RN NCLEX Questions focus on client care, health promotion, disease prevention, and the nursing process.
NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 5 with Rationale
Question 1.
The nurse has just received the change-of-shift report on clients in the labor, birth, recovery, and postpartum unit. Which of these clients should the nurse assess first?
(a) an 18-year-old single primigravid client, in labor for 9 hours, with cervical dilation at 6 cm, 0 station, contractions occurring every 5 minutes, and receiving epidural anesthesia
(b) a 24-year-old primiparous client who gave vaginal birth to a 7-lb, 3-oz (3,260-g) boy 1 hour ago, has a firm fundus and scant lochia rubra, and is attempting to breastfeed
(c) a 26-year-old multigravid client, in labor for 8 hours, with cervical dilation at 8 cm, 1+ station, contractions every 3 to 4 minutes, and receiving no anesthesia
(d) a 30-year-old multiparous client who gave birth to a 6-lb, 5-oz (2,863-g) girl by cesarean 3 hours ago, has a firm fundus and scant lochia rubra, and is receiving morphine by patient-controlled analgesia
Answer:
(c) a 26-year-old multigravid client, in labor for 8 hours, with cervical dilation at 8 cm, 1+ station, contractions every 3 to 4 minutes, and receiving no anesthesia
Rationale:
The client who should be assessed first is the multigravid client who has been in labor for 8 hours and whose cervix is 8 cm dilated at 1+ station with contractions every 3 to 4 minutes. A multigravid client typically has a shorter labor than does a primigravid, and this client’s station is 1+, which means that the birth of the fetus is imminent.
Question 2.
A nurse has been working with a battered woman who is being discharged and returning home with her husband. The nurse says, “All this work with her has been useless. She’s just going back to him as usual.” Which statement by a nursing colleague would be most helpful to this nurse?
(a) “Her reasons for staying are complex. She can leave only when she’s ready and can be safe.”
(b) “I know it’s frustrating to work with clients who don’t follow our advice.”
(c) “You did your best. You’ll see her again and have another chance.”
(d) “These women almost never leave for good because of their emotional and financial dependency.”
Answer:
(a) “Her reasons for staying are complex. She can leave only when she’s ready and can be safe.”

Rationale:
The colleague needs to provide the nurse with information about spouse abuse. Giving information about reasons for staying is useful for decreasing the nurse’s frustration. Although expressing empathy is appropriate, it does not help the nurse understand the client’s needs and behaviors.
Telling the nurse that there will be another chance is not helpful and fails to educate the other nurse about the dynamics of abuse. Although dependence is a problem, women who are abused can overcome this and leave if they have support, not criticism. Saying that abused women almost never leave does not help the nurse understand the client’s needs and behavior.
Question 3.
The nurse is to administer ergonovine maleate 200 meg IM. The ampule label reads 0.2 mg/mL. The nurse should administer how many milliliters? Record your answer using a whole number.
......................... mL.
Answer:
1 mL
Rationale:
First, convert micrograms to milligrams:
200 meg = 0.2 mg.
Then:
0.2 mg / X mL = 0.2 mg / lmL X = 1 mL.
Question 4.
An infant is admitted to the hospital with dehydration secondary to viral gastroenteritis. Which room assignment is the most appropriate for this infant?
(a) a semiprivate room with an 8-year-old child who has had an appendectomy
(b) a semiprivate room with a 10-year-old child with a closed head injury
(c) a private room
(d) a semiprivate room with a 4-year-old child with leukemia
Answer:
(c) a private room
Rationale:
Viral gastroenteritis may be communicable, and all of the other children are already at risk for infection. The infant should be placed in a private room.
Question 5.
An older adult is being admitted to the hospital after falling from a 6-foot ladder. Which information is essential for the nurse to obtain at this time? Select all that apply.
(a) symptoms at the time of the fall
(b) history of a previous fall
(c) location of the fall
(d) activity at the time of the fall
(e) time of the fall
(f) trauma after the fall
(g) who was present at the time of the fall
Answer:
(a) symptoms at the time of the fall
(b) history of a previous fall
(c) location of the fall
(d) activity at the time of the fall
(e) time of the fall
(f) trauma after the fall
Rationale:
The acronym SPLATT (symptoms, previous fall, location, activity at the time, time, and trauma) can guide the assessment of an older adult who has fallen. It may be helpful to know if there was someone with the person when the fall occurred to present a bystander’s perspective, but the information is not necessary, and it is more important to get the client to describe in his or her own words what happened.
Question 6.
The nurse is caring for a client with influenza. What is the most effective way to decrease the spread of these microorganisms?
(a) washing the hands frequently
(b) having separate personal care items for the client
(c) using disposable equipment
(d) placing the client in isolation
Answer:
(a) washing the hands frequently
Rationale:
The hands spread disease-causing organisms. Frequent handwashing is essential to decrease the spread of microorganisms. Having separate personal care items for each client does not eliminate the potential for contamination of these items. When practical, using disposable equipment is preferable to sterilization, but it does not override frequent, thorough handwashing for control of infection. Isolating people known to be harboring disease- causing organisms is a cornerstone of infection con-trol, but health care personnel must still wash their hands to avoid spreading disease.
Question 7.
The nurse should be especially alert for what problem when caring for a term neonate, who weighed 10 lb (4,500 g) at birth, 1 hour after a vaginal birth?
(a) hypoglycemia
(b) hypercalcemia
(c) hypermagnesemia
(d) hyperbilirubinemia
Answer:
(a) hypoglycemia
Rationale:
The neonate would be considered large for gestational age (LGA) because the neonate weighs more than 4,000 g (90th percentile). Therefore, the nurse needs to assess for the possibility of complications. Hypoglycemia is a problem for the LGA neonate because glycogen stores are quickly used to maintain the weight. Other common complications for an LGA neonate include hyperbilirubinemia from the bruising and polycythemia, cephalhematoma, caput succedaneum, molding, phrenic nerve paralysis, and a fractured clavicle.
However, hyperbilirubinemia would not be evident 1 hour after birth. Hypercalcemia is not usually found in the LGA neonate. Hypocalcemia is common in infants of diabetic mothers. Hypermagnesemia may occur in neonates whose mothers received large doses of magnesium sulfate to treat severe preeclampsia.
Question 8.
A female client with infertility related to anovulatory cycles is prescribed menotropins. The nurse should assess the client for which possible adverse effects of this medication?
(a) pulmonary edema
(b) ovarian enlargement
(c) visual disturbances
(d) breast tenderness
Answer:
Rationale:
Ovarian enlargement, hyperstimulation syndrome, febrile reaction, and multiple pregnancies are considered adverse effects of menotropins. If ovarian enlargement occurs, the drug should be discontinued to prevent damage to the ovary. Pulmonary edema is not associated with menotropin use. Visual disturbances and breast tenderness are associated with the use of clomiphene citrate, another drug prescribed for infertility.
Question 9.
An older adult is admitted to the hospital with a sudden onset of severe pain in the back, flank, and abdomen. The client reports feeling weak; the blood pressure is 68/31 mm Hg. There has been no urine output. Bilateral leg pulses are weak, although bruit and pulsation are noted at the umbilicus. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Obtain consent for emergency surgery.
(b) Assess leg pulses with a Doppler test.
(c) Palpate the abdomen for the presence of a mass.
(d) Start an IV infusion.
Answer:
(d) Start an IV infusion.

Rationale:
The symptoms noted are classic symptoms of leaking abdominal aneurysm and shock; the client needs immediate fluid volume replacement. Assessing the pulses with a Doppler will be of no additional diagnostic value. Palpating the abdomen on a client with a suspected abdominal aneurysm is contraindicated and could lead to rupture. After emergency fluid resuscitation, consent Q for surgery is needed.
Question 10.
The nurse is teaching a client who will be undergoing a lung resection. The client is told that two chest tubes will be placed during surgery. When the nurse is evaluating the effectiveness of the tube placed lowest in the pleural cavity, what is the purpose of this chest tube?
(a) preventing clots
(b) removing air
(c) removing fluid
(d) facilitating “milking” of the tubes
Answer:
(c) removing fluid
Rationale:
Fluid accumulates in the base of the pleura postoperatively. The lower chest tube, called the posterior or lower tube, will drain serous and sero- sanguineous fluid that accumulates as a result of the surgical procedure. A larger-diameter tube is usually used for the lower tube to ensure drainage of clots. Air rises, and the anterior or upper tube is used to remove air from the pleural space. The practice of “milking” the tubes to prevent clots is becoming less common; the surgeon’s prescriptions must be followed regarding this procedure.
Question 11.
The nurse is giving care to an infant in an oxygen hood (see figure). Which interventions are indicated? Select all that apply.
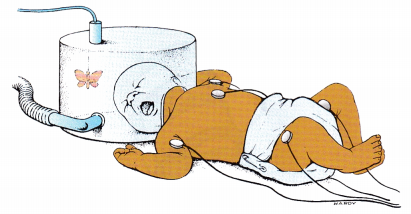
(a) Assure that the oxygen is not blowing directly on the infant’s face.
(b) Place the butterfly mobile on the outside of the hood.
(c) Immobilize the infant with restraints.
(d) Remove the hood for 10 minutes every hour.
(e) Encourage the parents to visit the child.
Answer:
(a) Assure that the oxygen is not blowing directly on the infant’s face.
(b) Place the butterfly mobile on the outside of the hood.
(e) Encourage the parents to visit the child.
Rationale:
When an oxygen hood is used, the nurse should be sure the oxygen source is not directed on the infant’s face to avoid skin irritation. Mobiles can be used to provide visual stimulation, but they should not be placed inside of the hood where they are a potential choking hazard. It is not necessary to restrain the infant unless there is an indication to do so, and the health care provider (HCP) HO has written the prescription.
There should be as little movement in and out of the hood as possible in order to maintain the warm and humid oxygen levels. The nurse should encourage the parents to visit the child and provide verbal and tactile stimulation.
Question 12.
A nurse assesses an 82-year-old for depression. Because of the client’s age, the nurse’s assessment should be guided by which factor?
(a) Sadness of mood is usually present, but it is masked by other symptoms.
(b) Impairment of cognition usually is not present.
(c) Psychosomatic tendencies do not tend to dominate.
(d) Antidepressant therapies are less effective in older adults.
Answer:
(a) Sadness of mood is usually present, but it is masked by other symptoms.
Rationale:
Older adult clients are a high-risk group for depression. The classic symptoms of depression frequently are masked, and depression presents differently in the aging population. Depression in late life is underdiagnosed because the symptoms are incorrectly attributed to aging or medical problems. Impairment of cognition in a previously healthy older adult client or psychosomatic problems may be the presenting symptom of depression. Antidepressant therapy is usually effective.
Question 13.
The nurse teaches a pediatric client about an upcoming procedure. Which approach indicates that the nurse has selected the correct technique for the client’s developmental level?
(a) using dolls and stories to prepare school-age children
(b) preparing an adolescent a few days in advance of the procedure
(c) using puppets and storytelling to prepare a preschooler
(d) preparing a toddler a few hours prior to the procedure
Answer:
(c) using puppets and storytelling to prepare a preschooler
Rationale:
Preschool-age children are best prepared for procedures using play techniques such as puppets and storytelling. School-age children have a grasp of logic and respond well to diagrams, illustrations, videos, and books. Adolescents need to feel that they have had input into their care. They also need more time to build self-confidence. It is best to prepare adolescents a week in advance of a procedure. Toddlers should be prepared just before a procedure will occur.
Question 14.
A 20-year-old single parent brings her toddler into the emergency department because he “fell.” The child has bruises on his face, arms, and legs; his mother says that she did not witness the fall. The nurse suspects child abuse. While examining the child, the mother says, “Sometimes 1 guess I’m pretty rough with him. I’m alone, and I just don’t know how to manage him.” The nurse should ask the mother if she would find it helpful to have which type of referral?
(a) a support group for single parents
(b) a parenting education program
(c) a women’s support group
(d) a support group for abusive parents
Answer:
(b) a parenting education program
Rationale:
The mother’s statements reveal that she is having problems with parenting. Therefore, a referral to a parenting education program is the most appropriate measure at this time. Support groups such as those for single parents, women, or abuse do not address the need identified by this client.
Question 15.
The nurse on the postpartum unit is planning to complete assessments during the last half hour of the shift. Which assessment should be accomplished first?
(a) a postpartum couplet with the infant who has had transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) at birth and now has a respiratory rate of 60 breaths/min
(b) a newly admitted postpartum client who is receiving magnesium sulfate at 3 g an hour initiated 10 hours ago for preeclampsia; her infant ate poorly previously and has not eaten for 4 hours
(c) a mother who had a cesarean birth and is 6 hours after birth with the baby in special care nursery; the mother has not yet seen her baby
(d) a couplet with baby born at 36 weeks’ gestation; the 5-lb (2,268-g) infant had initial blood glucose of 35 mg/dL (1.9 mmol/L) and when taken to the room had a glucose of 46 mg/dL (2.6 mmol/L)
Answer:
(b) a newly admitted postpartum client who is receiving magnesium sulfate at 3 g an hour initiated 10 hours ago for preeclampsia; her infant ate poorly previously and has not eaten for 4 hours
Rationale:
The infant who has not eaten in 4 hours is the highest priority of this group of couplets. The last feeding was 4 hours ago, and the prior poor feeding puts this infant at risk. An assessment of this infant is needed from a safety perspective since the mother had magnesium sulfate. The nurse should question whether the poor feeding may be a result of magnesium sulfate in the newborn’s system by evaluating respiratory rate, tone, and current ability to feed.
The couplet with an infant with TTN and a respiratory rate of 60 is within normal limits but should have the respiratory rate reevaluated to assure normalcy. The mother who had a cesarean birth should be evaluated to determine when she will be able to go to the special care nursery to see her infant. Urgency concerning taking her to the nursery will also depend on the condition of the newborn. The newborn of 36 weeks’ gestation is currently within normal blood glucose range but would need to be monitored frequently because of the small infant size and prior low blood glucose.
Question 16.
An abused child is admitted to the hospital, and the nurse is aware that a court appearance may be necessary. To plan for this eventuality, what should be the priority?
(a) Remember the parents’ and child’s behavior when the child was admitted.
(b) Document physical findings and behaviors observed during the child’s admission.
(c) Formulate subjective opinions about the cause of any injuries.
(d) Prepare answers to questions that may be asked by the attorneys.
Answer:
(b) Document physical findings and behaviors observed during the child’s admission.
Rationale:
When dealing with child abuse, the priority is accurate and complete documentation of physical findings and observed behaviors on the child’s record. Court proceedings usually occur sometime after the nurse’s involvement with the child and family, and memories fade.
Thus, careful documentation of the facts, not hearsay or subjective opinion, is essential. Objective data, not subjective opinions, are key. Preparing answers to questions that may be asked by the attorneys is not a priority for the nurse when the child is admitted. This may become appropriate later.
Question 17.
When assessing a client withdrawing from alcohol, the nurse notes that the client is anxious, experiencing nausea, is restless, and has a tremor when both arms are extended. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Continue to assess the client.
(b) Move the client to a quieter room.
(c) Administer a benzodiazepine as prescribed.
(d) Transfer the client to an acute care psychiatric unit.
Answer:
(c) Administer a benzodiazepine as prescribed.
Rationale:
The client is exhibiting signs and symptoms of withdrawal, and the nurse should administer the benzodiazepine to manage the anxiety, nausea, and restlessness and to prevent seizures. After administering the medication, the nurse will continue to assess the client and ensure the client is in a quiet environment. There is no need to transfer this client to the psychiatric unit based on the information provided.
Question 18.
A female client is experiencing bladder control problems. Which finding indicates the success of nursing interventions to promote urinary continence for this client?
(a) continence for 24 hours a day
(b) improvement in bladder control
(c) self-monitoring for urine retention
(d) compliance with drinking and voiding schedule
Answer:
(a) continence for 24 hours a day
Rationale:
The ultimate goal is to promote urinary continence. Thus, the client being continent for 24 hours a day demonstrates definitive evidence that this goal has been met. Self-monitoring for urine retention is an important aspect of achieving the outcome, but it addresses only one area and does not reflect goal achievement. The same is true for compliance with the drinking and voiding schedule.
Question 19.
Before administering morphine to a client with pain of 8 on a pain scale, the nurse should assess which vital signs? Select all that apply.
(a) blood pressure
(b) respiration rate
(c) pulse
(d) temperature
(e) level of consciousness
Answer:
(b) respiration rate
(e) level of consciousness
Rationale:
Morphine can cause respiratory depression, leading to respiratory arrest. Morphine can also decrease levels of consciousness. The nurse should assess the client’s respiratory rate before administration and throughout the course of analgesic treatment. The nurse should also assess the client’s level of consciousness. Morphine does not affect the blood pressure, pulse rate, or body temperature.
Question 20.
A client is to receive 1 unit of packed red blood cells over 2 hours. There is 250 mL in the infusion bag. The IV administration infusion set delivers 10 gtt/mL. At what flow rate (in drops per minute) should the nurse run the infusion? Record your answer using a whole number.
..................... gtt/min.
Answer:
21 gtt/min
Rationale:
One unit of packed red blood cells contains 250 mL, and this is to infuse over 2 hours (120 minutes). First, determine the number of mL/min by dividing 250 mL by 120 minutes:
250/120 = 2.1 mL/min.
Then, multiply by the drop factor of 10 gtt/mL:
2.1 x 10 = 21 gtt/min.
Question 21.
A mother states that she is very angry with the health care provider who diagnosed her child with leukemia. Which statement helps the nurse understand this mother's reaction?
(a) Anger is a natural result of a sense of loss and helplessness.
(b) Parents of sick children are usually unable to control their anger.
(c) Anger is rarely demonstrated by parents when coping with a sick child.
(d) The mother cannot overcome her anger in an acceptable manner.
Answer:
(a) Anger is a natural result of a sense of loss and helplessness.
Rationale:
Anger is a natural result of feelings of loss and helplessness in normal, healthy people. It is a natural response to coping with a sick child. Nurses should recognize anger in clients and families. Parents are usually able to control their anger in a socially acceptable manner. Nurses can assist clients and families to overcome helplessness and anger in an acceptable manner.
Question 22.
Which nursing strategy would be effective in managing a client who has Alzheimer’s disease and wanders?
(a) Encourage participation in activities such as board games.
(b) Discourage wandering by allowing the behavior at selected intervals.
(c) Involve the client in activities that promote walking.
(d) Promote safety by restraining the client in a geriatric chair.
Answer:
(c) Involve the client in activities that promote walking.
Rationale:
Supervised activities that promote walking are behavioral management strategies that help a client such as this. The client’s cognitive and memory impairment would not be conducive to playing board games. Allowing the behavior at selected intervals would further encourage the client to wan-der. The client should not be restrained in a chair.
Question 23.
A child who had a cast applied to his arm earlier this morning tells the nurse that his fingers are numb. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Notify the health care provider (HCP) who applied the cast.
(b) Cut the cast to loosen it.
(c) Assess the circulation to the fingers.
(d) Ensure that the arm is positioned correctly.
Answer:
(c) Assess the circulation to the fingers.
Rationale:
With a new problem of numbness in the fingers, the nurse needs to first assess the circulation to evaluate color, evidence of swelling, and presence of pulses to determine whether there is any circulatory compromise. Once the nurse has evaluated the child’s circulatory status, the next action would be to verify the arm’s position above the level of the heart. Notifying the HCP would not be done until the child’s neurovascular stains and position are checked. Cutting the cast would be done only with an HCP’s prescription.
Question 24.
A nurse is planning staffing for a nursing unit in which the primary need of the clients is learning how to manage their health problems. Which combination is the ideal mix of staff for this unit?
(a) three registered nurses (RNs)
(b) one RN and two licensed practical/vocational nurses (LPNs/VNs)
(c) one LPN/VN and two unlicensed assistive personnel (UAPs)
(d) one RN, one LPN/VN, and one UAP
Answer:
(a) three registered nurses (RNs)
Rationale:
The ideal staffing for a nursing unit focused on client teaching and learning is to have three registered nurses. It is within the scope of practice for the RN m to assess, plan, implement, coordinate, and evaluate client learning. It is not within the scope of practice for LPNs/VNs 2 and UAP to provide client teaching.
Question 25.
An unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) is taking care of a child in the arm restraint shown in the figure. What should the nurse instruct the UAP to do to provide care for this child?
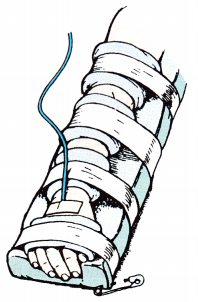
(a) Unpin the restraint and perform range-of-motion exercises.
(b) Unwrap the restraint and bathe the arm using warm water.
(c) Leave the restraint in its current position.
(d) Remove one tape at a time while bathing the child’s arm.
Answer:
(c) Leave the restraint in its current position.
Rationale:
The restraint should remain in position. Removing the restraint or untaping the restraint will risk dislodging the IV.
Question 26.
While helping clients brought to a crisis center during a severe flood, the nurse interviews a client whose pregnant wife is missing and whose home has been destroyed. The client keeps talking rapidly about his experience and says, “I can’t see how I can ever rebuild my life.” Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate?
(a) “If you start organizing your life now, I’m sure all will be fine.”
(b) “This has been a terrible experience. Tell me more about how you feel.”
(c) “Let me note a few of the things you said before you continue with your story.”
(d) “Spend some time thinking about this so that we can continue this conversation tomorrow.”
Answer:
(b) “This has been a terrible experience. Tell me more about how you feel.”
Rationale:
At the time of a major crisis, the client suffering a great loss is best helped by being encouraged to talk about his experience and describe his feelings. Crisis interventions focus on reestablishing emotional equilibrium and preventing decompensation.
Telling the client that everything will be fine is a cliche and inappropriate. Asking the client to stop talking so that the nurse can write notes places more emphasis on the nurse’s needs than on the client’s needs. Telling the client to think more about what happened for further discussion the next day is not helping him with the crisis.
Question 27.
The nurse manager is completing the annual performance appraisals for the registered nurses on the unit. Prior to the meeting with the nurse manager, what is the most important action the nurse who is receiving the appraisal can do to focus on performance improvement and career growth?
(a) Record the date and time of the meeting on the calendar.
(b) Review the job description prior to the meeting.
(c) Determine performance goals for the upcoming year.
(d) Establish a wage increase to request.
Answer:
(c) Determine performance goals for the upcoming year.
Rationale:
Determining the nurse’s own performance goals for the upcoming year is the most important and proactive action. Sharing this information during the appraisal allows the manager the opportunity to offer needed support and sets the performance objectives for the upcoming year.
While the nurse can record the date and time of the meeting on the calendar, developing performance goals will be helpful during the appraisal conference and important to career development. Reviewing the job description is an important action but does not contribute to future planning. The result of the performance appraisal is the determinant for the wage increase.
Question 28.
Which action should the nurse include in the plan of care for a child with leukemia who has an absolute neutrophil count of 400/mm3 (0.4 x 109/L)?
(a) Restrict staff and visitors with active infections.
(b) Place the child in strict isolation.
(c) Consult with the primary care provider to administer an antiemetic.
(d) Increase the child's oral fluid intake.
Answer:
(a) Restrict staff and visitors with active infections.
Rationale:
The child’s neutrophil count is low (the normal range is 3,000 to 5,000 cells/mm [3 to 5 x 10fl/L]), predisposing the child to infection. If an infection occurs, the child will have difficulty combating it. Therefore, staff and visitors should be restricted to those without an active infection. Typically, neutropenic precautions, not strict isolation, would be used to protect the child from exposure to infection.
The hospitalized child would be placed in a private room with visitors and staff screened for illnesses. Temperature would be monitored every 4 hours. Low neutrophil counts do not increase the likelihood of vomiting; therefore, an antiemetic is not needed. Increasing the child’s oral fluid intake may be necessary; however, doing so is unrelated to the child’s neutrophil count.
Question 29.
A client with asthma has been prescribed beclomethasone via metered-dose inhaler. To determine if the client has been rinsing the mouth after each use of the inhaler, the nurse should inspect the client’s mouth for which health problem?
(a) gingival hyperplasia
(b) oral candidiasis
(c) ulceration
(d) dental caries
Answer:
(b) oral candidiasis
Rationale:
Beclomethasone is an inhaled steroid used for the maintenance treatment of asthma. The steroid can precipitate overgrowth of fungus, such as oral Candida albicans. Rinsing the mouth well after each use decreases the incidence of oral fungal infections. Beclomethasone does not cause gingival hyperplasia, ulceration, or caries.
Question 30.
The nurse finds a client lying on the floor next to the bed. After returning the client to bed, assessing for injury, and notifying the health care provider (HCP), the nurse fills out an incident report. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Give the incident report to the nurse-manager.
(b) Place the incident report on the medical record.
(c) Call the family to inform them.
(d) Omit mentioning the fall in the medical record documentation.
Answer:
(a) Give the incident report to the nurse-manager.
Rationale:
The incident report should be given to the nurse-manager. The incident report should not be placed on the medical record because it is considered a confidential communication and cannot be subpoenaed by a client or used as evidence in lawsuits. It is appropriate, ethical, and legally required that the fall be documented in the medical record. Unless there is a change in the client’s condition reflecting an injury from the fall, there is no need to notify the family. If the family does need to be notified, the nurse-manager or the HCP should place the call.
Question 31.
The nurse is caring for four clients in labor. Which client is at most risk for a postpartum hemorrhage?
(a) a client who is a gravida 4 para 3 with a history of polyhydramnios with this pregnancy
(b) a client who is a gravida 1 para 0 at 34 weeks’ gestation with mild pregnancy-induced hypertension
(c) a client who is a gravida 4 para 0 with diet-controlled gestational diabetes being induced at term
(d) a client who is a gravida 2 para 1 term pregnancy with a history of genital herpes
Answer:
(a) a client who is a gravida 4 para 3 with a history of polyhydramnios with this pregnancy
Rationale:
The client who has had three prior births and has polyhydramnios has the potential for uterine atony and would be most at risk for a postpartum hemorrhage. The client at 34 weeks with mild pregnancy-induced hypertension would be at minimal risk because the uterus is not extraordinarily distended at this gestation.
The gravida 4 para 0 client, who has diet-controlled gestational diabetes, has a risk of hemorrhage from being induced, but her uterus should be able to contract appropriately after the birth as long as there is no history of macrosomia. A history of genital herpes is not a risk factor for a postpartum hemorrhage.
Question 32.
The mother of a 2-year-old who has been bitten by the family dog asks the nurse what to do about the bite, which appears to be a minor injury. What should the nurse tell the mother?
(a) “You need to take the child to the local urgent care center immediately.”
(b) “Wash the bite area with lots of running water, and then call your health care provider (HCP).”
(c) “Determine when the child’s latest tetanus vaccine was administered.”
(d) “Make an appointment to see the child’s HCP now to start rabies shots.”
Answer:
(b) “Wash the bite area with lots of running water, and then call your health care provider (HCP).”
Rationale:
General wound care is appropriate initially. This includes washing the bite area with lots of water because infections occur frequently with animal bites, especially those on the arms or hands. Next, the mother should be advised to follow up with the child’s HCP. A trip to the local care center would be warranted if the bite injury was extensive or there was severe bleeding. Although knowledge of when the child last had a tetanus vaccination is important, the child’s wound takes priority. For rabies injections, there needs to be a history of rabies or unusual behavior in the pet.
Question 33.
The nurse is discharging a client who has been hospitalized for preterm labor. The nurse determines that client needs further instruction when she makes which statement?
(a) “If I think I have a bladder infection, I need to see my obstetrician.”
(b) "If I have contractions, I should contact my health care provider (HCP).”
(c) “Drinking water may help prevent early labor for me.”
(d) “If I travel on long trips, I need to get out of the car every 4 hours.”
Answer:
(d) “If I travel on long trips, I need to get out of the car every 4 hours.”
Rationale:
Traveling is usually discouraged if preterm labor has been a problem as it restricts normal movement. A client should be able to walk around frequently to prevent blood clots and to empty her bladder at least every 1 to 2 hours.
Bladder infections often stimulate preterm labor, and to prevent them is of great importance to this client. Contractions that recur indicate the return of preterm labor, and the HCP needs to be notified. Dehydration is known to stimulate preterm labor, and encouraging the client to drink adequate amounts of water helps to prevent this problem.
Question 34.
The nurse is conducting a routine risk assessment at a prenatal visit. Which question would be the best to screen for intimate partner violence?
(a) “Is your partner excited about your pregnancy?”
(b) “How safe do you feel in your home?”
(c) “Does your partner have an arrest record?”
(d) “Does your partner own a gun?”
Answer:
(b) “How safe do you feel in your home?”
Rationale:
The act of screening for intimate partner violence is a key intervention to help open doors for at-risk women to discuss ways to improve their safety and well-being. Asking clients how safe they feel in their home is an open-ended, nonjudgmental way to elicit perceptions of safety.
Asking if a partner is excited about a pregnancy is not a good screening question because many couples are not excited to learn of an unplanned pregnancy. However, couples with healthy relationships eventually adjust. Having an arrest record and gun ownership do not automatically equate to having a history of violence.
Question 35.
A nurse is obtaining the history of an infant with suspected acute otitis media. What should the nurse ask the parent about?
(a) position of the infant when taking a bottle
(b) covering of the infant’s ears when out in the cold
(c) thorough drying of the infant’s ears after a bath
(d) immunization status of the infant
Answer:
(a) position of the infant when taking a bottle
Rationale:
A significant association between feeding position and otitis media exists. Children fed in a supine position have a high incidence of otitis media because of the reflux of milk into the eustachian tubes during feedings. Keeping the infant’s ears covered when out in the cold or thoroughly drying the ears after a bath has not been identified as a contributing factor to an infant’s development of ear infections. Although the infant’s immunization status is always important to ascertain, other factors, such as the position of the infant when taking a bottle, have more impact.
Question 36.
A 7-year-old has been diagnosed with bacterial meningitis. Who should receive chemoprophylaxis?
(a) all children at the school
(b) all household contacts and close contacts
(c) the entire community
(d) household contacts only
Answer:
(b) all household contacts and close contacts
Rationale:
Chemoprophylaxis should be given to household contacts and close contacts only. To prevent community outbreaks, chemoprophylaxis with rifampin 600 mg twice a day for 2 days or a single dose of ciprofloxacin 500 mg is indicated.
Question 37.
The mother of a newborn is concerned about the number of persons with heart disease in her family. She asks the nurse when she should start her baby on a low-fat, low-cholesterol diet to lower the risk of heart disease. At what age does the nurse should tell the client to start modifying her child's diet?
(a) birth
(b) age 2 years
(c) age 5 years
(d) age 10 years
Answer:
(b) age 2 years
Rationale:
Infants and toddlers younger than age 2 should not be placed on a fat-restricted diet because cholesterol and other fatty acids are required for continued neural growth. After age 2, it is believed that no harm is done by encouraging a child to eat a variety of foods, maintain a desirable body weight, limit saturated fat and cholesterol, and increase fiber.
Question 38.
The nurse is preparing to suction a tracheostomy for a client with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (see figure]. What should the nurse do next?
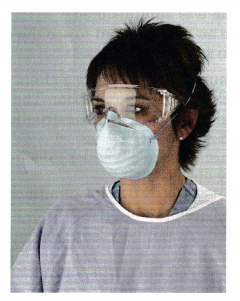
(a) Wear a powered air purifying respirator (PAPR) face shield.
(b) Use goggles that include the hairline.
(c) Change to a surgical mask.
(d) Proceed to suction the client’s tracheostomy.
Answer:
(d) Proceed to suction the client’s tracheostomy.
Rationale:
The nurse is wearing protective personnel equipment appropriate for suctioning the client: goggles, gown, and respirator mask. It is not necessary to wear a PAPR face shield to suction a tracheostomy. A surgical mask does not provide maximum protection.
Question 39.
A client is being treated for severe pediculosis. How should the nurse instruct the client to treat the problem in the eyebrows and eyelashes?
(a) applying petroleum jelly to lashes and brows three to four times a day
(b) applying a pediculicide with a cotton-tipped swab to the eyebrows three times a day
(c) applying lindane ointment to the lashes and eyelashes three times a day
(d) applying bacitracin ointment to the lashes and brows three times a day
Answer:
(a) applying petroleum jelly to lashes and brows three to four times a day
Rationale:
Petroleum jelly is thought to smother the lice. Lindane and other pediculicides should not be applied to the face or close to the eyes. Bacitracin ointment will not kill the lice.
Question 40.
The nurse discusses safety and accident prevention with the parent of a 9-month-old. The nurse understands that the teaching has been effective when the parent makes which statement?
(a) "I make sure that I keep my cleaning supplies locked up.”
(b) “Sometimes she plays in the bathroom when I’m cleaning in there.”
(c) “I’ve enrolled her in an infant water safety classes.”
(d) “I’ve found that those child-protective cabinet locks don’t work very well.”
Answer:
(a) "I make sure that I keep my cleaning supplies locked up.”
Rationale:
A major goal of safety and accident prevention focuses on having all cleaning supplies and medications locked up as infants become mobile. The child should not play in the bathroom even if the parent is present because the child will think that it is okay to play with these items when the parent is not present.
Water safety classes are not recommended for children under the age of 1 year. The child-protective cabinet locks should work unless they were installed incorrectly or are defective.
Question 41.
When the nurse is assessing a child receiving tobramycin sulfate, which findings would indicate that the child is experiencing adverse effects? Select all that apply.
(a) increased blood pressure
(b) weight gain
(c) rash
(d) fever
(e) ringing in the ears
(f) decreased heart rate
Answer:
(c) rash
(d) fever
(e) ringing in the ears
Rationale:
Common adverse effects of tobramycin include nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, fever, and rash. Hypertension, weight gain, and decreased heart rate are not associated with this drug.
Question 42.
The nurse is instructing the client who is taking gentamicin to monitor renal function. The nurse determines that the client needs additional instruction when the client makes which statement? “I should call you if:
(a) I notice that I am not urinating as much.”
(b) my urine looks dark or unusual.”
(c) my legs swell or I notice my skin looks puffy around my eyes.”
(d) I have a fever.”
Answer:
(d) I have a fever.”
Rationale:
Fever is generally not thought to be a sign of impaired renal function related to long-term use of gentamicin. The client should report signs of decreasing urinary function, such as decreased output, unusual appearance of the urine, or edema.
Question 43.
A school-age child is admitted to the hospital with a vasoocclusive sickle cell crisis. How should the nurse prioritize the client’s care? Place interventions in order of highest priority to lowest priority. All options must be used.
(a) Administer morphine for the pain.
(b) start oxygen per nasal cannula.
(c) start an IV infusion
(d) Draw blood for electrolyte and PH balance
Answer:
(c) start an IV infusion
(b) start oxygen per nasal cannula.
(a) Administer morphine for the pain.
(d) Draw blood for electrolyte and PH balance
Rationale:
The nurse first starts an IV as dehydration increases sickling of cells; maintaining fluid balance is a priority. The nurse next starts oxygen and then administers morphine for pain; these actions are followed by obtaining a blood sample for laboratory studies.
Question 44.
When teaching a group of parents about the potential for febrile seizures in children, which information should the nurse include?
(a) The exact cause is known.
(b) The seizures occur as the fever rises.
(c) Children older than age 3 years are most at risk.
(d) These seizures commonly occur after immunization administration.
Answer:
(b) The seizures occur as the fever rises.
Rationale:
Febrile seizures commonly occur as the fever rises. The exact cause of febrile convulsions is not known. Infants and young toddlers are the age- groups primarily affected. Febrile seizures typically do not follow immunization administration.
Question 45.
A 19-year-old primigravid client is being discharged home after hospitalization for hyperemesis gravidarum and is being referred to home health care. The nurse should develop a discharge plan that includes which interventions? Select all that apply.
(a) Refer the client to a nutritionist for the following day.
(b) Ensure that the client has a prescription for an antiemetic.
(c) Ask the health care provider for an anxiolytic prescription.
(d) Encourage return to normal routine when the client feels ready.
(e) Coordinate follow-up appointment with provider in 6 weeks.
(f) Discuss plan of care and discharge instructions with client.
Answer:
(a) Refer the client to a nutritionist for the following day.
(b) Ensure that the client has a prescription for an antiemetic.
(d) Encourage return to normal routine when the client feels ready.
(f) Discuss plan of care and discharge instructions with client.
Rationale:
The nurse case manager should refer the client to a nutritionist so the client is aware of and can be monitored regarding her food intake to assure transition to a normal pregnancy diet with intake of adequate nutrients to support growth and development of the fetus. A PRN (as needed) prescription for an antiemetic is useful to overcome occasional episodes of nausea and vomiting.
Encouraging a return to normal activities when the client feels ready gives the client a goal to look forward to, and activity is not contraindicated in hyperemesis when the client feels ready to initiate activity. Discussion of the plan of care and discharge instructions is a standard of care when discharging a client from a health care facility. There is no indication for an anxiolytic, and hyperemesis gravidarum typically is not associated with anxiety. Six weeks is too long to wait for a follow-up appointment post hospitalization.
Question 46.
The nurse is teaching a female client about taking folic acid supplements for folic acid deficiency anemia. What information should be included in the teaching plan?
(a) It will take several months to notice an improvement.
(b) Folic acid should be taken on an empty stomach.
(c) Iron supplements are contraindicated with folic acid supplementation.
(d) Oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, and lactation increase daily requirements.
Answer:
(d) Oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, and lactation increase daily requirements.
Rationale:
Oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, and lactation are situations that increase demand for folic acid. With supplementation, a response should cause the reticulocyte count to increase within 2 to 3 days after therapy has begun. It is not necessary to take folic acid on an empty stomach. A client may safely take both iron and folic acid supplementation.
Question 47.
The nurse makes a home visit to a primiparous client and her neonate at 1 week after a vaginal birth. Which finding should be reported to the health care provider (HCP]?
(a) a scant amount of maternal lochia serosa
(b) the presence of a neonatal tonic neck reflex
(c) a nonpalpable maternal fundus
(d) neonatal central cyanosis
Answer:
(d) neonatal central cyanosis

Rationale:
Although acrocyanosis may be present for 24 to 48 hours after birth, central cyanosis of the trunk indicates decreased oxygenation from respiratory distress or another disease state (e.g., cardiac anomalies). This should be reported to the HCP m and evaluated further. Maternal lochia serosa in scant amount is a normal finding 1 week postpartum, as is a nonpalpable maternal fundus. Presence of a neonatal tonic neck reflex is a normal finding in a 1-week-old neonate.
Question 48.
The nurse is obtaining a health history for a client with osteoporosis. What should the nurse ask the client about? Select all that apply.
(a) amount of alcohol consumed daily
(b) use of antacids
(c) dietary intake of fiber
(d) use of vitamin K supplements
(e) intake of fruit juices
Answer:
(b) use of antacids
(c) dietary intake of fiber
(d) use of vitamin K supplements
Rationale:
The nurse should ask the client about alcohol use because heavy alcohol use causes fluid excretion resulting in heavy losses of calcium in urine. If the client uses antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, a net loss of calcium can occur. If the client has a high-fiber diet, the fiber can bind up some of the dietary calcium. People with hip fractures have been found to have low vitamin K intakes; vitamin K plays an important role in production of at least one bone protein. Fruit juices do not affect calcium absorption.
Question 49.
Following a sexual assault the client tells the nurse that she is on long-lasting birth control and has no intention of taking any legal action against her assailant. The nurse advises the client that she stills needs follow-up care for early detection of which problem?
(a) sexually transmitted disease
(b) anxiety reaction
(c) periurethral tears
(d) menstrual difficulties
Answer:
(a) sexually transmitted disease
Rationale:
The postrape examination is important for detecting the possibility of sexually transmitted disease, which can be spread through rape. The client should also be examined for infection that can result from trauma. Additionally, if the victim or the rapist was not using a contraceptive, post- coital contraceptive methods should be discussed. The information provided does not indicate anxiety or physical injury, such as periurethral tears, and these are not the primary reason for the examination. Menstrual difficulties are not a common result of rape.
Question 50.
A hospitalized client fell on the floor and sustained a small laceration on the that requires stitches. The intern will suture the client’s hand at the client’s bedside and asks for bupivacaine with epinephrine and a suture kit in order to suture the laceration. Which issue should be resolved before proceeding with suturing?
(a) the intern’s ability to suture
(b) the client’s room as an aseptic environment
(c) bupivacaine with epinephrine used as the local anesthetic
(d) the cosmetic effect from not having a plastic surgeon do the suturing
Answer:
(c) bupivacaine with epinephrine used as the local anesthetic

Rationale:
The nurse should question the use of a local anesthetic agent with epinephrine on the hands or feet because the epinephrine is a vasoconstrictor and can cause ischemia and gangrene of extremities. The nurse should suggest that the intern use bupivacaine without epi-nephrine as the local anesthetic agent. An intern should be trained in suturing small superficial incisions, and the cosmetic effect should be acceptable. The client’s room should be a sufficiently aseptic environment because there is no other client in the room.
Question 51.
A 5-lb 8-oz (2.5 kg) baby was born 1 hour ago to a 19-year-old primigravida. What are the priority nursing assessments for the nurse to monitor?
(a) jaundice and physical assessment
(b) vital signs and gestational age assessments
(c) feedings and vital signs
(d) Apgar and gestational age assessments
Answer:
(c) feedings and vital signs
Rationale:
Infants should be monitored for hypoglycemia, temperature stability, and respiratory distress. The answer that best includes these components is monitoring the infant feedings and vital signs. Apgar assessments are done at 1 and 5 minutes of age, not at 1 hour of age.
The gestational age assessment is important for this infant, but, after completion, does not require additional monitoring. The infant should be regularly assessed for jaundice as part of the physical assessment, but this is not the priority assessment at this time.
Question 52.
When assessing a dark-skinned client for cyanosis, what area of the body will best reveal cyanosis?
(a) retinas
(b) nail beds
(c) oral mucous membranes
(d) inner aspects of the wrists
Answer:
(c) oral mucous membranes
Rationale:
In dark-skinned clients, cyanosis can best be detected by examining the conjunctiva, lips, and oral mucous membranes. Examining the retinas, nail beds, or inner aspects of the wrists is not an appro-priate assessment for determining cyanosis in any client.
Question 53.
Betamethasone syrup 0.9 mg has been prescribed. It is available in a 0.6 mg/5 mL solution. How many milliliters should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal place.
.................. mL.
Answer:
7.5 mL
Rationale:
0.9 mg / X mL = 0.6 mg / 5mL X = 7.5mL
Question 54.
A client at 37 weeks’ gestation is scheduled for an ultrasound. What should the nurse instruct the client to do before the test?
(a) Drink 1 to 2 L of fluid.
(b) Take nothing by mouth after midnight before the test.
(c) Plan to remain in the clinic for 4 hours after the test.
(d) Eat a high-fiber meal after the test.
Answer:
(a) Drink 1 to 2 L of fluid.
Rationale:
The client should plan to drink 1 to 2 L of fluid before an ultrasound to ensure a full bladder, which provides better visualization of the fetus. The client does not need to be on nothing- by-mouth status before the test. The client does not need to remain in the clinic for 4 hours after the test.
However, if the client were scheduled for a contraction stress test, she would be observed as an outpatient for 1 to 4 hours after the test to make certain that the contractions had stopped. The client does not need to eat a high-fiber meal after the test. A high-fiber meal typically is indicated after certain radiographic procedures, such as an upper gastroin-testinal series.
Question 55.
A 12-year-old boy has depression and posttrauma response. The boy’s father is now in jail for molesting him from ages 6 to 9. Given the typical reactions of incest victims, the nurse should assess the child for which behavior? Select all that apply.
(a) sexualized play
(b) aggression
(c) isolation at home
(d) running away
(e) truancy
Answer:
(a) sexualized play
(b) aggression
(d) running away
(e) truancy
Rationale:
Children typically act out their feelings (such as depression and anger) in response to incest. Sexualized play, aggression, running away, and truancy are typical acting-out behaviors. Isolation at home is not common for incest victims who are preadolescents.
Question 56.
The nurse has provided an in-service presentation to ancillary staff about standard precautions on the birthing unit. The nurse determines that one of the staff members needs further instructions when the nurse observes which action?
(a) use of protective goggles during a cesarean birth
(b) placement of bloody sheets in a container designated for contaminated linens
(c) wearing of sterile gloves to bathe a neonate at 2 hours of age
(d) disposal of used scalpel blades in a puncture-resistant container
Answer:
(c) wearing of sterile gloves to bathe a neonate at 2 hours of age
Rationale:
One of the staff members needs further instructions when the nurse observes the staff member wearing sterile gloves to bathe a neonate at 2 hours of age. Clean gloves should be worn, not sterile gloves. Sterile gloves are more expensive than clean gloves and are not necessary when bathing a neonate.
Wearing protective goggles during a cesarean birth is a standard blood precaution. Bloody sheets should be placed in a designated container. Scalpel blades, needles, syringes, and other equipment used during birthing should be disposed of safely in appropriate, labeled containers.
Question 57.
Which is true regarding delegation of client care responsibilities? Select all that apply.
(a) The nurse must know the nursing model that underlies care at the institution.
(b) The nurse delegates in accordance with demands on his/her time.
(c) The nurse confirms that the unlicensed assistive personnel has experience with the delegated activity.
(d) The nurse retains the right to determine which tasks are delegated.
(e) The nurse must document that the task has been delegated and to whom.
Answer:
(a) The nurse must know the nursing model that underlies care at the institution.
(c) The nurse confirms that the unlicensed assistive personnel has experience with the delegated activity.
(d) The nurse retains the right to determine which tasks are delegated.
Rationale:
Delegation involves the reassignment or transfer of selected aspects of a job to selected persons in selected situations. Although responsibility for completion of a task or activity can be delegated, accountability for that task remains with the RN. In delegating nursing acts, functions, or tasks, the RN QJ must consider the nursing model to determine the appropriate delegation of assignment.
Prior to delegation, the RN validates that the non-RN caregiver has orientation and experience in completion of the activity. The amount of time the nurse has does not direct the delegation procedure; the focus is on the task and capability of the staff to whom the task is delegated. It is not necessary to document that the task has been delegated and to whom; however, the outcome of the task should be documented by the nurse.
Question 58.
A child with leukemia had been in remission for several years, but death is now imminent. The nurse is assisting the parents as they prepare for the child’s death. Which approach will be most helpful?
(a) Reflect to the parents that the death of a child is more difficult than that of an adult.
(b) Help parents understand that grief is stronger when preceded by hope.
(c) Recognize that the parents have been prepared for this death since the time of diagnosis.
(d) Understand the parent’s trust in the health care system will be undermined by the death of their child.
Answer:
(b) Help parents understand that grief is stronger when preceded by hope.
Rationale:
Parents often experience greater grief when they have experienced the hope provided by the remission of their child’s disease. The nurse allows the parents to express this grief. Reactions to death of a family member are not based on the age of the dying family member. No matter how well prepared the parents may be for the death of their child, it will not make coping with death easier. Family members may displace anger and frustration on the health care system and health care providers (HCPs) 2, but death does not necessarily undermine trust.
Question 59.
The client has sore nares while a nasogastric (NG) tube is in place. Which nursing measure would be most appropriate to help alleviate the client’s discomfort?
(a) Reposition the tube in the nares.
(b) Irrigate the tube with a cool solution.
(c) Apply a water-soluble lubricant to the nares.
(d) Have the client change position more frequently.
Answer:
(c) Apply a water-soluble lubricant to the nares.
Rationale:
Applying a water-soluble lubricant to the nares helps alleviate sore nares when an NG tube is in place. Repositioning the tube does not eliminate the possibility of irritating the nares. Irrigating the tube with a cool solution or changing positions will not relieve the local irritation from the NG tube.
Question 60.
The nurse is instructing a client who follows Hindu dietary guidelines to increase protein in the diet. Which foods are appropriate to include in this client’s diet? Select all that apply.
(a) lentil soup
(b) hamburger
(c) steak
(d) veal cutlet
(e) broiled fish sandwich
Answer:
(a) lentil soup
(e) broiled fish sandwich
Rationale:
Hindus do not eat beef. Sufficient protein can be obtained from lentils and fish.
Question 61.
The nurse is evaluating the outcome of therapy for a client with osteoarthritis. Which finding indicates goals of therapy have been met?
(a) Joint degeneration has been arrested.
(b) The client is able to self-administer gold compound safely.
(c) The client feels better than on hospital admission.
(d) Joint range of motion has improved.
Answer:
(d) Joint range of motion has improved.
Rationale:
One outcome criterion for the client with osteoarthritis is improved joint mobility. It is probably not possible to arrest the disease. Gold compound is administered to clients with rheumatoid arthritis, not osteoarthritis. Outcome criteria should be specific; feeling better is too general to be useful.
Question 62.
A child with partial- and full-thickness burns is admitted to the pediatric unit. What should be the priority at this time?
(a) preventing wound infections
(b) evaluating vital signs frequently
(c) maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance
(d) managing the child’s pain
Answer:
(d) managing the child’s pain
Rationale:
Although monitoring vital signs frequently is important, for the first few days the primary concern in burn care is fluid and electrolyte balance, with the goal being to replace fluid and electrolytes lost. With burns, fluid and electrolytes move from the interstitial spaces to the burn injury and are lost.
These must be replaced. Once the child’s fluid and electrolyte status has been addressed and fluid resuscitation has begun, preventing wound infection is a priority and efforts to control the child’s pain can be initiated.
Question 63.
A normal, healthy 2-month old infant is brought to the clinic for the first diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DTaP) immunization. Which route is appropriate to administer this vaccine?
(a) oral
(b) intramuscular
(c) subcutaneous
(d) intradermal
Answer:
(b) intramuscular

Rationale:
DTaP vaccine is given intramuscularly and often in combination with other vaccines. The inactivated polio vaccine may be given in either the IM or subcutaneous route. The rotavirus vaccine is given orally. There are no approved intradermal vaccines for 2-month old infants.
Question 64.
A child has been prescribed diphenhydramine hydrochloride to help control the itching from atopic dermatitis. The nurse should instruct the parents to report which conditions? Select all that apply.
(a) weight loss
(b) drowsiness
(c) thick mucous
(d) nausea
(e) bradycardia
Answer:
(b) drowsiness
(c) thick mucous
(d) nausea
Rationale:
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is an antihistamine that blocks the effects of histamine at receptor sites and has atropine-like effects, such as dry mouth, nausea, drowsiness, tachycardia, and thickened bronchial secretions. Weight loss and bradycardia are not adverse effects of this medication.
Question 65.
Assessment of a client in active labor reveals the following: moderate discomfort; cervix dilated 3 cm, 0 station, and completely effaced; and fetal heart rate of 136 bpm. What should the nurse plan to do next?
(a) Assist the client with comfort measures and breathing techniques.
(b) Turn the client from the left side-lying position to the right side-lying position.
(c) Prepare the client for epidural anesthesia to relieve pain.
(d) Instruct the client that internal fetal monitoring is necessary.
Answer:
(a) Assist the client with comfort measures and breathing techniques.
Rationale:
The client’s assessment findings indicate that the client is in the latent phase of the first stage of labor. Therefore, the nurse should plan to assist the client with comfort measures and breathing techniques to relieve discomfort. The client can move around, walk, or ambulate at this phase of labor.
If the client chooses to remain in bed, a left side-lying position provides the greatest perfusion. It is too early for the client to have an epidural anesthetic. Epidural anesthesia is usually administered when the cervix is dilated 4 to 5 cm. The fetal heart rate is normal, so internal fetal monitoring is not warranted at this time.
Question 66.
The nurse observes that a client who has received midazolam for conscious sedation is having shallow respirations at a rate of 8 tolO breaths/min. The heart rate is 75 bpm; blood pressure is 95/65 mm Hg. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Encourage the client to deep-breathe.
(b) Have respiratory resuscitation equipment nearby.
(c) Administer oxygen as prescribed.
(d) Contact the health care provider for a prescription for naloxone.
(e) Notify the anesthesiologist.
Answer:
(a) Encourage the client to deep-breathe.
(b) Have respiratory resuscitation equipment nearby.
(c) Administer oxygen as prescribed.
Rationale:
The nurse should help the client take deep breaths. Resuscitation equipment should always be nearby when a client is recovering from anesthesia. The nurse can administer the oxygen as needed. The nurse does not need to contact the health care provider Q for a prescription for naloxone because naloxone is the antidote for morphine, not midazolam. It is not necessary to contact the anesthesiologist at this time.
Question 67.
The nurse is planning to assist the health care provider with a thoracentesis for a client who has a pleural effusion. Which position for the client would be appropriate for this procedure?
(a) lying supine with the arms extended
(b) lying prone with the head supported by the arms
(c) sitting upright and leaning on an overbed table
(d) side lying with the knees drawn up to the abdomen
Answer:
(c) sitting upright and leaning on an overbed table
Rationale:
The client should be seated upright with the arms raised and crossed in front and supported by the overbed table. The client’s head should rest on the arms. This position allows for outward expansion of the chest wall and promotes collection of the pleural fluid at the base of the thorax. Supine, prone, and side-lying positions will not allow for sufficient chest expansion.
Question 68.
A toddler is admitted with diarrhea and mild dehydration (< 5%). The nurse is reviewing the laboratory report of the stool specimen (see report). Based on the review of the laboratory report from the stool specimen, the nurse should perform which action first?
|
Test |
Result |
|
1. WBC |
Mildly elevated |
|
2. RBC |
Few |
|
3. Bacteria |
Positive for E. coil |
|
4. Ova and Parasites |
Negative |
(a) Start an IV infusion.
(b) Institute enteric precautions.
(c) Instruct the family to wash all family bed linens in hot water.
(d) Cleanse and protect the anal area.
Answer:
(b) Institute enteric precautions.
Rationale:
The stool specimen indicates the client has Escherichia coli in his stool. The nurse institutes enteric precautions and ensures that those who come in contact with the child perform good hand hygiene and wear a gown to prevent spread of infection. Restoring fluid balance is a goal of therapy, but because the dehydration is mild, oral rehydration is the first choice for replacing fluids.
The nurse also cleanses and protects the anal area from irritation from the diarrhea, but on an ongoing basis and not as the priority for care. It is not necessary for the family to wash all of their bed linens, as only those in contact with the client are contaminated
Question 69.
A client has a coxsackie B (viral) or trypano- somal (parasite) infection. The nurse should further assess the client for which health problem?
(a) myocarditis
(b) myocardial infarction
(c) renal failure
(d) liver failure
Answer:
(a) myocarditis
Rationale:
Intracellular microorganisms, such as viruses and parasites, invade the myocardium to survive. These microorganisms damage the vital organelles and cause cell death in the myocardium. The myocardium becomes weak, leading to heart failure; then T lymphocytes invade the myocardium in response to the viral infection.
The T lymphocytes respond to the viral infection by secreting cytokines to kill the virus, but they also kill the virus-infected myocardium. Myocardial infarction, renal failure, and liver failure are not direct conse-quences of a viral or parasitic infection.
Question 70.
The nurse is conducting a medication reconciliation for a client who is being admitted to the hospital. Which is true about the medication reconciliation process? Select all that apply.
(a) Medication reconciliation is an important client safety goal.
(b) Medication reconciliation is designed to obtain and communicate an accurate list of a client’s home medications across the continuum of care.
(c) Only nurses or health care providers (HCPs) can be involved in medication reconciliation.
(d) Medications are considered reconciled if a medication prescription exists that is therapeutically equivalent to the one prior to admission.
(e) A medication is considered to be any medication prescribed by an HCP.
Answer:
(a) Medication reconciliation is an important client safety goal.
(b) Medication reconciliation is designed to obtain and communicate an accurate list of a client’s home medications across the continuum of care.
(d) Medications are considered reconciled if a medication prescription exists that is therapeutically equivalent to the one prior to admission.
Rationale:
A National Patient Safety Goal of the Joint Commission is to accurately and completely reconcile medications across the continuum of care. The requirement is that there is a process for comparing the client’s current medications with those prescribed for the client while under the care of the health care organization. Clients are most at risk during transitions in care (hand-offs) across settings, services, providers, or levels of care.
The development, reconciliation, and communication of an accurate medication list throughout the continuum of care are essential in the reduction of transition- related adverse drug events. The client or client’s family is an integral component of medication reconciliation, particularly at the point of admission to, and discharge from, a health care facility. Any medications that the client uses, for example, over- the-counter medications, must be included in the reconciliation process.
Question 71.
A charge nurse asks a newly graduated registered nurse (RN) who normally works on a medical-surgical nursing unit to take care of two clients in the coronary care unit. The nurse has not had experience with taking care of clients on monitors or using the medications that these clients are taking. What should the new nurse do?
(a) Accept the assignment and then plan to ask the nurses in the coronary care unit to administer the medications for these clients.
(b) Explain to the charge nurse about his or her level of experience and express concerns about this assignment.
(c) Tell the charge nurse that the assignment was to the medical-surgical unit and refuse to go to the coronary care unit.
(d) Ask the charge nurse if the assignment can be reduced to taking care of one client.
Answer:
(b) Explain to the charge nurse about his or her level of experience and express concerns about this assignment.
Rationale:
The nurse should not accept an assignment to “float” to another nursing unit for which the nurse does not have experience or adequate preparation. The first step is to discuss the situation with the person making the assignment; if the situation is not resolved, the newly graduated nurse should ask to speak with the supervisor.
Question 72.
The nurse working in a newborn nursery is caring for several neonates. What precaution is most important for the nurse to take to prevent an infant abduction?
(a) Notify the hospital’s security staff about any one who appears unusual.
(b) Take several neonates to their mothers at the same time.
(c) Place the infant near the doorway of the mother’s room.
(d) Contact the hospital’s security staff if an exit alarm is triggered.
Answer:
(a) Notify the hospital’s security staff about any one who appears unusual.
Rationale:
The nurse should notify the hospital’s security staff about anyone who appears unusual. Typically, the abductor is an older woman who wishes to have a baby. The nurse should take only one baby at a time to a mother to prevent the neo-nate being taken to the wrong mother. Infants should never be left in the hallway. When in the mother’s room, the infant should be placed away from the doorway to prevent or minimize the risk of abduction of the neonate.
If an exit alarm is triggered, it is possible that an abductor is running away with an infant. Staff members should investigate the alarm immediately and stop the potential abductor. Hospital security can be alerted if someone is seen exiting the unit carrying a large bag or an infant.
Question 73.
The nurse assesses a teenage girl’s musculoskeletal system. According to the figure, the nurse should note that the girl which condition?
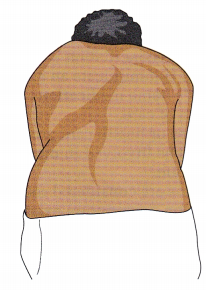
(a) kyphosis
(b) lordosis
(c) spondylolisthesis
(d) scoliosis
Answer:
(d) scoliosis
Rationale:
The teenage girl has scoliosis, the lateral deviation of the spine. Kyphosis is noted by a forward curvature of the shoulders. Lordosis is an inward curvature of the lower back. Spondylolisthesis is a slipping of the vertebrae out of position. Pain is the main finding with this condition, not curvature of the spine.
Question 74.
A child with type 1 diabetes is admitted to the emergency department with hot and dry skin, rapid and deep respirations, and a fruity odor to her breath. Which task, when performed by a new graduate registered nurse (RN), requires the RN preceptor to intervene?
(a) assessment of the child’s vital signs every 15 minutes
(b) verification of the child’s prescription for IV insulin infusion
(c) providing encouragement to the child to drink some orange juice
(d) verification of child’s glucose by finger stick
Answer:
(c) providing encouragement to the child to drink some orange juice
Rationale:
The client is exhibiting symptoms that are consistent with hyperglycemia. The RN does not give any additional glucose. All of the other interventions are appropriate for this client. The new graduate RN notifies the health care provider (HCP) J about the assessment findings.
Question 75.
The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) approaches the nurse and states, "The client doesn’t know what caused him to be so depressed. He must not want to tell me because he doesn’t trust me yet.” In responding to this staff member, which statement by the nurse will help the UAP understand the client’s endogenous depression?
(a) “The client’s depression is biochemical and isn’t caused by an outside stressor or problem. The client can’t tell you why he’s depressed because he really doesn’t know.”
(b) “Various stressors can cause the client’s depression. Perhaps the client isn’t willing to tell you at this time.”
(c) “The client’s depression comes from within the person as a reaction to a loss. You need to give the client more time to identify the cause or loss.”
(d) “Past childhood conflict is causing the client’s depression. It really isn’t important for the client to remember what happened years ago.”
Answer:
(a) “The client’s depression is biochemical and isn’t caused by an outside stressor or problem. The client can’t tell you why he’s depressed because he really doesn’t know.”
Rationale:
The cause of endogenous depression is believed to be biochemical and not a reaction to a loss. It is caused by an imbalance or decreased availability of norepinephrine, serotonin, and possibly dopamine, so the client cannot identify a specific outside cause or a loss.
Reactive depression is a reaction to a loss or a stressor. It is wrong to consider that lack of trust and slow thinking are reasons why the client will not identify the cause of his depression. Problems and stressors from past childhood conflicts may be present; however, the client can discuss them with the staff when he is willing or able.
Question 76.
A parent describes that she is trying to get her toddler to eat well but meal times with have become increasingly frustrating. Which behavior would the nurse suggest that the parent modify to make meals a more pleasant experience?
(a) keeping meal times to about 20 minutes
(b) eating in an environment with few distraction
(c) keeping food portions small
(d) offering several healthy choices
Answer:
(d) offering several healthy choices
Rationale:
It is best to keep choices simple for young children. Too many choices increase the likelihood of creating a picky eater. Meal times should be kept short to align with a toddler’s attention span. Distraction, especially television, should be minimized so the child can focus on eating. Small portions are less overwhelming for small children
Question 77.
Thirty minutes after a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube is inserted, the client appears to be having difficulty breathing. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Remove the tube.
(b) Deflate the esophageal portion of the tube.
(c) Determine whether the tube is obstructing the airway.
(d) Increase the oxygen flow rate.
Answer:
(c) Determine whether the tube is obstructing the airway.
Rationale:
If the gastric balloon should rupture or deflate, the esophageal balloon can move and partially or totally obstruct the airway, causing respiratory distress. The client must be observed closely. No direct action should be taken until the condition is accurately diagnosed.
Question 78.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with myasthenia crisis. What should the nurse do for this client? Place the nursing actions in order of highest priority to lowest priority. All options must be used.
(a) Check if the client missed a dose of medication.
(b) Asses the client for signs of infection
(c) Check the gag reflex.
(d) Prepare for inbulation.
Answer:
(d) Prepare for inbulation.
(c) Check the gag reflex.
(b) Asses the client for signs of infection
(a) Check if the client missed a dose of medication.
Rationale:
Clients with myasthenia crisis have severe muscle weakness that may result in respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. The nurse’s first action is to focus on assuring an adequate airway by preparing for intubation. The nurse can then assess for a gag reflex for risk of aspiration. Once the airway and risk for aspiration are assured, the nurse can assess the client for infection and medication schedule.
Question 79.
A school-age child is diagnosed with pediculosis. The parent is concerned about the spread of the lice to children who have been in contact with her child. What should the nurse instruct the parent to have her child avoid?
(a) sharing craft supplies
(b) having contact during a swimming class
(c) sharing batting helmets
(d) showering after football practice
Answer:
(c) sharing batting helmets
Rationale:
Pediculosis capitis, or head lice, can be spread by close contact or sharing of headgear or combs and brushes with other children. Sharing craft supplies, swimming, and showering usually do not provide close enough contact to permit transmission.
Question 80.
A 24-year-old nulligravid client with a history of irregular menstrual cycles visits the clinic because she suspects that she is “about 6 weeks pregnant.” An ultrasound is scheduled in 2 weeks. What should the nurse tell the client that the primary purpose of the test is?
(a) Assess gestational age.
(b) Determine a multifetal pregnancy.
(c) Identify the gender of the fetus.
(d) Discover fetal malformation.
Answer:
(a) Assess gestational age.
Rationale:
In the first trimester, ultrasound scanning typically is prescribed to determine the gestational age. This is especially important for a client with a history of irregular menstrual cycles to establish an accurate birth date. There is no reason at this point in pregnancy to determine whether twins are present. This might be indicated if the fundal height were larger than the gestational age may indicate.
Identifying the gender of the fetus is not a reason for an ultrasound examination unless there is a history of sex-linked genetic disorders. While an ultrasound may find a major fetal malformation at 6 weeks, the risk for birth defects remains high through the embryonic phase. Ultrasounds are typically done in the second trimester to assess for structural anomalies.
Question 81.
The nurse is beginning the shift and is assessing the oxygen exchange on a neonate. The nurse reviews the medical record for pulse oximetry reading for the last 8 hours.
|
TIME |
0700 |
0900 |
1100 |
1300 |
1500 |
|
Reading |
95% |
90% |
90% |
90% |
90% |
The pulse oximetry reading at 1530 is 75% taken on the infant’s right wrist. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer oxygen via mask.
(b) Obtain a pulse oximeter reading in a lower extremity.
(c) Reassess the oximetry reading in 30 minutes.
(d) Draw blood gases for oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Answer:
(a) Administer oxygen via mask.
Rationale:
The oxygen levels for this neonate have dropped during the last 8 hours; the nurse should administer oxygen, as the neonate is not obtaining adequate oxygenation on room air. The recommended pulse oximetry reading in a term neonate is 95% to 100%. Obtaining a pulse oximeter reading in a lower extremity is done to screen for congenital heart defects.
The priority is to correct the hypoxia first before gathering other assessments. Waiting to reassess the neonate could cause the neonate to have inadequate oxygen levels unnecessarily. While blood gases may be drawn, the first action is to administer the oxygen.
Question 82.
A client with a history of peptic ulcer disease is admitted to the hospital. Initial assessment reveals that the blood pressure is 96/60 mm Hg, with a heart rate of 120 bpm. The client just vomited coffee-ground-like material. Based on these data what should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer an antiemetic.
(b) Prepare to insert a nasogastric (NG) tube.
(c) Collect data regarding recent client stressors.
(d) Place the client in a modified Trendelenburg position.
Answer:
(b) Prepare to insert a nasogastric (NG) tube.
Rationale:
The nurse should prepare to insert an NG tube. The data collected provide evidence that the client is experiencing an upper gastrointestinal bleed secondary to a peptic ulcer. The client will be placed on nothing-by-mouth status, and an NG tube will be inserted to provide gastric decompression and alleviate vomiting.
Administering antiemetics is not a priority action for a client who is hypotensive and vomiting coffee-ground emesis. Assessment of client stressors is appropriate after emergency care has been provided and the client stabilized. A modified Trendelenburg position is inappropriate for clients who are vomiting.
Question 83.
As a nurse begins the shift on the obstetrical unit, there are several new admissions. When anticipating priorities for the shift, the client with which condition would be a candidate for induction?
(a) preeclampsia
(b) active herpes
(c) face presentation
(d) complete placenta previa
Answer:
(a) preeclampsia
Rationale:
The client with preeclampsia would be a candidate for the induction process because ending the pregnancy is the only way to cure preeclampsia. A client with active herpes would be a candidate for a cesarean birth to prevent the fetus from contracting the virus while passing through the birth canal. The woman with a face presentation will not be able to give birth vaginally due to the extended position of the neck. The client with a complete placenta requires a cesarean birth.
Question 84.
In the early postoperative period following abdominal surgery, the nurse notes a bright red, 3" x 5" (7.6 x 12.7 cm) area of drainage on the client’s dressing. What should be the nurse’s first action in response to this observation?
(a) Ignore it because drainage is normal.
(b) Increase the IV flow rate.
(c) Take the client’s vital signs.
(d) Change the dressing.
Answer:
(c) Take the client’s vital signs.
Rationale:
The sudden onset of bright red drainage of this magnitude needs to be further assessed. Assessing vital signs is an important nursing action to determine whether there have been any changes in the client’s status. Additional steps would include reinforcing the dressing and notifying the health care provider (HCP). Increasing the IV flow rate does not address the bleeding. Changing the dressing would be done only if the HCP prescribed it.
Question 85.
A 6-year-old client is diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). When asking this client to complete a task, what techniques should the nurse use to communicate most effectively with him?
(a) Obtain eye contact before speaking, use simple language, and have him repeat what was said. Praise him if he completes the task.
(b) Fully explain to the client the actions required of him and offer verbal praise and a food reward for task completion.
(c) Explain to the client what he is to do, the consequences if he does not comply, and follow through with praise or consequences as appropriate.
(d) Demonstrate to the client what he is to do, have him imitate the nurse’s actions, and give a food reward if he completes the task.
Answer:
(a) Obtain eye contact before speaking, use simple language, and have him repeat what was said. Praise him if he completes the task.
Rationale:
Because the client with ADHD is easily dis- tractible, it is important to obtain eye contact before explaining the task. Simple language and having him repeat what he is told are necessary because of his age. Praise encourages the client to repeat the task in the future as well as building the client’s self-esteem. A full explanation with verbal praise and a food reward is inappropriate because a food reward increases the chance that he will expect a physical reward for completing tasks.
In addition, a full explanation might be too confusing for someone his age. Explaining consequences focuses on punishment, rather than praise. Although demonstration and imitation is an effective teaching method, rewarding with food fosters dependence on food reward for task completion.
Question 86.
A 10-year-old child has blood glucose readings during a 24-hour period. Which reading requires the most immediate intervention?
(a) 50 mg/dL (2.8 mmol/L)
(b) 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L)
(c) 150 mg/dL (8.4 mmol/L)
(d) 200 mg/dL (11.2 mmol/L)
Answer:
(a) 50 mg/dL (2.8 mmol/L)
Rationale:
A normal blood is 70 to 110 mg/dL. Hypoglycemia is an immediate concern. When the brain does not have enough glucose, the client will become rapidly unconscious, and, if uncorrected, seizures and death can result. A reading of 100 mg/dL is normal, and no intervention is necessary. Readings of 150 and 200 mg/dL are elevated and could cause complications but complications from the elevation would not occur as rapidly.
Question 87.
A client has massive bleeding from esophageal varices. In what order from first to last should the interprofessional team provide care for this client? All options must be used.
(a) Control hemorrhaging.
(b) Replace fluids
(c) Relieve the client's anxiety
(d) Maintain a patent airway.
Answer:
(d) Maintain a patent airway.
(a) Control hemorrhaging.
(b) Replace fluids
(c) Relieve the client's anxiety
Rationale:
The goal that has the highest priority when a client has a massive bleed from esophageal varices is to maintain a patent airway. The nurse should position the client to prevent aspiration and assess respirations and oxygen saturation. The nurse should then assist the health care pro-vider (HCP) EH in controlling the hemorrhage by using esophageal balloon tamponade.
Octreotide may be administered to reduce portal pressure. The third priority is to restore circulating blood volume with blood and IV fluids. Esophageal bleeding is an anxiety-provoking event for the client, and although lifesaving measures are the priority, the nurse and health care team should explain procedures to the client and provide reassurance as needed.
Question 88.
Which instruction is most important for the nurse to include in the teaching plan for a client who is taking phenelzine?
(a) Eat a normal amount of salt in the diet.
(b) Drink 10 to 12 glasses of water each day.
(c) Allow 10 days to achieve therapeutic effects.
(d) Avoid foods high in tyramine.
Answer:
(d) Avoid foods high in tyramine.
Rationale:
A client who is taking phenelzine, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, needs to avoid foods that are rich in tyramine because this food-drug combination can cause hypertensive crisis. The client should be given a list of foods to avoid and should report headaches, palpitations, and a stiff neck to the health care provider (HCP) £3 immediately.
The client does not need to restrict or add salt to the diet. Drinking 10 to 12 glasses of water each day is important to teach the client who is receiving lithium therapy. Antidepressant drugs take 2 to 4 weeks to achieve therapeutic effects.
Question 89.
The nurse should closely monitor the client with an open fracture for which complication?
(a) avascular necrosis
(b) compartment syndrome
(c) osteomyelitis
(d) fat embolism syndrome
Answer:
(c) osteomyelitis
Rationale:
Clients with open fractures are particularly susceptible to infections. If not treated promptly, these infections can lead to the development of osteomyelitis. Localized symptoms of osteomyelitis include tenderness, swelling, and warmth at the site of infection, as well as unrelieved severe bone pain. Systemic symptoms include fever, chills, night sweats, and malaise.
Avascular necrosis occurs when the blood supply to a bone is interrupted, most commonly in intracapsular hip fractures. Compartment syndrome is most commonly associated with fractures of the distal humerus and proximal tibia; it results from an increase in pressure on the nerves and blood supply within a closed tissue compartment. Fat embolism syndrome is associated most frequently with fractures of the long bones, ribs, and pelvis, which may or may not be open fractures.
Question 90.
The nurse develops a health education program about preventing the transmission of hepatitis B. The nurse evaluates that the teaching has been effective when the participants identify which activity to be high risk for acquiring hepatitis B?
(a) frequent use of marijuana
(b) ingestion of large amounts of acetaminophen
(c) sharing needles for drug use
(d) ingestion of contaminated seafood
Answer:
(c) sharing needles for drug use
Rationale:
Sharing needles is associated with increased incidence of blood-borne diseases such as hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is not spread through marijuana use. Acetaminophen taken in large amounts can cause severe hepatic necrosis but does not cause hepatitis B. Contaminated seafood is responsible for transmission of hepatitis A.
Question 91.
An adult client being treated with antidepressants for a year has had antianxiety medication added to the treatment regimen. The client says to the nurse, “I’ve reached the bottom of the barrel now. I have to take both fluoxetine and clonazepam to control my symptoms.” What would be the best nurse reply to the client?
(a) “If the medications work, why worry? Just take them and be happy they’re effective.”
(b) “I can understand your concern. Those psychiatric medications are pretty potent.”
(c) “It seems you’re concerned your illness may be worsening. Tell me more about that.”
(d) “You seem to feel guilty about taking psychiatric medication for your illness. There’s nothing to feel guilty about.”
Answer:
(c) “It seems you’re concerned your illness may be worsening. Tell me more about that.”
Rationale:
The nurse should confirm the client’s concern about taking psychiatric medications. Suggesting that he feels guilty is probably too direct, may not be accurate, and may cut off further discussion. Expressing concern is likely to promote further discussion about the reasons for his concern. Telling the client that he is correct feeds any fear or guilt he may feel, and telling him not to worry demeans his concerns.
Question 92.
The nurse is assessing a client who has a long history of uncontrolled hypertension. The nurse should assess the client for damage in which area of the eye?
(a) iris
(b) cornea
(c) retina
(d) sclera
Answer:
(c) retina
Rationale:
The retina is especially susceptible to damage in a client with chronic hypertension. The arterioles supplying the retina are damaged. Such damage can lead to vision loss. The iris, cornea, and sclera are not affected by hypertension
Question 93.
While preparing to provide neonatal care instructions to a primiparous client who gave birth to a term neonate 24 hours ago, what should the nurse include in the client’s teaching plan?
(a) Term neonates generally have few creases on the soles of their feet.
(b) Strawberry hemangiomas deep, dark red dis colorations require laser therapy for removal.
(c) Milia are white papules from plugged sebceous ducts that disappear by age 2 to 4 weeks.
(d) If erythema toxicum is present, it will be treated with antibiotic therapy.
Answer:
(c) Milia are white papules from plugged sebceous ducts that disappear by age 2 to 4 weeks.
Rationale:
Milia are white papules resulting from plugged sebaceous ducts that disappear by age 2 to 4 weeks. Parents should be instructed to avoid scratching them to prevent secondary infection. Term neonates generally have many creases on the soles of their feet. Preterm neonates may have only a few creases due to their immaturity.
Strawberry hemangiomas are elevated areas formed by immature capillaries that will disappear over time. Port-wine stains are deep, dark red discolorations that require laser therapy for removal. Erythema toxicum is a newborn rash or “flea bite” rash that requires no treatment and disappears over time.
Question 94.
Two days after being placed in a cast for a fractured femur, the client suddenly has chest pain and dyspnea. The client is confused and has an elevated temperature. The nurse should assess the client for which health problem?
(a) osteomyelitis
(b) compartment syndrome
(c) venous thrombosis
(d) fat embolism syndrome
Answer:
(d) fat embolism syndrome
Rationale:
Clients with fractures of the long bones such as the femur are particularly susceptible to fat embolism syndrome (FES). Signs and symptoms include chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia, and cyanosis. Changes in mental status are caused by hypoxemia and can be the first symptoms noted in FES. The client can also be restless and febrile and can develop petechiae.
Osteomyelitis is infection of the bone; signs and symptoms of osteomyelitis do not include respiratory symptoms. Compartment syndrome causes signs of localized neurovascular impairment, not systemic symptoms. Venous thrombosis occurs in the lower extremities and is caused by venous stasis.
Question 95.
Which nursing goal is appropriate for the client with hepatitis B? The client will:
(a) adhere to measures to prevent the spread of infection to others.
(b) adhere to a low-sodium, low-protein diet.
(c) verbalize the importance of using sedatives to provide adequate rest.
(d) avoid social activities with friends after discharge from the hospital.
Answer:
(a) adhere to measures to prevent the spread of infection to others.
Rationale:
The client should be taught how to prevent the spread of hepatitis B to others. The client should eat a well-balanced, nutritional diet. There is no need to restrict sodium or protein. Sedatives should be avoided because these are usually detoxified by the liver. It is not necessary for the client to be isolated from family and friends.
Question 96.
An adolescent client on the psychiatric unit shows signs of mild intoxication. When questioned, he states that another client gave him beer, and he refuses to name the client. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Telephone the client’s parents.
(b) Call a community meeting.
(c) Urge the client to tell who gave him the beer.
(d) Call the primary care provider.
Answer:
(b) Call a community meeting.
Rationale:
In this situation, the nurse should call a community meeting. The community meeting serves as a forum for clients to voice their opinions about the environment, receive feedback from staff and other clients, and discuss community concerns, including exploring the problems of daily living. The community meeting can be used to increase peer support and handle confrontation when necessary.
For adolescents, peer pressure is generally more effective in changing behavior than the staff’s influence. Telephoning the client’s parents or urging the client to tell on his friends is authoritative and may lead to increased mistrust of the staff. Calling a primary care provider is not necessary at this time. Rather, a community meeting would be helpful to discuss the problem.
Question 97.
The client with benign prostatic hypertrophy is being transferred from the emergency department to a surgery unit. Which information should be included in the report from the nurse in the emergency department to the nurse responsible for admitting the client?
(a) “A urine specimen was obtained from the client and sent to the laboratory for analysis.”
(b) “The client was catheterized, and 1,100 mL of urine was obtained. The urine appeared cloudy, and a specimen was sent to the laboratory.”
(c) “The client is very cooperative. He is comfortable now that his bladder has been emptied. He had no ill effects from catheterization.”
(d) “The client was in the emergency department for 3 hours because of bladder distention. He is fine now but is being admitted as a possible candidate for surgery.”
Answer:
(b) “The client was catheterized, and 1,100 mL of urine was obtained. The urine appeared cloudy, and a specimen was sent to the laboratory.”
Rationale:
A report about the client’s condition should be as clear, pertinent, and concise as possible. It should be free of subjective information that could be interpreted differently by different caregivers. The report mentioning that a specimen was sent to the laboratory does not indicate how much urine had been drained from the client's bladder and how the urine appeared.
The report describing the client as cooperative is subjective and provides only limited client data. The report that mentions that the client was in the emergency department for 3 hours does not mention the treatment provided.
Question 98.
A client has received an overdose of sym-pathomimetic agents. The nurse should assess the client for which late signs of an overdose? Select all that apply.
(a) hypotension
(b) bradycardia
(c) seizures
(d) profound pyrexia
(d) hypertension
Answer:
(a) hypotension
(c) seizures
(d) profound pyrexia
Rationale:
As the homeostatic responses begin to decompensate, late clinical manifestations from a large overdose of sympathomimetic agents include loss of function of the hypothalamus such as temperature regulation, leading to profound pyrexia, and ectopic brain activity leading to seizures. Hypotension is a late sign that occurs as the vascular system collapses. Hypertension, an earlier sign, pre-cedes hypotension. Tachycardia occurs as a reflex to hypotension, a late sign.
Question 99.
While assessing a neonate at 4 hours after birth, the nurse observes an indentation with a small tuft of hair at the base of the neonate’s spine. The nurse should document this as what finding?
(a) spina bifida cystica
(b) spina bifida occulta
(c) meningocele
(d) myelomeningocele
Answer:
(b) spina bifida occulta
Rationale:
A small tuft of hair and an indentation at the base of the neonate’s spine is termed spina bifida occulta. This condition usually occurs between the L5 and Si vertebrae with failure of the vertebrae to completely fuse. There are usually no sensory or motor deficits with this condition. Spina bifida cystica includes meningocele, myelomeningocele, and lipomeningocele.
Meningocele is characterized by a saclike protrusion filled with spinal fluid and meninges. Usually, this condition is associated with sensory and motor deficits. Myelomeningocele is characterized by a saclike protrusion filled with spinal fluid, meninges, nerve roots, and spinal cord. With myelomeningocele, there are usually sensory and motor deficits.
Question 100.
Which client is at highest risk for developing a urinary tract infection?
(a) a woman who has given vaginal birth to two children
(b) a man with an indwelling urinary catheter
(c) a man with a past medical history of renal calculi
(d) a woman with well-controlled diabetes mellitus
Answer:
(b) a man with an indwelling urinary catheter
Rationale:
Indwelling catheters are considered to be a major contributor to nosocomial infections. Any client with an indwelling catheter is at high risk for developing a urinary tract infection. A history of previous births does not necessarily predispose a client to urinary tract infections.
Clients with a history of renal calculi are not necessarily at risk for developing urinary tract infections unless the renal calculi recur. Clients with diabetes mellitus are at a higher risk for developing urinary tract infections, but this risk can be decreased by maintaining good control over blood glucose levels.
Question 101.
A nurse administers indomethacin to a neonate. What should the nurse do to ensure that the nurse has identified the neonate correctly?
Select all that apply.
(a) Verify the infant’s full name with the parent.
(b) Ask another nurse to confirm that this is the neonate for whom the medication has been prescribed.
(c) Check the neonate’s identification band against the medical record number.
(d) Verify the date of birth from the medical record with the date of birth on the neonate’s identification band.
(e) Compare the number on the crib with the number on the neonate’s identification band.
Answer:
(a) Verify the infant’s full name with the parent.
(c) Check the neonate’s identification band against the medical record number.
(d) Verify the date of birth from the medical record with the date of birth on the neonate’s identification band.
Rationale:
The nurse should use at least two sources of identification prior to administering medication to any client, such as the medical record □ number and the client’s date of birth. Verifying the infant’s full name with the parent provides an additional verification. It is not safe practice to ask another nurse to verify the correct neonate. It is also not safe to use the room number or crib number as a source of identification because neonates’ locations in the hospital change frequently.
Question 102.
Which statement indicates that the client with a peptic ulcer understands the dietary modifications to follow at home?
(a) “I should eat a bland, soft diet.”
(b) “It’s important to eat six small meals a day.”
(c) “I should drink several glasses of milk a day.”
(d) “I should avoid alcohol and caffeine.”
Answer:
(d) “I should avoid alcohol and caffeine.”
Rationale:
Caffeinated beverages and alcohol should be avoided because they stimulate gastric acid production and irritate gastric mucosa. The client should avoid foods that cause discomfort; however, there is no need to follow a soft, bland diet. Eating six small meals daily is no longer a common treatment for peptic ulcer disease. Milk in large quantities is not recommended because it actually stimulates further production of gastric acid.
Question 103.
The client with a nasogastric (NG) tube has abdominal distention. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Call the health care provider (HCP).
(b) Irrigate the NG tube.
(c) Check the function of the suction equipment.
(d) Reposition the NG tube.
Answer:
(c) Check the function of the suction equipment.
Rationale:
When a client with a NG tube exhibits abdominal distention, the nurse should first check the suction machine. If the suction equipment is functioning properly, then the nurse should take other steps, such as repositioning the tube or checking tube patency by irrigating it. If these steps are not effective, then the HCP should be called.
Question 104.
A male client has been diagnosed as having a low sperm count during infertility studies. After giving instructions about causes of low sperm counts, the nurse determines that the client needs further instructions when the client says low sperm counts may be caused by which health problem?
(a) varicocele
(b) frequent use of saunas
(c) endocrine imbalances
(d) decreased body temperature
Answer:
(d) decreased body temperature
Rationale:
Increased, not decreased, body temperature resulting from occupations or infections can contribute to low sperm counts caused by decreased sperm production. Heat can destroy sperm. Varicocele, an abnormal dilation of the veins in the spermatic cord, is an associated cause of a low sperm count. The varicosity increases the temperature within the testes, inhibiting sperm production.
Frequent use of saunas or hot tubs may lead to a low sperm count. The temperature of the scrotum becomes elevated, possibly inhibiting sperm production. Endocrine imbalances (thyroid problems) are associated with low sperm counts in men because of possible interference with spermatogenesis.
Question 105.
The nurse instills 5 mL of normal saline before suctioning a client’s tracheostomy tube. Which indicates the instillation is effective?
(a) The secretions are thinned.
(b) The client coughs.
(c) There is minimal friction when the catheter is passed into the tracheostomy tube.
(d) There is humidification for the respiratory tract.
Answer:
(a) The secretions are thinned.
Rationale:
The primary purpose of instilling 5 mL of normal saline solution before suctioning a tracheostomy tube is to thin the secretions to be suctioned. The saline may stimulate a cough; however, this is not the reason for using saline. The tracheostomy tube is larger than the suction catheter, so the catheter will easily pass into the tube without lubrication. Humidification is provided by a nebulizer if needed.
Question 106.
A client with emphysema is receiving continuous oxygen therapy. Depressed ventilation is likely to occur unless the nurse ensures that the oxygen is administered in which way?
(a) cooled
(b) humidified
(c) at a low flow rate
(d) through nasal cannula
Answer:
(c) at a low flow rate
Rationale:
The client with emphysema has a chronically elevated carbon dioxide level. As a result, the normal stimulus for breathing in the medulla becomes ineffective. Instead, peripheral pressoreceptors in the aortic arch and carotid arteries, which are sensitive to oxygen blood levels, stimulate respirations. This is in response to low oxygen levels that have developed over time.
If the client receives high concentrations of oxygen, the blood level of oxygen will rise excessively, the stimulus for respiration will decrease, and respiratory failure may result. Oxygen is not cooled. Humidification or administration of the oxygen through nasal cannula will not prevent depressed ventilation if the flow rate of the oxygen is too high.
Question 107.
Before cataract surgery, the nurse is to instill several types of eye drops. The surgeon writes prescriptions for 5 gtt of antibiotic in OD and 3 gtt of topical steroid drops in OD. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Contact the surgeon to rewrite the prescription.
(b) Administer the antibiotic in the left eye and the steroid in the right eye.
(c) Administer both types of drops in the right eye.
(d) Contact the pharmacist for clarification of the prescription.
Answer:
(a) Contact the surgeon to rewrite the prescription.
Rationale:
The nurse should not administer drugs without a complete prescription. In this case, the prescription does not contain information about dosage and uses abbreviations that can cause confusion. The surgeon must write a prescription using complete dosages and without abbreviations before the nurse administers the drugs. Relying on the pharmacist for clarification is inappropriate.
Question 108.
Which instructions about breastfeeding should the nurse include when counseling the client?
(a) Apply ice packs to breasts while nursing.
(b) Wrap breasts with ace bandages.
(c) Avoid fruit juices with acid.
(d) Apply breast milk for mild nipple pain
Answer:
(d) Apply breast milk for mild nipple pain
Rationale:
For women with mild nipple trauma, applying breast milk to the nipples is an effective method to reduce pain and promote healing. Ice is applied to decrease breast milk supply, and ace bandages are only used to dry up breast milk. Fruit juice is a health drink while breastfeeding.
Question 109.
A client with rheumatoid arthritis tells the nurse that she feels “quite alone” in adjusting to changes in her lifestyle. Which response by the nurse will be most effective?
(a) referring the client and her husband for counseling to decrease her sense of isolation
(b) suggesting that the client develop a hobby to occupy her time
(c) telling the client about her community’s arthritis support group
(d) recommending that the client discuss her feelings with her religious advisor
Answer:
(c) telling the client about her community’s arthritis support group
Rationale:
The client should be encouraged to join the community arthritis support group so that she can share her feelings with others who are facing similar experiences with this chronic illness and can identify with her concerns. A hobby will not help her resolve her feelings of being alone. Seeking counsel-ing or discussing her feelings with a minister may be helpful, but these activities will not necessarily help the client to understand that there are many individuals who must adjust their lifestyles because of arthritis and that she is not alone.
Question 110.
Which intervention should the nurse include in the plan of care to ensure adequate nutrition for a very active, talkative, and easily distractible client who is unable to sit through meals?
(a) Direct the client to the room to eat.
(b) Offer the client nutritious finger foods.
(c) Ask the client’s family to bring the client’s favorite foods from home.
(d) Ask the client about food preferences.
Answer:
(b) Offer the client nutritious finger foods.
Rationale:
For the client who is unable to sit through meals to maintain adequate nutrition, the nurse should offer the client nutritious finger foods and fluids that he can consume while “on the run.” Foods high in protein and carbohydrates, such as half of a peanut butter sandwich, will help to maintain nutritional needs. Adequate fluid intake is necessary, especially if the client has been started on lithium therapy.
Directing the client to his room to eat is not helpful because the client will not stay in his room long enough to eat. Asking the client’s family to bring his favorite foods or asking the client about his food preferences is not helpful in ensuring adequate nutrition for the hyperactive client who is unable to sit and eat.
Question 111.
A client in a group home is very dependent on the staff but is able to make simple decisions.
The client asks, “Would you do my laundry? I don’t know how the machine works.” Which response would be best?
(a) “Sure, I have time; I can do it for you.”
(b) “You’ll have to wait; I don’t have time now.”
(c) “Can your family do it for you?”
(d) “Get your laundry; I'll show you how the machine works.”
Answer:
(d) “Get your laundry; I'll show you how the machine works.”
Rationale:
Telling the client to get her laundry and then showing her how to use the machine helps keep the client from becoming overly dependent on the nurse, establishes boundaries between the client and the nurse, and promotes positive self-worth. The statement “Sure, I have time; I’ll do it for you” is not therapeutic because it increases the client’s dependency.
Telling the client that she will have to wait because the nurse does not have time dismisses the client and insinuates that the nurse will do the laundry later, thus fostering dependency. Asking “Can your family do it for you?” is not appropriate because the client is capable of doing her own laundry. This statement places responsibility on the family instead of the client.
Question 112.
The nurse is caring for a client with chronic renal failure. The nurse should monitor the client for which adverse effects of hypermagnesemia?
(a) flushed skin
(b) lethargy
(c) severe thirst
(d) tremors
Answer:
(b) lethargy
Rationale:
Early signs and symptoms of hypermagnesemia include drowsiness, lethargy, nausea, and vomiting. Flushed skin is a sign of hypernatremia. Severe thirst is associated with hyperglycemia. Tremors are associated with hypomagnesemia.
Question 113.
The nurse determines the parents’ compliance with treatment for their infant who has otitis media. Which behavior would indicate that the parents are adhering to the treatment plan?
(a) cleaning the child’s ear canals with hydrogen peroxide
(b) administering continuous, low-dose antibiotic therapy
(c) instilling ear drops regularly to prevent cerumen accumulation
(d) holding the child upright when feeding with a bottle
Answer:
(d) holding the child upright when feeding with a bottle
Rationale:
Sitting or holding a child upright for formula feedings helps prevent pooling of formula in the pharyngeal area. When the vacuum in the middle ear opens into the pharyngeal cavity, formula (along with bacteria) is drawn into the middle ear. Cleaning the ear canals does not reduce the incidence of otitis media because the pathogenic bacteria are in the nasopharynx, not the external area of the ears.
Continuous low-dose antibiotic therapy is used only in cases of recurrent otitis media, when the child finishes a course of antibiotics but then develops another ear infection a few days later. Although accumulation of cerumen makes it difficult to visualize the tympanic membrane, it does not promote inner ear infections.
Question 114.
When giving a change-of-shift report, which statement by the nurse should be included? Select all that apply.
(a) “Client A is a 38-year-old female client of Dr. Born with cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.”
(b) “Client B’s pain is best relieved in the left lateral Sims’ position.”
(c) “Client C is just contrary today, and nothing is going to please him.”
(d) “Client D was able to walk around the unit twice today with no dizziness.”
(e) “Client E had visitors most of the day.”
(f) “Client F has had 100 mL drainage from the nasogastric tube.”
Answer:
(a) “Client A is a 38-year-old female client of Dr. Born with cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.”
(b) “Client B’s pain is best relieved in the left lateral Sims’ position.”
(d) “Client D was able to walk around the unit twice today with no dizziness.”
(f) “Client F has had 100 mL drainage from the nasogastric tube.”
Rationale:
When giving a change-of-shift report, the nurse should provide relevant and concise information about the client’s diagnosis, health care provider’s name, change in status, pain relief strategies, intake/output and level of activity. Calling a client “contrary” is critical in nature and judgmental on the nurse’s part. Indicating that the client had visitors all day does not provide sufficient information for ongoing care planning.
Question 115.
The nurse teaches unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) about caring for a client who is withdrawing from alcohol and street drugs. Which communication technique when observed by the nurse indicates the UAP has understood the instructions?
(a) using matter-of-fact manner and short sentences
(b) conveying a cheerful tone, using humor when appropriate
(c) speaking with a loud voice and giving general comments
(d) providing detailed explanations in a quiet voice
Answer:
(a) using matter-of-fact manner and short sentences
Rationale:
The nurse should teach personnel to communicate with clients who are withdrawing from alcohol and street drugs in a calm, matter-of-fact manner, using short sentences and a moderate tone of voice. This approach promotes orientation, reinforces cognitive-perceptual functions, and decreases anxiety.
A cheerful tone and humor are inappro-priate, possibly leading to misperceptions by the client with cognitive-perceptual impairment. Using general and abstract terms and a loud tone of voice increases anxiety and may lead to misunderstanding. Lengthy explanations delivered with a quiet voice will lead to frustration and increased anxiety.
Question 116.
A couple has completed testing and is a candidate for in vitro fertilization. The nurse is reviewing the procedure with them and realizes that further instruction is needed when the client makes which statement?
(a) “One of the greatest risks is multiple pregnancies.”
(b) “I’ll need to redefine how I view my job if I do become pregnant.”
(c) “The fertilization procedure can be done anytime during my cycle.”
(d) “We can use our own eggs and sperm or someone else’s.”
Answer:
(c) “The fertilization procedure can be done anytime during my cycle.”
Rationale:
The best opportunity for a successful pregnancy is when the normal menstrual cycle is created either naturally or through hormonal augmentation. Implantation can occur only when the levels of estrogen and progesterone are at particular levels. For many women, more than one fertilized egg is placed into the uterus. This increases the risk that more than one embryo will implant and reach maturity.
Couples can choose to utilize their own eggs and sperm if they have been determined to be healthy, or they can choose to use donor oocytes and sperm. For many women who utilize in vitro fertilization, a career has taken precedence over having a family, and these women will need to rebalance a career with the demands of pregnancy and parenting.
Question 117.
When obtaining the diet history from a client with anemia, the nurse should include questions specifically about which vitamins or minerals that are most likely missing in this client’s diet? Select all that apply.
(a) vitamin B6
(b) vitamin K
(c) vitamin B12
(d) iron
(e) vitamin C
Answer:
(a) vitamin B6
(c) vitamin B12
(d) iron
(e) vitamin C
Rationale:
Vitamins B6, B12, and iron are important in the production of red blood cells. Therefore, the nurse should question the client specifically about food intake that contains these vitamins and minerals. Vitamin C helps iron absorption and plays a small role in red blood cell production. Vitamin K has little role in the production of red blood cells.
Question 118.
What is the primary goal of nursing care during the emergent phase after a burn injury?
(a) Replace lost fluids.
(b) Prevent infection.
(c) Control pain.
(d) Promote wound healing.
Answer:
(a) Replace lost fluids.
Rationale:
During the emergent phase of burn care, one of the most significant problems is hypovolemic shock. The development of hypovolemic shock can lead to impaired blood flow through the heart and kidneys, resulting in decreased cardiac output and renal ischemia. Efforts are directed toward replacing lost fluids and preventing hypovolemic shock. Preventing infection and controlling pain are important goals, but preventing circulatory collapse is a higher priority. It is too early in the stage of burn injury to promote wound healing.
Question 119.
The nurse assesses for euphoria in a client with multiple sclerosis, looking for what characteristic clinical manifestations?
(a) inappropriate laughter
(b) an exaggerated sense of well-being
(c) slurring of words when excited
(d) visual hallucinations
Answer:
(b) an exaggerated sense of well-being
Rationale:
A client with multiple sclerosis may have a sense of optimism and euphoria, particularly during remissions. Euphoria is characterized by mood elevation with an exaggerated sense of well-being. Inappropriate laughter, slurring of words, and visual hallucinations are uncharacteristic of euphoria.
Question 120.
The nurse is assessing a client with a burn injury using the “rule of nines.” Which information will this assessment contribute to future care planning?
(a) amount of body surface area burned
(b) rehabilitation needs
(c) respiratory needs
(d) type of intravenous fluids required
Answer:
(a) amount of body surface area burned
Rationale:
The “rule of nines” is used to estimate the percentage of the client’s body surface area that was burned. Medical treatment, including fluid volume replacement therapy, is based on the percentage of body surface area burned. Rehabilitation needs are identified after the extent of the burn is established and are directed toward preserving the client’s functional ability. Respiratory needs are determined by the location of the burn and the potential for injury from inhalation in addition to vital signs and oxygenation levels.
Question 121.
When assessing a 2-month-old infant, the nurse feels a “click” when abducting the infant’s left hip. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Document the finding as normal for a 2-month-old.
(b) Check the lengths of the femurs to determine if they are equal.
(c) Instruct the mother to keep the leg in an adducted position.
(d) Reschedule the child for a follow-up assessment in 3 weeks.
Answer:
(b) Check the lengths of the femurs to determine if they are equal.
Rationale:
The “click” the nurse feels when abducting the femur is made by the head of the femur as it slips into the acetabulum. This is Ortolani’s sign and indi-cates a dislocated hip. This is not a normal finding for a 2-month-old. The nurse needs to gather additional information by checking for unequal leg lengths and asymmetry of the gluteal and thigh folds. Once the nurse has obtained additional assessment information, the nurse would notify the health care provider (HCP).
Usual medical treatment involves keeping the hip joint in an abducted position in a Pavlik harness. The goal of treatment is to keep the head of the femur centered in the acetabulum. Treatment needs to begin as soon as possible. Usually, the earlier treatment is started, the better the outcome.
Question 122.
Which laboratory test should the nurse monitor when the client is receiving warfarin sodium therapy?
(a) partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
(b) serum potassium
(c) arterial blood gas (ABG) values
(d) prothrombin time (PT)
Answer:
(d) prothrombin time (PT)
Rationale:
Warfarin sodium interferes with clotting. The nurse should monitor the PT and evaluate for the therapeutic effects of Coumadin. A therapeutic PT is between 1.5 and 2.5 times the control value; the PT should be established by the health care provider (HCP).
It may also be reported as an international normalized ratio, a standardized system that provides a common basis for communicating and interpreting PT results. The PTT is monitored in clients who are receiving heparin therapy. Serum potassium levels and ABG values are not affected by warfarin.
Question 123.
A client who had transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) 2 days earlier has lower abdominal pain. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Auscultate the abdomen for bowel sounds.
(b) Administer an oral analgesic.
(c) Have the client use a sitz bath for 15 minutes.
(d) Assess the patency of the urethral catheter.
Answer:
(d) Assess the patency of the urethral catheter.
Rationale:
The lower abdominal pain is most likely caused by bladder spasms. A common cause of bladder spasms after TURP is blood clots obstructing the catheter; therefore, the nurse’s first action should be to assess the patency of the catheter.
Auscultating the abdomen for bowel sounds would be appropriate after patency of the catheter has been estab-lished. The nurse should assess for bladder spasms before administering an analgesic. A sitz bath would not relieve bladder spasms that are caused by an obstructed catheter.
Question 124.
The nurse is ready to administer a partial fill of imipenem-cilastatin in the IV pump when a full partial fill bag of imipenem-cilastatin is found hanging at the client’s bedside. What should the nurse do?
(a) Discard the full partial fill of imipenem-cilastatin found hanging at the client’s bedside.
(b) Check the identifying information of the full partial fill of imipenem-cilastatin found hanging at the client’s bedside.
(c) Determine when the client received the last dose of the imipenem-cilastatin.
(d) Administer the new partial fill of imipenem-cilastatin.
Answer:
(c) Determine when the client received the last dose of the imipenem-cilastatin.
Rationale:
The nurse should first determine whether the client received the last dose of imipenem-cilastatin. If the client did not receive the last dose, the nurse should notify the health care provider (HCP) that the client did not receive the dose, receive prescriptions, document, implement the prescriptions, and complete an incident report. The nurse should not automatically discard the partial fill of imipenem-cilastatin found at the client’s bedside until further investigation is done.
The nurse should recognize the cost of medications such as imipenem-cilastatin and consult the pharmacist after identifying information on the partial fill bag that was found. After verifying all information, the nurse can administer the new partial fill of imipenem-cilastatin so that the client can receive the antibiotic on time.
Question 125.
A client with a moderate level of anxiety is pacing quickly in the hall and tells the nurse, “Help me. I can’t take it anymore.” What would be the nurse’s best initial response?
(a) “It would be best if you would lie down until you are calmer.”
(b) “Let’s go to a quieter area where we can talk if you want.”
(c) “Try doing your relaxation exercises to calm down.”
(d) “I’ll get some medicine to help you relax.”
Answer:
(b) “Let’s go to a quieter area where we can talk if you want.”

Rationale:
For a client with moderate anxiety, the nurse should initially lead the client to a less stimulating environment and help him discuss his feelings. Doing so helps the client to gain control over anxiety that could be overwhelming. Telling the client that it would be best to lie down until he is calmer is not appropriate because the client is too anxious to benefit from this intervention.
Suggesting that the client try relaxation exercises could be helpful after the nurse takes the client to a less stimulating environment and allows the client to vent and discuss his feelings. Getting some medication to help the client relax is an intervention that the nurse would carry out later after trying to help the client decrease anxiety through ventilation and relaxation exercises.
Question 126.
The nurse is developing a teaching plan with a client who is taking warfarin sodium. What should the nurse include in the plan?
(a) Consult the health care provider (HCP) before undergoing a tooth extraction.
(b) Avoid the use of a toothbrush during oral hygiene.
(c) Use rectal suppositories to treat constipation.
(d) Eat green leafy vegetables.
Answer:
(a) Consult the health care provider (HCP) before undergoing a tooth extraction.
Rationale:
Clients who are receiving anticoagulant therapy should consult the HCP QJ before undergoing any dental work that will cause bleeding such as a tooth extraction. The dentist should also be aware that the client is taking anticoagulants. A soft toothbrush is desirable for oral hygiene if the client is receiving anticoagulant therapy; it helps prevent the gums from bleeding.
Rectal suppositories are contraindicated during anticoagulant therapy because their insertion may cause bleeding. Stool softeners may be used instead to prevent straining, which also may promote bleeding. Green leafy vegetables should not be eaten in excess because of their vitamin K content, which may alter the effectiveness of the anticoagulant therapy.
Question 127.
A 30-year-old client hospitalized with a fractured femur that is being treated with skeletal traction has not had a bowel movement for 2 days. What should the nurse do?
(a) Administer a tap water enema.
(b) Place the client on the bedpan every 2 to 3 hours.
(c) Increase the client’s fluid intake to 3,000 mL/day.
(d) Request a prescription for a stool softener.
Answer:
(d) Request a prescription for a stool softener.
Rationale:
Constipation is a problem for clients in traction, and the nurse should request a prescription for a stool softener, which will be the most effective way to prevent and manage constipation. The nurse can also encourage the client to increase fluid intake. Treating constipation with diet, increased fluids, and stool softeners is preferred to the administration of an enema. Placing the client on the bedpan will not encourage a bowel movement. Range-of-motion movements maintain joint mobility but do not stimulate peristalsis.
Question 128.
A client is receiving a tube feeding and has developed diarrhea, cramps, and abdominal distention. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Change the feeding apparatus every 24 hours.
(b) Use a higher volume of formula because the formula may be too hypotonic.
(c) Slow the administration rate.
(d) Use a diluted formula, gradually increasing the volume and concentration.
(d) Anticipate changing to a lactose-free formula.
Answer:
(a) Change the feeding apparatus every 24 hours.
(c) Slow the administration rate.
(d) Use a diluted formula, gradually increasing the volume and concentration.
(d) Anticipate changing to a lactose-free formula.
Rationale:
Although about 50% of diarrhea in clients receiving tube feedings is caused by sorbitol- containing medications, the nurse should assess for other possible causes. Diarrhea can occur as a result of bacterial contamination if fresh formula is not used or stored in a refrigerator, or if the feeding apparatus is not changed at least every 24 hours. Lactose intolerance, rapid formula administration, low serum albumin level, and hypertonic solutions may also cause diarrhea. Hypotonic solutions would not be a likely cause of diarrhea, abdominal distention, or cramping.
Question 129.
A middle-aged client who has smoked two packs of cigarettes for the last 10 years is admitted with a diagnosis of lung cancer. The client reports having “no appetite” and exhibits symptoms of anorexia. The client is 5 feet, 8 inches (173 cm) tall and weighs 112 lb (50.8 kg). The client is now scheduled for a left lung lobectomy. The nurse should include which factor when planning to prevent postoperative pulmonary complications?
(a) The client tends to keep her real feelings to herself.
(b) The client ambulates and can climb one flight of stairs without dyspnea.
(c) The client is middle aged.
(d) The client’s weight relative to height is low.
Answer:
(d) The client’s weight relative to height is low.
Rationale:
Risk factors for postoperative pulmonary complications include malnourishment, which is indicated by the low weight relative to the client’s height. Although keeping feelings inside can be problematic, it would not be considered a postoperative risk for pulmonary complications. The absence of dyspnea on exertion is not indicative of postoperative complications. The client’s age does not necessarily place her at increased risk.
Question 130.
When developing the plan of care for a 12-year-old child who is to receive chemotherapy that is associated with nausea and vomiting, the nurse should plan to administer an antiemetic at which time?
(a) thirty minutes after the chemotherapy has started, then as needed
(b) thirty minutes before the chemotherapy starts, then routinely
(c) when the 12-year-old requests medication for nausea, then as needed
(d) on starting the chemotherapy infusion, then routinely
Answer:
(b) thirty minutes before the chemotherapy starts, then routinely
Rationale:
Administering an antiemetic before beginning chemotherapy and then routinely around the clock helps prevent nausea and vomiting. Waiting until the client requests it may be too late because nausea is already present.
Question 131.
The membranes of a multigravid client in active labor rupture spontaneously, revealing greenish-colored amniotic fluid. How does the nurse interpret this finding?
(a) passage of meconium by the fetus
(b) maternal intrauterine infection
(c) Rh incompatibility between mother and fetus
(d) maternal sexually transmitted disease
Answer:
(a) passage of meconium by the fetus
Rationale:
Greenish-colored amniotic fluid is caused by the passage of meconium, usually secondary to a fetal insult during labor. Meconium passage also may be related to an intact gastrointestinal system of the neonate, especially those neonates who are full term or of postdate gestational age.
Amnioinfusion may be used to treat the condition and dilute the fluid. Cloudy amniotic fluid is associated with an infection caused by bacteria or a sexually transmitted disease. Severe yellow-colored fluid is associated with Rh incompatibility or erythroblastosis fetalis.
Question 132.
A client’s arterial blood gas values are as follows:
The nurse should develop a care plan based on the fact the client is experiencing which clinical situation?
|
Test |
Result |
|
PH |
7.24 |
|
PacO2 |
35 MM Hg (6.7k pa) |
|
HCO3 |
15 mEq/L(15 mmol/L) |
(a) metabolic acidosis
(b) metabolic alkalosis
(c) respiratory acidosis
(d) respiratory alkalosis
Answer:
(a) metabolic acidosis
Rationale:
The pH of 7.24 indicates that the client is acidotic. The carbon dioxide level is normal, but the HCCV level is decreased. These findings indicate that the client is in metabolic acidosis.
This laboratory report does not indicate that the client is in metabolic alkalosis, respiratory alkalosis, or respiratory acidosis. This laboratory report does not indicate that the client is in metabolic alkalosis, respiratory alkalosis, or respiratory acidosis.
Question 133.
A client is suspected of having a slow gastrointestinal bleed. The nurse should evaluate the client for which sign?
(a) increased pulse
(b) nausea
(c) tarry stools
(d) abdominal cramps
Answer:
(c) tarry stools
Rationale:
Black, tarry stools indicate the presence of a slow upper gastrointestinal bleed. The longer the blood is in the system, the darker it becomes as the hemoglobin is broken down and iron is released. Vital sign changes, such as an increased pulse, are not evident with slow gastrointestinal bleeds. Nausea and abdominal cramps can occur but are not definitive signs of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Question 134.
The nurse is assessing a client’s knowledge about coronary syndrome that was diagnosed 4 years ago. When assessing the client’s learning needs, the nurse should take which information into consideration?
(a) The client has had the heart condition for 4 years and is probably very knowledgeable about this disease.
(b) The client’s learning needs may have changed over the course of the illness.
(c) The client's condition is presently stable, so there will be fewer learning needs.
(d) Clients are usually more motivated to learn about their condition when they are hospitalized.
Answer:
(b) The client’s learning needs may have changed over the course of the illness.
Rationale:
This client has lived with the diagnosis of coronary syndrome for 4 years, and depending on the progression of the illness, the learning needs may have changed. The client may at this time have more questions about the illness and how to manage it.
The nurse does not assume that the client is stable and knowledgeable about the illness just because the diagnosis was made 4 years ago. Clients are sometimes less likely to want to learn during hospitalization because they are not feeling well enough to learn.
Question 135.
Which suggestion should the nurse give to an adolescent athlete with Osgood-Schlatter disease of the left knee?
(a) Apply ice on the knee after playing.
(b) Use crutches until healing has occurred.
(c) Stop playing until healing has occurred.
(d) Make an appointment with a physical therapist.
Answer:
(a) Apply ice on the knee after playing.
Rationale:
Most adolescents with Osgood-Schlatter disease are able to continue to exercise and use ice afterward. Ibuprofen also may be prescribed. Because Osgood-Schlatter disease is self-limited, crutches or physical therapy are usually unnecessary, and the adolescent usually does not need to stop playing sports. Only in severe cases would the adolescent have to stop playing sports.
Question 136.
A client is taking iron supplements. What information should the nurse give the client?
(a) Iron supplements should be taken on an empty stomach.
(b) Do not use a bulk laxative.
(c) The stools will become darker.
(d) Liquid iron supplements will not discolor teeth.
Answer:
(c) The stools will become darker.
Rationale:
Iron supplements will darken the stools. Iron supplements should not be taken on an empty stomach because they can cause gastric irritation. Iron is constipating, and a daily bulk-forming laxative should be started prophylactically. A straw should be used when taking liquid iron to avoid discoloring the teeth.
Question 137.
What should the nurse teach a client with generalized anxiety disorder to help the client cope with anxiety?
(a) cognitive and behavioral strategies
(b) issue avoidance and denial of problems
(c) rest and sleep
(d) withdrawal from role expectations and role relationships
Answer:
(a) cognitive and behavioral strategies
Rationale:
A client with generalized anxiety disorder needs to learn cognitive and behavioral strategies to cope with anxiety appropriately. In doing so, the client’s anxiety decreases and becomes more manageable. The client may need assertiveness training, reframing, and relaxation exercises to adaptively deal with anxiety.
The nurse should not encourage the client to seek avoidance or denial, but rather be engaged using cognitive and behavioral strategies. The client should not withdraw from role respon-sibilities or relationships. The client does not need additional rest or sleep.
Question 138.
After a lobectomy for lung cancer, the nurse instructs the client to perform deep breathing exercises. What is the expected outcome of these exercises?
(a) Decrease blood flow to the lungs for rest and increased surface alveoli ventilation.
(b) Elevate the diaphragm to enlarge the thorax so that the lung surface area available for gas exchange is increased.
(c) Control the rate of air flow to the remaining lobe to decrease the risk of hyperinflation.
(d) Expand the alveoli and increase lung surface available for ventilation.
Answer:
(d) Expand the alveoli and increase lung surface available for ventilation.
Rationale:
Deep breathing helps prevent microatelectasis and pneumonitis and also helps force air and fluid out of the pleural space into the chest tubes. It does not decrease blood flow to the lungs or control the rate of air flow. The diaphragm is the major muscle of respiration; deep breathing causes it to descend, thereby increasing the ventilating surface.
Question 139.
Which is the correct technique when the nurse is applying an elastic bandage to a leg?
(a) Increase tension with each successive turn of the bandage.
(b) Start at the distal end of the extremity and move toward the trunk.
(c) Secure the bandage with clips over the area of the inner thigh.
(d) Overlap each layer twice when wrapping.
Answer:
(b) Start at the distal end of the extremity and move toward the trunk.
Rationale:
When applying an elastic bandage to a leg, start at the distal end and move toward the trunk in order to support venous return. Tension should be kept even and not increased with each turn to prevent circulatory impairment. Overlapping each layer twice when wrapping can also impair circulation. The clips securing the bandage should be placed on the outer aspect of the leg to avoid creating a pres-sure point on the other leg.
Question 140.
A nulliparous client says that she and her husband plan to use a diaphragm with spermicide to prevent conception. Which should the nurse include as the action of spermicides when teaching the client?
(a) destruction of spermatozoa before they enter the cervix
(b) prevention of spermatozoa from entering the uterus
(c) a change in vaginal pH from acidic to alkaline
(d) slowing of the movement of the migrating spermatozoa
Answer:
(a) destruction of spermatozoa before they enter the cervix
Rationale:
Spermicidal agents work by destroying the spermatozoa before they enter the cervix. In addi-tion, some spermicides alter the vaginal pH to a strong acidic environment, which is not conducive to survival of spermatozoa. Spermicides do notprevent the spermatozoa from entering the uterus, but the diaphragm or condom is a barrier.
Question 141.
A client is admitted with paranoia and visual hallucinations related to progressive dementia. The client continues to be restless and have hallucinations. The nurse calls the health care provider (HCP) and, after explaining the situation, background, and assessment, recommends that the HCP consider writing a prescription for which medication?
(a) methylphenidate
(b) lorazepam
(c) trazodone
(d) sertraline
Answer:
(d) sertraline
Rationale:
A low dosage of sertraline is helpful in controlling dementia-induced paranoia and hallucinations. Methylphenidate would be indicated for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lorazepam would be prescribed if the client were anxious and agitated. Trazodone would be used if depression were prominent.
Question 142.
The nurse is auscultating the lungs of a client with bacterial pneumonia. Which finding is expected?
(a) increased fremitus
(b) bilateral expiratory wheezing
(c) resonance on percussion
(d) vesicular breath sounds
Answer:
(a) increased fremitus
Rationale:
Increased fremitus can be present in bacterial pneumonia, indicating the presence of pulmonary consolidation. Additional findings would include crackles, bronchial breath sounds, and dullness on percussion. Bilateral expiratory wheezing and resonance on percussion are not present in bacterial pneumonia. Vesicular breath sounds are normal and would not be an expected finding in bacterial pneumonia.
Question 143.
A nurse notices that a newborn has a swelling in the scrotal area. The nurse interprets this swelling as indicative of hydrocele if what else occurs?
(a) The swollen bulge can be reduced.
(b) The increase in scrotal size is bilateral.
(c) The scrotal sac can be transilluminated.
(d) The bulge appears during crying.
Answer:
(c) The scrotal sac can be transilluminated.
Rationale:
is determined when the scrotal sac can be transilluminated. A swelling in the scrotal area that can be reduced indicates an inguinal hernia. Both hydroceles and hernias can enlarge the scrotal sac, and both can be either unilateral or bilateral. A hernia typically is more obvious during crying.
Question 144.
The nurse is screening clients for cancer prevention. Which is the recommended screening protocol for colon cancer in asymptomatic clients who have a low-risk profile?
(a) Fecal occult blood testing should be per formed annually after age 50 and up to age 75.
(b) Digital rectal examinations are recommended every 5 years after age 40.
(c) Sigmoidoscopy is recommended if symptoms of colon problems are present.
(d) A diet low in saturated fat should be implemented after age 50.
Answer:
Rationale:
The screening protocol recommended by the American and Canadian Cancer Societies for early detection of cancer in asymptomatic people includes the following: Beginning at age 50, men and women should have fecal occult blood test-ing, flexible sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy every year until age 75 unless determined otherwise by a health care provider (HCP). A diet low in saturated fat and high in fruit and fiber is not a screening protocol but is good dietary advice for all clients
Question 145.
A client with diabetes who takes insulin has a blood glucose level of 40 mg/dL (2.27 mmol/L). What should the nurse offer the client to begin to raise the blood glucose level? Select all that apply.
(a) one-half cup (120 mL) of orange juice
(b) one cup (240 mL) of milk
(c) one-quarter cup (60 mL) of tuna
(d) one tablespoon (15 mL) of peanut butter
(e) one slice of bread
(f) one-half cup (120 mL) of regular soda
Answer:
(a) one-half cup (120 mL) of orange juice
(b) one cup (240 mL) of milk
(e) one slice of bread
(f) one-half cup (120 mL) of regular soda
Rationale:
To treat a low blood glucose level, the nurse should provide the client with approximately 15 g of carbohydrate and monitor the blood glucose level within 15 minutes. The orange juice, milk, bread, or soda would provide approximately 15 g of carbohydrate. Meat or fish, such as tuna, does not contain carbohydrate. Processed peanut butter may contain small amounts of carbohydrate, but it is also high in fat and protein. Peanut butter is not a good option to raise a blood glucose level in a timely manner.
Question 146.
An infant diagnosed with increased intracra-nial pressure (ICP) on a regular diet vomits while eating dinner. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Put the child on nothing-by-mouth (NPO) status for 4 hours.
(b) Call to report this event to the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Wait a few minutes and then refeed the child.
(d) Administer the prescribed antiemetic.
Answer:
(c) Wait a few minutes and then refeed the child.
Rationale:
Increased ICP can cause vomiting, particularly in children whose fontanelles are closed. An infant with an open anterior fontanelle may have less vomiting because the cranium can respond, expanding with increased ICP. The best course of action is to wait a few minutes and then refeed the child. Putting the child on NPO status may not be helpful because this is not a gastrointestinal problem. Because this is an expected event, notifying the health care provider HCP) is not necessary. Antiemetics frequently make a client sleepy, making neurologic checks difficult to interpret.
Question 147.
When preparing to draw up 8 units of a shortacting insulin and 20 units of a long-acting insulin in the same syringe, the nurse should use which technique?
(a) Inject air in the vial with the long-acting insulin first.
(b) Draw up the long-acting insulin first.
(c) Draw up either insulin first.
(d) Use a high-dose insulin syringe.
Answer:
(a) Inject air in the vial with the long-acting insulin first.
Rationale:
The air is injected into the long-acting insulin first. Air is then injected into the short-acting insulin, and the short-acting insulin is withdrawn. Then the long-acting insulin is withdrawn. It does matter which insulin is drawn up first because the nurse does not want to contaminate the short-acting insulin with the long-acting insulin. It is
not necessary to use a high-dose insulin syringe to prepare 28 units of insulin.
Question 148.
The mother of an infant with iron deficiency anemia asks the nurse what she could have done to prevent the anemia. The nurse should teach the mother that it is helpful to introduce solid foods into the infant’s diet at which age?
(a) 3 months
(b) 6 months
(c) 8 months
(d) 10 months
Answer:
(b) 6 months
Rationale:
Solids should be introduced at 6 months. Full-term infants use up their prenatal iron stores within 4 to 6 months after birth. Milk contains insufficient iron.
Question 149.
A client has had abdominal surgery and is using an incentive spirometer. Which is the most effective way to evaluate the effectiveness of the client’s use of the spirometer? The client:
(a) has increased circulation in the extremities.
(b) is ready to ambulate without pain.
(c) has stronger abdominal muscles.
(d) can breathe more easily.
Answer:
(d) can breathe more easily.
Rationale:
Incentive spirometry promotes lung expansion and increases respiratory function. When used properly, an incentive spirometer causes sustained maximal inspiration and increased cardiac output. Incentive spirometry does not directly promote circulation in the extremities. Using incentive spirometry will not help relieve pain or strengthen abdominal muscles.
Question 150.
The nurse is caring for a client who is having an acute asthma attack. The nurse should notify the health care provider when the client has which symptom?
(a) loud wheezing
(b) tenacious, thick sputum
(c) decreased breath sounds
(d) persistent cough
Answer:
(c) decreased breath sounds
Rationale:
Diminished breath sounds during an acute asthma attack are a serious sign of airway obstruction, fatigue, and impending respiratory failure. Wheezing, coughing, and the production of sputum indicate the presence of airflow through the lungs and are less ominous symptoms
Question 151.
A client is receiving radiation therapy. What should the nurse teach the client about skin care?
(a) Avoid shaving with straight-edge razors.
(b) Clean the skin daily with antibacterial soap.
(c) Apply moisturizing lotion before and after each treatment.
(d) Keep the radiated area covered with a sterile gauze dressing.
Answer:
(d) Keep the radiated area covered with a sterile gauze dressing.
Rationale:
Clients should use an electric razor, instead of a straight-edge razor, on any skin areas that are receiving radiation. The skin should be cleaned daily with a mild soap, not harsh antibacterials. Lotion should be removed from the skin before any treatment and then reapplied after the treatment. The radiated skin area needs to be kept clean, dry, and open to air.
Question 152.
A client has had a cardiac catheterization. The femoral dressing has a bright bloody drainage. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Assess the airway.
(b) Administer oxygen.
(c) Apply pressure to the site.
(d) Assess the pulse in the left extremity.
Answer:
(c) Apply pressure to the site.
Rationale:
A moderate amount of bloody drainage could indicate active bleeding. The priority action is to apply pressure to the area and call for help. Assessing the airway or pulse or administering oxygen does not address the bleeding.
Question 153.
A pediatric client has been prescribed valproic acid for seizure control. The nurse should instruct the family that the child will need which periodic monitoring of which values? Select all that apply.
(a) complete blood count (CBC)
(b) C-reactive protein
(c) serum drug levels
(d) hepatic function
(e) platelets
(f) bleeding times
Answer:
(a) complete blood count (CBC)
(c) serum drug levels
(d) hepatic function
(e) platelets
(f) bleeding times
Rationale:
Thrombocytopenia and leukopenia are common adverse effects of valproic acid. A CBC, platelets , and bleeding times should be drawn prior to and periodically during therapy. Hepatotoxicity is also a side effect of valproic acid. Clients should have LDH, AST, ALT, bilirubin and ammonia levels drawn prior to and periodically during treatment. Serum drug levels are monitored as doses are increased to achieve a desired therapeutic level. Valproic acid is not associated with inflammation; thus C-reactive proteins are not routinely monitored.
Question 154.
Bacterial conjunctivitis has affected several children at a local day care center. A nurse should advise which measure to minimize the risk of infection?
(a) Close the day care center for 1 week to control the outbreak.
(b) Restrict the infected children from returning for 48 hours after treatment.
(c) Perform thorough handwashing before and after touching any child in the day care center.
(d) Set up a conference with the parents of each child to explain the situation carefully.
Answer:
(c) Perform thorough handwashing before and after touching any child in the day care center.
Rationale:
Bacterial conjunctivitis is very contagious. Attention should be paid to thorough handwashing, a major means of stopping the transmission of the disease. Closing the day care center for 1 week is not necessary because thorough handwashing will stop the spread of the infection. Keeping the children out for 48 hours is not necessary. A child may return to day care after being treated for 24 hours. Although the parents of each child should be told about the outbreak, doing so will not help to curtail or prevent the spread of the infection.
Question 155.
The nurse is evaluating the client’s risk for having a pressure sore. Which is the best indicator of risk for the client’s developing a pressure sore?
(a) nutritional status
(b) circulatory status
(c) mobility status
(d) orientation status
Answer:
(c) mobility status
Rationale:
The client’s mobility status is the best indicator of risk for development of a pressure sore. Nutritional and circulatory status are other factors that can contribute to pressure sore development, but immobility, even in the presence of adequate nutrition and circulation, is the leading cause of pressure sores. Disorientation can cause a client to neglect making needed position changes, but the underlying factor will be immobility.
Question 156.
A client with acute pancreatitis is put on nothing-by-mouth status, with the intent of not stimulating the pancreas. The client is prescribed an IV infusion of dextrose 5% in half-normal saline solution at 120 mL/h. After 3 days of this regimen, the nurse should observe the client for which adverse metabolic condition?
(a) ketosis
(b) hyperglycemia
(c) metabolic syndrome
(d) lactic acidosis
Answer:
(a) ketosis
Rationale:
Ketosis is an adaptation to prolonged fasting or carbohydrate deprivation. The body takes partially broken-down fat fragments and combines them into ketone bodies, which the brain can then use for energy. Hypoglycemia is more likely to occur than hyperglycemia, although glucagon assists in preventing this. Metabolic syndrome refers to syn-drome X, which includes an abnormal lipid profile and a tendency to gain weight in the abdomen. Lactic acidosis is a metabolic reaction that occurs when oxygen is reduced or not present.
Question 157.
While the nurse is assisting a client to ambulate as part of a cardiac rehabilitation program, the client has midsternal burning. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Stop and assess the client further.
(b) Obtain the client’s blood pressure and heart rate.
(c) Call for help and place the client in a wheelchair.
(d) Administer nitroglycerin.
Answer:
(a) Stop and assess the client further.
Rationale:
The nurse should stop and assess the client further. A chair should be available for the client to sit down. Obtaining the client's blood pressure and heart rate are important when exercising. These values can be used to predict when the oxygen demand becomes greater than the oxygen supply. Calling for help is not necessary for the midsternal burning. If the health care provider (HCP) has prescribed nitroglycerin, the nurse can administer it; however, stopping the activity may restore the oxygen balance.
Question 158.
The nurse is counseling a client about the prevention of coronary heart disease. Which vitamins should the nurse recommend the client include in the diet to reduce homocysteine levels? Select all that apply.
(a) vitamin K
(b) vitamin Be
(c) folate
(d) vitamin B12
(e) vitamin D
Answer:
(b) vitamin Be
(c) folate
(d) vitamin B12
Rationale:
Vitamin B11, folate, and vitamin B12 have been shown to reduce homocysteine levels. The effects of vitamins K and D have not been established with regard to homocysteine.
Question 159.
A client has been taking dexamethasone for 2 weeks. The nurse evaluates a client’s knowledge as deficient when the client makes which comment?
(a) “I can’t stop the medication all at one time.”
(b) “If I forget a dose, it’s no big deal; I’ll just take it when I remember it.”
(c) “When I get a cold, I need to let my health care provider (HCP) know.”
(d) “I need to watch for an allergic reaction when I first start taking this pill.”
Answer:
(b) “If I forget a dose, it’s no big deal; I’ll just take it when I remember it.”
Rationale:
The statement “If I forget a dose, it’s no big deal, I’ll just take it when I remember it” indicates a knowledge deficit. The nurse should reinforce that the client should take dexanrethasone as prescribed and at the same time each day. The drug has to be tapered off and cannot be stopped abruptly. The health care provider (HCP) Q should be notified when the client is under additional stress (e.g., infection, surgery, illness). The client can have an allergic reaction to inactive ingredients contained in dexamethasone.
Question 160.
A 3-month-old has moderate dehydration. The nurse should assess the client for which sign of moderate dehydration?
(a) oliguria
(b) bulging eyes
(c) sunken posterior fontanelle
(d) pale skin color
Answer:
(a) oliguria
Rationale:
A child with moderate dehydration, described as a loss of 50 to 90 mL/kg of body fluid, would have oliguria, gray skin color, increased pulse rate, and poor skin elasticity. Sunken eyes, not bulging, are a sign of dehydration. The anterior fonta- nelle may be sunken, but the posterior fontanelle is normally closed by 6 to 8 weeks of age. A child with mild dehydration, described as a loss of < 50 mL/kg of body fluid, would have pale skin color, decreased skin elasticity, decreased urine output, and normal or increased pulse rate.
Question 161.
The nurse is assessing a client who is suspected of being in the early symptomatic stages of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Which indication of infection should the nurse detect during this stage?
(a) whitish yellow patches in the mouth
(b) dyspnea
(c) bloody diarrhea
(d) raised, hyperpigmented lesions on the legs
Answer:
(a) whitish yellow patches in the mouth
Rationale:
Oropharyngeal candidiasis, or thrush, is the most common infection associated with the early symptomatic stages of HIV infection. Thrush is characterized by whitish yellow patches in the mouth. Various other opportunistic diseases can occur in clients with HIV infection, but they tend to occur later, after the diagnosis of acquired immu-nodeficiency syndrome has been made. Dyspnea can be indicative of pneumonia, which is caused by a variety of infective organisms. Bloody diarrhea is indicative of cytomegalovirus infection. Hyperpigmented lesions are indicators of Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Question 162.
A primiparous client who is breastfeeding develops endometritis on the third postpartum day. What instructions should the nurse give to the mother?
(a) The neonate will need to be bottle-fed for the next few days.
(b) The condition typically is treated with IV antibiotic therapy.
(c) The client may require oxytocin and frequent uterine massage.
(d) The client needs to remain in bed in a side-lying position as much as possible.
Answer:
(b) The condition typically is treated with IV antibiotic therapy.
Rationale:
Postpartum infection is a leading cause of maternal mortality in the United States. Typical treatment for the condition is IV antibiotic therapy with drugs such as clindamycin, gentamicin, or both. Cultures of the lochia will also be obtained. The neonate can continue to breastfeed as long as the mother desires. A switch to bottle-feeding is not necessary. The uterus tends to be firm, with increased cramping to rid the uterus of the infection. The client should be encouraged to remain in Fowler’s position when in bed to allow for drainage of the lochia.
Question 163.
After instructing a primiparous client who is breastfeeding on how to prevent nipple soreness during feedings, the nurse determines that the client needs further instruction when she makes which statement?
(a) “I should position the baby the same way for each feeding.”
(b) “I should make sure the baby grasps the entire areola and nipple.”
(c) “I should air-dry my breasts and nipples for 10 to 15 minutes after the feeding.”
(d) “I shouldn’t use a hand breast pump if my nipples get sore.”
Answer:
(a) “I should position the baby the same way for each feeding.”
Rationale:
The mother needs further instruction when she says “I should position the baby the same way for each feeding.” This can contribute to sore nipples. The position should vary for each feeding to prevent repeated pressure on the same area each time. Grasping the entire areola and nipple will help to decrease nipple soreness. Air-drying the breasts and not using a hand pump will help to decrease nipple soreness.
Question 164.
A client who has Meniere’s disease is experiencing an acute attack of vertigo. What should the nurse do to help the client manage the attack?
(a) Darken the client’s room and provide a quiet environment.
(b) Give the client cheese and crackers.
(c) Administer acetaminophen.
(d) Offer carbonated fluids.
Answer:
(a) Darken the client’s room and provide a quiet environment.
Rationale:
During an acute attack of vertigo, it is best for the client to lie down in a darkened, quiet room and to avoid sudden position changes. Because vertigo is frequently accompanied by nausea and vomiting, the client will not want to eat or drink. Headaches are not a component of the vertigo attack. Fluids are usually administered parenterally to maintain hydration and administer medications.
Question 165.
During a home visit to a primiparous client 1 week postpartum who is bottle-feeding her neonate, the client tells the nurse that her mother has suggested that she feed the neonate cereal so he will sleep through the night. What would be the nurse’s best response?
(a) “It’s permissible to give the baby cereal if it is thinned with formula.”
(b) “The time for starting cereal varies, so check with your pediatrician.”
(c) “Formula is the food best digested by the baby until about 4 to 6 months of age.”
(d) “If cereal is given too early in life, the undigested food can lead to a need for surgery.”
Answer:
(c) “Formula is the food best digested by the baby until about 4 to 6 months of age.”

Rationale:
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all neonates should receive only formula or breast milk for the first 4 to 6 months of life. Cereal will not help the neonate sleep through the night and may result in allergies and other digestive disorders.
Question 166.
A client reports being allergic to amoxicillin even though the medication administration record and armband do not indicate medication allergies. What should the nurse do about administering the drug to the client?
(a) Administer the prescribed medication.
(b) Withhold the medication.
(c) Administer another, similarly acting antibiotic.
(d) Call the family to verify the client’s statement.
Answer:
(b) Withhold the medication.
Rationale:
Once the client has stated that he is allergic to a substance, the nurse would be negligent to ignore the client’s statement and administer the substance. The nurse should check the medical record for allergies and call the health care provider (HCP) for an alternative antibiotic prescription.
Question 167.
While assessing a term neonate on a home visit to a primiparous client 2 weeks after vaginal birth, the nurse observes that the neonate is slightly jaundiced and the stool is a pale, light color. The nurse notifies the health care provider because these findings indicate which problem?
(a) biliary atresia
(b) Rh isoimmunization
(c) ABO incompatibility
(d) esophageal varices
Answer:
(a) biliary atresia

Rationale:
Jaundice that persists past the 3rd or 4th day of life and pale, light stools are associated with biliary atresia. Alkaline phosphatase levels will also be elevated. Surgical intervention is necessary to remove the blockage. Rh isoimmunization and ABO incompatibility are associated with neonatal anemia as the red blood cells are hemolyzed by the antibodies.
Esophageal varices are associated with cirrhosis of the liver and large amounts of bleeding when the vessels rupture. The child with esophageal varices will exhibit manifestations of anemia such as pallor and may experience hemorrhage and shock.
Question 168.
To reduce urethral irritation, where should the nurse tape the female client’s Foley catheter?
(a) inner thigh
(b) groin area
(c) lower abdomen
(d) lower thigh
Answer:
(a) inner thigh
Rationale:
To reduce urethral irritation and allow drainage, the nurse should tape the Foley catheter to a female client’s inner thigh. Taping the catheter also prevents excessive traction against the bladder neck. Taping the catheter to the groin or lower abdomen would not allow for proper drainage and would cause urethral discomfort. Taping the catheter to the lower thigh would pull on the catheter and cause urethral irritation.
Question 169.
A 6-year-old child has had heart surgery to repair tetralogy of Fallot. The nurse should include information about which topic when developing the discharge teaching plan?
(a) allowing the child to lead a normal, active life
(b) persuading the child to get enough rest
(c) treating hypercyanotic tet spells
(d) having the child out of school for a month
Answer:
(a) allowing the child to lead a normal, active life
Rationale:
Most parents find it especially difficult to allow a child who was unable to be normally active before corrective heart surgery to lead a normal and active life after surgery. These parents are less likely to be apprehensive about persuading the child of the need for rest, about postoperative complications, or having the child out of school for a month. Tet spells are no longer expected after the surgical repair.
Question 170.
A client is recovering from abdominal surgery and has a nasogastric (NG) tube inserted. Which is the expected outcome of inserting the NG tube in the client’s gastrointestinal tract?
(a) compression
(b) lavage
(c) decompression
(d) gavage
Answer:
(c) decompression
Rationale:
After abdominal surgery, the reason for inserting an NG tube is to decompress the gastrointestinal tract until peristaltic action returns. Compression may be used to control bleeding esophageal varices. Lavage is used to remove substances from the stomach or control bleeding. Gavage is used to provide enteral feedings.
Question 171 .
The nurse teaches the mother of a toddler who has had a cleft palate repair that her child is most at risk for developing which problem in the future?
(a) hearing problems
(b) poor self-concept
(c) a speech defect
(d) chronic sinus infections
Answer:
(c) a speech defect
Rationale:
The most common long-term problem experienced by children with cleft palate repair is speech problems. These children frequently need speech therapy for a period of time. Hearing problems may occur as a result of chronic ear infections and the placement of myringotomy tubes. A poor self-concept may develop in any child. However, if a child with a cleft palate receives adequate parenting and support, this should not occur. Chronic sinus infections are more commonly associated with asthma, not with this defect.
Question 172.
The nurse assesses a client who is receiving a tube feeding. Which situation would require prompt intervention from the nurse?
(a) The client is sitting upright in bed while the feeding is infusing.
(b) The feeding that is infusing has been hanging for 8 hours.
(c) The client has a gastric residual of 25 mL.
(d) The feeding solution is at room temperature.
Answer:
(b) The feeding that is infusing has been hanging for 8 hours.
Rationale:
Feeding solutions that have not been infused after hanging for 8 hours should be discarded because of the increased risk of bacterial growth. Sitting the client upright during the feeding helps prevent aspiration of the feeding. A gastric residual of 25 mL is considered acceptable. A gastric residual of 100 to 150 mL, or a residual >100% of the previous hour’s intake, indicates delayed emptying. The feeding solution should be at room or body temperature.
Question 173.
A client has been taking furosemide for 2 days. The nurse should review the laboratory record for changes in which blood level?
(a) an elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
(b) an elevated potassium
(c) a decreased potassium
(d) an elevated sodium
Answer:
(c) a decreased potassium
Rationale:
Furosemide is a loop diuretic and inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the proximal and distal renal tubules and the loop of Henle. Furosemide promotes sodium diuresis, resulting in a loss of potassium and serious elec-trolyte imbalances. Furosemide does not affect the BUN level.
Question 174.
When suctioning the respiratory tract of a client, it is recommended that the suctioning period not exceed how many seconds?
(a) 5 seconds
(b) 10 seconds
(c) 15 seconds
(d) 20 seconds
Answer:
(c) 15 seconds
Rationale:
Suctioning the respiratory tract for prolonged periods depletes the client’s oxygen supply and causes hypoxia. It is recommended that each suctioning period not exceed 15 seconds.
Question 175.
An 80-year-old client with severe kidney damage is placed on life support and dialysis. Care decisions are being made by his wife, who is showing signs of early Alzheimer’s disease. The client’s daughter arrives from out of town with a copy of the client’s living will, which states that the client did not want to be on life support. What action should the nurse take next?
(a) Immediately inform the health care provider (HCP) about the living will.
(b) Suggest to the daughter that she discuss her father’s wishes with her mother.
(c) Prepare to remove the client from life support.
(d) Make a copy of the living will, and give it to the client’s wife.
Answer:
(b) Suggest to the daughter that she discuss her father’s wishes with her mother.
Rationale:
The most appropriate action is to encourage the daughter to talk to her mother about the end- of-life issues first to reach a consensus or agreement. This is a family decision. Immediately informing the HCP Q or preparing to remove the client from life support would be premature if the family is not in agreement. Although a copy of the living will should be on the client’s medical record 3, it is up to the daughter to show it to her mother.
Question 176.
Prior to administering plasminogen activator (t-PA) to a client admitted with a stroke, the nurse should verify which information about the client? Select all that apply.
(a) is older than 65 years
(b) has had symptoms of the stroke less than 3 hours
(c) has a blood pressure within normal limits
(d) does not have active internal bleeding
(d) has not had an alcoholic beverage within the last 8 hours
Answer:
(b) has had symptoms of the stroke less than 3 hours
(c) has a blood pressure within normal limits
(d) does not have active internal bleeding
Rationale:
Contraindications for t-PA or alteplase recombinant therapy include current active internal bleeding, 3 hours or longer since the onset of symptoms of a stroke, and severe hypertension. Age older than 65 years and having had an alcoholic beverage are not contraindications for the therapy.
Question 177.
A client with peripheral arterial disease has had surgery for placement of an aortobifemoral bypass graft. Immediately following surgery, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Elevate the lower extremities.
(b) Assist the client to use incentive spirometry.
(c) Start the client on a liquid diet.
(d) Assess peripheral pulses every 4 hours.
Answer:
(b) Assist the client to use incentive spirometry.
Rationale:
The nurse should assist the client to use incentive spirometry every 1 to 2 hours postoperatively to prevent atelectasis and pneumonia. Starting a liquid diet is not the highest priority as the client will have an IV infusion and might have an NG tube; adequate fluid status can be main-tained until intestinal function returns. The client’s extremities are kept flat or lowered to promote circulation. Elevation of extremities is used to promote venous blood flow. The nurse assesses pulses and vital signs hourly in the early postoperative course.
Question 178.
How does the nurse identify the type of presentation shown in the figure?
(a) frank breech
(b) compound breech
(c) complete breech
(d) incomplete breech
Answer:
(c) complete breech
Rationale:
For a complete breech, the buttocks present, the feet and legs are flexed on the thighs, and the thighs are flexed on the abdomen. For a frank breech, the buttocks present with the hips flexed and the legs extended against the abdomen and chest. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
For a compound breech, the buttocks present together with another part, such as a hand. This is a rare occurrence. For an incomplete breech, one or both feet or the knees extend below the buttocks. This can also be termed a single footling or double footling breech.
Question 179.
Following cardiac bypass surgery, the client has been referred to a cardiac rehabilitation exercise program. The client has type 1 diabetes and has bilateral leg discomfort with walking. The client is exercising using a stationary bicycle. The nurse should evaluate the client’s response to exercise by assessing the presence of which condition?
(a) diabetic neuropathy
(b) muscle atrophy
(c) Raynaud’s disease
(d) transient ischemic attacks
Answer:
(a) diabetic neuropathy
Rationale:
A common complication of diabetes is diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy results from the metabolic and vascular factors related to hyperglycemia. Damage leads to sensory deficits and peripheral pain. Muscle atrophy can result from disuse, but it is not a direct consequence of diabetes. Raynaud’s disease is associated with vasospasms in the hands and feet. Transient ischemic attacks involve the cerebrum.
Question 180.
Which statement indicates that the client with hepatitis B has understood the nurse’s discharge teaching?
(a) “I won’t drink alcohol for at least 1 year.”
(b) “I must avoid sexual intercourse.”
(c) “I should be able to resume normal activity in a week or two.”
(d) “Because hepatitis B is a chronic disease, I know I'll always be jaundiced.”
Answer:
(a) “I won’t drink alcohol for at least 1 year.”
Rationale:
It is important that the client understand that alcohol should be avoided for at least 1 year after an episode of hepatitis. Sexual intercourse does not need to be avoided, but the client should be instructed to use condoms until the hepatitis B surface antigen measurement is negative. The client will need to restrict activity until liver function test results are normal; this will not occur within 1 to 2 weeks. Jaundice will subside as the client recovers; it is not a permanent condition.
Question 181.
A client who is taking olanzapine states he is being poisoned and refuses to take his scheduled medication. The nurse states, “If you don’t take your medication, you’ll be put into seclusion.” The nurse’s statement is an example of which legal concept?
(a) assault
(b) battery
(c) malpractice
(d) invasion of privacy
Answer:
(a) assault

Rationale:
The nurse’s statement exemplifies assault, which is the threat of being touched in an offensive way without consent Battery is touching another person without consent. Malpractice is care below the standard of care that results in injury. Invasion of privacy is a violation of a person’s right to be left alone.
Question 182.
A client who has been taking diazepam for 3 months for skeletal muscle spasms and lower back pain stopped taking the medication 2 days ago because it was no longer helping. Now the pain has increased. The nurse should assess the client for signs of withdrawal. Select all that apply.
(a) insomnia
(b) euphoria
(c) bradycardia
(d) diaphoresis
(e) tremor
(f) vomiting
Answer:
(a) insomnia
(d) diaphoresis
(e) tremor
(f) vomiting
Rationale:
Diazepam is a benzodiazepine that causes symptoms of withdrawal when stopped abruptly. The nurse should assess the client for tremors, agitation, irritability, insomnia, vomiting, sweating, tachycardia, headache, anxiety, and confusion. Euphoria or elevated mood is not a symptom of benzodiazepine withdrawal.
Question 183.
An IV infusion is to be administered through a scalp vein on an infant’s head. What should the nurse tell the parents to prepare them for the procedure?
(a) It may be necessary to remove a small amount of hair from the infant’s scalp.
(b) A sedative will be given to help keep the infant quiet.
(c) Visiting the infant will be delayed until the infusion has been completed.
(d) Holding the infant will be contraindicated while the infusion is being administered.
Answer:
(a) It may be necessary to remove a small amount of hair from the infant’s scalp.
Rationale:
Parents are typically quick to notice changes in their infant’s physical appearance. The removal of the infant’s hair may be upsetting to them if they have not been told why it is being done. Hair may be removed on the scalp at the site of needle insertion for IV therapy to provide better visualization and a smooth surface on which to attach tape to secure the needle. Sedatives are not ordinarily prescribed before IV fluid administration. In most instances, it is acceptable for parents to visit their infant while the IV solution is infusing. Holding the infant is encouraged to provide comfort.
Question 184.
Which nursing goal is most important for a client with acute pancreatitis?
(a) The client reports minimal abdominal pain.
(b) The client regains a normal pattern for bowel movements.
(c) The client limits alcohol intake to two to three drinks per week.
(d) The client maintains normal liver function.
Answer:
(a) The client reports minimal abdominal pain.
Rationale:
Abdominal pain can be a significant problem in acute pancreatitis. An expected outcome is to decrease or eliminate the pain the client is experiencing. Patterns of bowel elimination and liver function are not typically affected by pancreatitis. The client should avoid alcohol.
Question 185.
A nurse is caring for a child with type 1 diabetes mellitus at camp. The child is irritable and has a headache. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Administer 2 oz (60 mL) of orange juice.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) about the child’s status.
(c) Check the child’s blood glucose level.
(d) Send the child back to the planned activities.
Answer:
(c) Check the child’s blood glucose level.
Rationale:
The most appropriate initial response by the nurse would be to test the child’s blood glucose level. The child’s symptoms are consistent with hypoglycemia but could also be used by the child to avoid participation in planned activities. Administering milk or fruit juice during a mild reaction may also be appropriate if testing cannot be done. Notifying the HCP may be appropriate after the child’s glucose level has been obtained and emergency treatment has been initiated if the child is experiencing hypoglycemia. Returning the child to previous activities is not appropriate until either testing or administering treatment has been done.
Question 186.
A client tells the nurse that her bra fits more snugly at certain times of the month and she is concerned this may be a sign of breast cancer. The nurse should give the client which information about this situation?
(a) A change in breast size should be checked by her health care provider (HCP).
(b) Benign cysts tend to cause the breast to vary in size.
(c) It is normal for the breast to increase in size before menstruation begins.
(d) A difference in the size of her breasts is related to normal growth and development.
Answer:
(c) It is normal for the breast to increase in size before menstruation begins.
Rationale:
Normally, breasts are about the same size. They can vary in size before menstruation due to breast engorgement caused by hormonal changes. It is not necessary for an HCP Q to check this slight change in breast size. The changes in breast size this client described are most likely caused by hormonal changes, not a benign cyst or normal growth and development.
Question 187.
Which beliefs of traditional Chinese medicine found in Asian culture should the nurse consider when planning care for a follower of traditional Chinese medicine?
(a) Health is described as harmony between family members.
(b) Illness is caused by an imbalance of the yin and yang.
(c) Exercise to the point of overexertion can improve health.
(d) Illness is caused by a change in eating habits.
Answer:
(b) Illness is caused by an imbalance of the yin and yang.
Rationale:
Traditional Chinese medicine describes health as the balance of yin and yang. It describes health as harmony between the mind, body, and soul.
Question 188.
A client is scheduled for an intravenous pyelogram (IVP). In preparation for the procedure, what should the nurse ask the client?
(a) “Have you ever had an IVP before?”
(b) “Do you have any allergies?”
(c) “When was your last bowel movement?”
(d) “Have you ever experienced urinary incontinence?”
Answer:
(b) “Do you have any allergies?”
Rationale:
Before an IVP, the client should be assessed for allergies, particularly to iodine-based dyes that may be used during an IVP. Shellfish is a source of iodine, so people who are allergic to shellfish should inform the health care personnel and ask what type of dye is being used. Asking the client whether he or she has ever had an IVP before can help determine the degree of teaching needed before the procedure, but that is not the most important question. Neither the client’s last bowel movement nor urinary incontinence has any relationship to having an IVP.
Question 189.
Which oral contraceptive is considered safe for use while breastfeeding because it will not affect the breast milk supply once breastfeeding has been well established?
(a) estrogen
(b) estrogen and progestin
(c) progestin
(d) testosterone
Answer:
(c) progestin
Rationale:
Progestin alone has no effect on breast milk or breastfeeding once the milk supply is well established. Estrogen suppresses milk output. Testosterone is not given as an oral contraceptive.
Question 190.
The nurse is teaching the client to self- administer insulin. Which approach to establishing learning goals will likely be most effective? When the goals are established by the:
(a) nurse and client because both need to be responsible for teaching.
(b) health care provider (HCP) and client because the HCP is the manager of care and the client is the main participant.
(c) client because the client is best able to identify his or her own needs and how to meet those needs.
(d) client, nurse, pharmacist, and HCP so the client can participate in planning care with the entire team.
Answer:
(d) client, nurse, pharmacist, and HCP so the client can participate in planning care with the entire team.
Rationale:
Learning goals are most likely to be attained when they are established mutually by the client and members of the health care team, including the nurse, pharmacist, and the HCP. Learning is motivated by perceived problems or goals arising from unmet needs. The perception of the unmet needs must be the client's; however, the nurse, pharmacist, and HCP help the client arrive at his or her own perception of the need or reason to learn.
Question 191.
A multigravid client at 36 weeks’ gestation who is visiting the clinic for a routine visit begins to sob and tells the nurse, “My boyfriend has been beating me up once in a while since I became pregnant, but I can’t bring myself to leave him because I don’t have a job and I don’t know how I would take care of my other children.” What is the priority action by the nurse at this time?
(a) Contact a social worker for assistance and family counseling.
(b) Help the client make concrete plans for the safety of herself and her children.
(c) Tell the client that she should not allow anyone to hit her or her children.
(d) Provide the client with brochures on the statistics about violence against women.
Answer:
(b) Help the client make concrete plans for the safety of herself and her children.
Rationale:
In this situation, the client has indicated that she is not willing to leave the abusive boyfriend because of potential economic concerns and other children in the household. The nurse should explain the cycle of abuse (e.g., tension-building phase, battering incident, and honeymoon phase). The priority intervention is to assist the client to make concrete plans for the safety of herself and her children. The client should identify the safest, quickest routes out of the house and be able to identify where she will go once the cycle of violence escalates.
Contacting a social worker at this time is not appropriate because the client is not ready to leave the abusive situation. The nurse can tell the client that these services are available, but it is up to the client to determine whether a referral is necessary. Telling the client that she should not allow anyone to hit her or her children does not assist the client to make plans for her safety and the children’s safety should the violence escalate. The client may have a flat affect or feel extreme humiliation from the abuse. The client may also be feeling that the abuse is her fault.
When the client is ready to leave the abusive situation and receive continuous counseling, efforts can be made to increase her self-esteem and prevent additional violence. The client should be made aware of the available services in the community for women who are involved in abusive relationships. The location and phone numbers for available shelters should be provided to the client. Giving her a brochure related to the statistics about violence against women is not helpful and, if found by the abuser, may lead to further violence.
Question 192.
Several children were admitted yesterday. In which order of priority from first to last would the nurse assess these children? All options must be used.
(a) a 3-month-old infant with respiratory syncytial virus and stable vital signs
(b) a 10-month-old infant with pneumonia and respiratory rate of 50 breaths/min
(c) a 3-year-old child with acute pyelonephritis and a temperature of 104.5
(d) a 12 year-old child with a fractured femur and lacerated liver.
Answer:
(d) a 12 year-old child with a fractured femur and lacerated liver.
(c) a 3-year-old child with acute pyelonephritis and a temperature of 104.5
(b) a 10-month-old infant with pneumonia and respiratory rate of 50 breaths/min
(a) a 3-month-old infant with respiratory syncytial virus and stable vital signs
Rationale:
The child whose condition could change most quickly should be assessed first, and the most stable child should be assessed last. The child with a lacerated liver is at the highest risk for a rapid change in condition. Therefore, this child should be assessed first because the child is at high risk for hemorrhage. The next child to be assessed is the 3-year-old child with pyelonephritis and fever. The fever needs to be acted upon, but this assessment is not as critical as that for the child with a lacerated liver.
The normal respiratory rate for a 10-month-old infant is 30 breaths/min. Although the infant is tachypneic, this is expected with pneumonia. Additionally, the infant is not in acute respirator? distress. However, the increased respiratory rate needs evaluation, so the 10-month-old infant should be assessed before the 3-month-old infant with respiratory syncytial virus who has stable vital signs and is not in acute distress.
Question 193.
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim has been prescribed for a client who has a urinary tract infection. What should the nurse do when administering sulfonamides?
(a) Encourage the client to take the medication with meals.
(b) Instruct the client to drink at least eight glasses of water a day.
(c) Measure the client’s urine output.
(d) Instruct the client that the urine may turn reddish orange.
Answer:
(b) Instruct the client to drink at least eight glasses of water a day.
Rationale:
The client who is taking sulfadiazine should be instructed to drink at least eight glasses of water a day to prevent the development of crystallu- ria. Sulfadiazine should be taken on an empty stomach with a full glass of water. It does not require that the client’s urine output be measured and does not affect the color of the urine.
Question 194.
A client admitted with a diagnosis of dementia becomes agitated and violent. The nurse is reviewing the client’s medication record. Which prescribed medication would be expected to reduce agitation?
(a) tacrine
(b) ergoloid
(c) diazepam
(d) risperidone
Answer:
(d) risperidone
Rationale:
Risperidone is prescribed for severe agitation and has a rapid response. Ergoloid and tacrine stabilize and may improve the cognitive functioning of clients with dementia. Diazepam is an antianxiety agent that would not have the desired effect on the severe agitation, violence, and bizarre thoughts.
Question 195.
A client has been diagnosed with multi-infarct (or vascular) dementia (MID). When preparing a teaching plan for the client and family, the nurse should indicate which action as the most critical for slowing MID?
(a) administering anticoagulants such as warfarin
(b) administering benzodiazepines such as loraz-epam to decrease choreiform movements
(c) managing related symptoms such as depression
(d) managing the symptoms by increasing dopamine availability
Answer:
(a) administering anticoagulants such as warfarin
Rationale:
MID results from multiple small blood clots in the brain. Therefore, the most critical factor is using anticoagulants to reduce the risk of more infarcts. Administering benzodiazepines such as lorazepam to decrease choreiform movements is associated with Huntington’s disease.
Although depression is common with MID, managing depression-related symptoms will not slow the progression of MID. Managing symptoms by increasing dopamine availability is appropriate for clients with Parkinson’s disease.
Question 196.
While performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on a 5-year-old child, the nurse palpates for a pulse. Which site is best for checking the pulse during CPR in a 5-year-old child?
(a) femoral artery
(b) carotid artery
(c) radial artery
(d) brachial artery
Answer:
(b) carotid artery
Rationale:
Checking the carotid artery pulse in a child during CPR provides information about perfusion of the brain. The brachial pulse is checked in an infant because the infant’s short and typically fat neck makes it difficult to palpate the carotid pulse. The femoral and radial arteries might indicate perfusion to the peripheral body sites, but the critical need is for adequate circulation to the brain.
Question 197.
A nurse is assessing a client with nephrotic syndrome. The nurse should assess the client for which condition?
(a) hematuria
(b) massive proteinuria
(c) increased serum albumin level
(d) weight loss
Answer:
(b) massive proteinuria
Rationale:
Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by massive proteinuria caused by increased glomerular membrane permeability. Other symptoms include peripheral edema, hyperlipidemia, and hypoalbu- minemia. Because of the edema, clients retain fluid and may gain weight. Hematuria is not a symptom related to nephrotic syndrome.
Question 198.
A child with tetralogy of Fallot and a history of severe hypoxic episodes is to be admitted to the pediatric unit. What would be most important for the nurse to have at the bedside?
(a) morphine sulfate in a syringe ready to administer
(b) oxygen tubing and flow meter plugged in
(c) blood pressure cuff and stethoscope
(d) suction tubing and equipment
Answer:
(b) oxygen tubing and flow meter plugged in
Rationale:
Because the child has a history of severe hypoxic episodes, having oxygen readily available at the bedside is most important. Should the child experience another hypoxic episode, oxygen could be administered easily and quickly. Although morphine causes peripheral dilation, which causes the blood to remain in the periphery, decreasing system volume and oxygen administration is the priority. Also morphine is a controlled substance and must be stored securely at all times. Typically, a child with tetralogy of Fallot with episodes of hypoxia does not require suctioning.
Question 199.
The nurse is assessing the pain level in a client who typically gives a stoic response to describing the pain. Which comment from this client is expected?
(a) “Enduring pain is a part of God’s will.”
(b) “This pain is killing me.”
(c) “I’ve got to see a health care provider (HCP) right away.”
(d) “I can’t go on in pain like this any longer.”
Answer:
(a) “Enduring pain is a part of God’s will.”
Rationale:
Although individuals differ in their response to pain, the most likely attitude of a client who typically responds to pain stoically, is to endure pain as a part of God’s will, and to delay requesting pain medication. The nurse can validate the client’s response and respect his or her choice about receiving pain medication.
Question 200.
A client is voiding small amounts of urine every 30 to 60 minutes. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Palpate for a distended bladder.
(b) Catheterize the client for residual urine.
(c) Obtain a urine specimen for culture.
(d) Encourage an increased fluid intake.
Answer:
(a) Palpate for a distended bladder.
Rationale:
When a client voids frequent, small amounts, the nurse should suspect that the client is retaining urine. Palpating for a distended bladder is the first assessment that the nurse should perform to verify this suspicion. Obtaining a prescription to catheterize for residual urine may be appropriate as a follow-up activity. Obtaining a urine specimen for culture is not a first priority. The nurse would not encourage an increased fluid intake until further assessment of the situation is completed.
Question 201.
When making rounds, the nurse should assess which client first?
(a) a 16-month-old child with periorbital cellulitis who is to be discharged today
(b) a 7-year-old child who had an appendectomy yesterday and developed peritonitis
(c) a 10-year-old child who has just been admitted in sickle cell crisi
(d) a 16-year-old adolescent receiving a 3rd day of chemotherapy
Answer:
(c) a 10-year-old child who has just been admitted in sickle cell crisi
Rationale:
Of the clients listed, the newly admitted client should be assessed first. This is the client who is likely to be unstable and in pain. The child to be discharged today would be considered the most stable and therefore would be assessed last.
Question 202.
Which action has the highest priority for the care of a client with chronic renal failure?
(a) Apply corticosteroid creams to relieve itching.
(b) Achieve pain control with analgesics.
(c) Maintain a low-sodium diet.
(d) Measure abdominal girth daily.
Answer:
(c) Maintain a low-sodium diet.
Rationale:
It is appropriate for the client to be on a low-sodium diet to help decrease fluid retention. Dry skin and pruritus are common in renal failure. Lotions are used to relieve the dry skin, and antihistamines may be used to control itching; corticosteroids are not used. Pain is not a major problem in chronic renal failure, but analgesics that are excreted by the kidneys must be avoided. It is not necessary to measure abdominal girth daily because ascites is not a clinical problem in renal failure.
Question 203.
The father of an 18-month-old with no previous illness and who has been admitted to a surgery center for repair of an inguinal hernia tells the nurse that his child is having trouble breathing. The father does not think the child choked. After telling the clerk to call the rapid response team, the nurse should take which actions? Place in order from first to last. All options must be used.
(a) Notify the surgeon.
(b) start an intravenous infusion.
(c) Assess the effectiveness of the abdominal thrusts.
(d) Perform the abdominal thrust maneuver.
Answer:
(d) Perform the abdominal thrust maneuver.
(c) Assess the effectiveness of the abdominal thrusts.
(b) start an intravenous infusion.
(a) Notify the surgeon.
Rationale:
The most frequent cause of respiratory distress in a toddler with no previous illness is foreign body aspiration. After having the clerk call for the rapid response team , the nurse should assess the child for breaths, and then begin abdomi-nal thrusts. Next, the nurse (or rapid response team if present) should assess the effectiveness of the abdominal thrusts, and then start an intravenous infusion. Finally, the nurse can notify the surgeon.
Question 204.
The nurse is assessing a child’s skeletal traction and notices that the weights are on the floor. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Raise the weights so that the child can move up in bed.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) immediately.
(c) Put the foot of the bed on blocks.
(d) Move the child up in bed.
Answer:
(d) Move the child up in bed.
Rationale:
The traction weights should be hanging freely to maintain pull. The child needs to be moved up in bed with the weights left untouched to continue countertraction. Then the nurse can determine whether blocks are necessary to maintain the child in the correct position. Raising the weights is inap-propriate because doing so interferes with countertraction. The HCP does not need to be notified. The nurse can easily correct the problem by moving the child up in bed.
Question 205.
Compared to the food requirements of preschoolers and adolescents, the food requirements of school-age children are not as great because which factor is lower in these children?
(a) growth rate
(b) metabolic rate
(c) level of activity
(d) hormonal secretion rate
Answer:
(a) growth rate
Rationale:
Children ages 6 to 12 have a slower growth rate than do younger children and adolescents. As a result, their food requirements are comparatively less.
Question 206.
When assessing a 17-year-old client with depression for suicide risk, which question would be best?
(a) “What movies about death have you watched lately?”
(b) “Can you tell me what you think about suicide?”
(c) “Has anyone in your family ever committed suicide?”
(d) “Are you thinking about killing yourself?”
Answer:
(d) “Are you thinking about killing yourself?”
Rationale:
Asking whether the client is thinking about killing herself is the most direct and therefore the best way to assess suicide risk. Knowing whether the client has recently watched movies on suicide and death, what the client thinks about suicide, or about previous suicides of family members will not tell the nurse whether the client herself is thinking about committing suicide right now.
Question 207.
Which intervention should the nurse suggest to a parent to relieve itching in a child with chickenpox?
(a) generous amounts of fine baby powder
(b) oatmeal preparation baths
(c) soft towels moistened with hydrogen peroxide
(d) cool compresses moistened with a weak salt solution
Answer:
(b) oatmeal preparation baths
Rationale:
Because of their colloidal properties, oatmeal preparation baths typically help relieve the itching associated with chickenpox. Calamine lotion can be also be used if there are no open lesions. Baby powder is unlikely to relieve itching because it acts primarily to absorb moisture. A soft towel moistened with hydrogen peroxide is unlikely to relieve itching. Rather, hydrogen peroxide is used to clean wounds. A cool compress moistened with a weak salt solution is unlikely to relieve itching because it does not have any antipruritic properties.
Question 208.
A woman who has preeclampsia is receiving magnesium sulfate 20 g per 500 mL of lactated Ringers via infusion pump. The prescribed rate of infusion is 2 g/h. How many mL/h should the nurse set the infusion pump for? Record your answer using a whole number.
......................... mL/h.
Answer:
50 mL/h.
Rationale:
X = 500 mL/20 g x 2 g/h
X = 50 mL/h
Question 209.
Which technique is best for the nurse to use in evaluating the parents’ ability to administer ear drops correctly?
(a) Observe the parents instilling the drops in the child’s ear.
(b) Listen to the parents as they describe the procedure.
(c) Ask the parents to list the steps in the procedure.
(d) Inquire if the parents have performed the procedure before.
Answer:
(a) Observe the parents instilling the drops in the child’s ear.
Rationale:
Return demonstrations are the best way to evaluate a person’s ability to perform a skill. This technique enables the teacher to observe not only the learner’s sequencing of steps of the procedure but also the learner’s ability to perform the skill.
Question 210.
Ibuprofen is prescribed for a client with osteoarthritis. Which instruction about ibuprofen should the nurse include in the client’s teaching plan?
(a) Report the development of tinnitus.
(b) Increase vitamin B12 intake.
(c) Take with food or antacids.
(d) Have the complete blood count (CBC) monitored monthly.
Answer:
(c) Take with food or antacids.
Rationale:
Ibuprofen should be taken with food or antacids to avoid the development of gastrointestinal distress. Tinnitus is not an adverse effect of ibuprofen; it is a sign of salicylate toxicity. There is no need to increase vitamin Bl2 intake. The CBC is not typically monitored monthly, although clients should be told to report signs of unusual bleeding because ibuprofen can prolong bleeding time.
Question 211.
A staff member states, “I don’t know why Mary is so depressed. She lives in an exclusive part of town and has gorgeous clothes. Her husband seems to care about her very much. She really has it all.” What should the nurse conclude from the staff member’s statement?
(a) An accurate assessment of the client has been made.
(b) The staff member is jealous of the client.
(c) There is no reason for the client to be depressed.
(d) The staff member needs teaching about major depression.
Answer:
(d) The staff member needs teaching about major depression.
Rationale:
The nurse concludes that the staff member needs teaching about depression, specifically the biological basis of major depression, when the staff member states the client has no reason to be depressed because “she really has it all.” Major depression, or endogenous depression, is caused by alterations of neurotransmitters, primarily serotonin and norepinephrine. Genetics and hereditary also predispose an individual to develop depression.
Therefore, there may not be an external cause or a reason for depression to develop. Depression that occurs from an external cause is known as reactive depression, and it could be caused by a loss or a life stress.
Question 212.
The nurse is instructing the mother of a child with asthma about noting food triggers for asthma attacks. Which food would most likely be responsible for causing an allergic reaction?
(a) fish
(b) tossed salad
(c) pork chop
(d) oranges
Answer:
(a) fish
Rationale:
In asthma, the airways react to certain external and internal stimuli, including allergens, infections, exercise, and emotions. Food allergens commonly associated with asthma include soy, wheat, egg whites, dairy products, nuts, shellfish, and fish.
Question 213.
Which family should the nurse determine as most in need of follow-up?
(a) a single mother with a 7-month-old child whose immunizations are delayed
(b) a two-parent family whose 3-year-old has a fractured leg from an automobile accident
(c) a single parent with a toddler who has third-degree burns over 20% of the body
(d) a two-parent family with a foster child who has a history of caustic liquid ingestion
Answer:
(c) a single parent with a toddler who has third-degree burns over 20% of the body
Rationale:
Toddlers receive burns usually as the result of not being closely supervised. Toddlers are very inquisitive and need constant supervision; therefore, close follow-up is necessary. In addition, the child probably will need some type of wound care requiring involvement of the parent and possibly others. The amount of support available to the single parent of the 7-month-old child is not known.
Although immunization schedules need to be adhered to, it is very possible for a 7-month-old to be delayed in receiving immunizations because of illness or other conflicts. An automobile accident can happen to anyone and does not indicate a lack of safety or supervision. A history of caustic liquid ingestion in a foster child may have been from a time before the child began living with the foster parents; it does not indicate a lack of safety or supervision.
Question 214.
After several hours of induction with intravenous oxytocin administered along with a primary intravenous solution of lactated Ringer’s solution, assessment of a primigravida at 42 weeks’ gestation reveals a fetal heart rate near the baseline at 120 bpm and strong contractions occurring every 2 to 2.5 minutes and lasting 90 to 100 seconds. In what order from first to last should the nurse per-form the required actions? All options must be used.
(a) Position the client in a lateral position.
(b) Contact the primary care provider for futher prescriptions
(c) stop the intravenous flow of oxytocin
(d) Adminster oxygen at a rate of 8 to 10 L./min
Answer:
(c) stop the intravenous flow of oxytocin
(a) Position the client in a lateral position.
(d) Adminster oxygen at a rate of 8 to 10 L./min
(b) Contact the primary care provider for futher prescriptions
Rationale:
The nurse first should stop the intravenous flow of oxytocin because the client is exhibiting a hypertonic uterine contraction pattern caused by the oxytocin. Once the oxytocin infusion is stopped, the nurse should place the client in a lateral position to improve placental blood flow to the fetus. The nurse should next administer oxygen and then contact the primary care provider to report the situation and obtain further prescriptions.
Question 215.
When planning care for a group of clients, the nurse should identify which client as having the greatest risk for the development of pressure ulcers?
(a) a client who ambulates four times a day
(b) a client with an indwelling urinary catheter
(c) a client who has a decreased serum albumin level
(d) a client with an elevated white blood cell count
Answer:
(c) a client who has a decreased serum albumin level
Rationale:
Risk factors for the development of pressure ulcers include poor nutrition, indicated by a decreased serum albumin level. According to the Guidelines for Pressure Ulcers published by the Agency for Health care Research and Quality, other risk factors include immobility, incontinence, and decreased sensation.
A client who does not ambulate often can be repositioned frequently to prevent pressure ulcers. Having an indwelling urinary catheter does not normally increase the risk of developing a pressure ulcer unless pressure from the tubing impinges on urethral or other tissue. An elevated white blood cell count does not place a client at risk for pressure ulcers.
Question 216.
A 16-year-old primigravida at 36 weeks’ gestation who has had no prenatal care experienced a seizure at work and is being transported to the hospital by ambulance. What should the nurse do upon the client’s arrival?
(a) Position the client in a supine position.
(b) Auscultate breath sounds every 4 hours.
(c) Monitor the vital signs every 4 hours.
(d) Admit the client to a quiet, darkened room.
Answer:
(d) Admit the client to a quiet, darkened room.
Rationale:
Because of her age and report of a seizure, the client is probably experiencing eclampsia, a condition in which convulsions occur in the absence of any underlying cause. Although the actual cause is unknown, adolescents and women older than 35 years are at higher risk. The client’s environment should be kept as free of stimuli as possible. Thus, the nurse should admit the client to a quiet, darkened room.
Clients experiencing eclampsia should be kept on the left side to promote placental perfu-sion. In some cases, edema of the lungs develops after seizures and is a sign of cardiovascular failure. Because the client is at risk for pulmonary edema, breath sounds should be monitored every 2 hours. Vital signs should be monitored frequently, at least every hour.
Question 217.
An adult admitted to the hospital with a hemoglobin of 6.5 g/dL (65 g/L) is experiencing cerebral tissue hypoxia. What should the nurse do
next?
(a) Plan frequent rest periods throughout the day.
(b) Assist the client in ambulating to the bathroom.
(c) Check the temperature of the water before the client showers.
(d) Refer the client to occupational therapy for energy conservation interventions.
Answer:
(b) Assist the client in ambulating to the bathroom.
Rationale:
Cerebral hypoxia is commonly associated with dizziness. The greatest risk of injury to a client with dizziness is a fall. Frequent rests and energy conservation measures should be included in the client’s plan of care, but safety from falls is the greatest need. Checking the shower water temperature is not critical for this client, who will not be showering because of her fall risk.
Question 218.
A nurse is assessing an older adult with pneumonia. Where should the nurse place the stethoscope to listen for breath sounds that will indicate the client is fully oxygenating the lung on the right side?
Answer:
Rationale:
The nurse should auscultate the right lower lobe and listen as the client inhales and exhales. The nurse should be able to hear vesicular breath sounds.
Question 219.
During care, the client suddenly blurts out, “My doctor just told me that I’m going to have to have chemotherapy after all; I was hoping to avoid it.” Which is the nurse’s most therapeutic response?
(a) “Well, you’re under the care of our best oncologist; I’m certain the oncologist knows what’s best.”
(b) “What concerns you most about possible chemotherapy?”
(c) “You know, you can get a second opinion before you agree to any of that.”
(d) “I understand how you feel. I’d feel the same way. ”
Answer:
(b) “What concerns you most about possible chemotherapy?”
Rationale:
The most therapeutic nursing response is client centered and goal directed and provides an opportunity for the client to say more, for example, to express additional emotions, needs, or issues. Option (a) is nontherapeutic; it is a false reassurance. Option (c) is also nontherapeutic; the nurse offers a personal opinion of the client’s situation. Option (d) is also nontherapeutic; the nurse changes the subject and appears to be uncomfortable discussing the client’s concerns.
Question 220.
Two parents who are arguing in their infant’s room, with voices raised and getting louder, start to hit each other. The infant is crying. Which action should the staff nurse take next?
(a) Try to reason with both of the parents.
(b) Ask one of the parents to leave the room.
(c) Call security to come and break up the fight.
(d) Remove the infant from the room.
Answer:
(d) Remove the infant from the room.
Rationale:
The situation is escalating, and the nurse’s priority is to protect the infant from harm. Therefore, the removal of the infant from this situation should be the first action by the nurse. Reasoning at this point or asking one of the parents to leave the room would be ineffective and may serve to further escalate the situation. Calling security is necessary, but only after the nurse has removed the infant from the room.
Question 221.
A hospitalized client is experiencing “fight versus flight,” a stress-mediated physiologic response. As a result, the nurse should assess the client for which symptom?
(a) increased urinary output
(b) decreased arterial blood pressure
(c) increased blood glucose
(d) decreased mental acuity
Answer:
(c) increased blood glucose

Rationale:
Responses to physiologic stress, such as hospitalization, surgery, or pain, are a result of catecholamine release and specifically include increased heart rate and blood pressure, increased bronchiolar dilation, water retention and decreased urinary output, increased blood glucose, and increased mental acuity.
Question 222.
The nurse observes an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) sharing extensive stories of her own mother’s death with a dying client’s husband. Which statement demonstrates appropriate feedback for the nurse to offer to the UAP?
(a) “I thought that was really great how you talked with him; he seemed really scared.”
(b) “You provided excellent client education by sharing your stories.”
(c) “I think it helps clients to see us as real people, and friends too, when you share your own stories.”
(d) “It’s probably best to avoid talking about your personal experience very much; keep communication client centered.”
Answer:
(d) “It’s probably best to avoid talking about your personal experience very much; keep communication client centered.”
Rationale:
Therapeutic communication is always purposeful, goal-directed, and client-centered. If self-disclosure is used by the nurse or the UAP it should be very focused and limited to just enough to support further communication with the client. It is not always helpful (or educational) and often inappropriate to share personal stories with clients.
Question 223.
Assessment of a primigravida in active labor reveals cervical dilation at 9 cm with complete effacement and the fetus at +1 station. What should the nurse do when the primary care provider prescribes meperidine 50 mg intramuscular (IM) for the client?
(a) Administer the medication in the left ventrogluteal muscle.
(b) Be certain that naloxone is at the client’s bedside.
(c) Ask the primary care provider to validate the dosage of the drug.
(d) Refuse to administer the medication to the client.
Answer:
(d) Refuse to administer the medication to the client.

Rationale:
The nurse should refuse to administer the medication to the client because of the risk of respiratory depression in the neonate. Meperidine, given IM, peaks in 30 to 60 minutes and lasts 2 to 4 hours. Based on the assessment findings, the client most likely will be giving birth within that time frame, increasing the risk for respiratory depression in the neonate, a serious consequence.
Therefore, the nurse should not administer the drug. Naloxone should be readily available whenever narcotics that can result in respiratory depression are used. Asking the primary care provider to validate the dosage is not necessary. For clients in early labor, meperidine can be given IM in dosages ranging from 50 to 100 mg.
Question 224.
Which nursing action is appropriate when planning care for a client who is being battered? Select all that apply.
(a) Give information about a safe home.
(b) Provide a cell phone and the crisis help line telephone number.
(c) Help the client displace her feelings.
(d) Teach the client about the cycle of violence.
(e) Discuss the client’s legal and personal rights.
Answer:
(b) Provide a cell phone and the crisis help line telephone number.
(d) Teach the client about the cycle of violence.
(e) Discuss the client’s legal and personal rights.
Rationale:
When working with a battered client, the nurse should give information about a safe home and provide a cell phone and information about the crisis help line. The nurse should also help the client understand the cycle of violence as well as personal and legal rights. The nurse should help the client share and discuss her anger, frustration, guilt, shame, and other feelings. Displacing, that is, placing feelings onto another person or object, is not helpful to the client and is not a healthy way to handle feelings.
Question 225.
Which client is at greatest risk for obtaining inadequate nutrition?
(a) the client with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
(b) the client recovering from a femur fracture
(c) the client who is breastfeeding
(d) the client with burns to 45% of the body
Answer:
(d) the client with burns to 45% of the body
Rationale:
With illness or injury, there is a need to heal or recover. To accomplish this, the client must consistently consume adequate nutrition (and protein) to maintain a positive nitrogen balance and to experience necessary growth and/or healing. The client with burns has the greatest nutritional needs, due to the extent of the injury. Clients with diabetic neuropathy can be encouraged to follow the diabetic diet plan and manage pharmacological therapy to prevent further neuropathy.
The client with a fractured femur is not at risk for inadequate nutrition unless there is also a reason the client is not eating. The client who is breastfeeding needs additional calories, but if the client is eating a well-balanced diet with additional calories, the client is not at risk for obtaining inadequate nutrition.
Question 226.
The use of a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump is effective in which situation?
(a) The client achieves a therapeutic level of analgesia.
(b) The client does not become dependent on opioids postoperatively.
(c) There is decreased cost by decreasing use of intramuscular (IM) injections.
(d) The family can assist the client in managing the pain.
Answer:
(a) The client achieves a therapeutic level of analgesia.
Rationale:
PCA is used to manage postoperative or persistent pain. Clients can control the administration of their own medication within predetermined safety limits; there is not a risk of dependence on opioids when using PCAs is not a concern. Family members who are not authorized agents are cautioned not to push the button for the client because this overrides some of the safety features of the PCA system. The nurse retains the responsibility for monitoring the client. Cost is not the primary factor in pain management.
Question 227.
A client’s chest tube is connected to a drainage system with a water seal. The nurse notes that the fluid in the water seal column is fluctuating with each breath that the client takes. How should the nurse interpret this finding? Fluctuation means that:
(a) there is an obstruction in the chest tube.
(b) the client is developing subcutaneous emphysema.
(c) the chest tube system is functioning properly.
(d) there is a leak in the chest tube system.
Answer:
(c) the chest tube system is functioning properly.
Rationale:
Fluctuation of fluid with respirations in the water seal column indicates that the system is functioning properly. If an obstruction were present in the chest tube, fluid fluctuation would be absent. Subcutaneous emphysema occurs when air pockets can be palpated beneath the client’s skin around the chest tube insertion site. A leak in the system is indicated when bubbling occurs in the water seal column.
Question 228.
A client is taking metformin. To prevent lactic acidosis when taking this drug, the nurse should instruct the client to report which symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) hyperventilation
(b) muscle discomfort
(c) dizziness
(d) headache
(e) increased hunger
(f) tingling in the fingertips
Answer:
(a) hyperventilation
(b) muscle discomfort
(c) dizziness
Rationale:
There is a high risk of lactic acidosis when using metformin; 50% of the cases may be fatal. A black box warning for metformin is to instruct the client to stop the drug and immediately notify the prescriber about unexplained hyperventilation, muscle pain, malaise, dizziness, light-head-edness, unusual sleepiness, unexplained stomach pain, feelings of coldness, slow or irregular heart rate, or other nonspecific symptoms of early lactic acidosis. Headache, hunger, and tingling in the fingertips are not signs of lactic acidosis.
Question 229.
The nurse is serving on a task force to update the electronic health record. The task force should ensure that the revisions of the medical record will produce which outcome? Select all that apply.
(a) Aid in client care.
(b) Serve as a legal document.
(c) Have sufficient room for charting nurses’ notes.
(d) Facilitate data collection for clinical research.
(e) Guide performance improvement.
(f) Ensure that the revisions are written so the client can understand what is written.
Answer:
(a) Aid in client care.
(b) Serve as a legal document.
(d) Facilitate data collection for clinical research.
(e) Guide performance improvement.
Rationale:
The electronic health record should contain sufficient information to identify the client, support the diagnosis, justify treatment, document the client’s course and results, and facilitate continuity of care among health care providers (HCPs) m The medical record will facilitate client care, serve as a financial and legal record, aid in clinical research, support decision analysis, and guide professional and organizational performance improvement.
The medical record should be compiled concurrently and be completed at the time of discharge. Many disciplines may be authorized to make entries in the medical record. All health care personnel will document care on this record. The medical record is not written for clients; if clients need information, the nurse or appropriate health care professional can explain the information to them.
Question 230.
The nurse discovers that a hospitalized client with stage 4 esophageal cancer and major depression has a gun in the home. What is the best nursing intervention to help the client remain safe after discharge?
(a) Give the client the number of a 24-hour crisis phone line for use, if needed.
(b) Tell the health care provider (HCP) the client is too high risk for discharge at this time.
(c) Have the client promise to use the gun only for home protection.
(d) Talk with the HCP about requiring gun removal as a condition of discharge.
Answer:
(d) Talk with the HCP about requiring gun removal as a condition of discharge.
Rationale:
The only action that keeps the client safe is the removal of the gun. If the HCP is considering discharge, the client is medically stable and will not be able to remain in the medical hospital any longer. The client’s lack of current suicidal ideation means he cannot be hospitalized for psychiatric reasons. While helpful, the crisis phone line number and the client’s promise do not ensure safety.
Question 231.
A client with severe osteoarthritis and decreased mobility is moved to an assisted living facility. The nurse notices that the client smells of alcohol, is slurring words, and has six wine bottles in the trash. The client tells the nurse, “Those are my other pain medicines.” Which statements by the nurse are appropriate? Select all that apply.
(a) “I didn’t realize that your pain was not being managed with your current medication.”
(b) “It’s important for me to know how many bottles of wine you drank this week.”
(c) “I’m worried about the amount of wine you are drinking and its effects on your balance.”
(d) “How are you getting all this wine?”
(e) “I’m calling your health care provider (HCP) to have all of us talk about better pain control without the wine.”
Answer:
(a) “I didn’t realize that your pain was not being managed with your current medication.”
(b) “It’s important for me to know how many bottles of wine you drank this week.”
(c) “I’m worried about the amount of wine you are drinking and its effects on your balance.”
(d) “How are you getting all this wine?”
(e) “I’m calling your health care provider (HCP) to have all of us talk about better pain control without the wine.”

Rationale:
Acknowledging the client’s concern about pain and expressing the nurse’s concern about the client’s condition is important to help the client open up and gain a further assessment of the pain in this client. Awareness of the amount of wine consumed in a week will be helpful to guide which kind of detoxification will be needed. Expressing the nurse’s concern about the client’s safety is important.
How the client is getting the wine is least important because there are so many possibilities, such a weekly shopping trips in the facility van or having friends or family bring it in. Notifying the primary care provider about the situation and arranging for a joint conference are important for the client’s safety and recovery.
Question 232.
Which child most needs a referral for developmental language delay?
(a) the 1-year-old who does not have three words
(b) the 18-month-old who only points to one body part
(c) the 2-year-old who only combines two words
(d) the 4-year-old who is difficult to understand
Answer:
(d) the 4-year-old who is difficult to understand
Rationale:
More than 90% of children have speech that is totally intelligible at 4 years of age. Having one word at 1 year is the expectation. Having three words is a 15-month milestone. Pointing to one body part at 18 months and combining two words at 2 years would be a normal finding.
Question 233.
A client is being admitted with nursing home-acquired pneumonia. The unit has four empty beds in semiprivate rooms. The room that would be most suitable for this client is the one with which other client?
(a) a 60-year-old client admitted for investigation of transient ischemic attacks
(b) a 45-year-old client with an abdominal hysterectomy
(c) a 24-year-old client with non-Hodgkin’slymphoma
(d) a 55-year-old client with alcoholic cirrhosis
Answer:
(a) a 60-year-old client admitted for investigation of transient ischemic attacks
Rationale:
The client with a possible transient ischemic attack is the only client who has not had surgery and is not immunocompromised. The client with a recent surgery and incision should not be exposed to a client with infection. Clients with cancer or alcoholic cirrhosis are very susceptible to infection, and it would not be safe to expose them to a client with a respiratory infection.
