We are offering comprehensive collections of Practice NCLEX Questions to facilitate self-assessment and exam preparation.
NCLEX-PN Practice Test 2 with Rationale
Question 1.
When reducing the risk of infection transmission, which personal protective equipment (PPE) should the nurse don first?
(a) Gloves
(b) Mask
(c) Gown
(d) Goggles
For the following question, please refer to this chart.
|
Patient Information |
Initials:E.F Age: 67 Sex: Male Height: 5 10 Weight: 300 lbs. |
|
Problems |
Hypertension, obesity, atrial fibrillation, pre-diabetes. |
|
Medications |
COUMADIN, METAPROLOL, SUCCINATE, METFORMIN, HCTZ |
|
Labs |
RBCs: 60 Hgb:11.5 Hct: 39 WBC: 8.6 HDL: 70 LDL: 130 Triclycerides: 100 Total cholestreol: 200 A1c: 8.4 Glucose: 253 BUN: 30 creat: 1.2 |
Answer:
(b) Mask
Explanation:
The first piece of personal protective equipment the nurse should don is a gown, Choice (c). Choice (a), gloves, are donned next, followed by Choice S, mask, and ultimately, Choice (d) , goggles, are donned last. The nurse must follow this sequence to ensure protection against infection transmission.
Question 2.
The MD is starting insulin for this patient. You provide him with education about his insulin regimen for his diabetes. Appropriate education on side effects of insulin would include monitoring for signs and symptoms of what?
(a) Infection
(b) Electrolyte abnormalities
(c) Stroke
(d) Hypoglycemia
Answer:
(d) Hypoglycemia
Explanation:
The patient is currently on insulin. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are not correct because they are not potential adverse effects of insulin.
Question 3.
How should the nurse document the finding of a patient's elevated respiratory rate?
(a) Tachypnea
(b) Orthopnea
(c) Tachycardia
(d) Hyperthermia
Answer:
(a) Tachypnea
Explanation:
Tachypnea, Choice (a), describes an elevated respiratory rate. Tachypnea can be witnessed in a variety of patient presentations and must be carefully assessed. Rapid breathing is not always overt or labored, so taking the time to count respirations and complete a thorough examination is key. Orthopnea, Choice (b), represents labored breathing, while tachycardia, Choice (c), correlates to a rapid heart rate. Hyperthermia, Choice (d), involves an elevated body temperature.
Question 4.
A patient started having a reaction to a blood transfusion after approximately - of the 500 cc of blood had been transfused. Approximately how many cc of blood had the patient received? Round to the nearest whole number ..................... cc
Answer:
167 cc.
Rationale:
The patient received of 500 cc. 500 divided by is 166.666, which, rounded to nearest whole number, is 167 cc.
Question 5.
What is an example of health promotion? Select all that apply.
(a) Collecting a thorough and accurate health history
(b) Obtaining accurate vital signs
(c) Providing information on smoking cessation
(d) Setting the bed alarm
(e) Educating patient on a healthy diet
Answer:
(a) Collecting a thorough and accurate health history
(b) Obtaining accurate vital signs
(c) Providing information on smoking cessation
(e) Educating patient on a healthy diet
Explanation:
Collecting a thorough health history, collecting accurate vital signs, providing smoking cessation information, as well as information on a healthy diet are examples of health promotion and maintenance. Choice (d), setting the bed alarm, is an example of providing a safe and effective care environment.
Question 6.
The nurse is receiving reports at the beginning of the shift. One of the patients has been admitted to the hospital and is awaiting transfer to the ICU with an admitting diagnosis of obstructive shock. Which of the following findings are characteristic of obstructive shock?
(a) Jugular vein distention, peripheral edema, and pulmonary congestion
(b) Decreased urine output, increased BUN, and increased creatinine
(c) Chest pain, fatigue, and lightheadedness
(d) Problems with coordination, blurred vision, and partial paralysis
Answer:
(a) Jugular vein distention, peripheral edema, and pulmonary congestion
Explanation:
Jugular vein distention, peripheral edema, and pulmonary congestion are characteristics of blood volume backing up due to an obstruction. Decreased urine output, increased BUN, and increased creatinine are signs of renal failure. Chest pain, fatigue, and lightheadedness are signs of an Ml. Problems with coordination, blurred vision, and paralysis are symptomatic of a stroke.
Question 7.
The nurse is caring for a sixty-two-year-old woman with myalgia, fever, dyspnea, and decreased breath sounds. To assist with a more rapid diagnosis for possible viral pneumonia, the nurse should prepare the patient for which of the following tests?
(a) Pulmonary function tests
(b) Blood cultures
(c) CT scan
(d) Rapid antigen testing
Answer:
(d) Rapid antigen testing
Explanation:
Viral pneumonia, commonly caused by RSV, parainfluenza virus, and adenovirus, may be diagnosed by chest x-ray and viral cultures. Rapid antigen testing is now also being used for diagnosis and has the advantage of shortening the time for diagnosing this infection. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are incorrect, as these tests are not used to either diagnose viral pneumonia or shorten the diagnostic time.
Question 8.
What defense mechanism, characterized by unconsciously inhibiting thoughts and transferring symptoms, is associated with conversion disorder?
(a) Projection
(b) Repression
(c) Reaction formation
(d) Intellectualization
Answer:
(b) Repression
Explanation:
Conversion disorder is the transformation of emotional distress into physical manifestations. These physical manifestations initially appear to be linked to the nervous system, but they have no medical explanation and really originate in the psyche. Conversion disorder is often associated with repression (Choice 6), a defense mechanism that is characterized by inhibiting or forgetting thoughts the patient does not want to acknowledge. Conversion disorder represents the expression of the disavowed thoughts in the form of transferred symptoms. Projection, reaction formation, and intellectualization, while they are defense mechanisms, are not associated with conversion disorder. Therefore, Choices (a), (c), and (d) are incorrect.
Question 9.
The nurse is looking to locate the lower margin of the liver for assessment. Which abdominal quadrant should the nurse palpate? Place an X to mark your answer.
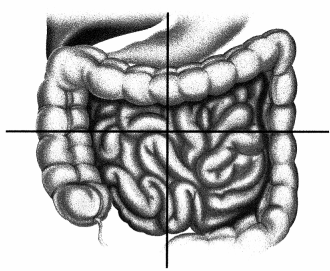
Answer:

Explanation:
The lower margin of the liver can be found in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. During palpation, the nurse should ask the patient to take a deep breath; this causes the liver to be displaced downward, and it can be further palpated in the right lower quadrant.
Question 10.
Where should the nurse palpate the right kidney for tenderness and enlargement in the patient struggling with anorexia nervosa? Place an X to mark your answer.
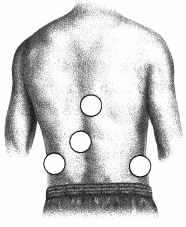
Answer:
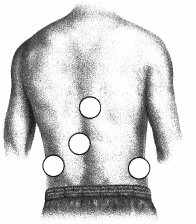
Explanation:
The right kidney is located lower than the left kidney as it accommodates the liver's positioning under the diaphragm and lower ribs. While generally difficult to palpate, an easily palpable, tender kidney is a significant cause for concern. The right kidney is more readily palpable than the left, especially in an underweight patient.
Question 11.
During an ECG, the nurse observes an abnormally lengthened PR interval (greater than 0.3). The nurse recognizes this finding as a characteristic of which of the following?
(a) Sinus rhythm
(b) Junctional rhythm
(c) Mobitz type I heart block
(d) Mobitz type II heart block
Answer:
(c) Mobitz type I heart block
Rationale:
In second-degree heart block, specifically Mobitz type I, the PR interval is lengthened and greater than 0.20. The PR interval for a normal sinus rhythm is 0.12-0.20. In a junctional rhythm, the impulse is starting at the AV node, so the P wave is absent. In Mobitz type II second-degree heart block, the P waves are not followed by the QRS complex. The atria and ventricles are asynchronously contracting.
Question 12.
Which of the following are examples of therapeutic communication? Select all that apply.
(a) Active listening
(b) Checking to see what time it is
(c) Folding your arms across your chest
(d) Asking clarifying questions
(e) Acknowledging the patient's feelings
Answer:
(a) Active listening
(d) Asking clarifying questions
(e) Acknowledging the patient's feelings
Explanation:
Active listening, asking clarifying questions, and acknowledging the patient's feelings are examples of therapeutic communication. Choices (b) and (c), checking the time and folding your arms across your chest, do not encourage communication.
Question 13.
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) As fluid levels decrease, electrolyte levels increase.
(b) As fluid levels increase, electrolyte levels increase.
(c) As fluid levels osmose, electrolyte levels diffuse.
(d) As fluid levels homogenize, electrolyte levels dissipate.
Answer:
(a) As fluid levels decrease, electrolyte levels increase.
Explanation:
Since electrolytes need to be suspended in a certain amount of liquid to move optimally and carry out their intended function, fluid level in the body is important. As fluid levels increase beyond a state of fluid-electrolyte balance, electrolyte levels will decrease, since there is too much fluid present. If fluid levels are too low, such as in a state of dehydration, there will be too many electrolytes per unit of fluid, which also prevents the electrolytes from carrying out their intended function.
Question 14.
During an abdominal physical assessment of a patient with gastrointestinal distress, which action should the nurse perform second?
(a) Percussion
(b) Auscultation
(c) Inspection
(d) Palpation
Answer:
(b) Auscultation
Explanation:
Auscultation, Choice (b), is the second step of an abdominal physical assessment. The nurse should first perform Choice (c), inspection, then Choice (b), auscultation, followed by Choice (a), percussion, and finally Choice (d), palpation. This sequence of techniques is unique to an abdominal physical assessment to promote accuracy in findings by not interfering with the results.
Question 15.
The nurse percusses the patient's lungs during a focused assessment. Which sound aligns with a normal finding?
(a) Tympany
(b) Hyper-Resonance
(c) Dullness
(d) Resonance
Answer:
(d) Resonance
Explanation:
Choice (d) demonstrates a normal finding when auscultating the patient's lungs. Choice (a) is not a normal finding over the lungs, rather normal over the stomach. Choice (b) not a normal finding, as it is indicative of air hyperinflation, such as with asthma. Choice (c) is not a normal finding over the lungs, rather normal over dense areas such as the liver.
Question 16.
The medical surgical nurse assesses the patient to have shortness of breath while in a recumbent position. How should the nurse document this finding?
(a) Orthopnea
(b) Dyspnea
(c) Tachypnea
(d) Bradypnea
Answer:
(a) Orthopnea
Explanation:
Choice (a) is correct as this finding represents the shortness of breath that is present specifically in a recumbent position. Choice (b) identifies difficulty breathing. Choice (c) identifies elevated breathing rate. Choice (d) correlates with decreased breathing rate.
Question 17.
During morning report, the oncoming nurse learns from the outgoing night nurse that a 38-year-old patient has been requesting discharge all night. Upon walking into the patient room to meet them after report, the patient exclaims, "I want to go home now!" Which action should the nurse implement FIRST?
(a) Page the physician for a consult for potential discharge
(b) Report suspected patient neglect to the nurse manager
(c) Administer a pm medication for anxiety
(d) Explore the patient's reasoning for requesting discharge
Answer:
(d) Explore the patient's reasoning for requesting discharge
Explanation:
Choice (d) designates the appropriate first action to be implemented by the nurse in response to the patient's request for discharge. Exploring the patient's reasoning for discharge is patient-centered and allows the nurse to gather additional information to formulate a clear understanding of the present issue(s) before deciding on next steps. Choice (a) may be an appropriate second step, depending on the patient's response to the original inquiry in step one. Choices (b) and (c), while potential actions that may be necessary at some point, are not priorities in this situation.
Question 18.
Which fasting blood sugar level is considered within normal range for a healthy client?
(a) 54 mg/dL
(b) 82 mg/dL
(c) 110 mg/dL
(d) 123 mg/dL
Answer:
(b) 82 mg/dL
Explanation:
Choice (b) represents a fasting blood sugar level that is within normal range, which is considered to be between 60-99 mg/dL. Choice (a) is a below normal finding. Choice (c) and Choice (d) are above normal findings and indicate the possible presence of pre-diabetes.
Question 19.
Which infection control precautions should the nurse implement to reduce the risk of transmission for a patient diagnosed with active tuberculosis?
(a) Standard
(b) Contact
(c) Droplet
(d) Airborne
Answer:
(d) Airborne
Explanation:
Choice (d) indicates the appropriate level of infection control to reduce the risk of transmission for a patient diagnosed with active tuberculosis. Choices (a), (b), and (c) would not provide enough protection in reducing this risk. Tuberculosis is an airborne disease; therefore, transmission of the bacillus, mycobacterium tuberculosis, must be minimized.
Question 20.
The nurse has an order to give 40 mEq of KCIIV to a patient over 4 hours. The KCI comes in bags with a concentration of 20 mEq/50mL. How many mL/hour should be given?
..................... mL/hr
Answer:
25 mL/hr
Explanation:
A total of 40 mEq of KCI will be given, for a total of 100 mL. 100 mL divided by 4 hours equals 25 mL/hr.
Question 21.
Which graphic illustrates the PR interval of the ECG strip?
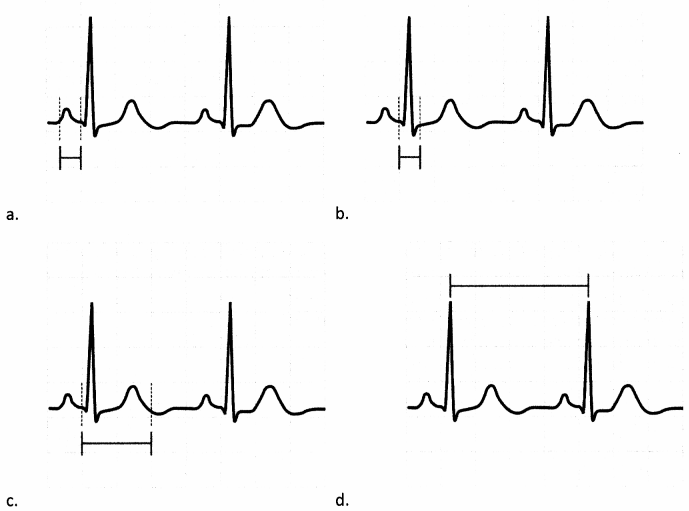
Answer:
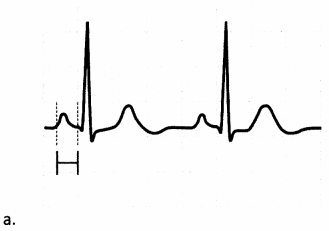
Explanation:
Choice (a) is correct. The PR interval, sometimes also termed the PQ interval, ranges from the start of the P wave (atrial depolarization) to the start of the QRS complex. Choices (b), (c), and (d) illustrate the QRS complex, QT interval, and RR interval, respectively.
Question 22.
What diet is best for the patient diagnosed with phenylketonuria (PKU)?
(a) Low protein
(b) High protein
(c) Low folic acid
(d) High folic acid
Answer:
(a) Low protein
Explanation:
A low protein diet, Choice (a), is the best diet for the patient diagnosed with phenylketonuria, as protein processing is affected in this condition. A high protein diet, Choice (b), should be avoided. The amino acids found within protein can exacerbate symptoms and lead to risky disease management. Folic acid levels are not closely correlated with phenylketonuria management. Thus, Choices (c) and (d) are incorrect.
Question 23.
All of the following ethnic groups are at increased risk for sickle cell anemia EXCEPT?
(a) African
(b) Asian
(c) Eastern European
(d) Middle Eastern
Answer:
(c) Eastern European
Explanation:
Choice (c) does NOT represent an ethnic group at an increased risk for sickle cell anemia. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are all ethnic groups that have a heightened risk for developing this inherited red blood cell disorder.
Question 24.
While completing a physical assessment for suspected aortoiliac occlusive disease on a 68-year-old patient, which locations should the nurse assess blood pressure and pulse to detect a blockage? Select all that apply.
(a) Thigh
(b) Arm
(c) Calf
(d) Foot
(e) Wrist
Answer:
(a) Thigh
(c) Calf
(d) Foot
Explanation:
Choices (a), (c), and (d) all represent the locations where the nurse should assess the patient's blood pressure and pulse to detect a blockage for a patient with suspected aortoiliac occlusive disease. This disease affects the iliac and femoral arteries. The blood pressure and pulse are taken in the thigh, calf, and foot to assess for inadequate blood flow that happens during a blockage. Choices 8 and (e) do not support the assessment of this lower body condition and therefore are not relevant for the nurse's physical assessment of the patient at this time.
Question 25.
Which test should the nurse anticipate in a patient who reports excessive fatigue, depression, and weight gain?
(a) Cortisol level
(b) T4 and TSH levels
(c) Blood glucose level
(d) Aldosterone level
Answer:
(b) T4 and TSH levels
Explanation:
Hypothyroidism occurs when there is an underproduction of T3 and/or T4 hormones. Low levels of these hormones may cause depression, excessive fatigue, chills, dry skin, lowered heart rate, constipation, and unexplained weight gain. Therefore, the nurse anticipates that the physician will order serum T4 levels. Cortisol, blood glucose, and aldosterone levels are not used in the diagnosis of hypothyroidism, making Choices (a), (c), and (d) incorrect.
Question 26.
The nurse is caring for a client who recently underwent radiation therapy to his abdomen. Based on the location of the radiation, the nurse expects which of the following side effects?
(a) Diarrhea
(b) Fatigue
(c) Trembling
(d) Muscle aches
Answer:
(a) Diarrhea
Explanation:
Based on the abdominal location of the radiation therapy, it is likely that the patient will experience gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, as a side effect.
Fatigue, trembling, and muscle aches are possible with radiation therapy but not specific to the organs of the abdomen.
Question 27.
The nurse reviews the following ventilator strips. Which, if any, displays tidal volume?
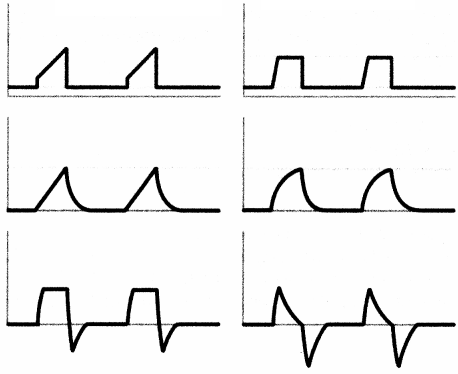
(a) Tidal volume is not displayed
(b) Ventilator strip 1 (top)
(c) Ventilator strip 2 (middle)
(d) Ventilator strip 3 (bottom)
Answer:
(c) Ventilator strip 2 (middle)
Explanation:
Choice (c) displays tidal volume, which involves the volume of air moving in and out of the lungs during respiration. Choice (a) is incorrect as the volume is noted within the reading of strip two. Choice (b) indicates pressure. Choice (d) indicates flow.
Question 28.
Which type of consent provides the nurse with the opportunity to conduct cardiopulmonary resuscitation on an unaccompanied unconscious patient?
(a) Expressed consent
(b) Opt-out consent
(c) Implied consent
(d) Informed consent
Answer:
(c) Implied consent
Explanation:
Implied consent, Choice (c), allows for the nurse to properly administer cardiopulmonary resuscitation to an unconscious patient. Implied consent is not expressly granted, though it is supported by the circumstance and inaction against the intervention. Choices (a), (b), and (d) are not appropriate because regardless of the terms of each type of consent, the patient is unable to consciously, therefore competently, engage in them, rendering them invalid.
Question 29.
Which medication does the nurse expect the patient with hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid condition, to be prescribed for disease management?
(a) Synthroid® (levothyroxine)
(b) Armour® Thyroid (thyroid desiccated)
(c) Cytomel® (liothyronine sodium)
(d) Tapazole® (methimazole)
Answer:
(d) Tapazole® (methimazole)
Explanation:
Tapazole® (methimazole), Choice (d), is a medication used for disease management in hyperthyroidism, an overactive thyroid condition. This condition occurs when the thyroid gland secretes an abundance of hormone and medication is used to reduce this process. Some symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, diaphoresis, and irritability. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are all medications used to treat the underactive thyroid condition known as hypothyroidism.
Question 30.
Your patient's urine sample is positive for a multi-drug resistant organism (MDRO). Which of the following should you do? Select all that apply.
(a) Prepare for Foley catheter insertion.
(b) Use airborne precautions.
(c) Notify the physician.
(d) Use standard precautions.
(e) Expect an order for antibiotics.
Answer:
(c) Notify the physician.
(d) Use standard precautions.
(e) Expect an order for antibiotics.
Explanation:
The physician must be notified so that appropriate antibiotics are ordered for the patient. A patient with an MDRO infection only requires standard precautions. Choice (a), inserting a Foley catheter, should be avoided in most cases and is not indicated for infection. Choice 8, airborne precautions, are not warranted as the MDRO is not an airborne infection.
Question 31.
During a code, the nurse is retrieving equipment to collaborate with the physician to provide airway support for a 10-year-old pediatric patient that weighs 32 kg. Which equipment should the nurse collect? Select all that apply.
(a) Endotracheal tube, 6.5 cuffed
(b) Chest tube, 16
(c) Laryngoscope blade, 1 straight
(d) Endotracheal tube, 3.5 cuffed
(e) Laryngoscope blade, 4 straight/cuffed
Answer:
(a) Endotracheal tube, 6.5 cuffed
(e) Laryngoscope blade, 4 straight/cuffed
Explanation:
Choices (a) and (e) indicate appropriate equipment for the nurse to retrieve to provide airway support for a 10-year-old patient that weighs 32 kg. Choices (b), (c), and (d) indicate appropriate equipment for a younger, smaller pediatric patient.
Question 32.
Nurses are responsible for which of the following elements of informed consent?
(a) Identification of alternatives to the planned procedure
(b) Description of associated risks and benefits
(c) Explanation of the planned procedure or diagnostic test
(d) Assessment of the patient's understanding of the information that is provided
Answer:
(d) Assessment of the patient's understanding of the information that is provided
Explanation:
While the physician is legally responsible for satisfying all elements of informed consent, nurses are ethically responsible for assessing the patient's ability to process and understand the implications of informed consent. Nurses protect the patient's autonomy by raising these questions and concerns. The remaining elements of informed consent are required of the physician, rather than the nurses.
Question 33.
The nurse is caring for an 8-year-old patient who just received a diagnosis of a greenstick fracture. Which of the following does the nurse recognize as correlating with this diagnosis?
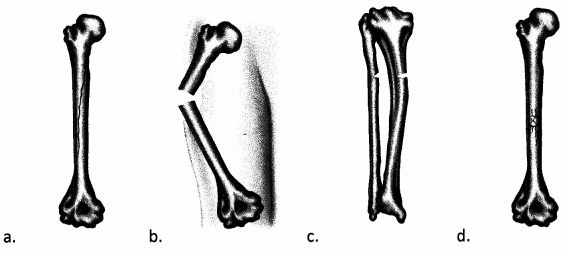
Answer:
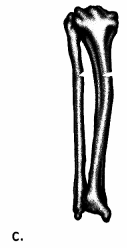
Explanation:
Choice (c) identifies the fracture view of a greenstick fracture, which is commonly found in young pediatric patients. This fracture-type involves the bone bending and cracking on one side. Choice (a) indicates a longitudinal fracture. Choice (b) indicates a compound fracture. Choice (d) indicates a comminuted fracture.
Question 34.
The nurse ensures to provide truthful engagements with their patients, which is ethically substantiated by what principle?
(a) Fidelity
(b) Veracity
(c) Autonomy
(d) Distributive justice
Answer:
(b) Veracity
Explanation:
The ethical principle of veracity is grounded in truth. Ethical practice is integrated into all aspects of nursing care. The nurse should be honest and tell the truth to patients and caregivers, as this is the basis to building trust in the relationship and supporting fair, autonomous, informed decision making.
Question 35.
In guiding practice, the nurse is aware of the nursing science and philosophy of law. What is this practice referred to as?
(a) Fundamentals of nursing
(b) Basic human rights
(c) Nursing process
(d) Nursing jurisprudence
Answer:
(d) Nursing jurisprudence
Explanation:
Nurses must practice with consideration to nursing science and philosophy of law. These laws stem from both state and federal statues and guide practice consideration. Nursing jurisprudence is the act of navigating nursing practice with these considerations as the managing foundation for care. Choice (a) involves basic nursing care. Choice (b) includes basic rights that all humans hold, whereas nursing process, Choice (c), involves sequential steps of the nursing practice.
Question 36.
Which of the following is not a risk factor for falls in the elderly?
(a) Using a cane to walk
(b) Inadequate lighting in a room
(c) Muscle weakness
(d) Slower reflexes
Answer:
(a) Using a cane to walk
Explanation:
Use of a cane is not a risk factor for falls in the elderly. A cane would actually benefit a person by giving them extra stability when walking. Poor lighting is a risk factor because it could cause someone to stumble over items on the floor or cause an imbalance by bumping into unseen furniture. Muscle weakness and slower reflexes are also risk factors for falls in the elderly.
Question 37.
During breakfast, a patient with dysphagia states, "Well, I haven't choked yet," then knocks on the wooden side-table. The nurse educates the unlicensed assistive personnel regarding this behavior. What is knocking on wood an example of?
(a) Cultural norm
(b) Undoing
(c) Repetitive behavior
(d) Compulsion
Answer:
(b) Undoing
Explanation:
Choice (b) indicates the patient's behavior to undo something that they hope will not take place. Undoing involves a sense of magic. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are not present in the patient's actions.
Question 38.
Which routine treatment for cystic fibrosis facilitates movement of secretions from small to large airways for subsequent expulsion?
(a) Antibiotics
(b) The six-foot rule
(c) Pulmonary function tests
(d) Chest physiotherapy
Answer:
(d) Chest physiotherapy
Explanation:
Chest physiotherapy, Choice (d), is a supportive treatment routinely used for the care of individuals with cystic fibrosis to facilitate movement of secretions from small to large airways. Once the secretions have mobilized, they are much more readily expressed via coughing. Chest physiotherapy involves postural drainage, followed by percussion and vibration to loosen thick mucus and mobilize secretions.
Choice (a), antibiotics, while used for those with cystic fibrosis who develop infections, are not prescribed for routine care to mobile secretions. The six-foot rule, Choice (b), signifies the practice of two individuals with cystic fibrosis maintaining a minimum 6-foot distance between one another to reduce the likelihood of spreading respiratory infections. Pulmonary function tests, Choice (c), are done to assess pulmonary function.
Question 39.
Upon retiring from practice after forty years, the nurse shares with their novice colleagues that they have experienced numerous healthcare documentation methods throughout their career. What is new technology that replaces a previously established technology identified as?
(a) Protocol
(b) Disruptive
(c) Gateway
(d) Recovery
Answer:
(b) Disruptive
Explanation:
Disruptive technology involves a modern technique that replaces and renders a previous technology obsolete. The current use of electronic health record (EHR) and electronic medical record (EMR) systems are examples of disruptive technologies. Choices (a), (c), and (d) do not involve technology that replaced previous technology.
Question 40.
The nurse is caring for a patient with bacterial meningitis. Which classic findings of this disease should the nurse expect to find on assessment?
(a) Fever, nuchal rigidity, headache
(b) Fever, vomiting, photophobia
(c) Confusion, decreased level of consciousness, photophobia
(d) Fatigue, muscle aches, decreased appetite
Answer:
(a) Fever, nuchal rigidity, headache
Explanation:
The classic manifestations of bacterial meningitis include fever, nuchal rigidity, and headache. Other manifestations may include nausea, vomiting, photophobia, confusion, and a decreased level of consciousness; therefore, Choices (b) and (c) are incorrect. Manifestations of viral meningitis may include fatigue, muscle aches, and decreased appetite, making Choice (d) incorrect.
Question 41.
When caring for a patient with autoimmune gastritis, the nurse should assess the patient for manifestations of which vitamin deficiency?
(a) Vitamin B-l
(b) Vitamin B-12
(c) Vitamin D
(d) Vitamin K
Answer:
(b) Vitamin B-12
Explanation:
In autoimmune gastritis, there is a deficiency of intrinsic factor, which is responsible for the absorption of vitamin B-12. Therefore, the patient with autoimmune gastritis will have a vitamin B-12 deficiency. As a result, Choices (a), (c), and (d) are incorrect.
Question 42.
While implementing a plan of care for a patient experiencing alcohol withdrawal, which supplement should the nurse include?
(a) Calcium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Vitamin D
(d) Thiamine
Answer:
(d) Thiamine
Explanation:
Choice (d), a vitamin found in food and supplements, is a key element of an alcohol withdrawal protocol. Thiamine is typically deficient in those with alcohol abuse and dependence and is replaced
during treatment. Choices (a), (b), and (c), while all potentially helpful supplements across a variety of conditions, are not specifically associated with the needs of the patient at this time.
Question 43.
During a level of consciousness assessment, the nurse finds no articulated verbal response with limited moaning, accompanied by arousal only after vigorous stimulation. How should the nurse document these findings?
(a) "The patient is lethargic."
(b) "The patient is obtunded."
(c) "The patient is stuporous."
(d) "The patient is comatose."
Answer:
(c) "The patient is stuporous."
Explanation:
Choice (c) identifies a stuporous patient exhibiting no articulated verbal response with limited moaning, accompanied by arousal only after vigorous stimulation. Lethargic, Choice (a), describes a patient who appears drowsy and arouses with gentle stimulation. Obtunded, Choice (b), describes a patient who responds to repeated external stimulation to maintain attention. A patient that is comatose, Choice (d), indicates they have no discernable response to stimulation. The levels of consciousness proceed with increasing severity from confused, to lethargic, to obtunded, to stuporous, and finally to comatose.
Question 44.
The nurse is reviewing the interpretation of the cardiac rhythm strip as sinus bradycardia. For this interpretation to be accurate, which heart rate must correlate with these findings?
(a) Below 60 beats per minute
(b) Above 150 beats per minute
(c) From 90-120 beats per minute
(d) From 121-150 beats per minute
Answer:
(a) Below 60 beats per minute
Explanation:
A diagnosis of bradycardia indicates the patient is experiencing a heart rate below 60 beats per minute, so Choice (a) is correct. Choices (b), (c), and (d) are within normal to high limits. The normal resting heart rate for adults is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
Question 45.
The patient must make a decision regarding the next steps in their plan of treatment and in doing so, is weighing out two significantly different care options. Which ethical provision does the nurse practice when ensuring that the patient has the right to make self-directed decisions?
(a) Beneficence
(b) Autonomy
(c) Non-Maleficence
(d) Justice
Answer:
(b) Autonomy
Explanation:
Autonomy, Choice (b), protects the patient's right to self-directed, independent decisions. Once the patient has received the information they need to make an informed selection of treatment, the patient, or proxy when indicated, autonomously makes the final decision for care. Beneficence, Choice (a), morally encourages the nurse to do right by the patient. Non-maleficence, Choice (c), supports not causing harm to the patient. Justice, Choice (d), stimulates ethical fairness for the patient.
Question 46.
Which position should the nurse help a patient into for pain management of acute appendicitis?
(a) High Fowler's position
(b) Fetal position
(c) Prone position
(d) Supine position
Answer:
(b) Fetal position
Explanation:
Choice (b) should be supported by the nurse, as it brings the knees to chest and typically encourages some pain relief in acute appendicitis. Choices (a), (c), and (d) represent positions that would likely exacerbate the patient's pain symptoms and should not be encouraged at this time.
Question 47.
While working with a patient struggling with schizophrenia and paranoid symptoms, which non- pharmacological therapeutic aid should the nurse suggest to support symptom management?
(a) Book
(b) Television
(c) Instrumental music
(d) Food
Answer:
(c) Instrumental music
Explanation:
Instrumental music, Choice (c), encourages symptom management in reducing psychotic and paranoid symptoms for a patient struggling with schizophrenia, as instrumental music does not contribute to disturbed thought patterns and soothes the ill mind. Books, television, and food all carry the capacity to encourage worsening symptoms and should be avoided. Patients with schizophrenia may worry that their food is poisoned or be influenced to expand on delusional or paranoid thinking when influenced by stories in a book or on television.
Question 48.
The nurse case manager requests extra paid days from the third party payer for the patient's length of stay in order to continue providing covered treatment. What is this process an example of?
(a) Concurrent review
(b) Prior authorization
(c) Retrospective review
(d) Prospective review
Answer:
(a) Concurrent review
Explanation:
The nurse case manager engages with third-party payers during a patient's inpatient stay in order to review current treatment, cost, and plans for additional care. This process, known as concurrent review, is a standard activity of the inpatient stay. Choice (b), prior authorization, is specific to medication or individual intervention. Choice (c), retrospective review, takes place after discharge to seek coverage for care. Choice (d), prospective review, happens before admission.
Question 49.
What ethical principle sets forth that the nurse must maintain truthful engagements with their patient?
(a) Justice
(b) Veracity
(c) Nonmaleficence
(d) Beneficence
Answer:
(b) Veracity
Explanation:
Choice (b) aligns with the ethical principle to maintain truthful engagements. Choice (a) aligns with ethical fairness. Choice (c) aligns with refraining from harm. Choice (d) promotes doing right by the patient.
Question 50.
The nurse applies a condom catheter. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Assist patient to low Fowler's position
(b) Roll condom catheter onto penis
(c) Put urinary drainage bag on bed
(d) Place elastic adhesive around top of condom catheter
Answer:
(a) Assist patient to low Fowler's position
(b) Roll condom catheter onto penis
(c) Put urinary drainage bag on bed
(d) Place elastic adhesive around top of condom catheter
Explanation:
The nurse applies a condom catheter via steps performed in the following order to ensure proper positioning of the patient and equipment for safe and effective placement. The nurse should assist the patient to low Fowler's position, put urinary drainage bag on bed, roll condom catheter onto penis, and then place elastic adhesive around top of condom catheter.
Question 51.
An aide enters a patient's room in response to the call light and sees a fire behind the television. What is the aide's first action?
(a) Activate the fire alarm.
(b) Use the nearest fire extinguisher.
(c) Move the patient to a safer location away from the room.
(d) Smother the fire with a blanket.
Answer:
(c) Move the patient to a safer location away from the room.
Explanation:
Use the acronym RACE to answer this question. The information given in the question leads to the fact that the patient is in the room, and that there is probably an electrical fire. The first action should be to rescue the patient by removing them from the room. Next, activate the fire alarm and then contain the fire by closing the door to the room. Extinguish the fire with the appropriate extinguisher if available. Choice (d), smothering the fire, is not appropriate for an electrical fire.
Question 52.
While caring for a patient with impaired renal function, the medical surgical nurse assesses ascites and dependent edema. Which electrolyte imbalance does the nurse suspect may be present?
(a) Hyperkalemia
(b) Hypokalemia
(c) Hypernatremia
(d) Hyponatremia
Answer:
(d) Hyponatremia
Explanation:
Choice (d) is correct as this imbalance can cause a buildup of fluid in the form of edema and ascites for patients with impaired renal function. Low sodium levels alter the fluid balance of the body, encouraging the retention seen in these findings. Choices (a), (b), and (c), while significant imbalances to measure, do not directly influence the development of ascites and dependent edema secondary to impaired renal function.
Question 53.
A nurse identifies that many collaborative peers have contributed to a possible sentinel event. Does the accredited hospital have to report the sentinel event to The Joint Commission after the nurse elevates their report of the incident?
(a) Yes, always report it.
(b) No, these are always internal only.
(c) Yes, in some cases.
(d) No, but it is encouraged.
Answer:
(d) No, but it is encouraged.
Explanation:
Choice (d) correctly aligns with the Joint Commission's standards, as sentinel events are not mandatory to report but are encouraged. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are inaccurate interpretations of the Joint Commission's role in accredited organization reporting of sentinel events.
Question 54.
The nurse prepares to suction nasopharyngeal secretions. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Attach catheter to suction tubing
(b) Don sterile gloves
(c) Assess breath sounds
(d) Power on suction device
Answer:
(c) Assess breath sounds
(d) Power on suction device
(b) Don sterile gloves
(a) Attach catheter to suction tubing
Explanation:
The nurse prepares to suction nasopharyngeal secretions by carrying out steps in the following order to ensure thorough removal of excess secretions. Assess breath sounds. Power on suction device. Don sterile gloves. Attach catheter to suction tubing.
Question 55.
While implementing a plan of care for a patient with heart failure, how should the nurse address activity?
(a) Increase activity and limit time in bed
(b) Remain on bed rest
(c) Alternate rest and activity
(d) Ambulate to the bathroom only
Answer:
(c) Alternate rest and activity
Explanation:
Choice (c) represents the appropriate level of activity for the patient with heart failure. Alternating rest with activity supports a reduced cardiac workload. Choice (a) would encourage a higher level of activity than the patient's condition can maintain. Choices (b) and (d) place unnecessary restrictions on the patient's activity.
Question 56.
What color stool does the nurse expect to note from a patient struggling with a bile duct blockage?
(a) White
(b) Green
(c) Black
(d) Red
Answer:
(a) White
Explanation:
A reduction in bile can also produce stool that is tan or clay-colored. As less bile is present, the stool becomes paler in color. Thus, Choice (a), white stool, is seen when a patient is struggling with a bile duct blockage. Green stool, Choice (b), is indicative of a high vegetable intake or antibiotic use. Black stool, Choice (c), can be seen with upper gastrointestinal bleeds or iron supplementation, whereas red stool, Choice (d), can be observed with lower gastrointestinal bleeds or foods with red dyes.
Question 57.
Which of the following patients is NOT at increased risk for the development of an embolism?
(a) A twenty-four-year-old with a broken femur
(b) An eighty-five-year-old female with a history of a stroke
(c) A sixty-two-year-old male with first-degree heart block
(d) A nineteen-year-old female two weeks postpartum
Answer:
(c) A sixty-two-year-old male with first-degree heart block
Explanation:
A first-degree heart block is NOT a direct risk factor for the development of an embolus. Women during pregnancy and in the postpartum period, individuals with a history of a previous stroke, and patients with fractures that involve long bones are all at risk for the development of an embolus.
Question 58.
While working with a female patient 25 years older than the male nurse, the nurse notices that the patient repeatedly shames him and questions his intentions during interventions. After elevating this concern, the nurse case manager discussed this occurrence with the patient. During the discussion, the patient reported that the nurse reminds her of her son, who has ongoing struggles with honesty and maintaining commitments. What is this skewed engagement an example of?
(a) Regression
(b) Countertransference
(c) Transference
(d) Repression
Answer:
(c) Transference
Explanation:
Choice (c), transference, is observed when one member of an interaction transfers thoughts or feelings that were originally about one person onto someone else. In this case, the patient is reminded of her son while interacting with the nurse, and she transfers the negative association she has with her son onto the nurse. Choice (b), countertransference, occurs when the clinician displaces their feelings onto the client. Choice (a), regression, involves reverting to an earlier version of the self, while Choice (d), repression, manifests itself through reducing emotions.
Question 59.
During an integumentary assessment of the hand, the nurse notes the patient's fingernails resemble upside-down spoons. Which of the patient's conditions is most likely responsible for this finding?
(a) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(b) Lung cancer
(c) Pneumonia
(d) Asthma
For the following question, please refer to this chart:
|
Name |
Monica Latte |
||
|
Problems |
DIABETES MELLITUS (CD-250.) HYPERTENSION, BENIGN ESSENTIAL (ICD-401.1) |
||
|
Medications |
HUMULIN INJ 70/30 20 U ac breakfast PRINIVL TABS 20 MG 1 qd |
||
|
History |
Hyperglycemic symptoms |
||
|
Vital Signs |
Height: 64 in Weight: 140 lbs. Temperature: 98.0 deg F Temperature site: oral Pulse: 72 Rhythm: regular Respiratory rate: 16 Blood pressure: 158/90 |
||
|
Physical Exam |
General Appearance: well developed, well nourished, no acute distress Eyes: conjunctiva and lids normal, PERRLA, EOMI. fundi WNL Ears, Nose, Mouth, Throat: TM clear, flares clear, oral exam WNI Respiratory: clear to auscultation and percussion, respiratory effort normal Cardiovascular: regular rate and rhythm, S1-S2, no murmur, rub or gallop, no bruits, peripheral pulses normal and symmetric, no cyanosis, clubbing, edema or varicosities Skin: clear, good turgor, color WNL, no rashes, lesions, or ulcerations Problems (including changes): Blood pressure is lower. Feet are inspected and there are no callouses, no compromised skin. No vision complaints. Impression: Sub optimal sugar, control with retinopathy and neuropathy, high glucometer readings. Will work harder on diet. Will increase insulin by 2 units. |
||
|
HbA1c test |
HbA1c level 6.0% |
||
|
Lipid Profile |
Cholestrol Total 210 mg/dl Triglycerides: 236 mg/dl LDL Cholestrol: 107 |
||
|
Metabolic panel |
ALK PHOS |
72 |
35- 100 |
|
BG RANDOM |
125 mg/dI |
70-125 |
|
|
CALCIUM |
16 mg/dI |
7-25 |
|
|
CHLORIDE |
9.6 mg/dI |
8.2-10.2 |
|
|
CO2 |
101 mmol/I |
96-109 |
|
|
CREATININE |
27 mmol/I |
23-29 |
|
|
PO4 |
0.7 mg/dI |
0.6-1.2 |
|
|
POTASSIUM |
2.9 mg/dI |
2.5-4.5 |
|
|
SGOT |
4.5 mmol/I |
3.5-5.3 |
|
|
BIU TOTAL |
31U/L |
0-40 |
|
|
URIC ACID |
0.7mgJdI |
0.0-1.3 |
|
|
LDH, TOTAL |
4.8 mg/dI |
3.4-7.0 |
|
|
SODIUM |
136 lUlL |
0-200 |
|
Answer:
(b) Lung cancer
Explanation:
Choice (b) is correct, as the nurse would associate upside-down spoon nails, also known as nail clubbing, with the patient's diagnosis of lung cancer. The nurse would observe the nails to appear reddish in color and sponge-like in appearance. Choices (a), (c), and (d) do not cause this change in the structure of the fingernail.
Question 60.
You are seeing the patient M.L. in a physician's office. You take her blood pressure, chart it, and confirm that she is taking her daily prescribed medications. What action should you anticipate from the physician?
(a) They will increase the dose of the current blood pressure medication.
(b) They will admit the patient to the hospital for blood pressure control.
(c) They will make no medication changes; the patient is already taking a blood pressure medication.
(d) They will discontinue the blood pressure medication because the blood pressure has improved since the last visit.
Answer:
(a) They will increase the dose of the current blood pressure medication.
Explanation:
The patient's blood pressure is still elevated. Choices (c) and (d) are incorrect because the patient's blood pressure is currently high. Choice (b) is incorrect because the patient's blood pressure is elevated but is not considered a medical emergency.
Question 61.
The critical care nurse is engaged in a nurse-to-nurse report with the medical-surgical step-down nurse and describes the patient's pitting edema as 2+. Which description aligns with the receiving nurse's understanding of a 2+ finding for planning care?
(a) Barely detectable indentation.
(b) Indentation takes 15 seconds to rebound.
(c) Indentation takes 30 seconds to rebound.
(d) Indentation takes greater than 30 seconds to rebound.
Answer:
(b) Indentation takes 15 seconds to rebound.
Explanation:
Choice (b) is observed with a 2+ response to pitting edema, which takes 15 seconds for the mild indentation to rebound. Choice (a) is observed with a 1+ response to pitting edema, which is an impression that is barely detectable. Choice (c) is observed with a 3+ response to pitting edema, which takes 30 seconds for the moderate indentation to rebound. Choice (d) is observed with a 4+ response to pitting edema, which takes greater than 30 seconds for the severe indentation to rebound.
Question 62.
While caring for a patient diagnosed with appendicitis, the nurse is providing patient education regarding the location of their appendix. Which abdominal region does the nurse highlight as the location of this organ? Place an X to mark your answer.
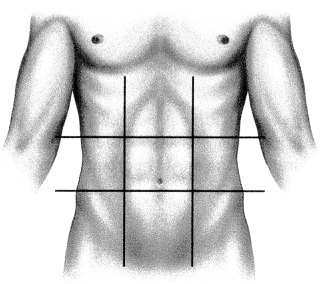
Answer:
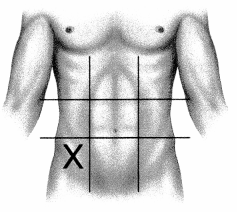
Explanation:
The right iliac region contains the appendix along with the cecum. This area is found at the right lower region of the abdomen and may be a source of discomfort for a patient experiencing appendicitis, which involves pain secondary to inflammation.
Question 63.
A fifty-five-year-old male is undergoing an endoscopy to discover the source of his hematemesis. The gastroenterologist encounters an active, bleeding lesion. What procedure using the application of heat to seal the lesion will probably be used next?
(a) Banding
(b) Biopsy
(c) Angioplasty
(d) Cauterization
Answer:
(d) Cauterization
Explanation:
The gastroenterologist will likely use cauterization, an application of heat, to seal the bleeding lesion. Banding is a procedure used to help stop bleeding in esophageal varices. Biopsy is where tissues are removed for histological analysis. Angioplasty is performed in cardiac catheterizations and involves balloon inflation and stent placement to open up occluded blood vessels.
Question 64.
What score represents the degree to which a patient's psychological symptoms impact their daily ' life?
(a) Apgar score
(b) AIMS score
(c) GAF score
(d) Withdrawal protocol score
Answer:
(c) GAF score
Explanation:
During a psychiatric evaluation, the clinician will determine the degree to which a patient's psychological symptoms impact their daily life. This score is then represented in the evaluation as a GAF score, which stands for Global Assessment of Functioning (Choice c).
An Apgar score measures a neonate's general condition at birth (Choice a), and an AIMS score measures side effects of antipsychotic medication use (Choice b). The withdrawal protocol (Choice d) concerns symptoms that, in a patient struggling with substance abuse, must be controlled with medication, typically a benzodiazepine.
Question 65.
The nurse is educating a patient regarding their anemic state. Which organ is the source of the bone's failure to produce red blood cells?
(a) Stomach
(b) Kidney
(c) Gallbladder
(d) Hypothalamus
Answer:
(b) Kidney
Explanation:
The kidney, Choice 6, is the source of the bone's failure to produce red blood cells leading to their current anemic state. The kidney is responsible for stimulating this activity. The organs in Choices (a), (c), and (d) do not directly affect the bone's failure to produce red blood cells.
Question 66.
The nurse is administering total parenteral nutrition (TPN) to the patient for the first time. He knows that he should administer the medication at which of the following rates?
(a) Slowly, at 50 percent of the prescribed dosage
(b) Quickly, at double the prescribed dosage
(c) Quickly, at three times the prescribed dosage
(d) Slowly, at 25 percent of the prescribed dosage
Answer:
(a) Slowly, at 50 percent of the prescribed dosage
Explanation:
The TPN should be administered slowly, at 50 percent of the prescribed dosage, when beginning therapy. TPN comes with many possible complications as the body adjusts to this different source of nutrition, so starting slowly is recommended. The other three answers are incorrect.
Question 67.
The nurse is looking over the patient's lab values for the day. He notices that one lab parameter has gone up significantly, signaling a possible infectious process at work. Which lab parameter is he likely drawing this conclusion from?
(a) Blood urea nitrogen
(b) Hematocrit
(c) Neutrophils
(d) Sodium level
Answer:
(c) Neutrophils
Explanation:
Neutrophils are the major component of the white blood cells. When their count is elevated, that means the white blood cells are hard at work fighting an infectious process. The nurse would need to investigate this conclusion further, possibly getting an order to draw some blood cultures if appropriate. Blood urea nitrogen is a waste product of the body. An elevated level would suggest failing kidneys but not an infection. Hematocrit is a component of red blood cells and is not part of the body's immune system. A high sodium level is an electrolyte abnormality that may have to do with the renal system or overall patient fluid status but not an infectious process.
Question 68.
A patient walks into the emergency department and collapses. The nurse identifies the condition as cardiopulmonary arrest, and resuscitation efforts are started. The nurse understands that, in addition to CPR, defibrillation, and the ACLS protocol, the most important factor for patient survival is which of the following?
(a) Administration of oxygen
(b) Establishing IV access
(c) Inserting a Foley catheter
(d) Time between the collapse and the start of resuscitation efforts
Answer:
(d) Time between the collapse and the start of resuscitation efforts
Explanation:
Time between the collapse and the start of resuscitation efforts is the most important factor in patient survival. Administering supplemental oxygen is a component of resuscitation efforts.
Establishing IV access is an essential component of resuscitation efforts. Inserting a Foley catheter to drain the urinary bladder is not related to survival.
Question 69.
The nurse is reviewing new medication orders for a patient with multiple diagnoses, including pernicious anemia. As the nurse has a clear understanding of this type of anemia, which treatment do they suspect to see ordered via subcutaneous injection for this patient?
(a) Iron
(b) Vitamin B-12
(c) Packed RBCs
(d) Stem cells
Answer:
(b) Vitamin B-12
Explanation:
Only vitamin B-12, Choice (b), should be an expected subcutaneous treatment for the patient with pernicious anemia. However, iron, packed RBCs, and stem cells are involved in various other forms of anemia. Multiple forms of anemia exist including iron-deficiency anemia, hemolytic anemia, and aplastic anemia, to name a few. In this case, the patient is suffering from pernicious anemia, an autoimmune condition in which the body is unable to absorb the vitamin B-12 consumed in one's diet, leading to deficiency. Vitamin B-12 injections are required to form healthy red blood cells.
Question 70.
The doctor has ordered a nasogastric (NG) tube to be placed by the nurse for gastric lavage. After placing the NG, the nurse expects which of the following tests to be performed to confirm the placement of the tube?
(a) Aspiration of laryngeal secretions for pH testing
(b) Chest radiograph
(c) Abdominal ultrasound
(d) Manual palpation of the gastric body for the catheter tip
Answer:
(b) Chest radiograph
Explanation:
A chest radiograph is the test of choice to confirm the placement of a nasogastric tube. The x-ray will show whether the catheter tip is in the gastric body or not. Aspiration of stomach contents, not laryngeal secretions, with a pH test is another, less preferred way to confirm placement.
The pH test may be misleading, as there may be gastric contents farther up the esophageal canal and not necessarily within the stomach in some patients with weakened sphincters. An abdominal ultrasound may show the catheter tip, but it is not the preferred method of evaluating placement. Manual palpation of the gastric body is not a way to confirm placement, as it would be very difficult to actually feel the catheter within the stomach.
Question 71.
During the morning community meeting for the adult intensive outpatient program, the clients are identifying their personal goals for the week. Which goal identified by the client struggling with substance abuse does the nurse recognize as realistic?
(a) Use the substance of choice in moderation.
(b) Stop needing to connect with their sponsor.
(c) Avoid places where they typically have used substances in the past.
(d) Use self-control to prevent all cravings.
Answer:
(c) Avoid places where they typically have used substances in the past.
Explanation:
For an individual struggling with substance abuse, avoiding places where they have typically used substances in the past is a realistic goal for intensive outpatient therapy (Choice c). It would not be realistic for the client to use their substance of abuse in moderation (Choice a), stop requiring connection with their sponsor (Choice b), or prevent all cravings via self-control (Choice d) during the week they are engaged in intensive treatment for substance abuse.
Question 72.
The nurse is educating a 43-year-old patient regarding their fracture, which has resulted in the fragmentation of the bones in their right hand after a motor vehicle accident. Which type of fracture represents this finding?
(a) Compound fracture
(b) Oblique fracture
(c) Comminuted fracture
(d) Greenstick fracture
Answer:
(c) Comminuted fracture
Explanation:
In a comminuted fracture, Choice (c), the bones break into multiple fragments, as they would have done during the motor vehicle accident. Comminuted fractures typically occur in the hands and feet in response to severe trauma. The nurse would educate the patient regarding the specific fracture that they are suffering from and plan treatment options in response.
A compound fracture, Choice (a), involves a fracture where the bones break through the skin. An oblique fracture, Choice (b), involves a fracture that breaks at an angle. A greenstick fracture, Choice (d), involves a fracture where the bones do not break all the way through.
Question 73.
Identify the ulna.
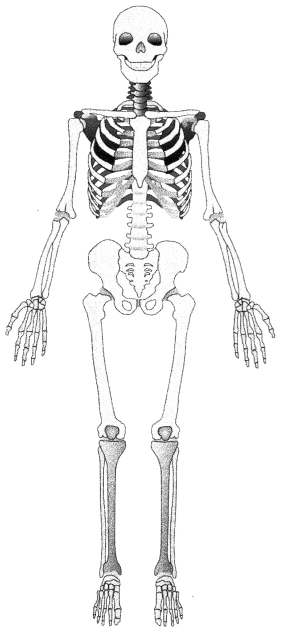
Answer:
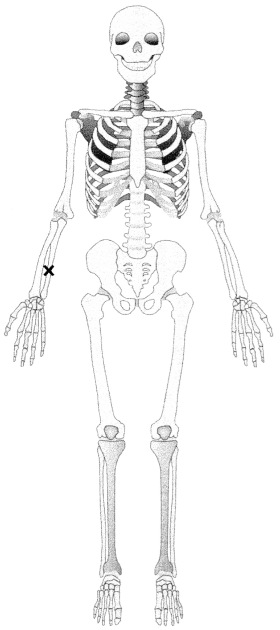
Explanation:
The ulna is the medial long bone between the elbow and wrist.
Question 74.
The nurse is facilitating a community pediatric health course and including Erikson's Psychosocial Theory to describe stages of development. Arrange the following stages in ascending order by typical age of experience. Include all options.
(a) Autonomy vs. shame
(b) Trust vs. mistrust
(c) Initiative vs. guilt
(d) Industry vs. inferiority
Answer:
(b) Trust vs. mistrust
(a) Autonomy vs. shame
(c) Initiative vs. guilt
(d) Industry vs. inferiority
Explanation:
The nurse educates on the following stages in ascending order according to Erikson's Psychosocial Theory to describe the age stages of development. The nurse educates that development ascends from trust vs. mistrust, to autonomy vs. shame, to initiative vs. guilt, to industry vs. inferiority.
Question 75.
Of the following tasks, which one is not considered "dirty"?
(a) Changing a diaper
(b) Assisting with oral care
(c) Changing a wound dressing
(d) Helping a patient get dressed
Answer:
(d) Helping a patient get dressed
Explanation:
Helping a patient get dressed is not considered a dirty task unless the clothing is soiled with any bodily fluid. (a), (b), and (c) are all tasks that involve bodily fluids and are considered dirty. Clean tasks should be performed first, followed by dirty tasks.
Question 76.
The nurse auscultates the patient's heart sounds and notes both an S3 and an S4 sound. Which rhythm aligns with this finding?
(a) Still's Murmur
(b) Regular Rhythm
(c) Summation Gallop
(d) Systolic Murmur
Answer:
(c) Summation Gallop
Explanation:
Choice (c) is correct as audible S3 and S4 sounds upon cardiac auscultation indicate summation gallop. Choice (a) sounds musical or vibratory. Choice (b) contains two audible heart sounds, SI and S2. Choice (d) is heard as a sound between the SI and S2 heartbeat cycle.
Question 77.
The nurse notices a patient's medication list contains a drug that is likely to lower her pulmonary vascular resistance. Which type of medicine is the nurse likely looking at to draw this conclusion?
(a) Diuretic
(b) Morphine
(c) Nitrate
(d) Calcium channel blocker
Answer:
(d) Calcium channel blocker
Explanation:
A calcium channel blocker can lower the pulmonary vascular resistance in a patient. Diuretics, morphine, and nitrates all have potent lowering effects on the systemic vascular resistance, as opposed to the pulmonary vasculature. Knowing the hemodynamic effects certain medications have is helpful in anticipating unwanted side effects and potential drug interactions.
Question 78.
The community health nurse understands that which child is most at risk for developing bronchiolitis?
(a) A six-month-old child
(b) A two-year-old child
(c) A child in kindergarten
(d) A high school student
Answer:
(a) A six-month-old child
Explanation:
Bronchiolitis, an inflammation of the small airways in the lung, most commonly affects children under the age of two, with the greatest incidence between 3 and 6 months old. Children age 2 and older, including children entering kindergarten or in high school, are less likely to be affected, making Choices (b), (c), and (d) inappropriate choices.
Question 79.
The pediatric nurse is caring for a child who has had three seizures lasting five to eight minutes over a thirty-minute period. The nurse understands that the child is experiencing which of the following conditions?
(a) Generalized seizures
(b) Focal seizures
(c) Status epilepticus
(d) Postictal state
Answer:
(c) Status epilepticus
Explanation:
Status epilepticus is prolonged seizure activity involving multiple seizures, each lasting five minutes or more, over a thirty-minute period of time. A generalized seizure is a seizure that originates in two or more networks of the brain, making Choice (a) incorrect. A focal seizure is one that originates in a single area of the brain, making Choice (b) incorrect. The postictal state follows a seizure and is characterized by alterations in consciousness and awareness and increased oral secretions, making Choice (d) incorrect.
Question 80.
The nurse is caring for a thirty-eight-year-old male who presents with marked left-sided scrotal swelling and distention of the abdomen. The nurse understands that which of the following is an UNEXPECTED finding in this patient?
(a) Diarrhea
(b) Tachycardia
(c) Rebound tenderness
(d) BUN 27
Answer:
(a) Diarrhea
Explanation:
The patient's manifestations are consistent with an incarcerated or strangulated hernia that is progressing to a small-bowel obstruction as evidenced by the abdominal distention. This complication is associated with decreased peristalsis and eventual absence of bowel activity, which means that diarrhea would be an uncommon manifestation.
Tachycardia and a BUN of 27 are related to fluid volume losses resulting from the accumulation of fluid proximal to the obstruction in the small bowel; therefore, Choices (b) and (d) are incorrect. Rebound tenderness is also an expected finding in a bowel obstruction due to the trapped gas and fluid proximal to the obstruction; therefore, Choice (c) is incorrect.
Question 81.
The nurse recognizes that a patient is having a severe reaction to Enoxaparin. What medication should be given to neutralize this medication and inhibit this reaction?
(a) Pilocarpine
(b) Romazicon
(c) Naloxone
(d) Protamine
Answer:
(d) Protamine
Explanation:
Choice (d) is the antidote given to counteract the effects of Enoxaparin. Choices (a), (b), and (c) represent medications used as antidotes for a wide variety of medications but will not neutralize this medication and inhibit the reaction.
Question 82.
Which abdominal quadrant does the nurse assess pain in the patient with cirrhosis of the liver?
(a) Left Lower Quadrant
(b) Right Lower Quadrant
(c) Left Upper Quadrant
(d) Right Upper Quadrant
Answer:
(d) Right Upper Quadrant
Explanation:
Choice (d) is correct as cirrhosis of the liver should be assessed in the right upper quadrant by palpating for an enlarged liver under the lower edge of the patient's right rib cage. Typically, the liver is unable to be palpated; however, if it is enlarged, the nurse can examine this via a focused assessment. Choices (a), (b), and (c) represent quadrants outside of the direct location of this organ's focused assessment.
Question 83.
A 57-year-old male comes in for an annual check-up. Current medications include HCTZ 25 mg PO daily. You anticipate that the provider will prescribe what medication for this patient?
|
Patient Information |
Name: Glen Delaney Age: 67 Sex: Male
|
|
Vital signs |
HR: 70 |
|
Labs |
RBC 5.0, Hgb 13.5, Hct 45, WBC 8, HDL 60, LDL 165, Triclycerides 200, Total Cholesterol 225, Aic 6.2, BUN 20, Creat 0.6 |
|
Medications |
HCTZ 25 mg PO daily |
(a) Lovastatin 20 mg PO daily
(b) Sliding scale insulin
(c) Metoprolol 25 mg PO daily
(d) Ferrous sulfate 325 mg PO TID
Answer:
(a) Lovastatin 20 mg PO daily
Explanation:
Choice (a) is correct. Lovastatin is used to lower cholesterol and triglycerides. Choice (b), sliding scale insulin, is not currently indicated as the patient does not have a diagnosis of diabetes. Choice (c), metoprolol, a beta blocker, is used to lower heart rate and blood pressure and is not indicated. Choice (d), ferrous sulfate, is a supplement used to treat iron deficiency anemia. The patient is not anemic, making Choice (d) incorrect.
Question 84.
The nurse is answering an HIV-positive patient's questions about the differences between the HIV-1 and HIV-2 viruses. Which information would the nurse tell this patient?
(a) HIV-2 is highly transmissible.
(b) HIV-1 is the dominant strain worldwide.
(c) HIV-2 is well studied and highly understood.
(d) HIV-1 is the weaker virus strain.
Answer:
(b) HIV-1 is the dominant strain worldwide.
Explanation:
Of the two types of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), HIV-1 is the dominant strain among global cases. HIV-2 is not highly transmissible, so Choice (a) is not correct. Since HIV-2 is poorly understood, Choice (c) is not correct. HIV-1 is the more severe strain, making Choice (d) an incorrect choice.
Question 85.
Patients on the cusp of respiratory failure may exhibit which of the following early signs and symptoms?
(a) Decreased respiratory rate
(b) Unconsciousness
(c) Cyanosis
(d) Agitation
Answer:
(d) Agitation
Explanation:
An early sign of respiratory distress is agitation, along with confusion and oxygen hunger. Later signs of respiratory distress occur when the patient has become fatigued because of the respiratory effort they have put forth. These signs include decreased respiratory rate, unconsciousness, and cyanosis.
Question 86.
The nurse is caring for a patient with myasthenia gravis. Altered transmission of which of the following neurotransmitters would the nurse understand guides the care of this patient?
(a) Serotonin
(b) Dopamine
(c) Acetylcholine
(d) Norepinephrine
Answer:
(c) Acetylcholine
Explanation:
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease caused by the altered transmission of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction due to antibody formation. Therefore, Choices (a), (b), and (d) are incorrect.
Question 87.
Your patient is complaining of pain at their IV site. You note phlebitis at the insertion site. What else should you do? Select all that apply.
(a) Tell the patient you will assess them again later.
(b) Discontinue the IV.
(c) Start IV fluids.
(d) Apply a warm compress.
(e) Start a new IV in a different location.
Answer:
(b) Discontinue the IV.
(d) Apply a warm compress.
(e) Start a new IV in a different location.
Explanation:
The IV should be removed and a warm compress should be applied as soon as possible to prevent further damage and for the patient's comfort. A new IV should be started in a different vein. Choice (c), starting IV fluids, would further damage the vessel with phlebitis. Choice (a), telling the patient you will assess them again later, is not helpful.
Question 88.
An English-speaking nurse is completing a history and physical on a newly admitted patient. How should the nurse communicate with a Spanish-speaking patient?
(a) Speak loud and slowly
(b) Use a monotone voice to avoid inflection
(c) Phone the interpreter line for assistance
(d) Request that a family member translate the discussion
Answer:
(c) Phone the interpreter line for assistance
Explanation:
Choice (c) indicates the appropriate professional response by the nurse to address the present language barrier. Choices (a) and (b) would not directly support communication that is free from misunderstanding and should be omitted. Choice (d) would not rely on a professional, non-biased party for translation and should be avoided if possible.
Question 89.
The nurse is caring for a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis. Which of the following statements is consistent with the cause of this disorder?
(a) This condition results from having excess insulin in the body.
(b) Poor management of diabetes can cause this disorder.
(c) Reduced glucose ingestion can lead to this disorder.
(d) Taking too much oral anti-diabetic medication can cause this disorder.
Answer:
(b) Poor management of diabetes can cause this disorder.
Explanation:
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acidotic metabolic state that can be caused by poor diabetic management, leading to hyperglycemia. Diabetic management involves regular visits to the healthcare provider, taking insulin or oral anti-diabetic agents as ordered, following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and monitoring blood glucose levels at home.
Hyperglycemia can occur when the patient does not have enough insulin in the body, making Choice (a) an incorrect answer. Since ingesting high glucose levels leads to hyperglycemia, not reduced glucose levels, Choice (c) is not the correct answer. It can also occur when the oral anti-diabetic management is not sufficient to control high blood glucose levels, making Choice (d) an incorrect answer.
Question 90.
What stage is this pressure ulcer?
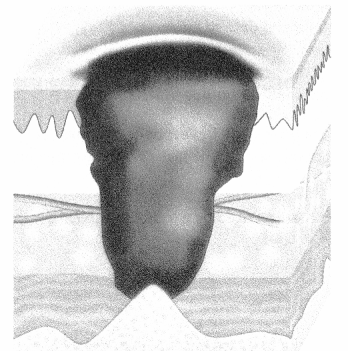
(a) Stage 1
(b) Stage 2
(c) Stage 3
(d) Stage 4
Answer:
(d) Stage 4
Explanation:
This patient has a stage 4 pressure ulcer. The skin breakdown goes down to the level of muscle and bone. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are pressure ulcers that are not as deep.
Question 91.
Which phase of the cardiac cycle involves atrial contraction and is represented by the P wave of the electrocardiogram?
(a) Phase One
(b) Phase Two
(c) Phase Three
(d) Phase Four
Answer:
(a) Phase One
Explanation:
Choice (a), phase one, correlates with atrial contraction, which is represented by the P wave of the electrocardiogram. Atrial contraction accounts for approximately ten percent of ventricular filling at rest. Choice (b) aligns with isovolumetric contraction, Choice (c) represents rapid ventricular ejection, and Choice (d) correlates with slow ventricular ejection, all subsequent processes of the cardiac cycle.
Question 92.
The nurse is viewing a record that contains diverse information from all providers involved in the patient's care. What type of communication system is the nurse using?
(a) Electronic health record (EHR)
(b) Electronic medication administration record (EMAR)
(c) Electronic medical record (EMR)
(d) Personal health record (PHR)
Answer:
(a) Electronic health record (EHR)
Explanation:
The electronic health record (EHR) is a document containing charted documentation from multiple providers across specialties supporting patient care. Choice (c), the medical record (EMR), is a charting system used by one provider, while the patient uses a personal health record (PHR) system (Choice d). Choice 6, electronic medication administration record (EMAR), involves documentation of medication only.
Question 93.
While providing education to a new graduate nurse, the senior nurse details the progression of intestinal obstruction leading to death. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should teach them. Include all options.
(a) Necrosis
(b) Ischemia
(c) Shock
(d) Mechanical obstruction
Answer:
(d) Mechanical obstruction
(b) Ischemia
(a) Necrosis
(c) Shock
Explanation:
The nurse details the progression of intestinal obstruction leading to death by teaching steps in the following order to demonstrate the physiological tissue breakdown and subsequent system¬wide failure. The progression is as follows: mechanical obstruction, ischemia, necrosis, and shock.
Question 94.
You are preparing to go into a patient's room to administer their morning medications. List the order in which the following things should occur:
(a) Confirm the patient's name and date of birth.
(b) Administer the medication.
(c) Confirm the five rights of medication administration.
(d) Educate the patient about medication side effects.
Answer:
(a) Confirm the patient's name and date of birth.
(c) Confirm the five rights of medication administration.
(d) Educate the patient about medication side effects.
(b) Administer the medication.
Explanation:
The correct order is (a), (c), (d), and (b). The patient's identity should be obtained before anything else is done. The other rights included in the five rights should be verified next. The patient can then be educated on the medication. Lastly, the medication is administered.
Question 95.
A patient calls the office to ask how many tablespoons of liquid cough syrup to give her child. The dose is 45 mL. How many tablespoons should she give? Round to the nearest tenth. ................ Tbsp
Answer:
3 Tbsp
Explanation:
1 Tbsp is equal to 15 mL, so 45 mL is equal to 3 Tbsp.
Question 96.
Which type of social norm is characterized by a moral or ethical component?
(a) Taboos
(b) Group norms
(c) Folkways
(d) Mores
Answer:
(d) Mores
Explanation:
Mores are social norms that are particularly characterized by a moral component. They are often established through religious systems, and violations of mores are likely to lead to formal or informal sanction. Folkways are the daily customs and traditions of a society. Taboos are the behaviors that are so strictly forbidden by a society that ostracism may occur if a person violates them.
Question 97.
Where should the nurse place the diaphragm of their stethoscope to assess the patient's apical pulse? Place an X to mark your answer.
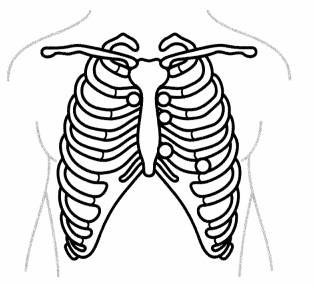
Answer:
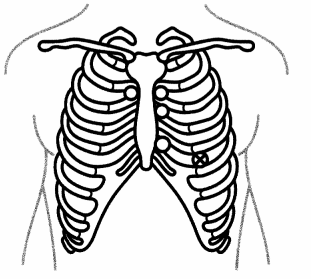
Explanation:
The apical pulse can be assessed at the apex of the heart, which is located at the fourth intercostal space at the midclavicular line. This location is the point of maximal impulse (PMI).
Question 98.
Which area of the body is the most distal to the heart? Place an X to mark your answer.
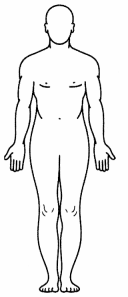
Answer:
Explanation:
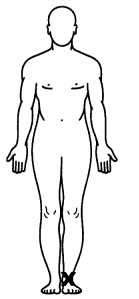
Distal locations indicate areas of the body that are further away from either the trunk or a given reference point, in this case the heart. The foot is the most distal area of the body from the heart. Conversely, proximal is closer to the trunk or a given reference point.
Question 99.
Which stage of disease is a patient noted to be experiencing when they are asymptomatic following exposure to a pathogenic organism?
(a) Incubation period
(b) Prodromal period
(c) Acute period
(d) Convalescence period
Answer:
(a) Incubation period
Explanation:
The incubation period, Choice (a), is the stage of disease where the individual often does not yet realize that they have been exposed to a pathogenic organism, as they are asymptomatic. This stage makes up the period of time from exposure to when symptoms become apparent. The prodromal period, Choice (b), represents the stage during which symptoms are first noted and may be vague in presentation.
The acute period, Choice (c), represents the stage of disease that has progressed to include a worsening of symptoms that are specific to pathogen and illness. The convalescence period, Choice (d), signifies the stage involving a gradual reduction of symptoms and recovery of health after illness.
Question 100.
During a respiratory physical assessment of a patient with shortness of breath, which action should the nurse perform second?
(a) Inspection
(b) Percussion
(c) Palpation
(d) Auscultation
Answer:
(c) Palpation
Explanation:
Palpate, Choice (c), represents the second step of a respiratory physical assessment. The nurse should first perform Choice (a), inspect, then Choice (c), palpate, followed by Choice fi, percuss, and finally Choice (d), auscultate. This sequence of techniques is standard for physical assessments except when performing an abdominal assessment to promote accuracy in findings.
Question 101.
Which image of the heart should the nurse use to provide patient education on atrioventricular septal defect?
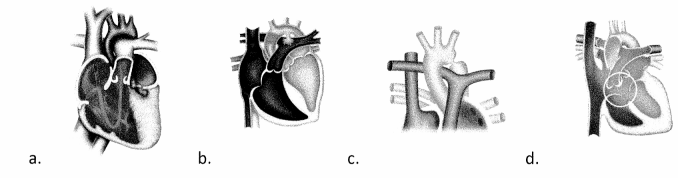
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice (d) represents the image of the heart that the nurse should use to provide patient education on atrioventricular septal defect. Choice (a) displays an image of hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Choice (b) displays an image of patent ductus arteriosus. Choice (c) displays an image of coarctation of the aorta. Providing an image to correlate with verbal discussion supports the patient to visualize their condition.
Question 102.
What is the specific pathology responsible for brain damage in Alzheimer's disease?
(a) Invasion of the cortex by infectious prions
(b) Multiple hemorrhagic strokes
(c) Deposition of amyloid-(3 plaques
(d) Formation of Lewy bodies
Answer:
(c) Deposition of amyloid-(3 plaques
Explanation:
The destruction of brain tissue in Alzheimer's disease is the result of amyloid-P plaque formation in the cerebral cortex. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is a rare form of dementia that results from tissue damage caused by infectious prions; therefore, Choice (a) is incorrect. Multiple hemorrhagic strokes may be a trigger for the deposition of amyloid-P plaque formation; however, this form of damage can exist without causing Alzheimer's disease. It is not the specific causative process for the disease; therefore, Choice (b) is incorrect. The formation of Lewy bodies is responsible for the damage associated with Parkinson's disease, not Alzheimer's disease; therefore, Choice (d) is incorrect.
Question 103.
The nurse prepares a chest drainage system. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Fill water-seal chamber to 2 cm
(b) Pour saline into suction control port
(c) Place funnel in tubing
(d) Stand drainage system upright
Answer:
(d) Stand drainage system upright
(c) Place funnel in tubing
(b) Pour saline into suction control port
(a) Fill water-seal chamber to 2 cm
Explanation:
The nurse prepares a chest drainage system via steps performed in the following order to ensure the equipment is properly functioning to assist with the facilitation of drainage and healing. The nurse should stand the drainage system upright, place the funnel in tubing, pour saline into the suction control port, and then fill the water-seal chamber to 2 cm.
Question 104.
Identify the maxillary sinus.
Answer:
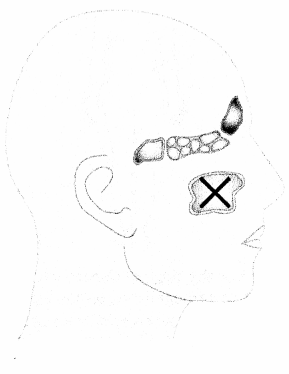
Explanation:
The maxillary sinuses are the most inferior of the paranasal sinuses. The frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses, listed front to back, are superior to the maxillary sinuses.
Question 105.
Review the electronic medication administration record. Which medication, if any, should be administered for pain management?
Electronic Medication Administration Record fEMAR)
Tab 1, EMAR Order 1 Carbamazepine 800 po qam
Tab 2, EMAR Order 2 Tramadol 50 mg po q6h
Tab 3, EMAR Order 3 Valsartan 80 mg po qam
(a) The patient needs a medication order for pain management.
(b) Carbamazepine
(c) Tramadol
(d) Valsartan
Answer:
(c) Tramadol
Explanation:
Choice (c) represents an analgesic medication prescribed for pain management. Choice (a) is incorrect, as the patient currently has an order for a medication that supports pain management. Choice (b) targets seizure disorders. Choice (d) targets hypertension.
Question 106.
Which communication technique hinders the discussion between the nurse and the patient?
(a) Empathetic engagement
(b) Open-ended questions
(c) Nurse-focused answers
(d) Restating
Answer:
(c) Nurse-focused answers
Explanation:
Choice (c) represents a hindrance to the development of a therapeutic nurse-to-patient discussion and should be avoided. Choice (a) displays understanding, Choice (b) encourages deeper dialogue, and Choice (d) shows comprehension of what the patient communicated.
Question 107.
Before administering Catapres® (clonidine), which action does the nurse delegate to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)?
(a) Assist the patient with eating their meal.
(b) Ask the patient for the time of their last bowel movement.
(c) Take the patient's vital signs.
(d) Deliver a heated blanket to the patient's lower extremities.
Answer:
(c) Take the patient's vital signs.
Explanation:
The nurse should ensure that the patient's vital signs are taken before administering Catapres® (clonidine), Choice (c), as this medication often reduces blood pressure and pulse. While this medication is indicated to treat hypertension, it also is used outside of this indication, such as in the management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, anxiety, and sleep.
Taking patient vital signs is an appropriate task to delegate to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Assisting the patient with eating their meal and asking about the time of their last bowel movement (Choices a and b), while important interventions in daily patient care, do not directly influence the administration of Catapres® (clonidine); therefore, they are not current priorities. Delivering a heated blanket, Choice (d), does not directly impact the administration of this medication and is typically reserved to support circulatory concerns.
Question 108.
Your patient has a stage 3 pressure ulcer on his sacrum. You are preparing to do a dressing change. List the order in which the following things should occur:
(a) Educate the patient.
(b) Gather supplies.
(c) Check the order.
(d) Change the dressing.
Answer:
(c) Check the order.
(b) Gather supplies.
(a) Educate the patient.
(d) Change the dressing.
Explanation:
The correct order is (c), (b), (a), and (d). The order should always be double checked before performing a dressing change. Once the order has been verified, the supplies can be obtained. Educating the patient follows, and lastly, the dressing is changed.
Question 109.
A patient is admitted with a diagnosis of heart block. The nurse is aware that the pacemaker of the heart is which of the following?
(a) AV node
(b) Purkinje fibers
(c) SA node
(d) Bundle of His
Answer:
(c) SA node
Explanation:
The SA, or sinoatrial, node is the heart's natural pacemaker. The AV node, which is positioned between the atria and ventricle, receives the impulse from the SA node. The Purkinje fibers are the end point of the conduction system. These fibers spread out across the ventricles after receiving the impulse through the Bundle of His. The Bundle of His receives the impulse from the AV node.
Question 110.
A fifteen-year-old male patient is prescribed Haldol® (haloperidol) while inpatient at a psychiatric hospital. The nurse is concerned after the patient complains of nipple discharge from the left breast with subsequent focused assessment findings revealing swelling, pain, and tenderness. What side effect of this medication is the nurse concerned the patient may be experiencing?
(a) Stevens-Johnson syndrome
(b) Nystagmus
(c) Gynecomastia
(d) Schizoaffective disorder
Answer:
(c) Gynecomastia
Explanation:
Choice (c), gynecomastia, describes the patient's current symptom presentation and is a side effect of Haldol® (haloperidol) and other psychotropic use. This condition is caused by a secondary hormonal imbalance in which estrogen is elevated. Choice (a) and Choice (b) are both associated with psychotropic use; however, they do not correlate with the patient assessment at this time.
Stevens- Johnson syndrome is a rare disorder of the skin and membranes, whereas nystagmus involves uncontrollable ocular movements. Schizoaffective disorder (Choice d) represents a psychiatric illness that may encourage the prescription of this medication, though not the side effects of its use.
Question 111.
The nurse manager of a busy unit continuously incorporates a charismatic leadership style, despite the challenging work environment. Which description aligns with the manager's style of leadership?
(a) Follows rules closely and avoids flexibility in action
(b) Incorporates eloquent communication that inspires junior staff to admire them
(c) Commits to the growth of each team member through high emotional intelligence and advanced conflict-resolution skills
(d) Judges team members on performance, while offering little support
Answer:
(b) Incorporates eloquent communication that inspires junior staff to admire them
Explanation:
Choice (b) incorporates the characteristics witnessed within the charismatic leadership style. Choice (a) incorporates characteristics of the bureaucratic leadership style. Choice (c) incorporates characteristics of the transformational leadership style. Choice (d) incorporates characteristics of the transactional leadership style.
Question 112.
What is the purpose of conducting an interdisciplinary 5 Whys Analysis?
(a) Report the near miss to the correct agency
(b) Identify the person at fault for an issue
(c) Understand the root cause of an incident
(d) Develop a chain-of-command for the elevation of a concern
Answer:
(c) Understand the root cause of an incident
Explanation:
Choice (c) describes the chief reason for conducting a 5 Whys Analysis, which is to understand the root cause of an incident. Choices (a) and (d) represent potential gains from conducting this analysis but not the main purpose. Choice (b) may be deduced from this analysis but is not the main goal. The focus is on understanding and planning rather than on punitive consequences.
Question 113.
What patient condition would require the nurse to wear a surgical mask?
(a) Severe acute respiratory syndrome
(b) Influenza B virus
(c) Asthma
(d) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Answer:
(b) Influenza B virus
Explanation:
Choice (b) requires the nurse to don a surgical mask while interacting with the patient. Choice (a) requires the nurse to don an N95 respirator while working with the patient. Choices (c) and (d) do not require respiratory shielding.
Question 114.
Which deviance theory explains deviance as a learned behavior?
(a) Labeling theory
(b) Differential association
(c) Strain theory
(d) Observational learning
Answer:
(b) Differential association
Explanation:
Differential association asserts that deviant behavior has been learned through observation of others. Labeling theory looks at the power of labels in marking certain behavior as deviant. Strain theory assigns blame to the society structure for the deviant behavior. Observational learning does not apply in this context, as it covers a much broader range of behaviors than just deviance.
Question 115.
Which ambulatory aid is NOT appropriate for patient-use following a cerebral vascular accident with left-sided affliction?
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice (a) should be omitted from consideration for patient-use following a cerebral vascular accident with left-sided affliction as crutches are contraindicated; canes and walkers should be considered. Choices (b), (c), and (d) indicate potential options for ambulatory support for this patient, as they provide steady reinforcement. Consultation with the care team regarding patient-specific needs assists in identifying the best ambulatory aid for each unique patient.
Question 116.
Which hormone's primary function is to influence the kidneys to balance the amount of water excreted in urine?
(a) Follicle-stimulating hormone
(b) Antidiuretic hormone
(c) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
(d) Luteinizing hormone
Answer:
(b) Antidiuretic hormone
Explanation:
Antidiuretic hormone is a hormone that primarily functions to encourage the kidneys to balance the amount of water excreted in the urine. This hormone supports healthy blood pressure and volume. Follicle-stimulating hormone, Choice (a), is involved with pubertal development in both males and females. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone, secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, regulates the production of cortisol and androgen. Thus, Choice (c) is incorrect. Luteinizing hormone, Choice (d), influences ovulation and the production of testosterone.
Question 117.
A nurse is looking to provide information regarding a patient to another nurse utilizing audiotape technology. What is this process referred to as?
(a) Consultation
(b) Case management
(c) Documentation
(d) Report
Answer:
(d) Report
Explanation:
The verbal handoff from nurse-to-nurse between shifts is referred to as a report. When the nurse uses an audiotape device to record critical components and an overall review of the shift for each patient, they are preparing a verbal recap of the care given for the next shift to consider. Choices (a), (b), and (c) do not involve leaving patient information on audiotape for another nurse to review.
Question 118.
During discharge education, the nurse recognizes that the patient has a clear understanding of most of the considerations for taking the prescribed Doxycycline for Lyme disease treatment. What statement made by the patient alerts the nurse that some additional teaching is necessary?
(a) "I will take my medication with a full glass of water."
(b) "I will not take iron supplements within two hours of this medication."
(c) "I can continue breastfeeding while on this medication."
(d) "I need to use a nonhormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy."
Answer:
(c) "I can continue breastfeeding while on this medication."
Explanation:
The patient should not continue breastfeeding, Choice (c), as breastfeeding is contraindicated with this medication because the medicine could affect bone and tooth development in the infant. Doxycycline should be taken with a full glass of water, and iron supplements should not be consumed within two hours of this medication to support maximum absorption and disease treatment.
Therefore, Choices (a) and (b) are incorrect because the statements indicate that the patient understands these factors. The patient needs to use a nonhormonal birth control method to prevent pregnancy, which would put a developing fetus at risk. Doxycycline can reduce the efficacy of hormonal birth control pills. Therefore, Choice (d) is incorrect.
Question 119.
While providing patient and family education regarding nervous system functions, which function does the nurse include in their teaching when discussing the parasympathetic nervous system?
(a) Bronchi dilation
(b) Reduced gastrointestinal motility
(c) Decreased heart rate
(d) Increased cardiac conduction
Answer:
(c) Decreased heart rate
Explanation:
Choice (c) is a function of the parasympathetic nervous system, along with such functions as bronchi constriction and increased gastrointestinal motility. Choices (a), 6, and (d) are all functions of the sympathetic nervous system.
Question 120.
Which statement made by the nurse encourages a therapeutic engagement with the patient awaiting test results post mastectomy?
(a) "Tell me more about how you feel."
(b) "If the margins aren't clear, you should explore your feelings with your therapist."
(c) "I have worked with many patients faced with your situation."
(d) "If it were me, I would wait until I knew more before deciding what to do next."
Answer:
(a) "Tell me more about how you feel."
Explanation:
While encouraging a therapeutic engagement with a patient awaiting test results post mastectomy, the nurse should produce a statement that encourages the patient to explore their feelings, such as that in Choice (a). The statements in Choices 6, (c), and (d) are nurse-centered, not patient- centered, and should be avoided.
Question 121.
While providing patient education, the nurse explains that the patient's medication dosage will need to be adjusted to find the most therapeutic level. What is this measured medication practice an example of?
(a) Medication compliance
(b) Medication reconciliation
(c) Medication titration
(d) Medication administration
Answer:
(c) Medication titration
Explanation:
Medication titration, Choice (c), involves titrating the dosage to reach a therapeutic level, as it encourages careful consideration to achieve the maximum benefit without adverse reaction. Medication compliance, Choice (a), involves patient agreement and fulfillment of medication intake. Medication reconciliation, Choice (b), describes the process of creating a list of medications taken. Medication administration, Choice (d), involves the practice of delivering medication for intake.
Question 122.
The nurse reviews the provider's order, which reads "750 mL of D5W to infuse over 7 hours." The drop factor is 10 gtts/mL. What drip rate should the nurse set this infusion at?
(a) 18 gtts/min
(b) 420 gtts/min
(c) 36 gtts/min
(d) 75 gtts/min
Answer:
(a) 18 gtts/min
Explanation:
Choice (a), 18 gtts/min, represents the appropriate drip rate for this patient's infusion. Choice (b), Choice (c), and Choice (d) represent common mistakes in drip rate miscalculation that must be avoided to prevent injury to the patient. Dividing the total volume in milliliters by the time in minutes, then multiplying that quotient by the drop factor in drops per milliliter calculates the drip rate. The drop factor can be found on the tubing package.
Question 123.
Your patient comes into the ER with an acute myocardial infarction (Ml). What signs and symptoms would you expect to see? Select all that apply.
(a) Chest pain
(b) Nausea and vomiting
(c) Shoulder pain
(d) Abnormal EKG
(e) Elevated cardiac enzymes
Answer:
(a) Chest pain
(b) Nausea and vomiting
(c) Shoulder pain
(d) Abnormal EKG
(e) Elevated cardiac enzymes
Explanation:
These are all signs and symptoms of an acute Ml.
Question 124.
The patient has had 64 ounces of water today. How many milliliters have they had? ................. mL
Answer:
1,920 mL
Explanation:
1 ounce is equal to 30 mL, so 64 ounces is equal to 1,920 mL.
Question 125.
Which member of the interdisciplinary team should the nurse consult with regarding patient dressing and hygiene aids?
(a) Physical therapist
(b) Social worker
(c) Occupational therapist
(d) Case manager
Answer:
(c) Occupational therapist
Explanation:
Choice (c) represents the member of the interdisciplinary team that the nurse should consult with regarding patient dressing and hygiene aids, as such aids are required for daily functioning and within the role of the occupational therapist. Choice (a) supports strength in movement. Choice (b) aligns services for quality of life and overall functioning. Choice (d) manages care coordination between disciplines.
Question 126.
The patient needs to use a nebulizer at home with 1 mL vials of albuterol. The concentration is 5 mg/mL. The patient needs 7.5 mg of albuterol. How many vials do they need? Round to the nearest tenth ...................... vials
Answer:
1.5 vias.
Explanation:
There are 5 mg in one vial. Therefore 1.5 vials are needed for 7.5 mg.
Question 127.
Which of the following drugs is often used for treatment of acute seizure activity?
(a) Memantine HCl
(b) Phenytoin
(c) Pregabalin
(d) Rifaximin
Answer:
(b) Phenytoin
Explanation:
Phenytoin is FDA approved for most types of seizures. Memantine is a neurological drug used to treat dementia. Pregabalin is a drug used to treat diabetic neuropathy. Rifaximin is a drug used to treat hepatic encephalopathy.
Question 128.
A patient is in the outpatient clinic for a same-day mole removal. Which type of anesthetic is most appropriate for this type of procedure?
(a) Nerve block
(b) Local
(c) Regional
(d) General
Answer:
(b) Local
Explanation:
A patient who is undergoing a minimally invasive procedure such as a mole removal will only need a local anesthetic such as topical lidocaine. A regional nerve block affects only one part of the body, usually targeting the epidural, spinal, or paravertebral regions. General anesthesia is used for major surgeries in which the patient needs to be rendered completely unconscious to perform the procedure.
Question 129.
While the nurse case manager is participating in the psychiatric treatment team meeting, they inquire about the discharges scheduled for the next day. Which patient does the nurse case manager advocate to be rescheduled for discharge several days out?
(a) The patient who had their last round of electroconvulsive therapy this morning
(b) The patient who needs a prior authorization to fill their medication post discharge
(c) The patient who started Clozaril® (clozapine) yesterday
(d) The patient complaining of a headache after missing lunch today
Answer:
(c) The patient who started Clozaril® (clozapine) yesterday
Explanation:
The patient who started Clozaril® (clozapine) yesterday should not be scheduled for discharge tomorrow, as this medication must be closely followed and blood work must be monitored for therapeutic level and neutropenia before scheduling a safe discharge home.
Choices (a), (b), and (d) represent patients who can all be safely discharged tomorrow, since their treatment considerations do not require additional time to support. Electroconvulsive therapy does not necessitate continued observation, a prior authorization can be completed the same day, and a headache after missing a meal is a normal finding.
Question 130.
Which of the following illustrations outlines the proper location for placement of an NG tube?
Answer:

Explanation:
Choice (b) points to the esophagus. A is the stomach, C is the duodenum, and D is the jejunum.
Question 131.
The nurse has a client who has recently undergone abdominal surgery with a large incision site. The nurse knows that which of the following is not a sign that the wound has become infected?
(a) Redness
(b) Coolness
(c) Heat
(d) Swelling
Answer:
(b) Coolness
Explanation:
The classic signs of infection are redness, heat, and swelling. If the wound is cool to the touch but appears normal otherwise, that is not suggestive of a developing infection. It may be a sign of decreased blood flow to the site, but the nurse should do a full assessment before jumping to that conclusion.
Question 132.
Which bed position supports the patient to assume a semi-Fowler's position?
Answer:

Explanation:
Choice (c) supports the patient to assume a semi-Fowler's position. Choice (a) supports a supine or prone position. Choice (b) supports a high-Fowler's position. Choice (d) supports a Trendelenburg position. A semi-Fowler's position is especially useful for promoting lung expansion and reducing the risk of aspiration.
Question 133.
What is the activity of providing patient-centered care via a modified scientific method of sequential steps called?
(a) Nursing process
(b) Ethical guidance
(c) Health maintenance
(d) Cultural competence
Answer:
(a) Nursing process
Explanation:
The nursing process contains five sequential steps that function as a guiding system for nursing care. The steps of the nursing process include: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation. These steps promote a rational method of organizing and implementing care.
Question 134.
After presenting to the emergency department with flu-like symptoms, the nurse takes the patient's vital signs. What stage of the nursing process is the nurse functioning in during this interaction?
(a) Planning
(b) Assessment
(c) Diagnosis
(d) Implementation
Answer:
(b) Assessment
Explanation:
Taking vital signs aligns with the assessment stage of the nursing process, so Choice (b) is correct. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are later stages to be engaged in after assessing the patient, which in this case involves taking their vital signs. The pneumonic ADPIE can be used to remember the stages of this process: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation.
Question 135.
After noting significant stress in the patient recovering from a motor vehicle accident, the homecare case manager recognizes the patient is exhibiting irritability, frustration, and poor concentration. The nurse also assesses that the patient's vital signs have improved since the previous home visit last week. Which stage of the general adaptation syndrome is the patient presently functioning in?
(a) Homeostasis
(b) Alarm
(c) Resistance
(d) Exhaustion
Answer:
(c) Resistance
Explanation:
Choices (a), (b), (c), and (d) all represent stages of the general adaptation syndrome. Flowever, only Choice (c), resistance, is correlated with the symptoms of irritability, frustration, and poor concentration, along with an improvement in vital signs. As the patient moves past the alarm stage and into the resistance stage, the blood pressure and pulse reduce to more normalized levels. Alarm (Choice b) is considered the second stage, as it directly follows the homeostatic period (Choice a), and then is continued by resistance (Choice c) and exhaustion (Choice d).
Question 136.
What signs and symptoms support the diagnosis of left-sided heart failure when found in a patient presenting to the emergency department with chest pain? Select all that apply.
(a) Sudden weight gain
(b) Pulsus alternans
(c) Nocturia
(d) Hepatomegaly
(e) Non-productive nocturnal cough
Answer:
(a) Sudden weight gain
(b) Pulsus alternans
(e) Non-productive nocturnal cough
Explanation:
Choices (a), (b), and (e) support a diagnosis of left-sided heart failure, while Choices (c) and (d) support a diagnosis of right-sided heart failure. Additional symptoms of left-sided heart failure include dyspnea and orthopnea. While a patient with left-sided heart failure may experience a sudden increase in weight as the disease progresses, additional fluid accumulates as diffuse edema and progressive weight increase is noted.
Question 137.
Which food item should the nurse encourage a patient to avoid because it would pose the greatest risk for someone with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)?
(a) Bokchoy
(b) Rice
(c) Wheat crackers
(d) Blue cheese
Answer:
(d) Blue cheese
Explanation:
Choice (d) indicates a food item that is risky for the patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) to consume. Blue cheese is an unpasteurized food item and should be omitted from the therapeutic diet, along with unpasteurized drinks, meats, and raw or undercooked animal products. Choices (a), (b), and (c) are considered safe to consume as they do not pose any direct risks to the health of a patient with AIDS.
Question 138.
The patient is on a 1,500 mL/24-hour fluid restriction. The 24-hour cycles are from 0600 to 0600. At midnight, the patient requests a drink. So far he has had 48 ounces of fluid to drink. How many milliliters can you give him until 0600? .................. mL
Answer:
60 mL
Explanation:
There are 30 ml per ounce. The patient has had 48 ounces, or 1,440 mL. 1,500 minus 1,440 mL is 60 mL.
Question 139.
The nurse is assessing the five-minute Apgar score of a newborn. The newborn has pink skin, an apical pulse rate of 120 beats per minute, cries when stimulated, and strong muscle tone. Which Apgar score would the nurse assign to this newborn?
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 8
(d) 10
Answer:
(d) 10
Explanation:
When performing a newborn Apgar assessment, the highest score that may be assigned is 10. This score indicates that the newborn has pink skin without evidence of cyanosis, an apical heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute, cries or pulls away when stimulated, firm muscle tone, and a strong cry. Therefore, Choices (a), (b), and (C) are incorrect.
Question 140.
A 28-year-old patient presents to a routine biannual appointment with endocrinology. Review the medical record. Which finding is outside of normal limits, especially given this patient's history?
Medical Record:
Tab 1, Medical diagnosis Grave's disease
Tab 2, Vital signs Heart rate 80 beats per minute, respirations 22 breaths per minute, blood pressure 122/82 mmHg, oxygen saturation 100% on room air, temperature 98.9 degrees Fahrenheit
Tab 3, Labs TSH 5.8 mlU/L, albumin 4.2 g/dL, glucose 98 mg/dL
(a) Glucose 98 mg/dL
(b) Albumin 4.2 g/dL
(c) TSH 5.8 mlU/L
(d) Heart rate 80 beats per minute
Answer:
(c) TSH 5.8 mlU/L
Explanation:
Choice (c) identifies an elevated TSH level, which is above 5 mlU/L. Given the patient's condition of Grave's disease, the TSH level is generally expected to be low. Choices (a), (b), and (d) indicate normal findings.
Question 141.
Blood type is a trait determined by multiple alleles, and two of them are co-dominant: IA codes for A blood and IB codes for B blood, while / codes for O blood and is recessive to both. If an A heterozygote individual and an O individual have a child, what is the probably that the child will have A blood?
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 75%
(d) 100%
Answer:
(b) 50%
Explanation:
The child has a 2 out of 4 chance (50%) of having A-type blood, since the dominant allele lA is present in two of the four possible offspring. The O-type blood allele is masked by the A-type blood allele since it is recessive. Test takers can sketch out a Punnett square to better visualize.
Question 142.
Which statement is NOT true about RNA?
(a) It can be single-stranded
(b) It has ribose sugar
(c) It contains uracil
(d) It only exists in three forms
Answer:
(d) It only exists in three forms
Explanation:
There are actually many different types of RNA. The three involved in protein synthesis are messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA). Others, including small interfering RNA, microRNA, and piwi-interacting RNA, are being investigated. Their known functions include gene regulation and facilitating chromosome wrapping and unwrapping. RNA, unlike DNA, can be single stranded (mRNA, specifically), has a ribose sugar (rather than deoxyribose, like in DNA), and contains uracil (in place of thymine in DNA).
Question 143.
What is the term used for the set of metabolic reactions that convert the energy in chemical bonds to ATP?
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Reproduction
(c) Active transport
(d) Cellular respiration
Answer:
(d) Cellular respiration
Explanation:
Cellular respiration is the term used for the set of metabolic reactions that convert the energy in chemical bonds to ATP. All cellular respiration starts with glycolysis in the cytoplasm, and in the presence of oxygen, the process will continue to the mitochondria. In a series of oxidation/reduction reactions, primarily glucose will be broken down so that the energy contained within its bonds can be transferred to the smaller ATP molecules. It's like having a $100 bill (glucose) as opposed to having one hundred $1 bills. This is beneficial to the organism because it allows energy to be distributed throughout the cell very easily in smaller allotments as needed, so that less is wasted.
When glucose is broken down, its electrons and hydrogen atoms are involved in oxidative phosphorylation in order to make ATP, while its carbon and oxygen atoms are released as carbon dioxide. available oxygen in the muscles can lead to anaerobic ATP production in a process called lactic acid fermentation. Alcohol fermentation is another type of anaerobic respiration that occurs in yeas . Anaerobic respiration is much less efficient than aerobic respiration, as it has a net yield of 2 ATP, while aerobic respiration's net yield exceeds 30 ATP.
Question 144.
Which of the following regarding bacterial spores is NOT true?
(a) Spores allow survival during adverse conditions
(b) Bacteria enter spore form during the lag phase
(c) Not all bacteria are capable of producing spores
(d) Spores can germinate into the vegetative form
Answer:
(b) Bacteria enter spore form during the lag phase
Explanation:
Not all bacteria are capable of producing spores, but those that can have a developed an advantage to survive during unfavorable environmental conditions. This most frequently occurs during the final stage of the bacterial growth cycle - decline or death. During this stage, the death rate of the population exceeds the new cell production rate, because the environment and resources cannot support the population. By surviving as a spore, the bacteria can flourish back to vegetative form when the adverse conditions subside.
Question 145.
What is unique about retroviruses?
(a) They can create spores
(b) They enter the host in RNA form then get converted to DNA form
(c) They enter the host in DNA form then get converted to RNA form
(d) They do not need a host to reproduce
Answer:
(b) They enter the host in RNA form then get converted to DNA form
Explanation:
Opposite to the normal flow of information in a cell, retroviruses enter the host cell in RNA form and then must get converted to DNA form via an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. Like all viruses, they need a host cell to reproduce. Viruses do not produce spores.
