NCLEX Prep Questions often emphasize prioritization and delegation, skills that are crucial for safe and effective nursing care.
NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 6 with Rationale
Question 1.
A client returns to the recovery room following left supratentorial surgery for treatment of a brain tumor. The nurse should place the client in which position to facilitate venous drainage?
(a) flat with the head turned to the right
(b) head elevated on two pillows
(c) head of the bed elevated to 30 degrees
(d) sidelying on left side
Answer:
(c) head of the bed elevated to 30 degrees
Rationale:
The head of the bed should be elevated 30 degrees to promote venous drainage and decrease intracranial pressure. The client’s head should be in a midline, or neutral, position. Clients with supratentorial surgery should be positioned on the nonoperative side to prevent displacement of the cranial contents by gravity.
Question 2.
After a bronchoscopy with biopsy, the nurse assesses the client. The nurse should report which finding to the health care provider?
(a) green sputum
(b) dry cough
(c) hemoptysis
(d) laryngeal stridor
Answer:
(d) laryngeal stridor
Rationale:
Laryngeal stridor is characteristic of respiratory distress from inflammation and swelling after bronchoscopy. It must be reported immediately. Green sputum indicates infection and would occur 3 to 5 days after bronchoscopy. A mild cough or hemoptysis is typical after bronchoscopy. If a tissue biopsy specimen was obtained, sputum may be blood streaked for several days.
Question 3.
Which activity is least effective in preventing sensory deprivation during a client’s stay in the cardiac care unit?
(a) watching television
(b) visiting with family
(c) reading the newspaper
(d) keeping the door closed to provide privacy
Answer:
(c) reading the newspaper
Rationale:
Keeping the client’s door closed is likely to contribute to feelings of isolation and sensory deprivation. Such activities as watching television, visiting with a relative, and reading a newspaper help prevent sensory deprivation and yet do not require physical effort.
Question 4.
A 57yearold woman with breast cancer who does not speak English is admitted for a lumpectomy. Her daughter, who speaks English, accompanies her. What should the nurse do in order to obtain admission information from the client?
(a) Ask the client’s daughter to serve as an interpreter.
(b) Ask one of the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) to serve as an interpreter.
(c) Use the limited knowledge of the client’s language learned in high school along with nonverbal communication.
(d) Obtain a trained medical interpreter.
Answer:
(d) Obtain a trained medical interpreter.
Rationale:
A trained medical interpreter is required to ensure safety, accuracy of history data, and client confidentiality. The medical interpreter knows the client’s rights and is familiar with the client’s culture. Using the family member as interpreter violates the client’s confidentiality. Using the UAP and limited Spanish and nonverbal communication do not ensure accuracy of interpretation and back translation into English.
Question 5.
The nurse assesses a child with suspected juvenile hypothyroidism. Which signs or symptoms should the nurse expect this child to manifest?
(a) short attention span and weight loss
(b) weight loss and flushed skin
(c) rapid pulse and heat intolerance
(d) dry skin and constipation
Answer:
(d) dry skin and constipation
Rationale:
Clinical manifestations of juvenile hypothyroidism include dry skin, constipation, sparse hair, and sleepiness. Short attention span, weight loss, moist flushed skin, rapid pulse, and heat intolerance suggest hyperthyroidism.
Question 6.
After discussing preconception needs with a nulliparous client who eats a primarily Asian diet, which client statement indicates the need for further instruction?
(a) “I should take folic acid supplements before I get pregnant.”
(b) “If I become pregnant, I can continue to eat sushi twice a week.”
(c) “I should continue to steam my vegetables rather than cooking them for a long time.”
(d) “Eating soy products can increase my protein levels once I am pregnant.”
Answer:
(b) “If I become pregnant, I can continue to eat sushi twice a week.”
Rationale:
The client needs further instructions when she says, “If I become pregnant, I can continue to eat sushi twice a week.” Raw fish, including tuna, should be avoided while the client is pregnant because of the risk of contamination with mercury and other potential teratogens. Folic acid supplements taken before the client gets pregnant and during pregnancy can help reduce the risk of neural tube defects. Steaming vegetables reduces the risk that vitamins will be lost in the cooking water. Soy products can increase the client’s protein levels.
Question 7.
A child is prescribed amoxicillin for otitis media. What should the nurse recommend the mother do when the child develops diarrhea?
(a) Begin clear fluids.
(b) Withhold food and fluids for 2 hours.
(c) Offer yogurt several times a day.
(d) Restrict the intake of pizza.
Answer:
(c) Offer yogurt several times a day.
Rationale:
Diarrhea is a common adverse effect of amoxicillin because the drug kills normal intestinal bacteria. Yogurt with live cultures helps restore the normal intestinal flora. Restricting the child to clear fluids will not help stop the diarrhea or recolonize the intestine. Withholding food and fluids for 2 hours is suggested when a child vomits. Pizza tends to be spicy and aggravates the diarrhea, but restricting its intake will not help the underlying problem.
Question 8.
A client fears chemotherapy because of the side effects. What is the nurse’s best response to the client’s concerns?
(a) “Your health has been excellent. It’s unlikely that you will experience serious side effects.”
(b) “We’ll give you medications to prevent the side effects, so you shouldn’t be too concerned.”
(c) “Each person responds differently to chemotherapy treatments. We’ll monitor your responses closely.”
(d) “You may choose not to take the chemother apy, but you must understand that this will have an adverse effect on the course of your disease.”
Answer:
(c) “Each person responds differently to chemotherapy treatments. We’ll monitor your responses closely.”
Rationale:
It is normal for the client who is beginning chemotherapy to be anxious and fearful about possible side effects. It is important that the nurse listen to the client’s concerns, correct any misconceptions, and explain the supportive care that will be provided during the chemotherapy treatments. The client needs to understand that individuals do respond differently to the treatments and the experience may be very different from those of other people.
A previously excellent health record does not necessarily ensure that the client will not experience side effects. Medications may lessen but not prevent the side effects, so client concerns should not be dismissed. Telling the client that he or she will die if treatment is refused does nothing to allay fears and concerns.
Question 9.
A nurse is caring for a client who has undergone a total laryngectomy for laryngeal cancer. What information is important to include in discharge teaching? Select all that apply.
(a) Provide humidity at home.
(b) Follow a bland diet.
(c) Learn how to suction.
(d) Have communication rehabilitation with a speech pathologist.
(e) Attend a smoking cessation program.
Answer:
(a) Provide humidity at home.
(c) Learn how to suction.
(d) Have communication rehabilitation with a speech pathologist.
(e) Attend a smoking cessation program.
Rationale:
Home care for a client with a total laryngectomy should include a highhumidity environment, laryngectomy tube care and suctioning, speech rehabilitation, and smoking cessation. The client is not restricted to a bland diet.
Question 10.
The client received electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) an hour ago and now has a headache. Which response by the nurse is best?
(a) “A headache is common after ECT.”
(b) “I’ll get some acetaminophen for you.”
(c) “A nap will help you feel better.”
(d) “Eat your breakfast and then let me know how you feel.”
Answer:
(b) “I’ll get some acetaminophen for you.”
Rationale:
Administering acetaminophen to the client with a postECT headache is the best action. Stating a headache is common after ECT and that napping will help the client feel better may be true, but it does not offer the client pain relief. Telling the client to eat breakfast and then to let the nurse know how the client feels conveys a lack of understanding to the client and dismisses the client’s concern.
Question 11.
The nurse interprets the rhythm strip (see figure) from a client’s bedside monitor as which rhythm?
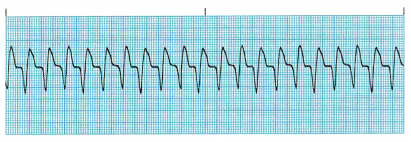
(a) normal sinus rhythm
(b) sinus tachycardia
(c) ventricular tachycardia
(d) ventricular fibrillation
Answer:
(c) ventricular tachycardia
Rationale:
This rhythm is ventricular tachycardia, which is characterized by an absent P wave and a heart rate of 140 to 220 bpm. Ventricular tachycardia requires immediate intervention, usually with lidocaine.
Question 12.
The nurse cares for a client who is 12 weeks pregnant and speaks Spanish only. Which interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care at the client’s initial visit? Select all that apply.
(a) Provide brochures in the client’s native language.
(b) Refer the client to a highrisk clinic.
(c) Discuss cultural differences and emphasize the differences between cultures.
(d) Arrange for an interpreter for her appointments.
(e) Discuss contraception and options.
(f) Review dietary intake and discuss nutrition.
Answer:
(a) Provide brochures in the client’s native language.
(d) Arrange for an interpreter for her appointments.
(f) Review dietary intake and discuss nutrition.
Rationale:
Providing culturally sensitive care includes providing printed material in the client’s native language. There is nothing to indicate that this client is a highrisk pregnancy. Discussing cultural differences is not a priority or important at the first visit. Clients need to have an interpreter for each prenatal visit to translate and interpret questions. Contraceptive options are not a priority for the first prenatal visit. Reviewing dietary intake and discussing nutrition are important components of early prenatal care.
Question 13.
When assessing speech development, the nurse should refer which child for further revaluation?
(a) a 4monthold who laughs out loud
(b) a 10monthold who says “dada” and “mama”
(c) a 1yearold who says three to five words
(d) an 18monthold who only says “no”
Answer:
(d) an 18monthold who only says “no”
Rationale:
An 18monthold child should be able to say 10 or more words. Lack of speech development may indicate a lack of social stimulation, a hearing deficiency, or developmental delay. Referring the child for an evaluation may increase the child’s chance of reaching the child’s potential. A 4month old child with a healthy central nervous system and normal mental development should be able to laugh out loud if the child’s environment has been caring and the child’s needs are met safely and consistently.
Children at age 10 months should be able to say the words “dada” and “mama” in response to the appropriate person. A 1yearold child should have the ability to speak three to five words plus “mama” and “dada.”
Question 14.
The client is started on simvastatin to lower cholesterol. The nurse should explain to the client that which laboratory test will be monitored to detect potential side effects while the client is taking this drug?
(a) complete blood count
(b) serum glucose
(c) total protein
(d) liver function tests
Answer:
(d) liver function tests
Rationale:
Liver function tests, including aspartate transaminase (AST), should be monitored before therapy, 6 to 12 weeks after initiation of therapy or after dose elevation, and then every 6 months. If AST levels increase to three times normal, therapy should be discontinued. Simvastatin does not influence serum glucose, complete blood count, or total protein. Serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels should be evaluated before initiating therapy, after 4 to 6 weeks of therapy, and periodically thereafter.
Question 15.
A family has taken home their newborn and later received a call from the child’s health care provider (HCP) that the phenylketonuria (PKU) levels for their newborn daughter are abnormally high. Additional testing confirmed the diagnosis of phenylketonuria. The parents refuse to believe the results as no one else in their family has the disease. What information should the nurse tell the parents about the disease?
(a) PKU is carried on recessive genes contributed by each parent.
(b) PKU is caused by a recessive gene contributed by either parent.
(c) PKU is cured by eliminating dietary protein for this child.
(d) PKU will not impact future births for the family.
Answer:
(a) PKU is carried on recessive genes contributed by each parent.
Rationale:
Phenylketonuria is a disease that is carried on the recessive genes of each parent. In order to be transmitted to a newborn, the infant inherits a recessive gene from each parent. Control of the disease is by reduction of the amino acid phenylalanine, which is present in all protein foods. The disease cannot be cured, but controlled. With each pregnancy, there is a 25% chance a child will inherit the disease.
Question 16.
During a postpartum examination, the mother of a 2weekold infant tearfully tells the nurse she feels very tired and thinks she is not a good mother to her baby. Which statement by the nurse would be best?
(a) “The hormonal changes your body is experiencing are causing you to feel this way.”
(b) “Most new mothers feel the same way that you do. I hear that a lot from others.”
(c) “You need to have your husband and family help you so that you can get some rest.”
(d) “I’m concerned about what you are experiencing. Tell me more about what you are thinking and feeling.”
Answer:
(d) “I’m concerned about what you are experiencing. Tell me more about what you are thinking and feeling.”
Rationale:
The nurse should convey empathy and invite the client to share more about her thoughts and feelings so that the nurse can assess the mother for possible postpartum depression, which usually occurs between 2 weeks and 3 months after the baby’s birth but also can occur later. Postpartum depression is a mood disorder with symptoms of tearfulness, mood swings, despondency, feelings of inadequacy, inability to cope with the baby, and guilt about performance as a mother. Postpartum depression commonly goes undetected because of poor recognition and lack of knowledge.
Hormonal changes during and after birth may account for some of the symptoms; however, the nurse should not assume that that is the case. Stating the client’s husband and family should help her is an assumption that they are not and dismisses the client’s concerns. Saying most new mothers feel the same way minimizes the client’s concerns and decreases the likelihood of further disclosure by the client.
Question 17.
The nurse caring for a client who has severe burns on the head, neck, trunk, and groin areas. Which position would be most appropriate for preventing contractures?
(a) high Fowler’s
(b) semiFowler’s
(c) prone
(d) supine
Answer:
(d) supine
Rationale:
Supine in extension is the position most likely to prevent contractures. Clients who have experienced burns will find a flexed position most comfortable. However, flexion promotes the development of contractures. The high Fowler’s and semiFowler’s positions create hip flexion. The prone position is contraindicated because of head and neck burns. In clients with head and neck burns, pillows should not be used under the head or neck to prevent neck flexion contractures.
Question 18.
After transurethral resection of the prostate, the nurse notices that the urine draining from the catheter is bright red, has numerous clots, and is viscous. Which nursing action is most appropriate?
(a) Irrigate the catheter to remove clots.
(b) Milk the catheter tube vigorously.
(c) Increase the client’s fluid intake.
(d) Assess vital signs and notify the surgeon.
Answer:
(d) Assess vital signs and notify the surgeon.
Rationale:
Blood clots are normal after transurethral resection of the prostate, but bright red urine can indicate a hemorrhage. The nurse should assess the client’s vital signs and notify the surgeon. Irrigation of the catheter may help remove clots, but it does not decrease bleeding. Milking a urinary catheter or increasing fluid intake is not effective for controlling bleeding or decreasing clots.
Question 19.
A client is to receive 2 g of metronidazole orally in a single dose. The medication is available in 500mg tablets. How many tablets should the nurse administer? Record your answer using a whole number.
....................... tablets.
Answer:
4 tablets
Rationale:
imm
Question 20.
A client asks the nurse to help make out a will. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “I’m not a lawyer, but I’ll do what I can for you.”
(b) “You have a long way to go before you’ll need to do that. Let’s wait on it a while, shall we?”
(c) “I don’t believe in getting involved in legal matters, but maybe I can find another nurse who will help you.”
(d) “You need to consult an attorney because I’m not trained in such matters. Is there a family lawyer you can call?”
Answer:
(d) “You need to consult an attorney because I’m not trained in such matters. Is there a family lawyer you can call?”
Rationale:
A will is an important legal document. It is best to have one prepared with the help of an attorney. It would be unwise to help the client or to seek another nurse’s help because a nurse is not a lawyer. Asking the client to delay preparing the will just avoids the problem.
Question 21.
After vaginal birth of a term neonate, the nurse determines that the placenta is about to separate when which event occurs?
(a) The uterus becomes oval shaped.
(b) The uterus enlarges.
(c) A sudden gush of dark blood appears.
(d) The client expends efforts pushing.
Answer:
(c) A sudden gush of dark blood appears.
Rationale:
A sudden gush of dark blood, a lengthening of the umbilical cord, a smaller uterus, and changing of the uterus to a round or spherical shape are impending signs of placental separation. Pushing effort from the client is not a reliable indicator for impending placental separation, nor is it necessary for placental expulsion.
Question 22.
When preparing to present a community program about women who are victims of physical abuse, the nurse should stress what information about the incidence of battering?
(a) Death from battering is rare.
(b) Battering is a major cause of injury to women.
(c) Lower socioeconomic groups are primarily affected.
(d) Physical abuse typically begins early in a relationship well before a woman gets pregnant.
Answer:
(b) Battering is a major cause of injury to women.
Rationale:
Battering is a major cause of injury to women. Although battering occurs in all socioeconomic groups, it may appear to be more common in members of lower socioeconomic groups because they are more likely to use emergency department services. Many women experience battery for the first time when they become pregnant. Death from battering is not rare.
Question 23.
A college student asks the nurse about the student’s grandfather, who just received a diagnosis of Huntington’s disease. The student wants to know if the student will have the disease too. What should the nurse tell the student? Select all that apply.
(a) “Huntington’s disease affects men more than women.”
(b) “Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant disease.”
(c) “Huntington’s disease doesn’t skip a generation.”
(d) “Huntington’s disease is a treatable disease.”
(e) “There’s a 75% chance you’ll have the disease.”
Answer:
(b) “Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant disease.”
(c) “Huntington’s disease doesn’t skip a generation.”
Rationale:
Huntington’s disease, or Huntington’s chorea, is an autosomal dominant genetic neurologic disease that affects descendants of an affected person at a 50% rate. Huntington’s disease does not skip generations and affects men and women equally. Huntington’s disease is genetically transmitted on chromosome 4, and death usually results from respiratory complications related to aspiration.
Question 24.
The nurse notices drops of a liquid on the hallway floor of a health care facility. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Place paper towels over the drops of liquid.
(b) Don clean gloves and wipe up the drops of liquid.
(c) Post “wet floor” signs around the area.
(d) Call the Environmental Services Department.
Answer:
(b) Don clean gloves and wipe up the drops of liquid.
Rationale:
Liquids found on the floor should be removed immediately. The nurse should first put on gloves and then wipe up the liquid. Following removal, Environmental Services should be contacted to thoroughly cleanse the floor with a disinfectant solution. Placing paper towels over the drops is a safety hazard. “Wet floor” signs will be posted after the floor is cleansed by Environmental Services.
Question 25.
A client is admitted with numbness and tingling of the feet and toes after having an upper respiratory infection and flu for the past 5 days. Within 1 hour of admission, the client’s legs are numb to the hips. What should the nurse do next? Select all that apply.
(a) Notify the family of the change.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the change.
(c) Place respiratory resuscitation equipment in the client’s room.
(d) Check for advancing levels of paresthesia.
(e) Have the client perform ankle pumps.
Answer:
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the change.
(c) Place respiratory resuscitation equipment in the client’s room.
(d) Check for advancing levels of paresthesia.
Rationale:
A client who has been admitted for numbness and tingling in the lower extremities that advances upward, especially after having a viral infection, has clinical manifestations characteristic of GuillainBarre syndrome. The HCP Q must be notified of the change immediately because this disease is progressively paralytic and should be treated before paralysis of the respiratory muscles occurs.
The nurse must assess the client continuously to determine how fast the paralysis is advancing. The family does not need to be called in to visit until the client is stabilized and emergency equipment is placed at the bedside. Performing ankle pumps will not relieve the numbness or change the course of the disease.
Question 26.
When assessing a client with heart failure, the nurse should immediately report which findings to the health care provider (HCP)? Select all that apply.
(a) bibasilar crackles
(b) blood pressure 108/62 mm Hg, heart rate 88 beats/min
(c) 02 saturation 94% on room air
(d) 2lb (0.9kg) weight gain in 5 days
(e) urine output of 20 mL/h
(f) confusion
Answer:
(e) urine output of 20 mL/h
(f) confusion
Rationale:
The nurse reports signs of decreased tissue perfusion to the HCP; these include a decrease in urine output and confusion. Crackles, edema, and weight gain are monitored closely, but are not as high a priority as decreasing tissue perfusion. Vital signs and oxygen saturation are within normal limits.
Question 27.
The nurse is caring for a client with an injury to the thalamus. What information should the nurse include in the care plan?
(a) Give higher doses of pain medication.
(b) Keep patches on the client’s eyes to prevent corneal abrasion.
(c) Monitor the temperature of the bathwater.
(d) Avoid turning the client.
Answer:
(c) Monitor the temperature of the bathwater.
Rationale:
The nurse should monitor the temperature of the bathwater because the client cannot feel whether the water is too hot or too cold. Damage to the thalamus does not result in loss of the corneal reflex. Loss of position and vibratory sense usually occurs with degeneration of the posterior column of the spinal cord; therefore, turning every 2 hours is critical to prevent skin breakdown related to increased capillary pressure. The nurse can give only the prescribed dosage of pain medication.
Question 28.
A client with paranoia is having a delusion. While the client is having the delusion, what nursing intervention is most indicated?
(a) Assist the client to relieve anxiety.
(b) Ask the client what is causing the feelings of anxiety.
(c) Present reality when the client asks about the delusion.
(d) Allow the client to express anger and intense emotions in appropriate ways.
Answer:
(c) Present reality when the client asks about the delusion.
Rationale:
When a client is experiencing delusion, the nurse should present reality. The nurse should tell the client that he or she does not hear the voice, see the image, or experience whatever other manifestation of the delusion that the client is experiencing. The client with paranoia is delusional, related to anxiety states, but cannot manage the anxiety
at this moment. Allowing expressions of anger or other intense emotions may be harmful to the client or others. Nurses should avoid “why” questions, because such questions tend to make the client defensive.
Question 29.
The nurse teaches a pregnant client about the need to take supplemental vitamins with iron during her pregnancy. The nurse should instruct the client to take the iron with which liquid to promote maximum absorption?
(a) milk
(b) tea
(c) hot chocolate
(d) orange juice
Answer:
(d) orange juice
Rationale:
Absorption of supplemental iron and nonmeat sources of iron is enhanced by combining them with meat or a good source of vitamin C. An acidic environment enhances iron absorption. Therefore, taking the iron on an empty stomach or with orange juice would be most effective. If gastrointestinal upset occurs, the client may take the drug with meals. However, doing so reduces iron absorption by 40% to 50%.
Because milk interferes with the absorption of iron, the client should avoid taking the iron with milk. Tea has been shown to interfere with the absorption of iron. Therefore, the client should avoid taking the iron with tea. Hot chocolate, a milk product, interferes with iron absorption. Thus, the client should avoid taking the iron with hot chocolate.
Question 30.
A client with major depression completes his morning care independently. When the nurse approaches the client with his medication, he tells the nurse that he is a failure as a husband and a father and is worthless. His wife told the nurse previously that the client is a good provider and a wonderful father and husband. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “You were able to shower and dress without help this morning.”
(b) “Your wife told me that you’re a good husband and father. ”
(c) “You don’t have any reason why you should feel that way. ”
(d) “This medication will help your thinking.”
Answer:
(a) “You were able to shower and dress without help this morning.”
Rationale:
Stating “You were able to shower and dress without any help this morning” points out a visible, realistic accomplishment and strength to the client with selfdeprecatory statements, thereby helping to increase the client’s selfworth. The statements “Your wife told me that you’re a good husband and father” and “You don’t have any reason why you
should feel this way” are not helpful because logical statements are ineffective in changing the thinking of a client who is depressed.
The client may agree with what the nurse states but be just as depressed because intellectual understanding does not help the severely depressed client. The statement “This medication will help your thinking,” although true, does not recognize the client’s accomplishment and will have no positive effect on his selfesteem.
Question 31.
The nurse is reviewing laboratory values of a client receiving clozapine. Which laboratory value should the nurse report to the health care provider (HCP)?
(a) WBC of 3,500/pL (3.5 x 107L)
(b) hemoglobin of 8.2 g/dL (82 g/L)
(c) sodium level of 136 mEq/L (136 mmol/L)
(d) hyaline casts in the urinalysis
Answer:
(a) WBC of 3,500/pL (3.5 x 107L)
Rationale:
A low WBC may indicate the development of agranulocytosis, a serious lifethreatening side effect of clozapine, and should be reported immediately. While a hemoglobin of 8.2 mg/dL (8.2 g/L) is low, it is not life threatening. The sodium level of 136 mEq/L (136 mmol/L) is normal. Hyaline casts are usually caused by dehydration and indicate the need for more fluids.
Question 32.
Four hours after a cast has been applied for a fractured ulna, the nurse assesses that the client’s fingers are pale and cool and capillary refill is delayed for 4 seconds. How should the nurse interpret these findings?
(a) Nerve impairment is developing in the fingers.
(b) Arterial blood supply to the fingers is decreased.
(c) Venous stasis is occurring in the fingers.
(d) The finding is normal for this recovery period.
Answer:
(b) Arterial blood supply to the fingers is decreased.
Rationale:
The pallor and cool temperature of the fingers and the decreased return time for capillary refill indicate decreased arterial blood supply to the fingers. These findings are not normal for any time in the recovery process. Nerve impairment includes numbness, tingling, and impaired movement of the fingers. Signs of venous stasis include edema and reddening of the fingers, not pallor and cool temperature.
Question 33.
The nurse is planning care for a client who has sustained a spinal cord injury. The nurse should assess the client for which symptom?
(a) anesthesia below the level of the injury
(b) tingling in the fingers
(c) pain below the site of the injury
(d) loss of vibratory sense
Answer:
(a) anesthesia below the level of the injury
Rationale:
The spinal cord connects the brain to the periphery. Destruction or interruption of the neuro sensory pathway results in loss of communication between the two systems. Transection of the spinal cord renders the individual in a complete state of anesthesia below the level of injury. Tingling in the fingers may be related to spinal cord disease or to improper positioning of the extremity. Loss of position and vibratory sense usually occurs when the individual has degeneration of the posterior column of the spinal cord.
Question 34.
A client who is paraplegic cannot feel the lower extremities and has been positioned on the side. The nurse should inspect which area that is a potential pressure point when the client is in a side lying position?
(a) sacrum
(b) occiput
(c) ankles
(d) heels
Answer:
(c) ankles
Rationale:
Common pressure points in the sidelying position include the ears, shoulders, ribs, greater trochanter, medial and lateral condyles, and ankles. The sacrum, occiput, and heel are pressure points in the supine position.
Question 35.
Which nursing interventions are appropriate when creating a plan of care to promote the devel opment of a preschooler? Select all that apply.
(a) Provide anticipatory guidance for parents.
(b) Help the parents understand their child’s behavior.
(c) Identify (leviatiOnS from normal growth and development patterns.
(d) Determine the child’s future development.
(e) Send the child to a day care center.
Answer:
(a) Provide anticipatory guidance for parents.
(b) Help the parents understand their child’s behavior.
(c) Identify (leviatiOnS from normal growth and development patterns.
Rationale:
Goals for promoting healthy development in preschoolers include anticipatory guidance, helping parents understand their child’s behavior, identifying deviations from the norm, and assessing parentchild interaction. No one can assess or determine the child’s future development, and trying to do so can limit the potential the child may achieve. Although learning to interact with others is important, sending the child to a day care center is not essential to promote healthy development. The nurse can encourage the parents to provide opportunities for the child to play with others.
Question 36.
An adolescent client is hospitalized with acute glomerulonephritis. The nurse reviews the client’s urine chemistry laboratory reports as noted below. Which finding does the nurse draw to the attention of the health care provider (HCP)?
|
Test |
Result |
|
Urine specific gravity |
1.035 (1.035) |
|
Protein |
12 mg/24 h (120 mg/d) |
|
Potassium |
35 mEq/24 h (35 mmol/d) |
|
Creatinine |
2 mg124 h (17.6 mmol/d) |
(a) urine specific gravity
(b) protein
(c) potassium
(d) creatinine
Answer:
(a) urine specific gravity
Rationale:
The nurse verifies that the HCP has noted the elevated specific gravity. Clients with glomerulonephritis have concentrated urine from oliguria caused by the inflammation of the glomeruli. The other laboratory results are in normal range.
Question 37.
A client exhibits pressured speech, a labile affect, euphoria, and hyperactivity. The client states, “I am the savior of the city.” The family states that the client has hardly slept or eaten for days. Which client need is a priority in the nurse’s plan of care?
(a) physical
(b) social
(c) spiritual
(d) cultural
Answer:
(a) physical
Rationale:
The client’s physical needs are a priority in the nurse’s plan of care. The lack of fluid and caloric intake can lead to dehydration and cardiac collapse. The lack of sleep and rest can lead to exhaustion and death. Social, spiritual, and cultural needs are important client needs but not as important as the physical needs during an acute manic episode.
Question 38.
The nurse teaches a parent to take a neonate’s temperature with a disposable digital thermometer. Where does the nurse tell the parent to place the thermometer?
(a) under the neonate’s tongue
(b) under the neonate’s arm
(c) into the neonate’s rectum
(d) into the neonate’s ear
Answer:
(b) under the neonate’s arm
Rationale:
The correct method of assessing a neonate’s temperature is to place the thermometer under the neonate’s arm for an axillary reading. The oral route is not appropriate for obtaining the temperature in a neonate because the neonate is unable to close the mouth around the thermometer, thus leading to an inaccurate reading. Additionally, inserting a thermometer into a neonate’s mouth may cause trauma to delicate tissues.
Rectal temperatures may be indicated in some circumstances, hut they are generally to be avoided in neonates because of the risk of injury to or perforation of the delicate rectal mucosa. Only a specialized tympanic membrane device should be used to obtain a temperature reading via the ear. Inserting a disposable digital thermometer into the neonate’s ear may cause trauma to the delicate tissues.
Question 39.
A neonate receives an IV infusion of dextrose 10% administered by an infusion pump. The nurse should verify the alarm settings on the infusion pump at which times? Select all that apply.
(a) when the infusion is started
(b) at the beginning of each shift
(c) when the neonate returns from Xray
(d) when the neonate moves in the crib
(e) after the parents have visited
Answer:
(a) when the infusion is started
(b) at the beginning of each shift
(c) when the neonate returns from Xray
Rationale:
The alarm settings on infusion pumps should be verified at the time the infusion is started, at the beginning of each shift, and when the client is moved. The neonate can move in bed, but if the alarm is triggered, the nurse should verify the settings. Unless the neonate has moved or been taken out of the crib, it is not necessary to check alarm settings after the parents visit.
Question 40.
A coworker confides in the nurse that she had been a lifelong friend of a client who committed suicide. The coworker states: “We just saw each other last week. I can’t believe she tried to kill herself. She told me she wanted to give me her expensive necklace because our friendship meant so much to her. She seemed really happy and content. I knew she had been feeling down the last few months. I should’ve known that something was wrong; I should’ve asked her about suicide.” The nurse determines the coworker is most likely experiencing which condition?
(a) secondary traumatic stress
(b) a boundary violation
(c) compassion fatigue
(d) moral distress
Answer:
(d) moral distress
Rationale:
Moral distress occurs when one is unable to act because of internal or external constraints. The nurse is not able to change the way she interacted with her friend the last time she saw her and is feeling anguish. Secondary traumatic stress is distress that is a result of hearing firsthand traumatic experiences of another. A boundary violation is behavior by a professional that has violated the limits of a professionalclient relationship. Compassion fatigue is disengagement on the part of the caregiving professional.
Question 41.
The nurse is caring for a critically ill client with the client’s mother and spouse in the room. The spouse begins to shout derogatory comments to the mother, blaming her for her spouse’s critical state. What should the nurse do?
(a) Try to calm both the mother and spouse by speaking in a soft voice.
(b) Step between the mother and spouse stating emphatically, “Stop!”
(c) Call the hospital Security Department.
(d) Report the details immediately to the supervisor.
Answer:
(c) Call the hospital Security Department.
Rationale:
Contacting the Security Department is a proactive response in a situation that may become more volatile. A soft voice by the nurse may not even be heard in this situation. To state “Stop!” in this situation is not helpful and does not deal with the escalating risk. Once Security has been notified, the nurse should also report the incident to the supervisor.
Question 42.
The nurse walks into the room and finds that a client who has just had surgery is diaphoretic, appears to have no respirations, and has a barely palpable pulse. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Activate emergency response system.
(b) Open the airway.
(c) Start rescue breathing.
(d) Start cardiac compressions.
Answer:
(a) Activate emergency response system.
Rationale:
After determining that a client is unresponsive the nurse should activate emergency response system. Because the client has a pulse but is not breathing, the nurse should open the airway and begin ventilations with a bag mask or mask with a oneway valve until the full code team responds. Using standard precautions with the mask protects the nurse from exposure to possible client microorganisms.
Question 43.
The nurse plans care for a neonate to prevent neonatal heat loss immediately after birth. What action should the nurse take to conserve heat and help the infant maintain a stable temperature?
(a) Nestle the neonate against the crib wall.
(b) Place the infant skin to skin with the mother.
(c) Bathe the neonate with warm water.
(d) Position the neonate lying in an open crib with a diaper on.
Answer:
(b) Place the infant skin to skin with the mother.
Rationale:
Thermoregulation of the neonate is a critical intervention for the nurse caring for neonates. The preferred method of thermoregulation for healthy term newborns is to place them skin to skin with the mother. Wrapping and placing a hat on the newborn is another way to conserve heat and prevent heat loss. With the neonate lying against
a crib wall, heat transfers away from the infant to the cooler surface (conduction).
If the neonate is wet, the warmer water on the surface of the neonate evaporates to the cooler air (evaporation). If the neonate is lying in an open crib with a diaper on, the body naturally loses heat to the surrounding cooler air as it radiates from the warm body to the cooler room (radiation).
Question 44.
The nurse observes that the client’s right eye does not close completely. Based on this finding, what should the nurse do?
(a) Have the client wear eyeglasses at all times.
(b) Place an eye patch over the right eye.
(c) Instill artificial tears once a day.
(d) Cleanse the eye with a clean washcloth every shift.
Answer:
(b) Place an eye patch over the right eye.
Rationale:
When the blink reflex is absent or the eyes do not close completely, the cornea may become dry and irritated. Placing a patch over the eye is the most appropriate intervention to prevent eye injury. Making sure the client wears eyeglasses at all times will not help protect the eye from injury. Instilling eye drops once a day will not adequately relieve the potential for injury from a dry and irritating ocular environment. A normal saline solution should be used to moisten the eye, not tap water.
Question 45.
A mother tells the nurse that she wants her 4yearold to stop sucking her thumb. When developing the teaching plan, the nurse should suggest which intervention?
(a) Apply a special medicine that tastes terrible on the thumb.
(b) Get the child to agree to stop the thumbsucking.
(c) Remind the child every time the mother sees the thumb in her mouth.
(d) Put the child in timeout every time the mother observes thumbsucking.
Answer:
(b) Get the child to agree to stop the thumbsucking.
Rationale:
A 4yearold is old enough to be able to cooperate and stop the behavior. Therefore, the first step is to obtain the child’s cooperation. When this has occurred, then the mother makes sure it is okay to remind the child when the behavior is viewed. Using a substance that does not taste good is not effective as the child may suck it off and it does not promote health behavior.
The mother also should be encouraged to praise the child when she sees her not engaging in the behavior; “timeout” is considered a punishment and does not promote the desired behavior.
Question 46.
The nurse administers an intramuscular injection to an infant. Indicate the appropriate site for this injection.
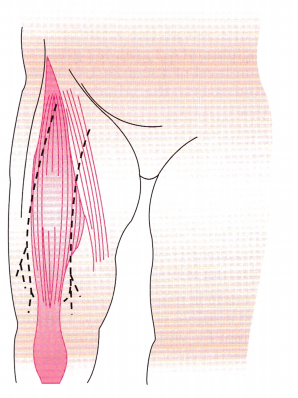
Answer:
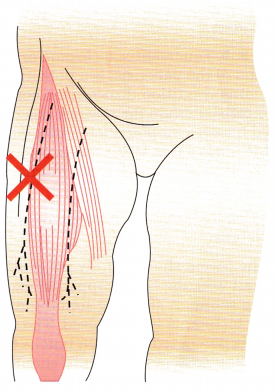
Rationale:
The vastus lateralis in the thickest part of the anterolateral thigh is a safe injection site for infants. The needle should be inserted at a 90degree angle to the long axis of the femur.
Question 47.
As part of a quality improvement team, the nurse uses the plandostudyact method to address unitbased alarm fatigue. The team has interviewed stakeholders to identity opportunities for reducing alarms and collaborated with the equipment vendors to gather alarm data. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Analyze the patterns to identify which devices account for the most alarms.
(b) Conduct a staff training on ways to reduce wave artifact alarms.
(c) Prioritize which alarm parameters need visual, audio, or secondary alerts.
(d) Revise default alarm parameters for the unit’s client population.
Answer:
(a) Analyze the patterns to identify which devices account for the most alarms.
Rationale:
After gathering alarm data, the nurse should “study” or analyze the data to identify which devices account for the most alarms. Once the data have been analyzed the nurse can “act” and make specific recommendations to reduce alarms. Conducting training on ways to reduce wave artifact, prioritizing how alarm limits are displayed, and revising default limits are all valid methods for reducing alarms. However, understanding the unit specific data helps the nurse design interventions that will have the most impact.
Question 48.
A primigravid client at 26 weeks’ gestation visits the clinic and tells the nurse that her lower back aches when she arrives home from work. The nurse should suggest that the client perform which exercise?
(a) tailor sitting
(b) leg lifting
(c) shoulder circling
(d) squatting
Answer:
(a) tailor sitting
Rationale:
Tailor sitting, also referred to as cobbler’s or butterfly pose, is an excellent exercise that helps to strengthen the client’s back muscles and also prepares the client for the process of labor. The client should be encouraged to rest periodically during the day and avoid standing or sitting in one position for a long time. Leg lifts are helpful for leg aches. Shoulder circling exercises are helpful for neck and upper backaches. Squatting is not helpful for alleviating lower backaches.
Question 49.
A client with diabetes is explaining to the nurse how to care for the feet at home. Which statement indicates that the client understands proper foot care?
(a) “When I injure my toe, I’ll plan to put iodine on it.”
(b) “I should inspect my feet at least once a week.”
(c) “It’s okay to go barefoot in the house.”
(d) “It’s important to dry my feet carefully after my bath.”
Answer:
(d) “It’s important to dry my feet carefully after my bath.”
Rationale:
It is important to dry the feet carefully after a bath to prevent a fungal infection. Clients with diabetes should seek medical attention when they injure their toes or feet to prevent complications. Iodine is highly toxic to the tissues. Clients with diabetes should inspect their feet daily and should wear shoes that support their feet while in the house.
Question 50.
A nurse is assessing a client who has a potential diagnosis of pancreatitis. Which risk factors predispose the client to pancreatitis? Select all that apply.
(a) excessive alcohol use
(b) gallstones
(c) abdominal trauma
(d) hypertension
(e) hyperlipidemia with excessive triglycerides
(f) hypothyroidism
Answer:
(a) excessive alcohol use
(b) gallstones
(c) abdominal trauma
(e) hyperlipidemia with excessive triglycerides
Rationale:
Pancreatitis, a chronic or acute inflammation of the pancreas, is a potentially lifethreatening condition. Excessive alcohol intake and gallstones are the greatest risk factors. Abdominal trauma can potentiate inflammation. Hyperlipidemia is a risk factor for recurrent pancreatitis. Hypertension and hypothyroidism are not associated with pancreatitis.
Question 51.
The nurse observes a parent of a child with cystic fibrosis performing chest. The nurse determines that the skill is being done correctly when the parent uses which technique?
(a) firmly but gently striking the chest wall to make a popping sound
(b) gently striking the chest wall to make a slapping sound
(c) percussing over an area from the umbilicus to the clavicle
(d) placing a blanket between the parent’s hand and the child’s chest
Answer:
(a) firmly but gently striking the chest wall to make a popping sound
Rationale:
The parent should firmly yet gently strike the chest wall with the hand cupped to make a hollow popping sound. A slapping sound indicates that an incorrect technique is being used. The area over the rib cage is percussed to loosen mucus from the underlying lung passages. The child should wear a thin piece of clothing (Tshirt) over the chest area
to protect the skin without diminishing the effect of the percussion.
Question 52.
The nurse should assess an older adult who has diminished hearing and vision for which condition?
(a) feelings of disorientation
(b) cognitive impairment
(c) sensory overload
(d) social isolation
Answer:
(d) social isolation
Rationale:
Social isolation is a concern for an older adult who has diminished hearing and vision. Feeling disoriented may be related to cognitive problems rather than diminished hearing and vision. Diminished hearing and vision is related to the aging process and does not result in impairment of the older adult’s thought processes. The client with impaired hearing and vision is unlikely to experience sensory overload.
Question 53.
At a wellchild check, the parents of a 4yearold child tell the nurse that they understand what their child says but others have difficulty.
What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “It’s very normal for parents to understand what their 4yearold is saying when others can’t.”
(b) “Your child may benefit from a referral to a speech pathologist for an evaluation.”
(c) “Do you think your child sounds like the other 4yearolds he plays with?”
(d) “I can do a screening at this visit to help rule out any hearing problems.”
Answer:
(b) “Your child may benefit from a referral to a speech pathologist for an evaluation.”
Rationale:
By age 4 a child should speak clearly enough to be understood by others. An articulation disorder occurs when a child cannot produce certain individual sounds, making speech difficult to understand. A speech pathologist can diagnose articulation disorders and provide specific treatments. A 4yearold child increasingly interacts with people other than parents.
They need to speak clearly enough to be understood or they will become frustrated in new social situations. Determining if a child can communicate as well as other children the same age is important, but the parents have already identified a problem, which needs a referral. The nurse can perform a hearing screen in the office to rule out major hearing loss, but this screening will not treat the problem.
Question 54.
To prevent development of peripheral neuropathies associated with isoniazid administration, what should the nurse teach the client to do?
(a) Avoid excessive sun exposure.
(b) Follow a lowcholesterol diet.
(c) Obtain extra rest.
(d) Supplement the diet with pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
Answer:
(d) Supplement the diet with pyridoxine (vitamin B6).
Rationale:
Isoniazid competes for the available vitamin B6 in the body and leaves the client at risk for developing neuropathies related to vitamin deficiency. Supplemental vitamin BB is routinely prescribed to address this issue. Avoiding sun exposure is a preventive measure to lower the risk of skin cancer. Following a lowcholesterol diet lowers
the individual’s risk of developing atherosclerotic plaque. Rest is important in maintaining homeostasis but has no real impact on neuropathies.
Question 55.
The health care provider (HCP) has prescribed nitroglycerin to a client with angina. The client also has closedangle glaucoma. The nurse should contact the HCP to discuss the potential for which drug interaction?
(a) decreased intraocular pressure
(b) increased intraocular pressure
(c) hypotension
(d) hypertension
Answer:
(b) increased intraocular pressure
Rationale:
Nitroglycerin causes vasodilation, which results in increased intraocular pressure. The vasodilatory effects of the medication can trigger an attack, causing pain and loss of vision. Hypotension is a common side effect of nitroglycerin, which dilates the blood vessels, but is not a concern in the client with glaucoma.
Question 56.
A nurse is taking a medication history on a client with multiple sclerosis before administering an initial dose of baclofen. What should the nurse check before administering the drug? Select all that apply.
(a) presence of muscle weakness
(b) history of muscle spasms
(c) serum creatinine level
(d) serum potassium level
(e) blood glucose
Answer:
(a) presence of muscle weakness
(b) history of muscle spasms
(c) serum creatinine level
(e) blood glucose
Rationale:
The nurse should ask the client with multiple sclerosis about areas of muscle weakness because baclofen may increase the weakness. The nurse should ask the client about a history of muscle spasms. Baclofen is effective against involuntary spasms resistant to passive movement for clients with multiple sclerosis and paralysis. Baclofen is not effective against the spasticity of cerebral origin, such as with cerebral palsy and Parkinson’s disease.
The nurse should ask the client about the client’s liver and renal function because baclofen is metabolized and excreted by these organs. The nurse should check the laboratory values reflecting the function of the kidneys and liver, which include serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels. The nurse should also check blood glucose levels because baclofen can increase blood glucose. Clients with diabetes taking antidiabetic medication may need to adjust the dosage. Potassium is not affected by the drug, so the nurse does not need to check the serum potassium level.
Question 57.
A client has been taking carbamazepine for 2 years. What should the nurse assess the client for? Select all that apply.
(a) bruising
(b) sore throat
(c) urine retention
(d) lightcolored stool
(e) hydration status
Answer:
(a) bruising
(b) sore throat
(d) lightcolored stool
Rationale:
The nurse should assess the client for signs of bone marrow depression, manifested by bruising or unusual bleeding, and signs of infection such as a sore throat. The nurse should also assess the client for signs of hepatic dysfunction, such as lightcolored stool or darkcolored urine. Although the nurse may want to check the client’s urinary function and hydration status, urine output and hydration are not specific monitoring needs related to longterm use of carbamazepine.
Question 58.
The nurse should assess the client with severe diarrhea for which acidbase imbalance?
(a) respiratory acidosis
(b) respiratory alkalosis
(c) metabolic acidosis
(d) metabolic alkalosis
Answer:
(a) respiratory acidosis
Rationale:
A client with severe diarrhea loses large amounts of bicarbonate, resulting in metabolic acidosis. Metabolic alkalosis does not result in this situation. Diarrhea does not affect the respiratory system.
Question 59.
A nurse is planning care for a client who has heart failure. Which goal is appropriate for a client with excess fluid volume?
(a) A weight reduction of 20% will occur.
(b) Pain will be controlled effectively.
(c) Arterial blood gas values will be within normal limits.
(d) Serum osmolality will be within normal limits.
Answer:
(d) Serum osmolality will be within normal limits.
Rationale:
Serum osmolality indicates the water balance of the body. A normal plasma osmolality between 275 and 295 mOsm/kg (mmol/kg) indicates that the fluid volume excess has been resolved. A weight reduction of 10% may not necessarily return the client to a state of normal serum osmolality. Clients with excess fluid volume do not necessarily have pain or abnormal arterial blood gas values.
Question 60.
A schoolage client is admitted to the hospital with the diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever. Which laboratory blood finding confirms that the child has had a streptococcal infection?
(a) high leukocyte count
(b) low hemoglobin count
(c) elevated antibody concentration
(d) low erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Answer:
(c) elevated antibody concentration
Rationale:
Exactly why rheumatic fever follows a streptococcal infection is not known, but it is theorized that an antigenantibody response occurs to an M protein present in certain strains of streptococci. The antibodies developed by the body attack certain tissues such as in the heart and joints. Antistreptolysin O titer findings show elevated or rising antibody levels. This blood finding is the most reliable evidence of a streptococcal infection.
Question 61.
A 12yearold client says, “Give me my pajamas. I’m not putting your silly gown on.” What is the most appropriate response by the nurse?
(a) “I know they’re funny, but everyone here wears them.”
(b) “You don’t mean that, now. A big guy like you knows how hospitals are.”
(c) “You’re upset because you feel awkward and embarrassed in these gowns.”
(d) “You’re upset because you think we’re unreasonable.”
Answer:
(c) “You’re upset because you feel awkward and embarrassed in these gowns.”
Rationale:
The nurse uses active listening, in which the client’s feelings are reflected back to him. Telling the client that everyone wears them does not consider the client’s feelings. Telling the client that what he said is not what he meant discounts the validity of his statement. Interpreting the reason for the client being upset as the rule being unreasonable does not take into account how it affects the client personally.
Question 62.
After the nurse teaches the parents of a 15-month-old child who has undergone cleft palate repair how to use elbow restraints, which statement by the parents indicates effective teaching?
(a) “We’ll keep the restraints in place continuously until our health care provider says it’s okay to remove them.”
(b) “We can take off the restraints while our child is playing, but we’ll make sure to put them back on at night.”
(c) “The restraints should be taped directly to our child’s arms so that they’ll stay in one place.”
(d) “We’ll remove the restraints temporarily at least three times a day to check his skin, then put them right back on.”
Answer:
(d) “We’ll remove the restraints temporarily at least three times a day to check his skin, then put them right back on.”

Rationale:
Elbow restraints help to keep the child from placing fingers or any other object in the mouth that would cause injury to the operative site. The restraints are worn at all times except when they are removed to check the skin. Because of the risk for skin breakdown, the restraints are removed periodically during the day to assess the child’s underlying skin. It is advisable to remove only one restraint at a time while keeping hold of the child’s hand on the unrestrained side.
Toddlers are quick and usually want to explore the area in the mouth that the surgery has made feel different. The restraints should be in place at all times during sleep and play to prevent inadvertent injury to the operative site. Taping the restraints directly to the skin is not advised because skin breakdown can occur when tape is reapplied to the same area over several weeks. The restraints can be fastened to clothing to keep them from slipping.
Question 63.
The nurse notes that a client is too busy investigating the unit and overseeing the activities of other clients to eat dinner. To help the client obtain sufficient nourishment, which plan would be best?
(a) Serve foods that the client can carry with her.
(b) Allow the client to send out for her favorite foods.
(c) Serve the client food in small, attractively arranged portions.
(d) Allow the client to enter the unit kitchen for extra food as necessary.
Answer:
(a) Serve foods that the client can carry with her.
Rationale:
Because the client is very active, it would be best to give her food she can carry with her and eat as she moves. Neither allowing the client to send out for her favorite foods nor serving food in small, attractively arranged portions will address her need to be active. Allowing the client in the unit kitchen is impractical, and she most likely would be too busy to eat anyway.
Question 64.
The nurse should encourage women to have a “Pap test” (Papanicolaou smear) for which reasons? Select all that apply.
(a) to detect precancerous and cancerous cells of the uterus
(b) to assess the effects of sex hormonal replacement
(c) to identify viral, fungal, and parasitic conditions
(d) to evaluate the response to chemotherapy or radiation therapy to the cervix
(e) to determine a diminished blood flow to the perineal mucous membrane
Answer:
(a) to detect precancerous and cancerous cells of the uterus
(b) to assess the effects of sex hormonal replacement
(c) to identify viral, fungal, and parasitic conditions
(d) to evaluate the response to chemotherapy or radiation therapy to the cervix
Rationale:
The purposes of the Pap (Papanicolaou) smear include to detect precancer ous and cancerous cells of the cervix; to assess the effects of sex hormonal replacement; to identify viral, fungal, and parasitic conditions; and to evaluate the response to chemotherapy or radiation therapy to the cervix.
Question 65.
The nurse administers prednisone to a preschool child with nephrosis. What should the nurse do to ensure that the nurse has identified the child correctly? Select all that apply.
(a) Ask another nurse to confirm that this is the correct dose and correct client for whom the prednisone has been prescribed.
(b) Check the child’s identification band against the medical record number.
(c) Verify the date of birth from the medical record with the date of birth on the client’s identification band.
(d) Compare the room number on the bed with the number on the client’s identification band.
(e) Ask the parent to state the client’s full name.
Answer:
(b) Check the child’s identification band against the medical record number.
(c) Verify the date of birth from the medical record with the date of birth on the client’s identification band.
(e) Ask the parent to state the client’s full name.
Rationale:
The nurse should use at least two sources of identification before administering medication to any client. The identification can include the medical record Q number and the client’s date of birth. It is not necessary to check the client and dose for this drug with another nurse. It is also not safe to use the room number or bed number as a source of identification as clients’ locations in the hospital are frequently changed. A parent may be used as additional safety check with very young children because the nurse cannot assume that the child will give a correct first name.
Question 66.
A client is scheduled to have surgery to relieve an intestinal obstruction. Prior to surgery, the nurse should verify that the client has followed which preoperative instructions?
(a) discontinued use of blood thinners
(b) eaten a lowresidue diet
(c) practiced abdominal muscle strengthening exercises
(d) signed a last will and testament
Answer:
(a) discontinued use of blood thinners
Rationale:
Nurses should verify that clients having surgery discontinued use of any blood thinners to prevent postoperative bleeding. Prior to bowel resection, the client should follow a highresidue diet with increased fluids. Abdominal tightening exercises are not necessary before this surgery. Clients may write a will before surgery, but the nurse does not have to inquire about it.
Question 67.
A client at 36 weeks’ gestation begins to exhibit signs of labor after an eclamptic seizure. The nurse should assess the client for which complication?
(a) abruptio placentae
(b) transverse lie
(c) placenta accreta
(d) uterine atony
Answer:
(a) abruptio placentae
Rationale:
After an eclamptic seizure, the client is at risk for abruptio placentae due to severe vasoconstriction resulting in hemorrhage into the decidua basalis. Abruptio placentae is manifested by a boardlike abdomen and an abnormal fetal heart rate tracing. Transverse lie or shoulder presentation, placenta accreta, and uterine atony are not related to eclampsia.
Causes of a transverse lie may include relaxation of the abdominal wall secondary to grand multiparity, preterm fetus, placenta previa, abnormal uterus, contracted pelvis, and excessive amniotic fluid. Placenta accreta, a rare phenomenon, refers to a condition in which the placenta abnormally adheres to the uterine lining. Uterine atony, or relaxed uterus, may occur after birth, leading to postpartum hemorrhage.
Question 68.
The nurse is preparing to administer propranolol to a client for control of migraine headaches. The client also has a prescription for sumatriptan as needed for a headache. The client’s pulse rate is 56 bpm. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Contact the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Assess blood pressure.
(c) Administer oxygen.
(d) Administer sumatriptan.
Answer:
(b) Assess blood pressure.
Rationale:
One of the actions of propranolol, a drug used in the treatment of migraine headaches, is to inhibit arterial vasodilation. The nurse should assess the client’s blood pressure to evaluate overall circulatory response to the medication.
Until the nurse determines the client’s blood pressure, there is no immediate need to contact the HCP There is no immediate need to administer oxygen. The client has not indicated pain; it is not necessary to administer the sumatriptan at this time.
Question 69.
A client with a history of type 1 diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease should have which immunization?
(a) influenza
(b) hepatitis A
(c) measlesmumpsrubella
(d) varicella
Answer:
(a) influenza
Rationale:
The client with diabetes and a chronic respiratory condition is most at risk for influenza and should receive the vaccine yearly. Diabetes and chronic respiratory conditions do not increase the risk of hepatitis A. An adult client is not as likely to need the measlesmumpsrubella or varicella immunizations, but titers can be checked if the client has not had childhood immunizations or the disease.
Question 70.
The mother of a toddler diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia asks what foods she should give her child. The nurse should evaluate the teaching as successful when the mother later reports that she feeds the toddler which foods?
(a) milk, carrots, and beef
(b) raisins, chicken, and spinach
(c) beef, lettuce, and juice
(d) eggs, cheese, and milk
Answer:
(b) raisins, chicken, and spinach
Rationale:
Good sources of dietary iron include red meats, poultry, green leafy vegetables, and dried fruits such as raisins. Milk products are poor sources of iron. Carrots are high in vitamin A.
Question 71.
When a child is able to grasp the idea that a ball continues to exist even though the child’s parent placed the ball under a hat, the child is in which stage in the development of logical thinking according to Piaget?
(a) sensorimotor
(b) preoperational
(c) concrete operations
(d) formal operations
Answer:
(a) sensorimotor
Rationale:
During the tertiary circular reaction stage of the sensorimotor stage (12 to 18 months of age), the infant comes to understand causality and object permanence, recognizing that objects placed out of sight continue to exist. During the preoperational stage (ages 2 to 6), the child’s perception is based on how he or she views an event. The concrete operational stage (ages 6 to 12) is the beginning of concrete, logical thinking. During the formal operational stage (ages 13 to 18), the child is able to perform abstract reasoning.
Question 72.
A nurse discusses with parents the procedures that will be performed on their neonate immediately after birth. The nurse determines that the instructions have been understood when the parent states that which procedure will be done to the neonate first?
(a) The neonate will be suctioned.
(b) The neonate will be dried and stimulated to cry.
(c) The neonate will be given oxygen.
(d) The neonate’s umbilical cord will be cut.
Answer:
(b) The neonate will be dried and stimulated to cry.
Rationale:
The neonate will be simultaneously dried and stimulated to cry immediately upon birth. If the neonate does not cry as a result of these measures, the ABCs (airway, breathing, and circulation) of cardiopulmonary resuscitation will be followed. Positioning the neonate and suctioning or clearing the airway ensure that the airway is clear so that the first breath the neonate takes is air, rather than fluid or particulate matter.
Breathing will be stimulated once the airway is clear, and then heart rate will be validated either apically or through the cord. The cord may be cut in order to hand the neonate to the mother for nursing. In many instances, the infant is placed on the mother’s abdomen before the cord is cut.
Question 73.
An infusion of lidocaine hydrochloride is running at 30 mL/h. The dilution is 1,000 mg/250 mL. What dosage is the client receiving per minute? Record your answer using a whole number.
.................. mg/min.
Answer:
2 mg/min
Rationale:
First, calculate the concentration of mg/mL:
imm
Next, multiply the number of milligrams per milliliter by the pump setting in milliliters per hour:
imm
Next, divide the milligrams per hour by 60 to obtain milligrams per minute:
120 mg/h -r 60 min = 2 mg/min.
Question 74.
A mother tells a nurse that her child has been exposed to roseola. After the nurse teaches the mother about the illness, which finding, if stated by the mother as the most characteristic sign of roseola, indicates successful teaching?
(a) fever and sore throat
(b) normal temperature followed by a lowgrade fever
(c) high fever followed by a drop and then a rash
(d) coldlike signs and symptoms and a rash
Answer:
(c) high fever followed by a drop and then a rash
Rationale:
Children with roseola have a high fever for 3 days, which drops suddenly. Then a nonpruritic rash appears, typically lasting for 1 to 2 days. High fever followed by a rash is a characteristic sign. Associated symptoms include cold symptoms, cough, and lymphadenopathy.
Question 75.
A nurse is instructing a client about using nitroglycerin patches in order to prevent tolerance to the drug. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Remove the patch every night.
(b) Use the patch only when chest pain occurs.
(c) Change the site of the patch every day.
(d) Apply the patch only on alternate days.
Answer:
(a) Remove the patch every night.
Rationale:
The client may become tolerant of the antianginal effects of nitrates. Removing nitrates for 8 hours each day is usually effective in preventing tolerance. Nitrate patches should not be used on an as-needed basis. Sites should be rotated daily to prevent skin irritation, but this is not related to tolerance. Removing the patch for only 8 hours is sufficient to prevent tolerance, and skipping days could impact the drug’s effectiveness.
Question 76.
A client’s abdominal incision eviscerates. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Take the client’s vital signs and call the health care provider.
(b) Lower the client’s head and elevate the feet.
(c) Cover the incision with a dressing moistened with sterile normal saline solution.
(d) Start an emergency infusion of IV fluids.
Answer:
(c) Cover the incision with a dressing moistened with sterile normal saline solution.
Rationale:
When an incision eviscerates, it is a medical emergency. The nurse’s first response is to apply a sterile dressing that has been moistened with sterile normal saline solution. The client should also be placed in semi-Fowler’s position to release any tension on the abdominal area. Vital signs should be taken, and an IV line may be started for emergency treatment; however, the first action is to protect the wound and abdominal contents.
Question 77.
The nursing staff has safely and successfully secluded and restrained a client with acute mania who threatened the nurse and threw a chair against the wall in the community room. Which statement by the nurse is most helpful to the client at this time?
(a) “Threatening others and throwing furniture is not allowed.”
(b) “You’ve been restrained until you can manage your behavior.”
(c) “Since you’ve been here before, you know what the rules are.”
(d) “We’re only doing this for your own good, so calm down.”
Answer:
(b) “You’ve been restrained until you can manage your behavior.”
Rationale:
The nurse should tell the client in a simple, matter-of-fact manner the purpose of the restraints to help the client understand why restraints are necessary. Long explanations and interactions with the acutely manic and agitated client are not appropriate or therapeutic at this time because the client with a high level of anxiety has difficulty focusing and processing.
Saying "Threatening others and throwing furniture is not allowed” could lead the client to believe he is being punished. Reminding the client that the client has “been here before and knows what the rules are” and “We are only doing this for your own good, so calm down” are condescending and verbalizing the expectation that the client can control the illness.
Question 78.
At what time should the blood be drawn in relation to the administration of the IV dose of gentamicin sulfate?
(a) 2 hours before the administration of the next IV dose
(b) 3 hours before the administration of the next IV dose
(c) 4 hours before the administration of the next IV dose
(d) just before the administration of the next IV dose
Answer:
(d) just before the administration of the next IV dose
Rationale:
To determine how low the gentamicin serum level drops between doses, the trough serum level should be drawn just before the administration of the next IV dose of gentamicin sulfate.
Question 79.
A client is taking 600 mg of valproic acid twice daily. The nurse should assess the client for which adverse effects? Select all that apply.
(a) tremors
(b) hair loss
(c) gastrointestinal upset
(d) anorexia
(e) weight gain
Answer:
(a) tremors
(b) hair loss
(c) gastrointestinal upset
(e) weight gain
Rationale:
Anorexia or loss of appetite is not associated with valproic acid. Adverse effects include tremors, transient hair loss, gastrointestinal upset, and weight gain.
Question 80.
A client has a cerclage placed at 16 weeks’ gestation. She has had no contractions, and her cervix is dilated 2 cm. The nurse is preparing the client for discharge. Which statement by the client should indicate to the nurse that the client needs further instruction?
(a) “I’ll need more frequent prenatal visits.”
(b) “I should call if I’m leaking fluid or have bleeding or contractions.”
(c) “I can have sex again in about 2 weeks.”
(d) “I can have nothing in my vagina until I’m at term.”
Answer:
(c) “I can have sex again in about 2 weeks.”
Rationale:
Intercourse commonly stimulates uterine contractions. The prostaglandins found in semen can also initiate contractions. After placement of a cerclage for advanced dilation and contractions, the client is considered at high risk for preterm birth and should be seen by her health care provider (HCP) HQ more frequently.
The client should call the HCP immediately if she sees signs of complications, such as leaking fluid (rupture of membranes), vaginal bleeding, and contractions (particularly with a cerclage in place). Anything in the vagina may initiate contractions and the labor process.
Question 81.
The nurse is admitting a 4yearold with a possible meningococcal infection. Which type of isolation is indicated?
(a) airborne precautions
(b) contact precautions
(c) droplet precautions
(d) standard precautions
Answer:
(c) droplet precautions
Rationale:
Meningococcal infections are spread through close mucous membrane or respiratory contact with large respiratory droplets. Meningococcal infections are not spread by small airborne organisms or contact with a person’s skin or contaminated items. Standard precautions, used when touching body fluids, are not sufficient to prevent the spread of meningitis.
Question 82.
While preparing to administer medications to a client, the nurse compares the medication in the medication box with the health care provider’s (HCP) prescriptions and discovers that the HCP has prescribed prednisone 15 mg PO for a client with cirrhosis and the medication in the client’s medication box is prednisolone 5 mg. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Call the pharmacy for prednisone 15 mg.
(b) Notify the charge nurse or supervisor.
(c) Call the HCP for clarification.
(d) Contact the pharmacy about the discrepancy.
Answer:
(d) Contact the pharmacy about the discrepancy.
Rationale:
The nurse should contact the pharmacy and report the error and check the discrepancy with the actual prescription. The nurse must be vigilant when comparing medication in the medication box to the prescription; prednisolone, for example, is three to five times more potent than prednisone. The nurse cannot make a pharmacy substitution change without prescriptive authority.
The prednisolone is not returned until a clarification prescription is obtained to determine the substitution drug and dosage is correct. It is not necessary to contact the charge nurse or supervisor, as the nurse must first clarify the prescription with the HCR The nurse reports the incident according to agency policy and notifies all involved of the change in the prescription.
Question 83.
A parent calls the clinic after her 4yearold choked on a peanut. The parent reports performing abdominal thrusts and the child is breathing normally now. What should the nurse tell the parent to do?
(a) Bring the child to the emergency department to check for airway obstruction.
(b) Test the child’s urine for blood from internal bleeding.
(c) Call the health care provider if the child begins to sweat and feels dizzy.
(d) Observe the child for difficulty breathing because the abdominal thrusts may have caused a pneumothorax.
Answer:
(a) Bring the child to the emergency department to check for airway obstruction.
Rationale:
The nurse should instruct the mother to bring the child to the emergency department. If aspirated, nuts may swell leading to an airway obstruction after the initial event; endoscopy may be required to remove remaining fragments. Bleeding from trauma to internal organs after abdominal thrusts is rare. There are no signs of shock to suggest anaphylaxis. There is no indication of the presence of a pneumothorax.
Question 84.
A client is taking nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain from rheumatoid arthritis. What instruction should the nurse give the client about NSAIDs?
(a) Take the prescribed medication with food and fluids.
(b) Gradually decrease the medication dosage.
(c) Rinse the mouth with water after taking NSAIDs.
(d) Avoid driving and using machinery while tak ing NSAIDs.
Answer:
(a) Take the prescribed medication with food and fluids.
Rationale:
Gastric upset is an adverse effect of NSAIDs. Taking these drugs with food and fluids minimizes this effect. The dosage of NSAIDs does not need to be tapered. Because NSAIDs do not cause drowsiness or stomatitis, the client does not need to restrict driving or rinse the mouth.
Question 85.
The nurse is assessing a neonate at 5 minutes after birth. The nurse records the Apgar score based on the findings in the chart below.
|
Appar at 5 minutes age birth Result |
|
|
Heart rate |
100bpm |
|
Res pi rations |
Irregular |
|
Color |
Pink |
|
Muscle tone |
Moving all four extermies |
|
Reflexes |
cough |
The nurse compares these findings to the Apgar score obtained at birth, as determined by the findings in the chart below.
|
Appar at 5 minutes age birth Result |
|
|
Heart rate |
120bpm |
|
Res pi rations |
slow |
|
Color |
Blue extermies |
|
Muscle tone |
flexine of extermies |
|
Reflexes |
glanice |
What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the neonatologist on call.
(b) Continue to assess the neonate.
(c) Apply an oxygen mask.
(d) Rub the neonate’s extremities.
Answer:
(b) Continue to assess the neonate.
Rationale:
The neonate’s Apgar score has been improving since birth. (The birth score is 6; the current score is 9.) The nurse should continue to assess the neonate. There is no indication that oxygen is needed since the color is improving, and stimulating the baby is not necessary as the baby is now flexing the extremities.
Question 86.
A nurse is concerned that a nurse colleague is diverting a narcotic medication. The nurse notes that the colleague administers pain medication in greater amounts than the nurse does when taking care of the same clients. These clients report unrelieved pain. What should the nurse do next? Select all that apply.
(a) Remain focused on own client assignment.
(b) Continue to monitor the colleague’s behavior.
(c) Report concerns to the supervisor.
(d) Ask the colleague about the clients’ lack of pain relief.
(e) Ignore the situation, as this is a supervisory responsibility.
Answer:
(c) Report concerns to the supervisor.
(d) Ask the colleague about the clients’ lack of pain relief.
Rationale:
In accordance with ethical principles and the nurse’s role to serve as an advocate for clients and protect their safety, the nurse must report the colleague’s suspicious behaviors to the supervisor. It would also be appropriate to follow up with the colleague to address continued client reports of lack of pain relief. Deciding to avoid getting involved places the nurse’s license at risk. Nurses are also responsible for reporting concerning behaviors of a nurse colleague.
Question 87.
The nurse should assess a newborn with esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) for which complications? Select all that apply.
(a) copious frothy mucus
(b) episodes of cyanosis
(c) several loose stools
(d) distended abdomen
(e) poor gag reflex
Answer:
(a) copious frothy mucus
(b) episodes of cyanosis
(d) distended abdomen
Rationale:
The initial signs of esophageal atresia and TEF include lots of frothy mucus and unexplained episodes of cyanosis usually caused by overflow of mucus from the esophagus. Distended abdomen occurs frequently from passing from the trachea to the stomach. Loose stools and poor gag reflex are not signs of TEF. Instead infants tend to cough frequently on the excessive secretions.
Question 88.
When developing a teaching plan for a client with an infected decubitus ulcer, the nurse should tell the client that which factor is most important for healing?
(a) adequate circulatory status
(b) scheduled periods of rest
(c) balanced nutritional diet
(d) fluid intake of 1,500 mL/day
Answer:
(a) adequate circulatory status
Rationale:
Adequate circulatory status is the most important factor in the healing process of an infected decubitus ulcer. Blood flow to the area must be present to bring nutrients and prescribed antibiotics to the tissues. Rest and a balanced diet are essential to health maintenance but are not the priority for healing an infected decubitus ulcer. A fluid intake of 2,000 to 3,000 mL/day, if not contraindicated, is recommended to provide hydration to the client’s tissues.
Question 89.
The nurse gives anticipatory guidance to the parents of a 5monthold infant about toy safety. What toys should the nurse recommend?
(a) plastic toy cars
(b) wooden puzzles
(c) stuffed animals
(d) soft, washable toys
Answer:
(d) soft, washable toys
Rationale:
Soft, washable toys are appropriate for infants, who tend to place everything in their mouths. These toys are not harmful. Plastic toys cannot be manipulated by a child of this age, and the child would put the car in the mouth, which may not be safe due to small parts that may be swallowed or aspirated. Games and puzzles are too advanced for a 5-month-old, and the child could put the pieces in the mouth and swallow them. Some stuffed animals have eyes that can be swallowed or aspirated.
Question 90.
One staff member in a psychiatric unit says to the nurse, “Why are we carrying out suicide precautions for someone who’s dying? It’s pointless and a waste of time.” What should the nurse do next?
(a) Assign the staff member to other clients.
(b) Ask the psychiatric clinical nurse specialist to meet with the staff member.
(c) Agree with the staff member and discontinue suicide precautions.
(d) Call for a multidisciplinary staff meeting.
Answer:
(d) Call for a multidisciplinary staff meeting.
Rationale:
The nurse should call for a multidisciplinary staff meeting because there is a need for staff members to share their feelings of anger, frustration, and grief. Because nurses focus on saving human lives, any feelings of hopelessness regarding a dying client can interfere with the client’s care and management.
Assigning the staff member to other clients ignores the staff member’s need to work through feelings. Calling the clinical nurse specialist to deal with the staff member does nothing to help other staff. The psychiatric clinical nurse specialist would be included in the staff meeting to help the entire staff deal with their feelings.
Question 91.
The nurse reviews the client’s laboratory report to determine the client’s blood level of valproic acid, which is 35 mcg/mL (243 pmol/L). Based on this report, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Withhold the next dose of valproic acid.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Give the next dose as prescribed.
(d) Take the client’s vital signs.
Answer:
(c) Give the next dose as prescribed.
Rationale:
The nurse should give the next dose as prescribed because the blood level is 35 mcg/mL, which is lower than the normal range of 50 to 100 mcg/mL. Withholding the next dose, notifying the HCP 2, and taking the client’s vital signs are not indicated in this situation.
Question 92.
After 2 days on a psychiatric unit, a client is still isolating himself in his room, except for meals. The client says he is uncomfortable around crowds of people. Which nursing intervention is the most appropriate initially?
(a) Play a game of checkers with the client in his room.
(b) Ask the client to attend a group session with the nurse.
(c) Invite the client to go for a walk with the nurse and one other client.
(d) Talk with the client in a corner of the crafts room.
Answer:
(c) Invite the client to go for a walk with the nurse and one other client.
Rationale:
Going for a walk with the nurse and another client is a more gradual introduction to being with others. The goal is to gradually encourage interaction with others; playing games in the client’s room promotes continued isolation. Going to a group session and participating in crafts are exposing the client to large groups too rapidly.
Question 93.
A nurse cares for a woman who gave birth to a term neonate at 0600. At 1600, the woman has a distended bladder and is reporting pain of 5 on a scale of 1 to 10. The nurse reviews the client’s output record. What should the nurse do first?
|
Ouput record |
||||
|
Time |
0800 |
1000 |
1100 |
1400 |
(a) Apply a warm, moist towel over the bladder.
(b) Ask the woman to sit on the toilet while the nurse runs water from the faucet.
(c) Administer acetaminophen with codeine.
(d) Use an inandout catheter to empty the bladder.
Answer:
(d) Use an inandout catheter to empty the bladder.
Rationale:
The client is not emptying her bladder after repeated attempts. The nurse should now use an in-and-out catheter to empty the bladder. While the other comfort measures may be helpful, this client has not completely emptied her bladder since birth and will be at risk for a urinary tract infection and postpartum hemorrhage.
Question 94.
The nurse observes that a client with a history of panic attacks is hyperventilating. What action should the nurse take?
(a) Have the client breathe into a paper bag.
(b) Instruct the client to put the head between the knees.
(c) Give the client a low concentration of oxygen by nasal cannula.
(d) Tell the client to take several deep, slow breaths and exhale normally.
Answer:
(a) Have the client breathe into a paper bag.
Rationale:
The best way to ease symptoms caused by hyperventilation is to have the client breathe into a paper bag. This helps to raise carbon dioxide level, which encourages deeper, slower breathing. The symptoms of hyperventilation will not be alleviated by having the client put the head between the knees, giving the client low concentrations of oxygen, or having the client take deep, slow breaths and exhaling normally.
Question 95.
A client at 40+ weeks’ gestation visits the emergency department because she thinks she is in labor. Which is the best indication that the client is in true labor?
(a) fetal descent into the pelvic inlet
(b) cervical dilation and effacement
(c) painful contractions every 3 to 5 minutes
(d) leaking amniotic fluid clear in color
Answer:
(b) cervical dilation and effacement
Rationale:
True labor is present when cervical dilation and effacement occur. Fetal descent into the pelvic inlet is an indication that labor will begin soon. However, for a nulligravid client, this may take 1 to 2 weeks. Painful contractions every 3 to 5 minutes may be Braxton Hicks contractions. Contractions that disappear when the client lies down are a sign of false labor. Although leaking amniotic fluid should be reported, it is not a sign of true labor.
Question 96.
The father of a 3weekold infant who has developed sepsis says that he feels guilty because he did not realize his infant was sick. Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate?
(a) “You should have realized something was wrong; he’s your son.”
(b) “Did you read the booklet on newborns that was sent home with you from the hospital?”
(c) “What you are feeling is normal; next time, you’ll know what to look for.”
(d) “Babies can get sick quickly, and parents don’t always realize it.”
Answer:
(d) “Babies can get sick quickly, and parents don’t always realize it.”
Rationale:
The signs and symptoms of sepsis in a neonate, such as changes in appearance and behavior, are almost imperceptible. Often, the parents’ only problem is that the neonate does not look “right.” Fever and localized response, which are clues to infections in older children, are often absent in the neonate.
Telling the father that he should have realized something was wrong is condescending and serves only to further the father’s guilt feelings. Asking the father whether he read the booklet from the hospital implies that the father is at fault. One experience would not necessarily ensure that the father would be able to detect sepsis another time.
Question 97.
A mother brings a 15monthold child to the wellbaby clinic. She states the child has been taking approximately 18 to 20 oz (540 to 600 mL) of whole milk per day from a bottle with meals and at bedtime. The nurse should suggest that she begin weaning the child from the bottle to avoid risking:
(a) malnutrition.
(b) anemia.
(c) dental caries.
(d) malocclusion.
Answer:
(c) dental caries.
Rationale:
Nursing bottle caries occur when a child is routinely given a bottle of milk or juice at nap and bedtime. When teeth become coated in sugar before sleep, the lack of activity in the child’s mouth for several hours during sleep allows the sugar to convert to acid, leading to decay. A child drinking 18 to 20 oz of whole milk in a day should not be malnourished, although she may lack essential vitamins and iron.
Anemia may occur if she is only drinking milk because it contains no iron; however, the mother indicates she is eating meals. Regardless, children of this age should be taking no more than 16 oz of milk per day, and most children at this age should be drinking from a cup. The mother should be instructed to wean the child to a cup one feeding at a time until the child is completely weaned to a cup for all feedings. The last bottle-feeding to be replaced is usually the night bottle. Malocclusion of the teeth does not occur at 15 months. If the child were to continue to suck on a bottle until age 4 years or later, then malocclusion may occur.
Question 98.
The registered nurse (RN) is teamed with a licensed practical/vocational nurse (LPN/VN) in caring for a group of cardiac clients on a pediatric unit. Which action by the LPN/VN indicates the nurse should intervene immediately?
(a) The LPN/VN assists a child to the bathroom 2 hours after a cardiac catheterization.
(b) The LPN/VN places an infant having a cyanotic episode in a kneechest position.
(c) The LPN/VN checks a child’s apical heart rate prior to administering digoxin.
(d) The LPN/VN brings breakfast to a child who is scheduled for an electrocardiogram.
Answer:
(a) The LPN/VN assists a child to the bathroom 2 hours after a cardiac catheterization.
Rationale:
Because the femoral artery is usually used as the access site during a cardiac catheterization, children are required to remain on bed rest (with the head only slightly elevated) for several hours after the procedure to avoid arterial bleeding at the site. A knee-chest position is the correct position for an infant during a cyanotic episode as it will create peripheral resistance to the extremities, shunting blood to the heart.
The apical heart rate is assessed prior to administering this medication; administration can be performed by an experienced LPN/VN S3, although medication is checked with the RN QJ prior to administration. Because echocardiography is noninvasive, there is no need to withhold meals before this procedure.
Question 99.
A client is taking vancomycin. The nurse should report which possible side effect to the health care provider?
(a) vertigo
(b) tinnitus
(c) muscle stiffness
(d) ataxia
Answer:
(b) tinnitus
Rationale:
The client should report tinnitus because vancomycin can affect the acoustic branch of the eighth cranial nerve. Vancomycin does not affect the vestibular branch of the acoustic nerve; vertigo and ataxia would occur if the vestibular branch were involved. Muscle stiffness is not associated with vancomycin.
Question 100.
The nurse hears a pregnant client yell, "Oh my! The baby is coming!” After placing the client in a supine position and trying to maintain some privacy, the nurse sees that the neonate’s head is being born. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Suction the mouth with two fingertips.
(b) Check for presence of a cord around the neck.
(c) Tell the client to bear down with force.
(d) Advise the mother that help is on the way.
Answer:
(b) Check for presence of a cord around the neck.
Rationale:
In an emergency in which the neonate’s head is already being born, the first action by the nurse should be to check for the presence of a cord around the neonate’s neck. If the cord is present, the nurse should gently remove it from around the neck. The mother should be told to breathe gently and avoid forceful bearing-down efforts, which could lead to lacerations.
Although blood and bodily fluid precautions are always present in client care, this is an emergency. If possible, the nurse should put on gloves. Suctioning the mouth can be done after the nurse has checked that the cord is not around the neonate’s neck. Telling the mother that help is on the way is not reassuring because emergency medical technicians may take some time to arrive. Birth is imminent because the neonate’s head is emerging.
Question 101.
The nurse cares for an infant following the surgical repair of a cleft lip. What does the nurse determine is the priority goal for this client?
(a) Manage pain.
(b) Prevent infection.
(c) Increase mobility.
(d) Develop parenting skills.
Answer:
(b) Prevent infection.
Rationale:
After surgery, the most important nursing goal is to prevent infection. Surgery involves an incision, which places the infant at risk for infection. The infant with this type of procedure does have discomfort, which can be relieved with acetaminophen, and managing pain is important but not the priority.
The infant may be in arm restraints or have the cuff of the sleeve pinned to the diaper or pants. It is important that the infant not touch the incision line or disrupt the sutures, but the infant is not at risk for problems related to immobility. There is no indication that the parents need to improve their skills, but the nurse can support the family as they would be reacting normally with a first reaction of shock.
Question 102.
A client with heart failure is given a prescription for torsemide. Two days after the drug therapy is started, which sign indicates the drug is having the intended outcome? The client:
(a) has an improved appetite and is eating better.
(b) weighs 7 lb (3 kg) less than the client did 2 days ago.
(c) is less thirsty than before the drug therapy.
(d) has clearer urine since starting torsemide.
Answer:
(b) weighs 7 lb (3 kg) less than the client did 2 days ago.
Rationale:
The primary reason to give a diuretic to a client with heart failure is to promote sodium and water excretion through the kidneys. As a result, the excessive body water that tends to accumulate in a client with heart failure is eliminated, which causes the client to lose weight. Monitoring the client’s weight daily helps evaluate the effectiveness of diuretic therapy. Clients should be advised to weigh themselves daily. An increased appetite or decreased thirst does not establish the effectiveness of the diuretic therapy, nor does having clearer urine after starting torsemide.
Question 103.
Which technique is correct when the nurse is inserting a rectal suppository for an adult client?
(a) Insert the suppository while the client bears down.
(b) Place the client in a supine position.
(c) Position the suppository along the rectal wall.
(d) Insert the suppository 2 inches (8 to 10 cm) into the rectum.
Answer:
(c) Position the suppository along the rectal wall.
Rationale:
The client should be placed in a side-lying position and encouraged to take a deep breath during the insertion of the suppository. Placing the suppository along the rectal wall promotes absorption of the medication and helps avoid placing it into a stool mass. The nurse should insert the suppository 3 to 4 inches into the rectum of an adult client.
Question 104.
When caring for the client with hepatitis B, which situation would expose the nurse to the virus?
(a) contact with fecal material
(b) a blood splash into the nurse’s eyes
(c) touching the client’s arm with ungloved hands while taking a blood pressure
(d) disposing of syringes and needles without recapping
Answer:
(b) a blood splash into the nurse’s eyes
Rationale:
Hepatitis B virus is spread through contact with blood, body fluids contaminated with blood, and such body fluids as cerebrospinal, pleural, peritoneal, and synovial fluids; semen; and vaginal secretions. The risk of transmission of hepatitis B through feces is low. Touching the client without gloves is acceptable when there is no danger of contact with blood or body fluids. Recapping a used needle is a common source of needlestick injuries; needles should be properly disposed of uncapped.
Question 105.
A young woman is brought from the emergency department (ED) to the psychiatric unit. ED staff report that she is not answering questions and has been sitting in the same position in the wheelchair for 45 minutes. When her arm was extended to draw blood, she did not move her arm back to a natural position. The client’s brother says he found her this way yesterday and could not get her to move on her own. Which nursing interventions does the nurse prioritize for the client’s first 24 hours on the unit? Select all that apply.
(a) Ask her to describe her stressors.
(b) Monitor her body positions to prevent injury.
(c) Offer her nutritional shakes every 3 hours.
(d) Encourage her to talk about her feelings.
(e) Assist her to the bathroom every 2 hours.
(f) Protect her from intrusions by other clients.
Answer:
(b) Monitor her body positions to prevent injury.
(c) Offer her nutritional shakes every 3 hours.
(e) Assist her to the bathroom every 2 hours.
(f) Protect her from intrusions by other clients.
Rationale:
Safety and physiological needs are crucial initially for a client who is unable to meet her own needs. Identifying her stressors and feelings will be important later when she is responding to questions and her environment
Question 106.
The nurse observes a group of children in a day care center. Which child warrants further assessment?
(a) a child who is 12 months of age who has bruises on one side of the head
(b) a child who is 3 years of age with a spiral fracture of the ulna whose mother does not know how the injury occurred
(c) a child who is 4 years of age who wears the same clothes to the center every day
(d) a child who is 2 years of age who has frequent episodes of untreated conjunctivitis
Answer:
(b) a child who is 3 years of age with a spiral fracture of the ulna whose mother does not know how the injury occurred
Rationale:
Signs of child abuse include injury with a history that is inconsistent with the nature of the injury, or unusual injuries for the age of the child. A spiral fracture of a child is always investigated as potential child abuse as this injury is often due to twisting of an extremity. It is not unusual for a child who is learning to walk to have bruises. Wearing the same clothes is not an indication of abuse or neglect. The child with conjunctivitis requires health care, but having frequent episodes is not an indication of abuse or neglect.
Question 107.
A client who had a hip placement at 0900 is receiving an autologous blood transfusion that was started at 1100. At the change of shift (1500), the nurse working on the day shift reports that there is 50 mL of the unit of blood remaining to be infused. Which is a priority nursing action for the nurse working on the evening shift?
(a) Keep the blood transfusing at the same rate.
(b) Increase the rate so it will infuse by 1600.
(c) Discontinue the blood transfusion at the beginning of the shift.
(d) Maintain the current rate, and discontinue the blood transfusion at 1700.
Answer:
(c) Discontinue the blood transfusion at the beginning of the shift.
Rationale:
In most agencies, it is a policy to discard the autologous blood after 4 hours of transfusing, due to an increased risk of infection. Increasing the infusion rate could cause fluid overload. Monitoring blood transfusions is a serious nursing responsibility, and because it is the change of shift, there is increased risk of error.
Question 108.
A client undergoes a nephrectomy. In the immediate postoperative period, which nursing intervention has the highest priority?
(a) Monitor blood pressure.
(b) Encourage the use of the incentive spirometer.
(c) Assess urine output hourly.
(d) Check the flank dressing for urine drainage.
Answer:
(c) Assess urine output hourly.
Rationale:
After a nephrectomy, a specific aspect of immediate postoperative management includes monitoring urine output at least hourly. Monitoring blood pressure and encouraging the use of incentive spirometry are other important considerations, but because of the surgical disruption of the urinary system, urine output is a priority. Measurement of urine output should also include an estimation of the amount of urine drainage on the flank dressing.
Question 109.
A client is admitted with fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin, and dried, cracked lips, tongue, and mouth. The hemoglobin is 9 g/dL (90 g/L), and red blood cell count is 3.5 million cells/mm3 (3.5 x 1012/L). What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Eat foods with good sources of iron.
(b) Limit fluid intake to 1,000 mL/day.
(c) Increase the amount of carbohydrates in the diet.
(d) Eat a serving of fish with high omega 3 content two times a week.
Answer:
(a) Eat foods with good sources of iron.
Rationale:
The client is demonstrating signs of anemia and should increase the iron in the diet. Foods such as red meats, beets, and cabbage are good sources of iron. The client should not limit the fluid intake to 1,000 mL/day, but should maintain an adequate fluid intake of about 3,000 mL/day. Carbohydrates will not provide the necessary dietary intake of iron. While fish is a healthy choice, beef, lamb, and iron- rich vegetables are more important in the diet at this time.
Question 110.
When assessing a neonate 1 hour after birth, the nurse observes that the neonate exhibits slight cyanosis when quiet but becomes pink when crying. The nurse is unable to pass a catheter through the left nostril. The nurse notifies the health care provider because the neonate most likely is exhibiting signs and symptoms of what problem?
(a) esophageal reflux disorder
(b) unilateral choanal atresia
(c) respiratory distress syndrome
(d) tracheoesophageal fistula
Answer:
(b) unilateral choanal atresia
Rationale:
Infants are obligatory nose breathers except when crying. The observation that the infant has slight cyanosis when quiet but becomes pink when crying and the inability to pass a catheter through the left nostril suggest that the neonate is exhibiting symptoms of unilateral choanal atresia. With this condition, one of the nasal passages is blocked by an abnormality of the septum. Surgical intervention is necessary to open the nostril.
Typically, a neonate with esophageal reflux disorder exhibits episodes of apnea and vomiting after eating. Respiratory distress syndrome commonly occurs in preterm neonates who lack surfactant to maintain lung expansion. Common findings include sternal retractions, tachypnea, grunting respirations, nasal flaring, cyanosis, pallor, hypotonia, and bradycardia. A neonate with tracheoesophageal fistula commonly exhibits cyanosis during feedings and vomiting.
Question 111.
A client is receiving digoxin, and the pulse range is normally 70 to 76 bpm. After assessing the apical pulse for 1 minute and finding it to be 60 bpm, the nurse should do what first?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Withhold the digoxin.
(c) Administer the digoxin.
(d) Notify the charge nurse.
Answer:
(b) Withhold the digoxin.
Rationale:
The nurse’s initial response should be to withhold the digoxin. The nurse should then notify the HCP if the apical pulse is 60 bpm or lower because of the risk of digoxin toxicity. The charge nurse does not need to be notified, but the nurse needs to document the notification and follow-up in the medical record.
Question 112.
When developing a teaching plan for parents of toddlers about poisonous substances, the nurse should emphasize which safety points? Select all that apply.
(a) Toddlers should be adequately supervised at all times.
(b) All poisonous substances should be kept out of the reach of children and stored in a locked cabinet if necessary.
(c) The difference between pediatric and adult dosages of medicines is significant, and adult dosages given to children can have serious, harmful effects.
(d) Syrup of ipecac should be administered fol lowing all ingestions of poisonous substances.
(e) Following any poisoning, the parents should call the Poison Control Center for instructions for appropriate treatment.
Answer:
(a) Toddlers should be adequately supervised at all times.
(b) All poisonous substances should be kept out of the reach of children and stored in a locked cabinet if necessary.
(c) The difference between pediatric and adult dosages of medicines is significant, and adult dosages given to children can have serious, harmful effects.
(e) Following any poisoning, the parents should call the Poison Control Center for instructions for appropriate treatment.
Rationale:
Safety measures for poisonous substances include close supervision of children, safely storing toxic substances, teaching proper dosages and differences between adult and child doses, and the proper way to contact the Poison Control Center for instructions. Poison Control should be notified as soon as the poisoning has occurred and airway and circulation have been assessed.
Poison Control will direct any further treatment. Syrup of ipecac is rarely used today in the treatment of ingested substances due to the potential for aspiration. It is contraindicated in cases of arsenic poisoning, seizures, and the ingestion of petroleum or corrosive substances.
Question 113.
A client on a psychiatric care unit has muscle spasms in the neck and stiffness in other muscles, and the eyes are rolling upward. The client had two PRN doses of haloperidol in the last 6 hours. Of the drugs that have been prescribed for the client as needed (see chart), which drug should the nurse administer?
(a) lorazepam
(b) amantadine
(c) diphenhydramine
(d) benztropine
Answer:
(d) benztropine
Rationale:
Dystonic adverse effects of haloperi- dol, especially oculogyric crises, are painful and frightening. IM benztropine is the fastest and most effective drug for managing dystonia. Lorazepam is an antianxiety medication and is not effective for treatment of dystonia. Although amantadine and diphenhydramine can be used for extrapyramidal symptoms, oral medications do not work as quickly, and amantadine may worsen psychotic symptoms.
Question 114.
After birth of a male neonate at 38 weeks’ gestation, the nurse dries the neonate and places him skin to skin on his mother’s chest. The nurse performs this action based on the understanding that one neonatal response to cold stress involves which factor?
(a) metabolism of brown adipose tissue
(b) decreased utilization of glycogen stores
(c) decreased utilization of calorie stores
(d) increased shivering to keep warm
Answer:
(a) metabolism of brown adipose tissue
Rationale:
Neonates burn brown adipose tissue (fat) as a response to cold stress. In addition, there is increased utilization of glycogen and calorie stores. Hypoglycemia may result from becoming stressed by a cold environment. Neonates do not have the ability to shiver.
Question 115.
Twenty-four hours after an appendectomy, a 16-year-old adolescent reports no pain when asked but is frowning and has the legs drawn to the fetal position. What should the nurse do?
(a) Administer pain medication.
(b) Ask the adolescent what is troubling him.
(c) Discuss the adolescent’s behavior with the parents.
(d) Offer a distracting activity such as a video game.
Answer:
(a) Administer pain medication.
Rationale:
While the adolescent is denying pain, he is displaying objective signs of pain. Adolescents may display stoic behavior minimize loss of control or to conform with cultural expectations. The nurse should administer an analgesic and assure the client that taking medication will speed the recovery process. The nurse must also reassess the client after administering the pain medication and document the response.
The reassessment is typically done 30 minutes after a parenteral analgesic and an hour after an oral analgesic. Asking the client about what is troubling him is unlikely to provide the nurse with additional information. The adolescent’s behavior is consistent with postoperative pain. If the parents are stoic, discussing the adolescent’s behavior may not be productive. At this stage of treatment, distractions can be used in conjunction with medication, but should not be substituted for them.
Question 116.
When developing the teaching plan for a pri-miparous client who is bottle-feeding her term neonate for the first feeding, what information should the nurse include?
(a) Fill the entire nipple of the bottle with formula.
(b) All term babies have well-developed sucking skills.
(c) Bubble the baby after 2 oz (60 mL) of formula have been taken.
(d) Propping of the bottle results in too much air being taken in by the baby.
Answer:
(a) Fill the entire nipple of the bottle with formula.
Rationale:
Formula should fill the entire nipple of the bottle while the baby is sucking. This decreases the amount of air taken in by the baby; taking in too much air can lead to regurgitation. Not all babies at term are born with well-developed sucking skills. Some neonates are sleepy and do not suck well.
For the first feeding, the baby should be bubbled after taking one-fourth to one-half ounce of formula and then again when the infant has finished the feeding. Bottle propping can lead to aspiration, decreased infant bonding, and aspiration of formula. However, it is not associated with the intake of too much air.
Question 117.
Which topic would be most important to include when teaching the parents how to promote overall toddler development?
(a) Language is the most important achievement.
(b) Discipline is critical to appropriate development.
(c) Safety is a priority concern for this age-group.
(d) Eating habits that follow into adulthood begin now.
Answer:
(c) Safety is a priority concern for this age-group.
Rationale:
Because of toddlers’ high energy and poor impulse control, safety is a priority concern for this age group. Language is important in toddler development, but it is not the most important at this time. While parents should set clear guidelines for behavior, the priority for toddlers is ensuring safety. Diet habits should be developed at this time, but the most important subject to teach parents of toddlers is safety.
Question 118.
A client has back pain 10 minutes after a unit of packed red blood cells (RBCs) was started. The client’s pulse, blood pressure, and respirations are stable, and similar to vital signs obtained before infusing the RBCs. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Turn off the infusion of the packed RBCs.
(b) Flush the Y-tubing with normal saline to clear the line.
(c) Send the remaining blood to lab.
(d) Prepare for cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
(e) Obtain a urine specimen to send to the laboratory.
Answer:
(a) Turn off the infusion of the packed RBCs.
(c) Send the remaining blood to lab.
(d) Prepare for cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
(e) Obtain a urine specimen to send to the laboratory.
Rationale:
When a client begins to have back pain with administration of blood, the nurse should suspect a hemolytic reaction, and the blood transfusion should be stopped immediately. Any remaining blood and the tubing should be sent to the lab. The nurse should prepare for a reaction from mild to severe, including the need for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, because even a small amount of mismatched blood can lead to a major reaction.
The nurse should obtain a urine specimen to send to the laboratory to check for hemoglobin because RBC hemolysis filters through the kidneys from the reaction. The nurse should stop the IV line with the Y-tubing for the blood and not flush the line with saline so that the client does not receive any more blood. The tubing should be changed so that a tube without blood can be used for infusions.
Question 119.
A primiparous client at 4 hours after a vaginal birth and manual removal of the placenta voids for the first time. The nurse palpates the fundus, noting it to be 1 cm above the umbilicus, slightly firm, and deviated to the left side, and notes painless dark red bleed mixed with clots. The nurse notifies the health care provider based on the interpretation that the assessment indicates which problem?
(a) perineal lacerations
(b) retained placental fragments
(c) cervical lacerations
(d) urine retention
Answer:
(b) retained placental fragments
Rationale:
At 4 hours postpartum, the fundus should be midline and at the level of the umbilicus. Whenever the placenta is manually removed after birth, there is a possibility that all of the placenta has not been removed. Sometimes, small pieces of the placenta are retained, a common cause of late postpartum hemorrhage. The client is exhibiting signs and symptoms associated with retained placental fragments. The client will continue to bleed until the fragments are expelled.
Perineal and cervical lacerations are characterized by bright red bleeding and a firmly contracted fundus at the level that is expected. Urine retention is characterized by a full bladder, which can be observed by a bulge or fullness just above the symphysis pubis. Also, the client’s fundus would be deviated to one side and boggy to the touch.
Question 120.
The nurse performs a gestational age assessment on male neonate born vaginally at 37 weeks’ gestation according to the mother’s estimated date of delivery. Which physical finding would the nurse expect to find at 37 weeks’ gestation?
(a) an anterior transverse crease on the soles
(b) extensive rugae on the scrotum
(c) some cartilage in the earlobes
(d) coarse and silky scalp hair
Answer:
(c) some cartilage in the earlobes
Rationale:
A neonate bom at 37 weeks’ gestation will have some cartilage in the earlobes, fine and fuzzy hair, scant to moderate rugae in the scrotum, and a breast nodule diameter of 4 mm. Neonates born before 36 weeks’ gestation will have only an anterior transverse crease on the soles of the feet. Extensive rugae on the scrotum are a typical finding in neonates born at 39 weeks’ gestation or later. Coarse and silky scalp hair typically is found in neonates that are born at 39 weeks or later.
Question 121.
Two family members are visiting their father who is experiencing acute delirium. They are upset that their father is so disoriented. “He knows who we are, but that’s about it. We don’t know what to say to him.” What should the nurse tell the family? Select all that apply.
(a) “Answer his questions simply, honestly, slowly, and clearly.”
(b) “Correct him when he’s hearing and seeing things that are not there.”
(c) “Occasionally remind him of the time, day, and place when he doesn't remember.”
(d) “Include him in your conversation, instead of talking about him while he’s present.”
(e) “Raise your voice a bit so you’re sure he hears you.”
Answer:
(a) “Answer his questions simply, honestly, slowly, and clearly.”
(c) “Occasionally remind him of the time, day, and place when he doesn't remember.”
(d) “Include him in your conversation, instead of talking about him while he’s present.”
Rationale:
Clear communication is crucial for a client with delirium. The family must include the client in all conversations and keep him oriented to time and place. It is inappropriate to argue with a client’s hallucinations because they are real to the client. Speaking more loudly will not help this client hear more distinctly and may increase the client’s confusion.
Question 122.
A 26-year-old is being treated for delirium due to acute alcohol intoxication. The client is restless, does not want to stay seated, and has a staggering gait. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Place the client in a chair with a waist restraint.
(b) Provide one-to-one supervision of the client until detoxification treatment can begin.
(c) Ask the client to sit in a chair next to the nurses’ station.
(d) Decrease stimuli by putting the client in bed with the room door closed.
Answer:
(b) Provide one-to-one supervision of the client until detoxification treatment can begin.
Rationale:
One-to-one supervision provides safety until appropriate detoxification can be given. Restraints are the last intervention after less restrictive alternatives have been tried. It is unlikely that the client can cooperate with staying in a chair. Putting the client in bed in his or her room puts the client at risk for falling, and a closed door prevents close observation.
Question 123.
The nurse is monitoring a client receiving a blood transfusion when the client develops a cough with shortness of breath. The client also has a headache and a racing heart. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Slow the infusion rate.
(b) Replace the blood with saline.
(c) Administer an antihistamine.
(d) Place the client flat with the feet elevated.
Answer:
(a) Slow the infusion rate.
Rationale:
The nurse should recognize that the client’s clinical manifestations indicate fluid overload and decrease the infusion rate so the client’s circulation can handle the extra fluid. Antihistamines are used for allergic reactions. The nurse should place the client in an upright position with the feet down so that blood or fluid volume can drain to the lower extremities and relieve some of the extra fluid load on the heart. The nurse does not need to replace the blood with another type of fluid because the client’s response is not a blood transfusion reaction.
Question 124.
The nurse should seek clarification about which prescription?
(a) Give 5,000 units bolus dose of heparin IV push.
(b) Give 200,000 units heparin by IV drip, and infuse over 24 hours.
(c) Give 40,000 units of heparin by IV drip, and infuse over 24 hours.
(d) Give 5,000 units of heparin IV piggyback every 4 to 6 hours.
Answer:
(b) Give 200,000 units heparin by IV drip, and infuse over 24 hours.
Rationale:
200,000 units of heparin is too large of a dose. Heparin may be given in a 5,000-unit bolus dose IV; then 20,000 to 40,000 units infused over 24 hours with a dose adjusted to maintain desired APTT, or 5,000 to 10,000 units IV piggyback every 4 to 6 hours.
Question 125.
A nurse is analyzing a client’s intake and output. The client has a temperature of 102°F (38.9°C) and is receiving 2,400 mL of IV fluids per 24 hours because the client is to have nothing by mouth. What information should the nurse obtain before planning nursing actions?
(a) the client’s body mass index
(b) the amount of insensible fluid loss through the lungs and skin
(c) when the client last ate
(d) the intravenous fluid intake during the last 8 hours
Answer:
(b) the amount of insensible fluid loss through the lungs and skin
Rationale:
Insensible fluid loss is invisible vaporization from the lungs and skin and assists in regulating body temperature. The amount of water loss is increased by accelerated body metabolism, which occurs with increased body temperature. The client’s body mass index does not directly influence calculating fluid therapy.
Question 126.
Two toddlers are arguing over a toy in the playroom. What should the nurse say to the children?
(a) “If you can’t play together, I’ll have to put you back in your rooms.”
(b) “Give the toy to me. Now neither of you will have it.”
(c) "Let me see if I can get both of you a similar toy.”
(d) “Let one of you play with it for a while, and then give it to the other.”
Answer:
(c) "Let me see if I can get both of you a similar toy.”
Rationale:
A toddler has not developed the concept of sharing, so two similar toys must be provided to prevent disagreements. Playing together in harmony is not the developmental level of a toddler. They play side by side, but not together. Threatening to put the children in their rooms does not solve the problem, nor does taking away the toy.
Question 127.
A client has been prescribed digoxin. Which symptom should the nurse tell the client to report as a potential indication of digoxin toxicity?
(a) urticaria
(b) shortness of breath
(c) visual disturbances
(d) hypertension
Answer:
(c) visual disturbances
Rationale:
Visual disturbances are a symptom of digoxin toxicity. These disturbances can include double, blurred, or yellow vision. Cardiovascular manifestations of digoxin toxicity include bradycardia hypotension, other dysrhythmias, and pulse deficit. Gastrointestinal symptoms include anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
Question 128.
A 9-month-old infant whose parents have emigrated to the country presents in the clinic with severe dehydration from vomiting. The infant was seen in the clinic just 3 days ago for a well-child visit, but now the family seems very distrustful of the health care team. What should the nurse ask the parents?
(a) “Have you been speaking with a healer?”
(b) “Did anything concern you about your last visit?”
(c) “Has immigration been causing you problems?”
(d) “Are you afraid your baby will be taken from you?”
Answer:
(b) “Did anything concern you about your last visit?”
Rationale:
In order to reestablish trust, the nurse should first try to determine if something happened at the last visit that was upsetting for the family. At a well-child visit, the health care provider (HCP) Q would have palpated the fontanelle. If it is now sunken from dehydration, the parents may blame the provider for the illness. The family may have talked with a traditional healer, but following this line of questioning first may appear that the nurse considers the healer as an adversary.
Asking about immigration makes a stereotypical assumption. Asking if the family is afraid the baby will be taken from them may be suggesting something the family has never considered and may cause unnecessary distress.
Question 129.
A 4-year-old child continues to come to the nurses’ station after being told children are not allowed there. What behavior is the child exhibiting?
(a) attention-seeking behavior
(b) aggressive behavior
(c) resistive behavior
(d) exaggerated stress behavior
Answer:
(a) attention-seeking behavior
Rationale:
The child wants attention from the nurse, even if the behavior is met by a negative response. Aggression, resistance against authority, and exaggerated stress are behaviors that can be associated with a 4-year-old. However, coming to the nurses’ station after being told not to do so is not an example of these behaviors.
Question 130.
A 5-month-old infant is brought to the emergency department with vomiting and diarrhea, which the parent states started 3 days ago. The nurse should conduct a focused assessment for which signs and symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) decreased or absent tearing
(b) dry mucous membranes
(c) sunken fontanelle
(d) clear, pale yellow urine
(e) bounding pulse
Answer:
(a) decreased or absent tearing
(b) dry mucous membranes
(c) sunken fontanelle
Rationale:
Clinical manifestations of dehydration include decreased tearing; dry mucous membranes; sunken fontanelles; weight loss; behavioral changes; scanty, concentrated urine; and a thready, fast pulse. Clear, pale yellow urine would indicate adequate hydration. A bounding pulse would indicate fluid volume excess.
Question 131.
A client’s burn wounds are being cleaned twice a day in a hydrotherapy tub. Which intervention should be included in the plan of care before a hydrotherapy treatment is initiated?
(a) Limit food and fluids 45 minutes before therapy to prevent nausea and vomiting.
(b) Increase the IV flow rate to offset fluids lost through the therapy.
(c) Apply a topical antibiotic cream to burns to prevent infection.
(d) Administer pain medication 30 minutes before therapy to help manage pain.
Answer:
(d) Administer pain medication 30 minutes before therapy to help manage pain.
Rationale:
Hydrotherapy wound cleaning is very painful for the client. The client should be medicated for pain about 30 minutes before the treatment in anticipation of the increased pain the client will experience. Wounds are debrided, but excessive fluids are not lost during the hydrotherapy session.
However, electrolyte loss can occur from open wounds during immersion, so the sessions should be limited to 20 to 30 minutes. There is no need to limit food or fluids 45 minutes before hydrotherapy unless it is an individualized need for a given client. Topical antibiotics are applied after hydrotherapy.
Question 132.
A neonate born to a primiparous client at,36 weeks’ gestation in a small, rural hospital is Q be transferred by ambulance to a level III nursery. Tp prepare the parents for the transfer, what should the nurse include in the plan of care?
(a) Instruct the parents that the neonate is in critical condition.
(b) Obtain the mother’s consent for the neonate’s transfer.
(c) Allow the parents to touch the neonate before transfer.
(d) Ask the father if he desires to ride in the ambulance during the transfer.
Answer:
(c) Allow the parents to touch the neonate before transfer.
Rationale:
When a neonate is being transferred to a neonatal care center (level III nursery), the parents should be allowed to see and touch the neonate, if possible, before transfer. The parents should be given the location and telephone number of the unit to which the neonate is being transferred. This helps to keep the parents informed. The parents are already aware of the neonate’s condition and should recognize that it is critical if the neonate is being transferred to a neonatal care center. The parents have signed consent Q for treatment on admission, and in most states another consent is not necessary.
Asking whether the father would like to ride in the ambulance with the neonate during the transfer is inappropriate. Most ambulances or transferring vehicles (e.g., helicopters, airplanes) do not allow family members to accompany the ill client. Space in the motor vehicle, helicopter, or plane is limited. In addition, most transferring vehicles do not have insurance to cover family members should an accident occur during transfer.
Question 133.
A client gives birth to a neonate at 30 weaks’ gestation. The neonate is stable on minimal ventiila- tor settings. The client’s previous infant, who wa!s born at 24 weeks gestation, did not survive. The family is Roman Catholic and requests that neonate be baptized as soon as possible. What response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “What would you like me to do to help arrange the baptism?”
(b) “Are you requesting the baptism because you are concerned that your infant might die?”
(c) “We have a unit chaplain who rounds daily and can perform the baptism.”
(d) “Your baby is much older and much more stable than the baby you lost.”
Answer:
(a) “What would you like me to do to help arrange the baptism?”
Rationale:
Patient-centered care involves honoring client preferences. It is common practice to baptize infants who are at risk of death in the Roman Catholic faith. While a 30-week gestation infant on minimal ventilator settings would be expected to survive, the family has had real experiences with neonatal death, and spiritual practices can provide comfort. The nurse should ask the family about their preferences and try to honor them.
The family may indeed be requesting the baptism because they are fearful their infant might die. The nurse can reassure the family that the infant is doing well but must also respect the client’s spiritual preferences. After the family shares their preferences, the nurse can offer the local chaplain as a resource.
Question 134.
A client with bipolar disorder, manic phase, shows little interest in eating. What should the nurse do to help the client meet recommended daily allowances of nutrients?
(a) Give the client half of a meat and cheese sandwich to carry with him.
(b) Inform the client that snacks are available only if he eats properly at mealtime.
(c) Tell the client to sit alone at mealtime so that he will not be distracted by others.
(d) Teach the client about proper nutrition.
Answer:
(a) Give the client half of a meat and cheese sandwich to carry with him.
Rationale:
The best nursing intervention is giving the client finger foods high in protein and calories that he can eat while he paces or walks. Informing the client that snacks are available if he eats properly at mealtime is inappropriate because the client is too busy and distracted to sit and eat an entire meal.
Telling the client to sit alone at mealtime to decrease distractions will not help him because the client is in a manic state, is easily distracted, and needs to move. Teaching the client about proper nutrition ignores his need for adequate intake. The client would be unable to focus on the nurse’s teaching.
Question 135.
A client has bursitis in the subacromial bursa. A nurse determines that the client understands teaching when the client makes which statement?
(a) “I’ll apply moist heat to my shoulder for 20 minutes three times each day.”
(b) “I’ll lift 30-lb (13.5-kg) weights at least three times each day.”
(c) “I’ll place an ice pack on my shoulder for 20 minutes three times each day.”
(d) “I’ll perform 360-degree circles with my arms extended at least three times daily.”
Answer:
(a) “I’ll apply moist heat to my shoulder for 20 minutes three times each day.”
Rationale:
Moist heat is a nonpharnracologic pain management strategy that may alleviate pain and reduce the dose of analgesic, if required. Heat dilates blood vessels and decreases inflammation. Lifting and circular exercises will aggravate the already inflamed joint. Cold constricts blood vessels.
Question 136.
A client has just undergone a lumbar puncture (LP). Which finding should the nurse immediately report to the health care provider (HCP)?
(a) The client’s oral intake was 1,200 mL in the past 8 hours.
(b) The client required analgesia for headache.
(c) A moderate amount of serous fluid was noted on the lumbar dressing.
(d) The client is concerned about the test results.
Answer:
(c) A moderate amount of serous fluid was noted on the lumbar dressing.
Rationale:
For an LP, a needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space to obtain a specimen of spinal fluid for diagnostic testing. Fluid on the lumbar dressing indicates cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage and must be reported to the health care provider (HCP) immediately.
The client should be encouraged to drink fluids after an LP to facilitate production of CSF. It is normal to have a mild headache due to the removal of CSF samples for laboratory analysis. Although the concerns of the client should be discussed with the HCP at some point, the CSF leakage is a priority and should be reported immediately.
Question 137.
The nurse is reviewing the lab report below for a client in hospice care with breast cancer and brain metastasis. According to the information in the chart, what should the nurse do next
|
Test |
Result |
|
Potassium |
4.0 mEqfL (mmol/L) |
|
Sodium |
142 mEqJL (mmol/L) |
|
Chloride |
100 mEq/L (mmol/L) |
|
Calcium |
12.4 mg/dL (3.1 mmoIIL) |
(a) Document these results on the medical record.
(b) Report the elevated potassium level immediately.
(c) Report the elevated calcium level immediately.
(d) Refrain from reporting the results because the client is in hospice care.
Answer:
(c) Report the elevated calcium level immediately.
Rationale:
The normal calcium level is 9.0 to 10.5 nrg/dL (2.25 to 2.63 mnrol/L). Hypercalcemia is commonly seen with malignant disease and nretastases. The other laboratory values are normal. Hypercalcemia can be treated with fluids, furose- mide, or administration of calcitonin. Failure to treat hypercalcemia can cause muscle weakness, changes in level of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and dehydration. Although the client is on hospice care, she will still need palliative treatment. Comfort and risk reduction are components of hospice care.
Question 138.
A nurse is caring for a primigravid client at 40 weeks’ gestation in active labor. Assessments include the following: cervix 5 cm dilated; 90% effaced; station 0; cephalic presentation and FHR baseline 135 bpm, decreases to 125 bpm shortly after onset of 5 uterine contractions and returns to baseline before the uterine contraction ends. Based on this assessment, what action should the nurse take first?
(a) Position the woman on her left side and administer oxygen via face mask.
(b) Document findings on the woman’s medical record and continue to monitor labor progress.
(c) Perform a vaginal exam to rule out umbilicalcord prolapse.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP) immediately and prepare for emergency cesarean birth.
Answer:
(b) Document findings on the woman’s medical record and continue to monitor labor progress.
Rationale:
The nurse would document these findings as “early” decelerations. Early decelerations are thought to be the result of vagal nerve stimulation caused by compression of the fetal head during labor. They are considered normal physiologic response to labor and do not require any intervention.
Early decelerations do not require position change or oxygen, as they are not a sign of fetal distress. Variable decelerations are thought to be due to umbilical cord compression. Early decelerations are not emergent and do not require immediate reporting to the health care provider (HCP) 2 or preparing for cesarean birth.
Question 139.
A child with a cardiac defect assumes a squatting position. The nurse should determine that the position is effective for the child by noting which finding?
(a) less energy required to play with toys on the floor
(b) less dyspnea
(c) relief of abdominal pressure
(d) improved muscle tone
Answer:
(b) less dyspnea
Rationale:
A child with a cardiac defect finds that squatting decreases venous return and workload to the heart and increases comfort and blood flow to the lungs. Squatting traps blood in the lower extremities so less blood is returned to the right atrium. Squatting does not make it easier for the child to play with toys. Squatting does not relieve abdominal pressure; it may even increase it slightly. Squatting has no effect on muscle tone. When done by a child with a cardiac defect, it is not meant as an exercise but is a compensatory process used to reduce dyspnea.
Question 140.
A client was brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident and has phrenic nerve involvement. The nurse should assess the client for which nursing problem?
(a) alteration in level of consciousness
(b) altered cardiac functioning
(c) ineffective breathing pattern
(d) alteration in urinary elimination
Answer:
(c) ineffective breathing pattern
Rationale:
The diaphragm is the major muscle of respiration; it is made up of two hemidiaphragms, each innervated by the right and left phrenic nerves. Injury to the phrenic nerve results in hemidia- phragm paralysis on the side of the injury and an ineffective breathing pattern. Consciousness, cardiac function, and urinary elimination are not affected by the phrenic nerve.
Question 141.
A primigravid client is seen for her first visit in the antenatal clinic and tells the nurse that her brother was born with cystic fibrosis (CF). When teaching the client about this disorder, the nurse should include which information? Select all that apply.
(a) Persons of Asian descent have the highest inheritance rates.
(b) To inherit CF, each parent must carry a recessive trait for the disease.
(c) If both parents carry the trait, each offspring has a 25% chance of inheriting the disease.
(d) Fetal testing can occur by checking the shape of the red blood cells.
(e) Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) can identify prenatally if their child carries the trait or has the disease.
Answer:
(b) To inherit CF, each parent must carry a recessive trait for the disease.
(c) If both parents carry the trait, each offspring has a 25% chance of inheriting the disease.
(e) Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) can identify prenatally if their child carries the trait or has the disease.
Rationale:
Cystic fibrosis is most common in those of the Caucasian race. As an autosomal recessive disease, for an infant to be affected, each parent must carry a recessive trait. If both parents carry the trait, each offspring has a 25% chance of inheriting the disease, a 50% chance of being a carrier, and a 25% chance of being unaffected. The shape of red blood cells is altered with sickle cell disease rather than CF. CVS testing can identify whether a fetus is or is not affected.
Question 142.
A client with a peritonsillar abscess has been hospitalized. Upon assessment, the nurse determines the following: a temperature of 103°F (39.4°C), body chills, and leukocytosis. The client begins to have difficulty breathing. In what order from first to last should the nurse perform the actions? All options must be used.
(a) CalI the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Open the airway.
(c) Start an IV access site.
(d) Explain the situation to the family.
Answer:
(b) Open the airway.
(c) Start an IV access site.
(d) Explain the situation to the family.
Rationale:
An open airway is essential to survival. The nurse should first ensure an open airway. Next, the nurse should start an IV and then notify the HCP L2. Finally, the nurse should inform the family of the situation and, if appropriate, allow them to remain with the client.
Question 143.
The nurse is teaching a client who has deep vein thrombosis. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “Report such signs as leg swelling, discomfort, redness, or warmth.”
(b) “Sit with your legs lower than the rest of your body.”
(c) “Walk at least every other day.”
(d) “Limit your fluids to 1 L each day.”
Answer:
(a) “Report such signs as leg swelling, discomfort, redness, or warmth.”
Rationale:
Prevention of another pulmonary embolus is important; the nurse should teach the client to observe for signs of clot formation to prevent a potentially fatal episode and maintain cardiopulmonary integrity and adequate ventilation and perfusion. Elevation of the lower extremities, not lowering them, promotes venous return to the heart. Ambulation must be done several times each day. Limiting fluid intake increases blood viscosity, promoting clot formation.
Question 144.
A multiparous client and her neonate, who has been cared for in the intensive care nursery for the past 3 days because of being small for gestational age, are to be discharged. Before their release, the mother tells the nurse, “I’ve been living in my car for the past 2 weeks.” What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the director of the birthing unit.
(b) Contact the hospital’s social worker.
(c) Contact the client’s health care provider (HCP).
(d) Notify the client’s family members.
Answer:
(b) Contact the hospital’s social worker.
Rationale:
When a client is being released from the hospital with her neonate and the nurse learns that the client is homeless, the nurse should contact the hospital’s or unit’s social worker. Social workers have access to resources to assist the client to find temporary shelter in emergencies. The director of the birthing unit does not need to be notified. The director’s responsibilities are primarily administrative.
The client’s HCP 2 can be notified once the social worker has offered assistance to the client. The HCP may cancel the release of the neonate until temporary housing is located. Notifying the client’s family is inappropriate. The client may not have any immediate family members, or there may be some stress between the client and family.
Question 145.
A client who is receiving a blood transfusion suddenly experiences chills and a temperature of 101°F (38.3°C). The client also has a headache and appears flushed. In what order from first to last should the nurse perform the actions? All options must be used.
(a) Obtain a blood culture from the client.
(b) Send the blood bag and administration set to the blood bank.
(c) Stop the blood infusion.
(d) Infuse normal saline to keep the vein open.
Answer:
(c) Stop the blood infusion.
(d) Infuse normal saline to keep the vein open.
(a) Obtain a blood culture from the client.
(b) Send the blood bag and administration set to the blood bank.
Rationale:
The client is experiencing a septic reaction to the blood transfusion. The nurse’s first action is to stop the infusion and notify the health care provider (HCP) Q and blood bank. The nurse then uses an infusion of normal saline to keep the vein open. Next, the nurse obtains a sample of the client’s blood for a blood culture, and last, the nurse sends the blood bag and the administration set to the blood bank for culture.
Question 146.
The fetus of a multigravid client at 38 weeks’ gestation is determined to be in a frank breech presentation. The nurse describes this presentation to the client as which fetal part coming in contact with the cervix?
(a) buttocks
(b) head
(c) both feet
(d) shoulder
Answer:
(a) buttocks
Rationale:
In a frank breech, the buttocks alone are at the cervix, while the knees are extended to rest on the chest. In a cephalic presentation, the head is the fetal body part first coming in contact with the cervix. Both feet at the cervix is termed double footling breech. In a shoulder presentation, one of the shoulders (actually the acromion process) presents to the cervix. Typically, the fetus is lying horizontally (transverse lie).
Question 147.
The nurse collects a urine specimen from a client for a culture and sensitivity analysis. What should the nurse do to preserve the specimen?
(a) Send it to the laboratory immediately.
(b) Place it on counter for the next specimen pickup.
(c) Assign an unlicensed assistive personnel to take it to the laboratory as soon as possible.
(d) Store it in the refrigerator until it can be sent to the laboratory.
Answer:
(a) Send it to the laboratory immediately.
Rationale:
A specimen for culture and sensitivity should be sent to the laboratory promptly so that a smear can be taken before organisms start to grow in the specimen.
Question 148.
A client in surgery has an endotracheal tube (ET) in place. The nurse should call a time-out if which requirements are not in place? Select all that apply.
(a) an identification band
(b) postoperative pain medication
(c) an IV line
(d) oxygen administration
(e) an anesthetist/anesthesiologist
Answer:
(a) an identification band
(c) an IV line
(d) oxygen administration
(e) an anesthetist/anesthesiologist
Rationale:
The nurse is responsible for the client’s safety in the operating room. The nurse should call a time-out yj if the client is not properly identified with an identification band. In addition, an IV line and oxygen should always be established when an ET tube is placed.
This practice applies whenever a client’s airway is compromised enough for intubation to occur, not only in the operating room environment. An anesthetist or anesthesiologist should be present during surgery to manage the airway. Postoperative pain medication is administered in the recovery room.
Question 149.
A multiparous client at 16 weeks’ gestation is diagnosed as having a fetus with probable anen- cephaly. The client has decided to continue the pregnancy based on religious beliefs and donate the neonatal organs after the death of the neonate. Which action by the nurse would be most appropriate?
(a) Explore his or her own feelings about the issues of anencephaly and organ donation.
(b) Contact the client’s minister to discuss the client’s options related to the pregnancy.
(c) Advise the client that the prolonged neonatal death will be very painful for her.
(d) Ask the client if she has discussed this with her family.
Answer:
(a) Explore his or her own feelings about the issues of anencephaly and organ donation.
Rationale:
Anencephaly is a neural tube defect that is not compatible with life, although some infants with anencephaly live for several days before death occurs. When the client has decided to continue the pregnancy and donate the neonatal organs after the death of the neonate, the nurse should remain nonjudgmental. The nurse should explore his or her feelings about the issue of anencephaly and organ donation.
The nurse should not make judgments about the client’s position, nor should the nurse try to persuade the client to terminate the pregnancy. Contacting the client’s minister to explore the client’s options is not appropriate. The client may have already discussed the matter with her minister. Telling the client that the neonatal death will be prolonged and painful to her is not helpful. Death may occur very soon after birth. Contacting the client’s family members is not appropriate. The client may wish not to discuss the matter with her family.
Question 150.
A 3-month-old infant is being discharged on digoxin. The nurse should instruct the parents to report which signs and symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) signs of constipation or painful straining
(b) decrease in the amount of infant formula taken or a refusal to take it
(c) pulse rate >140 bpm or <100 bpm
(d) signs that the infant is not following moving objects
(e) sudden vomiting or sudden drowsiness
Answer:
(b) decrease in the amount of infant formula taken or a refusal to take it
(c) pulse rate >140 bpm or <100 bpm
(d) signs that the infant is not following moving objects
(e) sudden vomiting or sudden drowsiness
Rationale:
Anorexia is commonly the first indication of digoxin toxicity. Arrhythmias are also common with digoxin toxicity. Although bradycardia is the most common sign of toxicity, other tachycardic arrhythmias can occur. A normal pulse rate for a 3-month-old child at rest is about 120 bpm.
Blurred vision can be associated with digoxin toxicity and may be detected in an infant if he or she stops following moving objects. Sudden vomiting or drowsiness can be associated with digoxin toxicity. Constipation is not associated with digoxin toxicity and is not an adverse effect of digoxin.
Question 151.
The nurse receives a report of a serum potassium level on an infant of 5.4 mEq/L (5.4 mmol/L). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the abnormal level.
(b) Call the laboratory to see how the specimen was obtained.
(c) Connect the infant to a cardiac monitor.
(d) Check the infant’s last 24-hour output.
Answer:
(b) Call the laboratory to see how the specimen was obtained.
Rationale:
If the specimen was from a fingerstick and not a venous sample, the potassium level can be falsely elevated. Because the finger is squeezed to obtain the sample, cells may have been broken from the pressure of squeezing. When the cells break, they release potassium, which will falsely elevate the potassium level in the result. Calling the HCP without first checking the source of the sample would not give the HCP accurate and complete information.
A cardiac monitor would not be necessary if the potassium level is falsely elevated. The last 24-hour output would only indicate that the infant is voiding in an adequate amount. This may or may not have an influence on the infant’s potassium level.
Question 152.
The nurse cares for a client who is breathing rapidly, pacing back and forth across the room, has lips tightly closed, and with arms crossed tightly across his chest. What action should the nurse do first?
(a) Assist client to a safe, calm environment.
(b) Place the client in an isolation room.
(c) Ask the client why he or she is so anxious.
(d) Administer PRN buspirone.
Answer:
(a) Assist client to a safe, calm environment.
Rationale:
The nurse should first ensure the safety of the severely anxious client in a safe, quiet, environment. The nurse should not leave the client alone. Asking the client “why” is not therapeutic. Buspirone is a maintenance medication that will not help relieve anxiety immediately.
Question 153.
The nurse is caring for a client who has a history of gastric bypass surgery and is now being seen for her first prenatal visit. Which interventions should be included in the plan of care? Select all that apply.
(a) Take a prenatal vitamin with 400 meg of folic acid.
(b) Refer the client to a registered dietician.
(c) Draw glucose levels at each prenatal visit.
(d) Counsel her that she will most likely gain all of her weight back.
(e) Check urine at each visit for protein and glucose.
(f) Monitor with nonstress tests beginning at 20 weeks.
Answer:
(a) Take a prenatal vitamin with 400 meg of folic acid.
(b) Refer the client to a registered dietician.
(e) Check urine at each visit for protein and glucose.
Rationale:
Prenatal care includes a general supplementation of 400 meg of folic acid, and clients with a history of gastric bypass should be referred to a dietician to determine adequate nutrient intake. All pregnant clients have their urine routinely checked for protein and sugar. There is no indication for checking glucose levels at each prenatal visit in clients who have undergone gastric bypass. Gastric bypass clients are not at risk of gaining all of their weight back. No evidence supports implementing stress tests at 20 weeks.
Question 154.
A nurse is planning care for a regressed, chronically ill client diagnosed with schizophrenia. What is the most appropriate milieu?
(a) confrontation and peer pressure to break down the client's denial
(b) reminder that all clients must participate fully in unit self-governance
(c) required attendance at group activities with equal participation from all clients
(d) nurturance and supportive interaction focusing on individual needs
Answer:
(d) nurturance and supportive interaction focusing on individual needs
Rationale:
Due to the client’s psychosis and difficulties coping, a positive, supportive environment is essential to limit further regression and help the client engage in her own treatment. Confrontation and peer pressure are the type of milieu more suited to a chemically dependent client. While involvement in self-governance can be therapeutic, forcing a psychotic client to participate in self-governance before he or she is ready could actually hinder treatment and recovery.
Although group activities are commonly required in treatment programs, a client who is very disturbed or confused is not forced to attend. Also, the client must participate when and how the client feels comfortable, rather than mandating a specific amount of participation. Equal participation by clients does not ensure a therapeutic milieu or speed the client’s recovery.
Question 155.
The nurse is assessing a client with irreversible shock. The nurse should document the progression of which expected finding?
(a) increased alertness
(b) circulatory collapse
(c) hypertension
(d) diuresis
Answer:
(b) circulatory collapse
Rationale:
Severe hypoperfusion to all vital organs results in failure of the vital functions and then circulatory collapse. Hypotension, anuria, respiratory distress, and acidosis are other symptoms associated with irreversible shock. The client in irreversible shock will not be alert.
Question 156.
The nurse is caring for a client who has been diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis. When assessing the client’s vital signs, the nurse notes an apical pulse of 150 bpm, a respiratory rate of 46 breaths/ min, and blood pressure of 100/60 mm Hg. The client appears anxious and restless. What should be the nurse’s first course of action?
(a) Call the rapid response team.
(b) Administer a sedative.
(c) Try to elicit a positive Homans’ sign.
(d) Increase the flow rate of intravenous fluids.
Answer:
(a) Call the rapid response team.
Rationale:
Pulmonary embolism is a potentially life- threatening complication of deep vein thrombosis. The client’s change in mental status, tachypnea, and tachycardia indicate a possible pulmonary embolism. The nurse should promptly call the rapid response team Administering a sedative with-out further evaluation of the client’s condition is not appropriate.
There is no need to elicit a positive Homans’ sign; the client is already diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis. Increasing the IV flow rate may be an appropriate action but not without first notifying the HCP.
Question 157.
Assessment of a primigravid client in active labor reveals cervical dilation at 9 cm with complete effacement and the fetus at +1 station. What is the most appropriate action for the nurse to take when the health care provider (HCP) prescribes morphine 2 mg IM for the client?
(a) Administer the medication in the left ventro-gluteal muscle.
(b) Be certain that naloxone is at the client’s bedside.
(c) Ask the HCP to validate the dosage of the drug.
(d) Refuse to administer the medication to the client.
Answer:
(d) Refuse to administer the medication to the client.
Rationale:
The nurse should refuse to administer the medication to the client because of the risk of respiratory depression in the neonate. Morphine, given IM, peaks in 30 to 60 minutes and lasts 4 hours. Based on the assessment findings, the client most likely will be delivering within that time frame, increasing the risk of respiratory depression in the neonate, a serious consequence. Therefore, the nurse should not administer the drug. Naloxone should be readily available whenever opioids that can result in respiratory depression are used. Asking the HCP to validate the dosage is not necessary.
Question 158.
A client has been hospitalized with a diagnosis of myasthenia gravis. The client has been talking on the phone. The nurse enters the room right after the client has recovered from choking on a sandwich. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Instruct the client to sit at a 30-degree angle in bed when eating.
(b) Tell the client to swallow when the chin is tipped down on the chest.
(c) Remind the client to rest after eating.
(d) Encourage the client not to talk while eating.
Answer:
(b) Tell the client to swallow when the chin is tipped down on the chest.
Rationale:
Bending the chin down toward the chest decreases the risk of food entering the trachea and causing aspiration into the lungs. The client should sit up at a 90-degree angle when eating. Eating and talking increase the risk of aspiration as well as muscle fatigue; the nurse should encourage the client to avoid talking while chewing and swallowing. The client should rest before eating because muscle fatigue can contribute to choking.
Question 159.
A nurse is assessing a client with a brain injury. What is a client’s cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) when the blood pressure (BP) is 90/50 mm Hg and the intracranial pressure (ICP) is 21? Round to the nearest whole number.
............................... mm Hg.
Answer:
42 mm Hg
Rationale:
To obtain CPP, use this formula
CPP = mean arterial pressure (MAP) - ICP.
To obtain the MAP, use this formula:
MAP = [systolic BP + (2 x diastolic BP)] + 3
MAP = [90 + (2 x 50)] H- 3 = 63.3 CPP = 63.3 - 21 = 42.3 mm Hg.
Question 160.
A client with a T2 to T3 spinal cord injury suddenly has a throbbing headache and blurred vision. The client is flushed and sweating on the upper trunk and face, and the hairs on the arms are raised. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Raise the head of the bed.
(b) Assess for hypotension.
(c) Check the client for a distended bladder.
(d) Logroll the client to see if the client is lying on a foreign object.
Answer:
(a) Raise the head of the bed.
Rationale:
The client with a spinal cord injury above T6 who suddenly experiences clinical manifestations of autonomic stimulation, such as flushing, sweating, and piloerection, is demonstrating life- threatening autonomic dysreflexia. The cluster of manifestation results from noxious stimuli, such as a full bladder, or lying on a foreign object, such as a plastic cap or crinkled paper, which the client cannot feel.
As soon as the noxious stimulus is removed, the manifestations begin to subside. When the client demonstrates clinical manifestations of autonomic dysreflexia, the nurse should first elevate the head of the bed immediately to decrease the intracerebral pressure caused by the hypertension that developed from autonomic stimulation. The nurse can next check for a distended bladder or foreign object. The client’s blood pressure will be elevated; the nurse should assess vital signs frequently.
Question 161.
A 17-year-old unmarried primigravida client at 10 weeks’ gestation tells the nurse that her family does not have much money and her dad just got laid off from his job. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Instruct the client in methods for low-cost, highly nutritious meal preparation.
(b) Determine whether the client qualifies for local assistance programs.
(c) Refer the client to a social worker for enrollment in a food assistance program.
(d) Ask the client if she has a job and the amount of income earned.
Answer:
(c) Refer the client to a social worker for enrollment in a food assistance program.
Rationale:
The nurse should refer the client to a social worker for assistance in enrolling in the WIC program. This program provides assistance for foods such as milk, cereal, and infant formula. Instructing the client in low-cost, highly nutritious meal preparation will not meet the client’s need for additional funds for food.
Determining whether the client qualifies for state assistance is part of the role of the social worker, not the nurse. Asking the client if she has a job and the amount of income earned is not within the role of the nurse. The social worker can determine whether the family income guidelines are met for state and federal assistance.
Question 162.
A client has impairments in immediate recall and short-term memory. A nurse is planning for the client’s daily activities. Which action by the nurse would be most effective?
(a) Write out the client’s schedule in large print, and show the client where the schedule is placed.
(b) Describe each activity and the time of the events at the beginning of the day.
(c) Take the client to each activity if the client does not attend on time.
(d) Tell the client about each activity 10 minutes before it begins.
Answer:
(d) Tell the client about each activity 10 minutes before it begins.
Rationale:
Telling the client about one activity at a time with 10 minutes’ notice gives the client time to prepare for that activity. Writing out the schedule does not ensure that the client will remember to look at it. It is overwhelming to explain an entire day’s schedule all at once to a client diagnosed with dementia. Leading a client to an activity after the fact does not allow the client to prepare.
Question 163.
A 17-year-old male client is being admitted to the adolescent psychiatric unit. He was brought in by the police after beating up two male peers.
The client says, “They said I was gay because I had sex with an older neighbor when I was 8 years old. I’m not gay!” Which nursing intervention would be appropriate? Select all that apply.
(a) Monitor the client’s level of anger and potential aggression.
(b) Help the client express anger safely.
(c) Assist the client in processing his feelings about the sexual abuse.
(d) Ask the client if he would like to attend a support group.
(e) Discuss the client’s attitude about going to jail after discharge.
Answer:
(a) Monitor the client’s level of anger and potential aggression.
(b) Help the client express anger safely.
(c) Assist the client in processing his feelings about the sexual abuse.
(d) Ask the client if he would like to attend a support group.
Rationale:
Safety of others is a priority, and the nurse must monitor the client’s anger and potential for aggression. The nurse should also find safe ways for the client to express the client’s anger and any other feelings about the abuse. A referral to a support group is appropriate because anger management groups are one way to assist the client in learning to manage anger. Nothing about jail is mentioned in the question. Discussion of jail does not help the client address the client’s issues with anger and the abuse causing the anger.
Question 164.
The nurse has been assigned to care for several postpartum clients and their neonates on a birthing unit. Which client should the nurse assess
first?
(a) a multiparous client at 48 hours postpartum who is being discharged
(b) a primiparous client at 2 hours postpartum who gave vaginal birth to a term neonate
(c) a multiparous client at 24 hours postpartum whose infant is in the special care nursery
(d) a primiparous client at 48 hours postpartum after cesarean birth of a term neonat
Answer:
(b) a primiparous client at 2 hours postpartum who gave vaginal birth to a term neonate
Rationale:
The primiparous client at 2 hours postpartum who delivered a term neonate vaginally should be assessed first because this client is at risk for postpartum hemorrhage. Early postpartum hemorrhage typically occurs during the first 24 hours postpartum. Once the nurse has assessed the client’s fundus, lochia, and vital signs, a determination about the stability of the client can be made. After this assessment, the nurse can provide care to the other clients, who are of lesser priority than the newly delivered primiparous client.
Question 165.
A client has been diagnosed with legionellosis (Legionnaires’ disease). The client asks, “How did I get this?” Which response by the nurse is the most accurate?
(a) “The bacteria are inhaled from contaminated water droplets.”
(b) “You inhaled the bacteria in a smoke-filled room. “
(c) “As ceiling fans circulate, bacteria are dis persed into the air.”
(d) “You may have swallowed bacteria-contami-nated water.”
Answer:
(d) “You may have swallowed bacteria-contami-nated water.”
Rationale:
Legionellosis is a pneumonia caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila that thrives in water that is 95°F to 115°F (35°F to 46°C). When a building’s hot water plumbing has water at this temperature, the bacteria thrive; then they may be transmitted via inhalation from air conditioning, showers, spas, and whirlpools. The bacteria are not transmitted via smoke or ceiling fan blades or by swallowing contaminated water.
Question 166.
A 4-year-old child who has been ill for 4 hours is admitted to the hospital with difficulty swallowing, a sore throat, and severe substernal retractions. The child’s temperature is 104°F (40°C), and the apical pulse is 140 bpm. The white blood cell count is 16,000/mm3 (16 x 109/L). What is the priority for nursing intervention?
(a) infection
(b) airway obstruction
(c) difficulty breathing
(d) potential for aspiration
Answer:
(b) airway obstruction
Rationale:
The child’s signs and symptoms in conjunction with the acute onset suggest possible croup or epiglottitis. The priority diagnosis at this time is airway obstruction. The airway may become completely occluded by the epiglottis at any time. Although the child has an infection, and the client has respiratory distress, the immediate priority is to establish and maintain a patent airway. No evidence is provided to support the potential for aspiration.
Question 167.
Which baseline laboratory data should be established before a client is started on tissue plasminogen activator or alteplase recombinant?
(a) potassium level
(b) Lee-White clotting time
(c) hemoglobin level, hematocrit, and platelet count
(d) blood glucose level
Answer:
(c) hemoglobin level, hematocrit, and platelet count
Rationale:
The baseline laboratory data that are established before a client is started on tissue plasminogen activator or alteplase recombinant include hematocrit, hemoglobin level, and platelet count.
Question 168.
A client is scheduled to undergo an upper gastrointestinal (GI) series. The nurse should give the client which instructions in preparation for the test? Select all that apply.
(a) “You will need to take a stool softener before the test to promote evacuation of the barium.”
(b) “Don’t eat or drink for 8 hours before the test.”
(c) “You can expect white stools for about 48 hours after the test.”
(d) “You’ll experience mild stomach pain during the test.”
(e) “It’s okay for you to smoke before the test.”
Answer:
(b) “Don’t eat or drink for 8 hours before the test.”
(c) “You can expect white stools for about 48 hours after the test.”
Rationale:
The client should be instructed not to eat or drink for 8 to 12 hours before the test. Stools will be white for up to 72 hours following the procedure as the barium is eliminated from the body. Laxatives and fluids will be encouraged after the procedure to help prevent barium impaction, but the client will not be given stool softeners or laxatives before the procedure. The client should not experience pain during the procedure. The nurse should also instruct the client to stop smoking at midnight the night before the test.
Question 169.
Which are appropriate identifiers to use when providing care or administering medications or treatments? Select all that apply.
(a) room number
(b) bed number
(c) medical record number
(d) name band
(e) social security (social insurance) number
Answer:
(c) medical record number
(d) name band
Rationale:
A National Patient Safety Goal of the Joint Commission is to improve the accuracy of client identification; to attain that goal, health care personnel must use at least two client identifiers when providing care, treatment, or services. The medical record Q number and name as printed on the cli-ent’s name band are appropriate identifiers. Because the client can change rooms and beds, these are not to be used as identifiers. Social security numbers are not used as identifiers for health care or treatment purposes.
Question 170.
The nurse interprets the rhythm strip below from a client’s bedside monitor as which rhythm?
(a) normal sinus rhythm
(b) sinus tachycardia
(c) atrial fibrillation
(d) ventricular tachycardia
Answer:
(c) atrial fibrillation
Rationale:
This rhythm is atrial fibrillation. It is characterized by an irregular QRS interval, no definite P waves before the QRS waves, and a ventricular rate >100 bpm.
Question 171.
The nurse is preparing to give an IM injection to an underweight client. Which site is the safest because it has the fewest amount of blood vessels and major nerves located in the area?
(a) deltoid
(b) dorsogluteal
(c) vastus lateralis
(d) triceps
Answer:
(c) vastus lateralis
Rationale:
The vastus lateralis site is the preferred IM site for all ages because it does not have any major nerves or blood vessels located near it. The deltoid and dorsogluteal muscles have major nerves and blood vessels located nearby. The triceps is not an acceptable muscle for IM injections because it is not well developed in most clients.
Question 172.
The nurse is planning to teach the client how to properly use a metered-dose inhaler to treat asthma. The nurse should tell the client to use which procedure?
(a) Rinse the mouth after each use of a steroid inhaler.
(b) Inhale quickly when administering the medication.
(c) Inhale the medication and then exhale through the nose.
(d) Cough and deep-breathe before inhaling the medication.
Answer:
(a) Rinse the mouth after each use of a steroid inhaler.
Rationale:
Clients should be instructed to rinse their mouths after using a steroid inhaler to avoid developing thrush. Clients should also be instructed to inhale slowly through the mouth and then hold the breath as they count to 10 slowly. It is not necessary for the client to cough and deep-breathe before using the inhaler.
Question 173.
A client is receiving a transfusion of packed red blood cells. What should the nurse do to safely administer the blood?
(a) Keep the blood refrigerated on the nursing unit until ready to administer.
(b) Stay with the client during the first 15 minutes to detect signs or symptoms of a reaction.
(c) Not infuse blood that has been hanging for more than 6 hours.
(d) Administer the blood quickly to prevent wasting it if the client develops a fever.
Answer:
(b) Stay with the client during the first 15 minutes to detect signs or symptoms of a reaction.
Rationale:
The nurse should stay with the client during the first 15 minutes of a blood transfusion because this is when reactions are most likely to occur. Blood products should never be refrigerated on the nursing unit. Blood that has not been infused after 4 hours should not be infused. The blood should be infused over the specific time prescribed by the health care provider (HCP) If a fever develops, the transfusion should be stopped immediately, and the blood reaction policy of the facility should be followed.
Question 174.
A client who is receiving a blood transfusion begins to have difficulty breathing. The nurse notes an elevated blood pressure and a cough. Based on these signs, the nurse should prepare to manage which complication?
(a) anaphylactic reaction
(b) circulatory overload
(c) sepsis
(d) acute hemolytic reaction
Answer:
(b) circulatory overload
Rationale:
The symptoms of difficulty breathing, elevated blood pressure, and cough are indicative of circulatory overload. Circulatory overload occurs when blood is infused more rapidly than the circulatory system can accommodate. Anaphylactic reactions are manifested by urticaria, wheezing, and shock. Sepsis begins with a rapid onset of chills and fever. Acute hemolytic reaction is typically mani-fested by chills, fever, low back pain, and flushing.
Question 175.
The nurse is teaching a client with peptic ulcer disease how to take sucralfate. Which statement indicates that the client understands how to take the medication?
(a) “I should take the sucralfate every evening at bedtime.”
(b) “It’s important that I take this drug on an empty stomach.”
(c) “I should avoid milk products while taking this drug.”
(d) “I should have my hemoglobin checked monthly while taking sucralfate.”
Answer:
(b) “It’s important that I take this drug on an empty stomach.”
Rationale:
Sucralfate should be taken on an empty stomach 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals and at bedtime. It is usually taken four times a day. There is no need to avoid milk products while taking the drug. Sucralfate does not affect hemoglobin levels.
Question 176.
The nurse is conducting an admission interview with a client and is assessing for risk factors related to the client’s safety. The nurse should include which targeted assessments? Select all that apply.
(a) suicide or self-harm ideation
(b) incentives that motivate the client
(c) recent use of substances of abuse
(d) allergic reactions or adverse drug reactions
(e) dietary preferences
Answer:
(a) suicide or self-harm ideation
(c) recent use of substances of abuse
(d) allergic reactions or adverse drug reactions
Rationale:
When assessing client safety, the nurse assesses suicide thoughts or plan, recent use of illicit drugs (as they may cause impaired judgment or thought processes), and previously experienced allergic reactions and adverse reactions to medications. Note that safety involves many aspects of care. Incentives and diet preferences (allergies would be previously noted) are not directly related to safety, although they may be part of an overall assessment.
Question 177.
An adult client has bacterial conjunctivitis. What should the nurse teach the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Use warm saline soaks four times per day to remove crusting.
(b) Apply topical antibiotic without touching the tip of the tube to the eye.
(c) Wash the hands after touching the eyes.
(d) Avoid touching the eyes.
(e) Observe isolation procedures by staying in the bedroom until the redness in the eye disappears.
Answer:
(a) Use warm saline soaks four times per day to remove crusting.
(b) Apply topical antibiotic without touching the tip of the tube to the eye.
(c) Wash the hands after touching the eyes.
(d) Avoid touching the eyes.
Rationale:
The client with conjunctivitis can use warm soaks to remove crusting. The nurse should teach the client to dispose of the soaks by wrapping them in a separate bag to avoid spread-ing bacteria. Topical antibiotics are used to treat the infection. The client should avoid contaminating the tip of the medication dispenser. Bacterial conjunctivitis requires containing the spread of the infection. The client should avoid touching the eyes. If the client does touch the eyes, the client should wash the hands after touching the eyes. The client does not need to be isolated.
Question 178.
A 31-year-old client, G3, TO, P2, AbO, LO at 32 weeks’ gestation is being admitted to the hospital with contractions of moderate intensity occurring every 3 to 4 minutes per the client report. The client is crying on admission; the history reveals that the client has previously had two nonviable fetuses at 30 weeks’ gestation. What nursing action would be the highest priority for this client?
(a) Assess maternal contraction and fetal heart rate pattern.
(b) Reassure the client that this baby will be healthy.
(c) Review history of prior fetal demises with client.
(d) Prepare for immediate administration of magnesium sulfate.
Answer:
(a) Assess maternal contraction and fetal heart rate pattern.
Rationale:
The physical aspects of care have a higher priority than do the psychosocial aspects. The client report is part of the electronic medical record > but the maternal contraction pattern and the fetal heart rate pattern must be completed immediately upon admission to establish a baseline. The need for a tocolytic agent cannot be determined until the maternal fetal unit has been assessed.
Assessment of the circumstances and etiologies of the prior fetal demises are important but are not of the highest importance. The psychosocial aspects are very important in the care of this client and can briefly be discussed as the physical aspects of assessment are being completed, but in-depth psychosocial care will need to wait until the physical aspects have been completed.
Question 179.
Which actions by the nurse will most likely ensure that the correct client receives a medication? Select all that apply.
(a) Have the client state his or her name.
(b) Check the name on the armband with the name on the medication.
(c) Learn to recognize the client.
(d) Check the client’s room number.
(e) Compare the date of birth on the client’s medical record to the date of birth on the client’s armband.
Answer:
(b) Check the name on the armband with the name on the medication.
(e) Compare the date of birth on the client’s medical record to the date of birth on the client’s armband.
Rationale:
Two sources of identification must be confirmed before administering medication to a client. A source of information can be the client’s record number, name, or date of birth, as noted on the client’s armband. A client may be confused or hard of hearing and may give a wrong name or answer to a wrong name; thus, having the client state his or her name or respond to his or her name is not safe practice. Client recognition is not sufficient identification for administering medication. Clients change rooms frequently, so a room number is not a source of identification for administering medication.
Question 180.
A nurse counsels a mother with young children after leaving her abusive husband 6 months ago. The mother says, “My 6-year-old is starting to act just like his father. I just don’t know how to handle this.” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “You’ll have to limit your son’s contact with his father.”
(b) “Counseling for your son would be helpful.”
(c) “Most boys outgrow these behaviors.”
(d) “Setting limits on his behavior is all you need to do now.”
Answer:
(b) “Counseling for your son would be helpful.”
Rationale:
Children who witness domestic violence commonly grow up to be victims or abusers. Counseling helps interrupt the pattern of violence in families. Limiting contact between the father and child does not address the child’s behavior, and outgrowing violent behaviors is not likely without other interventions. Setting limits on violent behaviors alone does not address the child’s feelings and needs.
Question 181.
A 40-year-old primigravid client with AB-positive blood visits the outpatient clinic for an amniocentesis at 16 weeks’ gestation. The nurse determines that the most likely reason for the client’s amniocentesis is to determine if the fetus has which problem?
(a) cri-du-chat syndrome
(b) ABO incompatibility
(c) erythroblastosis fetalis
(d) Down syndrome
Answer:
(d) Down syndrome
Rationale:
Because of the client’s age, the amniocentesis is most likely being done to evaluate for Down syndrome (trisomy 21). Women older than 35 years are at higher risk for having a child with Down syndrome. Cri-du-chat syndrome is a genetic disorder involving a short arm on chromosome 5. This disorder is not associated with mothers who are older than 35 years. The client is AB positive, so the amniocentesis is not being done for ABO incompatibility, in which the mother is type O and the fetus is type A, B, or AB. The amniocentesis is not being done to detect erythroblastosis fetalis because the mother is Rh positive.
Question 182.
The nurse-manager is developing a “read- back” procedure to reduce medication administration errors. What are purposes of the “read-back” requirement? Select all that apply.
(a) to prohibit prescriptions and test results from being communicated verbally or by telephone
(b) to make sure that prescriptions and test results that are communicated verbally or by telephone are clear to the receiver of the information
(c) to make sure that prescriptions and test results that are communicated verbally or by telephone are confirmed by the individual giving the information
(d) to minimize the risk of nonauthorized personnel from giving prescriptions that are communicated verbally or by telephone
(e) to encourage the use of electronic medical records
Answer:
(b) to make sure that prescriptions and test results that are communicated verbally or by telephone are clear to the receiver of the information
(c) to make sure that prescriptions and test results that are communicated verbally or by telephone are confirmed by the individual giving the information
Rationale:
A National Patient Safety Goal of the Joint Commission is to improve the effectiveness of communication among caregivers. The requirement for verbal or telephone prescriptions, or for telephonic reporting of critical test results, is to verify the complete prescription or test result by having the person receiving the information record and “read back” the complete prescription or test result.
Effective communication that is timely, accurate, complete, unambiguous, and understood by the recipient reduces error and results in improved client safety. “Read-back” procedures are not intended to discourage or prohibit telephone communications among health care providers (HCPs) Q or to promote use of electronic medical records Q. Safety procedures, such as provider identification codes, are in place for HCPs to give verbal or telephone prescriptions.
Question 183.
A female client who is hospitalized for an eating disorder weighs 15 lb (6.8 kg) less than the ideal body weight. Which goal is a priority for this client? The client:
(a) attends all eating disorder support groups.
(b) eats bigger meals at breakfast.
(c) gains 1 lb (0.5 kg) per week.
(d) reports an improved self-image.
Answer:
(c) gains 1 lb (0.5 kg) per week.
Rationale:
The actual desired weight gain of 1 lb (0.5 kg) per week is the most measurable goal for the client. Attending all eating disorder support groups is a goal, but it is not as important as actual weight gain. The client can eat a larger meal at breakfast and then not eat sufficient food and over exercise for the remainder of the day. The client’s improved self-image is important, but actual weight gain is again a priority.
Question 184.
A 16-year-old primiparous client has decided to place her baby for adoption. The adoptive parents are on their way to the hospital when the mother says, “I want to see the baby one last time.” What should the nurse do?
(a) Tell the client that it would be best if she did not see the baby.
(b) Allow the client to see the baby through the nursery window.
(c) Contact the health care provider (HCP) for advice related to the client’s visitation.
(d) Allow the client to see and hold the baby for as long as she desires.
Answer:
(d) Allow the client to see and hold the baby for as long as she desires.
Rationale:
The nurse should allow the client to see and hold the baby for as long as she desires. Such activities provide memories for the mother and assist in the grieving process. There is a possibility that the client may change her mind about the adoption. In most states, there is a defined period (6 months to 1 year or longer) before an adoption becomes final. If the client changes her mind about the adoption, the nurse should accept the client’s decision and notify the HCP and social worker.
Telling the client that it would be best if she did not see the baby is imposing the nurse’s value system on the client. Allowing the client to see the baby through the nursery window is inappropriate because the client should be allowed to touch and hold the baby. Contacting the HCP for advice related to the client’s visitation is not necessary.
Question 185.
A school nurse interviews the parent of a middle-school student who is exhibiting behavioral problems, including substance abuse, following a sibling’s suicide. The parent says, “I’m a single parent who has to work hard to support my family, and now I’ve lost my only son, and my daughter is acting out and making me crazy! I just can’t take all this stress!” Which concern regarding this family has priority at this time?
(a) the parent’s ability to emotionally support the adolescent in this crisis
(b) potential suicidal thoughts/plans of both family members
(c) the adolescent’s anger
(d) the parent’s frustration
Answer:
(b) potential suicidal thoughts/plans of both family members
Rationale:
The parent’s expression of stress and grief and the adolescent’s behavior and drug use could be preludes to suicide, especially since another member of the family succeeded in suicide. Suicide attempts are more likely in families in which there has been a previous suicide attempt or suicide death, especially for young people.
The parent’s ability to emotionally support the adolescent in this crisis has been compromised, but the safety of both supersedes this concern. Assuring the client’s and parent’s safety is more important than dealing with anger or frustration at this point. Though the emotional states of both the parent and the child are important, one is not more important than the other.
Question 186.
A 10-year-old child is admitted with a brain tumor. Which assessment made by the nurse is most critical to report to the child’s health care provider (HCP)?
(a) vomiting after lunch
(b) difficulty in recalling the day of the week
(c) blood pressure of 102/62 mm Hg
(d) 100 mL of concentrated urine voided at one voiding
Answer:
(b) difficulty in recalling the day of the week
Rationale:
A decrease or change in the level of consciousness is an early indication of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) and should be reported to the child’s HCP Q as soon as possible to try and control the pressure so that it does not increase further.
Vomiting can be a sign of increased ICP that occurs with a brain tumor, but it usually occurs unrelated to food and in the morning upon arising. Blood pressure increases with a brain tumor due to pressure on the brain stem. Concentrated urine is a sign of dehydration and is not related to the signs of a brain tumor.
Question 187.
A client with jaundice has poor appetite, nausea, and two episodes of emesis in the past 2 hours. The client reports having spasms in the stomach area. The client does not have pruritus. The nurse should develop a care plan for which symptom first?
(a) nausea
(b) poor appetite
(c) jaundice
(d) abdominal spasms
Answer:
(a) nausea
Rationale:
The nurse should first plan to relieve the nausea and vomiting; if these continue, the client is at risk for dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. The client’s poor appetite is likely related to the underlying health problem and is not the priority; the nausea may adversely affect the appetite, and relieving the nausea may allow the client an opportunity to eat and drink. The client has jaundice but does not have uncomfortable symptoms such as pruritus. The abdominal spasms may be related to nausea and vomiting and can be assessed again when the nausea and vomiting have stopped.
Question 188.
When planning for risk management for clients who are at risk for development of pressure ulcers, the nurse should first:
(a) identify at-risk clients on admission to the health care facility.
(b) place at-risk clients on an every-2-hour turning schedule.
(c) automatically place clients in specialty beds.
(d) provide at-risk clients with a high-protein, high-carbohydrate diet.
Answer:
(a) identify at-risk clients on admission to the health care facility.
Rationale:
All clients who are at risk for pressure ulcer development should be identified on admission to health care facilities so that preventive actions can be implemented by the nursing staff. These preventive actions need to be individualized to the client, so automatic placement of all at-risk clients on an every-2-hour turning schedule, a specialty bed, or a high-protein, high-carbohydrate diet is not appropriate.
Question 189.
The nurse teaches 17-year-old girl with has a severe gonorrheal infection about her disease. The nurse realizes that the girl understands the implications of her disease when the client makes which statement?
(a) “Once I’m treated, I’ll have immunity.”
(b) “My partner doesn’t need treatment.”
(c) “I won’t have any more problems once I learn to protect myself.”
(d) “I could have trouble getting pregnant.”
Answer:
(d) “I could have trouble getting pregnant.”
Rationale:
With a severe gonorrheal infection, scarring of the fallopian tubes may occur, and becoming pregnant may be difficult or impossible. If the girl’s partner is not treated, she can be reinfected. There is no immunity against gonorrhea, and, if exposed again, the girl can again become infected.
Although a condom may provide some protection against contracting gonorrhea, it is not an adequate protection against the condition and will not help clear up an existing infection. It is only with proper antibiotic administration that the condition can be eradicated.
Question 190.
After the nurse teaches the parent of a child with a spica cast about skin care, which parental action would indicate the need for additional teaching?
(a) application of powder to the skin under the cast
(b) inspection of the cast edges for smoothness
(c) application of plastic film to cover the perineal cast area
(d) inspection of areas inside the cast
Answer:
(a) application of powder to the skin under the cast
Rationale:
Powder should not be applied to the skin beneath the cast because powder can cause irritation and skin breakdown. The parent would need further teaching about avoiding this measure. Checking the smoothness of the cast edges, covering the cast around the perineum, and inspecting inside the cast are all appropriate actions for the child with a spica cast to help prevent skin breakdown.
Question 191.
The nurse-manager is teaching the staff about the medication reconciliation policy. The nurse teaches the staff that reconciliation is needed to ensure that clients are on the correct medications in which situations? Select all that apply.
(a) admission to the hospital
(b) transfer to the nursing home
(c) transfer of a client from surgery to the surgical unit
(d) admission to a home health agency from the hospital
(e) move from a double room to a single room on the same unit
Answer:
(a) admission to the hospital
(b) transfer to the nursing home
(c) transfer of a client from surgery to the surgical unit
(d) admission to a home health agency from the hospital
Rationale:
The goal of “medication reconciliation” is to ensure that clients are on the right medication after any transfer, admission, or discharge. It is not necessary to reconcile the medications if the client moves to a different room on the same floor. It is estimated that more than half of medication errors occur during these transitions, and medication rec-onciliation can reduce errors by 70% or more. The Joint Commission requirements mandate medication reconciliation programs.
Question 192.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is prescribed for a client following crush injury. Which finding indicates the drug has been effective?
(a) The pulse is weak and irregular.
(b) The serum potassium is 4.0 mEq/L (4.0 mmol/L)
(c) The ECG is showing tall, peaked T waves.
(d) There is muscle weakness on physical examination.
Answer:
(b) The serum potassium is 4.0 mEq/L (4.0 mmol/L)
Rationale:
Following crush injury, serum potassium rises to high levels. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a potassium binding resin. The resin combines with potassium in the colon and is then eliminated, and serum potassium levels should come back to normal. Normal serum potassium is 3.5 to 5.3. Weak, irregular pulse and tall peaked T waves on ECG are signs of hyperkalemia, and muscle weakness is a sign of hypokalemia.
Question 193.
The nurse is teaching a young female about using oxcarbazepine to control seizures. The nurse determines teaching is effective when the client makes which statement?
(a) “I’ll use one of the barrier methods of contraception.”
(b) “I’ll need a higher dose of oral contraceptive when on this drug.”
(c) “Since I’m 28 years old, I shouldn’t delay starting a family.”
(d) “I must weigh myself weekly to check for sudden gain in weight.”
Answer:
(a) “I’ll use one of the barrier methods of contraception.”
Rationale:
An alternative or additional method of birth control must be used since oxcarbazepine reduces the effectiveness of oral contraceptives. Higher doses of oral contraceptives will not help in achieving this purpose, but the client needs an addi-tional or alternative method of birth control. The client does not need advice about when to start her family. A side effect of oxcarbazepine may be weight gain, but it is typically gradual.
Question 194.
A client diagnosed with chronic renal failure is undergoing hemodialysis. Post dialysis, the client weighs 59 kg. The nurse should teach the client to make which dietary changes?
(a) Increase the amount of sodium in the diet to 4 g/day.
(b) Limit the total number of calories consumed each day to 1,000.
(c) Increase fluid intake to 3,000 mL each day.
(d) Control the amount of protein intake to 59 to 70 g/day.
Answer:
(d) Control the amount of protein intake to 59 to 70 g/day.
Rationale:
Hemodialysis clients have their protein requirements individually tailored according to their postdialysis weight. The protein requirement is 1.0 to 1.2 g/kg body weight per day. Hence, for a 59-kg weight, the amount of protein will be 59 to 70 g/day. Sodium should be restricted to 3 g/ day. The client should obtain sufficient calories; if calories are not supplied in adequate amount, the body will use tissue protein for energy, which will lead to a negative nitrogen balance and malnutri-tion. Fluid intake needs to be restricted. The fluid amount is restricted to 500 to 700 mL plus the urine output.
Question 195.
A client was treated for a streptococcal throat infection 2 weeks ago. The client now has been diagnosed with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. The client asks the nurse how to prevent this infection. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “See your health care provider for an early diagnosis and treatment of a sore throat.”
(b) “As long as you don’t have a fever, it’s sufficient to gargle daily with an antibacterial mouthwash.”
(c) “You may continue to utilize the previously prescribed antibiotics until they’re gone.”
(d) “Unscented bar soap may be used in showers.”
Answer:
(a) “See your health care provider for an early diagnosis and treatment of a sore throat.”
Rationale:
Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis usually follows a streptococcal throat or skin infection by 1 to 2 weeks. Streptococcus-iype infections require medical intervention with antibiotics. Antibacterial mouthwashes do not kill streptococci. Previously prescribed antibiotics may not be effective against streptococci and may also be expired. Bar soap fragrance has no impact on its ability to kill bacteria that reside on the skin.
Question 196.
Assessment of a primigravid client in active labor reveals a cervix dilated to 5 cm and completely effaced, with the fetus at -1 station. The client has indicated that she wants a “natural birth” with no analgesia or anesthesia. The health care provider (HCP) enters the room and tells the client that it is time for an epidural anesthetic. What would be the nurse’s best action at this time?
(a) Ask the client if she desires an epidural anesthetic.
(b) Tell the HCP that the client desires a “natural birth.”
(c) Tell the client that her labor will be more comfortable with an anesthetic.
(d) Ask the client to discuss this with her husband and then make a decision.
Answer:
(a) Ask the client if she desires an epidural anesthetic.
Rationale:
To be a true client advocate, the nurse should ask the client if she desires an epidural anesthetic even though the client has indicated a desire for “natural birth.” The client has a right to change her mind and also a right to refuse treatment. The client, not the nurse, should be the one to tell the HCP that she does not want an epidural anesthetic; the nurse should support the client’s decision.
Although telling the client that her labor will be more comfortable with an anesthetic provides the client with information, a statement such as this can be viewed as an attempt to change the client’s mind. The client may wish to discuss this situation with her husband, but she does not have to do so.
Question 197.
A client is ready to be discharged following an inguinal hernia repair. Which criteria must the client meet before the nurse can discharge the client? Select all that apply.
The client:
(a) has transportation home via a taxicab.
(b) is able to tolerate oral fluids.
(c) has pain no >5 on a scale of 1 to 10.
(d) can walk to the bathroom unassisted.
(e) has voided.
Answer:
(b) is able to tolerate oral fluids.
(d) can walk to the bathroom unassisted.
(e) has voided.
Rationale:
In order to meet the criteria for discharge from same-day surgery, the postoperative client must be able to take fluids by mouth, walk without hypotension, void, and be escorted by a responsible adult who will drive the client home. Transportation home via a taxicab is not a sufficient escort to assist a client home after surgery. The client may be discharged with severe pain as long as the client can ambulate safely. The nurse should make sure the client has a prescription for pain medication.
Question 198.
The nurse is administering eye drops to a client with glaucoma. Which technique is correct for instilling the eye drops? The eye drops are placed:
(a) in the lower conjunctival sac.
(b) near the opening of the lacrimal ducts.
(c) on the cornea.
(d) on the scleral surface.
Answer:
(a) in the lower conjunctival sac.
Rationale:
Eyedrops are correctly instilled by placing them in the lower conjunctival sac. Eyedrops should not be placed near the lacrimal ducts, to decrease the chance of the medication’s being systemically absorbed. Placing the drops on the cornea or sclera is uncomfortable for the client and may cause the medication to run out of the eye socket instead of being absorbed.
Question 199.
The nurse is teaching an older adult how to prevent falls. The nurse should tell the client to:
(a) turn on bright lights in the room so the client can see items in the room.
(b) instruct the client to rise slowing from a supine position.
(c) encourage the client not to use assistive devices as they reduce independence.
(d) instruct the client not to exercise painful joints.
Answer:
Rationale:
Normal age-related changes can predispose older adults to falling and include vision, hearing, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and neurological changes. One of the most common problems fac¬ing older adults is the loss of tissue elasticity that affects the arteries. This loss of elasticity results in a decrease in tissue recoil and leads to changes in blood pressure with position changes.
When they rise too quickly from a supine position, they feel light-headed and dizzy and can fall. The nurse should instruct clients to change positions slowly and to dangle the legs a few minutes when aris¬ing from a supine position. When aging, the lens of the eye becomes sensitive to very bright light that can cause a glare and visual disturbances that can lead to falls. Rooms should be well lit, but not with bright lights that cause a glare.
Neurological changes are seen in impaired reflexes and thus postural instability. This loss of postural stability leads to falls. The need of assistive devices (hand rails, cane, walkers) helps reduce falls and promote independence. If joint pain develops and remains untreated, it can cause older adults to become sedentary or immobile. This disuse of muscles contributes to muscle weakness and falls. Nursing interventions should be directed at encouraging regular ambulation and joint movement (range of motion).
Question 200.
Before inserting a nasogastric (NG) tube in an adult client, the nurse estimates the length of tubing to insert. Identify the point on the illustration where the nurse would end the measurement.
Answer:
Rationale:
When measuring for NG tube insertion, the nurse would end the measurement at the xiphoid process
Question 201.
The nurse is designing a benchmarking study to gather information about nursing care practices for wound care. Which sources of information are used for benchmarking? Select all that apply.
(a) government reports
(b) literature reviews
(c) standard-setting organizations
(d) databases
(e) clinical organization recommendations
Answer:
(a) government reports
(b) literature reviews
(c) standard-setting organizations
(d) databases
Rationale:
Benchmarking is a technique for learning from the success of others in an area where care improvement is desired by comparing the data from others with the data about the nursing problem for which improvement is sought. Sources of information for benchmarking include literature reviews, databases, unions, standard-setting organizations, local organizations, universities, the government, staff or customer interviews, and questionnaires. A recommendation from a clinical organization does not necessarily indicate that success has been attained.
Question 202.
A client scheduled for hip replacement surgery wishes to receive his own blood for the upcoming surgery. What should the nurse do?
(a) Document the client’s request on the medical record.
(b) Notify the hematology laboratory.
(c) Notify the surgeon’s office.
(d) Call the blood bank.
Answer:
(c) Notify the surgeon’s office.
Rationale:
The nurse should call the surgeon’s office so that arrangements can be made for the client to donate a unit of his blood for possible future autotransfusion. This must be done in sufficient time before surgery so that the client is not at risk for being anemic at the time of the scheduled procedure.
The client’s request must be scheduled through the surgeon’s office because the surgeon has ultimate responsibility for the client. The nurse can document that the surgeon’s office was notified of the client’s request. Notifying the hematology laboratory or blood bank is not an appropriate response.
Question 203.
A client is using an over-the-counter nasal spray containing pseudoephedrine to treat allergic rhinitis. Which instruction about this medication would be most appropriate for the nurse to provide for the client?
(a) Prolonged use of nasal spray can lead to nasal infections.
(b) Pseudoephedrine is an addictive drug and must be used cautiously.
(c) Overuse of pseudoephedrine can lead to increased nasal congestion.
(d) A common side effect of pseudoephedrine nasal spray is thrush.
Answer:
(c) Overuse of pseudoephedrine can lead to increased nasal congestion.
Rationale:
Overuse of nasal spray containing pseu- doephedrine can lead to rhinitis medicamentosa, which is a rebound effect causing increased swelling and congestion. Use of pseudoephedrine nasal spray does not cause infections or thrush. Pseudoephedrine is not addictive.
Question 204.
A 4-year-old child is admitted for an appen-dectomy. What is the most appropriate way for the nurse to prepare the child for surgery?
(a) Explain how to use a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump for pain control.
(b) Permit the child to play with the blood pressure cuff, electrocardiogram (ECG) pads, and a face mask.
(c) Show the child a video about the surgery.
(d) Show the child a visual analog scale (VAS) based on a scale from 0 to 10.
Answer:
(b) Permit the child to play with the blood pressure cuff, electrocardiogram (ECG) pads, and a face mask.
Rationale:
The best way to teach a child about surgery is through play. The nurse can let the child handle the items that will be used for monitoring, such as the blood pressure cuff and the ECG pads. The child will become more familiar with the face masks he sees the surgical team wearing in the operating room after playing with one and wearing it before surgery. A child of this age-group does not understand detailed explanations of how to use equipment, such as a PCA, a VAS, or even a video. The pain scale that should be used for children is the FACES scale.
Question 205.
The nurse is working on a hospital’s birthing unit when a primigravid client in active labor is to receive morphine. As the nurse enters the medication room, the nurse observes a coworker slipping a vial of morphine into the side pocket of the uniform. Which action would be most appropriate?
(a) Contact the hospital’s security chief.
(b) Notify the supervisor of the unit.
(c) Tell the coworker of the incident.
(d) Notify the federal drug agents about the incident.
Answer:
Rationale:
When a nurse observes the theft of an opioid, it is the responsibility of the nurse to report the incident to the supervisor of the unit. The supervisor of the unit can confront the coworker and notify the hospital’s chief of security about the incident. In some situations, the drug-abusing coworker may be offered drug counseling.
In situations in which the drugs are being sold, the police should be notified. The nurse should not confront the coworker because this may put the nurse in danger. It is not the responsibility of the nurse to notify federal drug agents about the incident.
Question 206.
Which information should the nurse include when teaching the family and a client who was prescribed benztropine, 1 mg PO twice daily, about the drug therapy?
(a) The drug can be used with over-the-counter cough and cold preparations.
(b) The client should not discontinue taking the drug abruptly.
(c) Antacids can be used freely when taking this drug.
(d) Alcohol consumption with benztropine therapy need not be restricted.
Answer:
(b) The client should not discontinue taking the drug abruptly.
Rationale:
The nurse should teach the client and family the importance of not discontinuing benz- tropine abruptly. Rather, the drug should be tapered slowly over a 1-week period. Benztropine should not be used with over-the-counter cough and cold preparations because of the risk of an additive anti-cholinergic effect. Antacids delay the absorption
of benztropine, and alcohol in combination with benztropine causes an increase in central nervous system depression; concomitant use should be avoided.
Question 207.
Which information should the nurse include in a teaching plan that addresses the adverse effects of antipsychotic medication?
(a) information about all potential adverse effects
(b) research data about rare adverse effects
(c) adverse effects that can be seen or felt
(d) percentages associated with each adverse effect
Answer:
(c) adverse effects that can be seen or felt
Rationale:
The nurse needs to focus on adverse effects that can be seen or felt, using a simple, brief, written description of the benefits of the medication and a list of common adverse effects and how to cope with them. The written format helps the client and family feel more in control by participating in treatment.
They also can use the written information as a helpful resource for review. Information about all potential adverse effects, including percentages associated with each, will cause undue anxiety in the client and possibly overwhelm the client and family, negatively affecting compliance. The nurse should use discretion in selecting the content of educational sessions.
Question 208.
A client has nephrotic syndrome. To aid in the resolution of the client’s edema, the health care provider prescribes 25% albumin. In addition to an absence of edema, the nurse should evaluate the client for which expected outcome?
(a) crackles in the lung bases
(b) blood pressure elevation
(c) cerebral edema
(d) cool skin temperature in lower extremities
Answer:
(b) blood pressure elevation
Rationale:
Albumin is a colloid that remains in the intravascular space, pulling fluid out of the intracellular and interstitial space. The client with nephrotic syndrome loses excessive amounts of protein, mainly albumin, in the urine. Because fluid is drawn into the intravascular space, blood pressure will increase. Crackles in the lung bases and cerebral edema are signs of circulatory overload or fluid volume excess. When edema is present in the lower extremities, the skin feels cool to the touch unless an infection is present.
Question 209.
A client has polycystic kidney disease. The client asks the nurse, “How did I get these fluid- filled bubbles on my kidneys?” How should the nurse respond to help the client understand risk factors for this disease?
(a) “Secondhand smoke puts you at greater risk for developing cysts.”
(b) “Exposure to dyes used to color fruits and vegetables increases the risk of polycystic kidney disease.”
(c) “There is a higher incidence of polycystic kidney disease among blood relatives.”
(d) “Drinking alcohol daily allows the kidneys to develop cysts.”
Answer:
(c) “There is a higher incidence of polycystic kidney disease among blood relatives.”
Rationale:
Although it is not clearly understood why cysts form in polycystic kidney disease, the condition is known to be inherited. Environmental exposures such as smoking and breathing secondhand smoke promote development of bladder cancer. Although drinking alcohol requires the kidneys to excrete the alcohol, it is not thought to cause the kidneys to develop cysts. Exposure to dyes used in foods does not increase the risk for polycystic disease.
Question 210.
A nurse is administering IV fluids to a dehydrated client. When administering an IV solution of 3% sodium chloride, what should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Measure the intake and output.
(b) Inspect the jugular veins for distention.
(c) Evaluate the client for neurologic changes.
(d) Encourage the client to drink more fluids.
(e) Insert an indwelling urinary catheter.
Answer:
(a) Measure the intake and output.
(b) Inspect the jugular veins for distention.
(c) Evaluate the client for neurologic changes.
Rationale:
A 3% sodium chloride solution is hypertonic; it will pull fluid into the intravascular compartment and may increase renal perfusion, so intake and output should be monitored. As fluid is pulled into the vasculature, the client may demonstrate signs of fluid overload such as jugular vein distention. Hypernatremia and hyperchloremia will produce neurologic signs and symptoms. Fluids should not be forced in a client with fluid
Question 211.
The nurse is working on a birthing unit with an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). The nurse determines that the UAP understands the type of information to report to the nurse when the UAP reports which information about one of the clients?
(a) an episode of nausea after administration of an epidural anesthetic
(b) contractions 3 minutes apart and lasting 40 seconds
(c) evidence of spontaneous rupture of the membranes
(d) sleeping after administration of IV nalbuphine
Answer:
(c) evidence of spontaneous rupture of the membranes
Rationale:
The nurse expects the UAPCQ assigned to several clients in labor to notify the nurse if the UAP observes that one of the clients has evidence of spontaneous rupture of the membranes. When the membranes rupture spontaneously, there is danger of a prolapsed cord, a medical emergency requiring a cesarean birth.
Nausea may occur after adminis-tration of an epidural anesthetic, but this is not a priority or emergency. Having contractions that are 3 minutes apart and last for 40 seconds is normal during active labor. Because nalbuphine is an analgesic, it is normal for a client to fall asleep after IV administration of this drug.
Question 212.
A client approaches the nurse and asks if she can change health care providers, as she feels her medications are not working the fourth day after being started on the mood stabilizer lithium carbonate. Which response by the nurse is the most appropriate?
(a) “Your medication will take from 1 to 3 weeks to become effective.”
(b) “Which health care provider would you like to be assigned to?”
(c) “Are you sure you want another health care provider?”
(d) “You can take another dose in the afternoon until you are feeling better.”
Answer:
(a) “Your medication will take from 1 to 3 weeks to become effective.”
Rationale:
Lithium carbonate’s onset is 7 to 14 days or longer. Asking about provider preferences or decisions to change providers would not make the medication work more quickly or address the client’s problem. Advising the client to take add additional medications is outside the scope of practices.
Question 213.
The nurse is planning a program about women’s health and cancer prevention for a community health fair. Which information should the nurse include? Select all that apply.
(a) Regular self-exams of the breast and vulva are important self-care activities.
(b) Cancer can be prevented by removing precancerous lesions of the vulva, cervix, or endometrium.
(c) Girls, age 11 to 12, should receive immunization for human papillomavirus (HPV) to prevent cervical cancer.
(d) Smoking cessation reduces the risk of cervical cancer.
(e) There is limited evidence that cancer in women is inherited.
Answer:
(a) Regular self-exams of the breast and vulva are important self-care activities.
(b) Cancer can be prevented by removing precancerous lesions of the vulva, cervix, or endometrium.
(c) Girls, age 11 to 12, should receive immunization for human papillomavirus (HPV) to prevent cervical cancer.
(d) Smoking cessation reduces the risk of cervical cancer.
Rationale:
Educating women about risk factors for cancers of the reproductive system is important. The nurse should encourage women to do breast and vulva self-exams. Limiting sexual activity during adolescence, using condoms, having fewer sexual partners, and not smoking reduce the risk of cervical cancer. Cancer can be prevented from occurring when screening reveals precancerous conditions of the vulva, cervix, or endometrium.
Also, routine screening increases the chance that a cancer will be identified in its early stage. Immunization against HPV is recommended for preteen girls to prevent cervical cancer. Many cancers in women, particularly breast cancer, have a genetic basis, and the woman’s genetic history is an important tool in identifying risk.
Question 214.
A 10-year-old client with rheumatic fever is on bed rest. Which diversional activity would be appropriate for the nurse to encourage?
(a) watching television with the roommate
(b) coloring picture books with the brother
(c) keeping up with the school work
(d) building a bird house
Answer:
(c) keeping up with the school work
Rationale:
The client should be encouraged to keep up with the school work. The developmental task of the school-age child is industry versus inferiority. Keeping up with the peers is very important to this age-group. Watching television does provide rest, but it does not lead to a feeling of accomplishment. Coloring pictures is not an appropriate pastime for this age-group. Making crafts may be too strenuous of an activity for a client on bed rest.
Question 215.
Clients who are receiving parenteral nutrition (PN) are at risk for development of which complication?
(a) hypostatic pneumonia
(b) pulmonary hypertension
(c) orthostatic hypotension
(d) fluid imbalances
Answer:
(d) fluid imbalances
Rationale:
Clients receiving TPN are at risk for a number of complications, including fluid imbalances such as fluid overload and hyperosmolar diuresis. Other common complications include hyperglycemia, sepsis, pneumothorax, and air embolism. Hypostatic pneumonia, pulmonary hypertension, and orthostatic hypotension are not complications of TPN.
Question 216.
The nurse is to administer a bolus starting dose of heparin to a child who is taking penicillin. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Check that the dose is appropriate for the child’s weight.
(b) Note that the onset of the medication will be immediate.
(c) Follow the administration of the bolus of heparin with an IV infusion of heparin 10 units/kg/h.
(d) Monitor partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
(e) Discontinue the penicillin until the PTT is at a therapeutic level.
Answer:
(a) Check that the dose is appropriate for the child’s weight.
(b) Note that the onset of the medication will be immediate.
(d) Monitor partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
Rationale:
Heparin dosage in children is based on the child’s weight. A bolus of heparin is administered by the IV route, and the onset of action is immediate. The PTT is an indicator of the effectiveness of heparin. Following the heparin with a continuous infusion of heparin would cause life- threatening anticoagulation in this child. Penicillin and cephalosporins potentiate the effects of heparin, so the heparin must be carefully titrated to obtain maximum effect without causing an overdose. However, the antibiotic should not be discontinued.
Question 217.
A client is receiving epidural analgesia and has not voided for the last 5 hours. Which action should the nurse take first?
(a) Encourage oral intake of fluids.
(b) Palpate for bladder distention.
(c) Review renal laboratory values.
(d) Stop the infusion of medication.
Answer:
(b) Palpate for bladder distention.
Rationale:
Urinary retention is a common occurrence with epidural analgesia. The nurse should first assess for bladder fullness. There is no indication that the client has a low fluid intake; encouraging fluids is not warranted. A review of laboratory results, specifically blood urea nitrogen and creatinine, may be indicated if urinary retention is first excluded as the cause. The infusion should only be stopped in an emergent situation such as excessive sedation.
Question 218.
The nurse is preparing to start an IV infusion. Before inserting the needle into a vein, the nurse applies a tourniquet to the client’s arm. Which finding indicates the tourniquet has been applied correctly?
(a) The veins are distended.
(b) The veins do not “roll.”
(c) The arm is immobilized.
(d) Arterial circulation is occluded.
Answer:
(a) The veins are distended.
Rationale:
Applying a tourniquet obstructs venous blood flow and, as a result, distends the veins. A tourniquet does not stabilize veins or immobilize the arm, nor is it applied to occlude arterial circulation.
Question 219.
Prochlorperazine is prescribed postoperatively. The nurse should evaluate the drug’s therapeutic effect when the client expresses relief from which symptom?
(a) nausea
(b) dizziness
(c) abdominal spasms
(d) abdominal distention
Answer:
(a) nausea
Rationale:
Prochlorperazine is administered postoperatively to control nausea and vomiting. Prochlorperazine is also used in psychotherapy because of its effects on mood and behavior. It is not used to treat dizziness, abdominal spasms, or abdominal distention.
Question 220.
A 17-year-old client has been admitted to the hospital for a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of bone cancer. The nurse should assess the client for which conditions? Select all that apply.
(a) cough
(b) dyspnea
(c) pain
(d) swelling
(e) fever
(f) anorexia
Answer:
(a) cough
(b) dyspnea
(c) pain
(d) swelling
Rationale:
Cough and dyspnea can be present at the time of diagnosis of bone cancer, indicating that the cancer has metastasized to the lungs. About one-quarter of all adolescents with bone cancer have lung metastasis at the time of diagnosis. Pain and swelling result from the inflammation caused by the bone tumor and the increased vascularity of the tumor.
At the time of diagnosis, fever, anorexia, and decreased range of motion have not occurred. The tumor involves the bone, so there is pain when pressure is exerted on the involved bone, but range of motion is not affected. Fever and anorexia can occur if extensive metastasis has occurred.
Question 221.
A nurse on the labor and birth unit transfers a primiparous client and her term neonate to the mother-baby unit 2 hours after the client gave vaginal birth to the neonate. Which information is a priority for the nurse to report to the nurse receiving the client on the mother-baby unit?
(a) firm fundus when gentle massage is used
(b) evidence of bonding well with the neonate
(c) labor that lasted 12 hours with a 1-hour second stage
(d) temperature of 99°F (37.4°C) and pulse rate of 80 bpm
Answer:
(a) firm fundus when gentle massage is used
Rationale:
The priority assessment is that the client has a firm fundus when gentle massage is used. This indicates that the client’s fundus may be soft or “boggy” when it is not massaged. The receiving nurse should assess the client’s fundus soon after admission and continue to monitor the client’s fundus, lochia, and pulse rate. Postpartum hemorrhage is associated with uterine atony. Maternal-infant bonding is a process that usually starts on day 2 and ends at week 1. A 12-hour labor is normal. The temperature and pulse are within normal limits.
Question 222.
A client who underwent cardiac surgery 2 days ago is recovering well. His wife, who is assisting with his care, says, “He’s doing too much. I told him to let me help, but he won’t let me.” The nurse says to the wife, “It sounds like you need to feel you can be more helpful to him.” In order to make the nonverbal behavior complement the words, what should the nurse do?
(a) Direct the eyes at the client.
(b) Direct the body and eyes at the wife and client.
(c) Avoid direct eye contact with the client and wife.
(d) Shift the eyes back and forth between the client and wife.
Answer:
(b) Direct the body and eyes at the wife and client.
Rationale:
Assuming cultural appropriateness of eye contact with the client and his wife, this body language would make the nurse’s nonverbal message congruent with the nurse’s verbal message and demonstrate empathy. Directing the eyes only toward the client, rather than including the wife, ignores the wife. Avoiding eye contact with the client and wife or shifting the gaze between the client and wife conveys a lack of assurance about the nurse’s focus and comments.
Question 223.
A nurse is having difficulty establishing a relationship with an aggressive client. What strategy will most likely improve the relationship?
(a) The nurse and the client agree to work to improve their involvement in the therapeutic relationship.
(b) The nurse establishes goals for having only positive interactions with the client.
(c) The nurse agrees to be submissive so the client can dominate the relationship.
(d) The nurse seeks assistance from colleagues to become more aware of the quality of the inter-actions and more sensitive to the dynamics of communication.
Answer:
(d) The nurse seeks assistance from colleagues to become more aware of the quality of the inter-actions and more sensitive to the dynamics of communication.
Rationale:
Colleagues can be a source of suggestions and validation of communication strategies. The nurse has identified difficulty with the relationship and should seek assistance before discussing improved involvement with the client because improved involvement may not be the most appropriate approach. Positive and negative interactions occur in relationships. The frequency of both types of interactions determines the quality of an interpersonal relationship. In a therapeutic relationship, both parties contribute to the relationship; neither one should dominate or be submissive.
Question 224.
The charge nurse on the postpartum unit has received a report about a client who has just experienced a fetal demise and will be ready for transfer out of the labor unit in about 2 hours. The client has asked her primary nurse if she can stay on the obstetrical unit since she has found support from the nursing staff there. What action should the charge nurse on the postpartum unit take?
(a) Request a room for this client on a unit without newborns.
(b) Ask the nurse in labor and birth to discharge the mother as soon as she is physically able to leave.
(c) Talk to the mother first and decide on a location that is mutually agreeable.
(d) Admit the mother to a private room on the postpartum unit.
Answer:
(a) Request a room for this client on a unit without newborns.
Rationale:
The nurse on the postpartum unit should discuss with the client what her wishes are and mutually agree on a location. The charge nurse better understands the current and future needs of the client experiencing this type of loss as the client may or may not be thinking well or clearly at the moment. The postpartum unit is full of sounds of infants, and although being in a room by herself may support the need for separation, it is often in the best interest of the client to locate her away from the noise of the babies.
Placing the client on another unit will remove her from the support she is seeking. On the other hand, she will not be hearing crying infants. This has often been the location for someone experiencing a loss. Discharging the mother home as soon as she is stable physically is also a possibility, but the nurse must also assess the client’s emotional stability and preferences for grieving.
Question 225.
A 12-month-old child is seen in the neighborhood clinic for a regular checkup. Which statement by the child’s mother about the influenza vaccine reflects the need for more teaching?
(a) “Yearly influenza vaccinations are recommended to begin as early as 6 months of age.”
(b) “The Haemophilus influenzae vaccine my child has already received helps protect against some forms of influenza.”
(c) “My child is too young to receive the live attenuated intranasal vaccine.”
(d) “The first time a child receives the influenza vaccine, a second dose is recommended in 1 month.”
Answer:
(b) “The Haemophilus influenzae vaccine my child has already received helps protect against some forms of influenza.”
Rationale:
Haemophilus influenzae is a bacterium that can cause severe disease in children younger than 5 years, but it does not cause influenza. Yearly vaccination for influenza is recommended to begin at 6 months. The live vaccine is not recommended for children younger than 2 years or with respiratory disease. A second vaccine, 4 weeks after the first, is recommended the first time a child younger than 9 years receives the flu vaccine.
Question 226.
A nurse is about to conduct a sexual history for a 16-year-old female who is accompanied by her mother. What is an appropriate question for the nurse to ask this client or her mother?
(a) “What do you think about having your mother leave the room now?”
(b) “Mother, do you think your daughter is sexually active?”
(c) “Mother, I am going to ask you to wait a few minutes in the waiting room now so I can complete the health history with your daughter.”
(d) “The two of you seem like you share every thing. I’m going to ask questions about sexual history now.”
Answer:
(c) “Mother, I am going to ask you to wait a few minutes in the waiting room now so I can complete the health history with your daughter.”
Rationale:
Confidentiality and privacy are critical developmental needs for the adolescent. These needs are important to enable the nurse to establish a relationship of trust with the adolescent. A sexual history should be conducted with a teen without parents.
Therefore, the nurse should not ask the mother to provide information or put the daughter in a position of having to make a decision about her mother remaining in the room. Inform the adolescent that this information is confidential and will not be shared with the parent. Inform the adolescent that issues of abuse or life-threatening issues are required by law to be disclosed to the authorities, and all other information is private.
Question 227.
A nurse is admitting an older female client to the gynecology surgical unit. When the nurse asks the client what medication she is taking at home, the client responds that she is taking a little red pill in the morning and a white capsule at night for her blood pressure. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Consult the pharmacist regarding identification of the medications.
(b) Show pictures to the client from the Physician’s Desk Reference to identify the medications.
(c) Consult the previous medical record from 2 years ago, and notify the health care provider regarding medications that must be prescribed.
(d) Ask a family member to bring the medications from home in the original vials for proper identification and administration times.
Answer:
(d) Ask a family member to bring the medications from home in the original vials for proper identification and administration times.
Rationale:
It is critical for medication safety to know the name, dosage, and times of administration of the medication taken at home. The family should bring the medication bottles to the hospital. The nurse should document the medication on the medical record Q3 from the bottles to ensure accuracy before the medication is prescribed and administered.
The pharmacist is a helpful resource, but the safest way to identify the medication is in its original container. It is not safe to assume the client could correctly identify the medications from a drug book. The medication regimen may have changed since the record 2 years ago.
Question 228.
A client who had undergone an abdominal hysterectomy is in the recovery room. The surgeon has prescribed a 250-mL bolus of normal saline over 1 hour to replace blood loss. The IV solution infusing in the client was 1,000 mL normal saline with 40 mEq of potassium chloride at 100 mL/h. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Increase the IV infusion rate to 250 mL/h for 1 hour.
(b) Add 250 mL of normal saline to the current infusion bag, and continue at 100 mL/h.
(c) Connect a 250-mL bag of normal saline to the Y-connector, and calculate to infuse over 1 hour.
(d) Contact the health care provider regarding continuation of the primary IV infusion during the bolus infusion.
(e) Administer the normal saline bolus via an IV infusion pump.
Answer:
(c) Connect a 250-mL bag of normal saline to the Y-connector, and calculate to infuse over 1 hour.
(d) Contact the health care provider regarding continuation of the primary IV infusion during the bolus infusion.
(e) Administer the normal saline bolus via an IV infusion pump.
Rationale:
The additional fluids should run through a separate line using a Y-connector. The nurse must contact the surgeon to clarify if the client should receive the additional 100 mL/h of IV fluids containing potassium chloride during the bolus infusion. Rapid infusion of potassium chloride can cause hyperkalemia with adverse cardiac outcomes such as arrhythmias. Bolus infusions of IV fluids should be run via an infusion pump to avoid excess fluid administration. Increasing the current IV infusion rate or adding additional fluids to the existing infusion is not safe because the current infusion contains potassium.
Question 229.
The nurse working the mother-baby unit teaches the client about the facility’s measures to prevent infant abduction. What precautions does the nurse discuss? Select all that apply
(a) Carry your baby in your arms back to the nursery if you plan to nap.
(b) Infant footprints and a color photograph are taken soon after birth.
(c) Only let staff wearing an appropriate ID badge transport your baby.
(d) Notify the staff about anyone who appears unusual.
(e) Make sure the staff compares your ID bracelets to your baby’s daily.
Answer:
(b) Infant footprints and a color photograph are taken soon after birth.
(c) Only let staff wearing an appropriate ID badge transport your baby.
(d) Notify the staff about anyone who appears unusual.
Rationale:
Infants should always be transported in a bassinette or crib in the hallways. A baby in arms outside of a parent room should trigger activation of infant abduction protocols. Footprints and a photograph taken by 2 hours after birth serve as ID should there be an unforeseen separation from the parent. Clients should only let staff wearing appropriate ID take their baby from their room. Clients should notify staff if they see anyone who looks suspicious on the unit. ID badges should be matched each and every time an infant is taken from or returned to the parent not just on a daily basis.
Question 230.
Clozapine therapy has been initiated for a client with schizophrenia who has been unresponsive to other antipsychotics. The client states, “Why do I have to have a blood test every week?” Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate?
(a) “Weekly blood tests are necessary to determine safe dosage and to monitor the effect of the medication on the blood.”
(b) “Weekly blood tests are done so that you can receive another week’s supply of the medication.”
(c) “Your health care provider (HCP) will want to know how well you’re progressing with the medication therapy.”
(d) “Everyone taking clozapine has to go through the same procedure because it’s required by the drug company.”
Answer:
(a) “Weekly blood tests are necessary to determine safe dosage and to monitor the effect of the medication on the blood.”
Rationale:
The client needs specific information about the effects of the drug, specifically that the drug can cause agranulocytosis. The statement about weekly blood tests to determine safe dosage and monitoring for effects on the blood gives the client specific information to ensure follow-up with the required protocol for clozapine therapy. Lack of accurate knowledge can lead to noncompliance with necessary follow-up procedures and noncompliance with medication.
The supply of medication is not dependent on blood testing. Telling the client that the HCPta wants to know the progress does not provide specific information for this client. The blood tests are not required by the drug company.
Question 231.
The nurse administers an intradermal injection to a client. Proper technique has been used if the injection site has which appearance?
(a) minimal leaking
(b) no swelling
(c) tissue pallor
(d) evidence of a bleb
Answer:
(d) evidence of a bleb
Rationale:
A properly administered intradermal injection shows evidence of a bleb at the injection site. There should be no leaking of medication from the bleb; it needs to be absorbed into the tissue. Lack of swelling at the injection site means that the injection was given too deeply. The presence of tissue pallor does not indicate that the injection was given correctly.
Question 232.
The sudden onset of which sign indicates a potentially serious complication for the client receiving an IV infusion?
(a) noisy respirations
(b) pupillary constriction
(c) halitosis
(d) moist skin
Answer:
(a) noisy respirations
Rationale:
A serious complication of IV therapy is fluid overload. Noisy respirations can develop as a result of pulmonary congestion. Additional symptoms of fluid overload include dyspnea, crackles, hypertension, bounding pulse, and distended neck veins.
Question 233.
The nurse is planning to start a blood transfusion. Which solution should the nurse select to prime the tubing when preparing to administer the blood?
(a) lactated Ringer’s solution
(b) normal saline
(c) 5% dextrose in half-normal saline
(d) 5% dextrose in water
Answer:
(b) normal saline
Rationale:
Only isotonic (normal) saline should be used when administering a blood transfusion. The use of dextrose or lactated Ringer’s solution will cause the hemolysis of red blood cells.
Question 234.
The health care provider (HCP) is calling in a prescription for ampicillin for a neonate. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Write down the prescription.
(b) Ask the HCP to come to the hospital and write the prescription on the medical record.
(c) Repeat the prescription to the HCP over the telephone.
(d) Ask the HCP to confirm that the prescription is correct.
(e) Ask the nursing supervisor to cosign the telephone prescription as transcribed by the nurse.
Answer:
(c) Repeat the prescription to the HCP over the telephone.
(d) Ask the HCP to confirm that the prescription is correct.

Rationale:
The nurse should write down the prescription, read the prescription back to the HCP EDI, and receive confirmation from the provider that the prescription is correct as understood by the nurse. It is not necessary for the HCP to come to the hospital to write the prescription on the medical record QJ or to have the nursing supervisor cosign the telephone prescription.
Question 235.
The nurse is planning care for a client who has been experiencing a manic episode for 6 days and is unable to sit still long enough to eat meals. Which choice will best meet the client’s nutritional needs at this time?
(a) a green salad topped with chicken pieces
(b) a peanut butter sandwich
(c) a bowl of vegetable soup
(d) favorite foods from home
Answer:
(b) a peanut butter sandwich
Rationale:
Giving the client finger foods that have protein, carbohydrates, and calories supplies energy and allows the client to eat while on the move. A salad or soup is very difficult for the client to eat while moving and may not supply the nutrients needed. Favorite foods from home may or may not be appropriate to eat while walking.
Question 236.
The nurse is conducting health assessments for school-age children. Which play preferences would the nurse anticipate finding in a 7-year-old girl?
(a) likes to play only with other girls
(b) prefers to play with her sister
(c) prefers to play team games
(d) likes to play alone
Answer:
(a) likes to play only with other girls
Rationale:
Seven-year-olds like to play with friends of the same sex. In early school-age years, children enjoy the company of same-sex friends. Relatives become second-choice friends to those from school. Team games can be competitive, and the ego of a 7-year-old may be too fragile to endure losing the game without losing self-confidence. Infants enjoy solitary play- The school-age child enjoys cooperative plav with friends of the same sex and age.
Question 237.
The nurse on a mental health unit cares for a client who asks the nurse for a date. What action should the nurse take in this situation?
(a) Avoid the embarrassing situation by walking away from the client.
(b) Confront the client for unprofessional behavior.
(c) Explain the limits of the nurse-client relationship.
(d) Understand that the client’s behavior is related to their illness.
Answer:
(c) Explain the limits of the nurse-client relationship.
Rationale:
The nurse sets professional limits by defining the therapeutic relationship, an important aspect of treatment when a client is testing limits or attempting to manipulate staff. Avoiding the behavior does not give a clear message to the client. Confronting the behavior may antagonize the client without also giving the limits expected of all clients. Rationalizing the behavior does not address the inappropriate behavior of the client and does not give a foundation for future expectations of behavior.
Question 238.
A woman who gave birth to a healthy baby 6 hours ago is having cramps in her legs. Upon further assessment, the nurse identifies leg pain on dorsi- flexion. What action should the nurse take?
(a) Tell the woman to massage the area.
(b) Apply warm compresses to the area.
(c) Instruct the woman on how to do ankle pumps.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Rationale:
The client is experiencing signs of thrombophlebitis. The nurse should notify the HCP Q3 because emboli formation is a potential risk. Massaging the area may cause the thrombus to dislocate and become an embolus. Warm compresses will increase circulation to the area and may precipitate embolus formation. Ankle pump exercises are helpful in preventing thrombophlebitis but will not prevent further risk of embolus formation at this time.
Question 239.
After instructing a middle-aged woman about osteoporosis after menopause, the nurse determines that the client needs further instruction when the client makes which statement?
(a) “A standard serving of yogurt is the equivalent of one glass of milk.”
(b) “Women who don’t eat dairy products should consider calcium supplements.”
(c) “Women of African descent are at the greatest risk for osteoporosis.”
(d) “Estrogen therapy at menopause can reduce the risk of osteoporosis.”
Answer:
(c) “Women of African descent are at the greatest risk for osteoporosis.”
Rationale:
Small-boned, fair-skinned women of northern European descent are at the greatest risk for osteoporosis, not women of African descent. One standard serving of yogurt is the equivalent of one glass of milk. Women who do not eat dairy products, such as women who are lactose intolerant, should consider using calcium supplements. Inadequate lifetime intake of calcium is a major risk factor for osteoporosis. Estrogen therapy, or some of the newer medications that are not estrogen based, can greatly reduce the incidence of osteoporosis.
Question 240.
A young adult is hospitalized with a seizure disorder. The client, who is in a bed with padded side rails, has a tonic-clonic seizure. In what order from first to last should the nurse take the actions? All options must be used.
(a) Loosen clothing around the client’s neck.
(b) Turn the client on his or her side.
(c) Clear the area around the client.
(d) suction the airway.
Answer:
(c) Clear the area around the client.
(a) Loosen clothing around the client’s neck.
(b) Turn the client on his or her side.
(d) suction the airway.
Rationale:
The goal of care for a client who is having a seizure is to prevent respiratory arrest and aspiration. The nurse should first clear the area around the client. Next, the nurse should loosen clothing around the client’s neck and turn the client on the side. As needed, the nurse can then suction the airway and administer oxygen.
Question 241.
A client with metastatic cancer of the liver tells the nurse about being concerned about the prognosis. How should the nurse respond to the client?
(a) Provide information for the client to consider a liver transplantation.
(b) Assure the client that the prescribed medications will shrink all tumor sites.
(c) Explain the effects of chemotherapy.
(d) Place emphasis on providing symptomatic and comfort measures.
Answer:
(d) Place emphasis on providing symptomatic and comfort measures.
Rationale:
There is no cure for metastatic cancer of the liver; palliative nursing care is required. Liver transplants are not recommended for the client with widespread malignant disease. Prescribed medications will not make metastatic lesions shrink. There is nothing to indicate that the client is receiving chemotherapy; therefore, explaining its effects would not be helpful.
Question 242.
The nurse delegates the care of a multiparous client who gave birth to a viable term neonate vaginally 30 hours ago and is preparing to be discharged to a licensed practical/vocational nurse (LPN/VN). The nurse should instruct the LPN/VN to notify the nurse if the client exhibits which sign or symptom?
(a) pulse rate of 100 bpm
(b) oral temperature of 99°F (37.2°C)
(c) large amounts of perspiration
(d) frequent voiding in large amounts
Answer:
(a) pulse rate of 100 bpm
Rationale:
During the first week postpartum, the client’s pulse rate should be slow, with an average of 60 to 70 bpm. A pulse of 100 bpm warrants further investigation to rule out a possible infectious process or postpartum hemorrhage. An oral temperature of 99°F (37.2°C) is within normal limits. Excessive perspiration and frequent voiding in large amounts are caused by the normal diuresis that occurs as the body returns to its prepregnant state.
Question 243.
A client with obsessive-compulsive disorder washes the hands multiple times daily and is late for meals and milieu activities. What is most appropriate for the nurse to do initially?
(a) Totally eliminate the client’s ritual.
(b) Allow the client to decide whether to attendmeals and activities.
(c) Inform the client that absence from meals and activities is not permitted.
(d) Remind the client about meal and activity times so that the ritual can be completed on time.
Answer:
(d) Remind the client about meal and activity times so that the ritual can be completed on time.
Rationale:
The nurse should remind the client about meal and activity times so that the ritual can be completed beforehand and not interfere with meals and activities. The client must be allowed to complete the ritual because it keeps anxiety in check. Totally eliminating the client’s ritual will increase anxiety and the need for the handwashing.
Allowing the client to decide to attend meals and activities is not appropriate or in the client’s best interest because the client must perform the ritual to assuage anxiety. Informing the client that absence from meals and activities is not permitted scolds the client, increasing anxiety and the need for the ritual.
Question 244.
A client with osteoarthritis purchased a copper bracelet to wear and tells the nurse that there is less pain now. Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) Tell the client that copper is best applied as copper-lined gloves.
(b) Warn the client not to spend any more money on quackery such as bracelets.
(c) Instruct the client to remove the bracelet because the copper in it can interfere with salicylate metabolism.
(d) Acknowledge that the client feels better, but encourage the client to continue with the prescribed therapy.
Answer:
(d) Acknowledge that the client feels better, but encourage the client to continue with the prescribed therapy.
Rationale:
The nurse should acknowledge that the client feels better but should also remind the client to continue the drug therapy and other self-care activities of rest, exercise, joint protection, and adequate nutrition. Wearing the copper-lined gloves is not harmful, and the nurse should not instruct the client to remove the gloves or label it quackery. Copper does not interfere with salicylate metabolism.
Question 245.
A woman with a history of a left radical mas-tectomy is being admitted for abdominal surgery. The woman has a swollen left arm. What should the nurse do to protect the client’s swollen arm?
(a) Take the blood pressure only in the unaffected arm.
(b) Start an IV line in the affected arm.
(c) Encourage a dependent position of the affected arm.
(d) Allow blood draws in the affected arm.
Answer:
(a) Take the blood pressure only in the unaffected arm.
Rationale:
Lymphedema occurs frequently after radical mastectomy when lymph nodes are removed. Aplasia, or the absence of lymph nodes, prevents proper lymph drainage. The tissue swelling is caused by obstructed lymph flow in the extremity. The blood pressure is taken in the unaffected arm to avoid further accumulation of lymphedema. An IV line should not be started in the affected arm. The nurse would encourage the client to elevate the extremity above the level of the heart. Blood draws in the affected arm should not be allowed.
Question 246.
The nurse has provided an in-service presentation to ancillary staff about standard precautions on the birthing unit. The nurse determines that one of the staff members needs further instructions when the nurse makes which observation?
(a) use of protective goggles during a cesarean birth
(b) placement of bloody sheets in a container designated for contaminated linens
(c) wearing of sterile gloves to bathe a newborn at 2 hours of age
(d) disposal of used scalpel blades in a puncture-resistant container
Answer:
(c) wearing of sterile gloves to bathe a newborn at 2 hours of age
Rationale:
One of the staff members needs further instructions when the nurse observes the staff member wearing sterile gloves to bathe a newly delivered neonate. Clean gloves should be worn, not sterile gloves. Sterile gloves are more expensive than clean gloves and are not necessary when bathing a newly delivered neonate. Goggles should be worn when there is a possibility of blood and body fluid spatter. Bloody sheets should be placed in labeled containers for contaminated linens. Scalpel blades are disposed of in specified containers.
Question 247.
The nurse has completed breastfeeding discharge instructions and determines the mother understands when she makes which statements? Select all that apply.
(a) “My calorie intake will need to increase by 1,0 calories per day.”
(b) “Any drugs that I take may pass through to my breast milk.”
(c) “Babies should have six to eight wet diapersper day after the first 3 days of life.”
(d) “I have the phone number for the lactation consultant if I have questions.”
(e) “Babies should be satisfied from the feeding for 5 to 6 hours after daytime feedings.”
Answer:
(b) “Any drugs that I take may pass through to my breast milk.”
(c) “Babies should have six to eight wet diapersper day after the first 3 days of life.”
(d) “I have the phone number for the lactation consultant if I have questions.”
Rationale:
Maternal intake will need to increase approximately 500 cal/day while breastfeeding. It is true that many drugs taken by the mother cross through breast milk. When any medication is taken by the breastfeeding mom, the medication should be determined to be safe with the OB’s or pediatrician’s office. Infants who have six to eight wet diapers per day have had an adequate intake of breast milk.
If there are fewer, the mother should try to increase the frequency of the infant’s feedings. Within the first 24 to 72 hours of life, there will be fewer wet diapers as the mother’s milk has not come in yet. Prior to discharge, clients should know how to access community resources to support breastfeeding. After a mother’s breast milk is in at about the 3rd day after birth, the infant should be satisfied for approximately IV2 to 3 hours after feeding. There is a need for more frequent feedings with breastfed infants than bottle-fed as the fat content in the breast milk is lower.
Question 248.
The nurse is auscultating for an aortic murmur. Indicate where the nurse should place the stethoscope to best evaluate the presence of this murmur.
Answer:
Rationale:
Correct answer: “X” right of the sternum at the second intercostal space is the best place for listening for the aortic valve sounds.
Question 249.
After a nasogastric (NG) tube has been inserted, which finding helps the nurse determine that the tube is in the proper place?
(a) The client is no longer gagging or coughing.
(b) The pH of the aspirated fluid is measured.
(c) Thirty milliliters of normal saline can be injected without difficulty.
(d) A whooshing sound is auscultated when 10 mL of air is inserted.
Answer:
(b) The pH of the aspirated fluid is measured.
Rationale:
Measuring the pH of the aspirated gastric fluid is the most accurate determination of the placement of the NG tube. A pH lower than 4 indicates that the tube is in the stomach. Whether or not the client is gagging or coughing is not an accurate way to determine if the tube is placed correctly. No fluids should be inserted into the tube until the placement has been determined. Inserting air into the tube and listening for the resulting whoosh can be used, but this is not as accurate as pH measurement.
Question 250.
A client has been diagnosed with early alcoholic cirrhosis. The client should be taught that which behavior could potentially reverse the pathologic changes occurring in the liver?
(a) Do not become fatigued.
(b) Avoid drinking alcohol.
(c) Eliminate smoking.
(d) Eat a high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet.
Answer:
(b) Avoid drinking alcohol.
Rationale:
Alcoholic cirrhosis is associated with excessive alcohol intake. In the early stages, the liver develops fatty changes. If alcohol intake stops, the fatty changes can be reversed. Avoiding overexertion is important in the client with cirrhosis, but it does not reverse the disease. Stopping smoking is a positive, healthy lifestyle change, but it does not have an impact on cirrhosis. A diet high in carbohydrates and low in fat is also recommended for the client with cirrhosis, but the diet does not reverse the pathologic changes that have occurred in the liver.
Question 251.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with sudden onset of chest pain. Which prescriptions should the nurse implement immediately? Select all that apply.
(a) Provide oxygen.
(b) Administer nitroglycerin.
(c) Administer aspirin.
(d) Insert a Foley catheter.
(e) Administer morphine.
(f) Administer acetaminophen.
Anwer:
(a) Provide oxygen.
(b) Administer nitroglycerin.
(c) Administer aspirin.
(e) Administer morphine.
Rationale:
When emergently managing chest pain, the nurse can use the memory mnemonic MONA to plan care: morphine, oxygen, nitroglycerin, and aspirin. A Foley catheter is not included in the emergent management of chest pain and can be inserted when the pain has been relieved and the client is stable. Acetaminophen is not used to manage chest pain.
Question 252.
Which measure should the nurse institute to help minimize joint pain in a child with rheumatic fever?
(a) massaging the affected joints
(b) applying ice to the affected joints
(c) limiting movement of the affected joints
(d) encouraging progressive weight bearing
Answer:
(c) limiting movement of the affected joints
Rationale:
In rheumatic fever, the jointsespecially the knees, ankles, elbows, and wristsare painful, swollen, red, and hot to the touch. Limiting movement of the affected joints typically minimizes pain. Massaging the joints likely will not aid in pain relief because the pain is due to the disease process and subsequent inflammation in the joint.
Applying ice to the affected joints likely will not aid in pain relief because the inflammation, edema, and effusion are too deep in the joint tissue. Exercise should be avoided because of the increased workload placed on the heart muscle. This is in contrast to usual recommendations for clients with other forms of arthritis. Despite joint involvement in rheumatic fever, permanent deformities do not occur.
Question 253.
To reduce the possibility of catheter-related urinary tract infections (CAUTIs), the nurse should take which precaution?
(a) Use sterile technique when providing catheter care.
(b) Ensure that clients who are incontinent have indwelling urinary catheters.
(c) Minimize urinary catheter use and duration of use in all clients.
(d) Clean the periurethral area with antiseptics.
Answer:
(c) Minimize urinary catheter use and duration of use in all clients.
Rationale:
Minimizing urinary catheter use and duration of use in all clients, particularly those at higher risk for CAUTI or mortality from catheterization such as women, older adults, and clients with impaired immunity, will reduce the opportunity for infection. The nurse should avoid the use of urinary catheters for clients who are incontinent;
a bladder training program and frequent use of the toilet are preferred; external catheters may be used if necessary in incontinent clients.
The nurse should not clean the periurethral area with antiseptics; cleansing the meatal surface during daily bathing or showering is appropriate. Using sterile technique to help reduce CAUTI is not necessary. Hand hygiene immediately before and after insertion or any manipulation of the catheter device or site is sufficient.
Question 254.
An older adult is admitted with new-onset confusion, headache, poor skin turgor, bounding pulse, and urinary incontinence has been drinking copious amounts of water. Upon reviewing the lab results, the nurse discovers a sodium level of 122 mEq/L (122 mmol/L). What actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
(a) Encourage fluids to 2,000 mL in 24 hours.
(b) Keep partial side rails up.
(c) Restrict fluids to 800 mL in 24 hours.
(d) Tell the family they may get the client up to walk in the halls.
(e) Prepare to insert a Foley catheter.
(f) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Answer:
(b) Keep partial side rails up.
(c) Restrict fluids to 800 mL in 24 hours.
(e) Prepare to insert a Foley catheter.
(f) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Rationale:
The client is hyponatremic; the nurse should notify the HCP y, restrict fluids, and prepare to insert a Foley catheter to ensure accurate intake and output. Side rails should be up in order to maintain client safety; it is not safe for the client to be ambulating in the hallway with family at this time. Encouraging fluids would not be beneficial and could be harmful.
Question 255.
Following the creation of an ileostomy, a client states, “Pm really worried about how I’m going to manage this thing.” What should the nurse do
first?
(a) Remind the client to focus energy on getting healthy.
(b) Determine the client’s exact concerns about the ileostomy.
(c) Arrange a meeting with the client’s case manager.
(d) Encourage the client’s spouse to talk with the client.
Answer:
(b) Determine the client’s exact concerns about the ileostomy.
Rationale:
While it is important to present options and help find solutions to the client’s financial concerns, the nurse must first listen carefully to those concerns and allow the client to verbalize related emotions in order to identify the client’s needs. Reminding the client to focus on getting well does not address the client’s concerns or needs.
Arranging a meeting with the case manager is premature as the nurse needs to first determine what the client’s needs are. Until the nurse understands the client’s needs, the nurse should not encourage the spouse to discuss the client’s bill with the busi-ness office.
Question 256.
A client who is being treated for nonhealing diabetic foot ulcers tells the nurse angrily, “I’m so frustrated with my doctors. The wound care doctor tells me this won’t heal and I need to have my toes amputated, and another doctor tells me I need to keep going with the antibiotics and dressing changes so I can save my foot. I just want to go home!” After listening to the client’s concerns, what should the nurse do?
(a) Contact the client’s case manager to set up a care conference.
(b) Assure the client that the health care providers (HCPs) know what they are doing.
(c) Remind the client of the responsibilities for health habits regarding diabetes.
(d) Review the FICPs’ progress notes with the client.
Answer:
(a) Contact the client’s case manager to set up a care conference.
Rationale:
The nurse is ultimately responsible to coordinate the client’s care while hospitalized; therefore, it is the nurse’s responsibility to arrange a care conference to help get the client’s questions, concerns, and frustrations addressed. Assuring the client that the HCPs Q know what they are doing does not address the client’s concern or frustration with receiving conflicting information.
While it is true that the client is ultimately responsible for health, asking the client to accept the consequences is a form of blaming the client. The HCPs’ progress notes will not provide information that will address the client’s concern or resolve the conflicting courses of action that the two HCPs are proposing.
Question 257.
While making rounds, the nurse enters a client’s room and finds the client on the floor between the bed and the bathroom. In which order of priority from first to last should the nurse take the actions? All options must be used.
(a) If no acute injury, get help, and carefully assist the client back to bed.
(b) Document as required by the facility.
(c) Assess the client’s current condition and vital signs.
(d) Notify the client’s health care provider (HCP) and family.
Answer:
(c) Assess the client’s current condition and vital signs.
(d) Notify the client’s health care provider (HCP) and family.
(a) If no acute injury, get help, and carefully assist the client back to bed.
(b) Document as required by the facility.
Rationale:
The nurse should first assess the client, and then, if there is no acute injury, help the client get back into bed. The nurse must notify the HCP and the family of the client who fell and, finally, document the event on the client’s health record.
Question 258.
After the birth of a viable neonate, a 20-year- old primiparous client comments to her mother and the nurse about the baby. Which comment would the nurse interpret as a possible sign of potential maternal-infant bonding problems?
(a) “He’s got my funny-looking ears!”
(b) “I think my mother should give him the first feeding.”
(c) “He’s a lot bigger than I expected him to be.”
(d) “I want to buy him a blue outfit to wear when we get home.”
Answer:
(b) “I think my mother should give him the first feeding.”
Rationale:
Avoidance, hostility, or low-key (passive) behavior toward the baby may be a cue to potential bonding problems. The nurse should encourage the client to give the baby the first feeding to begin the bonding process. Expressions of disappointment with the baby’s gender may also signal problems with maternal-infant bonding.
Comparing the baby’s features to her own indicates identification of the neonate as belonging to her, suggesting bonding with neonate. Comparing the actual neonate with the “fantasized neonate” is a normal maternal reaction. Wanting to buy a blue outfit indicates an interest in and connection with the neonate and is a sign of bonding.
Question 259.
A multigravid client in active labor at 39 weeks’ gestation has a history of smoking one to two packs of cigarettes daily. Which problem is the nurse most likely to find during the infant’s assessment?
(a) sedation
(b) hyperbilirubinemia
(c) low birth weight
(d) hypocalcemia
Answer:
(c) low birth weight
Rationale:
Neonates born to mothers who smoke tend to have lower-than-average birth weights. Neonates born to mothers who smoke also are at higher risk for stillbirth, sudden infant death syndrome, bronchitis, allergies, delayed growth and development, and polycythemia. Maternal smoking is not related to higher neonatal sedation, hyperbilirubinemia, or hypocalcemia. Smoking may cause irritability, not sedation.
Hyperbilirubinemia is associated with Rh or ABO incompatibility or the administration of intravenous oxytocin during labor. Approximately 50% of neonates born to mothers with insulin- dependent diabetes experience hypocalcemia during the first 3 days of life.
Question 260.
A multiparous client gives birth to twins at 37 weeks’ gestation. The twin neonates require additional hospitalization after the client is discharged. What is the most appropriate goal to include in the plan of care for the parents while the twins are hospitalized?
(a) Discuss how they will cope with twin infants at home.
(b) Participate in care of the twins as much as possible.
(c) Take turns providing 24-hour observation of the twins.
(d) Identify complications that may occur as the twins develop.
Answer:
(b) Participate in care of the twins as much as possible.
Rationale:
It is important that the parents be allowed to touch, hold, and participate in care of the twins whenever they desire. Ideally, this will be on a daily basis, to promote parent-infant bonding. It is not appropriate to discuss how the couple will cope with twin infants at home until they are ready to take the infants home. They are too overwhelmed at this point and are focused on the well-being of their infants while hospitalized.
Having the couple visit the twins to provide care on a 24-hour basis is not warranted. Identifying complications that may occur is not appropriate. If complications arise, the parents should be well informed and given opportunities for discussion related to the care provided.
Question 261.
A primigravid client in early labor tells the nurse that she was exposed to rubella at about 14 weeks’ gestation. After birth, the nurse should assess the neonate for which complication?
(a) hydrocephaly
(b) cardiac disorders
(c) renal disorders
(d) bulging fontanelles
Answer:
(b) cardiac disorders
Rationale:
Pregnant women who become infected with the rubella virus early in pregnancy risk having a neonate born with rubella syndrome. The symptoms include thrombocytopenia, cataracts, cardiac disorders, deafness, microcephaly, and motor and cognitive impairment. The most extensive neonatal effects occur when the mother is exposed during the first 2 to 6 weeks and up to 12 weeks’ gestation, when critical organs are forming. Bulging fontanelles are associated with increased intracranial pressure and bacterial meningitis. Rubella is not associated with renal defects.
Question 262.
A client has admitted use of cocaine prior to beginning labor. After the infant is born, the nurse should anticipate the need to include which actions in the infant’s plan of care?
(a) urine toxicology screening
(b) notifying hospital security
(c) limiting contact with visitors
(d) contacting local law enforcement
Answer:
(a) urine toxicology screening
Rationale:
A urine toxicology screening will be collected to document that the infant has been exposed to illegal drug use. This documentation will be the basis for legal action for the protection of this infant. If the infant tests positive for cocaine, the legal system will be activated to provide and ensure protective custody for this child. Hospital security would not become involved unless the mother is obtaining or using drugs on hospital premises.
The mother and infant have the same privileges as do any hospitalized clients unless the safety of the infant is jeopardized; thus, limiting contact with visitors would not be appropriate. Local law enforcement agencies would be contacted only if the mother initiates use of drugs on hospital premises, and such contact would be made through the hospital security system.
Question 263.
A neonate born at 30 weeks’ gestation and weighing 2,000 g is admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit. What nursing measure will decrease insensible water loss in a neonate?
(a) bathing the baby as soon after birth as possible
(b) use of eye patches with phototherapy
(c) use of humidity in the incubator
(d) use of a radiant warmer
Answer:
(c) use of humidity in the incubator
Rationale:
Adding humidity to the incubator adds moisture to the ambient air, which helps to decrease the insensible water loss. Bathing and the use of eye patches has no impact on insensible water loss. The use of a radiant warmer will increase the insensible water loss by drawing moisture out of the skin.
Question 264.
A septic preterm neonate’s IV was removed due to infiltration. The nurse prioritizes restarting the IV to help which complication?
(a) fever
(b) hyperkalemia
(c) hypoglycemia
(d) tachycardia
Answer:
(c) hypoglycemia
Rationale:
Neonates that are septic use glucose at an increased rate. During the time the IV is not infusing, the neonate is using the limited glucose stores available to a preterm neonate and may deplete them. Hypoglycemia is too little glucose in the blood; without the constant infusion of IV glucose, hypoglycemia will result. Fevers and hyperkalemia are not related to glucose levels. Tachycardia is the result of untreated hypoglycemia.
Question 265.
The client is Asian and non-English speaking. The nurse arranges for an interpreter who can speak the client’s dialect and begins the health assessment. The client is describing symptoms as numbness, feeling “hot under the skin,” and thinking too much. The nurse should next ask specific questions about which symptom?
(a) depression
(b) constipation
(c) pain
(d) hunger
Answer:
(c) pain

Rationale:
The client may be describing symptoms of pain. Culture-specific symptoms of “feeling bad” include numbness, thinking too much, and feeling hot under the skin. Asian clients may describe pain in terms of Yin and Yang (hot and cold). A nurse’s knowledge of pain associated with health problems is necessary to assist this client in managing pain. Clients from some cultures may associate mental health symptoms with evil spirits and will not report them as being unusual. Clients from Asian cultures may not describe symptoms locally but in a diffuse fashion.
