of drug addiction. Her last reported usage was 5 hours ago. She is 2 cm dilated with contractions every 3 minutes of moderate intensity. The health care provider prescribes nalbuphine 15 mg slow IV push for pain relief followed by an epidural when the client is 4 cm dilated. Within 10 minutes of receiving the nalbuphine, the client states she thinks she is going to have her baby now. Of the drugs available at the time of the birth, which should the nurse avoid using with this client in this situation?
(a) lidocaine 1%
(b) naloxone
(c) local anesthetic
(d) pudendal block
Answer:
(b) naloxone
Rationale:
Naloxone would not be used in a client who has a history of drug addiction. Naloxone would abruptly withdraw this woman from the drug she is addicted to as well as the nalbuphine. The withdrawal would occur within a few minutes of injection and, if severe enough, could jeopardize the mother and fetus. Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and numbs rather than decreases the effects of nalbuphine. The local anesthetic and the pudendal block are both appropriate for this birth but are used to numb the maternal perineum for birth.
Question 6.
A full-term client is admitted for induction of labor. When admitted, her cervix is effaced 25% but has not dilated. The initial goal is cervical ripening prior to labor induction. Which drug will prepare her cervix for induction?
(a) nalbuphine
(b) oxytocin
(c) dinoprostone
(d) betamethasone
Answer:
(c) dinoprostone
Rationale:
Cervical ripening, or creating a cervix that is soft, anterior, and dilated to 2 to 3 cm, must occur before the cervix can efface and dilate with oxytocin. Drugs to accomplish this goal include dinoprostone, misoprostol, and prostaglandin E2. Nalbuphine is a narcotic analgesic used in early labor and has no influence on the cervix. Betamethasone is a corticosteroid given to mature fetal lungs.
Question 7.
The nurse is explaining the medication options available for pain relief during labor. The nurse realizes the client needs further teaching when the client makes which statement?
(a) “Nalbuphine and promethazine will give relief from pain and nausea during early labor.”
(b) “I can have an epidural as soon as I start contracting.”
(c) “If I have a cesarean, I can have an epidural.”
(d) “If I have an emergency cesarean, I may be put to sleep for the birth.”
Answer:
(b) “I can have an epidural as soon as I start contracting.”
Rationale:
Typically, a client will be able to have an opidural when she is 3 to 4 cm dilated or the active phase of Labor has been established. Waiting until the cervix is dilated to this pointensures that the client is in labor and the epidural is less likely to haltlabor contractions. Nalbuphine and promethazine are used to provide relief tint il the client is about 7cm dilated. If given after this time, narcotics may cause neonatal respiratory depression in the neonate. The majority of clients have an epidural or spinal for a cesarean birth. The only time general anesthesia is used is for an emergency cesarean birth.
Question 8.
When instilling erythromycin ointment into the eyes of a neonate 1 hour old, the nurse would explain to the parents that the medication is used to prevent which problem?
(a) chorioretinitis from cytomegalovirus
(b) blindness secondary to gonorrhea
(c) cataracts from beta-hemolytic streptococcus
(d) strabismus resulting from neonatal maturation
Answer:
(b) blindness secondary to gonorrhea
Rationale:
The instillation of ervthromvcin into the neonate’s eyes provides prophvlaxis for ophthalmia neonatorum, or neonatal blindness caused 1w gonorrhea in the mother. Erythromvcin is also effective in the prevention of infection and conjunctivitis from Ghlarnvdia trachomatis. The med icat ion may result in redness of the neonate’s eyes, but this redness will eventually disappear. Ervthrornvcin ointment is not effective in treating neonatal chorioretinitis from cytornegalovirus.
No effective treatment is available for a mother with cytornegalovirus. Ervthromycin ointment is not effective in preventing cataracts. Additionall. neonatal infection with beta-hemolvtic streptococcus results in pneumonia, bacterial meningitis, or death. Cataracts in the neonate may be congenital or may result from maternal exposure to
rubella. Ervthromycin ointment is also not effective for preventing and treating strahismus (crossed eyes). Infants may exhibit intermittent strabismus until 6 months of age.
Question 9.
The health care provider prescribes ampicil- lin 100 mg/kg/dose for a newly admitted neonate. The neonate weighs 1,350 g. How many milligrams should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal place.
...................... mg
Answer:
135 mg
Rationale:
The recommended dose of anipicillin for a neonate is loo mg/kg per dose. First, determine the a cesarean birth. The only time general anesthesia is used is for an emergency cesarean birth. neonate’s weight in kilograms, and then multiply the kilograms by 100 mg. The nurse should use this formula:
1,000 g = 1 kg 1,350 g = 1.35 kg 100 mg x 1.35 kg = 135 mg/kg
Question 10.
The nurse caring for a postterm client scheduled for an induction of labor has completed the necessary assessments. The client has been placed on electronic fetal monitoring, and venous access has been established. After reviewing a titrated prescription for oxytocin (see graphic), the nurse should perform what action next?
|
History |
Physical |
Precautions |
|
1. Start IV infusion of oxytocin 30 unitsl500 mL lactated Ringers at 2 milliunits/min |
||
|
2. Increase by 1 to 2 milliunitslmin q3Omìn until adequate progress of labor is established and/or contractions are q2-3 minutes apart |
||
|
3. Discontinue oxytocin infusion immediately for uterine hyperactivity or fetal distress. |
||
(a) Begin the oxytocin infusion at 2 milliunits/min.
(b) Contact the health care provider to clarify the prescription.
(c) Ensure that adult resuscitation equipment is in the room.
(d) Implement a two-nurse verification of a high-alert medications.
Answer:
(b) Contact the health care provider to clarify the prescription.
Rationale:
Titration prescriptions must include the medication name, route, starting rate of infusion (dose/min), incremental units the rate can be increased or decreased, frequency for incremental doses (how often dose [rate] can be increased or decreased), maximum rate (dose) of infusion, and an objective clinical endpoint. This prescription does not contain a maximum rate and therefore must be clarified before administering the medication.
The nurse cannot begin the infusion without clarification. Oxytocin infusions are not associated with respiratory or cardiac arrests to require the placement of adult resuscitation equipment in the room. Oxytocin is a high alert medication that should be verified by two nurses, but only after the prescription is clarified.
Question 11.
The nurse is initiating intravenous (IV) therapy in a newborn. What should the nurse include in the plan of care? Select all that apply.
(a) Offer oral sucrose during the IV insertion.
(b) Ensure the site is covered with a sterile transparent dressing.
(c) Use IV boards to secure an IV near an area of flexion.
(d) Flush the IV site every 4 hours.
(e) Document the IV status hourly.
Answer:
(a) Offer oral sucrose during the IV insertion.
(b) Ensure the site is covered with a sterile transparent dressing.
(c) Use IV boards to secure an IV near an area of flexion.
(e) Document the IV status hourly.
Rationale:
Oral sucrose is an effective measure to reduce procedural pain. A sterile transparent dressing helps reduce infection while making the insertion site visible for continual assessment. Due to the fragility of an infant’s blood vessels, hourly assessments for infiltrations are important to prevent tissue or skin damage. Immobilizing the joint reduces the risk of venous damage. Routine flushing is not necessary for IV maintenance.
Question 12.
An infant has been diagnosed with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) and is receiving therapeutic weaning doses of methadone. What measure is most needed to ensure client safety when administering methadone?
(a) Document vital signs for drug administration.
(b) Notify the health care provider of the administration of the medication.
(c) Obtain an independent double check of the medication from another nurse.
(d) Wake the infant for an assessment prior to the administration of the medication.
Answer:
(c) Obtain an independent double check of the medication from another nurse.
Rationale:
Methadone is a controlled narcotic that needs an independent double check before the drug is given to assure the rights of drug administration. Vital signs are not necessary just before the administration of this drug. Infants with NAS will be assess-ment over a 3- to 6-hour period of time for behaviors; waking the infant for an assessment is not appropriate. The drug was prescribed by the health care provider fTJ, who is expecting the nurse to give and document the drug administration. No other notification is necessary unless there are other concerns.
Question 13.
The nurse is teaching an adolescent with asthma how to tise a metered-dose inhaler. In which order should the nurse instruct the client to follow the steps from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Put the inhaler in your mouth.
(b) Breathe out.
(c) Depress the top of the inhaler.
(d) Begin to slowly breathe in.
(e) Holdthebreath5to 10 seconds.
(f) Shake the inhaler.
Answer:
(b) Breathe out.
(c) Depress the top of the inhaler.
(d) Begin to slowly breathe in.
(e) Holdthebreath5to 10 seconds.
(a) Put the inhaler in your mouth.
Rationale:
When dispensing medication from an inhaler, the client should first shake the inhaler and then breathe out through the mouth before putting the inhaler in the mouth. The client then presses the canister to dispense the medication and inhales slowly. The client should hold the breath for 5 to 10 seconds before exhaling.
Question 14.
An adolescent girl is prescribed amoxicillin for an ear infection. The nurse should teach the adolescent about the risks associated with her concurrent use of which medication?
(a) over-the-counter antihistamines
(b) oral contraceptives
(c) multiple vitamins
(d) ibuprofen
Answer:
(b) oral contraceptives
Rationale:
When a person is taking amoxicillin as well as an oral contraceptive, it renders the contraceptive less effective. Because pregnancy can occur in such a situation, the nurse should advise the client to use additional means of birth control during the time she is taking the antibiotic. There are no risks associated with the concurrent use of amoxicillin and over- the-counter antihistamines, vitamins, or ibuprofen.
Question 15.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the first choice in treating a child with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Which adverse effects should the nurse include in the teaching plan for the parents? Select all that apply.
(a) weight gain
(b) abdominal pain
(c) blood in the stool
(d) folic acid deficiency
(e) reduced blood clotting ability
Answer:
(b) abdominal pain
(c) blood in the stool
(e) reduced blood clotting ability
Rationale:
Adverse effects from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include abdominal pain, blood in stool, and reduced clotting ability. Weight gain is common with corticosteroids. Folic acid deficiency is associated with methotrexate therapy.
Question 16.
An 18-month-old with a congenital heart defect is to receive digoxin twice a day. Which instructions should the nurse give the parents?
(a) Digoxin enables the heart to pump more effectively with a slower and more regular rhythm.
(b) Signs of digoxin toxicity include increased pulse and visual disturbances.
(c) Digoxin is absorbed better if taken with meals.
(d) Repeat the digoxin dosage if the child vomits within 15 minutes of administration.
Answer:
(a) Digoxin enables the heart to pump more effectively with a slower and more regular rhythm.
Rationale:
Digoxin’s effect is to slow the rate of the electrical conduction through the heart and increase the strength of the heart’s contraction. Signs of toxicity include anorexia and decreased heart rate, not visual changes or increases in heart rate. Digoxin should be taken 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after meals in order to obtain better absorption of the drug. If the child vomits within 15 minutes of administration, the dose should not be repeated because it is not known how much of the medication has been absorbed.
Question 17.
The health care provider prescribes 30 mg of methylphenidate to a child with autism. The meth- ylphenidate is to be given in two divided doses.
The concentration is 10 mg/5 mL. How many mL of methylphenidate should the nurse give per dose? ........................ mL
Answer:
7.5 mL.
Rationale:
\(\frac{\mathrm{mL}}{\text { dose }}=\frac{5 \mathrm{~mL}}{10 \mathrm{mg}} \times \frac{30 \mathrm{mg}}{1 \text { day }} \times \frac{1 \text { day }}{2 \text { doses }}=\frac{7.5 \mathrm{~mL}}{\text { dose }}\)
Question 18.
A child weighing 23 kg is admitted to the hospital for a surgical procedure. The nurse reviews the standing intravenous fluid prescription (see exhibit). At what hourly rate should the nurse infuse the maintenance fluid?
|
Insert a peripheral IV |
|
|
Infuse Dextrose 5% in 0.45% saline per weight protocol: |
|
|
Weight |
mL/kg/day |
|
First 10 kg (weight kg or less) |
100 mLilcglday |
|
For the next 10 kg (weight 10 - 20 kg) |
50 mLJkg/day |
|
More than 20 kg, a child requires 20 mLIlcg/day |
20 mi/kg/day |
........................ mL/h
Answer:
65 mL/h
Rationale:
10 kg x 100 mL = 1,000 mL
10 kg x 50 mL = 500 mL
3 kg x 20 mL = 60 mL
1,000 mL + 500 mL + 60 mL = 1,560 mL/day
\(\frac{1,560 \mathrm{~mL}}{24}\) = 65 mL/h
Question 19.
The parents of a child on sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim for a urinary tract infection report that the child has a red, blistery rash. What instructions should the nurse give the parents?
(a) Apply an anti-itch lotion to the affected areas at least twice a day.
(b) Discontinue the medicine and come for immediate further evaluation.
(c) Use sunblock and avoid midday sun while on the medication.
(d) Increase the child’s fluid intake to at least 2,500 mL/day.
Answer:
(b) Discontinue the medicine and come for immediate further evaluation.
Rationale:
Sulfonamides have been associated with severe adverse reactions. A blistering rash may be a sign of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a severe allergic reaction that manifests as skin lesions. This reaction is life threatening and requires immediate attention. Lotion should not be applied to skin with blisters. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may cause pho-tosensitivity, but this usually appears as a mild red rash, not blisters. Increasing the child’s fluid intake may help the urinary tract infection but does not address the rash.
Question 20.
What should be part of the nurse’s teaching plan for a child with epilepsy being discharged on a regimen of phenytoin?
(a) Drink plenty of fluids.
(b) Brush teeth after each meal.
(c) Have someone be with the child during waking hours.
(d) Report signs of infection.
Answer:
(b) Brush teeth after each meal.
Rationale:
Phenytoin can cause gingival hyperplasia. Children taking phenytoin should brush their teeth after every meal and at bedtime and visit their dentist on a regular basis. Drinking plenty of fluids is not required while taking phenytoin. A child on phenytoin does not need to be observed during waking hours because the seizures should be under control. Infections do not occur with an increased incidence in clients receiving phenytoin.
Question 21.
A client’s intravenous (IV) site on the left arm is cool, pale, and swollen, and the alarm on the infusion pump is sounding. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Reset the alarm on the infusion pump.
(b) Assess the site for infiltration.
(c) Elevate the client’s left arm.
(d) Stop the infusion.
Answer:
(b) Assess the site for infiltration.
Rationale:
Pallor, coolness of the skin, swelling and/ or discomfort may occur at the insertion site if an IV infiltrates because IV fluid is being deposited in the subcutaneous tissue rather than in the vein. When the pressure in the tissues exceeds the pressure in the tubing, the flow of the IV solution will stop, eventually causing the alarms on the pump to sound. The nurse should first determine the reason for the alarm. Once the nurse has determined that the infusion has infiltrated, the nurse will turn the alarm off and then can elevate the client’s arm and stop the infusion.
Question 22.
The health care provider has prescribed a saline lock for a client. In which order from first to last should the nurse implement this prescription? All options must be used.
(a) Use the nondominant hand to stabilize the vein by pulling the skin taut.
(b) Apply clean gloves. and locate and clean the venipuncture site.
(c) Stabilize the catheter and apply dressing to secure the saline lock.
(d) Insert an over-the-needle catheter, advancing the catheter once flashback is observed.
Answer:
(b) Apply clean gloves. and locate and clean the venipuncture site.
(c) Stabilize the catheter and apply dressing to secure the saline lock.
Rationale:
Clean gloves must be donned prior to any invasive procedure in order to protect both the client and the nurse from encountering bodily fluids. The vein is stabilized prior to needle insertion so the vein is less likely to “roll” and the catheter may be more easily threaded into the vein. Flashback signifies that the needle is in the vein, and the catheter is advanced into the vein, using the needle as a guide. Once the catheter is in the vein and connected to the saline lock, they must be stabilized and secured with a transparent dressing so the nurse can monitor the site.
Question 23.
At 0900, the nurse started an infusion of I L of D5NS infusing at a keep-vein-open rate. At 0945, the client reports a pounding headache, is dyspneic, is experiencing chills, and has a heart rate of 116 bprn. The nurse notes that the IV hag has 400 mL remaining. The nurse should take which action first?
(a) Slow the IV infusion.
(b) Assess the client’s blood pressure.
(c) Remove the IV catheter.
(d) Call the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(a) Slow the IV infusion.
Rationale:
The nurse notes that 600 mL of D5NS has infused over 45 minutes. The client is showing signs of circulatory overload, and the first action the nurse should take is to slow the IV infusion as the source of the problem. The nurse can then elevate the head of the bed to improve the client’s ability to breathe and notify the HCP of the change in condition. The nurse should not remove the IV catheter unless there is infiltration as the open line may be needed for administration of medications.
Question 24.
A client is receiving a transfusion of two units of packed red blood cells. Thirty minutes after starting the transfusion of the first unit, the nurse determines the client is having a reaction and stops the infusion. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Remove the IV line and obtain a culture of the tip.
(b) Wait 15 minutes and restart the blood transfusion.
(c) Run normal saline at a keep-vein-open rate.
(d) Call the health care provider (HCP) to report the suspected transfusion reaction.
Answer:
(c) Run normal saline at a keep-vein-open rate.
Rationale:
Infusing normal saline at a slow rate will maintain IV access and help maintain the client’s intravascular volume. Culturing the catheter tip is not necessary because the catheter should not be removed and the concern is transfusion reaction, not infection. If a transfusion reaction is suspected, the nurse should not restart the blood. The HCP should be notified of the suspected reaction after the nurse has stopped the infusion of blood and started an infusion of normal saline.
Question 25.
A client had surgery 6 hours ago. The client has a prescription for a narcotic for pain every 3 to 4 hours. The last dose was administered at 1500. When the nurse enters the room at 1800, the client is restless and grimacing. What action should the nurse take first?
(a) Ask the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) to help reposition the client.
(b) Administer the narcotic to relieve the pain.
(c) Assess the client to determine the cause of the grimacing.
(d) Turn the lights down to minimize the client’s restlessness.
Answer:
(c) Assess the client to determine the cause of the grimacing.
Rationale:
The nurse should carefully assess the client to determine the reason for the grimacing and restlessness. The nurse should not assume by the client’s nonverbal communication that the client is in pain and requires pain medication; the nurse must validate the message rather than making assumptions. The nurse should assess the client first before changing the client’s position or turning down the lights.
Question 26.
A client has a triple lumen central line with lactated Ringer’s (LR) currently infusing at 80 mL/h. The health care provider writes a new prescription for total parenteral nutrition, 1,500 mL to infuse over 24 hours plus lipids to infuse at 250 mL over 12 hours. What is the new infusion rate for LR if the total fluid intake for 24 hours is prescribed to be 125 mL/h? ....................... mL/h
Answer:
41mL/h
Rationale:
To determine the prescribed infusion rate, the nurse needs to calculate the drip rate for all drugs:
TPN: 1,500 mL divided by 24 hours = 62.5, rounded to 63 mL/h
Lipids: 250 mL divided by 12 hours = 20.8 rounded to 21 mL/h
LR: 125 (total fluid intake) - (63 + 21) = 41 mL/h (decreased from 80 mL/h)
Question 27.
Upon entering the room, a nurse notes that there is a cap missing on the central venous access device. The client is experiencing shortness of breath, coughing, and chest pain. What would the nurse do first after replacing the cap on the open port?
(a) Reassure the client that the symptoms will resolve very quickly.
(b) Place the client in low Fowler’s position to facilitate easier breathing.
(c) Obtain an electrocardiogram (EKG) to rule out possible myocardial infarction.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the incident.
Answer:
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the incident.
Rationale:
The client has signs of an air embolus. An air embolism occurs when a bolus of air enters the client’s body through an open access in the venous system. Once the cap has been replaced, no more air will enter. The HCP Q should be informed immediately. The chest pain will not resolve on its own, and an EKG would be obtained immediately after notifying the HCP. Having the client sit in the low Fowler’s position will not improve oxygenation.
Question 28.
When delivering medication through an intermittent peripheral access device, the nurse should take which action immediately after cleaning the access port with an antimicrobial swab?
(a) Aspirate to check for a blood return.
(b) Flush the line with a normal saline flush.
(c) Reconfirm the client’s identity.
(d) Instill the medication.
Answer:
(a) Aspirate to check for a blood return.
Rationale:
Prior to flushing the line and adding the medication, gently aspirating will determine the patency of the device. A return of blood indicates the line is in the vein. After determining the line is patent, the nurse can flush the line with saline. This is not the time to reconfirm that this is the correct client because this has been accomplished prior to beginning this procedure. The medication can only be administered after the nurse has flushed the line with saline.
Question 29.
The nurse is to administer omeprazole to a female client. What information should the nurse obtain from the client before administering the drug?
(a) Does the client have a history of gastrointestinal ulcers?
(b) Is the client sexually active or pregnant?
(c) Does the client have an ulcer induced by Helicobacter pylori?
(d) Will the client be able to crush the pill if necessary?
Answer:
(b) Is the client sexually active or pregnant?
Rationale:
Omeprazole has not been approved or determined safe to use during pregnancy as it might have an adverse effect on the fetus. It is highly likely the client has some type of gastro-intestinal condition, and this category of drugs is used for ulcers. Omeprazole has been recommended to treat H. pylori ulcers in combination with other medications. This medication should never be crushed as it will render the medication ineffective.
Question 30.
Which statement by a client who is taking atorvastatin indicates a need for further teaching?
(a) “I’ll increase my activity level to lower my cholesterol.”
(b) “My diet should include foods that are low in saturated fat.”
(c) “I should always take this medication with grapefruit juice.”
(d) “My liver and kidney function will be checked to make sure there is no toxicity.”
Answer:
(c) “I should always take this medication with grapefruit juice.”
Rationale:
Grapefruit juice is contraindicated when taking this medication because it slows the metabolism of the drug, which increases the levels of it in the client’s system, potentially causing liver damage or rhabdomyolysis. Increasing exercise will be a part of a healthy plan to decrease cardiac disease. Low-fat diets will also help to lower the chances of coronary artery disease. Liver and kidney function tests will help to determine the client’s ability to metabolize and excrete the medication.
Question 31.
A client is to take rosuvastatin. What information should the nurse determine prior to administering the drug?
(a) Can the client swallow a pill, or does the client need a liquid form?
(b) Is the client of Asian descent?
(c) Will the client be able to afford the medication?
(d) Does the client have a history of cardiovascular disease?
Answer:
(b) Is the client of Asian descent?
Rationale:
Rosuvastatin has been shown to reach higher serum levels in persons of Asian descent and should not be used in this group of clients. There is no liquid form for this medication. The cost is always important, but this is not the most significant concern at this point. It is not uncommon to have this drug prescribed to clients with a history of cardiovascular disease as a means of prevention of the progression of the disease.
Question 32.
The nurse reviews a client’s medication administration record and notes the scheduled medications (see chart). When planning to administer the medications, the nurse must administer which medication within 30 minutes of its scheduled administration time?
|
History |
Physical |
Prescriptions |
Diagnostics |
|
Lisinopril 20 mg by mouth 1 time daily. |
|||
|
Ampicillin 500 mg by mouth every 6 hours. |
|||
|
Metoprolol 25 mg by mouth 2 times daily. |
|||
(a) lisinopril
(b) ampicillin
(c) metoprolol
(d) pneumococcal vaccine
Answer:
(b) ampicillin
Rationale:
Time-critical medications are those medications that can cause client harm or sub- therapeutic blood levels and should be administered within 30 minutes of the scheduled time. These include antibiotics, anticoagulants, immunosuppressants, insulin, and antiseizure medications.
Non-time-critical medications, such as lisinopril, metoprolol, and the pneumococcal vaccine should generally be administered within 1 to 2 hours of the scheduled time. However, agency policy dictates the window of time to administer non-time-critical medications and may vary by institution.
Question 33.
The nurse is to inject an intravenous medication via a locked peripheral intravenous port. The nurse flushes the port with saline, administers the intravenous medication, and again flushes the port with saline. During this process, when should the nurse clean the injection port with an antiseptic swab?
(a) before entering the capped injection port the first time
(b) when administering the intravenous medication
(c) at each entry of the capped injection port
(d) after the first and last entry of the capped injection port
Answer:
(c) at each entry of the capped injection port
Rationale:
The nurse should clean the capped injection port prior to each time it is entered. It is not necessary to clean the injection port at other times, and the other options do not address the importance of cleaning a port prior to every entry.
Question 34.
A client has several intravenous infusions, each running to a separate location. Which intravenous infusion line does the nurse select to attach secondary tubing to infuse an intravenous piggyback medication over 30 minutes? The line with:
(a) 25,000 units of heparin sodium in 250 mL 5% dextrose in water at 10 mL/h.
(b) 1,000 mL normal saline at 50 mL/h.
(c) 350 mL of packed red blood cells at 100 mL/h.
(d) parenteral nutrition at 83 mL/h.
Answer:
(b) 1,000 mL normal saline at 50 mL/h.
Rationale:
The nurse should use the intravenous line with the normal saline. When the intravenous piggyback medication is infusing, the primary line will not infuse. Therefore, the nurse should not interfere with the infusion of heparin, even if com-patible, because the partial thromboplastin time may become subtherapeutic. Additionally, no medication line should ever be added to blood or blood products or to parenteral nutrition
Question 35.
When injecting an intravenous push medication into intravenous tubing with a solution infusing, the nurse should select which injection port?
(a) the port adjacent to the drip chamber
(b) the port just above the automated infusion pump
(c) the port just below the automated infusion pump
(d) the port closest to the client
Answer:
(d) the port closest to the client
Rationale:
The nurse should inject the medication in the port closest to the client. Administering the medication higher in the tubing makes flushing the tubing difficult and has the potential to interfere with the rate of administration, either
of which could alter complete delivery of the medication.
Question 36.
When administering an intravenous medication, the nurse should explain which teaching points to the client? Select all that apply.
(a) date the medication will expire
(b) incompatibilities with other medications
(c) name of the medication
(d) purpose of the medication
(e) possible adverse effects
(f) manufacturer of the medication
Answer:
(c) name of the medication
(d) purpose of the medication
(e) possible adverse effects
Rationale:
The nurse should always tell the client the name of the medication. The nurse should also tell the client, in lay terms, the purpose of the medication and potential adverse effects that the client may experience and should report to the nurse. The expiration date and incompatibilities with other medications should be noted by the nurse, but they do not need to be communicated to the client. The client does not need to know the manufacturer of the medication.
Question 37.
Prior to administering an opioid prescribed for pain management, the nurse assesses the client using the Pasero Opioid-Induced Sedation Scale (POSS) (see chart). The nurse assigns a score of 3 based on assessment criteria for the scale. What should the nurse do next?
imm
(a) Continue to administer the medication because the client is well sedated.
(b) Increase the dose if the client becomes restless.
(c) Contact the health care provider (HCP) to request a decreased dose of the medication.
(d) Prepare to administer a reversal agent.
Answer:
(c) Contact the health care provider (HCP) to request a decreased dose of the medication.
Rationale:
A standardized sedation scale such as the Pasero Opioid-Induced Sedation Scale (POSS) is used to monitor the client for excessive sedation. A score of 3 on this scale indicates the client is oversedated, and the nurse should contact the HCP to request to administer 25% to 50% less of the medi-cation for this dose. The nurse should not administer the medication or increase the dose. A reversal agent, such as naloxone, is not warranted unless the client has reached a POSS score of 4 or is showing signs of respiratory depression.
Question 38.
In the first 12 hours after starting a patient- controlled analgesia (PCA) infusion to administer an opioid, what shoidd the nurse monitor every 1 to 2 hours? Select all that apply.
(a) arterial blood gas values
(b) level of sedation
(c) muscle strength
(d) oxygen saturation
(e) vital signs
Answer:
(b) level of sedation
(d) oxygen saturation
(e) vital signs
Rationale:
When a client is receiving an infusion of self-administered analgesia, the nurse should monitor level of sedation, oxygen saturation and vital signs. Oxygen saturation reading may be obtained by oximetry or capnography. The latter are helpful in the identification of respiratory depression secondary to opioid use.
Arterial blood gas values will provide oxygenation levels as well, but the invasive nature of arterial blood gases is not necessary for a client beginning patient-controlled analgesia. Muscle strength may be impacted with excessive analgesia, but it is not a routine part of client monitoring with patient-controlled analgesia.
Question 39.
The nurse is adding the 8-hour intake for a client with a quadruple lumen central line intravenous access. See the intake-output record below. Based on the documentation, the nurse should document the client’s intake as how many mL? Record your answer in whole numbers.
............................. mL
Answer:
1,474 mL.
Rationale:
An intravenous infusion at 83 mL/h will infuse 664 mL over 8 hours. The vancomycin volume is 250 mL, and the Vi liter of normal saline is 500 mL. Ice melts to one half of its volume in water. Since a cup is 240 mL, and the client consumed V2 a cup or 120 mL, the client had a total oral intake of 60 mL. This totals 664 mL +
250 mL + 500 mL + 60 mL = 1,474 mL.
Question 40.
A nurse has attempted to insert a peripheral intravenous catheter into the median cubital vein of client who has one arm amputated above the elbow. The nurse was not successful in inserting the catheter into the vein. In which location does the nurse next attempt catheter insertion?
(a) basilic vein of the forearm
(b) cephalic vein of the upper arm
(c) cephalic vein of the wrist
(d) dorsal metacarpal vein
Answer:
(a) basilic vein of the forearm
Rationale:
The nurse should attempt to use insertion sites from most distal to proximal. Therefore, the nurse should next attempt to insert the intravenous catheter in the cephalic vein of the upper arm. The metacarpal vein, the hand, and the wrist and forearm sites are all distal to the median cubital vein.
Question 41.
A nurse has inserted a peripheral intravenous catheter. Which type of dressing is most appropriate to use to cover the insertion site?
(a) transparent
(b) adhesive
(c) hydrocolloid
(d) gauze
Answer:
(a) transparent
Rationale:
A transparent dressing is optimal since it allows assessment of the insertion site. A sterile gauze dressing must be changed every 48 hours or more often if needed according to agency protocol. Adhesive bandages are not occlusive, cover a small surface area, and often irritate the skin. Hydrocolloid and foam dressings are used on pressure ulcers and not peripheral intravenous sites.
Question 42.
The client has a peripheral intravenous infusion of 1,000 mL 0.9% sodium chloride infusing at 125 mL/h and received 4 g piperacillin/0.5 g tazobactam in 100 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride as a 4-hour intravenous piggyback infusion. How should the nurse document the client’s intravenous intake for an 8-hour shift? Record your answer in whole numbers.
............................ mL
Answer:
600 mL
Rationale:
Because the primary infusion does not run when an intravenous piggyback is infusing, the normal saline at 125 mL/h was off during the 4-hour infusion of the piperacillin and tazobactam. Therefore, the client received 500 mL of the 0.9% sodium chloride infusion and 100 mL of the antibiotic infusion to total 600 mL.
Question 43.
A client with a history of smoking and peripheral artery disease reports leg pain. The health care provider has prescribed 400 mg of pentoxifylline by mouth three times a day. What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) “Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery when first taking this medication.”
(b) “Avoid smoking while taking this medication.”
(c) “Don’t stop taking this medication without approval of your health care provider.”
(d) “Decrease the amount of green leafy vegetables you eat.”
(e) “You’ll need to have weekly labs drawn with this medication.”
Answer:
(a) “Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery when first taking this medication.”
(b) “Avoid smoking while taking this medication.”
(c) “Don’t stop taking this medication without approval of your health care provider.”
Rationale:
Pentoxifylline is used to treat pain for clients with peripheral vascular disease. The drug does not have an immediate action, and it is important that this medication is taken until a therapeutic effect has been achieved. Smoking causes vasoconstriction, and pentoxifylline causes vasodilation.
Pentoxifylline can also cause dizziness or blurred vision; the nurse should instruct clients taking this medication to avoid driving and operating heavy machinery until they know how it affects them. Pentoxifylline does not require weekly laboratory studies, and clients taking pentoxifylline do not have to restrict the amount of green leafy vegetables they eat.
Question 44.
The nurse is instructing a client about how to take clopidogrel. Which statement by the client would indicate the need for further teaching? Select all that apply.
(a) “I should inform all of my health care providers that I take clopidogrel.”
(b) “I understand I may experience a fever while taking clopidogrel.”
(c) “I should apply pressure to any injuries that won’t stop bleeding.”
(d) “I’ll take omeprazole to prevent gastrointestinal upset.”
(e) “I’ll need to have my platelets monitored.”
Answer:
(b) “I understand I may experience a fever while taking clopidogrel.”
(d) “I’ll take omeprazole to prevent gastrointestinal upset.”
Rationale:
Clopidogrel is an antiplatelet agent. A potential side effect of this medication is neutropenia. The client should report an elevated body temperature as this could indicate neutropenia and should be reported to the primary care provider. Omeprazole is contraindicated in clients taking clopidogrel. Omeprazole utilizes the same CYP2C19 pathway and can interfere with the metabolism of clopidogrel.
Question 45.
A client is receiving warfarin for newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation. Which laboratory result would indicate that the nurse should withhold the medication and contact the health care provider?
(a) an INR (international normalized ratio) of 1.8
(b) an INR of 4.8
(c) a partial thromboplastin time (APTT) level of 65 seconds
(d) an APTT level of 70 seconds
Answer:
(b) an INR of 4.8
Rationale:
INR is the diagnostic test used to determine the effectiveness of warfarin. The therapeutic range for clients with atrial fibrillation is 2-3. The nurse should contact the health care provider because the client’s INR exceeds the normal range. APTT is the diagnostic test for client’s receiving heparin.
Question 46.
Following surgery, a client is receiving morphine 5 mg IV every 2 hours PRN for pain. To ensure safe medication administration when administering this drug, which actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
(a) Assess the client’s pain level 45 to 60 minutes after giving the medication.
(b) Check the medication administration record to see when the last dose was administered.
(c) Consult a drug manual to determine whether the amount prescribed is safe.
(d) Document the reason the medication was given in the client’s electronic health record.
(e) Use two identifiers to confirm that the medication is given to the correct client.
Answer:
(b) Check the medication administration record to see when the last dose was administered.
(c) Consult a drug manual to determine whether the amount prescribed is safe.
(d) Document the reason the medication was given in the client’s electronic health record.
(e) Use two identifiers to confirm that the medication is given to the correct client.
Rationale:
To administer this drug safely and following the rights of medication administration for this drug, the nurse should verify the medication is the right drug, right dose, right route, right time, right client, and the right documentation. The nurse should use two identifiers prior to administering any medication.
It is also essential to determine when the last dose is given and whether or not the amount the prescribed is correct. Documenting the reason for the medication is an important part of the documentation. The nurse should evaluate the client’s response to the morphine within the 15 to 30 minutes after administering the drug.
Question 47.
The nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for rivaroxaban. The nurse understands that teaching has been effective when the client makes which comments? Select all that apply.
(a) “I’ll take this medication with a full glass of water.”
(b) “I’ll take this medication at the same time each day.”
(c) “I’ll take a dose I miss as soon as I remember.”
(d) “I’ll report any bleeding from my gums to my health care provider.”
(e) “I’ll stop taking this medication if I have an upset stomach.”
Answer:
(b) “I’ll take this medication at the same time each day.”
(c) “I’ll take a dose I miss as soon as I remember.”
(d) “I’ll report any bleeding from my gums to my health care provider.”
Rationale:
Rivaroxaban is an anticoagulant, and it should be taken the same time every day. Rivaroxaban can be taken with or without food; it is not necessary to take the medication with a full glass of water. If a dose is missed, clients should take the medication as soon as they remember and then take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. A client should not stop taking rivaroxaban abruptly as clotting may occur.
Question 48.
A client reports having crushing chest pain. The electrocardiogram shows ST elevations indicating an anterior myocardial infarction. The client takes captopril twice a day and nitroglycerin sublingual PRN. The nurse reviews the client’s vital signs and blood tests to report to the health care provider. Which information indicates that the client cannot receive fibrinolytic therapy? Select all that apply.
(a) a blood urea nitrogen of 20 mg/dL (14.28 mmol/L) and creatinine 1.1 mg/dL (97.2 pmol/L)
(b) a diastolic blood pressure of 105 mm Hg
(c) a history of aspirin and enoxaparin use
(d) a hip replacement within the past 3 weeks
(e) a systolic blood pressure of 185 mm Hg
Answer:
(d) a hip replacement within the past 3 weeks
(e) a systolic blood pressure of 185 mm Hg
Rationale:
The client would not be eligible to receive fibrinolytic therapy due to meeting exclusion criteria that include a diastolic blood pressure >115 mm Hg, a systolic blood pressure >180 mm Hg, decreased renal function as evidenced by elevated blood urea nitrogen or creatinine, and major surgery within the past 3 weeks.
The client does not report current use of aspirin or enoxaparin
Question 49.
The nurse is preparing to administer benazepril to a client with hypertension. To help minimize potential adverse effects, the nurse should review which of the client’s laboratory results? Select all that apply.
(a) ALT and AST
(b) albumin
(c) BUN and creatinine
(d) blood glucose levels
(e) serum electrolytes
Answer:
(c) BUN and creatinine
(e) serum electrolytes
Rationale:
Benazepril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. ACE inhibitors have the ability to cause severe renal insufficiency and exacerbate it in other susceptible clients. Therefore, the client should have the BUN and creatinine levels monitored frequently.
In addition, ACE inhibitors can cause hyperkalemia because of the inhibition of aldosterone. Clients receiving ACE inhibitors need to have their potassium levels monitored. ACE inhibitors have no effect on liver enzymes such as AST or ALT, blood glucose levels, or albumin.
Question 50.
A client who is 85 kg has a prescription for acyclovir 10 mg/kg in 100 mL sodium chloride to infuse over 1 hour. The client’s IV infusion infiltrates 8 minutes before the infusion is completed. How much of the acyclovir has the client received? Round to one decimal point.
........................ mg
Answer:
736.67 mg
Rationale:
X mg = 85 kg x 10 mg/l kg = 850 mg/60 min x (60 - 8 min) = 736.67 mg
Question 51.
The nurse administers the wrong dose of a medication. Instead of giving furosemide 20 mg orally, the nurse forgets to break the tablet in half and gives furosemide 40 mg orally. The client experienced no harm as a result. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Continue to monitor the client’s vital signs and urinary output.
(b) Notify the health care provider, supervisor, client, and family.
(c) Complete an incident report, outlining the events of the incident.
(d) Document the time and amount of medication given and inform the case manager.
(e) Nothing, because no harm came to the client and no further action is needed.
Answer:
(a) Continue to monitor the client’s vital signs and urinary output.
(b) Notify the health care provider, supervisor, client, and family.
(c) Complete an incident report, outlining the events of the incident.
Rationale:
The medication given was double the amount prescribed, and it is important to document the amount given and continue to monitor the client. An incident report needs to be completed that outlines the events, provides the client status, and documents that all parties involved were notified of the events and the client’s current status.
The incident report is a process used by health care organizations to monitor events that occur. Documenting this information on the client’s chart allows a legal team the option to subpoena the document. Doing nothing prevents a health care organization from analyzing the near misses or errors that occur and to facilitate identification of system processes that need to be changed.
Question 52.
The nurse is developing a care plan with a client who is receiving ziprasidone and has stopped taking the drug. Which side effects that may occur and be a reason the client is noncompliant with taking this medication should the nurse discuss? Select all that apply.
(a) somnolence
(b) weight gain
(c) urticaria
(d) constipation
(e) headache
Answer:
(a) somnolence
(b) weight gain
(d) constipation
(e) headache
Rationale:
Ziprasidone can cause somnolence, drowsiness, weight gain (can be excessive), constipation, and headache; these side effects may preclude noncompliance with this medication. Urticaria is not a common side effect of ziprasidone.
Question 53.
A client taking risperidone reports stiff muscles, difficulty breathing, and increased perspiration. When the nurse asks the client what day it is, the client answers, “Christmas” when it is late July. Which action should the nurse perform first?
(a) Call the client’s family member.
(b) Isolate the client in a private room.
(c) Administer the next dose of risperidone.
(d) Check the client’s vital signs.
Answer:
(d) Check the client’s vital signs.
Rationale:
Clients taking risperidone may develop signs and symptoms of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. The client’s vital signs may be markedly elevated. The nurse should then contact the health care provider (HCP). The nurse would not call the family at this point in the incident.
Isolating the client in a private room is not a priority for the client with neuroleptic malignant syndrome. The medication will be held if the client does have neuroleptic malignant syndrome, so administering another dose is not therapeutic.
Question 54.
A client with major depressive disorder is receiving phenelzine. The nurse intervenes when the client orders which food for lunch?
(a) pepperoni pizza
(b) yogurt with fruit
(c) Salisbury steak
(d) green beans
Answer:
(a) pepperoni pizza
Rationale:
Clients taking phenelzine, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, cannot take foods with high tyra- mine content. Pepperoni is a sausage with a high tyramine content. Yogurt with fruit, Salisbury steak, and green beans have little or no tyramine.
Question 55.
The nurse is caring for an older adult experiencing depression and chronic pain. The client is requesting a prescription for an opioid pain medication similar to the one prescribed for knee surgery 5 years ago. What education should the nurse provide for the client? Select all that apply.
(a) Physical dependence can develop quickly with opioid medications.
(b) Opioid use is appropriate in chronic pain accompanied by depression.
(c) Opioid use is more appropriate for acute pain than chronic pain.
(d) Opioid use increases the risk for cognitive impairment.
(e) Treatment for depression can improve pain symptoms as well as depression.
(f) Using opioids to control chronic pain will decrease the level of depression.
Answer:
(a) Physical dependence can develop quickly with opioid medications.
(c) Opioid use is more appropriate for acute pain than chronic pain.
(d) Opioid use increases the risk for cognitive impairment.
(e) Treatment for depression can improve pain symptoms as well as depression.
Rationale:
Additional caution and increased monitoring to lessen the increased risk for opioid use disorder is needed among clients with mental health conditions (including depression, anxiety disorders, and posttraumatic stress disorder). When used for acute pain, opioids should be used for fewer than 7 days due to the risk for dependence. Cognitive impairment is a common risk of opioid therapy among older adults.
Adequate treatment for depression can have a positive impact on chronic pain levels. There is an increased risk for drug overdose among clients with depression, making opioids more of a risk to use for chronic pain. Opioids are not the best therapeutic option for controlling chronic pain: nonpharmacologic and nonopioid pain medications should be used to manage chronic pain.
Question 56.
The client with depression is taking a prescribed antidepressant that can cause anticholinergic side effects. The nurse anticipates that this client is at particular risk for developing which anticholinergic side effect?
(a) vomiting
(b) constipation
(c) diarrhea
(d) weight loss
Answer:
(b) constipation
Rationale:
The anticholinergic effects of the client’s medication may cause blurry vision, urine retention, constipation and dry mouth. Gastrointestinal motility may be further compromised by a decreased level of activity associated with depression. Constipation needs to be addressed to prevent additional gastrointestinal problems. Anticholinergic effects do not result in vomiting, diarrhea, or weight loss.
Question 57.
The nurse is caring for a client who is taking haloperidol. The client comes to the nurses’ station and states that he feels frightened and his muscles hurt. He is unable to turn his head to look at the nurse, his face is stiff, and he cannot move his tongue very well. Which prescribed PRN medication would be appropriate for the nurse to administer?
(a) benztropine
(b) meperidine
(c) diphenhydramine
(d) lorazepam
Answer:
(a) benztropine
Rationale:
The client is experiencing the side effect of dystonia, an extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Treatment for EPS is with an antiparkinson drug class, which includes benztropine. Lorazepam is prescribed for anxiety, which may be appropriate for fear, but it does not resolve the underlying pathophysiological process. Diphenhydramine is an antihistamine commonly used in allergy reactions and may cause sleepiness. Meperidine is a narcotic pain medication that will not resolve the cause of the client pain.
Question 58.
A client recently diagnosed with depression has been prescribed sertraline and is now being discharged. Which statement by the spouse indicates understanding of the medication teaching?
(a) “We should monitor for increased depression if my spouse takes any cold or allergy medication.”
(b) “We can expect improvement of my spouse’s mood and energy within the next 1 to 2 weeks.”
(c) “I can give my spouse the herb St. John’s wort as a sleep aid until the depression is better.”
(d) “I should remind my spouse to take the medication in the morning before going to work.”
Answer:
(d) “I should remind my spouse to take the medication in the morning before going to work.”
Rationale:
The client and spouse need to understand features of taking sertraline hydrochloride, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It should be taken in the morning to counter the expected side effect of insomnia. It takes 4 to 6 weeks for the SSRI to reach therapeutic levels, and St. John’s wort should not be taken with any other type of antidepressant medication; it may also interact with multiple medications. Cold or allergy medications do not affect the effectiveness of an SSRI.
Question 59.
The nurse is caring for a client who has been prescribed a benzodiazepine medication for acute anxiety. What information is most important for the nurse to include when teaching the client about the medication?
(a) “Take the medication as prescribed as there is risk for addiction.”
(b) “You can only take this medication for a few days due to the side effects.”
(c) “This medication may keep you awake, so plan to take it in the morning.”
(d) “This medication should be taken with food for best absorption.”
Answer:
(a) “Take the medication as prescribed as there is risk for addiction.”
Rationale:
Benzodiazepines are a central nervous system depressant, and the client should be monitored on a regular basis for increased tolerance and risk for addiction. While there is a risk for tolerance and addiction, the medication can be safely used with proper monitoring. Drowsiness, not wake-fulness, is a common side effect, and food is not needed to increase absorption.
Question 60.
The client’s health care provider prescribes buspirone hydrochloride for increased anxiety. The nurse understands the health care provider’s choice of this medication is based on what principle?
(a) Buspirone is often administered on an as- needed basis.
(b) Buspirone does not have any drug side effects.
(c) Buspirone is not habit forming.
(d) Buspirone is chemically similar to benzodiazepine medications.
Answer:
(c) Buspirone is not habit forming.
Rationale:
Buspirone is not habit forming, is administered on a schedule, and does not work immediately. Buspirone may have side effects such as chest pain, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, or nausea. Buspirone hydrochloride is not chemically or pharmacologically related to benzodiazepines or other sedative medications.
Question 61.
A nurse overhears the following conversation between coworkers: “Older people have lost many friends and family and also have health problems. Their anxiety and worries can be so severe that they need higher doses of benzodiazepines than most people.” What is the most appropriate response for the nurse to make to the coworkers?
(a) “You're right. Many older adults have had anxiety for so long that it’s more difficult to treat.”
(b) “That’s not right. Older people need lower doses than most people because of reduced liver and kidney function.”
(c) “You’re wrong. It’s not safe to use benzodiazepines at all in older adults because of the side effects.”
(d) “Older people should get the same dose as any other adult. It doesn’t make any difference.”
Answer:
(b) “That’s not right. Older people need lower doses than most people because of reduced liver and kidney function.”
Rationale:
Reduced liver and kidney function are expected in older adults; benzodiazepines and many other medications should be administered cautiously to the elderly. Older adults are also at increased risk for falls because of oversedation that can occur with benzodiazepines. While benzodiazepines may be prescribed in lower doses, they can still be used in older adults with monitoring for safety.
Question 62.
After administering naloxone, an opioid antagonist, the nurse should monitor the client carefully for which problem?
(a) cerebral edema
(b) kidney failure
(c) seizure activity
(d) respiratory depression
Answer:
(d) respiratory depression
Rationale:
After administering naloxone, the nurse should monitor the client’s respiratory status carefully because the drug is short acting and respiratory depression may recur after its effects wear off. Cerebral edema, kidney failure, and seizure activity are not directly related to opioid overdose or naloxone therapy.
Question 63.
A client is taking increased amounts of alprazolam for about 6 months for anxiety. She asks the nurse how she can “get off the alprazolam.” What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “There will be an immediate discontinuation of the alprazolam, and haloperidol will be available if needed.”
(b) “Instead of alprazolam, you’ll take lorazepam in decreasing doses and frequency over a period of 3 to 4 days.”
(c) “The alprazolam will be tapered down over a period of 48 hours.”
(d) “Alprazolam will be available on an as-needed basis for 4 to 5 days.”
Answer:
(b) “Instead of alprazolam, you’ll take lorazepam in decreasing doses and frequency over a period of 3 to 4 days.”
Rationale:
Lorazepam, as opposed to alprazolam, is available in dosage ranges that allow more gradual tapering down of doses over 3 to 4 days. Haloperidol is not effective for benzodiazepine withdrawal. Tapering alprazolam in 48 hours is too rapid. Offering alprazolam as a PRN does not deal with the need to gradually reduce the dose and frequency over time.
Question 64.
What should the nurse include in the teaching plan for the parents of a child who is receiving methylphenidate?
(a) Give the medication at the same time every evening.
(b) Have the child take two doses at the same time if the last dose was missed.
(c) Give the single-dose form of the medication early in the day.
(d) Allow concurrent use of any over-the-counter medications with this drug.
Answer:
(c) Give the single-dose form of the medication early in the day.
Rationale:
The single-dose form of methylphenidate should be taken 10 to 14 hours before bedtime to prevent problems with insomnia, which can occur when the daily or last dose of the medication is taken within 6 hours (for multiple dosing) or 10 to 14 hours (for single dosing) before bedtime.
It is recommended that a missed dose be taken as soon as possible; the dose is skipped if it is not remembered until the next dose is due. Any other medication, including over-the-counter medications, should be discussed with the health care provider (HCP) [Q] before use to eliminate the risk of a possible drug interaction.
Question 65.
The nurse is reviewing the laboratory report with the client’s lithium level prior to administering the 1700 hours dose. The lithium level is 1.8 mEq/L (1.8 mmol/L). The nurse should:
(a) administer the 1700 hours dose of lithium.
(b) hold the 1700 hours dose of lithium.
(c) give the client 240 mL of water with the lithium.
(d) give the lithium after the client’s supper.
Answer:
(b) hold the 1700 hours dose of lithium.
Rationale:
The nurse should hold the 1700 hours dose of lithium because a level of 1.8 mEq/L (1.8 mmol/L) can cause adverse reactions, including diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscle weakness, and lack of coordination, which are early signs of lithium toxicity. The nurse should report the lithium level to the health care provider (HCP) (Til), including any symptoms of toxicity. Administering the 1700 hours dose of lithium, giving the client the lithium with 240 mL of water, or giving it after sup-per would result in an increase of the lithium level, thus increasing the risk of lithium toxicity.
Question 66.
A client is receiving paroxetine 20 mg every morning. After taking the first three doses, the client tells the nurse that the medication upsets the stomach. What instructions should the nurse give to the client?
Take the medication:
(a) an hour before breakfast.
(b) with some food.
(c) at bedtime.
(d) with 4 oz (120 mL) of orange juice.
Answer:
(b) with some food.
Rationale:
Nausea and gastrointestinal upset are common, but usually temporary, side effects of paroxetine. Therefore, the nurse would instruct the client to take the medication with food to minimize nausea and stomach upset. Other more common side effects are dry mouth, constipation, headache, dizziness, sweating, loss of appetite, ejaculatory problems in men, and decreased orgasms in women.
Taking the medication an hour before breakfast would most likely lead to further gastro-intestinal upset. Taking the medication at bedtime is not recommended because paroxetine can cause nervousness and interfere with sleep. Because orange juice is acidic, taking the medication with it, especially on an empty stomach, may lead to nausea or increase the client’s gastrointestinal upset.
Question 67.
The client who has been taking venlafax- ine 25 mg PO three times a day for the past 2 days states, “This medicine isn’t doing me any good. I’m still so depressed.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “Perhaps we’ll need to increase your dose.”
(b) “Let’s wait a few days and see how you feel.”
(c) “It takes about 2 to 4 weeks to receive the full effects.”
(d) “It’s too soon to tell if your medication will help you.”
Answer:
(c) “It takes about 2 to 4 weeks to receive the full effects.”
Rationale:
The client needs to be informed of the time lag involved with antidepressant therapy. Although improvement in the client’s symptoms will occur gradually over the course of 1 to 2 weeks, typically it takes 2 to 4 weeks to get the full effects of the medication. This information will help the client be compliant with medication and will also help in decreasing any anxiety the client has about not feeling better. The client’s dose may not need to be increased; it is too early to determine the full effectiveness of the drug.
Additionally, such a statement may increase the client’s anxiety and diminish self-worth. Telling the client to wait a few days discounts the client’s feelings and is inappropriate. Although it is too soon to tell whether the medication will be effective, telling this to the client may cause the client undue distress. This statement is somewhat negative because it is possible that the medication will not be effective, possibly further compounding the client’s anxiety about not feeling better.
Question 68.
A client taking mirtazapine is disheartened about a 20-lb (9 kg) weight gain over the past 3 months. The client tells the nurse, “I stopped taking my mirtazapine 15 days ago. I don’t want to get depressed again, but I feel awful about my weight.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “Focusing on diet and exercise alone should control your weight.”
(b) “Your depression is much better now, so your medication is helping you.”
(c) “Look at all the positive things that have happened to you since you started mirtazapine.”
(d) “I hear how difficult this is for you and will help you approach your health care provider about it.”
Answer:
(d) “I hear how difficult this is for you and will help you approach your health care provider about it.”
Rationale:
The nurse should express concern for the client and offer to help the client speak with the HCP Q, which will lend support to the client’s concerns. The client who has stopped the medication must be taken seriously because medication noncompliance could result in a recurrence of symptoms of depression.
Telling the client to focus on diet and exercise ignores the client’s feelings and subtly implies the weight gain is the client’s fault. Pointing out that the medication has helped and that positive things have happened since the depression lifted may be true, but it does not address the client’s current feelings or needs.
Question 69.
A client comes to the mental health clinic saying that he feels so down and lacking in energy with “loss of interest in everything.” He tells the nurse that he received some samples of a new medication from his health care provider last week to relieve his depression. The nurse recalls that this client has a history of bipolar disorder with hospitalization for a significant manic episode. With this knowledge, the nurse would have special concern if he is taking which category of medication?
(a) atypical antipsychotics
(b) mood stabilizers/antimanics
(c) antianxiety agents/benzodiazepines
(d) selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants
Answer:
(d) selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants
Rationale:
The most urgent consideration for intervention and for teaching is the fact that for individuals with a history of bipolar disorder, antidepressants when taken alone can push the person into mania.
Antipsychotics are sometimes pre-scribed for clients with bipolar disorder and would not pose a special concern. Individuals with bipolar disorder are typically treated with mood stabilizers, and benzodiazepines are sometimes used in the short term to give a client relief before the mood stabilizers can take effect.
Question 70.
When preparing to insert an IV catheter to administer fluids to a client who is going to surgery, the nurse selects the median cubital vein. Identify the location of the median cubital vein on the illustration.
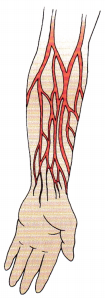
Answer:
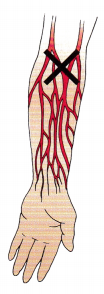
Rationale:
The median cubital vein is located in the approximate center of the antecubital space.
Question 71.
The mother of a 28-year-old client who is taking clozapine states, “Something’s wrong. My son is drooling like a baby.” What response by the nurse would be most helpful?
(a) “I wonder if he’s having an adverse reaction to the medicine.”
(b) “Excess saliva is common with this drug; here’s a paper cup for him to spit into.”
(c) “Don’t worry about it; this is only a minor inconvenience compared to its benefits.”
(d) “I’ve seen this happen to other clients who are taking clozapine.”
Answer:
(b) “Excess saliva is common with this drug; here’s a paper cup for him to spit into.”
Rationale:
Telling the mother that excess saliva is a common adverse effect of the drug is most helpful because it gives her information about the problem, thereby helping to decrease her anxiety about what is occurring with her son. By offering the paper cup, the nurse also demonstrates concern for the client, thereby leading to increased trust.
Saying “I wonder if he is having an adverse reaction to the medicine” shows the nurse’s lack of knowledge about the drug, decreases confidence in the nurse, and indicates poor judgment. Saying “Don’t worry about it, it’s only a minor inconvenience compared to its benefits” or telling the mother that the nurse has seen this happening to other clients is insensitive and does not assuage the mother’s anxiety.
Question 72.
Which medication should the nurse anticipate administering in the event of a heparin overdose?
(a) warfarin sodium
(b) protamine sulfate
(c) vitamin K
(d) atropine sulfate
Answer:
(b) protamine sulfate
Rationale:
Protamine sulfate is a heparin antagonist. It is administered intravenously very slowly (over at least 10 minutes). Warfarin sodium and ASA have anticoagulant properties and would be contraindicated. Atropine sulfate is an anticholinergic drug and would not be effective in treating a heparin overdose.
Question 73.
The nurse has administered aminophylline to a client with emphysema. Which indicates the medication has been effective?
(a) relief from spasms of the diaphragm
(b) relaxation of smooth muscles in the bronchioles
(c) efficient pulmonary circulation
(d) stimulation of the medullary respiratory center
Answer:
(b) relaxation of smooth muscles in the bronchioles
Rationale:
Aminophylline, a bronchodilator that relaxes smooth muscles in the bronchioles, is used in the treatment of emphysema to improve ventilation by dilating the bronchioles. Aminophylline does not have an effect on the diaphragm or the medullary respiratory center and does not promote pulmonary circulation.
Question 74.
When teaching a client with bipolar disorder who has started to take valproic acid about possible side effects of this medication, the nurse should instruct the client to report which side effect?
(a) increased urination
(b) slowed thinking
(c) sedation
(d) weight loss
Answer:
(c) sedation
Rationale:
Valproic acid causes sedation as well as nausea, vomiting, and indigestion. Sedation is important because the client needs to be cautioned about driving or operating machinery that could be dangerous while feeling sedated from the medication. Valproic acid does not cause increased urination, slowed thinking, or weight loss. However, some clients may experience weight gain.
Question 75.
A 36-month-old child weighing 20 kg (44 lb) is to receive ceftriaxone 2 g IV every 12 hours. The recommended dose of ceftriaxone is 50 to 75 mg/kg/day in divided doses. How should the nurse proceed?
(a) Administer the medication as prescribed.
(b) Administer half the prescribed dose.
(c) Call the laboratory to check the therapeutic serum level of ceftriaxone.
(d) Withhold administering the ceftriaxone, and notify the child’s health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(d) Withhold administering the ceftriaxone, and notify the child’s health care provider (HCP).
Rationale:
The child’s HCP should be notified because the maximum daily recommended dosage for ceftriaxone for this child’s weight would be 1,500 g/day, and giving this dose would administer 4 g/day. The nurse cannot administer a different dose than that prescribed. There is no therapeutic serum level of ceftriaxone.
Question 76.
The health care provider’s (HCP’s) prescription for an intravenous infusion is 3% normal saline to infuse at 125 mL/h. The client’s most recent sodium level is 132 mEq/L (132 mmol/L). What should the nurse do next?
(a) Hang 0.9% normal saline at 125 mL/h.
(b) Start the IV solution as prescribed.
(c) Consult the prescriber about the prescription.
(d) Hang the IV solution prescribed at 62 mL/h.
Answer:
(c) Consult the prescriber about the prescription.
Rationale:
Three percent saline is a hypertonic solution, which will pull fluid from the interstitial and intracellular spaces into the bloodstream. Its use is usually reserved for severe hyponatremia (sodium <115 mEq/L). If this client were experiencing a fluid volume deficit, this IV solution could worsen the condition.
The nurse should consult with the HCP 3 about this prescription. The nurse does not have prescribing rights and cannot change the prescription. The IV rate of 62 mL/h may still be dangerous for this client, and the rate was prescribed at 125 mL/h.
Question 77.
A client is admitted to the emergency department experiencing syncope. The nurse speaks with the family concerning the client’s condition and current medications. The client’s family states that the client takes several medications and has brought all the client’s medications with them. To determine the correct medications required for this client, the nurse performs which step of the required process to ensure safe administration of medications?
(a) verification
(b) clarification
(c) documentation
(d) reconciliation
Answer:
(b) clarification
Rationale:
Clarification is the process of confirming the appropriate medication and doses for any client. Verification is the process of collecting medication history. Reconciliation is the process of documenting medication prescription changes for a client across the continuum of care. Documentation is included as a step in the three steps of a formal medication reconciliation program.
Question 78.
A primigravid client who was successfully treated for preterm labor at 30 weeks’ gestation had a history of mild hyperthyroidism before becoming pregnant. What instructions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
(a) Continue taking low-dose oral propylthiouracil as prescribed.
(b) Discontinue taking the methimazole until after the birth of the neonate.
(c) Consider breastfeeding the neonate after the birth.
(d) Contact the health care provider (HCP) if bra dycardia occurs.
Answer:
(a) Continue taking low-dose oral propylthiouracil as prescribed.
Rationale:
Although thioamides such as propylthiouracil methimazole are considered teratogenic to the fetus and can lead to congenital hyperthyroidism (goiter) in the neonate, they still represent the treatment of choice. The client should be regulated on the lowest possible dose. Hyperthyroidism is associated with preterm labor and a low-birth- weight infant, so the client should contact the HCPD if the contractions begin again. The client should not be urged to breastfeed because medications such as propylthiouracil and methimazole are secreted in breast milk. Tachycardia (not bradycardia) is associated with thyroid storm, a medical emergency, and should be reported to the HCP.
Question 79.
The health care provider prescribes an intramuscular injection of vitamin K for a term neonate. The nurse explains to the mother that this medication is used to prevent which problem?
(a) hypoglycemia
(b) hyperbilirubinemia
(c) hemorrhage
(d) polycythemia
Answer:
(c) hemorrhage
Rationale:
Vitamin K acts as a preventive measure against neonatal hemorrhagic disease. At birth, the neonate does not have the intestinal flora to produce vitamin K, which is necessary for coagulation. Hypoglycemia is prevented and treated by feeding the infant. Hyperbilirubinemia severity can be decreased by early feeding and passage of meconium to excrete the bilirubin.
Hyperbilirubinemia is treated with phototherapy. Polycythemia may occur in neonates who are large for gestational age or post term. Clamping of the umbilical cord before pulsations cease reduces the incidence of polycythemia. Generally, polycythemia is not treated unless it is extremely severe.
Question 80.
A client’s peripheral intravenous access does not have a blood return. To determine patency, what should the nurse assess? Select all that apply.
(a) presence of localized swelling
(b) date of intravenous catheter insertion
(c) saline flush is met with resistance
(d) client’s report of discomfort with flushing
(e) location of the catheter
Answer:
(c) saline flush is met with resistance
(d) client’s report of discomfort with flushing
Rationale:
Swelling indicates infusion into the soft tissue rather than the vein. While ease of flushing may or may not indicate patency, meeting resistance indicates that the intravenous catheter is not patent. Infiltration may cause client discomfort and is also an indicator of patency. The date of catheter insertion should be noted, as should catheter location, but these are not indicators of catheter patency.
