Regular practice with NCLEX PN Practice Questions enhances critical thinking skills, which are vital for making sound clinical decisions.
NCLEX-PN Practice Test 1 with Rationale
Question 1.
When preparing a patient for the insertion of a central venous access device (CVAD), the nurse explains that the benefits of a CVAD include all except which of the following?
(a) Easier-to-obtain frequent blood draws
(b) Administration of large amounts of medications and fluids
(c) Decreased peripheral sticks and peripheral inflammation
(d) Decreased risk of infection
Answer:
(d) Decreased risk of infection
Explanation:
Though there are many benefits to the CVAD, it still poses a risk for infection to the patient, even more so than a peripheral device, as it is more centric to the patient's circulatory system and vital organs. The CVAD has many benefits, including being able to provide easy access for blood draws; the capacity to deliver large amounts of blood, drugs, and fluids to the patient; and decreasing peripheral sticks and the inflammation that goes along with those. The use of the CVAD must be carefully decided, weighing the pros against the cons.
Question 2.
Which statement best describes the evaluation phase of the nursing process?
(a) Subjective, objective, and psychosocial data are gathered in this phase.
(b) Nursing diagnoses are formulated during the evaluation phase.
(c) Evaluation happens across the continuum of the nursing process.
(d) This phase often begins with educating the patient on expected outcomes.
Answer:
(c) Evaluation happens across the continuum of the nursing process.
Explanation:
The final phase of the nursing process is evaluation; however, evaluation happens across the continuum of the nursing process, not just at the end. The nurse frequently evaluates the effectiveness of care plans, adjusts as necessary, and reevaluates. Data is collected during the assessment phase. Nursing diagnoses are formulated in the diagnosis phase. The implementation phase often begins with educating the patient on expected outcomes.
Question 3.
Which of the following items rules a person out for being an organ donor?
(a) Elderly
(b) Overweight
(c) Substance abuse
(d) Resolved case of depression
Answer:
(c) Substance abuse
Explanation:
Substance abuse, as well as chronic disease, alcohol abuse, and communicable diseases potentially rule out a person from being an organ donor. A strict list of criteria must be met for organ donation to occur. These criteria ensure the health and viability of the organs and tissues to be donated. Age, weight, and previous psychiatric illness do not necessarily rule a person out for organ donation.
Question 4.
Which ocular positioning aligns with the patient's diagnosis of exotropia?
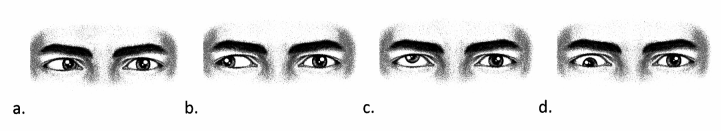
Answer:

Explanation:
Choice (b) aligns with the ocular positioning that accompanies a diagnosis of exotropia with an outward turn. Choice (a) aligns with esotropia, with an inward turn. Choice (c) aligns with hypertropia, with an upward turn. Choice (d) aligns with hypotropia, with a downward turn.
Question 5.
Of the following patients, which one has the highest risk for skin injury?
(a) An elderly woman in an assisted-living facility who ambulates with a cane
(b) An eighty-year-old man in the hospital recovering from hip surgery
(c) A seventy-year-old man hospitalized for pneumonia
(d) An elderly woman who is incontinent of stool and is showing signs of confusion
Answer:
(d) An elderly woman who is incontinent of stool and is showing signs of confusion
Explanation:
An elderly woman who is incontinent of stool will need frequent linen changes and cleansing of her bottom. The constant moisture has a very high potential for causing skin breakdown. She is also showing signs of confusion, which means she may become agitated and unaware of her surroundings, leading to potential bruises or tears on her extremities. The other patient scenarios described are also at risk for skin injury. However, with the information given, (d) is the patient with the highest risk.
Question 6.
The nurse is providing telephonic guidance to a 31-year-old patient who is 36 weeks pregnant regarding distinguishing between true and false labor. Which contraction findings does the nurse explain are likely due to false labor? Select all that apply.
(a) Consistently regular and closer together
(b) Cease with walking
(c) Felt in abdomen above umbilicus
(d) Radiate to lower abdomen from lower back
(e) Temporarily regular
Answer:
(b) Cease with walking
(c) Felt in abdomen above umbilicus
(e) Temporarily regular
Explanation:
Choices (b), (c), and (e) typically align with false labor, which also includes cessation of contractions when comfort measures are included. Choices (a) and (d) typically indicate true labor, which becomes more intense while walking and continues regardless of comfort.
Question 7.
By definition, competent bacteria can do which of the following?
(a) Transformation
(b) Transduction
(c) Conjugation
(d) Form a sex pilus
Answer:
(a) Transformation
Explanation:
Competent bacteria can perform the process of transformation, wherein they can absorb and incorporate foreign DNA from their environment into their own chromosomal DNA. Some bacteria are naturally competent, while others, under certain laboratory conditions, can become competent. Transduction is a term used with viral replication and is the process by which some portion of the host cell's chromosome gets packaged and transferred out of the cell in the new copy of the virus, and then gets incorporated into the next host cell when the virus delivers its viral DNA.
Question 8.
The nurse is providing patient instruction on obtaining a sterile specimen, also known as a clean catch, for an uncircumcised male patient. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should instruct the patient to perform them. Include all options.
(a) Clean meatus
(b) Retract foreskin
(c) Catch urine stream in cup uninterrupted
(d) Void a small amount into toilet
Answer:
(b) Retract foreskin
(a) Clean meatus
(d) Void a small amount into toilet
(c) Catch urine stream in cup uninterrupted
Explanation:
The nurse should instruct the patient to perform the steps for collecting a sterile specimen in the following order to maintain aseptic technique so that testing is accurate and reliable. The patient should retract the foreskin, clean the meatus, void a small amount into the toilet, and then catch the urine stream in a cup uninterrupted.
Question 9.
What is the last stage in Freud's model of the five stages of human development?
(a) Latent stage
(b) Adult stage
(c) Genital stage
(d) Self-Actualization stage
Answer:
(c) Genital stage
Explanation:
The Genital stage starts in adolescence and lays the groundwork for future life relationships. As one enters adolescence, sexual identity and orientation begin to develop. Values regarding sexuality, views
about the opposite sex, and the process of interacting with others on a more intimate level occur. These more mature elements of relationship-building lay the foundation for future relationships, but not only from a sexual standpoint. Choice (a), the Latent stage, occurs from age 6 to puberty, and it is a time when the child's sexual energy becomes somewhat dormant. Choices (b) and (d) are not included in Freud's model of human development.
Question 10.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Self-destruction ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming oneself, while global destruction ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming others.
(b) Suicidal ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming oneself, while homicidal ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming others.
(c) Internal ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming oneself, while external ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming others.
(d) Intrinsic ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming oneself, while extrinsic ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming others.
Answer:
(b) Suicidal ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming oneself, while homicidal ideation is characterized by thoughts of harming others.
Explanation:
Suicidal ideation is characterized by recurrent thoughts of suicide, ranging from passive ideation to active ideation. Homicidal ideation is characterized by thoughts or plans to kill another person or a group of people.
Question 11.
Which of the following terms refers to a state in which the client has a lower than normal count of platelet cells?
(a) Neutropenia
(b) Anemia
(c) Thrombocytopenia
(d) Leukopenia
Answer:
(c) Thrombocytopenia
Explanation:
Thrombocytopenia means that there are a lower than normal number of platelets in the blood. The term comes from the root word "thrombocyte." The prefix "thrombo-" means clot, and the suffix "-cyte" means cell. These cells are responsible for the body's ability to stop bleeding by forming a clot. Neutropenia and leukopenia are used interchangeably to refer to a lowered white blood cell count. Neutrophils, the root word for neutropenia, are the largest portion of the white blood cells. If the neutrophils are significantly lowered, then leukopenia results, thus the interchangeability of the words Anemia refers to a lower than normal count of red blood cells and reduces the body's ability to carry and deliver oxygen.
Question 12.
The action created by a drug is known as what?
(a) Pharmacology
(b) Side effect
(c) Adverse reaction
(d) Intended effect
Answer:
(a) Pharmacology
Explanation:
The nurse should review the pharmacology, or the action created by a drug, of the patient's current medications. Knowing the pharmacological effects of these medications and those of the scheduled preoperative medications can help keep the patient safe. Side effects and adverse reactions are included in the pharmacology. The intended effect does not include possible side effects or adverse reactions.
Question 13.
Upon analysis of the following fetal heart rate and maternal contraction readings gained from electronic fetal monitoring, which fetal heart pattern does the nurse determine?
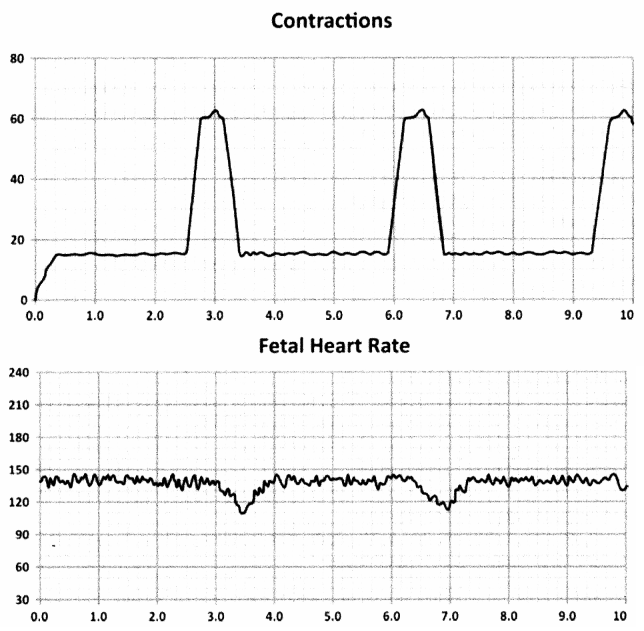
(a) Early deceleration
(b) Adequate acceleration
(c) Late deceleration
(d) Prolonged acceleration
Answer:
(c) Late deceleration
Explanation:
Choice (c) aligns with the deceleration seen of the fetal heart rate after the maternal contractions are witnessed. Choice (a) would involve deceleration before the contractions. Choices (b) and (d) would both involve acceleration instead of the deceleration indicated by the depressions on the reading.
Question 14.
Which intervention should the nurse NOT include while maintaining seizure precautions for a patient with epilepsy?
(a) Padded side-rails
(b) Suction by the bedside
(c) Side-rails down
(d) Ambu-bag in room
Answer:
(c) Side-rails down
Explanation:
Choice (c) should NOT be implemented for a patient with epilepsy. Side-rails should be up to discourage patient falls during seizure activity. Choice (a) provides additional protection from injury. Choices (b) and (d) include equipment that should be ready for use in case it is needed during a seizure. The nurse should support the patient into a side-lying position and maintain their airway.
Question 15.
Where should the nurse place the bell or diaphragm of their stethoscope to auscultate the pulmonic area during a focused cardiac assessment? Place an X to mark your answer.
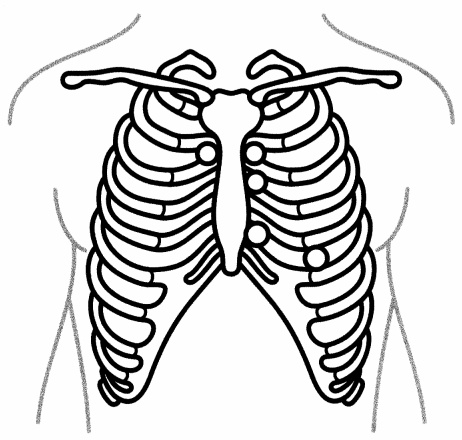
Answer:
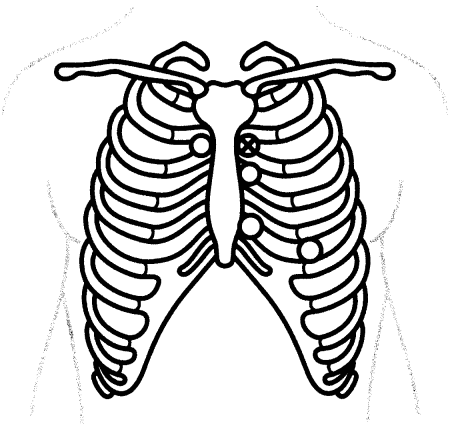
Explanation:
The pulmonic valve is located at the second intercostal space to the left sternal border. The nurse should place the bell or diaphragm of their stethoscope at this location to engage in pulmonic valve auscultation.
Question 16.
While caring for a pediatric patient, the nurse is providing discharge instructions to the patient and family regarding the oral administration of a liquid treatment, which is available as 5 mg/mL. The patient is prescribed 40 mg. How many mL should the patient's parent plan to administer? ..........................
Answer:
8mL
Explanation:
The nurse should instruct the patient and family to use the dosage calculation of "dose ordered" divided by "dose on hand." In this case, the parent should divide 40 mg by 5 mg/mL to yield 8 mL.
Question 17.
The nurse is providing patient education when the patient inquires, "What is the plan to help with my fatigue, hair thinning, and weight gain?" Which medication from the patient's electronic medication administration record does the nurse identify as supporting targeted relief for the patient's symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Electronic Medication Administration Record (EMAR)
|
Tab 1, Morning |
Levothyroxine 88 mcg po qam Lithobid 300 mg BID Simethicone 150 mg po TID after meals (0800) |
|
Tab 2, Afternoon |
Simethicone 150 mg po TID after meals (1300) Simethicone 150 mg po TID after meals (1800) |
|
Tab 3, Night |
Lithobid 300 mg po BID Zolpidem tartrate 5 mg po qhs |
(a) Levothyroxine
(b) Simethicone
(c) Lithobid
(d) Zolpidem tartrate
Answer:
(a) Levothyroxine
Explanation:
Choice (a) is a synthetic hormone replacement prescribed for hypothyroidism, which targets symptoms such as fatigue, hair thinning, and weight gain. Choice 6 promotes a reduction in flatulence. Choice (c) is prescribed for mood disorders. Choice (d) targets poor sleep.
Question 18.
Which of the following ECG strips indicates atrial flutter?
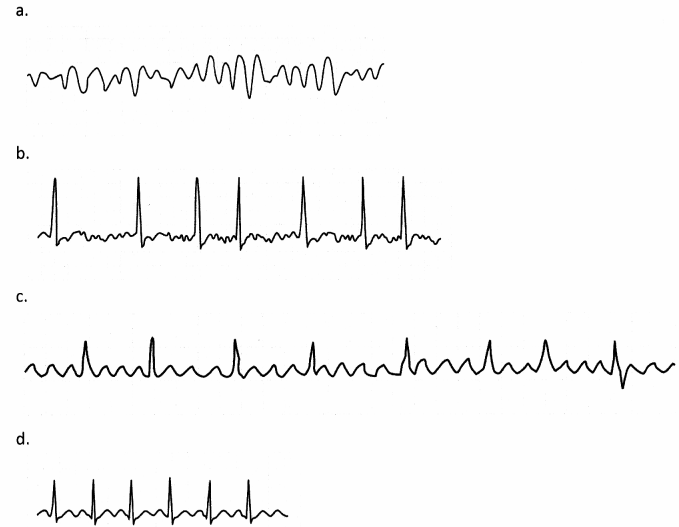
Answer:

Explanation:
Choice (b) is correct. Atrial flutter is a type of supraventricular tachycardia, often indicated by flutter waves at a high rate between 200 and 300 BPM, as seen in Choice (b).
Question 19.
The nurse is caring for a patient in the emergency department who has manifestations of * diverticulitis. The patient asks the nurse to explain the difference between diverticulosis and
diverticulitis. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Diverticulosis rarely occurs in adults.
(b) Diverticulitis is associated with chronic NSAID use.
(c) The initial treatment for diverticulitis is surgery to remove the affected bowel segment.
(d) The patient's age at onset of diverticulosis is associated with the risk of diverticulitis.
Answer:
(d) The patient's age at onset of diverticulosis is associated with the risk of diverticulitis.
Explanation:
There is evidence that patients who are diagnosed with diverticulosis before the age of fifty have a greater risk for episodes of diverticulitis, which may be due to an unidentified difference in the infective process, living longer, or delays in seeking care for the initial episode. The presence of diverticulosis is age-dependent, affecting less than 5 percent of individuals less than forty years old and up to 65 percent of individuals over eighty years old; therefore, Choice (a) is incorrect.
Diverticulitis is caused by infection of the diverticula due to impacted fecaliths and other cellular debris, which results in overgrowth of normal colonic bacteria with progression to an inflammatory process that is responsible for the clinical manifestations of the acute attack. Therefore, Choice (b) is incorrect. Initial episodes of diverticulitis are treated with bowel rest, antibiotics, and IV fluids. Emergency surgical intervention of an initial attack is required only for severe manifestations, and an elective colectomy is recommended after three episodes of diverticulitis; therefore, Choice (c) is incorrect.
Question 20.
In Erikson's eight stages of development, Identity versus Role Confusion begins at age 12 and contains all EXCEPT which of the following challenges?
(a) Working through and understanding multiple changes and demands placed upon the child as he or she moves toward adulthood
(b) Increasing understanding of sexual, hormonal, and other physical changes that are occurring
(c) Finding a long-term partner and starting a family
(d) Assessing one's talents, sexual preferences, and vocational interests
Answer:
(c) Finding a long-term partner and starting a family
Explanation:
Developing a long-term relationship and starting a family are concepts more closely associated with stage six of Erikson's Model, Intimacy versus Isolation, which occurs from age 18 through age 40. During this period, one is faced with the challenge of coming to terms with sexual preference, choosing a career path, and determining where, with whom, and how one plans to live. Long-term, future- oriented thinking is required. This phase is important, in that if not successfully mastered, the following phases Generativity versus Stagnation and Ego Integrity versus Despair may lead to emotional pain and anxiety in later life.
Question 21.
When reviewing their knowledge of the stages of infections, the nurse knows that which period precedes the first symptoms of the infection?
(a) Prodromal period
(b) Colonization of organism
(c) Incubation period
(d) Convalescent period
Answer:
(c) Incubation period
Explanation:
The incubation period is the point in time where the organism has already invaded the person's body through a portal of entry, is multiplying, and is getting ready to manifest the first symptoms of infection. The colonization occurs right after entry into the body where the organism takes up residence in the host and prepares to multiply. The prodromal period is when the person develops general signs or symptoms (such as fatigue, headache, fever, etc.) before developing more specific signs and symptoms that help point towards a diagnosis. The convalescent period is when the person is recovering from the illness.
Question 22.
When taking a history from a pregnant woman with placenta previa, the nurse would expect the patient to report which of the following?
(a) Maternal age of twenty-eight years
(b) First pregnancy
(c) Previous C-section
(d) One previous vaginal delivery
Answer:
(c) Previous C-section
Explanation:
Placenta previa is the abnormal placement of the placenta over the internal cervical os or within 2 centimeters of the internal cervical os. The risk factors for placenta previa are previous C-section, maternal age greater than thirty-five years, and increased number of previous pregnancies, making Choices (a), (b), and (d) incorrect. Other risk factors include infertility treatments, multiple births, previous abortions, and smoking or cocaine use.
Question 23.
The nurse reviews the following cardiac telemetry strips during physiotherapy. Which, if any,
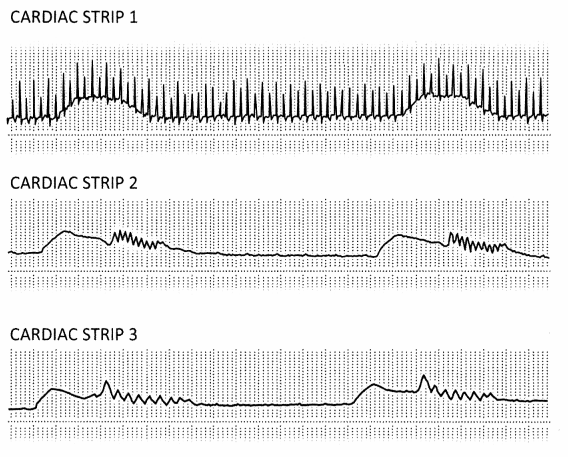
(a) Chest wall clapping is not noted
(b) Cardiac strip 1
(c) Cardiac strip 2
(d) Cardiac strip 3
Answer:
(b) Cardiac strip 1
Explanation:
Choice (b) shows traces of chest wall clapping. Choice (a) is incorrect as chest wall clapping is visibly present. Choice (c) indicates vibration. Choice (d) indicates shaking.
Question 24.
Which type of law deals with misdemeanors and felonies?
(a) Criminal law
(b) Constitutional law
(c) Common law
(d) Stationary law
Answer:
(a) Criminal law
Explanation:
Criminal law has to do with the arrest, prosecution, and incarceration of those who commit misdemeanors and felonies. Constitutional law has to do with the laws set forth by the Constitution of the United States of America. Common law is based on legal precedents. Stationary is not a term used to describe laws. Stationary sounds similar to "statutory," which has to do with laws passed down by legislative bodies such as a state's legislature. There are statutes criminalizing certain acts, such as assault.
Question 25.
How should the nurse evaluate the following cardiac rhythm noted on a patient's electrocardiogram?

(a) Normal sinus rhythm
(b) Sinus bradycardia
(c) Sinus tachycardia
(d) Supraventricular tachycardia
Answer:
(a) Normal sinus rhythm
Explanation:
Choice (a) aligns with the patient's electrocardiogram as it shows a regular rhythm and rate with each QRS complex preceded by a normal P wave and constant PR interval. Choices (b), (c), and (d) all fall outside of normal and do not correlate to the characteristics of the normal sinus rhythm seen on this strip.
Question 26.
The nurse assesses drainage from a client's chest tube for all except which of the following?
(a) Consistency
(b) Quantity
(c) Heart rate
(d) Color
Answer:
(c) Heart rate
Explanation:
The nurse may assess the rate of heart beats but not necessarily from chest tube drainage. The three common parameters for assessing drainage are consistency, quantity, and color. These are all ways to monitor and record chest output.
Question 27.
Which of the following are vulnerable populations at high risk of being abuse and neglect victims?
(a) Men, women, and children
(b) Immigrants, women, and minority races
(c) Children, women, and the elderly
(d) Children, pets, and immigrants
Answer:
(c) Children, women, and the elderly
Explanation:
Children, women, and the elderly are vulnerable populations due to tendencies to be physically weaker than their attackers, possibly disabled, unable to communicate, or dependent in some other way.
Question 28.
The nurse is caring for a patient struggling with changes to their behavior, memory, speech, hearing, and vision secondary to a traumatic brain injury sustained during a motor vehicle accident. Which lobe does the nurse understand to be the site of injury causing these symptoms? Place an X to mark your answer.
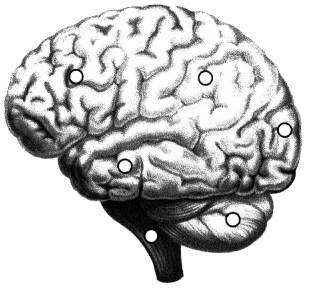
Answer:
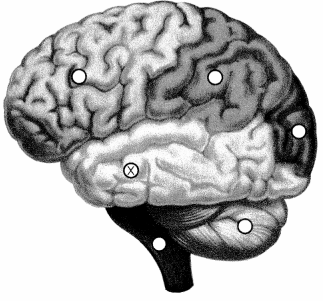
Explanation:
A traumatic injury to the temporal lobe causes changes to behavior, memory, speech, hearing, and vision. This lobe is located anterior to the occipital lobe and posterior to the frontal lobe, beneath the lateral fissure.
Question 29.
Which statement is typical of data the nurse collects on a woman hospitalized with abruptio
(a) "I am a smoker."
(b) "I am twenty-five years old."
(c) "I do not drink alcohol."
(d) "I have no history of placental abruption."
Answer:
(a) "I am a smoker."
Explanation:
Abruptio placenta is the premature separation of the placenta from the wall of the uterus. Common risk factors for this condition are smoking, maternal hypertension, trauma (such as car accidents, falls, or assaults), cocaine or alcohol abuse, maternal age greater than thirty-five or less than twenty-years-old, and previous history of abruptio placenta. Therefore, (b), (c), and (d) are not correct.
Question 30.
There is an interruption in the patient's care when their case is shifted from one health care environment to another in a way that causes ambiguity over who is responsible for care. What is this
called?
(a) Continuity of care
(b) Fluidity of care
(c) Fragmentation of care
(d) Division of care
Answer:
(c) Fragmentation of care
Explanation:
Fragmentation of care occurs when the patient's case is shifted from one health care environment to another, in such a way that ambiguity over who is responsible for the patient's overall case results. This leads to errors and prolonged inaction as well as patient frustration. Continuity of care is the opposite of fragmentation of care and is the ideal. Continuity of care means the plan of care stays consistent across many different health care environments that the patient may find themselves in. Choices (b) and (d), fluidity and division, are not terms used for these concepts.
Question 31.
In receiving a new patient upon admission to an inpatient room, the nurse delegates appropriate tasks to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). What equipment is appropriate for the UAP to safely start on the patient?
(a) Cervical traction
(b) Ventilator
(c) Hemovac drain
(d) Sequential compression device
Answer:
(d) Sequential compression device
Explanation:
The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) is able to assist with patient equipment by supporting placement of the sequential compression devices (SCDs). It would not be within the UAP's scope to apply cervical traction (Choice a), a hemovac drain (Choice c), or a ventilator (Choice 6).
Question 32.
According to Piaget, the process by which old ideas or beliefs must be replaced with new ones due to obtaining new and more factual information is called which of the following?
(a) Schemas
(b) Assimilation
(c) Object permanence
(d) Accommodation
Answer:
(d) Accommodation
Explanation:
Accommodation occurs when one recognizes that previous beliefs were incorrect or no longer beneficial, based upon learning and integrating new information. Accommodation should occur throughout one's life as new information enters the consciousness and the process of assimilation occurs. If one is unable to accommodate new ideas, then it is difficult to grow emotionally and intellectually. If an individual continues to insist that using a yellow legal pad and an encyclopedia is just as efficient as using a computer to complete a complex research project, accommodation has failed to occur.
This forces the person to work at a "snail's pace" in comparison to using technology to more quickly and accurately complete the task. Choice (a) is incorrect in that schemas are a set of thoughts and ideas that fit together and present the person with a belief, or even a script, for life. Choice (b) is incorrect because assimilation refers to the process of integrating the new information gained through accommodation. Choice (c) refers to object permanence, a process in which an infant learns that even though a person or object leaves the room, that person still exists, and this understanding reduces anxiety and fear of abandonment.
Question 33.
Following a traumatic brain injury during a sporting event, the patient reports loss of their sense of smell. Which cranial nerve is responsible for the sense of smell? Place an X to mark your answer.
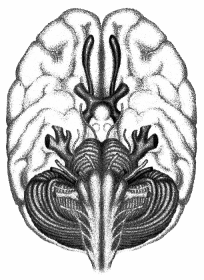
Answer:
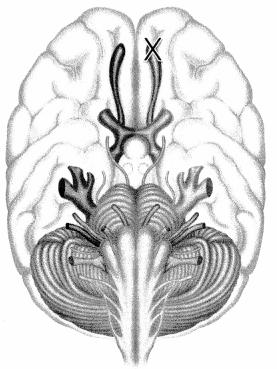
Explanation:
The olfactory nerve, one of twelve cranial nerves, represents a more frequently injured nerve and is characterized by a loss of smell. Injury to this nerve prevents the transmission of the sensation of smell to the patient's brain. It is the first and shortest cranial nerve.
Question 34.
What part of supervision involves the nurse giving the staff member tips for a better performance, using utmost respect and professionalism?
(a) Delegation
(b) Follow-up
(c) Documentation
(d) Coaching
Answer:
(d) Coaching
Explanation:
Sometimes the supervising nurse must coach the staff member to whom they have delegated a task to ensure a better performance the next time. The nurse should use the utmost professionalism and respect during these encounters, ensuring the staff member is receptive and the criticism is constructive. Follow-up is investigating that the task was done. Delegation is handing out a task to an appropriate staff member. Documentation needs to occur following each task that is performed, and the delegating nurse needs to ensure this is performed for all care activity.
Question 35.
A state board of nursing has a set amount of continuing education requirements that the nurse must fulfill each year to maintain their license. Which type of law is this?
(a) Statutory law.
(b) Administrative law.
(c) Constitutional law.
(d) Common law.
Answer:
(b) Administrative law.
Explanation:
Administrative law is the type of law given by administrative bodies such as a state's nursing board. Constitutional law is specific to the United States Constitution and does not rule on nursing administrative issues. Common law is based on legal precedents. Statutory law involves legislative bodies such as a state's legislature.
Question 36.
The nurse caring for a patient postcardiac catheterization will perform which specific intervention to monitor for the development of life-threatening dysrhythmias?
(a) Keep the patient flat on their back for at least six hours postprocedure.
(b) Take regular vital signs, especially heart rate and blood pressure.
(c) Regularly observe the patient's ECG via cardiac monitoring, according to facility protocol.
(d) Regularly observe the incision site, looking for bruising, swelling, and redness.
Answer:
(c) Regularly observe the patient's ECG via cardiac monitoring, according to facility protocol.
Explanation:
Observing and recording the patient's heart rhythm via ECG is the specific intervention necessary to monitor for the development of dysrhythmias postcardiac catheterization. All of the other interventions listed are correct postcardiac catheterization care but not specific to dysrhythmias. The nurse will keep the patient flat to assist with incision healing, take regular vital signs, such as heart rate, and blood pressure., and monitor for bleeding and hematoma at the incision site to evaluate the patient's overall stability.
Question 37.
A patient needs invasive hemodynamic monitoring as they are being admitted to the ICU for hemorrhagic shock. The nurse will expect an order for which type of line to be inserted?
(a) PICC line
(b) Port-a-cath
(c) Dialysis catheter
(d) Right-heart catheter
Answer:
(d) Right-heart catheter
Explanation:
A right-heart catheter., also called a Swan-Ganz catheter, or pulmonary artery catheter., is threaded through a patient's central veins, into the superior vena cava, terminating at the pulmonary artery. This type of catheter is used for hemodynamic monitoring, giving information about the patient's preload, and cardiac output.. A PICC line., or peripherally inserted central catheter, can be used for medication and fluid administration but does not give information about hemodynamics.
A port-a-cath is another type of central line used for similar purposes as the PICC line and can be kept in the patient for an extended period. A dialysis catheter is a long-term access device for patients receiving regular treatments of dialysis but is not used for hemodynamic monitoring.
Question 38.
A patient presents to the emergency department via ambulance after experiencing a fire accident while camping. The nurse is assisting with determining the percentage of surface area directly impacted by the burns. What region of the patient's body, when affected anteriorly and posteriorly, combines to a total 36% surface area? Place an X to mark your answer.
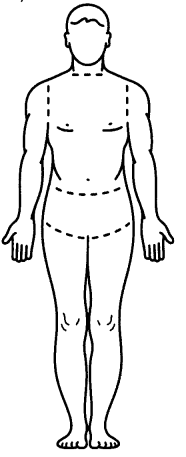
Answer:
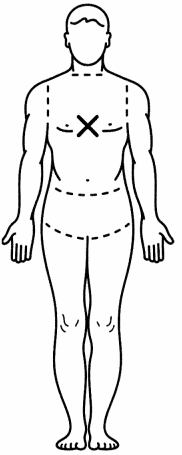
Explanation:
The anterior and posterior aspects of the patient's torso cover 18% surface area each, thus totaling to 36% when both aspects are affected. Additionally, the anterior head accounts for 4.5%, the posterior head 4.5%, the anterior leg 9%, the posterior leg 9%, the anterior arm 4.5%, the posterior arm 4.5%, and finally the perineum 1%.
Question 39.
When establishing priorities for the patient, the nurse considers Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Which level must be attained first before moving higher on the pyramid?
(a) Esteem
(b) Physiological
(c) Love
(d) Safety
Answer:
(b) Physiological
Explanation:
The patient's physiological needs must be met first and foremost, before any other level of the hierarchy can be addressed. Maslow's description of the physiological needs include hunger, thirst, breathing, sleep, and homeostasis. Safety is the next level; it addresses morality, family, and security of the body. Love comes next in Maslow's hierarchy, involving relationships with family and friends.
Esteem is one level higher than love, involving self-esteem, confidence, achievement, and respect of others.
Question 40.
When administering a medication, the nurse observes all except which of the following rights?
(a) Right medication
(b) Right medical facility
(c) Right time frame
(d) Right person
Answer:
(b) Right medical facility
Explanation:
Right medical facility is not part of the six patient medication administration rights. The six rights are the following: right medication, right route, right time frame, right patient, right dosage, and right documentation.
Question 41.
While caring for a patient with tension headaches post motor vehicle accident, the nurse views a new order for butalbital 50 mg/acetaminophen 300 mg/caffeine 40 mg tablets to be given PO q4h pm headache. If the patient consumes the maximum daily dose of 6 tablets, how much caffeine will the patient consume in a 24 hour period?
............................
Answer:
240 mg
Explanation:
The medication includes 40 mg of caffeine per tablet, therefore the nurse should multiply 40 mg/tablet by 6 tablets to yield 240 mg, which is the daily maximum total of caffeine consumption as ordered.
Question 42.
Which of the following is a nurse legally mandated to report?
(a) Marital status
(b) Gunshot wounds
(c) Religious beliefs
(d) Urinary tract infections
Answer:
(b) Gunshot wounds
Explanation:
Nurses are legally mandated to report gunshot wounds, dog bites, communicable disease, neglect, and abuse. Marital status, religious beliefs, and urinary tract infections are not legally mandated items for the nurse to report.
Question 43.
A nurse is caring for a patient who doesn't have pressure sores but is at risk for them due to immobility. How often should the patient be repositioned?
(a) Because the patient doesn't have pressure sores, it's not necessary to reposition them.
(b) The patient only needs to be repositioned when they express discomfort.
(c) The patient should be repositioned at least once every two hours.
(d) The patient should be repositioned each time perineal care is provided.
Answer:
(c) The patient should be repositioned at least once every two hours.
Explanation:
Even if no pressure sores are present, all immobile patients should be repositioned at least once every two hours. For Choice (a), the patient should be repositioned at least once every two hours to prevent pressure sores from developing. Again in Choice (b), an immobile patient should be repositioned at least once every two hours. However, if the patient expresses discomfort, the nurse can reposition the patient even if they were repositioned less than two hours ago. For Choice (d), while it might be appropriate to coordinate care in this manner, again the patient should be repositioned at least once every two hours whether or not any other care is being provided.
Question 44.
In Skinner's theory of operant conditioning, the term shaping refers to which of the following?
(a) Attempts to change behavior through a series of small shocks
(b) Changing behavior through rewarding the person each time an approximation of the desired behavior occurs
(c) Exploring superstitions that might impact one's willingness to make behavioral changes
(d) Giving a person a reward only when the desired behavior is perfected
Answer:
(b) Changing behavior through rewarding the person each time an approximation of the desired behavior occurs
Explanation:
Changing behavior through rewards for approximation of desired behavior is the correct answer. Skinner demonstrated that behavior can be learned by rewarding actions that are similar to the desired behavior. If one wants to teach a dog to chase and catch a Frisbee thrown to the end of a field, the dog must first be rewarded for sniffing the Frisbee, then grasping the Frisbee, and then catching it when thrown four feet, then six, then ten. This process is called successive approximation.
Choice (a) refers to a form of behavioral change through punishment. Choice (c) refers to superstitions, meaning that one can sometimes be confused as to which behavior is soliciting the reward. Some athletes wear the same pair of "lucky" socks each game, thinking this behavior leads to the reward of winning. In reality, the behavior that leads to the win can be anything from practicing harder to playing a team that is not highly skilled; therefore, the behavior is superstitious. Choice (d) is a poor form of teaching a person to learn a new behavior because it may take much trial and error before perfection is achieved.
Question 45.
The nurse is teaching the family of a patient with early Alzheimer's disease about medication options to treat the disease. Which statement by the patient's daughter indicates an understanding of the effects of these medications?
(a) "Early treatment may cure my mom's Alzheimer's disease."
(b) "Hopefully, medication can place my mom in remission."
(c) "We may be able to slow the disease progression with early treatment."
(d) "Early treatment has not been shown to have an effect on this disease."
Answer:
(c) "We may be able to slow the disease progression with early treatment."
Explanation:
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease, a chronic progressive form of dementia, is supportive; however, cholinesterase inhibitors and N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists have been demonstrated to slow the disease progression if they are started early in the course of the disease. Choices A and B are incorrect since early use of these medications will not cure the disease or cause it to enter remission. Choice D is incorrect because these medications have been shown to work for a limited time, if started early in the disease.
Question 46.
One's cultural background is based primarily upon which of the following?
(a) The color of one's skin
(b) Whether one lives in an urban or rural society
(c) The prevalence of racism in one's current environment
(d) A combination of factors, including where one was born, at what point in time one was born, and the sociological practices and standards in which one was raised
Answer:
(d) A combination of factors, including where one was born, at what point in time one was born, and the sociological practices and standards in which one was raised
Explanation:
Culture is a complex and multi-faceted concept and is related to when, where, and with whom one was raised. Those in the metal health field should always consider and discuss a client's cultural practices because these strongly impact beliefs, ethics, and behavior. The other three answer choices are all important elements in understanding cultural background, but it is the combination of these and other factors that make up one's cultural background.
Question 47.
A client has just had a catheter placed in their chest for the purpose of total parenteral nutrition (TPN) administration. The chest x-ray shows that the catheter has slipped and caused a leakage of air into the pleural space. What is this condition called?
(a) Pneumothorax
(b) Hemothorax
(c) Hydrothorax
(d) Pneumonia
Answer:
(a) Pneumothorax
Explanation:
A leakage of air into the pleural cavity outside of the lungs is called a pneumothorax. This may happen as a complication of central line placement for TPN. Hemothorax results when blood is leaked into the pleural cavity. Hydrothorax refers to a leakage of water into the pleural cavity. Pneumonia is an infection that forms in the lungs as the result of an infectious organism and may cause fluid to accumulate in the bases of the lungs.
Question 48.
The nurse needs to assess a normal, uncomplicated patient in the doctor's office for a yearly physical. Which is the best spot to assess for this patient's pulse?
(a) Radial
(b) Femoral
(c) Popliteal
(d) Carotid
Answer:
(a) Radial
Explanation:
The nurse assessing a stable, uncomplicated patient will most likely go for the radial pulse. The femoral pulse, found in the groin, would be an invasion of the patient's privacy and not appropriate for this type of routine checkup. The popliteal pulse, found behind the knee, would be an unusual and hard- to-reach spot for a routine pulse assessment. The carotid pulse is reserved for emergency situations such as cardiac arrest to assess for pulselessness before starting cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
Question 49.
Identify the following rhythm:

(a) Normal sinus rhythm
(b) Atrial fibrillation
(c) Sinus tachycardia
(d) Sinus bradycardia
Answer:
(c) Sinus tachycardia
Explanation:
The rhythm shown demonstrates sinus tachycardia. Sinus tachycardia originates from the sinus node but has a faster rate than normal sinus rhythm.
Question 50.
All EXCEPT which of the following are true of an area with an extremely high population density?
(a) Competition for resources is intense
(b) Greater strain on public services exists
(c) More people live in rural areas
(d) More people live in urban areas
Answer:
(c) More people live in rural areas
Explanation:
Population density, which is the total number of people divided by the total land area, generally tends to be much higher in urban areas than rural ones. This is true due to high-rise apartment complexes, sewage and freshwater infrastructure, and complex transportation systems, allowing for easy movement of food from nearby farms. Consequently, competition among citizens for resources is certainly higher in high-density areas, as are greater strains on infrastructure within urban centers.
Question 51.
Which model of care seeks to promote continuity of patient care across their health journey, ensuring proper case coordination, proactivity, and patient-centeredness?
(a) Community health model
(b) Public health model
(c) Patient-managed care
(d) Patient-centered medical home
Answer:
(d) Patient-centered medical home
Explanation:
The patient-centered medical home (PCMH) is a model of care that promotes wellness for the patient through proactivity, care coordination, and patient-centered planning. PCMH is a model that seeks to combat fragmentation of care and the problems that come with it. The other three terms are not applicable to the description, though community and public health organizations do play a role in promoting community wellness.
Question 52.
What most accurately describes the blood sugar samples in this graph?
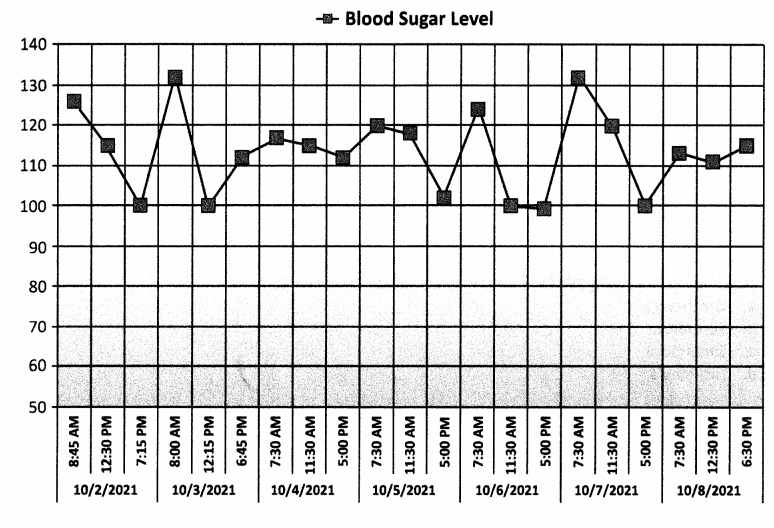
(a) Out of control
(b) Under control
(c) Too high
(d) Too low
Answer:
(b) Under control
Explanation:
The blood sugars represented on this graph are under control.
Question 53.
The nurse is working with an 82-year-old patient who suffered a Colies fracture during a fall. Which splint does the nurse identify as most supportive for this patient?
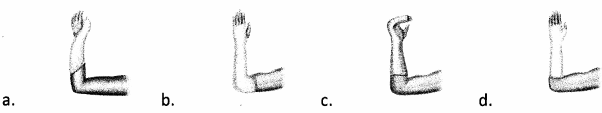
Answer:
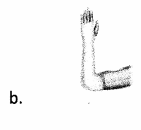
Explanation:
Choice (b) indicates the most supportive splint for a patient struggling with a Colies fracture post fall. This fracture-type involves falling on an outstretched hand, which fractures and displaces distal radius. Choice (a) is indicated for a thumb dislocation. Choice (c) is indicated for a 4th or 5th metatarsal fracture. Choice (d) is indicated for a wrist sprain.
Question 54.
The nurse walks into a patient's room and witnesses the patient violently convulsing with rigid muscles. The patient is completely unconscious. The nurse immediately recognizes this is what type of seizure?
(a) Myoclonic
(b) Absence
(c) Grand Mai
(d) Tonic
Answer:
(c) Grand Mai
Explanation:
This type of seizure with muscle rigidity, convulsions, and unconsciousness is called a grand mal seizure. An absence seizure involves a brief loss of consciousness where the patient may stare into space. A myoclonic seizure involves the body making jerking movements. A tonic seizure is characterized by rigidity and stiffness of the muscles.
Question 55.
Before using a patient's newly placed PICC line, the nurse knows which test must be performed?
(a) CT scan
(b) Chest x-ray
(c) MRI
(d) Ultrasound
Answer:
(b) Chest x-ray
Explanation:
The patient must have a chest x-ray to confirm correct placement of the PICC line. Correct placement will show that the PICC line tip is resting in the distal end of the superior vena cava, right at the cavoatrial junction. The other three imaging studies are not routinely ordered to confirm PICC line placement.
Question 56.
The nurse in the ICU takes over for a patient who has been experiencing respiratory acidosis. The nurse checks the daily labs and finds which of the following values that suggests the patient is still acidotic?
(a) 7.38 pH
(b) 7.25 pH
(c) 7.42 pH
(d) 7.48 pH
Answer:
(b) 7.25 pH
Explanation:
The patient with a pH value of 7.25 is still very much acidotic and needs further therapy to return them to normal. The other values listed fall in the normal range of 7.35 to 7.45 or in the alkalotic range, which is greater than 7.45.
Question 57.
Which of the following CVADs is an example of a non-tunneled catheter?
(a) Groshong's
(b) Subclavian
(c) Small-bore
(d) Hickman's
Answer:
(b) Subclavian
Explanation:
A subclavian catheter is an example of a non-tunneled central venous access device. Jugular and femoral lines are other examples of non-tunneled catheters. Examples of tunneled catheters include Groshong's, small-bore, Hickman's, and Broviac's.
Question 58.
After the nurse assesses the patient's vital signs and finds an elevated heart rate, elevated respirations, and low blood pressure, which position should the nurse place the patient in?
(a) Fowler's
(b) Right-lateral recumbent
(c) Passive leg raise
(d) Prone
Answer:
(c) Passive leg raise
Explanation:
Choice (c), passive leg raise, supports proper positioning for a patient with vital signs indicative of shock. The patient is supine with the legs elevated 8-12 inches. It is the nurse's priority to enhance circulation and assess the need for additional interventions. Choice (a) aligns with a raised upper body, while Choice (b) is side lying, and Choice (d) is face down, none of which support improved vital signs and symptom management of shock for the patient at this time.
Question 59.
During an inpatient hospitalization, a patient is struggling with an acute exacerbation of Meniere's disease. Which device would be most helpful to this patient during this time?
(a) Leg lifter
(b) Shower chair
(c) Button hook
(d) Voice box
Answer:
Explanation:
The patient with Meniere's disease, an inner ear vestibular condition, struggles with symptoms of tinnitus and severe vertigo. A shower chair, Choice (b), is crucial for this patient in order to prevent falls while showering. The patient should be encouraged to use the shower chair during every shower, and if available, grab bars as well, as symptoms can exacerbate in the shower and may lead to unsteady balance. A leg lifter is not a necessary device to offer this patient at this time, as it does not correlate with the patient's condition; thus, Choice (a) is incorrect. Button hooks and voice boxes, Choices C and Choice (d), while supportive, do not align with symptoms of this condition.
Question 60.
Which is the simplest nerve pathway that bypasses the brain?
(a) Autonomic
(b) Reflex arc
(c) Somatic
(d) Sympathetic
Answer:
(b) Reflex arc
Explanation:
The reflex arc is the simplest nerve pathway. The stimulus bypasses the brain, going from sensory receptors through an afferent (incoming) neuron to the spinal cord. It synapses with an efferent (outgoing) neuron in the spinal cord and is transmitted directly to muscle. There is no interneuron involved in a reflex arc. The classic example of a reflex arc is the knee-jerk response. Tapping on the patellar tendon of the knee stimulates the quadriceps muscle of the thigh, resulting in contraction of the muscle and extension of the knee.
Question 61.
The nurse responds to a 71-year-old patient presenting to the emergency department with signs and symptoms of septic shock. The patient was discharged from the medical-surgical floor last week after being treated for pneumonia. What findings support a septic shock diagnosis? Select all that apply.
(a) Metabolic acidosis
(b) Respiratory alkalosis
(c) Narrowing pulse pressure
(d) Increased cardiac output
(e) Hypertension
Answer:
(a) Metabolic acidosis
(b) Respiratory alkalosis
Explanation:
During septic shock, metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis are expected findings, along with a symptom presentation of shortness of breath, temperature changes, confusion, and diaphoresis. Thus, Choices (a) and (b) are correct. Choice (c) is incorrect, as the patient would likely experience a widening pulse pressure, not one that is narrowing. Choice (d) is incorrect, as the patient would display a decreased cardiac output. Choice (e) is incorrect, as the patient would typically present with hypotension in this case.
Question 62.
The nurse is obtaining the patient's height and weight and the patient willingly steps on the scale without much prompting. Which type of consent was given?
(a) Verbal
(b) Written
(c) Implied
(d) Assumed
Answer:
(c) Implied
Explanation:
The patient has given implied consent. There is neither verbal nor written confirmation of consent; rather, both parties silently agree without a formal conversation about the topic. Assumed is not a term used for consent, though both parties are assuming that consent is given. Written consent involves a signed legal document by the patient and usually follows a conversation about the plan of care or procedure with the physician performing it. Verbal consent is given by the patient, affirming verbally their consent to the procedure to be done.
Question 63.
A patient is admitted to the hospital from the emergency department with stomach pain and blood emesis. The nurse knows that which of the following tests is likely to be performed on the patient based on their symptoms?
(a) Sigmoidoscopy
(b) Upper endoscopy
(c) Anoscopy
(d) Colonoscopy
Answer:
(b) Upper endoscopy
Explanation:
Based on the symptoms of stomach pain and bloody emesis that the patient reported, they will likely be scheduled for an upper endoscopy. An upper endoscopy, also called an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), visualizes the internal mucosa of the upper gastrointestinal (Gl) tract. A sigmoidoscopy visualizes the sigmoid portion of the colon. An anoscopy is performed to visualize the area just inside the anus. A colonoscopy is performed to assess and intervene within the entire colon, usually used for early detection of colon cancer.
Question 64.
The nurse is educating a female client who is to undergo a mammography. Which of the following statements would not be appropriate regarding mammography education?
(a) "This test allows the practitioner to visualize small lumps that they may not have been able to palpate."
(b) "It is recommended that you get a mammography once every year after the age of forty for early detection of breast cancer."
(c) "The mammography is a type of computed tomography used to visualize the breast tissue."
(d) "This test takes x-ray images of the breast tissue, identifying any masses that may be cancerous."
Answer:
(c) "The mammography is a type of computed tomography used to visualize the breast tissue."
Explanation:
The mammography test is a type of x-ray, not computed tomography. While CT scans may be performed, x-rays are the gold standard for early detection of breast cancer. The patient is recommended to get the test once every year after the age of forty for early breast cancer detection. The test can pick up masses that may not be manually palpable to the patient or the practitioner.
Question 65.
The patient has an order for acetaminophen 650 milligrams Q6H prn for pain, not to exceed 2 grams in 24 hours. How many doses of acetaminophen can the patient have in 24 hours? Round to the nearest whole number ..................... mg
Answer:
3 doses 2 grams
Explanation:
3 doses. 2 grams of acetaminophen are equal to 2000 mg. 2000 mg (total) divided by 650 mg (per dose) is equal to 3.077, or 3 doses.
Question 66.
Which form of consent does an unconscious patient provide when brought into the emergency department after an accident?
(a) Denied consent
(b) Explicit consent
(c) Implied consent
(d) Expressed consent
Answer:
(c) Implied consent
Explanation:
When an unconscious patient is brought in for emergency care, they are agreeing to the care by way of implied consent. However, it is important to note that implied consent could never overrule a patient's denial to receive care. It is implied that an unconscious patient brought to the emergency room would want to be treated. Therefore, Choice (a) is incorrect. A patient would need to be conscious and verbal to provide explicit or expressed consent, so Choices (b) and (d) are incorrect. A patient's action and conduct to willingly receive the medical care, even if not expressed verbally, functions as the basis for implied consent.
Question 67.
Which statement is typical of data collected on a patient with Grave's disease?
(a) Female over age forty
(b) Female under age forty
(c) Male over age forty
(d) Male under age forty
Answer:
(b) Female under age forty
Explanation:
Hyperthyroidism occurs when there is an overproduction of T4 and/or T5 by the thyroid gland. Women under age 40 are most likely to be diagnosed with this disorder. This makes Choices (a), (c), and (d) incorrect.
Question 68.
The patient has an order for 240 mg of Tylenol for her pediatric patient. Tylenol comes in 160 mg per 5 mL. How many milliliters does the nurse administer to the patient?
(a) 7.5 mL
(b) 5 mL
(c) 12.5 mL
(d) 10 mL
Answer:
(a) 7.5 mL
Explanation:
The correct answer is 7.5 mL. The answer is obtained by using the desired dose divided by the amount on hand multiplied by the volume, or the D/H x V formula. By taking the desired dose (240 mg), dividing it by the amount on hand (160mg), and multiplying it by the volume the drug is formulated in (5 mL), the nurse will then arrive at the correct dose of 7.5 mL.
Question 69.
Which of the following hemodynamic parameters is measured in beats per minute per meter squared of the patient's body surface area?
(a) Cardiac index
(b) Cardiac output
(c) Mean arterial pressure
(d) Stroke volume
Answer:
(a) Cardiac index
Explanation:
The cardiac index reflects the quantity of blood pumped by the heart per minute per meter squared of the patient's body surface area. Cardiac output measures how much blood the heart pumps out per minute in liters. The mean arterial pressure, or MAP, shows the relationship between the amount of blood pumped out of the heart and the resistance the vascular system puts up against it. The stroke volume measures how much blood the heart pumps in milliliters per beat.
Question 70.
The nurse walks into the room where the patient is clutching his chest, sweating, and appears short of breath. The patient reports he is experiencing chest pain that is crushing and severe, with some pain in his left arm as well. The nurse knows that this type of chest pain is most likely associated with which following medical condition?
(a) Myocardial infarction
(b) Gastroesophageal reflux
(c) Pneumonia
(d) Pleuritis
Answer:
(a) Myocardial infarction
Explanation:
The chest pain described is most likely cardiac in origin, so the patient could be experiencing a myocardial infarction, or heart attack. Chest pain associated with gastroesophageal reflux is more often described as a burning sensation, without the other symptoms described. Pneumonia and pleuritis may both cause the patient to have a different type of chest pain, in which a sharp, stabbing sensation is felt upon breathing.
Question 71.
Which of the following is a function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
(a) Stimulating the fight-or-flight response
(b) Increasing heart rate
(c) Stimulating digestion
(d) Increasing bronchiole dilation
Answer:
(c) Stimulating digestion
Explanation:
The sympathetic nervous system initiates the "fight-or-flight" response and is responsible for body changes that direct all available energy towards survival. Digestion is completely sacrificed so that energy can be diverted to increase heart rate and breathing (thus, bronchiole dilation). The liver is stimulated to release glycogen to provide available energy. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulating everyday activities like digestion.
Question 72.
The nurse walks into the hospital room of a 12-year-old pediatric patient who appears to be choking on breakfast. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Ask the patient if they are choking
(b) Begin CPR
(c) Initiate abdominal thrusts
(d) Lower the patient to the ground
Answer:
(a) Ask the patient if they are choking
(c) Initiate abdominal thrusts
(d) Lower the patient to the ground
(b) Begin CPR
Explanation:
After the nurse observed a 12-year-old pediatric patient who appears to be choking on breakfast, the nurse proceeds to manage the situation by carrying out steps in the following order to ensure the patient's condition is as suspected and safely perform interventions according to the findings. Ask the patient if they are choking, initiate abdominal thrusts, lower the patient to the ground, and then begin CPR.
Question 73.
A nurse is delegating a task to a certified nursing assistant (CNA). Which of the following factors must the nurse consider?
(a) The school the CIMA received their training from
(b) Other team members the CNA associates with
(c) Strengths and weaknesses of that CNA
(d) What time the CNA gets off work
Answer:
(c) Strengths and weaknesses of that CNA
Explanation:
The nurse must consider the strengths and weaknesses of a particular CNA before delegating a task to them. This will best assist the nurse in making a sound decision. The school that the CNA received their training from, the other staff members they associate with, and what time they get off work are irrelevant to their performance as a CNA. The nurse must be aware of and careful of their own personal bias and prejudice when deciding to whom to delegate tasks. Each person must be judged fairly based on their merit, attitude, and performance.
Question 74.
The nurse is caring for a fifty-two-year-old female patient with metabolic syndrome. Which of the following is the nurse NOT likely to assess?
(a) Low HDL cholesterol level
(b) High triglyceride level
(c) Fatty deposits on the upper back
(d) History of a stroke
Answer:
(c) Fatty deposits on the upper back
Explanation:
Metabolic syndrome, also called Syndrome X, is the presence of comorbid cardiovascular and insulin-related conditions. Those with metabolic disease may have excess belly fat, not excess fat on the upper back. Choices (a) and (b) are incorrect since patients with metabolic syndrome must have three or more of the following conditions: hypertension, elevated fasting blood glucose levels, low HDL cholesterol, high triglycerides, and excess belly fat. Patients with this disorder are typically overweight or obese and are at an increased risk for organ failure, heart attack, and stroke, making Choice (d) incorrect.
Question 75.
An aide is caring for a patient with a known respiratory infection. The patient is on droplet precautions. What is the minimum PPE required when caring for this patient?
(a) Gloves, gown, N-95 respirator
(b) Gown, eyewear, gloves, and a disposable mask
(c) Gloves and a disposable mask
(d) Disposable mask, sterile gloves, and eyewear
Answer:
(c) Gloves and a disposable mask
Explanation:
Gloves and a disposable mask are all that are required for droplet precaution; however, additional PPE may be used if desiring extra protection. The key word in this question is minimum. Choice (a) is not correct because an N-95 mask is not required. Choice (d) is not correct because sterile gloves are not needed and eyewear is optional. Choice (b) would give the most coverage for protection but it is not the minimum PPE required.
Question 76.
A woman who has entered her twenty-fourth week of pregnancy is preparing to take the oral glucose tolerance test, which will screen for which condition of pregnancy?
(a) Hyperemesis gravidarum
(b) Preeclampsia
(c) Iron-deficiency anemia
(d) Gestational diabetes
Answer:
(d) Gestational diabetes
Explanation:
The oral glucose tolerance test is performed between the twenty-fourth and twenty-eighth week of pregnancy to screen for gestational diabetes. Hyperemesis gravidarum is a severe form of morning sickness that occurs in the first trimester but sometimes continues until the third trimester.
Preeclampsia is detected through blood pressure monitoring. Iron-deficiency anemia may be detected first through symptoms of fatigue, weakness, and dizziness and then confirmed with a blood test showing a low hemoglobin and hematocrit count. These components of the red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen to the organs and tissues of the body and can drop during pregnancy.
Question 77.
Middle school student Johnny stores an epinephrine injection pen in his locker, lunch bag, and pencil case. Johnny likely suffers from which of the following?
(a) Homicidal ideation
(b) Narcolepsy
(c) Depression
(d) A severe allergy
Answer:
(d) A severe allergy
Explanation:
Severe allergies can be life-threatening and lead to anaphylaxis. An epinephrine injection pen is the first line of defense if a person comes into contact with an allergen to which he or she has a serious or life-threatening reaction.
Question 78.
On admission, you learn that your patient has fallen at home three times in the last six months. What should you do to ensure the patient's safety? Select all that apply.
(a) Educate and instruct the patient to call for help when getting out of bed.
(b) Write a plan of care on the risk of falls.
(c) Set the bed alarm.
(d) Notify the RN.
(e) Check on the patient every two hours.
Answer:
(a) Educate and instruct the patient to call for help when getting out of bed.
(c) Set the bed alarm.
(d) Notify the RN.
(e) Check on the patient every two hours.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), and (e): Educating the patient and setting the alarm are appropriate interventions, as the patient has a history of falling. The RN should be included in the plan of care for this patient. The patient should be checked on frequently to make sure they are safe and are following instructions. Choice B is incorrect because writing a plan of care is not within the LPN's scope of practice.
Question 79.
A twenty-two-year-old male comes in with a gunshot wound to the right upper quadrant of his abdomen. The bleeding has been controlled, the wound was closed, and he has been hemodynamically stabilized. What solid organ of the abdomen does the nurse suspect might have been hit by the gunshot?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Liver
(d) Colon
Answer:
(c) Liver
Explanation:
The liver is a solid organ located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. When a penetrating wound such as a gunshot has occurred to the abdomen, it is important to be mindful of organ damage underneath the point of penetration. The small intestine, stomach, and colon are all hollow organs located in different areas of the abdomen.
Question 80.
The nurse prepares to don personal protective equipment (PPE). Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Gloves
(b) Goggles
(c) Mask
(d) Gown
Answer:
(d) Gown
(c) Mask
(b) Goggles
(a) Gloves
Explanation:
The nurse prepares to don personal protective equipment (PPE) via steps performed in the following order to ensure infection control is maintained by safely applying equipment in layers to later avoid contamination of equipment or self. The nurse should don the gown, mask, goggles, and lastly, gloves.
Question 81.
Which instrument should the nurse select for use in debridement?
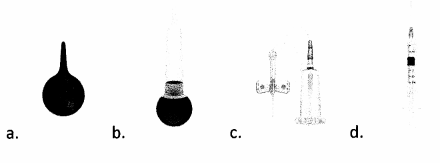
Answer:

Explanation:
Choice (b) indicates the proper instrument selection for the nurse to use for debridement, as this tool supports irrigation. Choice (a) supports suctioning, such as of vomit and mucus. Choice (b) supports sampling, such as of blood and bodily fluids. Choice 0 supports injections, such as of medication.
Question 82.
A nurse is charged with negligence. Which type of offense is negligence?
(a) Intentional tort
(b) Libel
(c) Slander
(d) Unintentional tort
Answer:
(d) Unintentional tort
Explanation:
Negligence, along with malpractice, is a type of unintentional tort. Intentional torts include false imprisonment, batter, and assault. Libel and slander, in which false statements are made as a form of defamation, both fall under the category of intentional tort.
Question 83.
What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
I. Regulate body temperature
II. Send stimulatory and inhibitory instructions to the pituitary gland
III. Receive sensory information from the brain
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) I, II, and III
Answer:
(d) I, II, and III
Explanation:
The hypothalamus is the link between the nervous system and endocrine system. It receives information from the brain and sends signals to the pituitary gland, instructing it to release or inhibit the release of hormones. Aside from its endocrine function, it controls body temperature, hunger, sleep, and circadian rhythms, and it is part of the limbic system.
Question 84.
A thirty-three-year-old female presents to the emergency room complaining of vomiting blood. Which description of the hematemesis indicates an active upper Gl bleed?
(a) Coffee ground
(b) Bright red
(c) Large amount
(d) Small amount
Answer:
(b) Bright red
Explanation:
Bright red blood that is being vomited usually indicates an active upper Gl bleed. Coffee ground blood indicates the blood has been sitting in the stomach for a while, indicating a slower bleed. The amount of blood, whether large or small, does not indicate active bleeding necessarily. For instance, a large bleed that has not fully manifested itself might result in a relatively small amount of blood vomited.
Question 85.
Approximately what percentage of people in the United States struggle with mental illness in a given year?
(a) 20-25%
(b) 4-8%
(c) 10-15%
(d) 75-80%
Answer:
(a) 20-25%
Explanation:
Approximately 20-25 percent of the population in the United States struggles with a mental disorder in any given year. That is 1 out of every 4 or 5 people. It is estimated that a smaller percentage, 4-8 percent, struggle with a severe or serious mental illness. The United States has a high level of mental disorders as compared to other countries.
Question 86.
What category of psychological disorders is characterized by a mood that fluctuates between mania and depression?
(a) Manic-depressive disorder
(b) Anxiety disorders
(c) Trauma-related disorders
(d) Bipolar disorders
Answer:
(d) Bipolar disorders
Explanation:
Bipolar disorder was formerly called manic-depressive disorder and is characterized by fluctuations in mood, from bouts of depression to periods of mania or euphoria. There are different types of bipolar disorder, some types having milder forms of mania or depression than others. Anxiety disorders are characterized by persistent worry, anxiety, or fear. Trauma-related disorders develop in reaction to stressful and traumatic experiences that a person has endured.
Question 87.
Which sound should be assessed using the bell of the stethoscope for proper detection?
(a) Bruit
(b) Inspiratory wheeze
(c) S2 heart sound
(d) Stridor
Answer:
(a) Bruit
Explanation:
Choice (a) should be assessed using the bell of the stethoscope for detection. Choices 6, (c), and (d) should be auscultated with the diaphragm of the stethoscope. The bell supports auscultation of low frequency sounds, while the diaphragm filters low sounds out. The bell is helpful for detecting abnormal heart sounds and bruits.
Question 88.
The nurse is caring for a forty-eight-year-old patient assessed to have an elevated white blood cell count following anesthesia. What is the normal range for white blood cells in a healthy adult patient?
(a) 2,000-3,000/pL
(b) 4,000-11,000/pL
(c) 15,000-16,000/pL
(d) 21,000-36,000/pL
Answer:
(b) 4,000-11,000/pL
Explanation:
Choice (b) represents the normal range for white blood cells in a healthy adult patient. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are outside of the normal range and would indicate a potential problem requiring further assessment by the nurse at this time. Choice (a) is below normal range. Choices (c) and (d) are above normal range.
Question 89.
Which of the following lab values suggests the client is experiencing hypokalemia?
(a) 3.2 mEq/L
(b) 3.5 mEq/L
(c) 5.0 mEq/L
(d) 5.5 mEq/L
Answer:
(a) 3.2 mEq/L
Explanation:
A normal range for serum potassium is between 3.5 and 5.1 mEq/L; thus, 3.2 is the correct answer. 3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L suggest a normal serum potassium. A level of 5.5 mEq/L suggests a hyperkalemic state. The nurse should report hypokalemia and will prepare to administer potassium supplementation if ordered by the physician.
Question 90.
You suspect that your patient who is receiving a blood transfusion is experiencing a transfusion reaction. List the order in which the following things should occur:
(a) Notify RN.
(b) Notify MD.
(c) Stop transfusion.
(d) Check vital signs.
Answer:
(c) Stop transfusion.
(a) Notify RN.
(d) Check vital signs.
(b) Notify MD.
Explanation:
The transfusion should be stopped immediately to ensure that the patient is safe and the reaction is minimized. The RN should be made aware so that the team of nurses can collaborate.
Vital signs should be taken before notifying the physician, so that you can inform the physician about them.
Question 91.
You present information on advanced directives to your patient. Your patient states that they do not want to be resuscitated in the event their heart should stop. That is, they have a "do not resuscitate" order, or DNR. What actions should you take? Select all that apply.
(a) Enter an order for DNR status.
(b) Give the patient medication to keep them comfortable.
(c) Notify the physician.
(d) Provide support using therapeutic communication.
(e) Put a "do not resuscitate" sign in the patient's room.
Answer:
(c) Notify the physician.
(d) Provide support using therapeutic communication.
Explanation:
The physician should be notified of the patient's wishes so they can direct care appropriately. The LPN can answer questions about advance directives. Choice (a) is incorrect because only physicians can order a DNR. Choices (b) and (e) are incorrect because the patient is not a DNR until the physician orders it.
Question 92.
The nurse identifies a patient care safety risk while rounding on the unit at the start of shift. Which member of the care team should the nurse elevate this concern to?
(a) Director of nursing
(b) Charge nurse
(c) Chief nursing officer
(d) Nursing supervisor
Answer:
(b) Charge nurse
Explanation:
Choice (b) indicates the appropriate team member for the nurse to elevate a patient care safety risk to. Choices (a), (c), and (d) fall higher in the nursing chain of command, therefore should not yet be prompted to handle this concern at this time.
Question 93.
The nurse has a patient who reports that he is 155 pounds. The nurse needs to record the patient's weight in kilograms. Knowing that 1 kilogram is equal to 2.2 pounds, the nurse then calculates the patient's weight to be what in kilograms?
(a) 60 kg
(b) 70 kg
(c) 341 kg
(d) 300 kg
Answer:
(b) 70 kg
Explanation:
The correct conversion of the patient's weight is 70 kilograms. This answer is found by dividing the weight in pounds, 155, by the number of kilograms that are found in a pound, 2.2, which gives the nurse the correct answer. The other three answers are incorrect.
Question 94.
Which heart rate does the nurse consider within normal range for the two-week-old patient?
(a) 54 beats per minute
(b) 171 beats per minute
(c) 198 beats per minute
(d) 62 beats per minute
Answer:
(b) 171 beats per minute
Explanation:
Choice (b) indicates a normal assessment finding for a two-week-old patient. Choices (a), (c), and (d) are outside of the normal range for the age of this patient, as the heart rate should be between 70 and 190 beats per minute. This rate is applicable for the first month of life. At one month of age, the normal heart rate adjusts to 80 to 160 beats per minute.
Question 95.
Which of the following is not a preventative measure for pressure-ulcer formation?
(a) Padding bony areas on the body
(b) Repositioning the patient at least every two hours
(c) Keeping the patient in a sitting position while in their bed
(d) Changing soiled linens and clothing promptly
Answer:
(c) Keeping the patient in a sitting position while in their bed
Explanation:
Keeping a patient in a sitting position in their bed puts extra pressure on their coccyx and bottom due to gravity; therefore, this option is not a preventative measure for pressure-ulcer formation. Choices (a), (b), and (d) are interventions that should be done to help prevent pressure ulcers.
Question 96.
As the nurse is receiving reports on her patients for the day, she knows that which patient will take top priority in being assessed and treated?
(a) 33-year-old female who is nauseous and needs an antiemetic administered
(b) 49-year-old female who is scheduled for a cardiac catheterization and needs to sign the informed consent
(c) 55-year-old male who is being discharged later today and has a question about his care at home
(d) 78-year-old male who is complaining of shortness of breath
Answer:
(d) 78-year-old male who is complaining of shortness of breath
Explanation:
The nurse will see the patient who is complaining of shortness of breath first. Airway, breathing, and circulation are always the highest priority for the nurse to address, as they can quickly become life- threatening situations. Maintaining proper respiration is a vital function to the patient's well-being, and stabilization is necessary immediately. The woman who is nauseous and needs antiemetics such as Zofran is the second priority, as she is actively ill and there is something the nurse can do to help her symptoms.
The nurse's third priority will be the patient who needs to sign the informed consent. The nurse needs to ensure she gets that signed before the patient leaves the floor, although there are nurses in the cardiac catheterization lab who can obtain the consent if need be. The patient who has a question about discharge is the last priority, as there is no immediate threat to his health and the doctor will need to see the patient before he is discharged anyway.
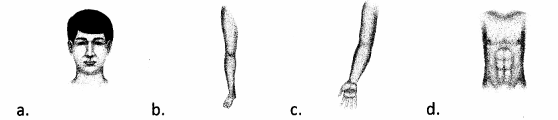
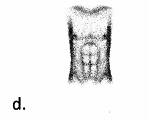
Question 97.
Which body surface correlates to an 18% burn percentage in an adult patient?
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice (d) correlates to an 18% burn percentage in an adult patient. Choice (a) correlates to a 4.5% burn percentage. Choice (b) correlates to a 9% burn percentage. Choice (c) correlates to a 4.5% burn percentage. The nurse applies burn percentage to patient care and triage of thermal injuries.
Question 98.
Which signs and symptoms discovered during a head-to-toe assessment of a patient recently admitted to the hospital would the nurse attribute to parasympathetic functioning? Select all that apply.
(a) Reduced motility of gastrointestinal tract
(b) Pupil constriction
(c) Bronchi constriction
(d) Increased heart rate
(e) Urinary excretion
Answer:
(b) Pupil constriction
(c) Bronchi constriction
(e) Urinary excretion
Explanation:
Choices (b), (c), and (e) are attributed to parasympathetic nervous system functioning when completing a head-to-toe assessment of a patient recently admitted to the hospital, along with decreased heart rate and increased gastrointestinal motility. Choices (a) and (d) are attributed to sympathetic nervous system functioning, along with increased cardiac conduction and dilated pupils. Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are branches of the autonomic nervous system.
Question 99.
A nursing student is interested in becoming a case manager. Which of the following will be required to attain this nursing role?
(a) Additional case management training, certification, and clinical hours
(b) Passing the NCLEX licensure exam
(c) Graduating with an associate's or baccalaureate degree in nursing
(d) Obtaining the required clinical hours before graduating with a nursing degree
Answer:
(a) Additional case management training, certification, and clinical hours
Explanation:
To become a case manager, the nurse needs to fulfill requirements beyond their initial nursing degree. These requirements include case management-specific training, clinical hours following the case management team, and passing a case management certification exam. The initial passing of the NCLEX, clinical hours required for the nursing degree, and the nursing degree itself are all required before beginning case management training.
Question 100.
The nurse looks for which of the following signs that the patient is having an allergic reaction after administering a drug?
(a) Aching and stiffness
(b) Coughing and fever
(c) Fever and chills
(d) Itching and rash
Answer:
(d) Itching and rash
Explanation:
Itching and the development of a rash are signs that the patient is having an allergic reaction to a medication. These two symptoms are signs that the body's inflammatory response has been kicked into overdrive because of a drug allergy. The other symptoms listed are not commonly associated with an allergic reaction.
Question 101.
Which scores from the Norton Scale for Assessing Risk of Pressure Ulcers indicate that the patient is susceptible to ulcers? Select all that apply.
(a) 5
(b) 7
(c) 10
(d) 14
(e) 19
Answer:
(a) 5
(b) 7
(c) 10
(d) 14
Explanation:
Choices (a), (b), (c), and (d) indicate that the patient is susceptible to ulcers. When using the Norton Scale for Assessment Risk of Pressure Ulcers, a score of 14 or less indicates susceptibility. Choice (e) is outside of the susceptibility range. This scale rates five criteria that include: physical condition, mental condition, activity, mobility, and incontinence.
Question 102.
High levels of dopamine are associated with which of the following?
(a) Parkinson's disease
(b) Alzheimer's disease
(c) Schizophrenia
(d) Personality disorders
Answer:
(c) Schizophrenia
Explanation:
Schizophrenia is highly genetic and is associated with high levels of dopamine in the brain. Parkinson's disease is correlated to low levels of dopamine, so treatments for schizophrenia can sometimes cause Parkinson's disease. Alzheimer's disease is associated with a deficit in the neurotransmitter acetylcholine rather than dopamine. There has been no strong link connecting dopamine to personality disorders.
Question 103.
A patient calls the doctor's office asking how many milliliters of ibuprofen she should give her nine- month-old baby. The baby weighs 18 pounds. The ibuprofen comes in drops with a concentration of 50 mg/1.25 mL. The dose is 75 mg. The nurse tells the patient to give her baby how many milliliters? Round to the nearest tenth of a decimal ................. mL
Answer:
1.88 mL
Explanation:
If the drops come in a concentration of 50 mg/1.25 mL, then 1.875 is the correct mL for 75 mg. 1.875 rounded to the nearest hundredth is 1.88 mL.
Question 104.
The school nurse notices that a kindergartener seems to have trouble making certain letter sounds when they talk. Which type of referral would be appropriate in this circumstance?
(a) Dietician
(b) Social services
(c) Physical therapist
(d) Speech therapist
Answer:
(d) Speech therapist
Explanation:
The nurse could appropriately make a speech therapy referral in this child's case, connecting the child and the child's family to needed services. The other three options of a dietician, physical therapist, and social services are not appropriate for this specific scenario.
Question 105.
You walk into a patient's room and find them sweating and complaining of heart palpitations. Earlier that day, the patient's heart rate was 60 beats per minute and the heart rhythm was normal sinus. You check their pulse, and it is now 150 beats per minute. Their Sp02 is 88 percent. You do an EKG at the bedside, and it shows that the patient is now in atrial fibrillation. What should you do? Select all that apply.
(a) Check the patient's blood pressure and oxygen saturation.
(b) Notify the physician.
(c) Administer oxygen.
(d) Check on your other patients right away.
(e) Stay with the patient.
Answer:
(a) Check the patient's blood pressure and oxygen saturation.
(b) Notify the physician.
(c) Administer oxygen.
(e) Stay with the patient.
Explanation:
It is important to know what the patient's other vital signs are before proceeding. The physician must be notified for a heart rate of 150 bpm. The administration of oxygen is appropriate for an SpO2 of 88 percent. It is important to stay with this patient until the patient has stabilized. Choice (d) is incorrect because this unstable patient takes priority.
Question 106.
Which term refers to a route of medication administration other than through the gastrointestinal tract?
(a) Parenteral
(b) Enteral
(c) Motor
(d) Buccal
Answer:
(a) Parenteral
Explanation:
Parenteral is the term that refers to any route outside of the gastrointestinal tract, also referred to as the alimentary canal. Motor is not a viable answer choice. Enteral also refers to the Gl tract or intestines. Buccal refers to the cheeks, or inner oral cavity.
Question 107.
Studies have shown that which of the following practices has the most positive impact on patients?
(a) Personalized comfort measures in their post-operation room, such as a favorite snack or book
(b) Internet and television access during their clinical stay
(c) An attentive communication style between their nurses and physicians
(d) Visible operation and safety checklists that staff members regularly check and notate
Answer:
(c) An attentive communication style between their nurses and physicians
Explanation:
Patients respond favorably to positive intrapersonal communication between their attending nurses and physicians. The other options may be nice for patients, but studies indicate that nurse and physician relationships have the most impact on a patient's overall experience.
Question 108.
The patient reports that he feels dizzy and lightheaded when he stands up after sitting for a long time. What would be the appropriate intervention performed by the nurse to assess the cause of these symptoms?
(a) Taking the patient's temperature
(b) Observing the patient's rate of breathing and effort of breathing
(c) Assessing bilateral radial pulses and comparing strength
(d) Lying/sitting/standing blood pressure readings
Answer:
(d) Lying/sitting/standing blood pressure readings
Explanation:
The nurse should assess for orthostatic hypotension by performing lying/sitting/standing (LSS) blood pressure readings. If the readings trend downward significantly, up to twenty points in mmHg on the systolic side, the patient probably has orthostatic hypotension. Assessing for the patient's temperature and rate of breathing and comparing bilateral radial pulses can all be performed for the sake of having additional data but do not follow the symptoms this specific patient reported.
Question 109.
Which of the following choices illustrates the prone position?
Answer:
Explanation:
Choice (c) is correct. The patient is laying on their front, which is the prone position. Choice (a) is the side position, Choice (b) is supine, and Choice (d) is semi-Fowler's.
Question 110.
Which assessment technique would the nurse employ to obtain subjective data?
(a) Auscultation
(b) Palpation
(c) Percussion
(d) Patient interview
Answer:
(d) Patient interview
Explanation:
The patient interview adds subjective assessment data to the nurse's findings. Auscultation, palpation, and percussion yield objective assessment data.
Question 111.
The nurse heard the doctor telling the patient how he needed to change his diet and get more exercise to better manage his diabetes. The nurse knows that the patient did not want to hear this and that the patient has been vocal in the past about not needing to change anything about his lifestyle. The nurse senses that the patient feels angry and frustrated by his conversation with the doctor. The patient is very agitated when the nurse comes to collect vital signs and tells her that he thinks she is lazy. Which defense mechanism is the patient displaying?
(a) Intellectualization
(b) Undoing
(c) Reaction formation
(d) Displacement
Answer:
(d) Displacement
Explanation:
The patient is displaying displacement, in which he is taking his negative feelings toward the doctor and expressing them toward the nurse, unreasonably. Reaction formation is when a person feels negatively but reacts positively. Intellectualization is when a person focuses on minute details of the situation rather than coping with the negative emotions associated with it. Undoing is when a person has done something wrong and acts excessively in the opposite way to redeem themselves of prior wrongdoing.
Question 112.
Which of the following is a commonly used anticoagulant that works by preventing the activation of thrombin?
(a) Paxil
(b) Warfarin
(c) Heparin.
(d) Aspirin
Answer:
(c) Heparin.
Explanation:
Heparin, works by enhancing the effect of antithrombin III which prevents the activation of thrombin and thus prevents fibrinogen from being converted to fibrin. It is important to note that heparin does not get rid of pre-existing clots, it helps prevent clot expansion and formation of new clots. Paxil® is used to treat anxiety and depression.. Coumadin® (warfarin) works by blocking Vitamin K dependent clotting factors. Aspirin works on platelet aggregation.
Question 113.
What is one social factor that influences hunger motivation?
(a) Lateral area of the hypothalamus
(b) Body perception
(c) Coercion
(d) Metabolism
Answer:
(b) Body perception
Explanation:
Body perception, a social construct that dictates norms around what is attractive or unattractive, socially influences a person's hunger motivation. Coercion is not a factor in hunger motivation. Both the lateral hypothalamus and the metabolism are examples of biological motivations rather than social factors.
Question 114.
The nurse is providing patient education to a client newly diagnosed with diabetes. Which organ does the nurse explain is responsible for secreting insulin to regulate blood glucose levels?
(a) Liver
(b) Kidney
(c) Pancreas
(d) Spleen
Answer:
(c) Pancreas
Explanation:
Choice (c), the pancreas, is responsible for secreting insulin, which maintains proper blood glucose levels. Choices (a), (b), and (d), while important organs for supporting various homeostatic processes, do not secrete insulin.
Question 115.
The nurse is assessing a patient's IV access site and finds it to be cool and swollen. The IV pump is beeping, and fluid appears to be leaking around the site. The nurse suspects which of the following IV
therapy complications?
(a) Clot formation
(b) Fluid overload
(c) Infection
(d) Infiltration
Answer:
(d) Infiltration
Explanation:
The IV appears to have become dislodged, causing an infiltration of the surrounding tissues. This is marked by coolness and swelling of the site. The leaking of the fluid also suggests an infiltration of the IV site. A clot in the line would cause an obstruction to IV fluids and medications but not swelling of the surrounding tissue. Fluid overload would present systemic symptoms in the patient rather than localized swelling and coolness. An infected site would be warm rather than cool.
Question 116.
The nurse knows that all except which of the following factors put a patient at risk for aspiration?
(a) Difficulty swallowing and weakened gag reflex
(b) Liver failure
(c) Weakened upper and lower esophageal sphincter reflexes
(d) Enteral feedings
Answer:
(b) Liver failure
Explanation:
Liver failure is not a direct correlation with a patient's risk for aspirating. A weakened gag or swallow reflex, weakened upper and lower esophageal sphincters, and enteral feedings are all risk factors for aspiration. Patients with these risk factors should be monitored carefully during feeding times and have the head of their bed kept elevated to between 45 and 90 degrees while receiving feedings.
Question 117.
The senior nurse educates the novice nurse on developmental psychology in relation to patient milestones and care planning. Arrange the following staged tasks in ascending order by age stages of development according to Sullivan's Interpersonal Theory. Include all options.
(a) Anxiety reduction via oral gratification
(b) Satisfying peer relationships
(c) Delay in gratification
(d) Satisfying same-sex relationships
Answer:
(a) Anxiety reduction via oral gratification
(c) Delay in gratification
(b) Satisfying peer relationships
(d) Satisfying same-sex relationships
Explanation:
The nurse educates on the following staged tasks in ascending order according to Sullivan's Interpersonal Theory to describe the age stages of development. The nurse educates that development ascends from anxiety reduction via oral gratification, to delay in gratification, to satisfying peer relationships, to satisfying same-sex relationships.
Question 118.
What does the Patient Self Determination Act of the United States offer protection for?
(a) Patient rights to make healthcare decisions without coercion
(b) Patient rights to influenced decisions by nurses
(c) Patient rights to confidentiality in portal systems
(d) Patient rights to electronic prescriptions
Answer:
(a) Patient rights to make healthcare decisions without coercion
Explanation:
The Patient Self Determination Act of the United States, passed in 1990, sets forth that a patient is able to make decisions regarding the specifics of their treatment and the extent of nontreatment. While a patient is encouraged to decide what is best for them, they must be supported to do so without coercion or intimidation. Choices 8, (c), and (d) do not reflect protections found within this act.
Question 119.
In order to calculate certain medications' dosages, the nurse must first convert the patient's weight in pounds to kilograms. If a patient is 148 pounds, what is their weight in kilograms? Record your answer using one decimal place. .......................
Answer:
67.3 kg
Explanation:
The nurse should understand that 1 kg equals 2.2 pounds. In this case, the nurse should divide 148 by 2.2 to yield 67.3 kg. The nurse should be prepared with the patient's weight in kilograms prior to surgery.
Question 120.
The doctor orders 20 mg of metoprolol for a patient. The medication is supplied in tablets of 5 mg each. How many tablets will the nurse give? .................... tablets
Answer:
4 tablets.
Explanation:
20 mg of metoprolol divided by 5 mg per tablet equals 4 tablets.
Question 121.
A patient with a Swan-Ganz catheter in the ICU is being assessed by the nurse for the first time during the shift. The nurse notices which number on the hemodynamic profile is abnormal and needs further investigating?
(a) Mean arterial pressure: 75 mmHg
(b) Cardiac output: 2L/min
(c) Central venous pressure: 5 mmHg
(d) Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure: 6 mmHg
Answer:
(b) Cardiac output: 2L/min
Explanation:
The patient's cardiac output is very low, suggesting a possible bleed or hypotensive crisis. Normal cardiac output falls between 4 and 8 L/min. All the other values listed are within normal range. Normal mean arterial pressure is between 70 and 100 mmHg. Normal central venous pressure is between 2 and 6 mmHg. Normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is between 4 and 12 mmHg.
Question 122.
The nurse is having her annual tuberculosis exam, or Mantoux test, performed. This test, which entails the injection of TB proteins or antigens, involves which route of administration?
(a) Subcutaneous
(b) Intrathecal
(c) Intradermal
(d) Sublingual
Answer:
(c) Intradermal
Explanation:
The Mantoux test, or annual tuberculosis test most nurses must undergo as part of facility policy, involves an intradermal injection of the TB proteins or antigens. The dermal layer of the skin is accessed, as opposed to a subcutaneous injection, which goes deeper into the skin. An intrathecal injection goes into the spinal canal. Sublingual refers to a route of administration of a drug that will go under the tongue.
Question 123.
The nurse is caring for a 24-year-old patient when they suddenly lose consciousness and the EKG turns to asystole. Where should the nurse assess the patient for a pulse?
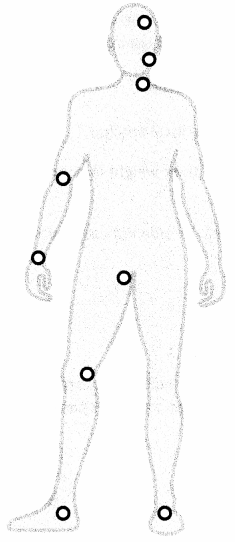
Answer:
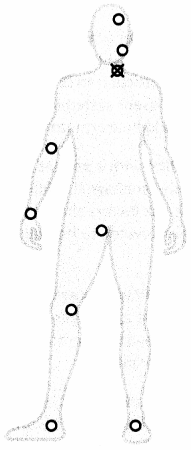
Explanation:
The carotid pulse can be assessed along either side of the throat. If the patient is arresting the nurse should not check this pulse for more than 10 seconds before beginning chest compressions.
Question 124.
While caring for a patient who is unable to consume nutrition by mouth, the nurse administers enteral nutrition via tube feeding. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Verify tube placement
(b) Elevate head of bed
(c) Measure residual
(d) Obtain desired amount of formula
Answer:
(b) Elevate head of bed
(a) Verify tube placement
(c) Measure residual
(d) Obtain desired amount of formula
Explanation:
The nurse administers enteral nutrition via tube feeding by carrying out steps in the following order to reduce the risk of aspiration and ensure safe tube placement with appropriate nutrition delivery. The nurse should elevate head of bed, verify tube placement, measure residual, and then obtain desired amount of formula.
Question 125.
When administering a blood-thinning drug such as warfarin, the nurse will be mindful of which type of synergistic drug that could put the patient at risk for excessive bleeding?
(a) Aspirin
(b) Lasix
(c) Lisinopril
(d) Protonix
Answer:
(a) Aspirin
Explanation:
The platelet-aggregation inhibitor, aspirin, has the potential to work synergistically with warfarin in a way that would increase the patient's risk for bleeding. Synergistic drugs work together in ways that enhance each one's individual effectiveness, sometimes for the patient's good but sometimes to the patient's detriment. Lasix, lisinopril, and Protonix are other frequently used drugs that would not work synergistically with warfarin in any significant hemostatic way.
Question 126.
A patient is admitted with prolonged vomiting, greater than three days. The nurse knows this patient will need what type of therapy to counteract a dangerous result of prolonged vomiting?
(a) Intravenous (IV) fluids
(b) Antibacterial medications
(c) Anti-nausea medications
(d) Physical therapy
Answer:
(a) Intravenous (IV) fluids
Explanation:
One of the most serious side effects of prolonged vomiting is dehydration, thus the patient needs fluids to restore him back to a more normal, hydrated status. Antibiotics may be used in a case of severe bacterial infection, but not likely in this case. Anti-nausea medication will likely be used to stop the vomiting but will do nothing to fix the resulting dehydration. Physical therapy is not typically necessary for such a case unless the patient was bedridden for a long time, which does not seem to be the case here.
Question 127.
The nurse is evaluating the patient's understanding of ways to reduce their risk of colon cancer post discharge. Which statement made by a patient supports a clear understanding of the plan for wellness?
(a) "I will have an annual endoscopy."
(b) "I will eat more produce from my garden."
(c) "I will go on daily jogs."
(d) "I will eat more red meat from my local butcher."
Answer:
(b) "I will eat more produce from my garden."
Explanation:
Choice (b) represents an understanding of ways to reduce colon cancer risk post discharge. Increasing fruits and vegetables in the diet is one way to support a reduction in risk. Choice (a) is incorrect because this invasive routine is not supported. Choice (c) is incorrect; exercise does not directly correlate to a reduction of risk. Choice (d) is incorrect, as red meat is associated with a heightened risk of colon cancer.
Question 128.
The patient weighs 87.5 kg. What is their weight in pounds? Round to the nearest tenth ....................... pounds
Answer:
192.5 pounds.
Explanation:
There are 2.2 kg per pound, so 87.5 kg times 2.2 kg per pound equals 192.5 pounds.
Question 129.
During lunchtime in the dining area, an aide notices a patient grabbing their throat. What should the aide's first action be?
(a) To call for help
(b) Have the patient stand up
(c) Ask the patient if they are choking
(d) To try to open the patient's mouth
Answer:
(c) Ask the patient if they are choking
Explanation:
The first thing to do is to check to see if the patient is choking. They may nod their head if they are asked about choking, and they will not be able to talk. If the person is choking, help them stand up so that the Heimlich maneuver can be started. Choice (a), calling for help, would not be necessary unless the person becomes unconscious or if help is needed with the Heimlich. Choice (d) is incorrect because it is not appropriate to look in the person's mouth for a lodged piece of food, as the nurse could make the obstruction worse, as well as waste precious time.
Question 130.
Which of the following will provide the nurse with lists of medications, generic and brand names, and expected outcomes and is maintained by an expert panel of medical practitioners?
(a) Patient medication list from home
(b) Facility procedure manual
(c) Formulary
(d) Electronic health record
Answer:
(c) Formulary
Explanation:
The formulary is an excellent tool the nurse can access that will give them up-to-date information about drugs, their safety and effectiveness, and their generic and brand names. It is maintained and updated by a team of experts. The patient medication list is a separate document and is not used for broad medication reference. The facility procedure manual will give the nurse information about how to respond to a fire and other such facility information but not information in reference to medications. The electronic health record is a document used specifically in reference to the patient but not for general informational purposes.
Question 131.
Identify the aorta:
Answer:
Explanation:
The aorta leads directly from the left ventricle and to the systemic circuit:
Question 132.
As the nurse advocates for the patient seeking emergency services, they explain that the patient has a right to receive care regardless of their ability to pay. What law is the nurse referencing in this scenario?
(a) Emergency Healthcare Act
(b) Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act
(c) The Stark Law
(d) False Claims Act
Answer:
(b) Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act
Explanation:
The Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA) was enacted in 1986 in order to protect an individual's right to receive emergency care regardless of their ability to pay for services. The patient has a right to be stabilized and treated. Choice (a) is fictitious, and Choices (c) and (d) do not involve protection of emergent care regardless of ability to pay.
Question 133.
Based on the following chart, what medication do you anticipate that the physician will order?
|
Patient Information |
Name: Anthony price Age: 43 Sex: Male |
|
Vital signs |
Heart Rate: 95 BP: 150/23 RR: 25 SPO2: 94% |
|
History |
43-year old male admitted to hospital with exacerbation of CHF including a 15-pound weight gain in 1 month. |
|
Problems |
CHF, HTN, Obesity, pre-diabetes |
|
Medications |
Metformin 500 mg po BID; Hydrocholothaized 50 mg po daily; carvedoil 25 mg po daily; Lovastain 20 mg po daily. |
(a) Aspirin 81 mg po daily
(b) Lantus 20 units SQ BID
(c) Warfarin 2.5 mg po daily
(d) 40 mg Lasix IV push BID
Answer:
(d) 40 mg Lasix IV push BID
Explanation:
Choice (d) is correct. Lasix is a diuretic used to remove excess fluid in heart failure. Choice (a), aspirin, would not help correct fluid overload. Choice (b), Lantus, is a long-acting insulin. Although the patient has a slightly elevated A1C and he may be considered prediabetic, his current glucose is normal and a diagnosis of diabetes has not been made. Choice (c), warfarin, is a blood thinner and is not indicated in heart failure.
Question 134.
Which of the following is a commonly used anticoagulant that works by blocking the body's ability to adhere platelets together?
(a) Paxil
(b) Coumadin
(c) Heparin
(d) Aspirin
Answer:
(d) Aspirin
Explanation:
Aspirin works by inhibiting platelet aggregation to prevent clot formation. Paxil® is used to treat anxiety and depression. Coumadin® (warfarin) works by blocking Vitamin K dependent clotting factors. Heparin enhances the effect of antithrombin III to inhibit thrombin activation.
Question 135.
Your patient is on 60 mg Lasix po daily. What should you prepare to monitor the patient closely for? Select all that apply.
(a) Increased urine output
(b) Electrolyte disturbances
(c) Muscle cramps
(d) Dizziness
(e) Dehydration
Answer:
(a) Increased urine output
(b) Electrolyte disturbances
(c) Muscle cramps
(d) Dizziness
(e) Dehydration
Explanation:
Increased urine output, electrolyte disturbances, muscle cramps, dizziness, and dehydration are all potential side effects of diuretics.
Question 136.
The nurse prepares to collect a urine specimen from an indwelling catheter using the closed-system method. Arrange the following steps in the order the nurse should perform them. Include all options.
(a) Cleanse specimen collection port
(b) Clamp drainage tubing
(c) Allow urine to pool in drainage tubing
(d) Insert sterile needle into specimen collection port
Answer:
(b) Clamp drainage tubing
(c) Allow urine to pool in drainage tubing
(a) Cleanse specimen collection port
(d) Insert sterile needle into specimen collection port
Explanation:
The nurse prepares to collect a urine specimen from an indwelling catheter using the closed-system method via steps performed in the following order to collect sufficient urine for sampling and maintain aseptic technique. The nurse should clamp drainage tubing, allow urine to pool in drainage tubing, cleanse specimen collection port, and then insert sterile needle into specimen collection port.
Question 137.
The nurse knows that which type of the following electrolyte supplements is contraindicated if the patient is on an ACE inhibitor such as lisinopril?
(a) Magnesium
(b) Calcium
(c) Potassium
(d) Sodium
Answer:
(c) Potassium
Explanation:
Patients on lisinopril are at risk for hyperkalemia; thus, the supplementation of potassium is to be done under careful clinical supervision or not at all. Lisinopril causes the body to hold on to more potassium than usual, and in renal-compromised patients, the risk for hyperkalemia is ever present. The other three electrolytes mentioned can cause toxic states in the body in low and high concentrations but not as life threatening as the cardiac disturbances a hyperkalemic state can bring about.
Question 138.
The nurse is caring for a patient with manifestations of peptic ulcer disease. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Stomach pain begins 20 to 30 minutes after eating.
(b) The condition is associated with an increased risk of malignancy.
(c) Endoscopy is used to establish hemostasis.
(d) Chronic NSAID use is the most common etiology.
Answer:
(c) Endoscopy is used to establish hemostasis.
Explanation:
Endoscopy is used to diagnose the condition and to cauterize hemorrhagic sites. The treatment algorithm for peptic ulcer disease recommends surgical intervention if two endoscopic attempts at hemostasis are unsuccessful. The pain related to peptic ulcer disease does not begin until the ingested food has reached the duodenum; therefore, the pain does not begin for 2 to 3 hours after a meal, while the onset of pain with gastric ulcers is 20 to 30 minutes after a meal.
Choice (a) is incorrect. Gastric ulcers are associated with an increased incidence of malignancy, not peptic ulcers; therefore, Choice (b) is incorrect. NSAID use is a commonly-associated cause of peptic ulcer disease. However, even excluding patients who use NSAIDs, more than 60 percent of the cases of peptic ulcer disease are related to H. pylori infection; therefore, Choice (d) is incorrect.
Question 139.
A patient has had three separate blood pressure readings of 138/88,132/80, and 135/89, respectively. The nurse anticipates the patient to be categorized by the physician as which of the following?
(a) Prehypertensive
(b) Normal
(c) Stage 1 hypertension
(d) Stage 2 hypertension
Answer:
(a) Prehypertensive
Explanation:
Prehypertension is defined as systolic pressures ranging between 120 and 139 mmHg or diastolic pressures between 80 and 89 mmHg. Normal blood pressure is less than 120/80 mmHg. Stage 1 hypertension ranges from 140 to 159 mmHg systolic or 90 to 99 mmHg diastolic. Stage 2 hypertension is greater than or equal to 160 mmHg systolic or greater than or equal to 100 mmHg diastolic.
Question 140.
Which term refers to when someone influences another person to do a greater behavior or action, by first getting them to agree to a small step?
(a) Door-in-face phenomenon
(b) Central route to persuasion
(c) Foot-in-door phenomenon
(d) Role-playing
Answer:
(c) Foot-in-door phenomenon
Explanation:
The foot-in-door phenomenon is when a person persuades someone to do a greater act after having agreed to something small. Once they have agreed to the more minor action or favor, they are more likely to agree to something bigger. The central route to persuasion is a means of persuasion based on the actual arguments, message, or characteristics. The door-in-face phenomenon is the opposite of foot-in-door in that a person first asks for a big request and when that is denied, he or she requests something smaller. Role-playing is a way in which behavior influences attitude because the mere act of playing a role can powerfully influence a person to take on the feelings and attitudes of the role.
Question 141.
Which of the following is NOT a major function of the respiratory system in humans?
(a) To provide a large surface area for gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
(b) To help regulate the blood's pH
(c) To help cushion the heart against jarring motions
(d) To produce vocalization
Answer:
(c) To help cushion the heart against jarring motions
Explanation:
Although the lungs may provide some cushioning for the heart when the body is violently struck, this is not a major function of the respiratory system. Its most notable function is that of gas exchange for oxygen and carbon dioxide, but it also plays a vital role in the regulation of blood pH. The aqueous form of carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, is a major pH buffer of the blood, and the respiratory system directly controls how much carbon dioxide stays and is released from the blood through respiration. The respiratory system also enables vocalization and forms the basis for the mode of speech and language used by most humans.
Question 142.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the forebrain?
(a) To regulate blood pressure and heart rate
(b) To perceive and interpret emotional responses like fear and anger
(c) To perceive and interpret visual input from the eyes
(d) To integrate voluntary movement
Answer:
(a) To regulate blood pressure and heart rate
Explanation:
The forebrain contains the cerebrum, the thalamus, the hypothalamus, and the limbic system. The limbic system is chiefly responsible for the perception of emotions through the amygdala, while the
cerebrum interprets sensory input and generates movement. The occipital lobe receives visual input, while the primary motor cortex in the frontal lobe is the controller of voluntary movement. The hindbrain, specifically the medulla oblongata and brain stem, control and regulate blood pressure and heart rate.
Question 143.
What is the action of glucagon?
(a) It increases the cellular uptake of carbohydrates
(b) It stimulates insulin secretion by the beta cells in the pancreas
(c) It stimulates the liver to release stored glucose
(d) It increases the cellular absorption of insulin
Answer:
(c) It stimulates the liver to release stored glucose
Explanation:
Glucagon is released by the alpha cells of the pancreas when blood glucose levels fall below normal. Glucagon then stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen to glucose. The glucose is then released to the circulating blood, increasing the serum glucose level. This is the process of glycogenolysis. Insulin secretion will further decrease the blood glucose level. Insulin is not absorbed by the cells. It remains in the circulating blood volume stimulating the cellular absorption of glucose.
Question 144.
The liver is responsible for many vital body functions. Which of the following functions is potentially harmful to the body?
(a) Conversion of ammonia to urea
(b) Breakdown of hemoglobin
(c) Cholesterol production
(d) Glycogen storage
Answer:
(c) Cholesterol production
Explanation:
Cholesterol is necessary for the formation of cellular membranes, vitamin D, and some hormones. However, overproduction of cholesterol may contribute to cardiovascular disease. Hemoglobin is processed in order to store iron for use as needed. Ammonia, which is toxic, is converted to urea, which is then excreted by the kidneys. Glycogen is stored until the body requires additional glucose to maintain blood sugar levels.
Question 145.
Most catalysts found in biological systems are which of the following?
(a) Special lipids called cofactors
(b) Special proteins called enzymes
(c) Special lipids called enzymes
(d) Special proteins called cofactors
Answer:
(b) Special proteins called enzymes
Explanation:
Biological catalysts are termed enzymes; enzymes are proteins with conformations that specifically manipulate reactants into positions that decrease the reaction's activation energy. Lipids do not usually affect reactions, and while cofactors can aid or be required for the proper functioning of enzymes, they do not make up the majority of biological catalysts.
