Working through NCLEX PN Study Guide can boost confidence and reduce test anxiety by building familiarity and competence.
NCLEX-RN Comprehensive Test 1 with Rationale
Question 1.
A client with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome confides that he is homosexual and his employer does not know his HIV status. Which response by the nurse is best?
(a) “Would you like me to help you tell your employer?”
(b) “The information you confide in me is confidential.”
(c) “I must share this information with your family. ”
(d) “I must share this information with your employer.”
Answer:
(b) “The information you confide in me is confidential.”
Rationale:
The nurse is responsible for maintaining confidentiality of this disclosure by the client. The nurse cannot discuss the client’s health problems with the family or employer. It is the client’s reprehensibil- ity to inform others if he or she chooses to do so.
Question 2.
An older adult client is being admitted to same-day surgery for cataract extraction. The client has several diamond rings. What information should the nurse give the client about how the rings will be secured during surgery?
(a) The rings will be taped on the fingers before the surgery.
(b) The rings will be placed in an envelope, the client will sign the envelope, and the envelope will be placed in a safe.
(c) The rings will be locked in the narcotic box.
(d) The nursing supervisor will hold onto the rings until the client returns from the recovery room.
Answer:
(b) The rings will be placed in an envelope, the client will sign the envelope, and the envelope will be placed in a safe.
Rationale:
Under the policy for valuables, the nurse documents the description on an envelope with the client, the client and nurse sign the envelope, and the valuables envelope is locked in the safe. The other options increase the risk of loss or damage to the client’s valuables.
Question 3.
Under which circumstance may a nurse communicate medical information without the client’s consent?
(a) when certifying the client’s absence from work
(b) when requested by the client’s family
(c) when treating the client with a sexually transmitted infection
(d) when prescribed by another health care provider (HCP)
Answer:
(c) when treating the client with a sexually transmitted infection
Rationale:
Sexually transmitted infections are communicable diseases that must be reported. The nurse is responsible for reporting these diseases to the appropriate public health agency and to otherwise maintain the client’s confidentiality. The client’s family cannot request release of medical information without the client’s consent. An HCP’s D prescription is not a substitute for a client’s consent to release medical information in the absence of a communicable disease.
Question 4.
A young adult is brought to the emergency department with his fiancee after being involved in a serious motor vehicle accident. His Glasgow Coma Scale score is 7, and he demonstrates evidence of decorticate posturing. Which action is appropriate for obtaining permission to place a catheter for intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring?
(a) The nurse will obtain a signed consent from the client’s fiancee because he is of legal age and they are engaged to be married.
(b) The health care provider (HCP) will get a consultation from another health care provider and proceed with placement of the ICP catheter until the family arrives to sign the consent.
(c) Two nurses will receive a verbal consent by telephone from the client’s next of kin before inserting the catheter.
(d) The health care provider will document the emergency nature of the client’s condition and that an ICP catheter for monitoring was placed without consent.
Answer:
(d) The health care provider will document the emergency nature of the client’s condition and that an ICP catheter for monitoring was placed without consent.
Rationale:
In a life-threatening emergency where time is of the essence in saving life or limb, consent Q is not required. This client has a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 7, which indicates a comatose state. The client cannot be aroused, withdraws in a purposeless manner from painful stimuli, exhibits decorti-cate posturing, and may or may not have brain stem reflexes intact. The placement of the ICP monitor is crucial to determine cerebral blood flow and prevent herniation.
The client's fiancee cannot sign the consent because, until she is his wife or has designated power of attorney, she is not considered his next of kin. The HCP [J should insert the catheter in this emergency. He does not need to get a consultation from another HCP. When consent is needed for a situation that is not a true emergency, two nurses can receive a verbal consent by telephone from the client’s next of kin.
Question 5.
The nurse notices that a cart being used to transport a client has a nonfunctioning clasp on the safety belt. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Call the safety/security department to report the problem.
(b) Use a draw sheet to secure the client during transport.
(c) Contact the clinical engineering department to repair the clasp.
(d) Request that the transporter bring a different cart with a functional clasp.
Answer:
(d) Request that the transporter bring a different cart with a functional clasp.
Rationale:
The nurse ensures client safety during transport and therefore requests another cart for transport. The other options do not ensure client safety. Method of transportation and person transporting the client are documented by the nurse responsible for the transfer. The clasp needs to be repaired. Contacting the security department is not appropriate.
Question 6.
When coaching clients to improve their health, which strategy is the most effective for the nurse to use to help clients take an active role in their health care?
(a) Ask clients to complete a questionnaire.
(b) Provide clients with written instructions.
(c) Ask clients for their views of their health and health care.
(d) Ask clients if they have any questions about their health.
Answer:
(c) Ask clients for their views of their health and health care.
Rationale:
One of the best strategies to help empower clients to manage their health is to ask them their view of situations and to respond to what they say. This technique acknowledges that clients’ opinions have value and relevance to the interview. It also promotes an active role for clients in the process. Use of a questionnaire or written instructions is a means of obtaining information but promotes a passive client role. Asking whether clients have questions encourages participation, but alone, it does not acknowledge their views.
Question 7.
The nurse is planning care for a client who chews the lingers constantly. Before applying mitten restraints, the nurse could try which interventions? Select all that apply.
(a) Ask the client to rub lotion over the hands every day after bathing.
(b) Encourage physical activity, such as ambulation.
(c) Provide frequent contacts for communication and socialization.
(d) Provide family education.
(e) Encourage involvement of family and friends.
Answer:
(b) Encourage physical activity, such as ambulation.
(c) Provide frequent contacts for communication and socialization.
(d) Provide family education.
(e) Encourage involvement of family and friends.
Rationale:
Socialization and communication, in addition to increased activity, are all means to aid in prevention of self-injury. Education of family members may foster development of strategies to prevent self-injury; hence, mitten restraints could be avoided. Applying lotion after bathing may not be appropriate when the skin is broken and not intact.
Question 8.
A client with major depression states, “Life is not worth living anymore. Nothing matters.” Which response by the nurse is best?
(a) “Are you thinking about killing yourself?”
(b) “Things will get better, you know.”
(c) “Why do you think that way?”
(d) “You should not feel that way.”
Answer:
(a) “Are you thinking about killing yourself?”
Rationale:
When the client verbalizes that life is not worth living anymore, the nurse needs to ask the client directly about suicide by saying. “Are you thinking about killing yourself?” Asking directly does not provoke suicide but conveys concern, understanding, and the worth of the client. Commonly, the client experiences a sense of relief that someone finally hears him. It also helps the nurse plan responsible care by identifying the client who is at risk for suicide.
The nurse should then evaluate the seriousness of the suicidal ideation by inquiring about the intent and plan. Stating “Things will get better” offers hope too soon without first evaluating the intent of the suicidal ideation. Asking “Why do you think that way?” implies a lack of understand-ing and knowledge on the part of the nurse. Major depression usually is endogenous and biochemically based. Therefore, the client may not know why he does not want to live. Saying “You should not feel that way” admonishes the client, decreases selfworth, and conveys a lack of understanding.
Question 9.
A client with bipolar disorder has been prescribed olanzapine 5 mg two times a day and lamotrigine 25 mg two times a day. Which adverse effects should the nurse report to the health care provider immediately? Select all that apply.
(a) rash
(b) nausea
(c) sedation
(d) hyperthermia
(e) muscle rigidity
Answer:
(a) rash
(d) hyperthermia
(e) muscle rigidity
Rationale:
Lamotrigine, an antiepileptic, is used as a mood stabilizer for clients with bipolar disorder and has been found to be effective for the depressive phase of bipolar disorder. Common adverse effects are dizziness, headache, sedation, tremors, nausea, vomiting, and ataxia. The development of a rash needs to be reported and evaluated by the health care provider ILL] because it could indicate the start of a severe systemic rash known as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a toxic epidermal necrolysis, which would necessitate the discontinuation of lamotrigine. Hyperthermia in conjunction with muscle rigidity suggests the development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a life-threatening complication associated with olanzapine.
Question 10.
The nurse is planning care for an older adult with a pressure ulcer (see figure). What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Elevate the head of the bed to 50 degrees.
(b) Obtain daily cultures.
(c) Cover with protective dressing.
(d) Reposition the client every 2 hours.
(e) Request an alternating pressure mattress.
Answer:
(c) Cover with protective dressing.
(d) Reposition the client every 2 hours.
(e) Request an alternating pressure mattress.
Rationale:
The client has a stage II pressure ulcer. The nurse should take measures to relieve the pressure, treat the local infection, and protect the wound. The nurse should keep the ulcer covered with a protective dressing. The client should turn every 2 hours and use an alternating pressure mattress to relieve pressure on the buttocks. The head of the bed should be elevated no more than
30 degrees. All wounds have bacteria, and obtaining frequent cultures (unless prescribed otherwise) is not necessary.
Question 11.
A client takes hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) for treatment of hypertension. The nurse should instruct the client to report which effects? Select all that apply.
(a) muscle twitching
(b) abdominal cramping
(c) diarrhea
(d) confusion
(e) lethargy
(f) muscle weakness
Answer:
(b) abdominal cramping
(e) lethargy
(f) muscle weakness
Rationale:
HCTZ is a thiazide diuretic used in the management of mild to moderate hypertension and in the treatment of edema associated with heart failure, renal dysfunction, cirrhosis, corticosteroid therapy, and estrogen therapy. It increases the excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule of the kidneys. It promotes the excretion of chloride, potassium, magnesium, and bicarbonate. Side effects include drowsiness, lethargy, and muscle weakness but not muscle twitching. Although there may be abdominal cramping, there is no diarrhea. The client does not become confused as a result of taking this drug.
Question 12.
A client has been taking imipramine for depression for 2 days. His sister asks the nurse, “Why is he still so depressed?” Which response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “Your brother is experiencing a very serious depression.”
(b) “I will be sure to convey your concern to his health care provider.”
(c) “It takes 2 to 4 weeks for the drug to reach its full effect.”
(d) “Perhaps we need to change his medication.”
Answer:
(c) “It takes 2 to 4 weeks for the drug to reach its full effect.”
Rationale:
The nurse needs to inform the sister that it takes 2 to 4 weeks before a full clinical effect occurs with the drug. The nurse should let her know that her brother will gradually get better and symptoms of depression will improve. Telling the sister that her brother is experiencing a very serious depression does not give the sister important information about the medication. Additionally, this statement may cause alarm and anxiety. Conveying the sister’s concern to the health care provider (HCP) Q does not provide her with the necessary information about the client’s medication. Telling the sister that the client’s medication may need to be changed is inappropriate because a full clinical effect occurs after 2 to 4 weeks.
Question 13.
Which finding requires immediate intervention when planning care for an adolescent with cystic fibrosis (CF)?
(a) delayed puberty
(b) chest pain with dyspnea
(c) poor weight gain
(d) large, foul-smelling, bulky stools
Answer:
(b) chest pain with dyspnea
Rationale:
Chest pain and dyspnea are signs of a pneumothorax and should be treated immediately. Delayed puberty is common in adolescents with CF and is caused by poor nutrition. Poor weight gain is common in children with CF because so little is absorbed in the small intestine. Large, foul-smelling stools indicate noncompliance with taking enzymes and should be addressed, but respiratory complications are the greatest concern.
Question 14.
Assessment of a client starting on lithium reveals dry mouth, nausea, thirst, and mild hand tremor. Based on an analysis of these findings, what should the nurse do next?
(a) Withhold the lithium, and obtain a STAT lithium level.
(b) Continue the lithium, and immediately notify the health care provider (HCP) about the assessment findings.
(c) Continue the lithium, and reassure the client that these temporary side effects will subside.
(d) Withhold the lithium, and monitor the client for signs and symptoms of increasing toxicity.
Answer:
(c) Continue the lithium, and reassure the client that these temporary side effects will subside.
Rationale:
The client is exhibiting temporary side effects associated with beginning lithium therapy. Therefore, the nurse should continue the lithium and explain to the client that the temporary side effects of lithium will subside. Common side effects of lithium are nausea, dry mouth, diarrhea, thirst, mild hand tremor, weight gain, bloating, insomnia, and light-headedness. Immediately notifying the HCP 2 about these common side effects is not necessary.
Question 15.
A client newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism asks the nurse how long it will be necessary to take the prescribed levothyroxine sodium. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) “It will be necessary to take the medication for the rest of your life.”
(b) “Since the medication is expensive, the health care provider will check your progress and the dose may be able to be reduced in a few months.”
(c) “If your thyroid responds to the medication, the medication can be gradually withdrawn in 1 to 2 years.”
(d) “The medication can be discontinued when your thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level is normal.”
Answer:
(a) “It will be necessary to take the medication for the rest of your life.”
Rationale:
Thyroid replacement is a lifelong maintenance therapy. The medication is usually given as one dose in the morning. It cannot be tapered or discontinued because the client needs thyroid supplementation to maintain health. The medication cannot be discontinued after the TSH level is normal; the dose will be maintained at the level that normalizes the TSH concentration.
Question 16.
After the nurse teaches a client about bipolar disorder, which statement indicates that the client has developed insight about the diagnosis?
(a) “I enjoy feeling high. I don’t need much sleep then and get really creative.”
(b) “My medicine really helped me. I know I won't need it in about another week.”
(c) “I’m cured now. I was really wild for a while even though I got into trouble.”
(d) “I know I’m getting sick when I don't need much sleep and start buying things.”
Answer:
(d) “I know I’m getting sick when I don't need much sleep and start buying things.”
Rationale:
The client's statement “I know I’m getting sick when I don’t need much sleep and start buying things” indicates insight into her illness because the client recognizes symptoms that can lead to relapse. The statement “I enjoy feeling high; I don’t need much sleep then and get really creative” gives no indication that the client recognizes the detrimental effects of bipolar disorder.
The statements about not needing medicine in another week and being cured indicate the client’s lack of understanding about the chronic nature of the disorder. The client is not cured from bipolar disorder, but symptoms of the disorder are usually managed when she is stabilized on medication. Medication may be needed by the client for many years or throughout her life.
Question 17.
A client admitted with a gastric ulcer has been vomiting bright red blood. The hemoglobin level is 5.11 g/dL (51.1 g/L), and blood pressure is 100/50 mm Hg. The client and family state that their religious beliefs do not support the use of blood products and refuse blood transfusions as a treatment for the bleeding. The nurse should collaborate with the health care provider and family to plan to take which action next?
(a) Discontinue all measures.
(b) Notify the hospital attorney.
(c) Attempt to stabilize the client through the use of fluid replacement.
(d) Give enough blood to keep the client from dying.
Answer:
(c) Attempt to stabilize the client through the use of fluid replacement.
Rationale:
The most appropriate response is to continue all treatments and attempt to stabilize the client using fluid replacement without administering blood or blood products. It is imperative that the health care team respects the client’s religious beliefs and wishes, even if they are not those of the health care team. Discontinuing all measures is not an option. The health care team should continue to provide the best care possible and does not need to notify the attorney.
Question 18.
A client is receiving nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage the pain of rheumatoid arthritis. What information should the nurse give to the client about taking these medications?
(a) Take NSAIDs at least three times per day.
(b) Exercise the joints at least 1 hour after taking the medication.
(c) Take antacids 1 hour after taking NSAIDs.
(d) Take NSAIDs with food.
Answer:
(d) Take NSAIDs with food.
Rationale:
NSAIDs irritate the gastric mucosa and should be taken with food. NSAIDs are usually taken once or twice daily. Joint exercise is not related to the drug administration. Antacids may interfere with the absorption of NSAIDs.
Question 19.
A client is to receive an IM injection using a Z-track injection technique. The nurse holds the gauze pledget against an IM injection site while removing the needle from the muscle. What is the intended outcome of this technique?
(a) Seal off the track left by the needle in the tissue.
(b) Speed the spread of the medication in the tissue.
(c) Avoid the discomfort of the needle pulling on the skin.
(d) Prevent organisms from entering the body through the skin puncture.
Answer:
(a) Seal off the track left by the needle in the tissue.
Rationale:
When administering an injection using the Z-track method, holding the gauze pledget against the site while removing the needle from the muscle helps to seal off the track left by the needle in the tissue. The Z-track technique does not speed the spread of the medication or lessen the discomfort of an injection. Wiping the skin with alcohol prior to administering the injection prevents the likelihood of microorganisms from entering the body.
Question 20.
When a client with alcohol dependency begins to talk about not having a problem with alcohol, what is the best approach for the nurse to use?
(a) Question the client about how much alcohol the client consumes each day.
(b) Confront the client about being intoxicated 2 days ago.
(c) Point out how alcohol has gotten the client into trouble.
(d) Ask the client about his or her reasons for not staying sober.
Answer:
(c) Point out how alcohol has gotten the client into trouble.
Rationale:
When a client talks about not having a problem with alcohol, the nurse needs to point out how alcohol has gotten the client into trouble. Concrete facts are helpful in decreasing the client’s denial that alcohol is a problem. The other approaches allow the client to use defense mecha-nisms, such as rationalization, projection, and minimization, to explain his or her actions. Therefore, these approaches are not helpful.
Question 21.
The nurse is caring for a toddler in contact isolation for respiratory syncytial virus. In what order from first to last should the nurse remove personal protective equipment (PPE)? All options must be used.
(a) gloves
(b) goggles
(c) gown
(d) mask
Answer:
(a) gloves
(c) gown
(b) goggles
(d) mask
Rationale:
There are two acceptable ways of removing PPE. The nurse should remove the dirtiest items first. Typically, these items are the gloves followed by the gown. In the alternative method, the gloves and gown may be removed at the same time. It is then recommended that the nurse perform hand hygiene and remove the goggles, which may fit over the mask. Finally, the mask is removed from behind. The nurse should then again perform hand hygiene when all PPE has been removed.
Question 22.
The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for an adult recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mel- litus. What is the first step in this process?
(a) Establish goals.
(b) Choose video materials and brochures.
(c) Assess the client’s learning needs.
(d) Set priorities of learning needs.
Answer:
(c) Assess the client’s learning needs.
Rationale:
Before development and implementation of the teaching plan, it is vital to determine what the client currently knows regarding diabetes and what the client needs to know.
Question 23.
A client with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus has a finger stick blood sugar of 483 dL/mL (483 mmol/L). What should the nurse do first?
(a) Start an intravenous infusion.
(b) Repeat the finger stick in 30 minutes.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of the results.
(d) Obtain a serum glucose level as prescribed.
Answer:
(d) Obtain a serum glucose level as prescribed.
Rationale:
The nurse should first obtain a serum glucose level for a more accurate information about the client’s blood sugar level. The nurse should not wait for 30 minutes to obtain another fingerstick blood sugar when more accurate information will be obtained with a blood glucose level. The nurse should have more information about the glucose level before contacting the HCP EH. It is not necessary to start an intravenous infusion at this point.
Question 24.
A female client who has diagnosis of borderline personality disorder is manipulative and very disruptive on the hospital unit. She is not dangerous to herself or others but is clearly not making any therapeutic progress. She consistently refuses any medications. The nurse realizes that legally, this client has which option?
(a) Refuse treatment.
(b) Receive forced treatment if the nursing team concurs.
(c) Be medicated if her family signs permission for treatment.
(d) Be guided to accept treatment recommendations by threatening loss of privileges.
Answer:
(a) Refuse treatment.
Rationale:
A client who has not been deemed a danger to self or others or who has not been declared incompetent retains the right to refuse treatment. Legal protocols need to be followed to initiate treatment against an adult client’s wishes, even if the family wishes treatment to occur. Punitive threats of retaliation or loss of privileges are ethically unacceptable in administering treatment.
Question 25.
A client admitted in an acute psychotic state hears terrible voices in the head and thinks a neighbor is upset with the client. What is the nurse’s best response?
(a) “What has your neighbor been doing that bothers you?”
(b) “How long have you been hearing these terrible voices?”
(c) “We won’t let your neighbor visit, so you’ll be safe.”
(d) “What exactly are these terrible voices saying to you?”
Answer:
(d) “What exactly are these terrible voices saying to you?”
Rationale:
The nurse needs to collect additional information about the client’s report about hearing voices. Assessing the content of hallucinations is essential to determine whether they are command hallucinations that the client might act on. Asking about what the neighbor has been doing or telling the client that the neighbor will not visit indirectly reinforces the delusion about the neighbor. Although determining the onset and duration of the voices is important, the nurse needs to assess the content of the hallucinations first.
Question 26.
A client who has a prescription to receive nothing by mouth (NPOj is constantly asking for a drink of water. Which nursing intervention is the most appropriate?
(a) Reexplain why it is not possible to have a drink of water.
(b) Offer ice chips every hour to decrease thirst.
(c) Offer the client frequent oral hygiene care.
(d) Divert the client’s attention by turning on the television.
Answer:
(c) Offer the client frequent oral hygiene care.
Rationale:
The most appropriate intervention is to offer the client frequent mouth care to moisten the dry oral mucosa. Reexplaining why the client cannot drink may be helpful but will not relieve the thirst. Ice chips cannot be given to a client who is on NPO status. Diverting the client's attention does not help manage the thirst.
Question 27.
An older adult who is to be on bed rest has become incontinent of urine. To prevent pressure ulcers, the nurse should do which tasks? Select all that apply.
(a) Use a sanitary napkin to absorb urine.
(b) Institute a turning schedule.
(c) Inspect the groin for wetness.
(d) Have client wear incontinence briefs.
(e) Anchor a Foley catheter.
Answer:
(b) Institute a turning schedule.
(c) Inspect the groin for wetness.
(d) Have client wear incontinence briefs.
Rationale:
This client is at risk for pressure ulcers because of age, being on bed rest, and being incontinent. The nurse assesses all pressure points and the groin area, assures that the client changes positions every 2 hours, and has the client wear incontinence pads containing absorbent material (specially designed to absorb many times its weight in water) or disposable incontinence briefs. Sanitary napkins are not designed to contain/absorb urine. Anchoring a Foley catheter increases the risk for infection.
Question 28.
A mother tells the nurse that her 10-year-old daughter has an increase in hair growth and breast enlargement. The nurse explains to the mother and daughter that after the symptoms of puberty are noticed, menstruation typically occurs within which time frame?
(a) 6 months
(b) 12 months
(c) 30 months
(d) 36 months
Answer:
(c) 30 months
Rationale:
After the symptoms of puberty, such as increased hair growth and enlargement of the breasts, are noticed, menstruation typically begins within 30 months.
Question 29.
A nurse is teaching a new mother how to prevent burns in the home. Which statement by the mother indicates more teaching is required?
(a) “I will set my hot water heater to 49°C (120°F).”
(b) “I will not hold my infant while drinking coffee.”
(c) “I will heat my infant’s formula in the microwave.”
(d) “I will keep loose appliance cords tied up on the counter.”
Answer:
(c) “I will heat my infant’s formula in the microwave.”
Rationale:
Infant formula should never be heated in the microwave; the formula may heat at different temperatures and can burn the infant’s mouth. Plastic bottle liners may also burst with the heat. Setting your hot water heater a couple of degrees cooler will help keep hot water in the house cooler (recommended since 1974 by the Consumer Product Safety Commission). Small children are at risk for scald injury from hot tap water due to their decreased reaction time, their curiosity, and the thermal sensitivity of their skin. Avoiding holding infants while drinking coffee can prevent possible spills onto children. Keeping cords tied up on the counter prevents children from pulling on dangling cords and spilling hot liquids over themselves.
Question 30.
After the nurse teaches a primigravid client at 10 weeks’ gestation about the recommendations for exercise during pregnancy, which client statement indicates successful teaching?
(a) “While pregnant, I should avoid contact sports.”
(b) “Even though I’m pregnant, I can learn to ski next month.”
(c) “While we are on vacation next month, I can continue to scuba dive.”
(d) “Sitting in a hot tub after exercise will help me to relax.”
Answer:
(a) “While pregnant, I should avoid contact sports.”
Rationale:
The client understands the instructions when she says she should avoid contact sports because they may result in injury to the client and the fetus. Learning to ski while pregnant is not recommended because injury may occur. Scuba diving should be avoided because depth pressures could cause fetal damage. Hot tubs should be avoided during the first trimester because sitting in them can result in fetal hyperthermia and fetal hypoxia. Mild exercises, such as walking, can help strengthen the muscles and prevent some discomforts such as backache.
Question 31.
The health care provider has prescribed intravenous chemotherapy to be administered to a client every day for the next week. The nurse assigned to the client has not been trained to handle chemotherapy agents. What is the nurse’s most appropriate response?
(a) Send the client to the oncology floor for administration of the medication.
(b) Ask a nurse from the oncology floor to come to the client and administer the medication.
(c) Ask another nurse to help mix the chemother apy agent.
(d) Ask the pharmacy to mix the chemotherapy agent and administer it.
Answer:
(a) Send the client to the oncology floor for administration of the medication.
Rationale:
The nurse should call the oncology unit to institute a transfer. The nurse handling chemotherapy agents should be specially trained. It is an unwise use of nursing resources to send a nurse from one unit to administer medications to a client on another unit. It is better to centralize and send the client who needs chemotherapy to one unit. Even if the pharmacy mixes the agent, the drug must be administered by a specially trained nurse.
Question 32.
Which is an appropriate outcome for a client with rheumatoid arthritis who is receiving antiinflammatory drugs and physical therapy?
The client will:
(a) manage joint pain and fatigue to perform activities of daily living.
(b) maintain full range of motion in joints.
(c) prevent the development of further pain and joint deformity.
(d) take anti-inflammatory medications as needed for pain.
Answer:
(a) manage joint pain and fatigue to perform activities of daily living.
Rationale:
An appropriate outcome for the client with rheumatoid arthritis is that the client will adopt self-care behaviors to manage joint pain, stiffness, and fatigue and be able to perform activities of daily living. Range-of-motion (ROM) exercises can help maintain mobility, but it may not be realistic to expect the client to maintain full ROM. Depending on the disease progression, there may be further development of pain and joint deformity, even with appropriate therapy. It is important for the client to understand the importance of taking the prescribed drug therapy even if symptoms have abated.
Question 33.
A nurse has been exposed to hepatitis B through a needlestick injury. Which actions should be included in the postexposure management plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Wash the injection site with soap and water.
(b) Wipe the site with undiluted bleach solution.
(c) Administer hepatitis B immune globulin.
(d) Administer hepatitis B vaccine.
(e) Notify the nurse’s supervisor.
Answer:
(a) Wash the injection site with soap and water.
(c) Administer hepatitis B immune globulin.
(d) Administer hepatitis B vaccine.
(e) Notify the nurse’s supervisor.
Rationale:
The postexposure management plan following a needlestick injury when the client has hepatitis B must be instituted immediately. The nurse should first wash the site of the needlestick with soap and water. An antiseptic agent may be used following washing the site, but a strong bleach solution is too caustic. The nurse should then receive both hepatitis B immune globulin and the hepatitis B vaccine. The incident must be reported to the nurse’s supervisor and other departments within the health care organization as required.
Question 34.
When instilling ear drops on a 2-year-old child, the nurse should pull the pinna in which directions?
(a) down and back
(b) down and slightly forward
(c) up and back
(d) up and forward
Answer:
(a) down and back
Rationale:
When instilling ear drops on a child younger than age 3 years, the nurse should pull the pinna down and back. This helps open the ear canal to ensure drops reach the tympanic membrane. For an older child, the nurse should pull the pinna up and back.
Question 35.
An older adult alert and oriented client is admitted to the hospital for treatment of cellulitis of the left shoulder. Which fall prevention strategy is most appropriate for this client?
(a) Keep all the lights on in the room at all times.
(b) Use a night-light in the bathroom.
(c) Keep all four side rails up at all times.
(d) Use a medical alert system.
Answer:
(b) Use a night-light in the bathroom.
Rationale:
Many falls occur when older clients attempt to get to the bathroom at night. The risk is even greater in an unfamiliar environment. Use of a night-light in the bathroom enables the older adult client to see the way to the bathroom. Keeping the lights on in the room at all times may contribute to sensory overload and prevent adequate rest. Raised side rails paradoxically contribute to falls when the older client tries to climb over them to get to the bathroom. The upper side rails may be raised, but it is not recommended that all four side rails be elevated. Camera monitoring can be used but does nothing to prevent a fall.
Question 36.
A client has been prescribed hydrochlorothiazide to treat heart failure. What adverse effect should the nurse instruct the client to report to the health care provider?
(a) urinary retention
(b) muscle weakness
(c) confusion
(d) diaphoresis
Answer:
(b) muscle weakness
Rationale:
Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic. Muscle weakness can be an indication of hypokalemia. Polyuria is associated with this diuretic, not urinary retention. Confusion and dia-phoresis are not side effects of hydrochlorothiazide.
Question 37.
The son of a client with Alzheimer’s disease excitedly tells the nurse, “Mom was singing one of her favorite old songs. I think she’s getting her memory back!” What response by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) “She still has long-term memory, but her short-term memory will not return.”
(b) “I’m so happy to hear that. Maybe she is getting better.”
(c) “Don’t get your hopes up. This is only a temporary improvement.”
(d) “I’m glad she can sing even if she can't talk to you.”
Answer:
(a) “She still has long-term memory, but her short-term memory will not return.”
Rationale:
The ability to remember an old song is related to long-term memory, which persists after short-term memory is lost. Therefore, the nurse should respond by providing the son with this information. Stating that the nurse is happy to hear about the change and that the client is getting better is inappropriate and inaccurate. This statement ignores the issue of long-term versus short-term memory. Telling the client not to get his hopes up because the improvement is only temporary is inappropriate. The information provided does not indicate that the client has expressive aphasia, which would be suggested by the statement that the client cannot talk to the son.
Question 38.
A client has the leg immobilized in a long leg cast. Which finding indicates the beginning of circulatory impairment?
(a) inability to move toes
(b) cyanosis of toes
(c) sensation of cast tightness
(d) tingling of toes
Answer:
Rationale:
Tingling and numbness of the toes would be the earliest indication of circulatory impairment. Inability to move the toes and cyanosis are later indicators. Cast tightness should be investigated because cast tightness can lead to circulatory impairment; it is not, however, an indicator of impairment.
Question 39.
A multigravid client at 34 weeks’ gestation who is leaking amniotic fluid has just been hospitalized with a diagnosis of preterm premature rupture of membranes and preterm labor. The client’s contractions are 20 minutes apart, lasting 20 to 30 seconds. Her cervix is dilated to 2 cm. The nurse reviews prescriptions (see chart]. Which prescrip-tion should the nurse initiate first?
Prescription:
Continuous external fetal and contraction monitoring IV of D5LR @ 125 mL/h
l&O catheterization for urinalysis and culture and sensitivity
Betamethasone 12 mg IM daily x 2 days
(a) Initiate fetal and contraction monitoring.
(b) Start the intravenous infusion.
(c) Obtain the urine specimen.
(d) Administer betamethasone.
Answer:
(a) Initiate fetal and contraction monitoring.
Rationale:
The nurse should initiate fetal and contraction monitoring for this client upon arrival to the unit. This gives the nurse data regarding changes in fetal and maternal contraction status before completing the other prescriptions. Next, the betamethasone would be given to begin the maturation process for the fetal lungs. The nurse should then start an intravenous infusion to provide a line for immediate intravenous access, if needed, and provide hydration for the client. The nurse should obtain the urine specimen prior to administering any antibiotic therapy, if prescribed.
Question 40.
The nurse notes that the client seems anxious. Which strategy should the nurse use to enhance communication?
(a) Ask about the source of the anxiety.
(b) Maintain a distance of 6 to 12 inches.
(c) Sit down to talk with the client.
(d) Maintain a neutral facial expression.
Answer:
Rationale:
Sitting down to talk with the client enhances communication because it shows a willingness to take the time to listen. Asking direct questions limits the communication and decreases the client’s ability to discuss his or her concerns. Maintaining a distance of only 6 to 12 inches with a client is likely to make him/her uncomfortable as the nurse is in the client’s personal space; 18 inches to 4 feet (not 6 to 12 inches) while speaking allows most clients to feel comfortable, thereby enhancing communication. A concerned expression, not a neutral one, demonstrates interest and attention.
Question 41.
The nurse is developing an education plan for clients with hypertension. The nurse should emphasize which long-term goal for the clients?
(a) Develop a plan to limit stress.
(b) Participate in a weight reduction program.
(c) Commit to lifelong therapy.
(d) Monitor blood pressure regularly.
Answer:
(c) Commit to lifelong therapy.
Rationale:
The most appropriate long-term goal for the client with hypertension is to commit to lifelong therapy. A significant problem in the long-term management of hypertension is compliance with the treatment plan. It is essential that the client understand the reasons for modifying lifestyle, taking prescribed medications, and obtaining regular health care. Limiting stress, losing weight, and monitoring blood pressure are important aspects of care for the client with hypertension; however, the treatment plan must be individualized to include aspects of care that are appropriate for each client.
Question 42.
When the nurse is developing a plan of care to manage a client’s pain from cancer, what should the nurse plan to do?
(a) Individualize the pain medication regimen for the client.
(b) Select medications that are least likely to lead to addiction.
(c) Administer pain medication as soon as the client requests it.
(d) Change pain medications periodically to avoid drug tolerance.
Answer:
(a) Individualize the pain medication regimen for the client.
Rationale:
The nurse should work with the client to individualize the plan of care for managing pain. Cancer pain is best managed with a combination of medications, and each client needs to be worked with individually to find the treatment regimen that works best. Cancer pain is commonly undertreated because of fear of addiction. The client who is in pain needs the appropriate level of analgesic and needs to be reassured that addiction is unlikely. Cancer pain is best treated with regularly scheduled doses of medication. Administering the medication only when the client asks for it will not lead to adequate pain control. As drug tolerance develops, the dosage of the medication can be increased.
Question 43.
After the nurse explains to a multigravid client at 36 weeks’ gestation who is diagnosed with severe hydramnios about the possible complications of this condition, which client statement indicates the need for further instruction?
(a) “Because I have hydramnios, I may gain weight. ”
(b) “Hydramnios has been associated with gastro intestinal disorders in the fetus.”
(c) “I should continue to eat high-fiber foods and avoid constipation.”
(d) “I can continue to work at my job at the auto mobile factory until labor starts.”
Answer:
(d) “I can continue to work at my job at the auto mobile factory until labor starts.”
Rationale:
The client needs further instructions when she says, “I can continue to work at my job at the automobile factory until labor starts.” The goal is to avoid preterm labor. Because the client is experiencing severe hydramnios, she will most likely be maintained on bed rest to increase uteroplacental circulation and reduce pressure on the cervix. Hydramnios has been associated with increased weight gain caused by increased amni- otic fluid volume. Hydramnios has been associated with gastrointestinal disorders in the fetus, such as tracheoesophageal fistula with stenosis or intestinal obstruction. The client should continue to eat high-fiber foods and should avoid straining, which could lead to ruptured membranes. Stool softeners may also be prescribed. The client should report any symptoms of fluid rupture or labor.
Question 44.
The nurse is instructing a client on how to care for skin that has become dry after radiation therapy. Which statement by the client indicates that the client understands the teaching?
(a) “I should take antihistamines to decrease the itching I’m experiencing.”
(b) “It’s safe to apply a nonperfumed lotion to my skin.”
(c) “A heating pad, set on the lowest setting, will help decrease my discomfort.”
(d) “I can apply an over-the-counter cortisoneointment to relieve the dryness.”
Answer:
(b) “It’s safe to apply a nonperfumed lotion to my skin.”
Rationale:
Irradiated skin can become dry and irritated, resulting in itching and discomfort. The client should be instructed to clean the skin gently and apply nonperfumed, nonirritating lotions to help relieve dryness. Taking an antihistamine does not relieve the skin dryness that is causing the itching. Heat should not be applied to the area because it can cause further irritation. Medicated ointments should not be applied to the skin without the prescription of the radiation therapist.
Question 45.
A nurse is preparing to administer an intravenous medication to a client. In addition to the client’s name, which additional identifier does the nurse check?
(a) allergies
(b) health care provider’s name
(c) birth date
(d) room number
Answer:
(c) birth date
Rationale:
The nurse is required to check the name and a second identifier. This varies by institution but typically includes the client’s birth date or account number. The health care provider’s name and room number may change during a health care encounter. While the nurse should note if the client is allergic to the medication, verifying allergies is not a client identifier.
Question 46.
Which measure should be implemented promptly after a client’s nasogastric (NG) tube has been removed?
(a) Provide the client with oral hygiene.
(b) Offer the client liquids to drink.
(c) Encourage the client to cough and deep breathe.
(d) Auscultate the client’s bowel sounds.
Answer:
(a) Provide the client with oral hygiene.
Rationale:
The nurse’s first action after the removal of an NG tube is to provide the client with oral hygiene. Then it is appropriate to give the client liquids to drink if the client is no longer on nothing-by-mouth status. There is no association between removal of an NG tube and having the client cough and deep breathe. Auscultating the client’s bowel sounds should be done before removal of the NG tube.
Question 47.
The nurse is making a home visit to an older adult who is living with his son’s family. The client has scald burns on the hands, both forearms, and on the neck (10% first- and second-degree bums). What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Cleanse the wounds with cool water.
(b) Apply antibiotic cream.
(c) Remove clothing near the area.
(d) Call for transport to a hospital.
(e) Cover the burns with sterile dressing.
(f) Investigate the possibility of elder abuse.
Answer:
(a) Cleanse the wounds with cool water.
(c) Remove clothing near the area.
(d) Call for transport to a hospital.
(f) Investigate the possibility of elder abuse.
Rationale:
The nurse can administer first aid by rinsing the area with cool water and removing clothing in the area. Because the burns are near the neck, the nurse should then call for transport to a hospital. The client’s age and the extent of the burns require care by a health care team. Additionally, the nurse considers that the client may be a victim of elder abuse and investigates further as needed.
The nurse should refrain from cleansing the wound, applying cream, or covering the area.
Question 48.
An infant is to receive the diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (DTaP) and inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) immunizations. The child is recovering from a cold and is afebrile. The child’s sibling has cancer and is receiving chemotherapy. Which action is most appropriate?
(a) Give the DTaP and withhold the IPV.
(b) Administer the DTaP and IPV immunizations.
(c) Postpone both immunizations until the sibling is in remission.
(d) Withhold both immunizations until the infant is well.
Answer:
(b) Administer the DTaP and IPV immunizations.
Rationale:
At this time, the infant can be given the vaccines. The fact that the child’s sibling is immu- nosuppressed because of chemotherapy is not a reason to withhold the vaccines. The fact that the child has a cold is not grounds for delaying the immunizations. However, if the child had a high fever, the immunizations would be delayed.
Question 49.
The nurse creates a program to decrease the primary cause of disability and death in children. What is the most important action to include in the plan?
(a) Encourage legislators to draft legislation to promote prenatal care.
(b) Require all children to be immunized.
(c) Teach accident prevention and safety practices to children and their parents.
(d) Hire a nurse practitioner for each of the schools in the community.
Answer:
(c) Teach accident prevention and safety practices to children and their parents.
Rationale:
The primary cause of disability and death in children is injury from accidents. Teaching safety measures to children and their parents is the best way to decrease injury and accidents. Legislation for prenatal care is not a primary prevention for accidents. Communicable diseases are not the primary cause of disability and death in children; therefore, requiring immunizations is not an appropriate strategy for this health problem. Having nurse practitioners in schools is not a primary prevention measure for accidents.
Question 50.
A tour bus has overturned on an exit ramp. Many passengers are injured, but there are no fatalities. The injured passengers will be transported to an emergency center. The nurse at the emergency center who will receive the passengers should plan to respond to which situation in addition to treating injuries?
(a) The accident victims will be experiencing grief and mourning.
(b) Passengers may be experiencing feelings of victimization.
(c) Someone should be available to coordinate calls from relatives about the passengers.
(d) Some of the passengers will need psychiatric hospitalization.
Answer:
(b) Passengers may be experiencing feelings of victimization.
Rationale:
Major accidents can induce feelings similar to those of victims of other kinds of disasters and crime. Therefore, the nurse should also be prepared to assist the passengers with their feelings of victimization. Passengers may mourn the loss of a vacation, but with no fatalities, major grief reac-tions are not expected. Other personnel can take calls from relatives while the nurse helps the passengers. Psychiatric hospitalization is a premature assumption.
Question 51.
The nurse teaches the parents of an infant who has had surgery to correct imperforate anus how to position the infant to prevent tension on the perineum. The nurse determines more teaching is needed when the parents put the infant in which position?
(a) abdomen, with legs pulled up under the body
(b) back, with legs suspended at a 90-degree angle
(c) left side, with hips elevated
(d) right side, with hips elevated
Answer:
(a) abdomen, with legs pulled up under the body
Rationale:
When placed on the abdomen, a neonate pulls the legs up under the body, which puts tension on the perineum. Therefore, after surgery, the neonate should be positioned either supine with the legs suspended at a 90-degree angle or on either side with the hips elevated.
Question 52.
When developing the plan of care for a 14-year-old boy who is bored due to being immobilized in a cast, which activity is most appropriate?
(a) playing a card game with a boy the same age
(b) putting together a puzzle with his mother
(c) playing video games with a 9-year-old
(d) watching a movie with his younger brother
Answer:
(a) playing a card game with a boy the same age
Rationale:
Teenagers usually enjoy activities with peers in preference to socializing with their parents or siblings. Peer relationships help the adolescent develop self-identity.
Question 53.
After surgery to create a urinary diversion, the client is at risk for a urinary tract infection.
What should the nurse do to prevent a urinary tract infection?
(a) Clamp the urinary appliance at night.
(b) Empty the urinary appliance before it is one-third full.
(c) Limit the client’s walking with the appliance.
(d) Change the urinary appliance daily.
Answer:
(b) Empty the urinary appliance before it is one-third full.
Rationale:
The urinary appliance should be emptied before the pouch is one-third full to prevent urinary reflux. The appliance should be attached to a leg bag at night to allow for adequate drainage. The urinary appliance is not changed daily. If no leakage occurs and the client’s skin remains free from irritation, the appliance can be left in place for 1 week or more. The client can ambulate as tolerated.
Question 54.
A client with cancer of the throat had a tracheostomy tube inserted 2 days ago. The client has moderate secretions and can take deep breaths without pain. When suctioning a client’s tracheostomy tube, what should the nurse do?
(a) Oxygenate the client before suctioning.
(b) Insert the suction catheter about 2 inches (5cm) into the cannula.
(c) Use a bolus of sterile water to stimulate cough.
(d) Use clean gloves during the procedure.
Answer:
(a) Oxygenate the client before suctioning.
Rationale:
Preoxygenating the client before suctioning helps prevent the development of hypoxia during the procedure. The suction catheter is inserted about 5 to 6 inches (12.7 to 15 cm) into the cannula. A bolus of 3 to 5 mL of sterile normal saline solution may be inserted into the cannula before suctioning to stimulate coughing and loosen secretions. The nurse uses sterile technique when suctioning a client.
Question 55.
A 14-month-old child has a severe diaper rash. Which recommendation should the nurse provide to the parents?
(a) Continue to use the baby wipes.
(b) Change the diaper every 4 to 6 hours.
(c) Wash the buttocks using mild soap.
(d) Apply powder to the diaper area.
Answer:
(c) Wash the buttocks using mild soap.
Rationale:
Because the toddler has a severe diaper rash, it may be best to change all that the parents are doing. The buttocks need to be washed thoroughly with mild soap and dried well. In fact, it is helpful to leave the diaper off and expose the buttocks to the air. Baby wipes commonly contain additives and perfumes that may be irritating to the baby’s sensitive skin. The diaper needs to be changed more often than every 4 to 6 hours. Otherwise, the moist diaper environment will continue to irritate the skin, causing the rash to worsen. Powder has limited absorbing ability and will most likely irritate the area more. In addition, some powders contain perfumes or are scented and can irritate the skin.
Question 56.
An adolescent thinks she has infectious mononucleosis. The nurse should assess the client for which symptoms? Select all that apply.
(a) sore throat
(b) malaise
(c) weight loss
(d) rash
(e) swollen lymph glands
Answer:
(a) sore throat
(b) malaise
(e) swollen lymph glands
Rationale:
The common presenting symptoms of infectious mononucleosis vary greatly but commonly include fever, malaise, sore throat, and lymphadenopathy. Skin rash, cold symptoms, abdominal pain, and weight loss are rarely presenting symptoms, abdominal pain, and weight loss are rarely presenting symptoms.
Question 57.
While assessing the fundus of a multiparous client on the first postpartum day, the nurse performs handwashing and puts on clean gloves. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Place the nondominant hand above the sym physis pubis and the dominant hand at the umbilicus.
(b) Ask the client to assume a side-lying position with the knees flexed.
(c) Perform massage vigorously at the level of the umbilicus if the fundus feels boggy.
(d) Place the client on a bedpan in case the uterine palpation stimulates the client to void.
Answer:
(a) Place the nondominant hand above the sym physis pubis and the dominant hand at the umbilicus.
Rationale:
The nurse should place the nondominant hand above the symphysis pubis and the dominant hand at the umbilicus to palpate the fundus. This prevents uterine inversion and trauma, which can be very painful to the client. The nurse should ask the client to assume a supine, not side-lying, position with the knees flexed. The fundus can be palpated in this position, and the perineal pads can be evaluated for lochia amounts. The fundus should be massaged gently if the fundus feels boggy. Vigorous massaging may fatigue the uterus and cause it to become firm and then boggy again. The nurse should ask the client to void before fundal evaluation. A full bladder can cause discomfort to the client, the uterus to be deviated to one side, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Question 58.
What should be the nurse’s priority assessment after an epidural anesthetic has been given to a nulligravid client in active labor?
(a) level of consciousness
(b) blood pressure
(c) cognitive function
(d) contraction pattern
Answer:
(b) blood pressure
Rationale:
Administration of an epidural anesthetic can result in a hypotensive effect on maternal blood pressure. Therefore, the priority assessment is the mother’s blood pressure. Ephedrine or wedging the client to a position to keep pressure off the vena cava, such as on the left side, can be used to elevate maternal blood pressure should it drop too low. Epidural anesthesia has no effect on the level of consciousness or the client’s cognitive function. Although the client’s contraction pattern may decrease in frequency after administration of the anesthesia, the priority assessment is the client’s blood pressure. After blood pressure is maintained, contractions can be assessed.
Question 59.
The nurse is reviewing the serum electrolyte levels of a client with heart failure who has been taking digoxin for 6 months. The nurse should report which finding from the lab report to the health care provider?
(a) hyponatremia
(b) hypomagnesemia
(c) hypocalcemia
(d) hypokalemia
Answer:
(d) hypokalemia
Rationale:
Hypokalemia is one of the most common causes of digoxin toxicity. It is essential that the nurse carefully monitor the potassium levels of clients taking digoxin to avoid toxicity. Low serum potassium levels can cause cardiac dysrhythmias. Sodium, magnesium, and calcium levels are not significantly affected by the use of digoxin.
Question 60.
After abdominal surgery 3 days ago the client continues to have pain every 4 to 6 hours ranging from 3 to 7 on a 10-point scale. The client has prescriptions for morphine 10 mg IM every 3 to 4 hours and acetaminophen with codeine 30 mg every 3 to 4 hours as needed for pain. The client has been taking the morphine every 4 hours for the past 3 days but tells the nurse that the morphine is no longer lasting 4 hours and wants to receive pain medication every 3 hours. The nurse reviews the progress notes that indicate the client has obtained pain relief for 5 to 6 hours after receiving the morphine. What should the nurse do to help the client manage the pain?
(a) Administer the morphine every 3 hours.
(b) Suggest that the client take the acetaminophen with codeine every 3 hours.
(c) Continue to administer the morphine every 4 hours.
(d) Encourage the client to ambulate more frequently.
Answer:
(b) Suggest that the client take the acetaminophen with codeine every 3 hours.
Rationale:
Evidence indicates that acetaminophen with codeine provides pain relief for most clients with moderate pain. Because the progress notes indicate that the client is obtaining relief from the morphine for more than 4 hours and has moderate pain, the nurse can suggest that the client try taking the acetaminophen with codeine every 3 hours. The goal for this client is to gradually use less pain
medication. The client can be encouraged to ambulate, but that will not be sufficient to manage the postoperative pain at this point.
Question 61.
The nurse assesses a 7-month-old infant’s growth and development. Which behavior should the nurse consider unusual?
(a) drinking from a cup and spilling little of the liquid
(b) raising the chest and upper abdomen off the bed with the hands
(c) imitating sounds that the nurse makes
(d) crying loudly in protest when the mother leaves the room
Answer:
(a) drinking from a cup and spilling little of the liquid
Rationale:
Infants at age 7 months are not capable of drinking from a cup without spilling. At age 6 months, infants can partially lift their weight on the hands, enjoy imitating sounds, and are developing separation anxiety.
Question 62.
A 13-year-old client is dying of cancer. When providing care for this client, the nurse should incorporate the developmental tasks for this age. According to Erikson’s developmental model, the child normally is expected to be working on which psychosocial issue?
(a) lifetime vocation
(b) social conscience
(c) personal values
(d) sense of competence
Answer:
(c) personal values
Rationale:
According to Erikson, a child of 13 years is normally seeking to meet the need to develop personal identity. Personal values are a component of this identity. Developing a conscience is a component of achieving initiative during the preschool years. Developing a sense of competence is a component of achieving industry in the school-age years. Developing a lifetime vocation is a component of achieving generativity in adulthood.
Question 63.
The nurse is performing Leopold’s maneuvers on a woman who is in her 8th month of pregnancy. The nurse is palpating the uterus as shown below. Which maneuver is the nurse performing?
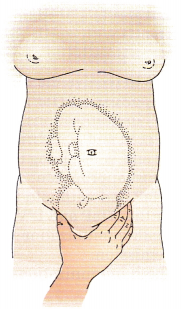
(a) first maneuver
(b) second maneuver
(c) third maneuver
(d) fourth maneuver
Answer:
(c) third maneuver
Rationale:
The third maneuver is used to identify the presenting part. This maneuver is used to identify the part of the fetus that lies over the inlet to the pelvis. While facing the client, the nurse places the tips of the first three fingers on the side of the woman’s abdomen above the symphysis pubis and palpates deeply around the presenting part to identify its contour and size. The first maneuver involves using the tips of the fingers of both hands to palpate the uterine fundus. The second maneuver identifies the back of the fetus, and the fourth maneuver identifies the cephalic prominence.
Question 64.
The nurse is instructing an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) on the prevention of postoperative pulmonary complications. Which statement indicates that the UAP has understood the nurse’s instructions?
(a) “I will turn the client every 2 hours.”
(b) “I will keep the client’s head elevated.”
(c) “I should suction the client every 2 hours.”
(d) “I will have the client take 5 to 10 deep breaths every hour.”
Answer:
(d) “I will have the client take 5 to 10 deep breaths every hour.”
Rationale:
Having the client deep breathe hourly is the most appropriate action for the UAP to take to help prevent pulmonary complications. The client should be turned at least every 2 hours or as needed for this particular client. Keeping the client’s head elevated will not prevent pulmonary complications. Suctioning the client is not a UAP’s responsibility, nor does it prevent pulmonary complications.
Question 65.
During an appointment with the nurse, a client says, “I could hate God for that flood.” The nurse responds, “Oh, don’t feel that way. We’re making progress in these sessions.” The nurse’s statement demonstrates a failure to do what?
(a) Look for meaning in what the client says.
(b) Explain to the client why he may think as he does.
(c) Add to the strength of the client’s support system.
(d) Give the client credit for solving his own problems.
Answer:
(a) Look for meaning in what the client says.
Rationale:
The nurse’s response fails to identify the meaning in what the client has said. The nurse needs to explore the client’s statement about hating God for that flood because the meaning of the client’s statement is unclear. Also, statements such as “Don’t feel that way” are not helpful because they ignore the client’s feelings and his interpretation of the situation in which he finds himself. Explaining to the client why he may think as he does (offering a rationale) is inappropriate. The nurse’s response fails to identify the meaning in what the client has said and is not supportive. There is no evidence that the client is solving his problems.
Question 66.
The nurse observes that the client with multiple sclerosis looks untidy and sad. The client suddenly says, “I can’t even find the strength to comb my hair,” and bursts into tears. Which response by the nurse is best?
(a) “It must be frustrating not to be able to care for yourself.”
(b) “How many days have you been unable to comb your hair?”
(c) “Why hasn’t your husband been helping you?”
(d) “Tell me more about how you’re feeling.”
Answer:
(d) “Tell me more about how you’re feeling.”
Rationale:
By asking the client to tell more about how she is feeling, the nurse is not making any assumptions about what is troubling the client. The nurse should acknowledge the client’s feelings and encourage her to discuss them. Saying that this situation must be frustrating involves assumptions by the nurse about why the client is crying and is not a therapeutic response. Asking how long the client has been unable to comb her hair takes the focus off her feelings and inhibits therapeutic communication. Inquiring why the client’s husband has not helped insinuates that the husband is not helping enough, which is inappropriate, takes the focus off the client’s feelings, and inhibits therapeutic communication.
Question 67.
The nurse is planning care for an obese female client. The client experiences dribbling urine when she coughs, sneezes, and changes positions. The nurse should instruct the client to promote urinary health by encouraging which actions? Select all that apply.
(a) Increase consumption of fluids such as coffee and tea.
(b) Use an indwelling catheter.
(c) Participate in a weight loss program.
(d) Perform muscle-strengthening exercises (Kegel exercises).
(e) Use adult diapers as needed.
Answer:
(c) Participate in a weight loss program.
Rationale:
The goal is to promote health in this client who has stress incontinence. Participating in a weight loss program or support group may decrease the intra-abdominal pressure contributing to the incontinence. Participating in swimming, bicycling, or low-impact exercise is beneficial to weight loss. Kegel exercises are helpful in developing muscle control. Wearing adult diapers will absorb leaked urine and prevent excoriation. Clients with urinary stress incontinence are encouraged to avoid drinks with caffeine and alcohol. Perineal care is essential to prevent skin breakdown, but the client does not require a Foley or straight catheter at this time.
Question 68.
A term primigravida was involved in a car accident 3 hours ago. She is having labor contractions every 4 minutes, and her cervical exam is dilated 3 cm, 100% effaced, and station -1. She is crying uncontrollably and states her pain is constant and severe, rating it at 10/10. What is the nurse’s the priority action?
(a) Reassure the woman and assist with nonphar- macologic pain interventions.
(b) Assess intensity of contractions and determine if she would like an epidural.
(c) Notify the provider of the pain and request an assessment for potential abruption.
(d) Perform a vaginal exam and coach the woman with breathing exercise for pain control.
Answer:
(c) Notify the provider of the pain and request an assessment for potential abruption.
Rationale:
The woman is at risk for placental abruption due to her recent car accident. Symptoms of a placental abruption include unrelenting pain and a rigid board-like abdomen. She may or may not have vaginal bleeding. In contrast, labor contractions are intermittent. The priority action by the nurse should be to ensure that this client is further evaluated by her HCP El- Subsequent actions could include assisting with pain control measures, assessing contractions, and checking cervical dilation.
Question 69.
A nurse interviews the parent of a middle school student who is exhibiting behavioral problems, including substance abuse, following a sibling’s suicide. The parent says, “I’m a single parent who has to work hard to support my family, and now I’ve lost my only son, and my daughter is acting out and making me crazy! I just can’t take all this stress!” Which issue is the priority?
(a) parent’s ability to emotionally support the adolescent in this crisis
(b) potential suicidal thoughts/plans of both family members
(c) the adolescent’s anger
(d) the parent’s frustration
Answer:
(b) potential suicidal thoughts/plans of both family members
Rationale:
The parent’s expressions of stress and grief and the adolescent’s behavior and drug use could be preludes to suicide, especially since another member of the family succeeded in suicide. Suicide attempts are more likely in families in which there has been a previous suicide attempt or suicide death, especially for young people. Though the family’s emotional states are important, one is not more important than the other. Obviously, the parent’s ability to emotionally support the adolescent in this crisis has been compromised, but the safety of both supersedes this concern.
Question 70.
Following surgery, the nurse is to apply sequential compression device to the client’s legs. Prior to applying the device, what is most important for the nurse to do?
(a) Confirm the client’s identity using two client identifiers.
(b) Position the client in the bed.
(c) Explain the sequential compression therapy to the client.
(d) Determine the size of sleeve that is needed.
Answer:
(a) Confirm the client’s identity using two client identifiers.
Rationale:
The nurse must use at least two ways to identify clients. This is done to make sure that each client gets the correct medication/s and/or treatment/s. Although all of the remaining actions need to be done, none of the others would be the first action.
Question 71.
The nurse is caring for a previously healthy adult who is alert and oriented and is being admitted to the hospital for unexplained vomiting and abdominal pain. The client has intravenous fluids infusing through a saline lock and has been ambulating in the hallway with a steady gait. Using the Morse Fall Risk Scale (see chart), what is this cli-ent’s total score and risk level?
|
Item |
Scale |
Scoring |
|
1. History of falling, immediate or within 3 months |
No 0 |
|
|
2. Secondary diagnosis |
No 0 |
|
|
3. Ambulatory aid Bed rest/nurse assist Crutches/cane/walker Furniture |
|
|
|
4. IV/heparin lock |
No 0 |
|
|
5. Gait/transferring Normal/bed rest) immobile Weak 1m paired |
|
|
|
6. Mental status Oriented to own ability Forgets limitations |
|
|
Answer:
Rationale:
This client’s only risk factor is IV access, making this client low risk for a fall. The nurse must remember to reevaluate a client’s risk for fall after any change in condition, upon transfer to another unit within the hospital, or after a fall. In most acute care facilities, a fall risk is completed at least every 24 hours, if not every shift.
Question 72.
Which statements made by a pregnant woman in the first trimester are consistent with this stage of pregnancy? Select all that apply.
(a) “My husband told his friends we’ll have to give up the convertible for a minivan.”
(b) “Oh my, how did this happen? I don’t this now.”
(c) “I can’t wait to see my baby. Do you think it will have my blond hair and blue eyes?”
(d) “I used a princess theme for decorating the room.”
(e) “I wonder how it will feel to buy maternity clothes and be fat.”
(f) “We went to the mall yesterday to buy a crib and dressing table.”
Answer:
(a) “My husband told his friends we’ll have to give up the convertible for a minivan.”
(b) “Oh my, how did this happen? I don’t this now.”
(e) “I wonder how it will feel to buy maternity clothes and be fat.”
Rationale:
The first trimester is when the couple works through the psychological task of accepting the pregnancy. These statements describe the client and her partner coping with the pregnancy, how it feels, and how it will impact their lives. The feelings include pleasure, excitement, and ambivalence. Wondering what the baby will look like and planning for the baby’s room occur later in the pregnancy.
Question 73.
A client comes to the emergency department (ED) with abdominal pain. This is the client’s third visit to the ED in the past month with the same pain. When the nurse asks the client about taking prescribed medications, the nurse discovers the client has stopped taking the prescribed medication because of the cost of the medication. What would the nurse do first?
(a) Refer the client to social services.
(b) Explain to the client the importance for tak ing the prescribed medication.
(c) Help the client make a budget that will include purchasing medication.
(d) Ask the health care to suggest a less costly medication.
Answer:
(d) Ask the health care to suggest a less costly medication.
Rationale:
Noncompliance with medication usage is often due to the high cost of the medication. The nurse should ask the health care provider Q to prescribe a lower cost medication, if possible.
A referral to social services would be appropriate if the client needed assistance to improve quality of life. Prevention of disease and health maintenance are not always common practices in many cultures where health care access is limited. Clients may stop taking medication when symptoms are gone, or take more on days when they are not feeling well. It is important for the nurse to take time to educate the client on the importance of taking the medication on a consistent basis. The case manager would link the client to community resources that would assist the client with budget management.
Question 74.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with crushing chest injuries sustained in a car accident. The nurse is assessing the client’s respiratory status. Which sign indicates a possible complication that the nurse should report to the health care provider immediately?
(a) oxygen saturation of 70% on room air
(b) increased fremitus
(c) absent breath sounds on the affected side
(d) pain on the affected side of 6 on a scale of 1 to 10 when the client breathes
Answer:
(c) absent breath sounds on the affected side
Rationale:
Accumulation of air in the pleural cavity after a crushing chest injury may be assessed by unilateral diminished or absent breath sounds and is indicative of a pneumothorax. The nurse should notify the health care provider An oxygen saturation of 70 percent is expected when a client has a crushing chest injury. Fremitus is a sign of increased lung consolidation. Moderate to severe pain is an expected finding following a crushing chest injury.
Question 75.
A primigravid client at 35 weeks’ gestation is scheduled for a biophysical profile. After instructing the client about the test, which client statement about what the test measures indicates effective teaching?
(a) amniotic fluid volume
(b) placement of the placenta
(c) amniotic fluid color
(d) fetal gestational age
Answer:
(a) amniotic fluid volume
Rationale:
The biophysical profile typically measures five parameters to assess the fetus: fetal breathing, movement, and tone; amniotic fluid volume; and fetal heart reactivity. The test uses a scale of 0 to 2 for each parameter with a maximum score of 10.
