The ultimate goal of practicing Practice NCLEX Questions is to gain the knowledge and confidence necessary to pass the licensure exam and embark on a successful nursing career.
NCLEX Musculoskeletal Health Problems Questions
Musculoskeletal Health Problems NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
On a visit to the clinic, a client reports the onset of early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
The nurse should conduct a focused assessment for which symptoms?
(a) limited motion of joints
(b) deformed joints of the hands
(c) early morning stiffness
(d) rheumatoid nodules
Answer:
Explanation:
Initially, most clients with early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis report early morning stiffness or stiffness after sitting still for a while. Later symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include limited joint range of motion; deformed joints, especially of the hand; and rheumatoid nodules.
Question 2.
A client with rheumatoid arthritis states, “I cannot do my household chores without becoming tired. My knees hurt whenever I walk.” Which goal for this client should take priority?
(a) Conserve energy.
(b) Adapt self-care skills.
(c) Develop coping skills.
(d) Employ a housekeeping service.
Answer:
(a) Conserve energy.

Explanation:
Based on the information from the client, the nurse should develop a plan with the client that will conserve energy and decrease episodes of fatigue. Although the client may develop a self-care deficit related to the increasing joint pain, the client is voicing concerns about household chores and difficulty around the house and yard, not self-care issues. Over time, the client may have difficulty coping, but that is not the current concern. Employing cleaning services may not be within the client’s budget, and the client should first try a plan that balances rest and activity.
Question 3.
Of the clients listed, who is at risk for developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? Select all that apply.
(a) a client who is between the age of 20 and 50 years
(b) a client who has had an infectious disease with the Epstein-Barr virus
(c) a client who is male
(d) a client who possesses the genetic link HLA-DR4
(e) a client who also has osteoarthritis
Answer:
(a) a client who is between the age of 20 and 50 years
(b) a client who has had an infectious disease with the Epstein-Barr virus
(d) a client who possesses the genetic link HLA-DR4
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d). RA affects women three times more often than men between the ages of 20 and 55 years. Research has determined that RA occurs in clients who have had infectious disease, such as the Epstein-Barr virus. The genetic link, specifically HLA-DR4, has been found in 65% of clients with RA. People with osteoarthritis are not necessarily at risk for developing RA.
Question 4.
A client is in the acute phase of rheumatoid arthritis. In which order of priority from first to last should the nurse establish the goals? All options must be used.
(a) Relieve pain.
(b) Preserve joint function.
(c) Maintain usual ways of accomplishing tasks.
(d) Prevent joint deformity.
Answer:
(a) Relieve pain.
(b) Preserve joint function.
(d) Prevent joint deformity.
(c) Maintain usual ways of accomplishing tasks.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (c). Pain relief is the highest priority during the acute phase because pain is typically severe and interferes with the client’s ability to function. Preserving joint function is the next goal to set, followed by preventing joint deformity during the acute phase to promote an optimal level of functioning and reduce the risk of contractures. Maintaining usual ways of accomplishing tasks is the goal with the lowest priority during the acute phase. Rather, the focus is on developing less stressful ways of accomplishing routine tasks.
Question 5.
The nurse teaches a client about heat and cold treatments to manage arthritis pain. Which statement indicates that the client still has a knowledge deficit?
(a) “I can use heat and cold as often as I want.”
(b) “With heat, I should apply it for no longer than 20 minutes at a time.”
(c) “Heat-producing liniments can be used with ther heat devices.”
(d) “Ten to fifteen minutes per application is themaximum time for cold applications.”
Answer:
(c) “Heat-producing liniments can be used with ther heat devices.”
Explanation:
Heat-producing liniment can produce a bum if used with other heat devices that could intensify the response to the heat. Heat and cold can be used as often as the client desires. However, each application of heat should not exceed 20 minutes, and each application of cold should not exceed 10 to 15 minutes. Application for longer periods results in the opposite of the intended effect: vasoconstric-tion instead of vasodilation with heat and vasodilation instead of vasoconstriction with cold.
Question 6.
The client with rheumatoid arthritis tells the nurse, “I have a friend who took gold shots and had a wonderful response. Why didn’t my health care provider let me try that?” Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate?
(a) “It’s the health care provider’s prerogative to decide how to treat you. The health care provider has chosen what is best for your situation.”
(b) “Tell me more about your friend’s arthritic condition. Maybe I can answer that question for you.”
(c) “That drug is used for cases that are more advanced than yours. You’re not eligible for this treatment now.”
(d) “Every person is different. What works for one client may not always be effective for another.”
Answer:
(d) “Every person is different. What works for one client may not always be effective for another.”
Explanation:
The nurse’s most appropriate response is one that is therapeutic. The basic principle of therapeutic communication and a therapeutic relationship is honesty. Therefore, the nurse needs to explain truthfully that each client is different and that there are various forms of arthritis and arthritis treatment. To state that it is the HCP’s prerogative to decide how to treat the client implies that the client is not a member of his or her own health care team and is not a participant in his or her care. The statement also is defensive, which serves to block any further communication or questions.
Asking the client to tell more about the friend presumes that the client knows correct and complete information, which is not a valid assumption to make. The nurse does not know about the client’s friend and should not make statements about another client’s condi-tion. Stating that the drug is for advanced disease demonstrates that the nurse is making assumptions that are not necessarily valid or appropriate. Also, telling the client that he or she is not eligible for the drug now is not within the scope of the nurse’s practice.
Question 7.
The teaching plan for the client with rheumatoid arthritis includes rest promotion. What position of the involved joints should the nurse tell the client to avoid when at rest?
(a) keeping all joints aligned
(b) elevating the affected joints
(c) lying in a prone position
(d) maintaining the joints in a flexed position
Answer:
(d) maintaining the joints in a flexed position
Explanation:
Positions of flexion should be avoided to prevent loss of functional ability of affected joints. Proper body alignment during rest periods is encouraged to maintain correct muscle and joint placement. Lying in the prone position is encour-aged to avoid further curvature of the spine and internal rotation of the shoulders.
Question 8.
After teaching the client with rheumatoid arthritis about measures to conserve energy in activities of daily living involving the small joints, which activity observed by the nurse indicates the need for additional teaching?
(a) pushing with palms when rising from a chair
(b) holding packages close to the body
(c) sliding objects
(d) carrying a laundry basket with clinched fingers and fists
Answer:
(d) carrying a laundry basket with clinched fingers and fists
Explanation:
Carrying a laundry basket with clinched fingers and fists is not an example of conserving energy of small joints. The laundry basket should be held with both hands opened as wide as possible and with outstretched arms so that pressure is not placed on the small joints of the fingers. When rising from a chair, the palms should be used instead of the fingers so as to distribute weight over the larger area of the palms. Holding packages close to the body provides greater support to the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints because muscles of the arms and hands are used to stabilize the weight against the body.
This decreases the stress and weight or pull on small joints such as the fingers. Objects can be slid with the palm of the hand, which distributes weight over the larger area of the palms instead of stressing the small joints of the fingers to pick up the weight of the object to move it to another place.
Question 9.
After teaching the client with severe rheumatoid arthritis about prescribed methotrexate, which statement indicates the need for further teaching?
(a) “I will take my vitamins while I am on this drug.”
(b) “I must not drink any alcohol while I am taking this drug.”
(c) “I should brush my teeth after every meal.”
(d) “I will continue taking my birth control pills.”
Answer:
(a) “I will take my vitamins while I am on this drug.”
Explanation:
Because some over-the-counter vitamin supplements contain folic acid, the client should avoid self-medication with vitamins while taking methotrexate, a folic acid antagonist. Because methotrexate is hepatotoxic, the client should avoid the intake of alcohol, which could increase the risk for hepatotoxicity. Methotrexate can cause bone mar-row depression, placing the client at risk for infection. Therefore, meticulous mouth care is essential to minimize the risk of infection. Contraception should be used during methotrexate therapy and for 8 weeks after the therapy has been discontinued because of its effect on mitosis. Methotrexate is considered teratogenic.
Question 10.
A 25-year-old client taking hydroxychloroquine for rheumatoid arthritis reports difficulty seeing out of the left eye. What does this finding indicate?
(a) development of a cataract
(b) possible retinal degeneration
(c) part of the disease process
(d) a coincidental occurrence
Answer:
(b) possible retinal degeneration
Explanation:
Difficulty seeing out of one eye, when evaluated in conjunction with the client’s medication therapy regimen, leads to the suspicion of possible retinal degeneration. The possibility of an irreversible retinal degeneration caused by deposits of hydroxychloroquine in the layers of the retina requires an ophthalmologic examination before therapy is begun and at 6-month intervals. Although cataracts may develop in young adults, they are less likely, and damage from the hydroxychloroquine is the most obvious at-risk factor. Eyesight is not affected by the disease process of rheumatoid arthritis.
Question 11.
A client with rheumatoid arthritis is taking high doses of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. What should the nurse teach the client about taking these medications?
(a) “Take prescribed medication with food to lessen the likelihood of an upset stomach.”
(b) “Do not stop taking the medication suddenly; the dose needs to be decreased gradually.”
(c) “Use mouthwash to rinse the mouth after taking this medication.”
(d) “Do not drive or use heavy machinery if dizziness occurs.”
Answer:
(a) “Take prescribed medication with food to lessen the likelihood of an upset stomach.”
Explanation:
Gastric upset is a side effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications; taking medication with food minimizes this effect. Corticosteroids affect adrenal gland function and are discontinued by lowering the dose gradually, but this is not true of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. It is not necessary to rinse the mouth, as stomatitis is not a usual side effect. Dizziness is not an effect of this drug.
Question 12.
A client with rheumatoid arthritis tells the nurse, “I know it’s important to exercise my joints so that I won’t lose mobility, but my joints are so stiff and painful that exercising is difficult.” Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate?
(a) “You’re probably exercising too much. Decrease your exercise to every other day.”
(b) "Tell the health care provider about your symptoms. Maybe your analgesic medication can be increased.”
(c) “Stiffness and pain are part of the disease. Learn to cope by focusing on activities you enjoy.”
(d) “Take a warm tub bath or shower before exercising. This may help with your discomfort.”
Answer:
(d) “Take a warm tub bath or shower before exercising. This may help with your discomfort.”
Explanation:
Superficial heat applications, such as tub baths, showers, and warm compresses, can be helpful in relieving pain and stiffness. Exercises can be performed more comfortably and more effectively after heat applications. The client with rheumatoid arthritis must balance rest with exercise every day, not every other day. Typically, large doses of analgesics, which can lead to hepatotoxic effects, are not necessary. Learning to cope with the pain by refocusing is inappropriate.
Question 13.
Which information should the nurse include in the teaching session when preparing a client for arthrocentesis? Select all that apply.
(a) “A local anesthetic agent may be injected into the joint site for your comfort.”
(b) “A syringe and needle will be used to withdraw fluid from your joint.”
(c) “The procedure, although not painful, will provide immediate relief.”
(d) “We will want you to keep your joint active after the procedure to increase blood flow.”
(e) “You will need to wear a compression bandage for several days after the procedure.
Answer:
(a) “A local anesthetic agent may be injected into the joint site for your comfort.”
(b) “A syringe and needle will be used to withdraw fluid from your joint.”
(d) “We will want you to keep your joint active after the procedure to increase blood flow.”
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d). An arthrocentesis is performed to aspirate excess synovial fluid, pus, or blood from a joint cavity to relieve pain or to diagnose inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. A local agent may be used to decrease the pain of the needle insertion through the skin and into the joint cav-ity. Aspiration of the fluid into the syringe can be very painful because of the size and inflammation of the joint.
Usually, a steroid medication is injected locally to alleviate the inflammation; a compression bandage is applied to help decrease swelling; and the client is asked to rest the joint for up to 24 hours afterward to help relieve the pain and promote rest to the inflamed joint. The client may experience pain during this time until the inflammation begins to resolve and swelling decreases.
Question 14.
A client with osteoarthritis will undergo an arthrocentesis on a painful, edematous knee. What information should be included in the nursing plan of care? Select all that apply.
(a) Explain the procedure.
(b) Administer preoperative medication 1 hour before surgery.
(c) Instruct the client to immobilize the knee for 2 days after the surgery.
(d) Assess the site for bleeding.
(e) Offer pain medication.
Answer:
(a) Explain the procedure.
(d) Assess the site for bleeding.
(e) Offer pain medication.
Explanation:
(a), (d), (c). To prepare a client for an arthrocentesis, the nurse should tell the client that a local anesthetic administered by the health care provider (HCP) fT] will decrease discomfort. There may be bleeding after the procedure, so the nurse should check the dressing. The client may experience pain. The nurse should offer pain medication and evaluate outcomes for pain relief. Because a local anesthetic is used, the client will not require preoperative medication. The client will rest the knee for 24 hours and then should begin range-of-motion and muscle-strengthening exercises.
Question 15.
A postmenopausal client is scheduled for a bone density scan. What should the nurse instruct the client to do?
(a) Remove all metal objects on the day of the scan.
(b) Consume foods and beverages with a high content of calcium for 2 days before the test.
(c) Ingest 600 mg of calcium gluconate by mouth for 2 weeks before the test.
(d) Report any significant pain to the health care provider at least 2 days before the test.
Answer:
(a) Remove all metal objects on the day of the scan.
Explanation:
Metal will interfere with the test. Metallic objects within the examination field, such as jewelry, earrings, and dental amalgams, may inhibit organ visualization and can produce unclear images. Ingesting foods and beverages days before the test will not affect bone mineral status. Short-term cal-cium gluconate intake will also not influence bone mineral status. The client may already have had chronic pain as a result of a bone fracture or from osteoporosis.
Question 16.
A health care provider (HCP) prescribes a lengthy X-ray examination for a client with osteoarthritis with severe pain. Which action by the nurse would demonstrate client advocacy?
(a) Contact the X-ray technician to see if the lengthy session can be divided into shorter sessions.
(b) Contact the HCP to determine if an alternative examination could be scheduled.
(c) Request a prescription for acetaminophen prior to the examination.
(d) Request padding and careful positioning for the hard X-ray table.
Answer:
(a) Contact the X-ray technician to see if the lengthy session can be divided into shorter sessions.

Explanation:
Shorter sessions will allow the client to rest between the sessions. Changing the HCP’s prescription to a different examination will not provide the information needed for this client's treatment. Acetaminophen is a nonopioid analgesic and an antipyretic, not an anti-inflammatory agent; thus, it would not help this client avoid the adverse effects of a lengthy X-ray examination. Although the X-ray table is hard, it is not possible to provide padding and obtain the needed diagnostic X-rays.
Question 17.
Which condition should the nurse assess when completing the history and physical examination of a client diagnosed with osteoarthritis?
(a) anemia
(b) osteoporosis
(c) weight loss
(d) local joint pain
Answer:
(d) local joint pain
Explanation:
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease with local manifestations such as local joint pain. Rheumatoid arthritis has systemic manifestation such as anemia and osteoporosis. Weight loss occurs in rheumatoid arthritis, whereas most clients with osteoarthritis are overweight.
Question 18.
Which information should be included in the teaching plan for a client with osteoporosis? Select all that apply.
(a) Maintain a diet with adequate amounts of vitamin D.
(b) Choose foods with high calcium content.
(c) Use alcohol in moderation.
(d) Swim as a good exercise to maintain bone mass.
(e) Avoid high-fat foods.
Answer:
(a) Maintain a diet with adequate amounts of vitamin D.
(b) Choose foods with high calcium content.
(c) Use alcohol in moderation.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c). A diet with adequate amounts of vitamin D aids in the regulation, absorption, and subsequent utilization of calcium and phosphorus, which are necessary for the normal calcification of bone. Figs, broccoli, and almonds are very good sources of calcium. Moderate intake of alcohol has no known negative effects on bone density, but excessive alcohol intake does reduce bone density. Swimming, biking, and other non-weight-bearing exercises do not maintain bone mass. Walking and running, which are weight-bearing exercises, do maintain bone mass. The client should eat a balanced diet but does not need to avoid high-fat foods.
Question 19.
Which statement indicates that the client with osteoarthritis understands the effects of capsaicin cream?
(a) “I always wash my hands right after I apply the cream.”
(b) “After I apply the cream, I wrap my knee with an elastic bandage.”
(c) “I keep the cream in the cabinet above the stove in the kitchen.”
(d) “I also use the same cream when I get a cut or a burn.”
Answer:
(a) “I always wash my hands right after I apply the cream.”
Explanation:
Capsaicin cream, which produces analgesia by preventing the reaccumulation of substance P in the peripheral sensory neurons, is made from the active ingredients of hot peppers. Therefore, clients should wash their hands immediately after applying capsaicin cream, if they do not wear gloves, to avoid possible contact between the cream and mucous membranes.
Clients are instructed to avoid wearing tight bandages over areas where capsaicin cream has been applied because swelling may occur from inflammation of the arthritis in the joint and lead to constriction on the peripheral neurovascular system. Capsaicin cream should be stored in areas between 59°F and 86°F (15°C and 30°C). The cabinet over the stove in the kitchen would be too warm. Capsaicin cream should not come in contact with irritated and broken skin, mucous membranes, or eyes. Therefore, it should not be used on cuts or burns.
Question 20.
At which time should the nurse instruct the client to take ibuprofen, prescribed for left hip pain secondary to osteoarthritis, to minimize gastric mucosal irritation?
(a) at bedtime
(b) on arising
(c) immediately after a meal
(d) on an empty stomach
Answer:
(c) immediately after a meal
Explanation:
Drugs that cause gastric irritation, such as ibuprofen, are best taken after or with a meal, when stomach contents help minimize the local irritation. Taking the medication on an empty stomach at any time during the day will lead to gastric irritation. Taking the drug at bedtime with food may cause the client to gain weight, possibly aggravating the osteoarthritis. When the client arises, he or she is stiff from immobility and should use warmth and stretching until he or she gets food in the stomach.
Question 21.
The client diagnosed with osteoarthritis tells the nurse, “My friend takes steroid pills for her rheumatoid arthritis. Should I be taking steroids, too?” What should the nurse explain to the client?
(a) Intra-articular corticosteroid injections are used to treat osteoarthritis.
(b) Oral corticosteroids can be used in osteoarthritis.
(c) A systemic effect is needed in osteoarthritis.
(d) Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are two similar diseases.
Answer:
(a) Intra-articular corticosteroid injections are used to treat osteoarthritis.
Explanation:
Corticosteroids are used for clients with osteoarthritis to obtain a local effect. Therefore, they are given only via intra-articular injection. Oral corticosteroids are avoided because they can cause an acceleration of osteoarthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are two different diseases.
Question 22.
After teaching a client with osteoarthritis about the importance of regular exercise, which statement indicates the client has understood the teaching?
(a) “Performing range-of-motion exercises will increase my joint mobility.”
(b) “Exercise helps to drive synovial fluid through the cartilage.”
(c) "Joint swelling should determine when to stop exercising.”
(d) “Exercising in the outdoors year-round promotes joint relaxation.”
Answer:
(b) “Exercise helps to drive synovial fluid through the cartilage.”
Explanation:
Weight -bearing exercise plays a very important role in stimulating regeneration of cartilage, which lacks blood vessels, by driving synovial fluid through the joint cartilage. Joint mobility is increased by weight-bearing exercises, not range- of-motion exercises, because surrounding muscles, ligaments, and tendons are strengthened. Pain is an early sign of degenerative joint bone problems. Swelling may not occur for some time after pain, if at all. Osteoarthritic pain is worsened in cold, damp weather; therefore, exercising outdoors is not recommended year-round in all settings.
Question 23.
A client in a double hip spica cast is constipated. The surgeon cuts a window into the front of the cast. Which outcome is intended?
The window in the cast will allow:
(a) the nurse to palpate the superior mesenteric artery.
(b) the surgeon to manipulate the fracture site.
(c) the nurses to reposition the client.
(d) relief from pressure due to abdominal distention.
Answer:
(d) relief from pressure due to abdominal distention.
Explanation:
The hip spica cast is used for treatment of femoral fractures; it immobilizes the affected extremity and the trunk securely. It extends from above the nipple line to the base of the foot of both extremities in a double hip spica. Constipation, possible due to lack of mobility, can cause abdominal distention or bloating. When the spica cast becomes too tight due to distention, the cast will compress the superior mesenteric artery against the duodenum. The compression produces abdominal pain, abdominal pressure, nausea, and vomiting.
To relieve the compression, the surgeon can cut a “window” in the cast. The nurse should assess the abdomen for decreased bowel sounds, not the superior mesenteric artery. The surgeon cannot manipulate a fracture through a small window in a double hip spica cast. The nurse cannot use the window to aid in repositioning because the window opening can break and negate the effect of the cast.
Question 24.
A client has an intracapsular hip fracture.
The nurse should conduct a focused assessment to detect which change near the fracture?
(a) internal rotation
(b) muscle flaccidity
(c) shortening of the affected leg
(d) absence of pain area
Answer:
(c) shortening of the affected leg
Explanation:
With an intracapsular hip fracture, the affected leg is shorter than the unaffected leg because of the muscle spasms and external rotation. The client also experiences severe pain in the region of the fracture.
Question 25.
A client with an extracapsular hip fracture is scheduled for surgical internal fixation with the insertion of a pin. What can the nurse can tell the client about the reason for this type of treatment for the fracture?
(a) Hemorrhage at the fracture site is prevented.
(b) Neurovascular impairment risk is decreased.
(c) The risk of infection at the site is lessened.
(d) The client is able to be mobilized sooner.
Answer:
(d) The client is able to be mobilized sooner.
Explanation:
Insertion of a pin for the internal fixation of an extracapsular fractured hip provides good fixation of the fracture. The fracture site is stabilized, and fractured bone ends are well approximated. As a result, the client is able to be mobilized sooner, thus reducing the risks of complications related to immobility. Internal fixation with a pin insertion does not prevent hemorrhage or decrease the risk of neurovascular impairment, which are potential com-plications associated with any joint or bone surgery. It does not lessen the client’s risk of infection at the site.
Question 26.
A client with an extracapsular hip fracture returns to the nursing unit after internal fixation and pin insertion with a drainage tube at the incision site. Her husband asks, “Why does she have this tube inserted in her hip?” Which response would be best?
(a) “The tube helps us to detect a wound infection.”
(b) “This way we will not have to irrigate the wound.”
(c) “Fluid will drain and not accumulate at the site.”
(d) “We have a way to administer antibiotics into the wound.”
Answer:
(c) “Fluid will drain and not accumulate at the site.”
Explanation:
The primary purpose of the drainage tube is to prevent fluid accumulation in the wound. Fluid, when it accumulates, creates dead space. Elimination of the dead space by keeping the wound free of fluid greatly enhances wound healing and helps prevent abscess formation. Although the characteristics of the drainage from the tube, such as a change in color or appearance, may suggest a possible infection, this is not the tube’s primary purpose. The drainage tube does not eliminate the need for wound irrigation or provide a way to instill antibiotics into the wound.
Question 27.
A client with a hip fracture has undergone surgery for insertion of a femoral head prosthesis. Which activity should the nurse instruct the client to avoid?
(a) crossing the legs while sitting down
(b) sitting on a raised commode seat
(c) using an abductor splint while lying on the side
(d) rising straight from a chair to a standing position
Answer:
(a) crossing the legs while sitting down
Explanation:
Any activity or position that causes flexion, adduction, or internal rotation of >90 degrees should be avoided until the soft tissue surrounding the prosthesis has stabilized, at approximately 6 weeks. Crossing the legs while sitting down causes internal rotation and can lead to dislocation of the femoral head from the hip socket. Sitting on a raised commode seat prevents hip flexion and adduction. Using an abductor splint while side-lying keeps the hip joint in abduction, thus preventing adduction and possible dislocation. Rising straight from a chair to a standing position is acceptable for this client because this action avoids hip flexion, adduction, and internal rotation of >90 degrees.
Question 28.
The nurse is caring for an older adult male who had open reduction internal fixation of the right hip 24 hours ago. The client is now experiencing shortness of breath and reports having “tightness in my chest.” The nurse reviews the recent lab results. The nurse should report which lab results to the health care provider?
(a) hematocrit (Hct): 40% (0.4]
(b) serum glucose: 120 mg/dL (6.7 mmol/L]
(c) troponin: 1.4 mcg/L (1.4 pg/L)
(d) erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR):
22 mm/h
Answer:
(c) troponin: 1.4 mcg/L (1.4 pg/L)
Explanation:
Troponin is a cardiac biomarker and is normally almost undetectable in the blood. A level of 1.4 means there has likely been some damage to the heart muscle. Though serum glucose (normal 60 to 100 mg/dL [3.3 to 5.5 mmol/L]) and ESR (normal is <20 for males >50 years old) are slightly elevated, this could be explained by normal stress and inflammatory response to surgery. The hematocrit is low (normal 40 to 45 [0.4 to 0.5] for men) but also not unexpected for a client following surgery.
Question 29.
The nurse advises the client who has had a femoral head prosthesis placement on the type of chair to sit in during the first 6 to 8 weeks after surgery. Which chair would be the correct type to recommend?
(a) a desk-type swivel chair
(b) a padded upholstered chair
(c) a high-backed chair with armrests
(d) a recliner with an attached footrest
Answer:
(c) a high-backed chair with armrests

Explanation:
A high-backed straight chair with armrests is recommended to help keep the client in the best possible alignment after surgery for a femoral head prosthesis placement. The use of this type of chair helps to prevent the dislocation of the prosthesis from the socket. A desk-type swivel chair, padded upholstered chair, or recliner should be avoided because it does not provide for good body alignment and can cause the overly flexed femoral head to dislocate.
Question 30.
The nurse is to apply a sequential compression device (intermittent pneumatic compression). Identify the area of the compression device that is placed on the client’s calf.
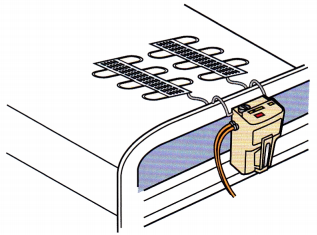
Answer:
The air cell should be centered on the back of the client’s calf.
Question 31.
The nurse is assessing the home environment of an elderly client who is using crutches during the postoperative recovery phase after hip pinning. Which poses the greatest hazard to the client as a risk for falling at home?
(a) a 4-year-old cocker spaniel
(b) scatter rugs
(c) snack tables
(d) rocking chairs
Answer:
(b) scatter rugs
Explanation:
Although pets and furniture, such as snack tables and rocking chairs, may pose a problem, scatter rugs are the single greatest hazard in the home, especially for elderly people who are unsure and unsteady with walking. Falls have been found to account for almost half the accidental deaths that occur in the home. The risk of falls is further compounded by the client’s need for crutches.
Question 32.
An older adult with a hip fracture is to use an alternating air pressure mattress at home to prevent pressure ulcers while recovering from surgery. The nurse is showing the client’s family how to place the mattress (see below). What should the nurse instruct the family to do?
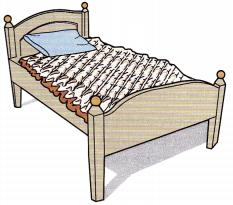
(a) Turn the mattress over so the air cells face the mattress of the bed, and cover the mattress with a bedsheet.
(b) Put a thick pad over the pressure mattress to prevent soiling, and place the bedsheet on top of the pad.
(c) Make the bed with the bedsheet on top of the pressure mattress.
(d) Place the sheet on the bed, and then remove the pillow to allow full use of the mattress on the neck.
Answer:
(c) Make the bed with the bedsheet on top of the pressure mattress.

Explanation:
To obtain best results, one sheet should be used to cover the mattress. The air cells should be facing up as shown. Thick pads should not be used; if the client is incontinent, a “breathable” incontinent pad can be added. The client can use a pillow as needed.
Question 33.
A client had a posterolateral total hip replacement 2 days ago. What information should the nurse include in the client’s plan of care? Select all that apply.
(a) When using a walker, encourage the client to keep the toes pointing inward.
(b) Position a pillow between the legs to maintain abduction.
(c) Allow the client to be in the supine position or in the lateral position on the unoperated side.
(d) Do not allow the client to bend down to tie or slip on shoes.
(e) Place ice on the incision after physical therapy.
Answer:
(b) Position a pillow between the legs to maintain abduction.
(c) Allow the client to be in the supine position or in the lateral position on the unoperated side.
(d) Do not allow the client to bend down to tie or slip on shoes.
(e) Place ice on the incision after physical therapy.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d), (e). A client who has had a posterolateral total hip replacement should not adduct the hip joint, which would lead to dislocation of the ball out of the socket; therefore, the client should be encouraged to keep the toes pointed slightly outward when using a walker. An abduction pillow should be kept between the legs to keep the hip joint in an abducted position. The client should rotate between lying supine and lateral on the unoperated side, but not on the operated side. Ice is used to reduce swelling on the operative side. The client should not flex the operated hip beyond a 90-degree angle, such as when bending down to tie or slip on shoes. Doing so could lead to joint dislocation.
Question 34.
Which information should the nurse include when performing discharge teaching with a client who had an anterolateral approach for a total hip replacement? Select all that apply.
(a) Avoid turning the toes or knee outward.
(b) Use an abduction pillow between the legs when in bed.
(c) Use an elevated toilet seat and shower chair.
(d) Do not extend the operative leg backward.
(e) Restrict motion for 2 weeks after surgery.
Answer:
(a) Avoid turning the toes or knee outward.
(c) Use an elevated toilet seat and shower chair.
(d) Do not extend the operative leg backward.

Explanation:
(a), (c), (d). A client who has had a total hip replacement via an anterolateral approach has almost the opposite precautions as those for a client who has had a total hip replacement through the posterolateral approach. The hip joint should not be actively abducted. The client should avoid turning the toes or knee outward. The client should keep the legs side by side without a pillow or wedge. The client should use an elevated toilet seat and shower chair and should not extend the operative leg backward. The client should perform range-of-motion exercises as directed by the physical therapist.
Question 35.
The nurse is assessing a client for neurologic impairment after a total hip replacement. Which finding indicates impairment in the affected extremity?
(a) decreased distal pulse
(b) inability to move
(c) diminished capillary refill
(d) coolness to the touch
Answer:
(b) inability to move
Explanation:
Being unable to move the affected leg suggests neurologic impairment. A decrease in the distal pulse, diminished capillary refill, and coolness to touch of the affected extremity suggest vascular compromise.
Question 36.
The nurse is instructing a client who will have a total hip replacement tomorrow. Which information is most important to include in the teaching plan at this time?
(a) Teach how to prevent hip flexion.
(b) Demonstrate coughing and deep-breathing techniques.
(c) Show the client what an actual hip prosthesis looks like.
(d) Assess the client’s fears about the procedure.
Answer:
(d) Assess the client’s fears about the procedure.
Explanation:
The nurse should first identify and discuss the client’s fears about the procedure. Only then can the client begin to hear what the nurse has to share about the individualized teaching plan designed to meet the client’s needs. In the preoperative period, the client needs to learn how to correctly prevent hip flexion and to demonstrate coughing and deep breathing. However, this teaching can be effective only after the client’s fears have been assessed and addressed. Although the client may appreciate seeing what a hip prosthesis looks like, so as to understand the new body part, this is not a necessity.
Question 37.
After surgery and insertion of a total hip prosthesis, a client develops severe sudden pain and an inability to move the extremity. What do these findings indicate?
The client:
(a) is developing an infection.
(b) is bleeding in the operative site.
(c) has a joint dislocation.
(d) has glue seepage into soft tissue.
Answer:
(c) has a joint dislocation.
Explanation:
The joint has dislocated when the client with a total joint prosthesis develops severe sudden pain and an inability to move the extremity. Clinical manifestations of an infection would include inflammation, redness, erythema, and possibly drainage and separation of the wound. Bleeding could be external (e.g., blood visible from the wound or on the dressing) or internal and manifested by signs of shock (e.g., pallor, coolness, hypotension, tachycardia). The seepage of glue into soft tissue would have occurred in the operating room, when the glue is still in the liquid form. The glue dries into the hard, fixed form before the wound is closed.
Question 38.
A client who had a total hip replacement 2 days ago has developed an infection with a fever, profuse diaphoresis, and dehydration. The nurse establishes a care plan to make the client comfortable. Which goals are appropriate? Select all that apply.
(a) Drink 2,000 mL of fluid per day.
(b) Understand how to manage the incision.
(c) Have bed linens changed as needed.
(d) Have cool and dry skin.
(e) Remain on complete bed rest.
Answer:
(a) Drink 2,000 mL of fluid per day.
Explanation:
To make the client who has a fever, diaphoresis, and dehydration comfortable, the nurse should help the client increase the fluid intake, make sure the bed linens are changed as needed, and offer cool cloths to keep the skin cool and dry. The client is not ready to learn to manage the incision. The client does not need to be on bed rest, but rather should get out of bed as tolerated to promote lung expansion and muscle strength.
Question 39.
A client had a total hip replacement today. How should the nurse position the client when the client is transferred from the transport cart to the bed?
(a) Place weights alongside the affected extremity to keep the extremity from rotating.
(b) Elevate both feet on two pillows.
(c) Keep the lower extremities adducted by use of an immobilization device around both legs-
(d) Maintain the affected extremity in slight abduction using an abduction splint or pillows placed between the thighs.
Answer:
(d) Maintain the affected extremity in slight abduction using an abduction splint or pillows placed between the thighs.
Explanation:
After total hip replacement, proper positioning by the nurse prevents dislocation of the prosthesis. The nurse should place the client in a supine position and keep the affected extremity in slight abduction using an abduction splint or pil-lows or Buck’s extension traction. The client must not abduct or flex the operated hip because this may produce dislocation.
Question 40.
Following a client’s total hip replacement, what should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) With the aid of a coworker, turn the client from the supine to the prone position every 2 hours.
(b) Encourage the client to use the overhead trapeze to assist with position changes.
(c) For meals, elevate the head of the bed to 90 degrees.
(d) Use a fracture bedpan when needed by the client.
(e) When the client is in bed, prevent thromboembolism by encouraging the client to do toe-pointing exercises.
Answer:
(b) Encourage the client to use the overhead trapeze to assist with position changes.
(d) Use a fracture bedpan when needed by the client.
(e) When the client is in bed, prevent thromboembolism by encouraging the client to do toe-pointing exercises.
Explanation:
(b), (d), (e). Following total hip replacement, the client should use the overhead trapeze to assist with position changes. The head of the bed should not be elevated more than 45 degrees; any height >45 degrees puts a strain on the hip joint and may cause dislocation. To use a fracture bedpan, instruct the client to flex the unoperated hip and knee to lift the buttocks onto the pan. Toe-pointing exercises stimulate circulation in the lower extremities to prevent the formation of thrombi and potential emboli. The prone position is avoided shortly after a total hip replacement.
Question 41.
A client is to have a total hip replacement. What nursing actions should the preoperative plan include? Select all that apply.
(a) Administer antibiotics as prescribed to ensure therapeutic blood levels.
(b) Apply leg compression device.
(c) Request a trapeze be added to the bed.
(d) Teach isometric exercises of quadriceps andgluteal muscles.
(e) Demonstrate crutch walking with a three-point gait.
(f) Place Buck’s traction on the bed.
Answer:
(a) Administer antibiotics as prescribed to ensure therapeutic blood levels.
(c) Request a trapeze be added to the bed.
(d) Teach isometric exercises of quadriceps andgluteal muscles.
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d). Administration of antibiotics as prescribed will aid in the acquisition of therapeutic blood levels during and immediately after surgery to prevent osteomyelitis. The nurse can request that a trapeze be added to the bed so the client can assist with lifting and turning. The nurse should also demonstrate and have the client practice isometric exercises (muscle setting) of quadriceps and gluteal muscles.
The client will not use crutches after surgery; a physical therapy assistant will initially assist the client with walking by using a walker. The client will not use Buck’s traction. The client will require antiembolism stockings and use of a leg compression device to minimize the risk of thrombus formation and potential emboli; the leg compression device is applied during surgery and maintained per prescription.
Question 42.
The nurse is teaching the client to administer enoxaparin following a total hip replacement. What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Report promptly any difficulty breathing, rash, or itching.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of unusual bruising.
(c) Avoid all aspirin-containing medications.
(d) Wear or carry medical identification.
(e) Expel the air bubble from the syringe before the injection.
(f) Remove the needle immediately after the medication is injected.
Answer:
(a) Report promptly any difficulty breathing, rash, or itching.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP) of unusual bruising.
(c) Avoid all aspirin-containing medications.
(d) Wear or carry medical identification.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d). Client/family teaching should include advising the client to report any symptoms of unusual bleeding or bruising, dizziness, itching, rash, fever, swelling, or difficulty breathing to HCP immediately. Instruct the client not to take aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs without consulting the HCP while on therapy. A low-molecular-weight heparin is considered to be a high-risk medication, and the client should wear or carry medical identification. The air bubble should not be expelled from the syringe because the bubble ensures the client receives the full dose of the medication. The client should allow 5 seconds to pass before withdrawing the needle to prevent seepage of the medication out of the site.
Question 43.
A client who had a total hip replacement 4 days ago is worried about dislocation of the prosthesis. How should the nurse respond to the client’s concern?
(a) “Don’t worry. Your new hip is very strong.”
(b) “Use of a cushioned toilet seat helps to prevent dislocation.”
(c) “Activities that tend to cause adduction of the hip tend to cause dislocation, so try to avoid them.”
(d) “Decreasing use of the abductor pillow will strengthen the muscles to prevent dislocation.”
Answer:
(c) “Activities that tend to cause adduction of the hip tend to cause dislocation, so try to avoid them.”
Explanation:
Dislocation precautions include the following: avoid extremes of internal rotation, adduction, and 90-degree flexion of affected hip for at least 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure. Use of an abduction pillow prevents adduction. Decreasing use of the abductor pillow does not strengthen the muscles to prevent dislocation. Informing a client to “not worry” is not therapeutic. A cushioned toilet seat does not prevent hip dislocation.
Question 44.
The nurse is assessing a client who had a left hip replacement 36 hours ago. Which findings indicate the prosthesis is dislocated? Select all that apply.
(a) The client reported a “popping” sensation in the hip.
(b) The left leg is shorter than the right leg.
(c) The client has sharp pain in the groin.
(d) The client cannot move the right leg.
(e) The client cannot wiggle the toes on the left leg.
Answer:
(a) The client reported a “popping” sensation in the hip.
(b) The left leg is shorter than the right leg.
(c) The client has sharp pain in the groin.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c). Dislocation of a hip prosthesis may occur with positioning that exceeds the limits of the prosthesis. The nurse must recognize dislocation of the prosthesis. Signs of prosthesis dislocation include acute groin pain in the affected hip, shortening of the affected leg, restricted ability or inability to move the affected leg, and reported “popping” sensation in the hip. Toe wiggling is not a test for potential hip dislocation.
Question 45.
A client who has had a total hip replacement has a dislocated hip prosthesis. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Stabilize the leg with Buck’s traction.
(b) Apply an ice pack to the affected hip.
(c) Position the client toward the opposite side of the hip.
(d) Notify the orthopedic surgeon.
Answer:
(d) Notify the orthopedic surgeon.
Explanation:
If a prosthesis becomes dislocated, the nurse should immediately notify the surgeon. This is done so the hip can be reduced and stabilized promptly to prevent nerve damage and to maintain circulation. After closed reduction, the hip may be stabilized with Buck’s traction or a brace to prevent recurrent dislocation. If prescribed by the surgeon, an ice pack may be applied postreduction to limit edema, although caution must be utilized due to potential muscle spasms. Some orthopedic surgeons may prescribe the client be turned toward the side of the reduced hip, but that is not the nurse’s first response.
Question 46.
The nurse has established a goal with a client to improve mobility following hip replacement. Which outcome is realistic at the time of discharge from the surgical unit?
The client can:
(a) walk throughout the nursing unit with a walker.
(b) walk the length of a hospital hallway with minimal pain.
(c) be more independent when transferring from bed to chair.
(d) raise the affected leg 6 inches (15.2 cm) with assistance.
Answer:
(c) be more independent when transferring from bed to chair.
Explanation:
Expected outcomes at the time of discharge from the surgical unit after a hip replacement include the following: increased independence in transfers, participates in progressive ambulation without pain or assistance, and raises the affected leg without assistance. The client will not be able to walk throughout the hospital, walk for a distance without some postoperative pain, or raise the affected leg more than several inches. The client may be referred to a rehabilitation unit in order to achieve the additional independence, strength, and pain relief.
Question 47.
Following a total joint replacement, which complication has the greatest likelihood of occurring?
(a) deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
(b) polyuria
(c) displacement of the new joint
(d) wound evisceration
Answer:
(a) deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Explanation:
DVT is a complication of total joint replacement and may occur during hospitalization or develop later when the client is home. Clients who are obese or have a previous history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism are at high risk. Immobility produces venous stasis, increasing the client’s chance of developing a venous thromboembolism. Signs of DVT include unilateral calf tenderness, warmth, redness, and edema (increased calf circumference). Findings should be reported promptly to the health care provider (HCP) for definitive evaluation and therapy. Polyuria may be indicative of diabetes mellitus. Displacement of the new joint is unlikely. Wound evisceration is more likely to occur after abdominal surgeries.
Question 48.
In preparation for total knee surgery, a 200-lb (90.7-kg) client with osteoarthritis must lose weight. Which exercise should the nurse recommend as best if the client has no contraindications?
(a) weight lifting
(b) walking
(c) aquatic exercise
(d) tai chi exercise
Answer:
(c) aquatic exercise

Explanation:
When combined with a weight loss program, aquatic exercise would be best because it cushions the joints and allows the client to burn off calories. Aquatic exercise promotes circulation, muscle toning, and lung expansion, which promote healthy preoperative conditioning. Weight lifting and walking are too stressful to the joints, possibly exacerbating the client’s osteoarthritis. Although tai chi exercise is designed for stretching and coordination, it would not be the best exercise for this client to help with weight loss.
Question 49.
The client has just had a total knee replacement. When assessing the client, which finding should lead the nurse to suspect possible nerve damage?
(a) numbness
(b) bleeding
(c) dislocation
(d) pinkness
Answer:
(a) numbness
Explanation:
The nurse should suspect nerve damage if numbness is present. However, whether the damage is short-term and related to edema or long-term and related to permanent nerve damage would not be clear at this point. The nurse needs to continue to assess the client’s neurovascular status, including pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia, and paralysis (the five Ps). Bleeding would suggest vascular damage or hemorrhage. Dislocation would suggest malalignment. The pink color would suggest adequate circulation to the area. Numbness would suggest neurologic damage.
Question 50.
After knee arthroplasty, the client has a sequential compression device (SCD). What should the nurse do?
(a) Elevate the SCD on two pillows.
(b) Change the settings on the SCD to make the client more comfortable.
(c) Stop the SCD to remove dressings, and bathe the leg.
(d) Discontinue the SCD when the client is ambulatory.
Answer:
(d) Discontinue the SCD when the client is ambulatory.
Explanation:
After knee arthroplasty, the knee will be extended and immobilized with a firm compression dressing and an adjustable soft extension splint in place. An SCD will be applied. The SCD can be discontinued when the client is ambulatory, but while the client is in bed the SCD needs to be maintained to prevent thromboembolism. The SCD should be positioned on the bed, but not on two pillows. Settings for the SCD are prescribed by the orthopedic surgeon. Initial dressing changes are completed by the orthopedic surgeon and changed as needed per prescription.
Question 51.
A client returns from the first session of scheduled physical therapy following total knee replacement surgery. The nurse assesses that the client’s knee is swollen, slightly erythematous, and painful. The client rates the pain as 7 out of 10 and has not had any scheduled or PRN pain medication today. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Gently massage the area to increase circula tion to reduce pain.
(b) Administer pain medication as prescribed.
(c) Elevate the leg and apply a cold pack.
(d) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(e) Call physical therapy to cancel the next treatment.
Answer:
(b) Administer pain medication as prescribed.
(c) Elevate the leg and apply a cold pack.
Explanation:
(b), (c). It is anticipated that there might be some swelling, redness, and discomfort immediately after activity, including physical therapy. Ideally, pain medication could be offered or given prior to therapy to reduce posttreatment pain but should be administered now. Elevation and cold packs can also reduce swelling and decrease pain. It is not appropriate to notify the HCP as pain and swelling are normal after therapy. It is also not appropriate to massage the area. This will increase circulation and therefore increase swelling and pain.
Question 52.
The nurse is preparing a client who has had a knee replacement with a metal joint to go home. What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Notify health care provider (HCP) about the joint prior to invasive procedures.
(b) Inform the HCP prior to having magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
(c) Notify airport security that the joint may set off alarms on metal detectors.
(d) Refrain from carrying items weighing more than 5 lb (2.3 kg).
(e) Eat a low-fat, low-carbohydrate diet.
Answer:
(a) Notify health care provider (HCP) about the joint prior to invasive procedures.
(b) Inform the HCP prior to having magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
(c) Notify airport security that the joint may set off alarms on metal detectors.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c). The nurse should instruct the client to notify the dentist and other HCPs of the need to take prophylactic antibiotics if undergoing any procedure (e.g., tooth extraction) due to the potential of bacteremia. The nurse should also advise the client that the metal components of the joint may set off the metal-detector alarms in airports. The client should also report having the metal joint prior to having MRI studies because, depending on the type of joint replacement, the implanted metal components could be pulled toward the large magnet core of the MRI. Any weight bearing that is permitted is prescribed by the orthopedic surgeon and is usually not limited to 5 lb (2.3 kg). After surgery, the client can resume a normal diet with regular fluid intake.
Question 53.
The laboratory notifies the nurse that a client who had a total knee replacement 3 days ago and is receiving heparin has an activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) of 95 seconds. After verifying the values, the nurse calls the health care provider (HCP). What prescription for the client should the nurse recommend the HCP consider?
(a) protamine sulfate
(b) vitamin K
(c) warfarin
(d) packed red blood cells
Answer:
(a) protamine sulfate
Explanation:
The aPTT is at a critical value, and the client should receive protamine sulfate as the antidote for heparin. Vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin. Packed red blood cells are administered to increase the hematocrit.
Question 54.
The nurse is assessing a client’s left leg for neurovascular changes following a total left knee replacement. Which are expected normal findings? Select all that apply.
(a) moderate edema of the left knee
(b) skin warm to touch
(c) capillary refill response of <3 seconds
(d) moves toes
(e) pain absent
(f) pulse on left leg weaker than right leg
Answer:
(a) moderate edema of the left knee
(b) skin warm to touch
(c) capillary refill response of <3 seconds
(d) moves toes
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d). Postoperatively, the knee in a total knee replacement is dressed with a compression bandage, and ice may be applied to control edema and bleeding. Recurrent assessment by the nurse for neurovascular changes can prevent loss of limb. Normal neurovascular findings include color normal, extremity warm, capillary refill <3 seconds, moderate edema, tissue not palpably tense, pain controllable, normal sensations, no paresthesia, normal motor abilities, no paresis or paralysis, and pulses strong and equal.
Question 55.
On the evening of surgery for total knee replacement, a client wants to get out of bed. What should the nurse do to safely assist the client?
(a) Encourage the client to apply full weight bearing.
(b) Ask the HCP to prescribe a walker for the client.
(c) Place a straight-backed chair at the foot of the bed.
(d) Apply a knee immobilizer.
Answer:
(d) Apply a knee immobilizer.
Explanation:
The knee is usually protected with a knee immobilizer (splint, cast, or brace) and is elevated when the client sits in a chair. Pre- and postsurgery, the health care provider (HCP) Q prescribes weight-bearing limits and use of assistive devices for progressive ambulation. Positioning a straight- backed chair at the foot of the bed is not an action conducive to getting the client out of bed on the evening of surgery for a total knee replacement.
Question 56.
When preparing a client for discharge from the hospital after a total knee replacement, the nurse should include which information in the discharge plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Report signs of infection to health care pro vider (HCP).
(b) Keep the affected leg and foot on the floor when sitting in a chair.
(c) Remove anti embolism stockings when sleeping.
(d) The physical therapist will encourage progressive ambulation with use of assistive devices.
(e) Change the dressing daily.
Answer:
(a) Report signs of infection to health care pro vider (HCP).
(d) The physical therapist will encourage progressive ambulation with use of assistive devices.
Explanation:
(a), (d). After a total knee replacement, efforts are directed at preventing complications, such as thromboembolism, infection, limited range of motion, and peroneal nerve palsy. The nurse should instruct the client to report signs of infection, such as an increased temperature. To prevent edema, the affected leg must remain elevated when the client sits in a chair. The client will wear antiembolism stockings at all times, including when sleeping. After discharge, the client may undergo physical therapy on an outpatient basis per HCP prescription. The client should leave the dressing in place until the follow-up visit with the surgeon.
Question 57.
The nurse is observing a client who is recovering from back strain lift a box as shown below. What should the nurse do?

(a) Praise the client for using correct body mechanics.
(b) Suggest to the client to put both knees on the floor before attempting to lift the box.
(c) Advise the client to bend from the waist rather than stretching the back in this position.
(d) Instruct the client to keep the back straight by squatting with both knees parallel.
Answer:
(a) Praise the client for using correct body mechanics.
Explanation:
The client is using correct body mechanics for lifting because she is keeping her back as straight as possible and is holding the box close to her body. She is using her large leg muscles to lift the box. She is using a broad base of support by placing her feet as wide apart as possible. The other suggestions would cause the client to put a strain on her back.
Question 58.
A client has low back pain. What should the nurse instruct the client to avoid doing?
(a) keeping light objects below the level of the elbows when lifting
(b) leaning forward while bending the knees
(c) exceeding the prescribed exercise program
(d) sleeping on the side with legs flexed
Answer:
(c) exceeding the prescribed exercise program
Explanation:
The client with low back pain should not exceed the prescribed exercises even though the client may think, “If this will make me well, double will make me well quicker.” When exceeding prescribed exercise programs, the client’s muscle may be unconditioned and easily tired, leading to injury and increased pain. To use proper body mechanics when lifting light objects, the client should bring the item close to the center of gravity, which occurs when the object is kept below the level of the elbows.
Leaning forward while bending the knees allows for the muscles of the thigh to be used instead of those of the lower back. Sleeping on the side with the legs flexed is appropriate because the spine is kept in a neutral position without twisting or pulling on muscles.
Question 59.
A client is discharged with the following prescription for severe back pain from a herniated intravertebral disc: hydrocodone 5 mg, acetaminophen 500 mg, one-half to one tablet by mouth each 8 to 12 hours as needed. How should the nurse instruct the client to follow this prescription?
(a) Start with one-half tablet and take one every 12 hours.
(b) Start with one-half tablet and take one every 8 hours.
(c) Start with one tablet and then take one tablet every 8 hours.
(d) Start with one tablet and then take one tablet every 12 hours.
Answer:
(a) Start with one-half tablet and take one every 12 hours.
Explanation:
The nurse instructs the client to start the prescription by taking the least amount of the medication. The client is advised to monitor pain level and adjust the dosage according to the amount of pain relief.
Question 60.
A client attempting to get out of bed stops midway because of low back pain radiating down to the right heel and lateral foot. What should the nurse do in order of priority from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Apply a warm compress to the client’s back.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(c) Assist the client to lie down.
(d) Administer the prescribed celecoxib.
Answer:
(c) Assist the client to lie down.
(d) Administer the prescribed celecoxib.
(a) Apply a warm compress to the client’s back.
(b) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
(c), (d), (a), (b). When the client is not entirely able to get out of bed, the nurse should first assist the client to lie down for comfort/safety before administering the prescribed celecoxib. Applying a warm compress will further promote relaxation of skeletal muscles. The HCP £2 should be kept informed of the client’s status and nursing actions already taken.
Question 61.
A client with a ruptured intervertebral disc at L4-L5 stands with a flattened spine slightly tilted forward and slightly flexed to the affected side. How should the nurse interpret this finding?
The client has:
(a) motor changes.
(b) postural deformity.
(c) alteration of reflexes.
(d) sensory changes.
Answer:
(b) postural deformity.
Explanation:
Standing with a flattened spine slightly tilted forward and slightly flexed to the affected side indicates a postural deformity. Motor changes would include findings such as hypotonia or muscle weakness. Absent or diminished reflexes related to the level of herniation would indicate alteration in reflexes. Sensory changes would include findings such as paresthesia and numbness related to the specific tract of the herniation.
Question 62.
Which position would be most comfortable for a client with a ruptured disc at L5-S1 right?
(a) prone
(b) supine with the legs flexed
(c) high Fowler’s
(d) right Sims’
Answer:
(b) supine with the legs flexed
Explanation:
A supine position with the client’s legs flexed is the most comfortable position because it allows for the disc to recess off of the nerve, thus alleviating the pressure and pain. The prone position causes hyperextension of the spine and increased pressure of the disc on the nerve root on the right. A ruptured disc at L5-S1 right identifies a ruptured disc compressing the right nerve root exiting the L5-S1 spinous process; terms such as this are commonly used in the analysis of a magnetic resonance image, myelogram, or history and physical examination.
If the ruptured area of the disc were in the central area of the spinous process, the prone position and hyperextension might relieve the disc pressure on the nerve. A high Fowler’s or sitting position increases the pressure of the disc on the nerve root because of gravity, as does a right Sims’ position.
Question 63.
A client tells the nurse about having numbness from the back of the left buttock to the dorsum of the foot and big toe. The client is scheduled to undergo a laminectomy, and the operative consent form states “a left lumbar laminectomy of L3-L4.” What should the nurse do next?
(a) Have the client sign the consent form.
(b) Call the surgeon.
(c) Change the consent form.
(d) Review the client’s history.
Answer:
(b) Call the surgeon.

Explanation:
Based on the client’s comments, the nurse should call the surgeon to verify the location of the surgery. The client’s comments indicate radiculopathy of L4-L5, but the informed consent form states L3-L4. Radiculopathy of L3-L4 involves pain radiating from the back to the buttocks to the posterior thigh to the inner calf. The nurse must act as a client advocate and not ask the client to sign the consent until the correct procedure is identified and confirmed on the consent.
The nurse has no legal authority or responsibility to change the consent. The history is a source of information, but when the client is coherent and the history is contradictory, the health care provider (HCP) should be contacted to clarify the situation. Ultimately, it is the surgeon’s responsibility to identify the site of surgery specified on the surgical consent form.
Question 64.
Immediately after a lumbar laminectomy, the nurse administers ondansetron hydrochloride to the client as prescribed. The nurse determines that the drug is effective when which sign is controlled?
(a) muscle spasms
(b) nausea
(c) shivering
(d) dry mouth
Answer:
(b) nausea
Explanation:
Ondansetron hydrochloride is a selective serotonin receptor antagonist that acts centrally to control the client’s nausea in the postoperative phase. It does not control muscle spasms, shivering, or dry mouth.
Question 65.
After a laminectomy, the client states, “The doctor said that I can do anything I want to.” Which activity that the client intends to do indicates the need for further teaching?
(a) drying the dishes
(b) sitting outside on firm cushions
(c) making the bed walking from side to side
(d) sweeping the front porch
Answer:
(d) sweeping the front porch
Explanation:
Sweeping causes a twisting motion, which should be avoided because twisting can cause undue stress on the recently ruptured disc site, muscle spasms, and a potential recurrent disc rupture. Although the client should not bend at the waist, such as when washing dishes at the sink, the client can dry dishes because no bending is necessary. The client can sit in a firm chair that keeps the back anatomically aligned. The client should not twist and pull, so when making the bed, the client should pull the covers up on one side and then walk around to the other side before trying to pull the covers up there.
Question 66.
The nurse is developing the discharge teaching plan for a client after a lumbar laminectomy L4-L5. What action should the nurse encourage the client to avoid when returning to work in 6 weeks?
(a) placing one foot on a step stool during prolonged standing
(b) sleeping on the back with support under theknees
(c) maintaining average body weight for height
(d) sitting whenever possible
Answer:
(d) sitting whenever possible
Explanation:
After a lumbar laminectomy L4-L5, a client who is returning to work should avoid sitting whenever possible. If the client must sit, he or she should sit only in chairs that allow the knees to be higher than the hips and support the arms to maintain correct body alignment and reduce undue stress on the spine. Maintaining good body postures is most important after a lumbar laminectomy L4-L5. By 6 weeks after the surgery, the client should have regained stamina.
To maintain correct body posture, the client should also place one foot on a step stool during prolonged standing. Sleeping on the back with a support under the knees is effective in maintaining correct body posture. Maintaining an average weight for height is important in maintaining a healthy back because carrying extra weight causes undue stress on back muscles.
Question 67.
A male client underwent a lumbar spinal fusion yesterday. Which nursing assessment should alert the nurse to the development of a possible complication?
(a) lateral rotation of the head and neck
(b) clear yellowish fluid on the dressing
(c) use of the standing position to void
(d) nonproductive cough
Answer:
(b) clear yellowish fluid on the dressing
Explanation:
Clear yellowish fluid on the dressing may be cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This fluid must be tested for glucose to determine whether it is CSF. If so, the client is at great risk for an infection of the central nervous system, which has a high mortality rate. The client should be able to laterally rotate the head and neck, which is above the surgical site in the spinal column. During the nursing postoperative neuromuscular-vascular assessment of movement of the head and neck, the nurse should find results consistent with the preoperative baseline status. Using the standing position to void is normal for a male client.
Coughing is the body’s defense mechanism to help clear the lungs of the anesthetic agents and to ventilate the lungs in response to a sustained deep inspiration for ventilation of the lower lobes of the lungs. A frequent cough could place a strain on the incision site and should be avoided. Also, a productive cough of thick, yellow sputum would indicate the complication of a respiratory infection.

Question 68.
After the nurse teaches a client about wearing a back brace after a spinal fusion, which statement indicates effective teaching?
(a) “I will apply lotion before putting on the brace.”
(b) “I will be sure to pad the area around my iliac crest.”
(c) “I can use baby powder under the brace to absorb perspiration.”
(d) “I should wear a thin cotton undershirt under the brace.”
Answer:
(d) “I should wear a thin cotton undershirt under the brace.”
Explanation:
The client should wear a thin cotton undershirt under the brace to prevent the brace from abrading directly against the skin. The cotton material also aids in absorbing any moisture, such as perspiration, that could lead to skin irrita-tion and breakdown. Applying lotion is not recommended before applying the brace because further skin breakdown can result (related to the collection of moisture where microorganisms can grow). Applying extra padding (e.g., to the iliac crests) is not recommended because the padding can become wrinkled, producing more pressure sites and skin breakdown. Use of baby or talcum powder and lotion is not recommended because they can cause irritation and skin breakdown.
Question 69.
The nurse develops a teaching plan for a client scheduled for a spinal fusion. What should the nurse tell the client?
(a) The client will typically experience more pain at the donor site than at the fusion site.
(b) The surgeon will apply a simple gauze dressing to the donor site.
(c) Neurovascular checks are unnecessary if the fibula is the donor site.
(d) The client’s level of activity restriction is determined by the amount of pain.
Answer:
(a) The client will typically experience more pain at the donor site than at the fusion site.
Explanation:
Typically, the donor site causes more pain than the fused site does because inflammation, swelling, and venous oozing around the nerve endings in the donor site, where the subcutaneous tissue was removed, occur during the first 24 to 48 hours postoperatively. After surgery, the surgeon applies a pressure dressing to the donor site to compress the veins that were transected for the removal of subcutaneous tissue but that did not stop oozing blood after surgical cauterization.
Pressure on a transected vein, which is low pressure, stops the oozing and loss of blood from the venous site. When the donor site is the fibula, neurovascular checks must be performed every hour to ensure adequate neurologic function of and circulation to the area. The surgeon, not the degree or amount of pain, specifies activity restrictions.
Question 70.
A client who has had a lumbar laminectomy with a spinal fusion is sitting in a chair. Which is the correct position for this client?
(a) with the feet flat on the floor
(b) on a low footstool
(c) in any comfortable position with legs uncrossed
(d) on a high footstool so the feet are level with the chair seat
Answer:
(a) with the feet flat on the floor
Explanation:
A client who has had back surgery should place his feet flat on the floor to avoid strain on the incision. Placing the feet on a low or high footstool or in any other position of comfort with the legs uncrossed increases the pressure on the suture line and increases the inflammation around the involved nerve root, thereby increasing the risk of possible rerupture of the disc site.
Question 71.
The nurse develops a plan of care for a client in the initial postoperative period following a lumbar laminectomy. Which activity is contraindicated?
(a) assisting with daily hygiene activities
(b) lying flat in bed
(c) walking in the hall
(d) sitting all afternoon in her room
Answer:
(d) sitting all afternoon in her room
Explanation:
After a lumbar laminectomy, a client should not sit for prolonged periods in a chair because of the increased pressure against the nerve root and incision site. Assisting with daily hygiene is an appropriate activity during the initial postoperative period because, as with any surgical proce-dure, the client needs to return to an optimal level of functioning as soon as possible. There is no limitation on the client’s participation in daily hygiene activities except for individual responses of pain, nausea, vomiting, or weakness.
Lying flat in bed is appropriate because it does not cause stress on the spinal column where the laminectomy was per-formed and the disc tissue was removed. Positions that should be avoided are those that would cause twisting and flexion of the spine. Walking in the hall is an acceptable activity. It promotes good postoperative ventilation, circulation, and return of peristalsis, which are needed for all surgical clients. In addition, walking provides the postoperative lumbar laminectomy client an opportunity to build up endurance and muscle strength and to promote circulation to the operative and incision sites for healing without twisting or stressing them.
Question 72.
Which exercise should the nurse advise the client to avoid after a lumbar laminectomy?
(a) knee-to-chest lifts
(b) hip tilts
(c) sit-ups
(d) pelvic tilts
Answer:
(c) sit-ups
Explanation:
Sit-ups are not recommended for the client who has had a lumbar laminectomy because these exercises place too great a stress on the back. Knee-to-chest lifts, hip tilts, and pelvic tilt exercises are recommended to strengthen back and abdominal muscles.
Question 73.
Which factor contributes to the risk for amputation in a client with peripheral vascular disease? Select all that apply.
(a) uncontrolled diabetes mellitus for 15 years
(b) a 20-pack-year history of cigarette smoking
(c) a hemoglobin level of 14.2 g/dL
(d) a serum cholesterol concentration of 275 mg/dL (15.3 mmol/L)
(e) work that requires prolonged standing
Answer:
(a) uncontrolled diabetes mellitus for 15 years
(b) a 20-pack-year history of cigarette smoking
(d) a serum cholesterol concentration of 275 mg/dL (15.3 mmol/L)

Explanation:
(a), (b), (d). Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus is considered a risk factor for peripheral vascular disease (PVD) because of the macroangiopathic and microangiopathic changes that result from poor blood glucose control. Cigarette smoking is a known risk factor for peripheral vascular disease; nicotine is a potent vasoconstrictor. Serum cholesterol levels >200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) are considered a risk factor for peripheral vascular disease. The hemoglobin level is within normal range and is not a risk for PVD. Prolonged standing is a risk factor for venous stasis and varicose veins.
Question 74.
A client has severe arterial occlusive disease and gangrene of the left great toe. Which finding is expected?
(a) edema around the ankle
(b) loss of hair on the lower leg
(c) thin, soft toenails
(d) warmth in the foot
Answer:
(b) loss of hair on the lower leg
Explanation:
The client with severe arterial occlusive disease and gangrene of the left great toe would have lost the hair on the leg due to decreased circulation to the skin. Edema around the ankle and lower leg would indicate venous insufficiency of the lower extremity. Thin, soft toenails (i.e., not thickened and brittle) are a normal finding. Warmth in the foot indicates adequate circulation to the extremity. Typically, the foot would be cool to cold if a severe arterial occlusion were present.
Question 75.
A client with absent peripheral pulses and pain at rest is scheduled for an arterial Doppler study of the affected extremity. When preparing the client for this test, what should the nurse do?
(a) Have the client sign an informed consent form for the procedure.
(b) Administer a pretest sedative as appropriate.
(c) Keep the client tobacco free for 30 minutes before the test.
(d) Wrap the client’s affected foot with a blanket.
Answer:
(c) Keep the client tobacco free for 30 minutes before the test.
Explanation:
The client should be tobacco free for 30 minutes before the test to avoid false readings related to the vasoconstrictive effects of smoking on the arteries. Because this test is noninvasive, the client does not need to sign an informed consent form. The client should receive an opioid analgesic, not a sedative, to control the pain as the blood pressure cuffs are inflated during the Doppler studies to determine the ankle-to-brachial pressure index. The client’s ankle should not be covered with a blanket because the weight of the blanket on the ischemic foot will cause pain. A bed cradle should be used to keep even the weight of a sheet off the affected foot.
Question 76.
Which action is most helpful to promote circulation for the client with peripheral arterial disease?
(a) resting with the legs elevated above the level of the heart
(b) walking slowly but steadily for 30 minutes twice a day
(c) minimizing activity as much and as often as ossible
(d) wearing antiembolism stockings at all times when out of bed
Answer:
(b) walking slowly but steadily for 30 minutes twice a day
Explanation:
Slow, steady walking is a recommended activity for the client with peripheral arterial disease because it stimulates the development of collateral circulation needed to ensure adequate tissue oxygenation. The client with peripheral arterial disease should not minimize activity. Activity is necessary to foster the development of collateral circulation. Elevating the legs above the heart is an appropriate strategy for reducing venous congestion. Wearing antiembolism stockings promotes the return of venous circulation, which is important for clients with venous insufficiency. However, their use in clients with peripheral arterial disease may cause the disease to worsen.
Question 77.
What information should the nurse include in the teaching plan for a client with arterial insufficiency to the feet that is being managed conservatively?
(a) Lubricate the feet daily.
(b) Soak the feet in warm water.
(c) Apply antiembolism stockings.
(d) Wear firm, supportive leather shoes.
Answer:
(a) Lubricate the feet daily.
Explanation:
Daily lubrication, inspection, cleaning, and patting dry of the feet should be performed to prevent cracking of the skin and possible infection. Soaking the feet in warm water should be avoided because soaking can lead to maceration and subse-quent skin breakdown. Additionally, the client with arterial insufficiency typically experiences sensory changes, so the client may be unable to detect water that is too warm, thus placing the client at risk for burns.
Antiembolism stockings, appropriate for clients with venous insufficiency, are inappropriate for clients with arterial insufficiency and could lead to a worsening of the condition. Footwear should be roomy, soft, and protective and allow air to circulate. Therefore, firm, supportive leather shoes would be inappropriate.
Question 78.
A client says, “I hate the idea of being an invalid after they cut off my leg.” Which response by the nurse would be the most therapeutic?
(a) “At least you’ll still have one good leg to use.”
(b) “Tell me more about how you’re feeling.”
(c) “Let’s finish the preoperative teaching.”
(d) “You’re lucky to have a wife to care for you.”
Answer:
(b) “Tell me more about how you’re feeling.”
Explanation:
Encouraging the client who will be undergoing amputation to verbalize his feelings is the most therapeutic response. Asking the client to tell more about how he is feeling helps to elicit information, providing insight into his view of the situation and also providing the nurse with ideas to help him cope. The nurse should avoid value-laden responses, such as, “At least you will still have one good leg to use,” that may make the client feel guilty or hostile, thereby blocking further communication. Furthermore, stating that the client still has one good leg ignores his expressed concerns.
The client has verbalized feelings of helplessness by using the term “invalid.” The nurse needs to focus on this concern and not try to complete the teaching first before discussing what is on the client’s mind. The client’s needs, not the nurse’s needs, must be met first. It is inappropriate for the nurse to assume to know the relationship between the client and his wife or the roles they now must assume as dependent client and caregiver. Additionally, the response about the client’s wife caring for him may reinforce the client’s feelings of helplessness as an invalid.
Question 79.
The client asks the nurse, “Why won’t the health care provider tell me exactly how much of my leg he is going to take off? Don’t you think I should know that?” On which information should the nurse base the response?
(a) the need to remove as much of the leg as possible
(b) the adequacy of the blood supply to the tissues
(c) the ease with which a prosthesis can be fitted
(d) the client’s ability to walk with a prosthesis
Answer:
(b) the adequacy of the blood supply to the tissues
Explanation:
The level of amputation often cannot be accurately determined until during surgery, when the surgeon can directly assess the adequacy of the circulation of the residual limb. From a moral, ethical, and legal viewpoint, the surgeon attempts to remove as little of the leg as possible. Although a longer residual limb facilitates prosthesis fitting, unless the stump is receiving a good blood supply, the prosthesis will not function properly because tissue necrosis will occur. Although the client’s ability to walk with a prosthesis is important, it is not a determining factor in the decision about the level of amputation required. Blood supply to the tissue is the primary determinant.
Question 80.
A client who has had an above-the-knee amputation develops a dime-sized bright red spot on the dressing after 45 minutes in the postanesthesia recovery unit. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Elevate the stump.
(b) Reinforce the dressing.
(c) Call the surgeon.
(d) Draw a mark around the site.
Answer:
(d) Draw a mark around the site.
Explanation:
The priority action is to draw a mark around the site of bleeding to determine the rate of bleeding. Once the area is marked, the nurse can determine whether the bleeding is increasing or decreasing by the size of the area marked. Because the spot is bright red, the bleeding is most likely arterial in origin. Once the rate and source of bleeding are identified, the surgeon should be notified. The stump is not elevated because adhesions may occur, interfering with the ability to fit a prosthesis.
The dressing would be reinforced if the bleeding is determined to be of venous origin, characterized by slow oozing of darker blood that ceases with the application of a pressure dressing. Typically, operative dressings are not changed for 24 hours. Therefore, the dressing is reinforced to prevent organisms from penetrating through the blood-soaked areas of the initial postoperative dressing.
Question 81.
A client in the postanesthesia care unit with a left below-the-knee amputation has pain in the left big toe. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Tell the client it is impossible to feel the pain.
(b) Show the client that the toes are not there.
(c) Explain to the client that the pain is real.
(d) Give the client the prescribed opioid analgesic.
Answer:
(d) Give the client the prescribed opioid analgesic.
Explanation:
The nurse’s first action should be to administer the prescribed opioid analgesic to the client because this phenomenon is phantom sensation and interventions should be provided to relieve it. Pain relief is the priority. Phantom sensation is a real sensation. It is incorrect and inappropriate to tell a client that it is impossible to feel the pain. Although it does relieve the client’s apprehensions to be told that phantom sensations are a real phenomenon, the client needs prompt treatment to relieve the pain sensation. Usually, phantom sensation will go away. However, showing the client that the toes are not there does nothing to provide the client with relief.
Question 82.
The client with an above-the-knee amputation is to use crutches while the prosthesis is being adjusted. Which exercises will best prepare the client for using crutches?
(a) abdominal exercises
(b) isometric shoulder exercises
(c) quadriceps setting exercises
(d) triceps strengthening exercises
Answer:
(d) triceps strengthening exercises
Explanation:
Use of crutches requires significant strength from the triceps muscles. Therefore, efforts are focused on strengthening these muscles in anticipation of crutch walking. Bed and wheelchair push-ups are excellent exercises targeted at the triceps muscles. Abdominal exercises, range-of-motion and isometric exercises of the shoulders, and quadriceps and gluteal setting exercises are not helpful in preparing for crutch walking.
Question 83.
The nurse teaches a client about using crutches, instructing the client to support the weight primarily on which part of the upper body?
(a) axillae
(b) elbows
(c) upper arms
(d) hands
Answer:
(d) hands
Explanation:
When using crutches, the client is taught to support weight primarily on the hands. Supporting body weight on the axillae, elbows, or upper arms must be avoided to prevent nerve damage from excessive pressure.
Question 84.
The client is to be discharged on a low-fat, low-cholesterol, low-sodium diet. When coaching the client about the diet, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Determine the client’s knowledge level about cholesterol.
(b) Ask the client to name foods that are high in fat, cholesterol, and salt.
(c) Explain the importance of complying with the diet.
(d) Assess the client’s and family’s typical food preferences.
Answer:
(d) Assess the client’s and family’s typical food preferences.
Explanation:
Before beginning dietary instructions and interventions, the nurse must first assess the client’s and family’s food preferences, such as pattern of food intake, lifestyle, food preferences, and ethnic, cultural, and financial influences. Once this information is obtained, the nurse can begin teaching based on the client’s current knowledge level and then building on this knowledge base.
Question 85.
A client has a leg immobilized in traction. Which observation by the nurse indicates that the client understands actions to take to prevent muscle atrophy?
(a) The client adducts the affected leg every 2 hours.
(b) The client rolls the affected leg away from the body’s midline twice per day.
(c) The client performs isometric exercises to the affected extremity three times per day.
(d) The client asks the nurse to add a 5-lb (2.3-kg) weight to the traction for 30 min/day.
Answer:
(c) The client performs isometric exercises to the affected extremity three times per day.
Explanation:
Isometric contractions increase the tension within a muscle but do not produce movement. Repeated isometric contractions make muscles grow larger and stronger. Adduction of the leg puts work onto the hip joint as well as altering the pull of traction. Rolling the leg, or external rotation, alters the pull of traction. Additional weight should not be added to traction unless prescribed by the health care provider (HCP) it will not prevent muscle atrophy.
Question 86.
A client with a fractured tibia has an external fixation. The health care provider has prescribed a solution of 1/2 normal saline and 1/2 hydrogen peroxide to clean the pin site twice a day. In which order should the nurse cleanse the pin from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Inspect the site for redness, swelling, or discharge.
(b) Clean the pin with a cotton swab dipped in the prescribed solution, wiping from the insertion site to the tip of the pin.
(c) Clean the pin insertion site with a cotton swab dipped in the prescribed solution, removing the crust wiping away from the site.
(d) Clean the area around the pin insertion site with cotton swabs, dipped in the prescribed solution.
Answer:
(d) Clean the area around the pin insertion site with cotton swabs, dipped in the prescribed solution.
(c) Clean the pin insertion site with a cotton swab dipped in the prescribed solution, removing the crust wiping away from the site.
(b) Clean the pin with a cotton swab dipped in the prescribed solution, wiping from the insertion site to the tip of the pin.
(a) Inspect the site for redness, swelling, or discharge.
Explanation:
(d), (c), (b), (a). The nurse should first clean the area around the pin insertion site, wiping in one direction around the pin and discarding the swabs as they are used. The nurse should then remove any crust that may have formed around the pin. Next, the nurse should inspect the area for infection. Last, the nurse should clean the pin.
Question 87.
The client with a fractured tibia has been taking methocarbamol. Which finding indicates that the drug is having the intended effect?
(a) lack of infection
(b) reduction in itching
(c) relief of muscle spasms
(d) decrease in nervousness
Answer:
(c) relief of muscle spasms

Explanation:
Methocarbamol is a muscle relaxant and acts primarily to relieve muscle spasms. It has no effect on microorganisms, does not reduce itching, and has no effect on nervousness.
Question 88.
When developing a teaching plan for a client who is prescribed acetaminophen for muscle pain, which information should the nurse expect to include? Select all that apply.
(a) The drug can be used if the person is allergic to aspirin.
(b) Acetaminophen does not affect platelet aggregation.
(c) This drug causes little or no gastric distress.
(d) Acetaminophen exerts a strong anti-inflammatory effect.
(e) The client should have the international normalized ratio (INR) checked regularly.
Answer:
(a) The drug can be used if the person is allergic to aspirin.
(b) Acetaminophen does not affect platelet aggregation.
(c) This drug causes little or no gastric distress.

Explanation:
(a), (b), (c). Acetaminophen is an alternative for a client who is allergic to aspirin. It does not affect platelet aggregation, and the client does not need to have coagulation studies (such as INR). Acetaminophen causes little or no gastric distress. Acetaminophen exerts no anti-inflammatory effects.
Question 89.
A client who has been taking hydrocodone with acetaminophen at home for 6 weeks following a fractured tibia is admitted with a blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg, a pulse rate of 115 bpm, and respirations of 8 breaths/min and shallow. What do these findings indicate?
(a) expected common adverse effects of the hydrocodone
(b) hypersensitivity reaction to the acetaminophen
(c) possible habituation effect of the long-term drug use
(d) hemorrhage from gastrointestinal irritation associated with the pain medication
Answer:
(c) possible habituation effect of the long-term drug use

Explanation:
Hypotension and depressed respirations are signs of high levels of ingestion of hydrocodone, and the client may be developing a habit of taking this drug for a prolonged period. Expected common adverse effects of hydrocodone and acetaminophen would include drowsiness, confusion, blurred vision, and constipation. Hemorrhage from gastrointestinal irritation is not associated with this drug. Hypersensitivity reactions would be manifested by pruritus and rashes.
Question 90.
The nurse is caring for a client who is 30 years of age with a fracture of the right femur and left tibia. Both legs have casts. The nurse assesses the following: respirations are 30 per minute and are rapid and shallow; there is the presence of faint expiratory wheeze; and coughing produces thin pink sputum. The client is yelling at the nurse and wants to be released from the hospital; this is behavior unlike that previously reported. The last pain medication was administered 3 hours ago. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Cut slits in the top of the casts.
(b) Administer pain medication.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(d) Obtain a chest X-ray.
Answer:
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
The nurse’s first action is to notify the HCP because the client is likely experiencing a fat embolus. Fat emboli are associated with embolization of marrow or tissue fat or platelets and free fatty acids to the pulmonary capillaries, producing rapid onset of symptoms. Multiple fractures and fractures of the long bones or pelvis increase a client’s risk for developing a fat embolus; in addition, young adults between 20 and 30 years of age are at a higher risk for fat emboli with fractures.
When fat emboli do occur, hypoxia results; therefore, it is most important the nurse assess changes in level of consciousness and observe changes in behavior such as restlessness and irritability. The nurse does not cut the cast; there is no indication that the casts are obstructing circulation. ABGs are used to confirm the diagnosis, not a chest X-ray. The client’s behavior is a result of hypoxemia, not pain.
Question 91.
A client is being discharged following an open reduction and internal fixation of the left ankle and is to wear a non-weight-bearing cast for 2 weeks. What should the nurse teach the client to do when using crutches?
(a) Use a four-point gait.
(b) Maintain two to three finger widths between the axillary fold and underarm piece grip.
(c) Keep leg dependent when sitting.
(d) Maintain balance by supporting body’s weight on the axillae.
Answer:
(b) Maintain two to three finger widths between the axillary fold and underarm piece grip.
Explanation:
The nurse instructs the client to maintain two finger widths between the axillary fold and the underarm piece grip of the crutches to prevent pressure on the brachial plexus. The client is advised to use the three-point gait; in the four-point and two-point gait, there is partial weight bearing of both feet. The client is also advised to keep the affected leg elevated when sitting to prevent swelling and to use the arms, not the axillae, to maintain balance and support.
Question 92.
The nurse is caring for an adult with a grade III compound fracture of the right femur; the client has been placed in skeletal traction. What is the intended outcome of the traction?
(a) Prevent skin breakdown.
(b) Prevent movement in the bed.
(c) Preserve normal length of the leg.
(d) Reduce and immobilize the fracture.
Answer:
(d) Reduce and immobilize the fracture.
Explanation:
Skeletal traction is often used to regain normal length of the bone, but in this situation, the main purpose of the traction is to reduce and immobilize the fracture. This type of traction allows the client to move in bed without dislocating the frac-ture. This client has an open fracture, but skeletal traction will not prevent further skin breakdown.
Question 93.
An older adult is admitted with a fracture of the femur. What should the nurse assess first about this client?
(a) ability to change positions
(b) type of pain
(c) mechanism of injury
(d) extent of anxiety
Answer:
(c) mechanism of injury
Explanation:
The nurse first assesses the mechanism of injury to help determine related injuries, tests needed, and potential treatment options. The next step is to assess the location, type, quality, and intensity of the pain. Neurovascular stasis of the injured site is assessed after pain; therefore, the nurse checks for functional ability or changing positions. Although the nurse can also determine the extent of anxiety while assessing the injury and can use communication strategies to minimize anxiety, it is not the first priority for assessing this client.
Question 94.
When admitting a client with a fractured extremity, what area should the nurse assess first?
(a) the area proximal to the fracture
(b) the actual fracture site
(c) the area distal to the fracture
(d) the opposite extremity for baseline comparison
Answer:
(c) the area distal to the fracture
Explanation:
The nursing assessment is first focused on the region distal to the fracture for neurovascular injury or compromise. When a nerve or blood vessel is severed or obstructed at the actual fracture site, innervation to the nerve or blood flow to the vessel is disrupted below the site; therefore, the area distal to the fracture site is the area of compromised neurologic input or vascular flow and return, not the area above the fracture site or the fracture site itself.
The nurse may assess the opposite extremity at the area proximal to the fracture site for a baseline comparison of pulse quality, color, temperature, size, and so on, but the comparison would be made after the initial neurovascular assessment.
Question 95.
Which client statement identifies a knowledge deficit about cast care?
(a) “I will elevate the cast above my heart initially. ”
(b) “I will exercise my joints above and below the cast.”
(c) “I can pull out cast padding to scratch inside the cast.”
(d) “I will apply ice for 10 minutes to control edema for the first 24 hours.”
Answer:
(c) “I can pull out cast padding to scratch inside the cast.”
Explanation:
Clients should not pull out cast padding to scratch inside the cast because of the hazard of skin breakdown and subsequent potential for infection. Clients are encouraged to elevate the casted extremity above the level of the heart to reduce edema and to exercise or move the joints above and below the cast to promote and maintain flexibility and muscle strength. Applying ice for 10 minutes during the first 24 hours helps to reduce edema.
Question 96.
Which nursing action would be least appropriate for a client who is in a double hip spica cast?
(a) encouraging the intake of cranberry juice
(b) advising the client to eat large amounts of cheese
(c) establishing regular times for elimination
(d) having the client dangle at the bedside
Answer:
(b) advising the client to eat large amounts of cheese
Explanation:
The client in a double hip spica cast should avoid eating foods that can be constipating, such as cheese. Rather, fresh fruits and vegetables should be encouraged, and the client should be encouraged to drink at least 2,500 mL/day. Drinking cranberry juice, which helps keep urine acidic, thereby avoiding the development of renal calculi, is encouraged.
The client should be encouraged to establish regular times for elimination to promote regularity in bowel and bladder habits. The client will develop orthostatic hypotension unless the circulatory system is reconditioned slowly through dangling and standing exercises.
Question 97.
The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for a client about crutch walking using a two-point gait pattern. What information should the nurse include?
(a) Advance a crutch on one side, and then advance the opposite foot; repeat on the opposite side.
(b) Advance a crutch on one side, and simultaneously advance and bear weight on the opposite foot; repeat on the opposite side.
(c) Advance both crutches together, and then follow by lifting both lower extremities to the level of the crutches.
(d) Advance both crutches together, and then follow by lifting both lower extremities past the level of the crutches.
Answer:
(b) Advance a crutch on one side, and simultaneously advance and bear weight on the opposite foot; repeat on the opposite side.
Explanation:
A two-point gait involves partial weight bearing on each foot, with each crutch advancing simultaneously with the opposing leg. Advancing a crutch on one side and then advancing the opposite foot, and repeating on the opposite side, illustrates the four-point gait. When the client advances both crutches together and follows by lifting both lower extremities to the same level as the crutches, the gait is called a “swing-to” gait.
When the client advances both crutches together and follows by lifting both lower extremities past the level of the crutches, the gait is called a “swing-through” gait. The “swing-through” gait is often used by paraplegic clients because it allows them to place weight on their legs while the crutches are moved one stride ahead.
Question 98.
A client returned from surgery with a debrided open tibial fracture and has a three-way drainage system. The client’s vital signs are within normal limits. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Review the results of culture and sensitivity testing of the wound.
(b) Change the dressing at the surgery site.
(c) Determine if the client has increased pain from exposed nerve endings.
(d) Check laboratory results for electrolyte imbalances.
Answer:
(a) Review the results of culture and sensitivity testing of the wound.
Explanation:
The wound has a three-way drainage system in place to irrigate the debrided wound with normal saline or an antibiotic. Before the debridement, a sample of the wound would be taken for culture and sensitivity testing so that an organism- specific antibiotic could be administered to pre-vent possible serious sequelae of osteomyelitis. Therefore, the nurse should review the results of the culture and sensitivity report before initiating care.
A dressing would not be applied to an open wound. Rather, a wet-to-dry dressing most likely would be used, and the health care provider would write the exact prescription. There should not be increased pain related to the exposure of nerve endings in the subcutaneous tissue of the wound that was left open to the environment. The first priority is to determine if there is an infection as this is the biggest risk to the client; the nurse can check other lab values later.
Question 99.
A client has a left tibial fracture that required casting. Approximately 5 hours later, the client has increasing pain distal to the fracture despite the morphine injection administered 30 minutes ago. Which area should be the nurse’s next assessment?
(a) distal pulses
(b) pain with a pain rating scale
(c) vital sign changes
(d) potential for drug tolerance
Answer:
(a) distal pulses
Explanation:
The nurse should assess the client’s ability to move the toes and for the presence of distal pulses, including a neurovascular assessment of the area below the cast. Increasing pain unrelieved by usual analgesics and occurring 4 to 12 hours after the onset of casting or trauma may be the first sign of compartment syndrome, which can lead to permanent damage to nerves and muscles.
Although the nurse can use a pain rating scale or assess for changes in vital signs to objectively assess the client’s pain, the client’s comments suggest early and important signs of compartment syndrome requiring immediate intervention. The nurse should not confuse these signs with the potential for drug tolerance. This assessment might be appropriate once the suspicion of compartment syndrome has been ruled out.
Question 100.
A client with a fracture develops compartment syndrome. Which sign should alert the nurse to impending organ failure?
(a) crackles
(b) jaundice
(c) generalized edema
(d) dark, scanty urine
Answer:
(d) dark, scanty urine
Explanation:
The client with compartment syndrome may release myoglobin from damaged muscle cells into the circulation. This becomes trapped in the renal tubules, resulting in dark, scanty urine, possibly leading to acute renal failure. Crackles may suggest respiratory complications; jaundice suggests liver failure; and generalized edema may suggest heart failure. However, these are not associated with compartment syndrome.
Question 101.
After the nurse teaches the client about the use of skeletal traction, which statement made by the client about the purpose of the traction indicates the need for additional teaching?
(a) to align injured bones
(b) to provide long-term pull
(c) to apply 25 lb (11.3 kg) of traction
(d) to pull weight with a boot
Answer:
(d) to pull weight with a boot
Explanation:
Skeletal traction is NOT used to pull weight with a boot, and the nurse should explain to the client that skeletal traction involves the insertion of a wire or a pin into the bone to maintain a pull of 5 to 45 lb (2.3 to 20.4 kg) on the area which will align the injured bones by providing a longterm pull to realign the fracture.
Question 102.
The nurse is planning care for the client with a femoral fracture who is in balanced suspension traction. Which nursing care can be included in the plan of care?
(a) using a fracture bedpan when the client uses the trapeze to raise the hips
(b) turning the client side to side to give back care
(c) raising the head of bed to 90 degrees to sit the client up
(d) giving the client a complete bed bath
Answer:
(a) using a fracture bedpan when the client uses the trapeze to raise the hips
Explanation:
The client with a femoral fracture in balanced suspension traction can raise the hips using a trapeze in order to use the fracture bedpan while maintaining the line of the traction. The client should not turn side to side as it will disrupt the line of traction. The nurse can give back care when the client raises the body using the trapeze. The client should not be given a complete bed bath.
Rather, the client is encouraged to participate in self-care and movement in bed, such as with a trapeze. The client should be positioned so that the feet do not press against the footboard. Therefore, elevating the head of the bed no more than 25 degrees is recommended to keep the client horn moving down in the bed.
Question 103.
The client in balanced suspension traction is transported to surgery for closed reduction and internal fixation of a fractured femur. What should the nurse do when transporting the client to the operating room?
(a) Transfer the client to a cart with manually suspended traction.
(b) Call the surgeon to request a prescription to temporarily remove the traction.
(c) Send the client on the bed with extra help to stabilize the traction.
(d) Remove the traction and send the client on a cart.
Answer:
(c) Send the client on the bed with extra help to stabilize the traction.
Explanation:
The nurse should send the client to the operating room on the bed with extra help to keep the traction from moving to maintain the femur in the proper alignment before surgery. Transferring the client to a cart with manually suspended traction is inappropriate because doing so places the client at risk for additional trauma to the surrounding neurovascular and soft tissues, as would removing the traction. The surgeon need not be called because the decision about transferring the client is an independent nursing action.
Question 104.
A client is in balanced suspension traction to maintain alignment of a fractured tibia. Which activities are safe for the client?
(a) Eat while lying flat.
(b) Raise the hips using trapeze.
(c) Rotate side to side.
(d) Flex and extend the ankle on affected side.
Answer:
(b) Raise the hips using trapeze.
Explanation:
The client in balanced suspension traction can raise the hips using a trapeze. The client can then use the bedpan. The client can be in a sitting position to eat. The client should not move side to side but can turn toward the affected side. The client should not flex or extend the ankle on the affected side.
Question 105.
A client has a Pearson attachment on the traction setup. What is the purpose of this attachment?
(a) to support the lower portion of the leg
(b) to support the thigh and upper leg
(c) to allow attachment of the skeletal pin
(d) to prevent flexion deformities in the ankle and foot
Answer:
(a) to support the lower portion of the leg
Explanation:
The Pearson attachment supports the lower leg and provides increased stability in the overall traction setup. It also makes it easier to maintain correct alignment. It does not support the thigh and the upper leg or prevent flexion deformities in the ankle and foot. It is not attached to the skeletal pin.
Question 106.
Which sign indicates that a client with a fracture of the right femur may be developing a fat embolus?
(a) acute respiratory distress syndrome
(b) migraine-like headaches
(c) numbness in the right leg
(d) muscle spasms in the right thigh
Answer:
(a) acute respiratory distress syndrome
Explanation:
Fat emboli usually result in symptoms of acute respiratory distress syndrome, such as apprehension, chest pain, cyanosis, dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia, and decreased partial pressure of arterial oxygen resulting from poor oxygen exchange. Migraine-like headaches are not a symptom of a fat embolism, but mental confusion, memory loss, and a headache from poor oxygen exchange may be seen with central nervous system involvement.
Numbness in the right leg is a peripheral neurovascular response that most likely is related to the femoral fracture. Muscle spasms in the right thigh are a symptom of a neuromuscular response affecting the local muscle around the femoral fracture site.
Question 107.
Which goal is the priority for a client with a fractured femur who is in traction?
(a) Prevent effects of immobility while in traction.
(b) Develop skills to cope with prolonged immobility.
(c) Choose appropriate diversional activities during the prolonged recovery.
(d) Adapt to inactivity from the impaired mobility.
Answer:
(a) Prevent effects of immobility while in traction.
Explanation:
The priority for this client is to prevent the effects of prolonged immobility, such as by preventing skin breakdown and encouraging the client to take deep breaths, and use active range-of-motion exercises for the joints that are not immobilized. Although not the priority, the nurse also should seek ways to help the client adjust to and cope with the present state of immobility.
Emphasis should be placed on what the client can do, such as participating in daily care and exercises to maintain muscle strength. Finding diversional activities is not a priority at this moment. Although the client must adapt to the inactivity, helping the client develop coping skills is the priority at this time.
Question 108.
The client in traction for a fractured femur is having difficulty managing self-care activities. Which outcome indicates a successful completion of a goal of promoting independence for this client?
(a) The client assists as much as possible in care, demonstrating increased participation over time.
(b) The client allows the nurse to complete care in an efficient manner without interfering.
(c) The client allows the spouse to assume total responsibility for care.
(d) The client accepts that self-care is not possible while in traction.
Answer:
(a) The client assists as much as possible in care, demonstrating increased participation over time.
Explanation:
The client’s assisting as much as possible in self-care and increasing participation over time indicate that the client has accomplished self-care by gaining a sense of control. If the client lets the nurse complete the care without interfering, the behavior would indicate passivity, possibly from denial or depression. If the client allows the spouse to assume total responsibility, a successful outcome has not been reached. The client is able to accomplish self-care activities within the limits of immobilization from the traction.
Question 109.
The client with an open femoral fracture was discharged to home and reports having a fever, night sweats, chills, restlessness, and restrictive movement of the fractured leg. The nurse should interpret these findings as the client may be experiencing which complication?
(a) a pulmonary embolus
(b) osteomyelitis
(c) a fat embolus
(d) a urinary tract infection
Answer:
(b) osteomyelitis
Explanation:
Fever, night sweats, chills, restlessness, and restrictive movement of the fractured leg are clinical manifestations of osteomyelitis, which is a pyogenic bone infection caused by bacteria (usually staphylococci), a virus, or a fungus. The bonP is inaccessible to macrophages and antibodies for protection against infections, so an infection in this site can become serious quickly.
The client with a pulmonary or fat embolus would develop symptoms of pulmonary compromise, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, angina, and mental confusion. Signs and symptoms of urinary tract infection would include pain over the suprapubic, groin, or back region with fever and chills, with no restrictive movement of the leg.
Question 110.
The nurse is planning care for a client with osteomyelitis. The client is taking an antibiotic, but the infection has not resolved. What should the nurse advise the client to do?
(a) Use herbal supplements.
(b) Eat a diet high in protein and vitamins C and D.
(c) Ask the health care provider for a change of antibiotics.
(d) Encourage frequent passive range of motion to the affected extremity.
Answer:
(b) Eat a diet high in protein and vitamins C and D.
Explanation:
The goal of care for this client is healing and tissue growth while the client continues on long-term antibiotic therapy to clear the infection. A diet high in protein and vitamins C and D promotes healing. Herbal supplements may potentiate bleeding (e.g., ginkgo, ginger, turmeric, chamomile, kelp, horse chestnut, garlic, and dong quai) and have not been proven through research to promote healing. Frequent passive motion will increase circulation but may also aggravate localized bone pain. It is not appropriate to advise the client to change antibiotics as treatment may take time.
Question 111.
When planning to move a person with a possible spinal cord injury, the nurse should direct the team to move the client using which procedure?
(a) Limit movement of the arms by wrapping them next to the body.
(b) Move the person gently to help reduce pain.
(c) Immobilize the head and neck to prevent further injury.
(d) Cushion the back with pillows to ensure comfort.
Answer:
(c) Immobilize the head and neck to prevent further injury.
Explanation:
The priority concern is to immobilize the head and neck to prevent further trauma when a fractured vertebra is unstable and easily displaced. Although wrapping and supporting the extremities is important, it does not take priority over immo-bilizing the head and neck. Pain usually is not a significant consideration with this type of injury. Cushioning is contraindicated. The neck should be kept in a neutral position and immobilized. Flexion of the neck is avoided.
Question 112.
The nurse is caring for a client with a spinal cord injury. The client is experiencing blurred vision and has a blood pressure of 204/102 mm Hg. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Position the client on the left side.
(b) Control the environment by turning the lights off and decreasing stimulation for the client.
(c) Check the client’s bladder for distention.
(d) Administer pain medications.
Answer:
(c) Check the client’s bladder for distention.
Explanation:
The client is experiencing autonomic dysreflexia, which is a medical emergency. The nurse should immediately evaluate the client for bladder distention and be prepared to catheterize the client. Positioning the client on the left side, reducing environmental stimuli, and administering pain medications are not used to treat autonomic hyperreflexia.
Question 113.
The nurse is taking care of a client with a spinal cord injury. The extent of the client’s injury is shown below. Which finding is expected when assessing this client?
(a) inability to move the arms
(b) loss of sensation in the hands and fingers
(c) dysfunction of bowel and bladder
(d) difficulty breathing
Answer:
(c) dysfunction of bowel and bladder
Explanation:
This client has a spinal cord injury of the sacral region of the spinal cord and will have bladder and bowel dysfunction, as well as loss of sensation and muscle control below the injury. The other options are true of a client who has quadriplegia.
Question 114.
When the nurse is assessing the client with a cord transection above T5 for possible complications, which complication is least likely to occur?
(a) diarrhea
(b) paralytic ileus
(c) stress ulcers
(d) intra-abdominal bleeding
Answer:
(a) diarrhea
Explanation:
The client with a spinal cord transection above T5 is least likely to develop diarrhea. Rather, constipation due to atonia would be possible. The client with a spinal cord transection above T5 is at risk for development of a paralytic ileus because the sympathetic nerve innervation to the vagus nerve, which dominates all the vessels and organs below T5 (e.g., the intestinal tract), has been disrupted and, therefore, so has movement or peristalsis.
The client is at risk for development of stress ulcers because the sympathetic nerve innervation to the stomach has been disrupted, which results in an excessive release of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, allowing contact of hydrochloric acid with the stomach mucosa. The client does not feel subjective signs of stress ulcers (e.g., pain, guarding, tenderness) and therefore is at increased risk for bleeding because complications of an ulcer can develop before early diagnosis.
Question 115.
The nurse is assessing a client with a spinal cord injury for the development of deep vein thrombosis. Which is the most effective way to determine deep vein thrombosis in this client?
(a) Detect positive Homans’ sign.
(b) Rate the amount of pain.
(c) Assess for tenderness.
(d) Measure leg girth.
Answer:
(d) Measure leg girth.
Explanation:
Measuring the leg girth is the most appropriate method because the usual signs, such as a positive Homans’ sign, pain, and tenderness, are not present. Other means of assessing for deep vein thrombosis in a client with a spinal cord injury are through a Doppler examination and impedance plethysmography.
Question 116.
A client with a spinal cord injury has spinal shock. What should the nurse expect the client’s bladder function to be at this time?
(a) spastic
(b) normal
(c) atonic
(d) uncontrolled
Answer:
(c) atonic
Explanation:
During the period of spinal shock, the bladder is completely atonic and will continue to fill passively unless the client is catheterized. The bladder will not go into spasms or cause uncontrolled urination. Bladder function will not be normal during the period of spinal shock.
Question 117.
After 1 month of therapy, the client in spinal shock begins to experience muscle spasms in the legs and calls the nurse in excitement to report the leg movement. Which response by the nurse would be the most accurate?
(a) “These movements indicate that the damaged nerves are healing.”
(b) “This is a good sign. Keep trying to move all the affected muscles.”
(c) “The return of movement means that eventually you should be able to walk again.”
(d) “The movements occur from muscle reflexes that cannot be initiated or controlled by the brain.”
Answer:
(d) “The movements occur from muscle reflexes that cannot be initiated or controlled by the brain.”
Explanation:
The movements occur from muscle reflexes and cannot be initiated or controlled by the brain. After the period of spinal shock, the muscles gradually become spastic owing to an increased sensitivity of the lower motor neurons. It is an expected occurrence and does not indicate that healing is taking place or that the client will walk again. The movement is not voluntary and cannot be brought under voluntary control.
Question 118.
The client with a spinal cord injury asks the nurse why the dietitian has recommended to decrease the total daily intake of calcium. Which response by the nurse would provide the most accurate information?
(a) “Excessive intake of dairy products makes constipation more common.”
(b) “Immobility increases calcium absorption from the intestine.”
(c) “Lack of weight bearing causes demineralization of the long bones.”
(d) “Dairy products likely will contribute to weight gain.”
Answer:
(c) “Lack of weight bearing causes demineralization of the long bones.”
Explanation:
Long-bone demineralization is a serious consequence of the loss of weight bearing. An excessive calcium load is brought to the kidneys, and precipitation may occur, predisposing to stone formation. Excessive intake of dairy products may promote constipation. However, this is not the most accurate reason for decreasing calcium intake. Immobility does not increase calcium absorption from the intestine. Dairy products do not necessarily contribute to weight gain.
Question 119.
As a first step in teaching a woman with a spinal cord injury and quadriplegia about her sexual health, the nurse assesses her understanding of her current sexual functioning. Which statement by the client indicates she understands her current ability?
(a) “I won’t be able to have sexual intercourse until the urinary catheter is removed.”
(b) “I can participate in sexual activity but might not experience orgasm.”
(c) “I can’t have sexual intercourse because it causes hypertension, but other sexual activity is okay.”
(d) “I should be able to participate in sexual activity, but I’ll be infertile.”
Answer:
(b) “I can participate in sexual activity but might not experience orgasm.”
Explanation:
The woman with spinal cord injury can participate in sexual activity but might not experience orgasm. Cessation in the nerve pathway may occur in spinal cord injury, but this does not negate the client’s mental and emotional needs to creatively participate with her partner in a sexual relationship and to reach orgasm. An indwelling urinary catheter may be left in place during intercourse and need not be removed because the indwelling urinary catheter is placed in the urethra, which is not the channel used for sexual intercourse.
There are no contraindications, such as hypertension, to sexual activity in a woman with spinal cord injury. Sexual intercourse is allowed, and hypertension should be manageable. Because a spinal cord injury does not affect fertility, the client should have access to family planning information so that an unplanned pregnancy can be avoided.
Question 120.
A client with a spinal cord injury who has been active in sports and outdoor activities talks almost obsessively about his past activities. In tears, one day he asks the nurse, “Why can’t I stop talking about these things? I know those days are gone forever.” Which response by the nurse conveys the best understanding of the client’s behavior?
(a) “Be patient. It takes time to adjust to such a massive loss.”
(b) “Talking about the past is a form of denial. We have to help you focus on today.”
(c) “Reviewing your losses is a way to help you work through your grief and loss.”
(d) “It’s a simple escape mechanism to go back and live again in happier times.”
Answer:
(c) “Reviewing your losses is a way to help you work through your grief and loss.”

Explanation:
Spinal cord injury represents a physical loss; grief is the normal response to this loss. Working through grief entails reviewing memories and eventually letting go of them. The process may take as long as 2 years. Telling the client to be patient and that adjustment takes time is a cliched type of response, one that is not empathetic or responsive to the client’s needs.
Telling the client to focus on today does not allow time for the grief process, which is necessary for the client to work through and adjust to the loss. The client is not escaping but is reminiscing on what is lost, to work through the grieving process.
Question 121.
The nurse should assess which clients are at risk for falling? Select all that apply.
Client who is:
(a) 45 years of age, in hospice with terminal cancer, and receiving morphine every 2 hours
(b) 70 years of age, hospitalized for lung biopsy, and receiving no medications
(c) 62 years of age, recovering from breast biopsy in outpatient surgery, and has a fear of falling
(d) 80 years of age and in a locked facility for clients with cognitive impairment
(e) 75 years of age and recovering at home from hip replacement surgery on the left hip
Answer:
(a) 45 years of age, in hospice with terminal cancer, and receiving morphine every 2 hours
(c) 62 years of age, recovering from breast biopsy in outpatient surgery, and has a fear of falling
(d) 80 years of age and in a locked facility for clients with cognitive impairment
(e) 75 years of age and recovering at home from hip replacement surgery on the left hip
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (e). Clients who are at risk for falling include the client taking narcotics, the client with a known fear of falling, the client with cognitive impairment, and the client with gait problems. Age and setting are not necessarily risks for fallings.
Question 122.
Four days after surgery for internal fixation of a C3-C4 fracture, a nurse is moving a client from the bed to the wheelchair. The nurse is checking the wheelchair for correct features for this client. Which features of the wheelchair are appropriate for the needs of this client? Select all that apply.
(a) back at the level of the client’s scapula
(b) back and head that are high
(c) seat that is lower than normal
(d) seat with firm cushions
(e) chair controlled by the client’s breath
Answer:
(b) back and head that are high
(c) seat that is lower than normal
(e) chair controlled by the client’s breath
Explanation:
(b), (c), (e). The client with a C3-C4 fracture has neck control but may tire easily using sore muscles around the incision area to hold up the head. Therefore, the head and neck of the wheelchair should be high. The seat of the wheelchair should be lower than normal to facilitate transfer from the bed to the wheelchair. When a client can use the hands and arms to move the wheelchair, the placement of the back to the client’s scapula is necessary.
This client cannot use the arms and will need an electric chair with breath, chin, or voice control to manipulate movement of the chair. A firm or hard cushion adds pressure to bony prominences; the cushion should instead be padded to reduce the risk of pressure ulcers.
Question 123.
The nurse is planning care for a group of clients who have had total hip replacement. Of the clients listed below, who is at highest risk for infection and should be assessed first?
(a) a 55-year-old client who is 6 feet (180 cm) tall and weighs 180 lb (81.7 kg)
(b) a 90-year-old who lives alone
(c) a 74-year-old who has periodontal disease with periodontitis
(d) a 75-year-old who has asthma and uses an inhaler
Answer:
(c) a 74-year-old who has periodontal disease with periodontitis
Explanation:
Infection is a serious complication of total hip replacement and may necessitate removal of the implant. Clients who are obese, poorly nourished, or elderly and those who have poorly controlled diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or concurrent infections (e.g., dental, urinary tract] are at high risk for infection. Clients who are of normal weight and have well-controlled chronic diseases are not at risk for infection. Living alone is not a risk factor for infection.
Question 124.
The nurse is documenting care of a client who is restrained in bed with bilateral wrist restraints. Following assessment of the restraints, what should the nurse’s documentation include? Select all that apply.
(a) nutrition and hydration needs
(b) capillary refill
(c) continued need for restraints
(d) need for medication
(e) skin integrity
Answer:
(a) nutrition and hydration needs
(b) capillary refill
(c) continued need for restraints
(e) skin integrity
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e). A restraint is a method of involuntary physical restriction of a client’s freedom of movement, physical activity, or normal access to his/her body. The nurse must monitor and provide care to optimize the physical and psychological well-being of the client including, but not limited to, respiratory and circulatory status, skin integrity, and vital signs.
With each assessment, the nurse needs to ascertain that restraints are still required for client safety. The least restrictive intervention based on an individualized assessment of the client’s medical or behavioral status or condition is needed.
Question 125.
The nurse is instituting a falls prevention program. Which personnel should be involved in the program? Select all that apply.
(a) registered nurses
(b) insurance providers
(c) unlicensed assistive personnel
(d) housekeeping services
(e) family members
(f) client
Answer:
(a) registered nurses
(c) unlicensed assistive personnel
(d) housekeeping services
(e) family members
(f) client
Explanation:
(a), (c), (d), (e),(f). Client safety is a priority for the client, the client’s family, and all of the personnel working on this unit. All of these persons must be engaged in using strategies to prevent falls. The insurance provider does not need to be involved in developing a falls program.
Question 126.
The nurse unit manager is making rounds on a team of clients and notices a client with a color- coded armband that indicates the client is at risk for falling walking down the hall unassisted. The client is at the end of the hallway farthest from the client’s room, but is not tired. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Obtain a wheel chair, and take the client back to the room.
(b) Walk with the client back to the room, and assist the client to get in bed or a chair.
(c) Locate an unlicensed nursing personnel (UAP) to walk with the client back to the room.
(d) Instruct the client to walk only in the room at this time.
Answer:
(b) Walk with the client back to the room, and assist the client to get in bed or a chair.
Explanation:
The client is identified as being at risk for falling, and a staff member or family member should accompany the client when walking. The nurse should first accompany the client back the room. Because the client is not fatigued, the client does not need a wheelchair but must have assistance.
The nurse can delegate the task of ambulating the client to the UAP but it may take a while to locate one that it available at this time. Walking only in the room will not provide an opportunity for the client to gain strength and improve ambulation, but the nurse should remind the client to have assistance.
Question 127.
The health care provider has prescribed 5 mg warfarin orally for a hospitalized client. In planning care for this client, the nurse should verify that which services have been contacted? Check all that apply.
(a) pharmacy
(b) dietary
(c) laboratory
(d) discharge planning
(e) risk management
Answer:
(a) pharmacy
(b) dietary
(c) laboratory
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c). To assure client safety when using anticoagulants, the nurse should coordinate care at this time with the pharmacist, dietitian, and laboratory. The pharmacist will collaborate in teaching the client about using the drug; dietary services will plan a diet that limits foods that have high amounts of vitamin K (spinach, cabbage, blueberries) that will interfere with anticoagulation; and the laboratory will draw daily INR levels to assure accurate dosing.
Although the nurse coordinates discharge planning at the time of admission to the hospital, at this point it is too soon for discharge planning services to be involved because it is not known if the client will continue to take the warfarin when discharged. There is no indication that there has been an actual or potential error, and risk management is not needed at this time.
Question 128.
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are helping a client who has had knee surgery 2 days ago get into bed. As the nurse makes rounds, which information requires the nurse to intervene?
(a) The call light is pinned to the head of the bed in the client’s reach.
(b) The night light is dimmed, giving low-level lighting to the room.
(c) There is a clear path to the bathroom.
(d) The side rails on the head and foot of the bed are in the up position.
Answer:
(d) The side rails on the head and foot of the bed are in the up position.
Explanation:
Side rails are considered restraints and are not used at both the head and foot of the bed. Using side rails at the head of the bed will aid the client in sitting up and are safe, but using side rails at both the head and the foot of the bed presents risks for a client who might become wedged between the rail and the bed or attempt to climb over them.
The nurse discusses side rail use with the UAP and lowers the side rail at the foot of the bed. The nurse assures the bed is placed in low position. The accessible call light, dim lighting, and clear path to the bathroom are factors that contribute to fall prevention.
Question 129.
The nurse is going to lunch and is conducting a “hand-off of care” to the charge nurse. Which information should the nurse communicate to the charge nurse during the “hand-off of care” communication?
(a) Tell the charge nurse that the nurse is going to lunch.
(b) Verify that the charge nurse has assigned someone else to take care of the client.
(c) Give the charge nurse information about what care should be given while the nurse is at lunch.
(d) Remind the charge nurse about the client’s history and current medications.
Answer:
(c) Give the charge nurse information about what care should be given while the nurse is at lunch.

Explanation:
Hand-off dl of care communication is an interactive communication allowing the opportunity for questioning between the giver and receiver of client information, including up-to-date information regarding the client’s care, treatment, and services, as well as the client’s current condition and any recent or anticipated changes. “Hand-off” communication does occur when a nurse is leaving the nursing unit, but the purpose is not to let the charge nurse know that the nurse is going to lunch or to have someone else assigned to care for the client. “Hand-off” communication focuses on current information, not the client’s history.
Question 130.
The client has been diagnosed with septic arthritis in a hip joint. Which outcomes are desired from a client-focused teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Report pain that is severe enough to limit activities.
(b) Discuss how to take prescribed medications.
(c) Describe how the application of a heating pad set on “high” readily resolves edema.
(d) Describe the septic arthritis physiologic process.
(e) Explain the importance of supporting the affected joint.
(f) Describe how to use ambulatory aids and assistive devices.
Answer:
(a) Report pain that is severe enough to limit activities.
(b) Discuss how to take prescribed medications.
(d) Describe the septic arthritis physiologic process.
(e) Explain the importance of supporting the affected joint.
(f) Describe how to use ambulatory aids and assistive devices.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d), (e),(f). The nurse should determine that a client with rheumatoid arthritis can describe the septic arthritis physiologic process and knows how to relieve pain using pharmacologic and nonphar- macologic interventions. Prolonged immobility and limited activity may promote formation of a deep vein thrombosis and possibly subsequent pulmonary emboli.
The client should also understand the importance of supporting the affected joint, weight-bearing and activity restrictions, and how to use ambulatory aids and assistive devices safely to promote recovery of normal function. The local application of heat and cold to an injured body part can provide therapeutic benefits; however, “high” heat may cause a thermal injury and further promote edema formation. The client should inform the health care provider (HCP) about pain that is not relieved by the current management plan.
Question 131.
The nurse should perform passive range-of- motion (ROM) exercises on which clients? Select all that apply.
A client who:
(a) has septic joints.
(b) has temporary loss of sensation.
(c) is unconsciousness.
(d) has plantar flexion of the foot.
(e) has supination of the hand.
Answer:
(b) has temporary loss of sensation.
(c) is unconsciousness.
Explanation:
(b), (c). Passive ROM exercises are used to move the client’s joints through as full a ROM as possible. Passive ROM exercises improve or maintain joint mobility and help prevent contractures. These exer-cises are indicated for the client with temporary or permanent loss of mobility, sensation, or conscious-ness.
Exercises help with joint mobility, strength, and endurance. Plantar flexion of the foot and supi-nation of the hand may be normal joint movements if the client can do active ROM. Septic joints have infection that may be spread either hematogenously or through trauma.
Question 132.
A client is a moderate risk for falling using a fall risk assessment scale. What should the nurse instruct the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) to do?
(a) Remain with the client during toileting.
(b) Reorient the client to time and place every hour.
(c) Activate the bed and chair alarms.
(d) Apply a protective chest restraint.
Answer:
(c) Activate the bed and chair alarms.
Explanation:
The client has a moderate fall risk, and the nurse should direct the UAP to activate the bed and chair alarms. The UAP does not need to remain with the client during toileting unless the client’s risk for falling is high. There is no evidence the client is confused, and hourly reorientation could disrupt sleep. Protective devices to restrain clients are used for clients at high risk for a fall and require a prescription from a health care provider.
Question 133.
The nurse is planning care for a client who is at low risk for falling. What information would be included in the care plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Place call bell within easy reach.
(b) Secure locks on beds, stretchers, and wheel chairs.
(c) Remain with client during toileting.
(d) Keep the bed in the lowest position when possible.
(e) Place a commode next to bed for easy access.
(f) Employ a seat belt whenever a wheelchair is in use.
Answer:
(a) Place call bell within easy reach.
(b) Secure locks on beds, stretchers, and wheel chairs.
(d) Keep the bed in the lowest position when possible.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d). Since the client is at low risk for falling, it is not necessary to remain during toileting or to place a commode at the client’s bedside as the client is able to use the toilet. A wheelchair seat belt is used for clients with a moderate fall risk. The nurse should always make sure the call bell is within easy reach, that all locks are engaged when needed, and that the bed is in the lowest position.
