NCLEX Study Guide often includes detailed explanations and rationales, helping students grasp the underlying concepts.
NCLEX-PN Practice Test 3 with Rationale
Question 1.
Which of the following manifestations is considered to be a late sign of increased ICP?
(a) Mental confusion related to time
(b) Blurred vision
(c) BP of 170/40
(d) HR of 94 bpm
Answer:
(c) BP of 170/40
Explanation:
Cushing's triad of manifestations are late signs of increased ICP. Choice (c) is an example of widening pulse pressure. Normal pulse pressure = 40 mmHg. Choice C pulse pressure = 130 mmHg. Choices (a), (b), and (d) are all early signs of increased ICP, and therefore are incorrect.
Question 2.
Which manifestation would the nurse expect to find in a patient with severe glycogenosis?
(a) Liver failure
(b) Kidney failure
(c) Respiratoryfailure
(d) Congestive heart failure
Answer:
(b) Kidney failure
Explanation:
In glycogenosis, the patient's body is not able to convert stored glycogen to glucose when the body needs glucose. In severe cases, the patient can experience chronic gout, seizures, coma, intestinal sores, and kidney failure. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are not correct since liver failure, respiratory failure, and congestive heart failure are not common findings in severe glycogenosis.
Question 3.
During a patient-and-family-centered group at the psychiatric hospital, the nurse educator discusses anxiety disorders and identity development. Which development phase involves the GREATEST onset of psychiatric eating disorders?
(a) Infancy
(b) Young adulthood
(c) Late adulthood
(d) Adolescence
Answer:
(d) Adolescence
Explanation:
Eating disorders primarily develop during adolescence. Eating disorders are psychological disorders involving extreme disturbances in eating behavior, often accompanied by intrusive thoughts. While disordered eating can develop in infancy (Choice a) manifested through failure to thrive, the etiology differs. While young (Choice b) and late (Choice c) adulthood phases involve numerous disordered eating cases, some with similar etiology (psychological) and others that differ (stemming from physical manifestations), they do not result in the greatest number of initiated cases.
Question 4.
A 16-year-old patient presents to the emergency department with a previous diagnosis of anorexia nervosa by her outpatient provider. She is 64 inches tall and weighs 92 pounds. After further discussion, she reveals that she has been consuming only one meal per day for the past two weeks. While reviewing the patient's laboratory results to assess for potential electrolyte imbalances, which potassium result is
a cause for concern?
(a) 3.9 mEq/L
(b) 2.7 mEq/L
(c) 4.5 mEq/L
(d) 5.0 mEq/L
Answer:
(b) 2.7 mEq/L
Explanation:
Choice (b) is cause for concern because it is below the normal range and alerts the nurse that the patient is experiencing hypokalemia, low circulating potassium in the blood. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are within normal range and are not causes for concern at this time. The normal range for serum potassium is 3.5-5.0 mEq/L.
Question 5.
The nurse would expect a patient with urinary retention to report having experienced which of the following types of urinary incontinence?
(a) Stress incontinence
(b) Urge incontinence
(c) Overflow incontinence
(d) Functional incontinence
Answer:
(c) Overflow incontinence
Explanation:
Urinary retention occurs when a patient has cessation of urination or incomplete emptying of the bladder. This may lead to overflow incontinence as the bladder becomes overfilled with urine, which then is involuntarily released from the overfull bladder. Therefore, (a), (b), and (d) are not correct.
Question 6.
The nurse is evaluating the patient's progress related to pain reduction secondary to appendicitis. Which abdominal quadrant does the nurse ask the patient to rate their pain in?
(a) Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
(b) Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
(c) Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
(d) Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
Answer:
(a) Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
Explanation:
Choice (a) involves the quadrant where the appendix is located and where pain is typically felt. The nurse should ask the patient to rate their pain level in the right lower quadrant in order to provide effective pain management at this time. Choices 6, (c), and (d) represent quadrants outside of the appendix location.
Question 7.
Which approach to doffing personal protective equipment (PPE) supports infection control?
(a) Removing PPE at the nursing station
(b) Removing PPE at the bedside immediately following use
(c) Removing PPE in the patient's bathroom
(d) Removing PPE at the patient's doorway
Answer:
(d) Removing PPE at the patient's doorway
Explanation:
Personal protective equipment (PPE) must be removed at the patient's doorway. In addition, it would also be appropriate to remove PPE just outside the patient's room. PPE must not be removed at the nursing station (Choice a), at the bedside (Choice 6), or in the patient's bathroom (Choice c), as these occurrences would put infection control and safety at risk.
Question 8.
What process includes managing outcomes, corrective action plans, and variance trends?
(a) Performance improvement
(b) Information technology
(c) Utilization review
(d) Case management
Answer:
(a) Performance improvement
Explanation:
Performance improvement is an organizational process aimed at improving efficiency and measuring output. This system involves managing outcomes, corrective action plans, and variance trends.
Question 9.
The nurse prepares to obtain an arterial blood sample for analysis from a patient on anticoagulant therapy. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Apply pressure to site for 15 minutes
(b) Attach needle to heparin-containing syringe
(c) Perform Allen test
(d) Clean site
Answer:
(c) Perform Allen test
(d) Clean site
(b) Attach needle to heparin-containing syringe
(a) Apply pressure to site for 15 minutes
Explanation:
The nurse prepares to obtain an arterial blood sample for analysis from a patient on anticoagulant therapy by carrying out steps in the following order to collect a sample that has not coagulated so that the lab can effectively evaluate the efficacy of the patient's anticoagulant therapy. The nurse should perform Allen test, clean the site, attach a needle to a heparin-containing syringe, and then apply pressure to the site for 15 minutes.
Question 10.
What intervention should the nurse do first after receiving a pediatric admission with meningococcal meningitis?
(a) Obtain intravenous access.
(b) Initiate droplet precautions.
(c) Assess vital signs.
(d) Initiate standard precautions.
Answer:
(b) Initiate droplet precautions.
Explanation:
A patient with meningococcal meningitis must be placed on droplet precautions. After completing twenty-four hours of antibiotic therapy, the patient's treatment can transition to standard precautions. Droplet precautions involve the use of a private room. Every individual who enters the room must wear a mask. The nurse must prioritize this intervention before engaging in others. Choices (a) and (c) are not priority interventions, as they should take place after the patient is placed on the appropriate precaution level to prevent the spread of infection. Standard precautions, Choice (d), are not sufficient.
Question 11.
Which of the following statements is typical of a patient with hyperthyroidism?
(a) "I have been experiencing diarrhea."
(b) "I am always cold."
(c) "I have been gaining weight."
(d) "I am always tired."
Answer:
(a) "I have been experiencing diarrhea."
Explanation:
Typical findings in a patient with hyperthyroidism include feelings of anxiety, trouble focusing, feeling overheated, gastrointestinal problems such as diarrhea, insomnia, elevated heart rate, and unexplained weight loss. Choices S, (c), and (d) are not correct because experiencing cold or chills, weight gain, and excessive fatigue are manifestations of hypothyroidism.
Question 12.
Which color-coded catheter should the nurse select when planning to insert an indwelling catheter sized 16 Fr?
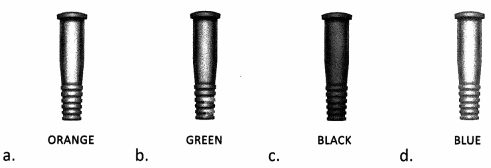
Answer:

Explanation:
Choice (a) indicates the appropriate catheter to meet the size necessity of 16 French units (Fr). Choice (b) indicates size 14 Fr. Choice (c) indicates size 10 Fr. Choice (d) indicates size 8 Fr. The nurse should opt to select the smallest size catheter that will adequately drain urine. Most adult patients will require a 14 or 16 Fr indwelling catheter to promote safe excretion of urine.
Question 13.
After delivering unexpected news, the nurse states, "Don't worry, everyone feels that way." Which block to communication is the nurse committing during this engagement?
(a) Judging
(b) Falsely reassuring
(c) Defending
(d) Belittling
Answer:
(d) Belittling
Explanation:
Choice (d) aligns with the nurse's statement, "Don't worry, everyone feels that way." Telling the patient that everyone feels as they do belittles the patient's unique experience and demonstrates a poor example of therapeutic communication, which hinders the nurse-patient relationship. Choice (a) projects the nurse's opinion. Choice (b) provides comfort in a misleading outcome. Choice Cguards a party, such as a provider. All communication blocks reviewed in this question encourage misunderstandings and failure to listen, which should be avoided in patient care environments.
Question 14.
Which precautions should the nurse engage in while caring for a patient with pertussis?
(a) Standard
(b) Contact
(c) Droplet
(d) Airborne
Answer:
(c) Droplet
Explanation:
Choice (c) involves appropriate precautions for the management of infection control in the patient with pertussis. This illness, also known as whooping cough, produces droplets that can spread when talking, coughing, and sneezing. Choice (a) and Choice (b) would provide inadequate protection with vulnerabilities in disease transmission. Choice (d) represents a higher level of precaution, which is not required for this patient at this time.
Question 15.
Which assessment findings should the nurse expect in a patient with Addison's disease?
(a) Excessive body hair
(b) Hypertension
(c) Excessive energy
(d) Fluid and electrolyte imbalances
Answer:
(d) Fluid and electrolyte imbalances
Explanation:
Addison's disease, also called adrenal insufficiency, occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. Since mineralocorticoids are involved in fluid and electrolyte balance, the patient with Addison's disease is likely to have fluid and electrolyte imbalances. Choice (a) is not correct since the excessive body hair growth in Cushing's syndrome is caused by an excess of glucocorticoid production. Choice (b) is not correct since hypertension does not typically occur in Addison's disease, but it may occur in Cushing's syndrome and Conn's syndrome. Choice (c) is not correct since patients with Addison's disease typically have fatigue.
Question 16.
After delegating care to the Licensed practical nurse (LPN), the Registered nurse (RN) is called in to the nurse manager's office to discuss appropriate delegation of tasks. Which delegated intervention should NOT have been assigned to the LPN?
(a) Administer Lasix® (furosemide) via intravenous push
(b) Hang the subsequent bag of normal saline for infusion
(c) Perform a wet-to-dry dressing change
(d) Insert a Foley catheter
Answer:
(a) Administer Lasix® (furosemide) via intravenous push
Explanation:
The licensed practical nurse (LPN) has the authority to perform dressing changes (Choice c), insert Foley catheters (Choice d), and hang subsequent bags of normal saline for infusion (Choice b). The LPN does not have the ability to push intravenous medications. The registered nurse (RN) should not have delegated the administration of Lasix (furosemide) via intravenous push to the LPN.
Question 17.
Which of the following is the best antibiotic treatment for pneumonia caused by community- acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)?
(a) Azithromycin
(b) Doxycycline
(c) Vancomycin
(d) Levofloxacin
Answer:
(c) Vancomycin
Explanation:
Community-associated, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) is notoriously resistant to most antibiotics, except vancomycin and linezolid, with linezolid quickly becoming the agent of choice for the treatment of CA-MRSA pneumonia.
Question 18.
While reviewing patient dietary plans, the nurse observes an order for a low sodium diet and quickly becomes concerned. Which patient diagnosis paired with this diet alerts the nurse to a potential order error?
(a) Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
(b) Congestive heart failure
(c) Chronic kidney disease
(d) Pulmonary hypertension
Answer:
(a) Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
Explanation:
Choice (a) is cause for concern for an order for an order for a low sodium diet, which must be avoided to prevent episodes of severe hypotension and an exacerbation of symptoms. Patients struggling with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome are at high risk for hypotension and should avoid interventions that may lead to the reduction of fluid retention with increased excretion by the body. Choices (b), (c), and (d), on the other hand, align with the need for a sodium-restricted diet to encourage fluid excretion for symptom management.
Question 19.
Your patient will be starting Coumadin for a new diagnosis of atrial fibrillation. What potential side effects should you include when you educate them about their medication? Select all that apply.
(a) Bleeding gums
(b) Chest pain
(c) Pain in calf
(d) Blood in urine or stool
Answer:
(a) Bleeding gums
(d) Blood in urine or stool
Explanation:
The most common complication of blood thinners is abnormal bleeding, which could show up in the gums, urine, or stool. Choices (b), (c), and (f), chest pain, calf pain, and cough, are not side effects of blood thinners.
Question 20.
Which diagnosis aligns with a symptom presentation that includes abnormal movements of the jaw, " lips, and tongue?
(a) Akinesia
(b) Paresthesia
(c) Akathisia
(d) Tardive Dyskinesia
Answer:
(d) Tardive Dyskinesia
Explanation:
Choice (d) aligns with tardive dyskinesia, an involuntary movement disorder that includes movements of the jaw, lips, and tongue, often seen as an adverse reaction to antipsychotic medication use. Choice (a) identifies the lack of movement, as the patient is unable to engage their muscles. Choice 6 involves an abnormal sensation of the skin, often described as pins and needles. Choice (c) involves restlessness with the urge to keep moving.
Question 21.
The outgoing nurse is providing a report to the oncoming nurse regarding a patient fall during the shift. What information collected using the PQRST method of pain assessment should the nurse include in their report of a 42-year-old patient with vertigo who fell in the shower?
(a) Pain, Quadrant, Radiate, Sensation, Timing
(b) Provoke, Quality, Region, Severity, Timing
(c) Pain, Quality, Radiate, Severity, Task
(d) Provoke, Quadrant, Region, Sensation, Tension
Answer:
(b) Provoke, Quality, Region, Severity, Timing
Explanation:
Choice (b) sets forth that when using the PQRST method the nurse should include information regarding the patient's pain that includes the following characteristics: provoke, quality, region, severity, and timing. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are incorrect as they do not provide accurate details of a PQRST method pain assessment for a nurse-to-nurse report. This method is exclusive to a focused pain assessment and includes specific characteristics.
Question 22.
The nurse sets up tracheostomy care equipment to prepare to clean a tracheostomy and perform a dressing change. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Open the tracheostomy care kit.
(b) Fill bowls with peroxide and/or saline.
(c) Place bowls and supply tray separately on the paper.
(d) Don sterile gloves.
Answer:
(a) Open the tracheostomy care kit.
(c) Place bowls and supply tray separately on the paper.
(b) Fill bowls with peroxide and/or saline.
(d) Don sterile gloves.
Explanation:
The nurse sets up tracheostomy care equipment via steps performed in the following order to prepare to clean a tracheostomy and perform a dressing change maintaining sterile technique. The nurse should open the tracheostomy care kit, place the bowls and supply tray separately on the paper, fill the bowls with peroxide and/or saline, and then don sterile gloves
Question 23.
All EXCEPT which of the following are components of Virchow's triad?
(a) Heart disease
(b) Hypercoagulability
(c) Endothelial injury/dysfunction
(d) Hemodynamic changes such as stasis or turbulence
Answer:
(a) Heart disease
Explanation:
Virchow's triad identifies factors that contribute to the thrombotic process associated with deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). The triad consists of hypercoagulability, endothelial injury/dysfunction, and hemodynamic changes such as stasis and turbulence. Heart disease is a risk factor for DVT and PE, but it is not part of Virchow's triad.
Question 24.
During the nurse-to-nurse report, the patient is described as struggling with aphasia. Which description correlates to this finding?
(a) Unable to perform movements
(b) Difficulty sitting still
(c) Difficulty swallowing
(d) Unable to understand or produce speech
Answer:
(d) Unable to understand or produce speech
Explanation:
Choice (d) correlates with aphasia, as the patient is unable to understand or produce speech. Aphasia is often witnessed with brain trauma or severe neurological conditions affecting the communication areas of the brain. This condition is also considered a language disorder. Choice (a) describes a patient with apraxia. Choice (b) describes a patient with akathisia. Choice (c) involves dysphagia.
Question 25.
While caring for a patient with sleep apnea, which oxygen delivery device should be used?
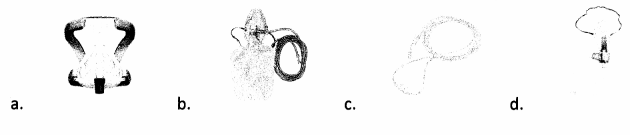
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice (a) indicates the appropriate oxygen delivery device for a patient with sleep apnea. CPAP machines work by increasing air pressure to prevent the throat from becoming obstructed. Choices (b), (c), and (d), while all helpful devices for respiratory support, do not deliver continuous pressure to prevent obstructive airway collapse.
Question 26.
While caring for a patient with a high thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level and a diagnosis of hypothyroidism, which symptom does the nurse NOT expect the patient to report?
(a) Muscle cramps
(b) Weight loss
(c) Fatigue
(d) Coarse hair
Answer:
(b) Weight loss
Explanation:
An elevated level of circulating thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) causes symptoms that correlate with hypothyroidism. Choice (a), muscle cramps, Choice (c), fatigue, and Choice (d), coarse hair, are all symptoms of this disease, while weight loss is a symptom of hyperthyroidism. In hyperthyroidism, the nurse would expect to see a low TSH level.
Question 27.
The nurse is reviewing dietary orders prior to breakfast. Which diet should be implemented for a patient with gout?
(a) Low-purine
(b) High-Fructose
(c) Low-Caffeine
(d) High-Fat
Answer:
(a) Low-purine
Explanation:
Choice (a) represents the diet that should be implemented for the patient with gout. Choices 6 and (c) should be avoided as they may exacerbate symptoms. Choice (d) is not necessary for this patient at this time. Purines can cause gout attacks and should be avoided. Some examples of high-purine foods include red meat, seafood, organ meat, and alcohol.
Question 28.
Which of the following is/are true regarding advance directives?
(a) They are an expression of the patient's preferences.
(b) They are based on a person's values and beliefs.
(c) They include identification of a surrogate.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation:
The patient's preferences, values, and beliefs, as well as indication of a surrogate decision maker, are all included in advance directives.
Question 29.
Identify the cornea.
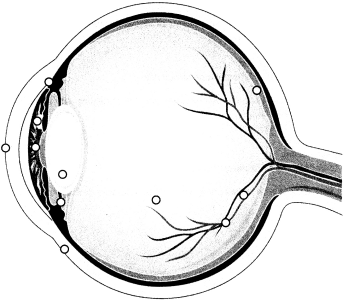
Answer:
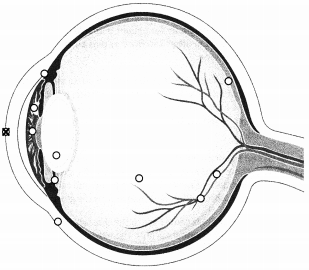
Explanation:
The cornea is the transparent part of the eye over the iris and pupil, curved to refract light towards the midline of the eye.
Question 30.
In order to support the patient in choosing the focus of a conversation, which therapeutic communication technique should the nurse use?
(a) Broad opening
(b) Use of silence
(c) Reflection
(d) Clarification
Answer:
(a) Broad opening
Explanation:
Choice (a) involves the nurse enabling the patient to choose the focus of the conversation. With broad openings, the patient is supported to lead the dialogue in a direction that they value. Choices 6, (c), and (d) represent therapeutic communication techniques, but they do not directly align with the process the nurse is seeking to use.
Question 31.
While caring for a patient status post drug overdose, which cardiac rhythm does the nurse interpret when evaluating this telemetry reading?

(a) Atrial fibrillation
(b) Ventricular tachycardia
(c) Atrial flutter
(d) Ventricular fibrillation
Answer:
(d) Ventricular fibrillation
Explanation:
Choice (d) represents the cardiac rhythm evaluated on this telemetry reading, which involves the right and left ventricles beating irregularly with flutter; this is life threatening. Choice (a) would involve excessive, rapid contraction of the right and left atria with absent P waves and irregular QRS complexes. Choice (b) would involve a wide QRS complex. Choice (c) would involve supraventricular tachycardia with no visible P waves.
Question 32.
The nurse becomes concerned after witnessing the provider use language that negatively impacts a patient's ability to make their own decision regarding their care without provider influence. Which ethical principle may the provider be violating at this time?
(a) Nonmaleficence
(b) Veracity
(c) Beneficence
(d) Autonomy
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice (d) supports the patient's right to engage in independent, self-directed decision-making. The provider must avoid language that impedes this right. Choice (a) involves avoiding patient harm. Choice 8 represents truthfulness. Choice (c) includes the moral imperative to do right by the patient.
Question 33.
Which precautions should the nurse engage in while caring for a patient with herpes zoster that is classified as disseminated inflection?
(a) Standard
(b) Reverse isolation
(c) Contact
(d) Airborne and contact
Answer:
(d) Airborne and contact
Explanation:
Choice (d) represents the proper infection control practices to reduce the transmission of herpes zoster for the patient with classified disseminated infection. Both airborne and contact precautions are necessary during this phase of illness. Choices (a), (b), and (d) would provide improper infection control and ’ increased risk.
Question 34.
While using the SBAR method of communication, which term aligns with the patient's laboratory findings?
(a) Situation
(b) Background
(c) Assessment
(d) Recommendations
Answer:
(c) Assessment
Explanation:
Choice (c) aligns with the patient's laboratory findings when utilizing the SBAR as a method of communication. SBAR stands for situation, background, assessment, and recommendations. Laboratory findings are a form of assessment data; therefore, they align with the assessment aspect of reports. Choice (a) includes the current condition. Choice (b) includes the context of the circumstance. Choice D includes the nurse's suggestions to respond to the situation.
Question 35.
During a homecare visit, the nurse provides patient education regarding the bedtime regimen of * aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide/simethicone. The patient's ordered dose is 30 mL by mouth. The patient explains that they plan to self-administer their dose using a standard tablespoon device they have available at home. How many tablespoons should the nurse instruct the patient to administer at bedtime? Record your answer to the nearest whole number.
.................. tbsp
Answer:
2 tbsp
Explanation:
The nurse should understand that 1 tbsp equals 14.8 mL and divide the total, 30 mL, by 14.8 mL/tbsp to yield 2.02 tbsp, expressed as 2 tbsp when rounded to the nearest whole number.
Question 36.
While completing a respiratory assessment for a patient with pneumonia, where should the nurse first auscultate lung sounds anteriorly? Place an X to mark your answer.
Answer:
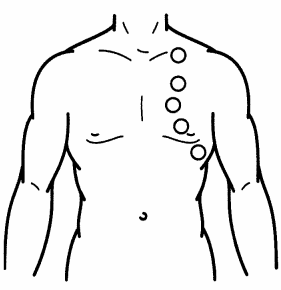
Explanation:
The nurse should ask the patient to breathe normally with their mouth open and place the diaphragm of their stethoscope above the clavicle to auscultate the apices bilaterally. Following this location, the nurse should then travel down to the middle and then lower lung fields bilaterally.
Question 37.
The provider just informed a patient that her baby is in frank breech presentation. Which graphic would the nurse correctly show when educating the patient about this type of presentation?
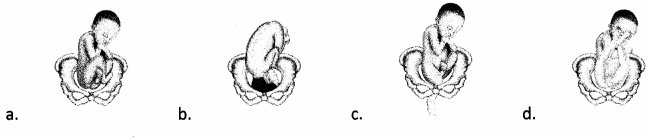
Answer:
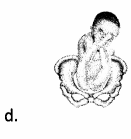
Explanation:
Choice (d) indicates a frank breech fetal presentation, which involves flexed thighs and extended legs. Choice A indicates a full breech, which involves flexed thighs and legs. Choice (b) indicates a normal presentation, which is head first with occiput anterior. Choice (c) indicates a footling breech, which involves a fetal foot entering the birth canal first.
Question 38.
The nurse ensures the patient is fully supported to make their own decisions, without coercion, regarding their care. What ethical principle guides this practice?
(a) Autonomy
(b) Utility
(c) Fidelity
(d) Conflict of interest
Answer:
(a) Autonomy
Explanation:
Choice (a) involves the patient's determination to self-directed decisions that are free from coercion. Choice (b) sets forth that actions are right or wrong depending on the level of pleasure they promote. Choice (c) endorses that the nurse will remain true to their professional commitments. Choice (d) involves conflicting concerns of multiple parties.
Question 39.
Your patient had an output of 3000 mL of urine in the last 24 hours. He drank 2000 mL and had IV fluids running at 50mL/hr. What was the net intake? ...................... mL
Answer:
200 mL
Explanation:
The patient drank 2000 mL and his total IV fluid intake was 1200 mL. 2,000 plus 1,200 equals 3,200 mL. Subtracting the urine output of 3,000 mL leaves 200 mL.
Question 40.
While advocating for the patient's individualized nutritional needs after reviewing the results of recent lab work, the nurse meets with the dietician to discuss the patient's hyponatremia. A unique meal plan is instituted. The nurse is aware that all EXCEPT which of following risk factors are commonly associated with this imbalance?
(a) Diarrhea
(b) Vomiting
(c) Diplopia
(d) Polydipsia
Answer:
(c) Diplopia
Explanation:
A patient struggling with hyponatremia is at increased risk for developing vomiting (Choice 6), diarrhea (Choice a), and polydipsia (Choice d). Diplopia, double vision, is not commonly associated with this imbalance.
Question 41.
Your patient is a 50-year-old woman who is 5'5" and weighs 182 pounds. What is her weight category?
|
|
Normal Weight |
Over Weight |
OBESE |
||||||||||||||
|
BMI Value: |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
|
Height(inches) |
Body Eeight(Kilograms/kg) |
||||||||||||||||
|
58” |
41 |
44 |
45 |
48 |
50 |
52 |
54 |
56 |
59 |
56 |
59 |
61 |
63 |
65 |
67 |
69 |
72 |
|
59” |
43 |
45 |
47 |
49 |
52 |
54 |
56 |
58 |
60 |
58 |
60 |
63 |
65 |
67 |
69 |
72 |
74 |
|
60” |
44 |
46 |
49 |
51 |
54 |
56 |
58 |
60 |
63 |
60 |
63 |
65 |
67 |
69 |
72 |
74 |
76 |
|
61“ |
45 |
48 |
50 |
53 |
55 |
57 |
60 |
62 |
65 |
62 |
65 |
67 |
69 |
72 |
74 |
79 |
79 |
|
62” |
47 |
49 |
52 |
54 |
57 |
59 |
62 |
64 |
67 |
64 |
67 |
69 |
72 |
74 |
77 |
82 |
82 |
|
63” |
49 |
51 |
54 |
56 |
59 |
61 |
64 |
66 |
69 |
66 |
69 |
72 |
74 |
77 |
79 |
84 |
84 |
|
64” |
50 |
53 |
55 |
58 |
61 |
64 |
66 |
68 |
71 |
68 |
71 |
74 |
77 |
79 |
82 |
87 |
87 |
|
65” |
52 |
54 |
57 |
60 |
63 |
65 |
68 |
71 |
73 |
71 |
73 |
76 |
79 |
82 |
84 |
90 |
90 |
|
66” |
54 |
56 |
59 |
62 |
64 |
67 |
70 |
73 |
76 |
73 |
76 |
78 |
81 |
84 |
87 |
93 |
93 |
|
67” |
55 |
57 |
61 |
64 |
66 |
69 |
72 |
75 |
78 |
75 |
78 |
81 |
84 |
87 |
90 |
96 |
96 |
|
68” |
57 |
59 |
63 |
65 |
68 |
72 |
74 |
78 |
80 |
78 |
80 |
83 |
86 |
89 |
92 |
98 |
98 |
|
69” |
58 |
61 |
64 |
68 |
70 |
73 |
77 |
80 |
83 |
80 |
83 |
86 |
89 |
92 |
95 |
101 |
101 |
|
70” |
60 |
63 |
66 |
69 |
73 |
76 |
79 |
82 |
85 |
82 |
85 |
88 |
92 |
95 |
98 |
104 |
104 |
|
71” |
62 |
65 |
68 |
71 |
75 |
78 |
81 |
84 |
88 |
84 |
88 |
91 |
94 |
98 |
101 |
107 |
107 |
|
72” |
64 |
67 |
70 |
73 |
77 |
80 |
83 |
87 |
90 |
87 |
90 |
93 |
97 |
100 |
103 |
110 |
110 |
|
73” |
65 |
68 |
72 |
75 |
79 |
83 |
86 |
89 |
93 |
89 |
93 |
96 |
98 |
103 |
107 |
113 |
113 |
|
74” |
67 |
70 |
74 |
78 |
81 |
84 |
88 |
92 |
95 |
92 |
95 |
99 |
102 |
106 |
110 |
116 |
117 |
|
75” |
69 |
73 |
76 |
80 |
83 |
87 |
91 |
94 |
98 |
94 |
98 |
102 |
105 |
109 |
113 |
119 |
120 |
|
76” |
71 |
74 |
78 |
82 |
86 |
89 |
93 |
97 |
100 |
97 |
100 |
104 |
108 |
112 |
116 |
112 |
123 |
|
Height(inches) |
Body Eeight(Kilograms/kg) |
||||||||||||||||
|
BMI Value: |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
|
|
Normal Weight |
Over Weight |
OBESE |
||||||||||||||
(a) Underweight
(b) Normal weight
(c) Overweight
(d) Obese
Answer:
(d) Obese
Explanation:
The patient is considered obese based on her height and weight.
Question 42.
While receiving nurse-to-nurse report from the emergency department on a pending transfer, the nurse learns that an incoming 43-year-old patient is struggling with delusional thinking. What understanding is necessary to ensure effective communication is used upon receiving this patient?
(a) The patient experiences insistent false beliefs despite invalidating evidence.
(b) The patient experiences perceptions irrelevant to actual external stimuli.
(c) The patient experiences acute, short-lasting confusion and disorientation.
(d) The patient experiences a gradual impairment in cognitive functioning.
Answer:
(a) The patient experiences insistent false beliefs despite invalidating evidence.
Explanation:
Choice (a) describes the patient's thought process when experiencing delusional thinking. The nurse must understand how delusional thinking impairs beliefs, as well as understanding and cooperation, to ensure the establishment of effective communication and a holistic plan of care. Choice (b) describes hallucinations. Choice (c) describes delirium. Choice (d) describes dementia.
Question 43.
All EXCEPT which of the following help define acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
(a) Timing
(b) Origin of edema
(c) Pulmonary artery wedge pressure
(d) Severity of hypoxemia
Answer:
(c) Pulmonary artery wedge pressure
Explanation:
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is defined by the timing, a chest x-ray, the origin of the edema, and the severity of hypoxemia. In terms of timing, the onset of symptoms in ARDS is within one week of the inciting incident. A chest x-ray should reveal bilateral lung infiltrates not explained by consolidation, atelectasis, or effusions. The edema origin is not explained by heart failure or fluid overload, and the severity of hypoxemia is based on the PaCh/FiCh ratio while on 5 cm of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP).
Question 44.
According to Erikson's Psychosocial Development Theory, how should the nurse educate new parents to respond to their newborn infant's needs?
(a) Wait for the infant to signal all needs.
(b) Allow the infant to signal some needs.
(c) Anticipate all infant needs.
(d) Provide a delayed response to the infant's signal.
Answer:
(b) Allow the infant to signal some needs.
Explanation:
Erikson's Psychosocial Development Theory involves eight stages centered on healthy development from infancy to late adulthood. The theory, designed by Erik and Joan Erikson in the twentieth century, encourages parents to allow the infant to signal some needs before responding, and then promptly respond with support.
Question 45.
What type of variance occurs when unwarranted tests are ordered and standard tests are neglected?
(a) Managed care
(b) Practitioner
(c) Dispensary
(d) Patient
Answer:
(b) Practitioner
Explanation:
When unwarranted tests are ordered and standard tests are omitted, the variance is identified to be from the practitioner source. The practitioner is modifying the standard process and is inconsistent with the customary treatment for a given symptom set or diagnosis. Choices (a), (c), and (d) do not represent the cause of the variance in this scenario.
Question 46.
The nurse case manager is interfacing with physical therapy regarding patient education on the use of a newly prescribed walker. Which of the following safety guidelines should the patient be educated on to safely use their new walker?
(a) Grooved rubber tips that cover the bottom of the walker's legs should not be used.
(b) Waxed floors support grip while ambulating.
(c) Step up onto curbs with the strong leg before the weak leg.
(d) Carry the walker up a set of stairs on the nonaffected side.
Answer:
(c) Step up onto curbs with the strong leg before the weak leg.
Explanation:
Choice (c) supports proper use of the new walker. The patient should be educated to step up onto curbs with their strong leg first. The weak leg can then follow as balance is regained atop the curb. Choice (a) is incorrect because it discourages the use of grooved rubber tips; however, they should be placed on the bottom of the walker's legs to improve floor grip and patient balance. Choice (b) is incorrect because it encourages the use of waxed flooring, though this would be unsafe as it could lead to patient falls. Choice (d) should be discouraged, as patients should not carry their walker up stairs.
Question 47.
Which term is used to describe quality of care over time?
(a) Standard of care
(b) Quality improvement
(c) Continuity of care
(d) Risk management
Answer:
(c) Continuity of care
Explanation:
Continuity of care is a longstanding process that involves an ongoing relationship between a patient and their providers, with shared goals to establish the most effective care. Continuity of care retains a focus on maintenance and wellbeing with cost-effective approaches in mind. The key to this relationship is longevity with health-maintenance engagements. Choice (a) signifies minimum standards, while Choice (b) and Choice (d) focus on reducing risks and improving care.
Question 48.
The triage nurse is assessing a patient's pain post motor vehicle accident. What does the PQRST method of pain assessment consist of?
(a) Presentation, Quality, Risk, Severity, Timing
(b) Presentation, Quality, Region, Source, Task
(c) Provoke, Quality, Region, Severity, Timing
(d) Provoke, Quality, Risk, Source, Task
Answer:
(c) Provoke, Quality, Region, Severity, Timing
Explanation:
When assessing pain, the PQRST method, which stands for provoke, quality, region, severity, and timing, can prove helpful. This technique encourages a comprehensive review of the patient's pain, which leads to appropriate intervention and management.
Question 49.
The nurse is preparing to deliver an oral suspension of doxycycline available as 25 mg/5 mL for a six- year-old patient who weighs 25 kg. The medication is to be delivered as 4.4 mg/kg of body weight per day in two equally divided doses. How many mL of oral suspension should the nurse deliver for the patient's morning dose? ............................. mL
Answer:
11 mL
Explanation:
The nurse should multiply 4.4 mg by 25 to yield 110 mg and then divide this by 2 doses to yield 55 mg/dose. The nurse should then divide 25 mg by 5 mL to yield 5 mg/mL. Now, in using the dosage calculation of "dose ordered" divided by "dose on hand," the nurse should divide 55 mg by 5 mg/mL to yield 11 mL to be delivered as the patient's morning dose.
Question 50.
Which diagnosis is chiefly responsible for hospital admission?
(a) Discharge diagnosis
(b) Secondary diagnosis
(c) Primary diagnosis
(d) Principle diagnosis
Answer:
(d) Principle diagnosis
Explanation:
The principle diagnosis is the chief reason for the patient's inpatient hospitalization, while the primary diagnosis (Choice c) is what requires the most resources during their stay. Oftentimes, the principle diagnosis will also turn out to be the primary diagnosis, although this is not always the case. Secondary diagnoses (Choice b) either coexist at the time of admission or develop during the
hospitalization in addition to the primary and principle diagnoses. The discharge diagnosis (Choice a) focuses on the diagnosis the patient leaves the hospital with.
Question 51.
When prioritizing care, which needs group does the nurse identify to be the most basic?
(a) Oxygen, nutrition, elimination
(b) Employment, freedom from danger
(c) Affection, belongingness, connection
(d) Learning, creating, understanding
Answer:
(a) Oxygen, nutrition, elimination
Explanation:
Basic human needs consist of oxygen, nutrition, hydration, elimination, temperature, rest, sex, and shelter. While Choices (b), (c), and (d), include needs important for stable wellbeing, they are considered secondary to the most basic, physiological needs for survival.
Question 52.
While working with expectant parents to discuss the pending home birth for their first child, the nurse teaches them what to expect during the periods of reactivity. How long does the first period of reactivity last for a newborn right after birth?
(a) 30 minutes
(b) 60 minutes
(c) 120 minutes
(d) 240 minutes
Answer:
(a) 30 minutes
Explanation:
The first period of reactivity following the birth of a newborn typically lasts 30 minutes. It takes place during the first 30 minutes of life and involves the initial episode of engagement with stimuli. After this activity and alertness ends, the newborn falls into a deep sleep.
Question 53.
Which of the following is a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy?
(a) Current anticoagulant therapy
(b) Over age 75
(c) Severe hepatic disease
(d) INR of 3.5
Answer:
(d) INR of 3.5
Explanation:
An INR of 3.5 is elevated and will cause bleeding complications if thrombolytic therapy is initiated before the INR returns to the normal level of less than or equal to 1.1.
Question 54.
The nurse is advocating for updates to the patient's interdisciplinary treatment plan during the morning team meeting. In discussing behavior from the previous night, the nurse describes that the patient was exhibiting detachment from self in present reality. What is this mechanism referred to as?
(a) Disconnection
(b) Dissociation
(c) Displacement
(d) Disillusion
Answer:
(b) Dissociation
Explanation:
Dissociation is an experience involving a disconnection from the present moment. Triggers for a dissociative episode typically include an overload of stimuli, often connected to a traumatic event.
Question 55.
A pediatric patient presents to primary care accompanied by their parent with signs and symptoms of conjunctivitis, an inflammatory infection of the eye's conjunctiva. Where is the conjunctiva located on the eye? Place an X to mark your answer.
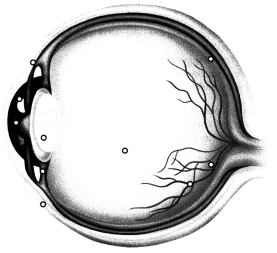
Answer:
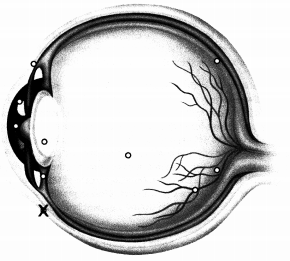
Explanation:
The conjunctiva of the eye covers the sclera and lines the inside of the eyelid. When this area of the eye becomes inflamed and infected, the condition is referred to as conjunctivitis and is very contagious. Signs and symptoms include redness, swelling, discharge, and excessive tearing.
Question 56.
All EXCEPT which of the following must be documented for physical restraints?
(a) Reason for intervention
(b) Restraint type
(c) Patient consent
(d) Patient behavior
Answer:
(c) Patient consent
Explanation:
Patient consent is not needed for a physical restraint. In order for a physical restraint to move forward, the reason for the intervention (Choice a), the type of restraint used (Choice b), and the supporting patient behaviors (Choice d) must be documented. The use of this intervention must be thoroughly documented and substantiated.
Question 57.
The public health nurse is providing community education on the connection between sexually transmitted infections and other ailments. In advocating for testing, which disease does the nurse explain is often associated with chlamydia and gonorrhea?
(a) Rheumatoid arthritis
(b) Celiac disease
(c) Pelvic inflammatory disease
(d) Systemic lupus erythematous
Answer:
Explanation:
Chlamydia and gonorrhea, sexually transmitted infections, are associated with the development of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). When bacteria from these infections travel upward to the reproductive organs from the vagina or cervix, pelvic inflammatory disease may develop. The disorders and diseases represented by Choicest, (b), and (d) are not associated with PID.
Question 58.
Which response by the unlicensed assistive personnel functioning in the role of cardiac monitor technician would warrant the nurse to intervene and educate?
(a) Monitoring cardiac telemetry
(b) Printing rhythm strips
(c) Interpreting cardiac rhythm
(d) Notifying the team of no discernible activity
Answer:
(c) Interpreting cardiac rhythm
Explanation:
The cardiac monitor technician, an unlicensed assistive member of the team, has the authority to monitor telemetry (Choice a), print rhythm strips (Choice fi), and notify the team when no discernible activity is detected (Choice d). The monitor technician should never interpret cardiac rhythm, as that is beyond their scope of practice.
Question 59.
Your patient is in for his 24-month check-up. He currently weighs 30 pounds. What approximate percentile is he in weight?
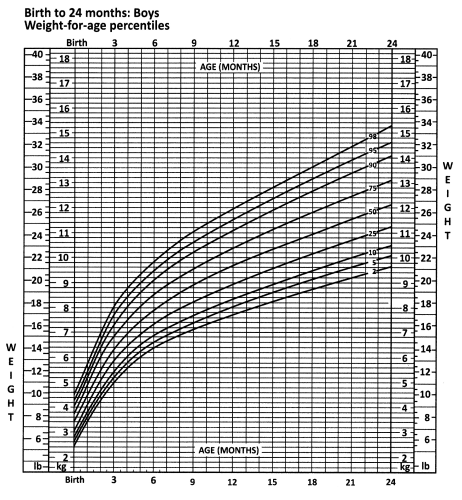
(a) 25th
(b) 50th
(c) 80th
(d) 98th
Answer:
(c) 80th
Explanation:
Tracing the growth line leads to approximately the 80th percentile.
Question 60.
The registered nurse witnesses the licensed practical nurse (LPN) take a radial pulse on an infant patient and decides that education on pediatric pulse sites is necessary. What site should the LPN have
used to take this patient's
(a) Brachial
(b) Femoral
(c) Pedal
(d) Popliteal
Answer:
(a) Brachial
(b) Femoral
(d) Popliteal
(c) Pedal
Explanation:
The nurse prepares to obtain a nasal specimen for culture by carrying out steps in the following order to maintain aseptic technique and collect sufficient quantity to perform effective testing: assist patient to an erect position with head tilted back, ask patient to blow nose, assess nasal passages for patency, and crush ampule in collection tube.
Question 61.
Which of the following statements correctly identifies the difference between the forgetfulness that is common to the normal aging process and the memory alterations associated with Alzheimer's disease?
(a) The processes are the same; however, memory alterations associated with Alzheimer's disease include only short-term memory loss.
(b) Forgetfulness is progressive and eventually results in the individual's inability to perform ADLs independently.
(c) Memory lapses associated with Alzheimer's disease improve with frequent cueing.
(d) The end stage of memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease is the inability to recognize family members.
Answer:
(d) The end stage of memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease is the inability to recognize family members.
Explanation:
Early manifestations of memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease are associated with short-term memory loss and the inability to assimilate new knowledge, with progressive impairment that affects long-term memory, mood, and independent functioning. The end stage of this process is the inability to recognize family members. The processes are not the same. Memory lapses associated with forgetfulness improve with cueing and do not progress to the inability to recognize family members. Therefore, Choices (a), 6, and (c) are incorrect.
Question 62.
Which action witnessed by the nurse of the unlicensed assistive personnel warrants further education?
(a) Applied lotion to the patient's arms after a bed bath
(b) Took vital signs on the ipsilateral arm post right-sided mastectomy
(c) Cut food into small pieces before feeding patient
(d) Rolled patient onto their side during linen change
Answer:
(b) Took vital signs on the ipsilateral arm post right-sided mastectomy
Explanation:
Vital signs must not be taken on the arm of the affected side (which is termed the ipsilateral side) post-mastectomy. Vital signs should be taken on the contralateral arm to support accurate readings and avoid aggravating possible lymphedema on the affected side, especially during blood pressure readings. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are all appropriate actions that do not warrant further education at this time.
Question 63.
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) Ninety-five percent of the patients diagnosed with multiple sclerosis will potentially advance to a non-remitting disease pattern.
(b) The clinically isolated incident is a definitive precursor of active MS.
(c) The primary-progressive form of MS is the most common presenting form of the disease.
(d) Prednisone is the medication of choice to slow progression in all forms of MS.
Answer:
(a) Ninety-five percent of the patients diagnosed with multiple sclerosis will potentially advance to a non-remitting disease pattern.
Explanation:
Ten percent of MS patients are initially diagnosed with the primary-progressive form of MS, which means that the disease is always active without periods of remission. The relapsing-remitting form of MS accounts for 85 percent of the patients diagnosed with MS, which means that they will eventually progress to the secondary-progressive form; this means that the disease is always active. The potential progression of an isolated incident to MS depends on the presence or absence of plaque formation on MRI scans.
The presence of alterations in the myelin sheath is strongly predictive of eventual progression. However, the absence of those lesions does not rule out the possibility of subsequent progression to MS; therefore, Choice (b) is incorrect. Only 10 percent of MS patients present with the primary-progressive form; therefore, Choice (c) is incorrect. Disease-modifying drugs are the preferred agents to treat MS. However, prednisone may be used if a patient is unable to tolerate the DMDs; therefore, Choice (d) is incorrect.
Question 64.
While working with a patient who is three days postop from a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), the nurse notices that the patient looks pale and feels cold while ambulating in their room. What action does the nurse take first to prevent a fall?
(a) Assist the patient back to bed.
(b) Encourage the patient to eat a snack.
(c) Increase the flow rate on the patient's nasal cannula.
(d) Assess the patient's vital signs.
Answer:
(a) Assist the patient back to bed.
Explanation:
The most immediate action the nurse should take after noticing that the patient looks pale and feels cold is to assist the patient back to bed to prevent a fall. Afterward, the nurse can assess the patient's nutrition and hemodynamic status (Choices 8, (c), and (d)).
Question 65.
A patient reports to the nurse that he is feeling anxious and dizzy, and his heart is racing. Which system-specific assessment will the nurse perform to investigate these symptoms?
(a) Assess the circulatory system by grading the patient's pitting edema.
(b) Obtain and compare bilateral peripheral pulses.
(c) Assess the patient's level of consciousness and motor and sensory function.
(d) Compare the patient's muscular strength bilaterally by having him push against resistance.
Answer:
(b) Obtain and compare bilateral peripheral pulses.
Explanation:
The nurse should hone in on the cardiac system by assessing the strength and rate of the patient's pulses, comparing them bilaterally. If the rate is above normal and the quality is weak, the nurse knows that the patient's heart is working extra hard, and the reason needs to be discovered. Assessing things like pitting edema, the patient's motor and sensory function, and muscular strength are not the most precise actions the nurse can take to quickly get to the bottom of the patient's symptomology. The nurse will use sound nursing judgment to determine which assessments to make on a patient and when.
Question 66.
A patient presents for a scheduled upper Gl endoscopy and explains that they have been experiencing black, tarry stools for the past three days. What does the nurse suspect may be causing the patient's melena?
(a) Consumption of iron supplements
(b) Gastrointestinal bleed
(c) Excess beets in the diet
(d) Charcoal from the oral preparatory solution
Answer:
(b) Gastrointestinal bleed
Explanation:
Black, tarry stool, known as melena, is a sign of a gastrointestinal bleed. The higher up in the " gastrointestinal track the bleed is, the darker the blood is in the stool. While Choice (c), the consumption of beets, and Choice (a), iron supplements, can affect the color of stool, they do not cause melena. Melena would not be seen from consuming a preparatory solution, and upper Gl tract endoscopies do not entail an oral preparatory solution (Choice d).
Question 67.
What color of wound prompts the licensed practical nurse to ask the registered nurse to assess for the need for debridement?
(a) Pink
(b) Red
(c) Yellow
(d) Black
Answer:
(d) Black
Explanation:
The licensed practical nurse would appropriately report a wound that is black in color to the registered nurse for further assessment, as wounds of this color may need to be debrided and should not be rewrapped by the licensed practical nurse without further review. Pink (Choice a), red (Choice 6), and yellow (Choice c) wounds do not signify the need to debride at this point.
Question 68.
During a home visit, the nurse notices that the 68-year-old client is struggling to follow the images and diagrams on the educational handout. What symptom prompts the nurse to encourage the patient to have an eye examination for possible macular degeneration?
(a) Flashes of light
(b) Distorted straight lines
(c) Poor peripheral vision
(d) Reduced depth perception
Answer:
(b) Distorted straight lines
Explanation:
Age-related macular degeneration causes numerous symptoms, including the distortion of straight lines. The lines may appear wavy to the individual struggling with this condition. Flashes of light (Choice a), poor peripheral vision (Choice c), and reduced depth perception (Choice d) can be witnessed in other ocular disorders but are not typical symptoms of macular degeneration.
Question 69.
Which medication alerts the nurse to contact the prescriber to verify the order due to contraindication for a patient with benign prostatic hypertrophy?
(a) Fluoxetine
(b) Acetaminophen
(c) Levothyroxine
(d) Ipratropium bromide
Answer:
(d) Ipratropium bromide
Explanation:
Ipratropium bromide, Choice d, is contraindicated for the patient with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) as the use of this medication could encourage the development of urinary retention. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are considered compatible medications for individuals struggling with BPH and do not warrant a phone call to the prescriber for order verification.
Question 70.
Identify the transverse colon.
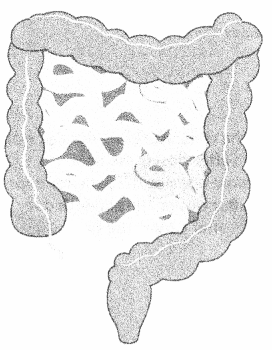
Answer:
Explanation:
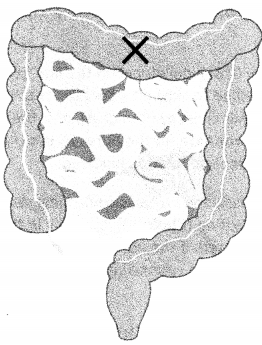
The transverse colon is the medial portion of the colon that travels laterally across the body from right to left, after the ascending colon and before descending colon in the digestive tract.
Question 71.
Which potential complication should the nurse educate the patient on regarding their newly placed * colostomy?
(a) Renal calculi
(b) Dehiscence
(c) Nocturnal enuresis
(d) Pernicious anemia
Answer:
(b) Dehiscence
Explanation:
The nurse must educate the patient regarding the risk for dehiscence of the new colostomy. If the stoma is retracted, it could lead to dehiscence at the mucocutaneous junction. Ultimately, the patient would be at risk for intraperitoneal contamination. Renal calculi (Choice a), nocturnal enuresis (Choice c) and pernicious anemia (Choice d) do not require education at this time, as they are not chief concerns associated with a new colostomy.
Question 72.
While responding to a code for potential cardiopulmonary arrest, the nurse prepares to engage in basic life support. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Check pulse
(b) Assess unresponsiveness
(c) Open airway
(d) Chest compressions
Answer:
(b) Assess unresponsiveness
(a) Check pulse
(d) Chest compressions
(c) Open airway
Explanation:
The nurse prepares to engage in basic life support while responding to a code for potential cardiopulmonary arrest by carrying out steps in the following order to ensure the patient's condition is thoroughly assessed, the interventions warranted, and properly executed: assess unresponsiveness, check pulse, chest compressions, and open airway.
Question 73.
While providing care to an infant patient, the nurse reviews the chart to find a history of intussusception, which is a contraindication for what vaccination?
(a) Rotavirus
(b) Polio
(c) Pneumococcal
(d) Haemophilus influenza type B
Answer:
(a) Rotavirus
Explanation:
The infant patient with a history of intussusception is not a candidate for the rotavirus vaccine. Intussusception involves a bowel blockage and bowel ischemia stemming from the colon folding into itself. Infants with a history of intussusception are at greater risk of developing intussusception again post rotavirus vaccination. Choices (b), (c), and (d) are not contraindicated by intussusception.
Question 74.
While the provider is educating a Japanese-American patient regarding a medication change, the patient continuously nods their head throughout the instruction. What does the patient's nodding signify?
(a) Cultural value of communication
(b) Agreement to take the medication
(c) Acceptance of the treatment plan change
(d) Understanding of the entirety of the instruction
Answer:
(a) Cultural value of communication
Explanation:
The cultural value of interpersonal harmony may be reflected in the head nodding expressed by the Japanese-American patient. The provider must not assume that the patient agrees (Choice b) or accepts the treatment change (Choice c), nor should they assume that the patient has a full understanding of the intervention (Choice d).
Question 75.
What should the nurse administer as a large initial infusion to quickly raise a patient's drug plasma level?
(a) Intermittent intravenous bolus
(b) Loading dose
(c) Onset bolus dose
(d) Maintenance dose
Answer:
(b) Loading dose
Explanation:
The loading dose, Choice (b), is administered at the original dose to start the patient off with a quickly accumulated level to reach therapeutic effect quickly. Once the loading dose is administered, the patient then continues on with maintenance doses, Choice (d), to maintain the therapeutic plasma concentration. Intermittent intravenous bolus, Choice (a), is administered occasionally, as a larger plasma concentration is desired, oftentimes at the drug's half-life. An onset bolus dose, Choice (c), is not a term that is used.
Question 76.
When should the nurse remove the respirator after working with a patient on airborne precautions?
(a) Outside the medication room after closing the door
(b) Inside the patient's room before opening the patient's door
(c) Outside the patient's room after closing the patient's door
(d) Inside the patient's bathroom after closing the door
Answer:
(c) Outside the patient's room after closing the patient's door
Explanation:
When working with a patient on airborne precautions, the nurse must remove their respirator outside of the patient's room after closing the patient's door. It would not be appropriate to remove the respirator outside of the medication room (Choice a), inside of the patient's room (Choice b), or in the patient's bathroom (Choice d).
Question 77.
While providing safety education to a group of patients diagnosed with personality disorders and struggling with urges to self-harm, which form of psychotherapy does the nurse integrate techniques from?
(a) Psychodynamic therapy
(b) Dialectal behavioral therapy
(c) Play therapy
(d) Humanistic therapy
Answer:
(b) Dialectal behavioral therapy
Explanation:
Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT), developed in the late 1980s, is a specific type of psychotherapy that is effectively applied to support populations struggling with personality disorders and urges to self-harm. Psychodynamic therapy (Choice a), play therapy (Choice c), and humanistic therapy (Choice d) would not be appropriate for the nurse to use given the context of the situation (nurse-facilitated group) and the patient population involved.
Question 78.
After receiving a counseling by the nurse manager regarding the nurse's poor time management skills, the nurse evaluates how to change their practice. What disciplinary action comes next if the nurse
fails to correct this deficit?
(a) Termination
(b) Suspension
(c) Oral warning
(d) Written warning
Answer:
(c) Oral warning
Explanation:
The standard progression of discipline involves counseling, oral warning, written warning (Choice d), suspension (Choice b), and termination (Choice a), typically in that order. For grand offenses, the earlier stages of discipline may be omitted. If the nurse fails to correct their behavior resulting in continued poor time management after the counseling, the next disciplinary action to be expected is an oral warning.
Question 79.
Review the medical record. Which intervention should be applied to support the therapeutic management of the patient's acute exacerbation of symptoms?
- Tab 1, Nursing Note (1254) Upon focused assessment, the patient is noted to be struggling with increased auditory hallucinations since returning from lunch. SBAR report given to psychiatrist. Space in quiet room offered and declined. Will continue to monitor.
- Tab 2, Nursing Note (1338) Offered patient pm olanzapine 5 mg po; patient declined. Patient continues to report auditory hallucinations; denies command hallucinations and urges to harm self and others. Patient seen pacing in hallway and living room.
- Tab 3, Nursing Note: (1407) Patient agreed to take olanzapine 5 mg po. Patient continues to pace in hallway and living room, now with hands on head coupled with argumentative verbal speech and paranoia. Will monitor for medication effectiveness and continue to provide a safe, therapeutic environment.
(a) Encourage patient to read a newspaper
(b) Avoid music
(c) Support patient to complete nightly ADLs
(d) Turn off the television
Answer:
(d) Turn off the television
Explanation:
Choice (d) should be included in the patient's treatment as television can provoke and promote auditory hallucinations and paranoia in patients struggling with these symptoms; therefore, it should be turned off. Choice (a) should be avoided as reading newspapers can also provoke and promote auditory hallucinations and paranoia. Choice (b) should be omitted; instead, the patient should be supported to use music to soothe symptoms as tolerated as this intervention is highly effective in supporting a reduction in these symptoms. Choice (c) should be omitted as the patient needs to be supported to find safe mental space before moving on to complete ADLs.
Question 80.
A patient is prescribed Atrovent (ipratropium bromide) for symptom management, however the nurse notices that the patient carries a diagnosis that conflicts with its use. Which health problem contraindicates the use of this drug?
(a) Benign prostatic hypertrophy
(b) Bronchitis
(c) Emphysema
(d) Rheumatoid arthritis
Answer:
(a) Benign prostatic hypertrophy
Explanation:
Patients diagnosed with benign prostatic hypertrophy should not use Atrovent (ipratropium bromide). The use of this drug could cause acute urinary retention and must be avoided.
Question 81.
The nurse is engaging in a root cause analysis post patient fall with injury. Arrange the following steps in the order they should be performed. Include all options.
(a) Identify possible causes
(b) Collect data
(c) Define problem
(d) Implement corrective actions
Answer:
(c) Define problem
(b) Collect data
(a) Identify possible causes
(d) Implement corrective actions
Explanation:
While engaging in a root cause analysis post patient fall with injury, the nurse is aware that steps should be carried out in the following order to identify the problem and establish a plan to correct it, while minimizing risk going forward. The nurse understands that the process is to define the problem, collect data, identify possible causes, and then implement corrective actions.
Question 82.
The nurse is educating the patient regarding nutritional intake and explaining potential side effects of total parenteral nutrition (TPN). While discussing these implications, the nurse used a medical term that this form of nutrition is also known as, which confused the patient. What term did the nurse interchangeably use?
(a) Oral nutritional supplementation
(b) Parenteral hyperalimentation
(c) PEG tube nutrition
(d) Peripheral parenteral nutrition
Answer:
(b) Parenteral hyperalimentation
Explanation:
Parenteral hyperalimentation, Choice (b), is a term used interchangeably with total parenteral nutrition (TPN). TPN is designed to be an individual's complete source of nutrition. Oral nutritional supplementation, Choice (a), describes nutrition consumed by mouth. PEG nutrition, Choice (c), describes nutrition delivered via a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube directly to the digestive system. Peripheral parenteral nutrition, Choice (d), involves nutrition that is complementary to another form of intake.
Question 83.
The nurse is caring for a patient who experiences acute anal pain during and after defecation with some hematochezia. The provider has just diagnosed the patient with anal fissure. When assisting the patient with hygiene after defecation, which of the following skin lesions would the nurse expect to find?
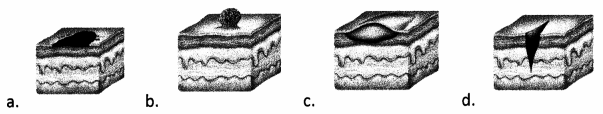
Answer:
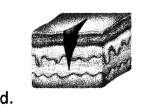
Explanation:
Choice (d) identifies what the nurse should expect to view upon examination of a patient with an anal fissure. This diagnosis involves a tear in the skin around the anus. Choice (a) indicates a view of a macule. Choice 8 indicates a view of a polyp. Choice (c) indicates a view of a nodule.
Question 84.
When does the case management role begin for the patient with a psychiatric illness?
(a) Upon presentation to the emergency department
(b) Upon status conversion from involuntary to voluntary
(c) Upon primary diagnosis
(d) Upon status conversion from voluntary to involuntary
Answer:
(c) Upon primary diagnosis
Explanation:
The patient with psychiatric illness is entitled to receive the benefit of care from the members of the interdisciplinary team including case management upon primary diagnosis at initial admission. This support is not reliant on patient's legal status for admission (Choices a, b, and d).
Question 85.
During the emergent phase of a burn injury, which of the following might a nurse expect to see?
(a) Decreased blood pressure
(b) Increased urine output
(c) Decreased heart rate
(d) Pink skin
Answer:
(a) Decreased blood pressure
Explanation:
In the emergent phase, hypovolemic shock is a potential issue due to excessive fluid and/or blood loss, which will cause a drop in blood pressure. Increased urine output is unlikely unless the patient is in fluid overload. With a drop in blood pressure, heart rate will increase due to increased myocardial contractility, and vasoconstriction will occur. A person in hypovolemic shock will have pale, clammy skin due to decreased fluid or blood volume in the body.
Question 86.
After receiving nurse-to-nurse report for a newly admitted patient with a diagnosis of impetigo, ' which assessment finding does the nurse expect to review upon examination?
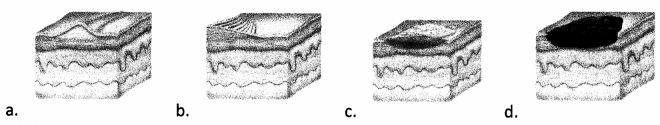
Answer:
Explanation:
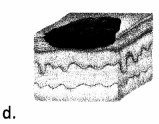
Choice (d) identifies the expected assessment finding for a patient with impetigo. This diagnosis establishes crusts that involve serious exudate. Choice (a) identifies scarring. Choice (b) identifies lichenification. Choice (c) identifies scaling.
Question 87.
While caring for a patient with renal failure who is on dialysis, which secondary diagnosis does the nurse educate that the patient is MOST at risk for developing?
(a) Systemic lupus erythematous
(b) Migraine headaches
(c) Anemia
(d) Crohn's disease
Answer:
(c) Anemia
Explanation:
Patients in renal failure who are on dialysis are at a heightened risk for developing anemia. Because the kidneys are responsible for signaling the bones to make red blood cells, if they fail to function properly, the body may lack sufficient red blood cells and the patient will develop signs and symptoms of anemia. The patient is not MOST at risk for developing systemic lupus erythematous (Choice a), migraine headaches (Choice b), or Crohn's disease (Choice d).
Question 88.
A 26-year-old woman wanders into the emergency department shivering and babbling incoherently. You know that it has been raining outside, it's cold, and the woman's clothing is soaked through. You recognize this as hypothermia, and after you escort her to a warm room and remove her wet clothing, what is the next thing you should do?
(a) Give her something warm to drink.
(b) Wrap a warm, dry blanket around her.
(c) Assess her vital signs.
(d) Warm her chest, neck, abdomen, and groin with an electric blanket or some other warming device.
Answer:
(d) Warm her chest, neck, abdomen, and groin with an electric blanket or some other warming device.
Explanation:
After the patient has been relocated to a warmer room and wet clothes have been removed, his or her core should immediately be warmed with a warming device. Giving something warm to drink is helpful but should occur only after the core temperature has begun to stabilize. Vital signs at this point wouldn't be assessed; temperature needs to have an opportunity to become stable. Wrapping a warm, dry blanket around the patient should happen after a significant amount of time is spent increasing core body temperature; the patient should initially be warmed from the inside out, not the other way around.
Question 89.
The nurse is caring for a patient with congestive heart failure and is reviewing their medications with them during medication teaching. The patient expresses concern about their potassium level after recalling an issue with low potassium when prescribed a diuretic in the past. Which medication does the nurse explain is a potassium-sparing diuretic during this teaching?
(a) Lasix® (furosemide)
(b) Demadex® (toresemide)
(c) Aldactone® (spironolactone)
(d) Microzide® (hydrochlorothiazide)
Answer:
(c) Aldactone® (spironolactone)
Explanation:
Aldactone® (spironolactone), Choice (c), is a potassium-sparing diuretic and supports the patient's concern regarding their potassium level at this time. This medication does not encourage the excretion of potassium via urine. Lasix® (furosemide) and Demadex® (toresemide) are loop diuretics and Aldactone® (spironolactone) is a thiazide diuretic. These medications do not specifically target conserving potassium in the body to address the patient's concern arising from their history. Therefore, Choices (a), (b), and (d) are incorrect.
Question 90.
Which accessory organ(s) contribute to digestive activities? Select all that apply.
(a) Salivary Glands
(b) Liver
(c) Large Intestine
(d) Pancreas
(e) Gallbladder
Answer:
(a) Salivary Glands
(b) Liver
(d) Pancreas
(e) Gallbladder
Explanation:
Salivary glands, the liver, the pancreas, and the gallbladder are all accessory organs that contribute to digestive activities. The large intestine, Choice (c), is not an accessory organ, as it is part of the digestive tract.
Question 91.
When administering total parenteral nutrition (TPN), what should the nurse direct the patient to do while changing the bag or bottle?
(a) Valsalva maneuver
(b) Deep breathing
(c) Count to ten, then swallow
(d) Plug ears
Answer:
(a) Valsalva maneuver
Explanation:
The patient should perform the Valsalva maneuver, Choice (a), while the nurse is performing bag or bottle changes or replacing tubing for total parenteral nutrition (TPN). This maneuver involves a moderately forceful expression of exhalation while one's mouth is closed and nose is pinched. It is encouraged to reduce the likelihood of an air embolus. Choices 6, Choice (c), and Choice (d) should not be encouraged, as they would not support a reduced likelihood of air embolus during this time.
Question 92.
Does the utilization review (UR) nurse have access to medical records in order to complete concurrent patient reviews?
(a) Yes, this process is supported via UR access to records.
(b) No, the utilization review nurse is not a direct member of the treatment team.
(c) No, the UR nurse only has access when obtaining prior authorization for medication.
(d) Yes, but the patient must sign a release for the UR nurse specifically.
Answer:
(a) Yes, this process is supported via UR access to records.
Explanation:
The utilization review nurse is part of the interdisciplinary team and is granted access to patient records. The UR nurse accesses medical records in order to secure financial payment from third-party payers by completing concurrent patient reviews that explore the medical services offered and their associated monetary costs.
Question 93.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an aerobic bacterium. What does this mean?
(a) It can sustain itself without the presence of oxygen.
(b) It grows in the presence of oxygen.
(c) It cannot detoxify oxygen.
(d) It does not use dissolved oxygen for its metabolic reactions.
Answer:
(b) It grows in the presence of oxygen.
Explanation:
Aerobic bacteria grow in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic bacteria can grow without available oxygen. Aerobic bacteria can actually detoxify oxygen through the use of certain enzymes to convert superoxide (an oxygen derivative, which is toxic to all organisms) to oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Aerobic bacteria need oxygen for metabolic reactions, while anaerobic bacteria do not.
Question 94.
While delivering a blood transfusion, the patient complains of a headache and double vision. Which action should the nurse take first?
(a) Call a rapid response.
(b) Slow the infusion rate.
(c) Stop the transfusion.
(d) Assess vital signs.
Answer:
(c) Stop the transfusion.
Explanation:
The nurse must stop the blood transfusion immediately after the patient complains of a headache and double vision. These symptoms may signify a transfusion reaction. Additional intervention, such as assessing vital signs (Choice d) and calling a rapid response (Choice a) may be indicated; however, these actions would take place after the transfusion has been stopped. Choice b, slowing the transfusion, is incorrect, as the correct response, stopping the transfusion, must take place.
Question 95.
While collecting a history and physical of a patient who may be infected with tuberculosis (TB), the nurse would ask all EXCEPT for which of the following?
(a) "Have you ever been exposed to tuberculosis?"
(b) "Have you traveled outside the country to places where TB is prevalent?"
(c) "Have you noticed that your appetite has increased lately?"
(d) "Have you recently had the flu, pneumonia, or foul-smelling saliva?"
Answer:
(c) "Have you noticed that your appetite has increased lately?"
Explanation:
One of the symptoms in TB infection is anorexia, or decreased appetite. The individual will also most likely exhibit a significant drop in weight. A comprehensive health history will inquire about past exposure to TB; recent travel to countries where TB is increased; and history of influenza, pneumonia, or foul-smelling sputum.
Question 96.
When healthcare providers see patients who are unconscious or not of a sound state of mind, what principle is utilized in order to provide treatment?
(a) Assumption
(b) Risky consent
(c) Informed consent
(d) Implied consent
Answer:
(d) Implied consent
Explanation:
When patients are physically or psychologically unable to provide verbal or written consent to treatment, healthcare providers rely on implied consent, acting on the belief that the patient would like the best treatment to benefit his or her life.
Question 97.
Which area is highlighted in this EKG tracing?
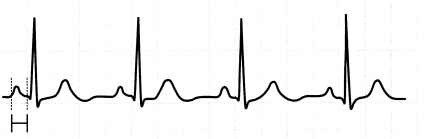
(a) The PR interval
(b) The QRS interval
(c) The QT interval
(d) The R-to-R interval
Answer:
(a) The PR interval
Explanation:
The highlighted section is the PR interval.
Question 98.
A small group of clinical nurses is choosing to improve an existing process related to patient discharge. They have identified that patients have a high re-admittance rate during the summer months. After mapping the current process, they note that patients leave the printout of discharge instructions that they are provided in their hospital room approximately 65% of the time. The nurses set up a meeting to review potential solutions. In which part of the PDCA cycle is this performance improvement plan?
(a) Plan
(b) Do
(c) Check
(d) Act
Answer:
(a) Plan
Explanation:
The nurses are in the planning stage. When they develop a change to implement, they'll be in the Do stage. Once the change has been implemented, they'll check the results and compare it to their baseline re-admittance and printout retention rates. Finally, they'll act to sustain any positive changes.
Question 99.
The nurse is concerned about hypokalemia potentiating digitalis toxicity. Which diuretic(s) does the nurse recognize in the patient's treatment plan is ordered to minimize the risk of this imbalance? Select all that apply.
(a) Spironolactone
(b) Furosemide
(c) Hydrochlorothiazide
(d) Eplerenone
(e) Triamterene
Answer:
Explanation:
Choices (a), (d), and (e) indicate potassium-sparing diuretics that may be considered for use in a patient at risk for hypokalemia and digitalis toxicity. Choices (b) and (c) may induce hypokalemia and require close monitoring for this expected side effect.
Question 100.
Before the nurse delegates tasks to other members of the team, they evaluate the role of each member. Which overarching legal directive defines role responsibilities?
(a) State rule
(b) Federal rule
(c) Hospital protocol
(d) Management delegation
Answer:
(a) State rule
Explanation:
Role responsibilities for each interdisciplinary member of the team are delineated under state rule. While Choice (b), federal rule, provides general guidelines, state rule defines the specifics regarding healthcare roles and responsibilities. Choice (c), hospital protocol, and Choice (d), management delegation, come secondary and cannot overrule state statue.
Question 101.
Which set of laws comprised the biggest healthcare reform in the last fifty years?
(a) The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
(b) The Privacy Act
(c) The HiTech PHI Act
(d) The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act
Answer:
(a) The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
Explanation:
Passed under President Barack Obama's term, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 reformed individual health insurance markets and expanded Medicaid coverage. Overall, it cut
uninsured patient numbers by approximately half. It is the largest healthcare reform since Medicaid and Medicare programs were developed in the 1960s.
Question 102.
While completing an assessment of a pregnant woman in her third trimester, the nurse takes this opportunity to educate the patient on what will be reviewed in her pending labs. What common pregnancy condition occurs in this trimester?
(a) Hypercalcemia
(b) Metabolic alkalosis
(c) Physiologic anemia
(d) Mastocytosis
Answer:
Explanation:
Pregnant women during their third trimester are at risk for developing physiologic anemia. Expanded maternal blood volume during this trimester contributes to the anemia. Choices (a), (Ib), and (d)
are not conditions that are commonly associated with third trimester pregnancy.
Question 103.
What is the most fundamental stage of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs that the nurse should consider when prioritizing a client's wellbeing?
(a) Love and belonging
(b) Safety
(c) Physiological
(d) Self-Actualization
Answer:
(c) Physiological
Explanation:
In consideration of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, the nurse practices with attention to client wellbeing and prioritizes care accordingly. The hierarchy includes the following five stages: physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. Physiological concerns make up the most fundamental stage of this theory and signify the most basic human needs for care.
Question 104.
The outpatient clinic nurse is preparing to deliver an intravenous therapy at a rate of 50 mg/hr. The available solution concentration is 2 mg/mL. Calculate the volume/hour for medication administration .................. mL/hr
Answer:
25 mL/hr
Explanation:
The nurse should use the intravenous dose rate calculation of "dose ordered" divided by "solution concentration" to yield the volume/hour for delivery. In this case, 50 mg/hr should be divided by 2 mg/mL to yield 25 mL/hr.
Question 105.
You prepare to administer a medication to your patient. You have never given this medication before and aren't familiar with it. Which of the following should you do? Select all that apply.
(a) Look up the medication in a reputable database before giving.
(b) Call the pharmacist.
(c) Give the medication because you are running behind and look it up when you have time.
(d) Ask the patient why they take it and then administer it.
(e) Call and ask the doctor.
Answer:
(a) Look up the medication in a reputable database before giving.
(b) Call the pharmacist.
Explanation:
A reputable source of medication information, such as a reputable database or a consultation with a pharmacist, should be used before giving the medication. It is never appropriate to give a medication without understanding its purpose. The patient may not know why they take the medication. The nurse should rely on other sources at their disposal besides the doctor.
Question 106.
When is the appropriate time to wash your hands? Select all that apply.
(a) When entering a patient's room
(b) After using the restroom
(c) Before eating
(d) After assisting with patient hygiene
(e) When leaving a patient's room
Answer:
(a) When entering a patient's room
(b) After using the restroom
(c) Before eating
(d) After assisting with patient hygiene
(e) When leaving a patient's room
Explanation:
It is appropriate to wash hands in each of these cases.
Question 107.
Which field of public health can nursing staff support by establishing symptom surveillance systems?
(a) Health policy
(b) Nutrition services
(c) Epidemiology
(d) Health promotion
Answer:
(c) Epidemiology
Explanation:
Epidemiology is the study of health symptom clusters and patterns of disease outbreak in a community. Since nursing staff are often the first people to notice repetitive symptoms in a community, their services can be a great benefit to public health workers.
Question 108.
During a prenatal educational group session, the community health nurse discusses infant care and growth considerations. In order to support the parents-to-be in understanding newborn health and mortality, what does the nurse share is the leading cause of death during the first month of life?
(a) Failure to thrive
(b) Congenital cardiac defect
(c) Infection
(d) Sudden infant death syndrome
Answer:
(d) Sudden infant death syndrome
Explanation:
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is the leading cause of infant mortality during the first month of life. SIDS involves the unexplained death of an infant, typically during sleep. The cause of SIDS is currently unknown.
Question 109.
Procardia® (nifedipine) has been prescribed for a patient in preterm labor. Which response by the nurse correctly describes why this medication has been ordered?
(a) "Since this medication blocks calcium, it should help to relax your uterine muscles."
(b) "We are hoping to control your pain with this medication."
(c) "This medication is designed to raise your blood pressure, which will help you feel better."
(d) "This medication will help increase the frequency of your contractions to help expedite the delivery."
Answer:
(a) "Since this medication blocks calcium, it should help to relax your uterine muscles."
Explanation:
Choice (a) describes why this medication would be ordered for a patient in preterm labor. It is important to relax the uterine muscles and reduce contractions. This medication works by blocking calcium and has indications for use outside of pregnancy and labor. Choice (b) is an ineffective response because this medication is not indicated for pain management. Choice (c) is ineffective, as this medication would lower, rather than raise, blood pressure. Choice (d) is incorrect because not only is that not the function of the medication, but in most cases, increasing the frequency of contractions for a mother in preterm labor would not be desirable.
Question 110.
Which suggestions regarding sleep maintenance hygiene should the nurse include in health maintenance teaching? Select all that apply.
(a) Increase fluids before bed
(b) Establish routine bed times
(c) Read in bed
(d) Increase physical exercise in the afternoon
(e) Use bedroom for sleeping only
Answer:
Explanation:
Choices (b), (d), and (e) are helpful suggestions for establishing a quality sleep hygiene regimen as these practices support improved sleep, which is necessary for a healthy lifestyle. Choices (a) and (c) foster diminished sleep because Choice (a) promotes nighttime waking and Choice (c) encourages difficulty with initiating sleep. A sound sleep hygiene plan includes elements that support initiating sleep, maintaining sleep, and achieving a healthy rested feeling upon waking.
Question 111.
Which of the following describes a reflex arc?
(a) The storage and recall of memory
(b) The maintenance of visual and auditory acuity
(c) The autoregulation of heart rate and blood pressure
(d) A stimulus and response controlled by the spinal cord
Answer:
(d) A stimulus and response controlled by the spinal cord
Explanation:
A reflex arc is a simple nerve pathway involving a stimulus, a synapse, and a response that is controlled by the spinal cord not the brain. The knee-jerk reflex is an example of a reflex arc. The stimulus is the hammer touching the tendon, which reaches the synapse in the spinal cord by an afferent pathway. The response is the resulting muscle contraction, which reaches the muscle by an efferent pathway.
None of the remaining processes are simple reflexes. Memories are processed and stored in the hippocampus in the limbic system. The visual center is located in the occipital lobe, while auditory processing occurs in the temporal lobe. The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system control heart and blood pressure.
Question 112.
While providing education to a student nurse, the senior nurse explains the ascending order of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs. Arrange the following needs in the order the nurse should prioritize them, starting with the most basic. Include all options.
(a) Physiological
(b) Love and belonging
(c) Self-esteem
(d) Safety and security
Answer:
(a) Physiological
(d) Safety and security
(b) Love and belonging
(c) Self-esteem
Explanation:
The nurse explains the ascending order of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs in the following order to illustrate the prioritization of nursing practice from the patient's most basic needs to their more advanced needs. The senior nurse teaches the student nurse that needs ascend from physiological, to safety and security, to love and belonging, to self-esteem.
Question 113.
The nurse is assessing the patient's circulatory system and perfusion to distal regions of the body. Where should the nurse expect to discover the dorsalis pedis pulse? Place an X to mark your answer.

Answer:
Explanation:
The dorsalis pedis pulse is found at the first intermetatarsal space on the dorsum of the foot. The nurse should palpate this pulse slightly lateral to the extensor tendon of the great toe in the mid-foot.
Question 114.
The nurse considers which of the following risk factors reported by the patient during the initial assessment to potentially be a trigger for the patient's current presentation of pain in the great toe? Select all that apply.
(a) Increased legumes in the diet
(b) Glass of wine daily with dinner
(c) Increased roughage in the diet
(d) Increased seafood in the diet
(e) Added weekly serving of liver
(f) Fruit juice with breakfast
Answer:
(b) Glass of wine daily with dinner
(d) Increased seafood in the diet
(e) Added weekly serving of liver
(f) Fruit juice with breakfast
Explanation:
Choices (b), (d), (e), and F all represent risk factors for triggering gout, an inflammatory condition with a hallmark sign of pain in the great toe. When high levels of uric acid circulate in the blood, urate crystals can accumulate in the joints, particularly that of the big toe. Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines, which are found in certain foods such as organ meats, steak, seafood, fruit juices, and alcoholic beverages. Choices (a) and (c) do not correlate to the patient's current symptom presentation and would not be suggestive risk factors at this time.
Question 115.
You bring your patient's morning medications into your patient's room. The patient states that they will not take the medications. What should you do in regard to this patient? Select all that apply.
(a) Educate the patient on risks of not taking the medications.
(b) Tell the patient they need to leave if they are not going to comply with the doctor's orders.
(c) Notify the physician.
(d) Insist that the patient take the medications.
(e) Hold the medications until you receive clarification from the physician.
Answer:
(a) Educate the patient on risks of not taking the medications.
(c) Notify the physician.
Explanation:
The patient should be educated on the importance of taking the prescribed medication. If the patient refuses the medication, the physician must be notified. Choices (b) and (d), calling security and arguing with the patient, are not appropriate measures.
Question 116.
At what time during a patient's stay are medical errors most likely to be made?
(a) During bloodwork
(b) During labor for pregnant patients
(c) When extra tests are ordered
(d) During any transition of care
Answer:
(d) During any transition of care
Explanation:
Transition of care requires many changes that almost always lead to a slight or major decline in quality of care. This can be mediated with strict standard operating procedures for transition and high levels of communication between caregivers.
Question 117.
The nurse is providing patient education regarding stent placement. During this discussion, the nurse uses this accompanying diagram of the heart for visualization. Which location does the nurse direct to when discussing the aorta? Place an X to mark your answer.
Answer:
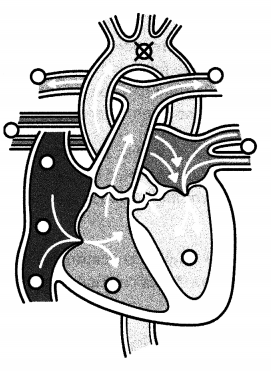
Explanation:
Most often during heart angioplasty, a catheter is advanced from either the femoral or radial artery to the aorta into the heart. The catheter must then be advanced into the coronary arteries.
Question 118.
A patient presents to urgent care complaining of pain. After closer examination, a diagnosis of two broken ribs is made and the patient is prescribed opiates for pain management. What additional medication does the nurse expect to see ordered at this time to combat a common side effect of this drug class?
(a) Dolophine® (methadone)
(b) Biaxin® (clarithromycin)
(c) Tegretol® (carbamazepine)
(d) Colace® (docusate sodium)
Answer:
(d) Colace® (docusate sodium)
Explanation:
Colace® (docusate sodium), Choice (d), can be prescribed alongside opiates to ease constipation, a common side effect of this drug class. Choice (a) represents a medication that is prescribed for opioid addiction and would not be prescribed at the time of opioid prescription for symptom management. Choice (b) and Choice (c) are both contraindicated for use while taking opiates and should be avoided at this time.
Question 119.
The nurse is confronted with an ethical dilemma when a patient with methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) of the nares is assigned a bed next to a patient with pneumonia in a double-occupancy room. In considering potential airborne transmission of the MRSA to the patient with pneumonia, the nurse does not agree with this bed assignment. After expressing this concern to the charge nurse with no resulting change, who should the nurse elevate this concern to next?
(a) Respiratory therapist
(b) Infection control practitioner
(c) Nursing supervisor
(d) Bed captain
Answer:
(c) Nursing supervisor
Explanation:
Ethical dilemmas in practice happen, and the nurse must be prepared to advocate for the patient. When reporting a concern, the nurse should first report up the chain of command (in this case, to the charge nurse). When the charge nurse failed to respond, the nurse would appropriately elevate this issue to the nursing supervisor. Choices (a), (b), and (d) do not follow the nursing chain of command.
Question 120.
After reviewing a patient's lab work, the nurse recognizes that the patient's antinuclear antibody (ANA) titer is 1:640 with a speckled pattern. What specialist consult does the nurse expect to see ordered next for diagnostic testing?
(a) Dermatology
(b) Cardiology
(c) Rheumatology
(d) Gastroenterology
Answer:
(c) Rheumatology
Explanation:
A high titer of 1:640 paired with a speckled pattern may be indicative of rheumatologic autoimmune diseases; thus, Choice (c) is the appropriate specialty for continued assessment and additional laboratory testing for this patient at this time. Choices (a), (b), and (d), while potentially appropriate referrals for the future, do not represent applicable specialties for the patient to consult with next.
Question 121.
Which set of laws was enacted in order to prevent healthcare facilities from turning away patients that needed life-sustaining care, regardless of ability to pay?
(a) The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010
(b) The American Health Care Act of 2017
(c) The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act of 1986
(d) The Medicare Introduction Act of 1965
Answer:
(c) The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act of 1986
Explanation:
The Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act of 1986 (EMTALA) was a direct response to healthcare facilities turning away patients that were unable to pay for treatment, even in life-or-death situations. However, facilities are not reimbursed for losses by this law, and this has had an effect on overall healthcare costs.
Question 122.
The psychiatric nurse is completing an assessment on a 58-year old female patient who just received electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Which statement by the patient warrants concern?
(a) "I don't remember my name."
(b) "Did I have a bowel movement this morning?"
(c) "My leg is aching."
(d) "Can I have medication for my headache?"
Answer:
(c) "My leg is aching."
Explanation:
The nurse should be concerned about the patient reporting an aching leg, as this is not a normal finding after electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Temporary amnesia, headache, mild confusion, and forgetfulness are all normal side effects of ECT and are to be expected; therefore, Choices (a), (b), and (d) are incorrect.
Question 123.
The patient's IV fluids are running at 75 mL/hr. How much fluid will they receive in 24 hours?.................. mL
Answer:
123.1,800 mL.
Explanation:
75 mL multiplied by 24 hours is equal to 1,800 mL total.
Question 124.
A patient reported throbbing pain at the site of an injury. The nurse reviewed the medication administration record to review orders for pain management. The nurse sees the order, "Ibuprofen 600 mg PO q6h pm pain. MDD=3." The patient has not yet taken this medication today. The nurse has 200 mg tablets of Ibuprofen available. How many tablets should the nurse administer at this time?
.................... tablets
Answer:
3 tablets
Explanation:
The dosage calculation to be used is "dose ordered" divided by "dose on hand." As the ’ medication label reads 1 tablet contains 200 mg of Ibuprofen, the nurse should divide 600 mg by 200
mg/tablet, which yields 3 tablets.
Question 125.
While caring for a patient with frequent urinary tract infections, the nurse prepares to irrigate the bladder. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Open roller clamp slowly
(b) Remove protective cover from tubing line
(c) Spike fluid bag and hang on pole
(d) Pinch fluid chamber until halfway filled
Answer:
(c) Spike fluid bag and hang on pole
(d) Pinch fluid chamber until halfway filled
(b) Remove protective cover from tubing line
(a) Open roller clamp slowly
Explanation:
While caring for a patient with frequent urinary tract infections, the nurse prepares to irrigate the bladder via steps performed in the following order to ensure the line is primed and hung higher than the insertion site: spike fluid bag and hang on pole, pinch fluid chamber until halfway filled, remove protective cover from tubing line, and open roller clamp slowly.
Question 126.
Your patient has an order to receive one unit of packed red blood cells. List the order in which the following things should occur:
(a) Check the patient's labs.
(b) Confirm the order.
(c) Identify the patient.
(d) Transfuse blood.
Answer:
(b) Confirm the order.
(a) Check the patient's labs.
(c) Identify the patient.
(d) Transfuse blood.
Explanation:
The correct order is (b), (a), (c), and (d). The order should always be verified before administering blood products. The patient's labs should be checked to verify that the blood product is appropriate for the patient. Verifying patient identification is vital to ensure the safe administration of blood. The blood can then be given.
Question 127.
Before hanging a medication soJution, the nursing student consults with a senior staff nurse to check their calculated solution concentration for a bag that reads 50 mg/250 mL. What solution concentration does the senior nurse calculate for this medication? ...........................
Answer:
0.2 mg/mL
Explanation:
The nurse should use the solution concentration calculation of "dosage in solution" divided by "volume of solution." In applying this calculation formula, the senior nurse should divide 50 mg by 250 mL to yield 0.2 mg/mL.
Question 128.
Which religion should the nursing supervisor take into account when working with the bed captain to assign patient rooms upon hospital admission?
(a) Catholicism
(b) Judaism
(c) Buddhism
(d) Islam
Answer:
(d) Islam
Explanation:
When working with the bed captain to assign patient rooms upon hospital admission, the nursing supervisor should consider the Muslim (Islam) patient's need to have a room that faces the direction of the Kaaba in the Hejazi city of Mecca. This is the direction that the patient will need to face when praying. The religions found within Choices (a), (b), and (c) do not influence room placement.
Question 129.
The nurse is part of a collaborative team supporting a patient to improve their health status secondary to a multiple myeloma diagnosis. While engaging in a bisphosphonate treatment plan, which imaging needs to be completed to assess progress?
(a) CT scan
(b) Ultrasound
(c) MRI
(d) Bone scan
Answer:
(d) Bone scan
Explanation:
A bone scan, Choice (d), must be completed to assess for progress after initiating a bisphosphonate medication regimen to strengthen bone health. CT scans, ultrasound, and MRIs, while potentially helpful imaging for various aspects of disease management, do not specifically address the patient's treatment with bisphosphonates and are not necessary at this time. Bisphosphonates are prescribed for patients with multiple myeloma to reduce pain and vertebral fractures. Bone scans examine their effectiveness.
Question 130.
Which statement about white blood cells is true?
(a) B cells are responsible for antibody production.
(b) White blood cells are made in the white/yellow cartilage before they enter the bloodstream.
(c) Platelets, a special class of white blood cell, function to clot blood and stop bleeding.
(d) Most white blood cells only activate during puberty, which explains why children and the elderly are particularly susceptible to disease.
Answer:
(a) B cells are responsible for antibody production.
Explanation:
When activated, B cells create antibodies against specific antigens. White blood cells are generated in red and yellow bone marrow, not cartilage. Platelets are not a type of white blood cell and are typically cell fragments produced by megakaryocytes. White blood cells are active throughout nearly all of one's life and have not been shown to specially activate or deactivate because of life events like puberty or menopause.
Question 131.
Which location should the nurse use to draw capillary blood from a newborn patient for phenylketonuria (PKU) screening?
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice A indicates the appropriate location for the nurse to retrieve capillary blood from a newborn patient for phenylketonuria (PKU) screening. Choices (b), (c), and (d) provide venous access points for potential use in other testing; however, they do not represent appropriate locations for PKU screening.
Question 132.
Why do arteries have valves?
(a) They have valves to maintain high blood pressure so that capillaries diffuse nutrients properly.
(b) Their valves are designed to prevent backflow due to their low blood pressure.
(c) The valves have no known purpose and thus appear to be unnecessary.
(d) They do not have valves, but veins do have valves.
Answer:
(d) They do not have valves, but veins do have valves.
Explanation:
Veins have valves but arteries do not. Valves in veins are designed to prevent backflow, since they are the furthest blood vessels from the pumping action of the heart and steadily increase in volume (which decreases the available pressure). Capillaries diffuse nutrients properly because of their thin walls and high surface area and are not particularly dependent on positive pressure.
Question 133.
An adolescent patient presents to the emergency department with a report of sustaining a head injury during a sporting event prior to arrival. Which assessment findings alert the nurse to the patient experiencing Cushing's triad?
(a) Bradypnea, tachycardia, widening pulse pressure
(b) Tachypnea, bradycardia, narrowing pulse pressure
(c) Bradypnea, bradycardia, widening pulse pressure
(d) Tachypnea, tachycardia, narrowing pulse pressure
Answer:
(c) Bradypnea, bradycardia, widening pulse pressure
Explanation:
Bradypnea, bradycardia, and widening pulse pressure accurately aligns with a patient " presentation of Cushing's triad post head injury. These assessment findings indicate that the patient is likely experiencing increased intracranial pressure at this time. Therefore, Choice (c) is correct. Choices (a), (b), and (d) do not represent assessment findings indicative of this physiological nervous system response.
Question 134.
Which communication technique informs a patient whether or not their expressed statement was accurately received as intended?
(a) Probing
(b) Restating
(c) Silence
(d) Focusing
Answer:
(b) Restating
Explanation:
While probing (Choice a), focusing (Choice d), and the use of silence (c) are all therapeutic communication techniques, restating specifically involves reiterating what was verbally expressed. This technique provides reassurance to the patient that the nurse is listening and has heard what they have said. It also fosters a therapeutic opportunity to ensure that the message was accurately received.
Question 135.
Identify the parietal lobe.
Answer:
Explanation:
The superior dorsal portion of the brain contains the parietal region.
Question 136.
If the pressure in the pulmonary artery is increased above normal, which chamber of the heart will be affected first?
(a) The right atrium
(b) The left atrium
(c) The right ventricle
(d) The left ventricle
Answer:
(c) The right ventricle
Explanation:
The blood leaves the right ventricle through a semilunar valve and goes through the pulmonary artery to the lungs. Any increase in pressure in the artery will eventually affect the contractibility of the right ventricle. Blood enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior venae cavae veins, and blood leaves the right atrium through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
Blood enters the left atrium from the pulmonary veins carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs. Blood flows from the left atrium to the left ventricle through the mitral valve and leaves the left ventricle through a semilunar valve to enter the aorta.
Question 137.
During a behavioral code, the nursing team responds to a patient who is trying to spit on them. What personal protective equipment (PPE) does the team decide to don during physical intervention for protection?
(a) Gloves and gown
(b) Gown
(c) Gloves and goggles
(d) Gown, gloves, mask with eye shield
Answer:
(d) Gown, gloves, mask with eye shield
Explanation:
While working with a patient who is attempting to spit on the staff during a behavioral code, the nurse should instruct the team to apply gowns, gloves, and masks with eye shields. Donning of this personal protective equipment (PPE) fosters safe infection control practices by protecting at-risk surfaces during the code. Choices (a), (b), and (c) would not protect all at-risk surfaces.
Question 138.
Which diagram of the lungs is associated with the disease process of cystic fibrosis?
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice (b) represents the diagram of the lungs that is associated with the disease process of cystic fibrosis, which affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. Choice (a) represents inflammatory asthma. Choice (c) represents pulmonary embolism. Choice (d) represents lung cancer.
Question 139.
How many milliliters does this measuring cup contain?
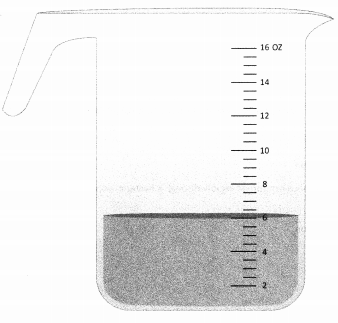
(a) 60
(b) 120
(c) 180
(d) 240
Answer:
(c) 180
Explanation:
Six ounces is equal to 180 milliliters. There are 30 milliliters per ounce.
Question 140.
What is the purpose of sodium bicarbonate when released into the lumen of the small intestine?
(a) It works to chemically digest fats in the chyme.
(b) It decreases the pH of the chyme to prevent harm to the small intestine.
(c) It works to chemically digest proteins in the chyme.
(d) it increases the pH of the chyme to prevent harm to the small intestine.
Answer:
(d) it increases the pH of the chyme to prevent harm to the small intestine.
Explanation:
Sodium bicarbonate, a very effective base, has the chief function to increase the pH of the chyme. Chyme leaving the stomach has a very low pH, due to the high amounts of acid that are used to digest and break down food. If this is not neutralized, the walls of the small intestine will be damaged and may form ulcers. Sodium bicarbonate is produced by the pancreas and released in response to pyloric stimulation so that it can neutralize the acid. It has little to no digestive effect.
Question 141.
Which type of viruses undergo the lytic cycle once inside the host?
(a) Animal viruses
(b) Bacteriophages
(c) Retroviruses
(d) Lysogenic viruses
Answer:
(b) Bacteriophages
Explanation:
Bacteriophages are DNA viruses that inject into the host bacterial cell, where they can undergo the lytic cycle and sometimes the lysogenic cycle, depending on the specific type of bacteriophage. Bacteriophages only infect bacteria. Animal viruses affect animal cells, retroviruses are a type of RNA virus, and lysogenic viruses are not an accepted term. Certain bacteriophages can enter the lysogenic cycle.
Question 142.
Which of the following correctly presents the order of steps in the lytic cycle?
(a) Attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, release
(b) Attachment, penetration, maturation, biosynthesis, release
(c) Penetration, attachment, biosynthesis, maturation, release
(d) Penetration, attachment, maturation, biosynthesis, release
Answer:
(a) Attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, release
Explanation:
The order of steps in the lytic cycle is attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, and release. In attachment, the bacteriophage comes in contact with the host cell as the capsid binds with the receptor. During penetration, the viral DNA enters the host cell. If a bacteriophage is capable of undergoing the lysogenic cycle, that cycle takes place after penetration. If not, biosynthesis occurs, where the components of the virus are synthesized to be assembled during the fourth stage, maturation. In the final stage, called the release, the virus leaves the host via lysis, immediately killing the host.
Question 143.
Which of the following can move genetic material from the plasmid to the chromosome or from the chromosome to the plasmid?
(a) Reverse transcriptase
(b) Transposons
(c) Pili
(d) Sex pilus
Answer:
(b) Transposons
Explanation:
Transposons can move genetic material from the plasmid to the chromosome or vice versa. Reverse transcriptase is the enzyme that retroviruses produce to facilitate the conversion of RNA to DNA once inside the host cell. Pili are tiny protein projections on the surface of some bacterial cells, which aid in the cell's ability to form attachments to other cells. The sex pilus is the connection that forms during conjugation.
Question 144.
Genetic variation can be introduced into bacteria through all EXCEPT which of the following ways?
(a) Mutation
(b) Binary fission
(c) Conjugation
(d) Transformation
Answer:
(b) Binary fission
Explanation:
Genetic variation can be introduced into bacteria through mutation, conjugation, or transformation, but not binary fission. In the process of binary fission, each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell. For this reason, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction. The single chromosome of the parent cell is replicated and then passed on to each of the two daughter cells. Variation can be introduced with conjugation and transformation because both processes involve the bacteria "mating" with another bacteria cell or picking up genetic material from their environment.
Question 145.
Antibiotic resistance can spread rapidly through a bacterial population through which of the following processes?
(a) Conjugation
(b) Transformation
(c) Binary fission
(d) Transduction
Answer:
(a) Conjugation
Explanation:
Antibiotic resistance can spread rapidly through conjugation. Conjugation is the process by which some bacterial cells can replicate their plasmid and pass it to another cell through a direct physical connection. Plasmids typically encode for antibiotic resistance. When the cell that contains the plasmid bridges to the other cell in a connection called a sex pilus, the copy of the plasmid is transferred so that both cells then contain the plasmid. Therefore, an additional cell over baseline conditions has gained the ability to be resistant to an antibiotic. The process of conjugation is very rapid, so resistance can spread quickly throughout a bacterial population.
