Practicing with Practice NCLEX Questions enables students to develop efficient test-taking strategies, such as elimination techniques and time management.
NCLEX Management of Care Questions - NCLEX Questions On Management of Care
Management of Care NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
The nurse is caring for a middle-aged woman who walks 3 miles every morning. The nurse notes that during her morning walk, the client called her son and stated that she thought she was having a heart attack. Which symptom, identified by the client, is the most common and consistent with a myocardial infarction (Ml)?
(a) palpitations
(b) lower extremity edema
(c) uncomfortable feeling of pressure in the chest
(d) nausea
Answer:
(c) uncomfortable feeling of pressure in the chest
Rationale:
An uncomfortable feeling of pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest is the predominant symptom of an Ml in women. Palpitations indicate an arrhythmia. Edema in the lower extremities is a later sign of cardiac failure. A feeling of nausea is less common when experiencing an Ml.
Question 2.
The nurse assists the client to the operating room table and supervises the operating room technician preparing the sterile field. Which action, completed by the surgical technician, indicates to the nurse that a sterile field has been contaminated? Select all that apply.
(a) A sterile object is held below the table surface and returned to the sterile field.
(b) The outer inch of the sterile towel hangs over the side of the table.
(c) A partially emptied container of sterile betadine is replaced within the sterile field.
(d) Sterile packages are opened with the first edge away from the technician.
Answer:
(a) A sterile object is held below the table surface and returned to the sterile field.
(c) A partially emptied container of sterile betadine is replaced within the sterile field.
Rationale:
Anything below the level of the table surface is considered unsterile. After opening a bottle of sterile solution (betadine), the contents must be used or discarded but not returned to the sterile field. The edges and sides of the towel extending below the side of the table are routinely considered unsterile. Sterile packages are routinely opened with the first edge away while the last flap is pulled toward the person opening the package.
Question 3.
The nurse is responsible for his own actions while on duty caring for clients. What is the name of this ethical principle? ........................
Answer:
Accountability
Rationale:
Accountability is the ethical principle that states that the nurse is responsible for his own actions while providing client care.
Question 4.
The nurse is caring for a client on the orthopedic unit who had a total knee replacement on the left side. The nurse knows the client will be ready for discharge when she
is able to do which of the following activities?
(a) ambulate 100 feet with crutches or walker
(b) get up and down a flight of stairs
(c) flex the surgical knee 30 degrees
(d) fix a snack
Answer:
(b) get up and down a flight of stairs
Rationale:
The ability to navigate a flight of stairs is a requirement for discharge after a total knee replacement. The client needs to be able to ambulate 75 feet. There is no set amount of flexion of the knee for discharge. Preparing a snack is not a standard requirement for discharge.
Question 5.
A client undergoes total shoulder replacement on the left shoulder. Which statements by the client indicates he requires further teaching? Select all that apply.
(a) "I look forward to soaking in my hot tub when I get home from surgery."
(b) "The surgery will eliminate my pain within 24 hours."
(c) "I will receive therapy for several weeks after my surgery."
(d) "Walking is an exercise I'll be able to do after surgery."
Answer:
(a) "I look forward to soaking in my hot tub when I get home from surgery."
(b) "The surgery will eliminate my pain within 24 hours."
Rationale:
After surgery, the client should avoid getting in a pool or tub as infection may occur. Longterm pain will be reduced, hopefully eliminated. Short-term pain will require pain medication to be administered as ordered. The client should be encouraged to take pain medication as frequently as needed. Physical therapy begins soon after surgery and may continue for several weeks, until full recovery occurs. Walking is considered a low-impact activity and would be encouraged after surgery.
Question 6.
Which diagnostic tool is most commonly used to determine the location of the myocardial damage?
(a) electrocardiogram (ECG)
(b) echocardiogram
(c) cardiac enzymes
(d) cardiac catheterization
Answer:
(a) electrocardiogram (ECG)
Rationale:
The ECG is most commonly used to initially determine the location of myocardial damage. An echocardiogram is used to view myocardial wall function after an Ml has been diagnosed. Cardiac enzymes will aid in diagnosing an Ml but not the location. While not performed initially, cardiac catheterization determines coronary artery disease and would suggest the location of myocardial damage.
Question 7.
The charge nurse is teaching unit nurses about droplet precautions. Which statement by one of the nurses indicates further teaching is needed by the charge nurse?
(a) "Mumps is a viral infection that requires droplet precautions."
(b) "Pharyngeal diphtheria is a viral infection that requires droplet precautions."
(c) "Pertussis is a bacterial respiratory infection that requires droplet precautions."
(d) "Mycoplasma pneumonia is a bacterial respiratory infection that requires droplet precautions."
Answer:
(b) "Pharyngeal diphtheria is a viral infection that requires droplet precautions."
Rationale:
Pharyngeal diphtheria is a bacterial respiratory infection, not viral. Mumps is a viral infection that requires droplet precautions. Pertussis and mycoplasma pneumonia are both bacterial respiratory infections that require droplet precautions. Droplets usually travel no farther than 3 feet from the client. Standard precautions along with a surgical mask must be worn when working within 3 feet of a client who is on droplet precautions.
Question 8.
The nurse is working with an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) in the medical-surgical unit. Which client should be assigned to the UAP?
(a) a client with cervical cancer who has an internal radiation implant
(b) a client who is receiving blood as treatment for hypovolemic shock
(c) a client who had an abdominal wound dehiscence 24 hours earlier and requires dressing changes
(d) a client who is post-op day 2 following a laparoscopic hernia repair and gets up to the chair for meals
Answer:
(d) a client who is post-op day 2 following a laparoscopic hernia repair and gets up to the chair for meals
Rationale:
The client who is post-op day 2 following a hernia repair and getting up to the chair is the most stable client for the UAP. Clients with internal radiation implants require special safety precautions, and all care personnel must be properly trained. Special handling procedures are required should the implant become dislodged and are beyond the scope of practice for a UAP.
The client receiving blood for hypovolemic shock is potentially unstable and is at greater risk for an emergency than the more stable client who can get up to the chair. Wound dehiscence is a serious complication of abdominal surgery and requires special management, including dressing changes.
The nurse may not delegate dressing changes to UAPs. The nurse is ultimately responsible for delegating tasks to the appropriate personnel and determining that the person is able to perform the task safely and correctly.
Question 9.
A client is being treated for pulmonary hypertension. The nurse knows that the involvement of nursing, pharmacy, cardiology, physical therapy, and nutritional services is an example of which of the following approaches?
(a) continuity of care
(b) case management
(c) quality improvement
(d) interdisciplinary
Answer:
(d) interdisciplinary
Rationale:
An interdisciplinary approach involves members from differing disciplines that are involved in attaining a common client outcome. Continuity of care, case management, and quality improvement are not related to the interdisciplinary approach.
Question 10.
An 84-year-old adult male requires nonurgent surgery. The client is considered to have diminished decision-making capacity due to a diagnosis of Alzheimer's. The nurse questions his ability to provide informed consent for the procedure. The best action for the nurse to take in this situation is which of the following?
(a) as this is nonurgent surgery with few risks, allow the client to sign the consent form
(b) contact administrative personnel for a determination consistent with hospital policy
(c) have the client's 54-year-old second cousin sign the consent form
(d) request the physician sign the consent form
Answer:
(b) contact administrative personnel for a determination consistent with hospital policy
Rationale:
Signing a consent form for a client with diminished capacity requires involvement of legal personnel with expertise on state regulations on these cases. The administrative personnel need to make a determination consistent with hospital policy. Allowing the client to sign the form violates the principles of informed consent. Involving the client's second cousin may be appropriate provided other more direct family members are unavailable. The physician is not able to sign for the client.
Question 11.
A nurse assigned to a client with congestive heart failure (CHF) is providing shift report.
Which nursing interventions would be appropriate to include? Select all that apply.
(a) The nurse should reduce fluid intake to less than 1,000 ml per shift.
(b) The nurse should keep the client in a supine position as much as possible.
(c) The nurse should encourage alternating activity with rest periods.
(d) The nurse should assess the ankles, legs, and feet for pitting edema.
Answer:
(c) The nurse should encourage alternating activity with rest periods.
(d) The nurse should assess the ankles, legs, and feet for pitting edema.
Rationale:
Inability of the myocardium to pump effectively will reduce the client's activity tolerance. Alternating activity with rest allows the client to function at her best. Assessment by the nurse is appropriate as pooling of fluid in the lower extremities results if the heart is unable to pump blood throughout the body. While clients with CHF need to be on strict intake and output, fluids do not necessarily need to be limited. Instead, the client's weight is a better assessment criteria of fluid overload. The client should be kept in a semi-Fowler's position.
Question 12.
A nurse is caring for a client in the immediate post-cardiac catheterization period. Which intervention should the nurse include in the client's care?
(a) monitor vital signs every 30 minutes for the first 2 hours
(b) assess the insertion site
(c) maintain the client in a prone position
(d) keep the client NPO for 2 hours
Answer:
(b) assess the insertion site
Rationale:
Assessment of the insertion site for bleeding is a priority. Should bleeding occur, additional compression may be needed. Vital signs are monitored every 15 minutes for 2 hours after the procedure, every 30 minutes during the next 2 hours, and then every hour for 2 hours. The head of the bed may be elevated up to 30 degrees. Clients post-catheterization may eat and drink as tolerated.
Question 13.
The nurse is preparing to interpret an electrocardiogram rhythm strip. Identify the order for interpreting the strip. Use all the options.
(a) measure the P-R interval
(b) determine the heart rate and rhythm
(c) analyze the P waves
(d) measure the QRS duration
Answer:
(b) determine the heart rate and rhythm
(c) analyze the P waves
(a) measure the P-R interval
(d) measure the QRS duration
Rationale:
A systematic approach to interpreting each strip is needed for consistency. Rate refers to frequency, determined by spaces between R and R. Rhythm is the interval of the pattern between R waves. The P wave is produced when the left and right atria depolarize. Regular intervals vary by less than 0.06 seconds.
The P wave should occur regularly; be one for every QRS complex; be smooth, rounded, and upright in appearance; and look similar. The P-R interval measures the time from the onset of atrial contraction to onset of ventricular contraction. The normal interval is 0.12 - 0.20 seconds. The QRS complex presents depolarization (contraction) of the ventricles. The normal interval is 0.06 - 0.12 seconds.
Question 14.
A client is admitted with inflammatory bowel syndrome (Crohn's disease). Which nursing measures would be included in the client's care plan? Select all that apply.
(a) high-fat diet
(b) lactulose therapy
(c) daily weight
(d) corticosteroids
Answer:
(c) daily weight
(d) corticosteroids
Rationale:
Daily weight provides information about fluid balance and effectiveness of the therapy regime. Corticosteroids taken on a short-term basis are known to reduce the inflammation associated with Crohn's disease. A high-fat diet may exacerbate the diarrhea associated with Crohn's disease. Lactulose would promote peristalsis and would be contraindicated.
Question 15.
The nurse is caring for an elderly client who is 1 day post-hip replacement surgery. Which nursing interventions should be included on the care plan? Select all that apply.
(a) apply compression stockings
(b) ambulate with walker
(c) encourage coughing and deep breathing every 2 hours
(d) limit fluid intake
Answer:
(a) apply compression stockings
(b) ambulate with walker
(c) encourage coughing and deep breathing every 2 hours
Rationale:
Applying compression stockings will assist in preventing a deep vein thrombosis. Ambulation post-surgery with a walker is done to prevent complications of immobility. Coughing and deep breathing will facilitate oxygenation of the body after receiving anesthesia. Fluid intake need not be restricted postop and may be encouraged depending on the client's medical history.
Question 16.
The school nurse is monitoring the diet of a child with cystic fibrosis. Which type of diet would the family be advised to follow?
(a) low calorie, high fiber
(b) low fiber, low fat
(c) low sodium, gluten free
(d) high fat, high calorie
Answer:
(d) high fat, high calorie
Rationale:
Because of malabsorption, clients with cystic fibrosis (CF) need one and a half to two times as many calories as people without CF. Following a high-fat, high-calorie diet will help meet these clients' nutritional needs. Other options are not appropriate for clients with CF.
Question 17.
A charge nurse is preparing client care assignments for the upcoming shift. A client who underwent a laminectomy is scheduled to return from the recovery care unit. Which staff member should receive this client?
(a) graduate nurse with 3 months of experience
(b) RN with 1 year of experience
(c) certified nursing assistant with 5 years of experience
(d) charge nurse with 2 years of experience
Answer:
(b) RN with 1 year of experience
Rationale:
As the client will require neurologic assessment, the RN should receive the client. The graduate nurse and certified nursing assistant both lack sufficient assessment skills. The charge nurse is needed to supervise the unit.
Question 18.
A toddler in gastric distress is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit. The toddler becomes anxious and tries to remove the IV. The mother offers to help calm the child. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) paint a smiley face on the dressing covering the IV site
(b) give the child a puzzle to complete
(c) ask the mother to read the child's favorite book
(d) administer a sedative to the child
Answer:
(c) ask the mother to read the child's favorite book
Rationale:
An intervention by the mother is both distracting and comforting to the toddler. Painting a smiley face on the dressing covering the IV site may focus the child's attention further to the dressing. A puzzle is above the cognitive level of the toddler. Sedation may mask symptoms of distress.
Question 19.
Which assignment made by a charge nurse should be questioned?
(a) a student nurse assigned to a newly admitted child with acute leukemia who is receiving a blood transfusion
(b) an RN assigned to a teenaged child diagnosed recently with bacterial meningitis
(c) a CNA assigned to a stable male client who is 3 days post-stroke
(d) an LPN assigned to a newly admitted child with acute leukemia who is receiving IV fluids
Answer:
(a) a student nurse assigned to a newly admitted child with acute leukemia who is receiving a blood transfusion
Rationale:
A student nurse would not be allowed to administer a blood transfusion without supervision. The remaining assignments are within the scope of practice of each health care practitioner.
Question 20.
A 4-month-old infant is admitted to the pediatric unit for a 10-day course of antibiotics. The parents are only able to visit on weekends. Which action indicates the nurse understands the emotional needs of the infant?
(a) The nurse care plan calls for soothing music to be played several times per day.
(b) The nurse self-assigns care for the infant each shift worked.
(c) The nurse assigns a male nurse to care for the infant as much as possible.
(d) The nurse places the infant in a room close to the nursing station.
Answer:
(b) The nurse self-assigns care for the infant each shift worked.
Rationale:
Continuity of care by the same nursing personnel helps build trust with the infant, an important developmental need at 4 months old. Playing music will influence the environment but is not the best choice for meeting the emotional needs of the infant. The gender of the nursing care provider is irrelevant. Placing the infant close to the nursing station will not address its emotional needs.
Question 21.
The school nurse is assessing the readiness of a 16-year-old athlete who is diabetic. As the teenager becomes more physically active during the day, which management strategies should the nurse advise? Select all that apply.
(a) monitor blood glucose level before exercise
(b) always carry some form of high-protein, high-fat snack
(c) let the coach know the athlete is a diabetic
(d) inject insulin at least 30 minutes prior to athletic event
Answer:
(a) monitor blood glucose level before exercise
(c) let the coach know the athlete is a diabetic
Rationale:
Blood glucose levels should be closely monitored before exercise. If the level is below 70, the athlete should have a snack. If it is above 300, the athlete should inject insulin consistent with the personal plan and retest. The coach should know the athlete is a diabetic and what the signs/symptoms of hypoglycemia are so he can help if this occurs. Snacks high in carbohydrates should be carried in case of hypoglycemia. Insulin injections should be consistent with the athlete's schedule. Administering insulin prior to an athletic event will increase chances for hypoglycemia.
Question 22.
The nurse is caring for a client with an infected leg wound. The client develops a fever of 102°F. Which action by the nurse is the priority for this client?
(a) obtain a wound culture
(b) administer acetaminophen
(c) administer IV antibiotic as scheduled
(d) perform the scheduled dressing change
Answer:
(c) administer IV antibiotic as scheduled
Rationale:
Administering the IV antibiotic is the priority because it will treat the infection that is causing the fever. Giving an antipyretic should follow the IV antibiotic. Since the client has scheduled antibiotics, a wound culture is not necessary. The dressing change is important but should be performed after the antibiotic is administered.
Question 23.
The nurse is performing a dressing change on a client with a stage 3 sacral wound. Once the old dressing is removed, the nurse would perform which step next?
(a) wash hands
(b) chart the findings
(c) assess the wound
(d) prepare the sterile field
Answer:
(c) assess the wound
Rationale:
When performing a dressing change, the nurse first removes the old dressing while wearing clean gloves. The wound is assessed by noting drainage color, amount, and odor if any drainage is present. The color of the skin around the wound and in the wound bed is assessed, and the wound may be measured to ensure that the wound is healing as planned. Once the wound is thoroughly assessed, the gloves are discarded, hand hygiene is performed, and the sterile field is prepared for the dressing change. Charting the dressing change is the last step.
Question 24.
A newly graduated nurse has completed hospital orientation and has just started working with her own clients. Which of the following assignments is most appropriate for this nurse?
(a) a nonverbal client hospitalized for seizures
(b) a client undergoing peritoneal dialysis at the bedside
(c) a client who had a negative heart catheterization the day before
(d) an elderly client who just returned from surgery for a below-the-knee amputation
Answer:
(c) a client who had a negative heart catheterization the day before
Rationale:
The client with the negative heart catheterization is the most stable of this group of clients. The client will most likely be on telemetry, which allows early monitoring of any changes in heart rhythm before physical signs are present. A nonverbal client with seizures is more unstable and will have a more difficult time communicating needs to the nurse.
Peritoneal dialysis is a more advanced skill and requires proper training and skill validation. An elderly client who just had a below-the-knee amputation is at greater risk of complications due to age, and is at higher risk of bleeding from the surgery.
Question 25.
The nurse is working with a newly hired unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Several activities of daily living need to be completed for the nurse's clients. Which task should the nurse delegate to the UAP?
(a) performing oral care on a client with a bleeding disorder
(b) turning a client with a tibial fracture with external fixation
(c) assisting a client admitted with COPD exacerbation to the chair
(d) reinforcing teaching on use of the inhaler for a client with asthma
Answer:
(c) assisting a client admitted with COPD exacerbation to the chair
Rationale:
The client with COPD exacerbation who can get up to the chair is the best choice for the UAP. Sitting upright in the bed or a chair allows for maximum ease of breathing and is the best position for coughing and clearing secretions. The nurse should perform oral care on clients with bleeding disorders due to the increased risk of bleeding. The client with a tibial fracture and external fixation must be positioned and turned in a specific manner so as to maintain fixation.
Turning clients with special turning requirements should not be delegated to inexperienced personnel. The nurse must verify that the UAP is properly trained in turning these clients. Reinforcement of teaching is still considered teaching and may only be done by the licensed nurse. The nurse is responsible for all tasks that are delegated and must ensure that they are performed safely.
Question 26.
The RN is assigning a client to the LPN. The RN understands that the best assignment for the LPN is which client?
(a) a client receiving blood for a Gl bleed
(b) a client with a PICC line requiring TPN
(c) a client who will receive enemas in preparation for a colonoscopy
(d) a client who needs preoperative teaching for bowel resection surgery
Answer:
(c) a client who will receive enemas in preparation for a colonoscopy
Rationale:
Administering enemas is within the scope of practice for LPNs. Administering blood and giving anything through any type of central line, including PICCs, is beyond the scope of practice for LPNs. Preoperative teaching must be done by the RN. The duties of an LPN may vary from state to state; it is the RN's responsibility to be familiar with the Nurse Practice Act of his state and to know the limitations of an LPN's duties.
Question 27.
A local volunteer singing group performs in the activity room of a long-term care facility.
The group's leader asks the nurse if they may take a photo of themselves with several of the clients. The nurse gives permission to the leader, who then posts the photo on Facebook. Upon notification of this situation, the facility administration immediately terminates the nurse. What Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) violation did the nurse commit?
(a) breach of confidentiality
(b) failure to seek administrative approval
(c) unethical conduct
(d) unprofessional conduct
Answer:
(b) failure to seek administrative approval
Rationale:
In allowing the outside group to take a photo of the clients, the nurse committed a breach of confidentiality. Each client must give consent to be photographed and have the picture posted on social media. Failure to gain such consent is a serious violation.
Had the nurse obtained administrative approval for the photograph, it would have been inadequate as only an individual may consent to have her image taken and shared with others. While the nurse failed to act in the best interest of the clients, the conduct is not necessarily unethical or unprofessional according to HIPAA.
Question 28.
A nurse manager and a case manager are talking to a group of new nurses about the differences of case management and care coordination. The nurse manager understands which to be true regarding the differences?
(a) With care coordination, the stakeholder can be an insurance company or a hospital.
(b) The main goal of case management is to promote a better quality of life for the client.
(c) Case management is based on a holistic approach and an understanding of client- family dynamics.
(d) In care coordination, the client defines the scope of work based on a plan that is created with input from the client.
Answer:
(d) In care coordination, the client defines the scope of work based on a plan that is created with input from the client.
Rationale:
Care coordination is limited in that the scope of work is based on a plan that is created with input from the client. The stakeholder in case management is an insurance company or a hospital. The main goal of care coordination is to promote a better quality of life for the client, while case management's goal also includes legal and financial issues that may involve stakeholders.
Additionally, eliminating noncompliance and overutilization of resources is addressed. Care coordination is based on a holistic approach and an understanding of client-family dynamics, with less emphasis on issues that affect stakeholders. Advocating for client needs is emphasized over stakeholder interests.
Question 29.
The newly graduated nurse is caring for an elderly client on the medical-surgical floor. The nurse recalls learning about client advocacy. Which actions by the nurse indicate an understanding of client advocacy? Select all that apply.
(a) The nurse speaks to the daughters regarding care-making decisions, since the client is elderly and may not understand.
(b) The nurse tells the family that they should really consider making the client an organ donor in case something happens.
(c) The nurse makes sure the client understands treatment options, including possible outcomes if the client refuses treatment.
(d) The nurse obtains an interpreter for the client if her native language is not English and she only understands her native language.
(e) The nurse asks the client for a copy of advance directives or a living will, or provides information if the client does not have one.
Answer:
(c) The nurse makes sure the client understands treatment options, including possible outcomes if the client refuses treatment.
(d) The nurse obtains an interpreter for the client if her native language is not English and she only understands her native language.
(e) The nurse asks the client for a copy of advance directives or a living will, or provides information if the client does not have one.
Rationale:
Responses (c), (d), and (e) are examples of how a nurse keeps the client's interest at the focus of care and maintains the role of client advocate. One of the duties is making sure that the client understands treatment options, including possible outcomes if the client refuses treatment. The nurse must also ensure that the client receives instruction in her native tongue if she does not speak English.
This is especially important when obtaining consent for surgery and other invasive procedures. Copies of living wills, advance directives, and other legal health care documents should be placed in the client's chart if available. Only speaking to family members regarding the client's care is rude and does not show consideration for the client's wishes for her care.
The nurse should not insist that any client become an organ donor. The nurse's opinion is secondary to the client's wishes. The nurse serves as a client advocate by following the client's wishes, not pushing what he thinks is best for the client
Question 30.
A nurse manager is educating a group of nursing students about the Patient's Bill of Rights.
The nurse knows that the student nurses have an understanding of the bill when one of the nurses makes which statement?
(a) "Clients have the right to view their medical records but may not copy any of the information contained in the records."
(b) "Clients may be declined care at an emergency department or need preauthorization for care if they do not have premium-level insurance."
(c) "Clients have the right to a quick and objective review of any claim that they levy against a health care facility, physician, or health care plan."
(d) "It is the admitting nurse's job to verify the client's past medical history, medications, and treatments, even if the client refuses to cooperate in giving the information."
Answer:
(c) "Clients have the right to a quick and objective review of any claim that they levy against a health care facility, physician, or health care plan."
Rationale:
The Patient's Bill of Rights gives all clients the right to a quick and objective review of any claim that they levy against a health care facility, physician, or health care plan. Clients also have the right to view and receive copies of their medical records. Anyone presenting to an emergency department, whether insured or not, has the right to receive life-saving treatment and stabilization, or be transferred to another, more appropriate facility if required.
It is against the law for an emergency department to refuse treatment to anyone, regardless of ability to pay. The client is responsible for providing correct information regarding past medical history, medications, and treatments. While the nurse is expected to make all reasonable efforts to corroborate client reports, the ultimate responsibility lies with the consumer of health care.
Question 31.
Nurses are expected to understand the principles of triage when caring for multiple clients. The ICU charge nurse is reviewing assignments. Based on the principles of triage, to which client would the charge nurse give priority for treatment? Select all that apply.
(a) a client on a ventilator who has an alarm sounding
(b) a client who has just returned from an open appendectomy
(c) a client ready to transfer to the floor after the nurse calls report
(d) a client who has been talking with family and is now unresponsive
(e) a client receiving a new antibiotic who complains of tingling in the mouth
(f) a client who has not eaten yet and is a type 2 diabetic with a morning blood sugar of 90
Answer:
(a) a client on a ventilator who has an alarm sounding
(b) a client who has just returned from an open appendectomy
(d) a client who has been talking with family and is now unresponsive
(e) a client receiving a new antibiotic who complains of tingling in the mouth
Rationale:
Principles of triage include treating the least stable clients first. In this scenario, there are four clients requiring immediate attention. When a piece of equipment alarms, the first course of action is to check the client, and then troubleshoot the alarm. The nurse should never ignore any alarm for any reason. Clients who have just returned from surgery, especially an open surgical approach, are at risk for loss of airway due to anesthesia, bleeding from the site, and other potential surgery-specific risks. A sudden change in level of consciousness requires immediate action to determine the cause.
Tingling in the mouth is a sign of a possibly serious allergic reaction and may occur if the client receives a new medication for the first time. This client is at high risk of anaphylactic shock. A client who is ready to transfer to the floor is stable and therefore not a priority situation. The client with diabetes who has a blood sugar of 90 is within a safe range and does not require emergent treatment or monitoring.
Question 32.
A nurse on a busy surgical floor is working with an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). The nurse understands that which task cannot be delegated to the UAP?
(a) assisting a stable client to set up her meal tray for easy access
(b) assisting a client with an arm cast onto the bedpan
(c) calling report on a client who is being transferred to the observation floor
(d) helping a client ambulate in the hall who is post-op day 2 from a cardiac catheterization with stent placement
Answer:
(c) calling report on a client who is being transferred to the observation floor
Rationale:
The nurse is responsible for knowing which tasks can and cannot be delegated. Ultimately, the nurse is responsible for the outcome of all delegated tasks. Only the licensed nurse can call and receive report on clients. UAPs may perform tasks with stable clients who will have predictable outcomes. Assisting stable clients set up meal trays or sit on a bedpan is within the realm of tasks that UAPs may perform. The client who had a cardiac stent placed is two days post-op, and there are no complications mentioned that would indicate this client is unstable.
Question 33.
The nurse in the senior dementia unit noticed an increase in client falls over the last six months. She worked with other unit nurses and the nurse manager to develop a new fall risk assessment tool and updated the unit policies regarding falls. Which activity did the nurse engage in?
(a) delegation
(b) peer review
(c) consultation
(d) client referral
(e) quality improvement
Answer:
(e) quality improvement
Rationale:
Quality improvement is the process by which a nurse identifies a need for practice improvement and develops policies and/or procedures to improve practice. Identifying and minimizing fall risk for clients who are high risk for falls is an example of the quality improvement process. Delegation is the process by which an RN assigns other tasks to assistive personnel or to an LPN.
Peer review is part of the review process when a scientific paper is presented to a medical or nursing journal for publication. Consultation is the process in which other health care providers, specialists, or social workers are involved in client care as the need arises. Client referral involves directing the client to a case worker or community service to assist in client needs. Referrals may be made to other health care facilities or rehabilitation facilities.
Question 34.
The ED nurse is attending orientation for nurses new to working in the ED. As part of the training, the ED nurse would expect to report which conditions to the proper authorities?
Select all that apply.
(a) West Nile virus
(b) herpes simplex
(c) gunshot wounds
(d) elder abuse or neglect
(e) bites from an unknown dog
Answer:
(a) West Nile virus
(c) gunshot wounds
(d) elder abuse or neglect
(e) bites from an unknown dog
Rationale:
West Nile virus is reportable due to the fact that it can easily be spread by mosquitoes over a large area. City and county municipalities are able to spray to prevent the spread of certain mosquito- borne diseases. Gunshot wounds must be reported to local police or sheriff departments.
Elder abuse and neglect, along with child abuse or neglect, must be reported to local authorities for follow-up investigation and to ensure client safety. Bites from unknown dogs must be reported due to the risk of rabies, especially in stray dogs. Herpes simplex is not a reportable condition. The ED nurse must be knowledgeable of facility policies and procedures for carrying out reporting required conditions.
Question 35.
The RN is precepting a nursing student in the surgical ICU. The client is diabetic and asks the student nurse about insulin. Which response by the RN is best?
(a) ask the family to step out of the room to ensure client privacy
(b) tell the client that he should ask the health care provider when she rounds
(c) inform the client that the student nurse cannot answer questions regarding medication
(d) allow the nursing student to answer the client's question while the RN is present and can provide additional information if needed
Answer:
(d) allow the nursing student to answer the client's question while the RN is present and can provide additional information if needed
Rationale:
Nursing students learn by doing, and educating clients about their medications is one of the most important skills in nursing. The student nurse should answer only when the precepting nurse is in the room. If any information is incorrect, the RN can gently offer the correct information and use it as a teaching moment for the student nurse. There is no reason to ask the family to step out of the room unless the client specifically requests it.
Passing off medication questions to the health care provider is inappropriate, unless the client is receiving a medication that is unfamiliar to the nurse or is an experimental drug. It is incorrect to tell the client that the student nurse cannot answer questions about medication. A student nurse precepting in the ICU has already passed several medication tests.
Question 36.
The nurse is caring for a client who is a Jehovah's Witness and is scheduled for hip replacement surgery. The client refuses to sign consent for blood due to religious reasons. The client's daughter has the power of attorney in case the client is unable to state his wishes regarding health care. The daughter tells the nurse, "I'm afraid if something goes wrong, dad might need blood. I want to sign a blood consent form since I'm his power of attorney." The daughter is not a Jehovah's Witness. Which action by the nurse is the best in this situation?
(a) notify the charge nurse so that she can ask the night shift nurse to handle the situation
(b) go and get a blood consent form for the daughter to sign, noting that she has power of attorney over the client
(c) notify the surgeon that the client's daughter has power of attorney and will be signing a blood consent form so that an order may be obtained for a type and cross
(d) remind the daughter that the client clearly does not wish to receive blood, and that a power of attorney cannot override client wishes that have been clearly stated when he was able to give or refuse consent.
Answer:
(d) remind the daughter that the client clearly does not wish to receive blood, and that a power of attorney cannot override client wishes that have been clearly stated when he was able to give or refuse consent.
Rationale:
The client has made his wishes known to the nurse by refusing to sign the consent for blood. Upon admission to the facility, all clients are asked about special religious beliefs that affect care. A power of attorney completed before the client arrives at the facility allows the client to personalize what he does not wish to have done, so he may refuse blood on the power of attorney and allow his daughter to make choices regarding artificial hydration or food, for example.
The nurse has an ethical duty based on the principle of client autonomy to not knowingly act against client wishes, even if she does not agree with them. Notifying the charge nurse to let the night shift nurse address the issue does not solve the problem and is irresponsible.
Getting a consent for the daughter to sign goes against client wishes, which were recorded upon admission. There is no need to notify the surgeon or to order a type and cross. To give blood to the client against his wishes is considered assault and battery and may result in legal action involving the health care providers, including the surgeon, nurse, and facility.
Although the client presents himself as a Jehovah's Witness, the nurse should still ask questions regarding transfusions, preferably out of the presence of friends or family members who may influence the client's true wishes. HIPAA allows the nurse to ask others to leave the room during the questioning process if the client is able to communicate, thereby preserving his privacy.
Question 37.
The nurse manager has approval to add one LPN to the RNs in the medical-surgical unit. Which nursing actions does the nurse manager expect the LPN to be able to perform according to most state board of nursing practice acts? Select all that apply.
(a) draw blood from a PICC line
(b) access a port with a Huber needle
(c) perform hemodynamic monitoring
(d) transcribe written physician orders
(e) perform finger-prick blood glucose testing
Answer:
(d) transcribe written physician orders
(e) perform finger-prick blood glucose testing
Rationale:
In most states, LPNs may transcribe written (but not verbal or telephone) orders and sign off. The RN normally signs off the orders after ensuring accuracy and whether they are completed. The RN is responsible for LPN orders she signs off on during her shift. LPNs can perform finger-prick blood glucose testing, and so can UAPs who have been trained and checked off on how to use the equipment.
In most states drawing blood from a PICC line may only be performed by an RN. Accessing a port may only be performed by an RN who has been certified competent in this skill. Hemodynamic monitoring is another advanced skill limited to RNs working in ICUs where they have demonstrated competency. Nurse practice acts vary slightly among the states. In some states, LPNs may perform limited activities with peripheral IVs after training and certification.
Question 38.
The nurse is caring for a client when the attending physician comes in to round on the client. At the nurses' station, the nurse smells alcohol on the physician's breath when he hands her the chart with new orders. Which action by the nurse is appropriate?
(a) notify the nurse manager and or/charge nurse
(b) confront the physician about the smell of alcohol
(c) tell the client and request a consult with another physician
(d) enter the new orders as written, since there was only a morning lab draw ordered
Answer:
(a) notify the nurse manager and or/charge nurse
Rationale:
The nurse has a legal and ethical duty to report any caregivers who may be impaired, whether it is a physician or an unlicensed assistive personnel. The nurse should immediately notify the nurse manager and/or the charge nurse. Facility policies will guide them on the proper response and whether to notify risk management or security.
Since the physician may be impaired, any orders written may require review by another health care provider before implementing. Confronting the physician may result in escalating a potentially volatile situation and is inappropriate. The client should not be informed at this time of the physician's possible impairment until the situation has been followed up per facility guidelines.
Another physician should not be consulted by the nurse, as this is a situation requiring intervention by management. The nurse should not enter orders that were written while the ordering physician was possibly impaired, even if it is a routine lab and seems to be an appropriate choice. The nurse assumes liability for entering any such orders and could be held liable if the order caused any harm to the client.
Question 39.
A newly graduated nurse has been assigned a client who has a chest tube following a thoracotomy. The new nurse is not experienced with chest tube management. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate regarding this assignment?
(a) ask for a different group of clients
(b) ask to be floated to another area in the facility
(c) refuse the assignment, since she is not familiar with chest tubes
(d) accept the assignment and ask for another nurse to help her with the chest tube
Answer:
(d) accept the assignment and ask for another nurse to help her with the chest tube
Rationale:
If the client is stable, the nurse should accept the assignment and ask for another nurse with ' knowledge of chest tubes to educate him on chest tube management. The licensed nurse should be open to learning new skills when there is someone on staff who can assist him. The nurse should learn how to position the tube, mark drainage, chart output, and understand troubleshooting, such as what to do if an air leak develops. Chest tube management is an expected skill set in critical care settings.
Stable clients may be on medical floors; training on equipment common to a care area of the facility should be readily available for new nurses. Asking for a different group of clients prevents the nurse from learning a valuable new skill set. Asking to be floated may disrupt staffing in other areas of the facility if no additional staff is needed. Refusing the assignment should be reserved for situations such as performing hemodialysis, which is not something quickly learned at the bedside.
If the nurse is in an area where no other nurses have chest tube experience, the nurse manager should be notified. In cases like this, a nurse may be able to come from the ICU every 2 hours or so to round on the client, check the chest tube, and show the new nurse how to manage the tube.
Question 40.
A nurse is precepting a nursing student in the pediatrics unit. The student nurse is preparing to administer an injection to a 14-month-old infant. Which statement by the student nurse indicates a need for further teaching by the licensed nurse?
(a) "I will use a needle that is 7/8 inch to 1 inch long."
(b) "I will give this injection at a 90-degree angle of insertion."
(c) "I will give this injection in the vastus lateralis with a 27-gauge needle."
(d) "I can give this injection with a 25-gauge needle in the dorsogluteal area."
Answer:
(d) "I can give this injection with a 25-gauge needle in the dorsogluteal area."
Rationale:
Injections on infants less than 18 months old should be done in the vastus lateralis, not the dorsogluteal area. The dorsogluteal area is not recommended for children less than 3 years of age. The correct needle length for this client is 7/8 inch to 1 inch in length. The injection should be given at a 90-degree angle. A 27-gauge needle is appropriate for injecting in the vastus lateralis.
Question 41.
The nurse is admitting a new client complaining of severe abdominal pain. When asked about valuables, the client says he has $ 1,500 cash in his wallet. He is from out of state and does not have anyone who can take his wallet into safekeeping for him. Which statement by the nurse best addresses this situation?
(a) "I can keep it locked up in the charge nurse's office for you."
(b) "It should be fine. Just hide it in a drawer when you go down for a CT scan."
(c) "I can call security to bring a form to fill out, and they will lock it up for you."
(d) "You will have to call someone to come get it. We can't let you keep it in your room."
Answer:
(c) "I can call security to bring a form to fill out, and they will lock it up for you."
Rationale:
The nurse should inform the client that it is not safe to keep valuables in the room, and that security can bring a form stating which items the client would like to have locked up. The nurse cannot force the client to place items with security, but should inform the client of the option. The charge nurse's is office is not a place to store client valuables. The client should not be encouraged to leave valuables in a drawer when he leaves the room. Insisting that the client call someone when the client has no one to call is counterproductive and may be interpreted as confrontational.
Question 42.
The nurse is caring for a client with dyspnea. Which interventions can the nurse delegate to an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)? Select all that apply.
(a) assessing lung sounds
(b) checking a pulse oximetry
(c) administering oxygen via nasal cannula
(d) encouraging the client to cough and deep breathe
(e) showing the client how to use an incentive spirometer
Answer:
(b) checking a pulse oximetry
(d) encouraging the client to cough and deep breathe
Rationale:
A UAP can obtain a pulse oximeter reading on a client once he has demonstrated competency in using the device, which clips onto the finger similar to a clothespin. In many facilities, this is part of taking routine vital signs. The UAP can also prompt the client to do coughing and deep breathing once the nurse has shown the client how to perform it; however, the nurse must be the one to initially 1 educate the client on the technique.
UAPs cannot teach or assess clients; this is an activity reserved for the nurse. Only the nurse can assess lung sounds. Administering oxygen must be done only by the nurse. If the client is already on nasal cannula and gets up to use the restroom, the UAP may assist the client back to bed and place the nasal cannula back on the client once the UAP has demonstrated the proper technique.
In no instance may the UAP be the one to initiate oxygen therapy, nor may he adjust the flow rate. The nurse should educate the client on incentive spirometer use. Depending on the facility, the nurse or respiratory therapist should assess and chart the client's number of attempts, the highest reading obtained, and gauge the work of breathing on a scale.
Question 43.
The ED nurse is working in triage on a summer weekend. The following clients present at the same time. Which client does the nurse anticipate being seen first?
(a) a 58-year-old man with abdominal pain and nausea
(b) an infant with fever, a shrill cry, diarrhea, and nuchal rigidity
(c) a 38-year-old jogger who twisted her ankle, has a good pedal pulse, and has no deformity
(d) a 46-year-old client who was working outside and has tachypnea, diaphoresis, and fatigue
(e) an ambulatory child who fell off a bicycle and hit his head on grass while wearing a helmet
Answer:
(b) an infant with fever, a shrill cry, diarrhea, and nuchal rigidity
Rationale:
Fever, a shrill cry, diarrhea, and nuchal rigidity indicate meningitis, which is a medical emergency. The infant must be placed on respiratory isolation immediately, monitored for seizures, and prepared for a lumbar puncture. Those in close contact with the infant may need prophylactic treatment as well. The client with abdominal pain and nausea is stable at this moment and can be seen later.
The jogger is not the top priority because she has a good pedal pulse and no deformity in the ankle, which indicates that she is stable. The client who was working outside and presents with tachypnea, diaphoresis, and fatigue is at risk for heat syncope and should rest in a cool area and be taught to limit exposure in extreme heat, take frequent breaks, and drink plenty of water. This client is also stable.
The child who fell off a bicycle onto grass while wearing a helmet is ambulatory, wore protection, and landed on a soft surface. Although he should still have an assessment to check for head injuries, he is not currently in a life- threatening situation like the infant.
Question 44.
The charge nurse in the medical unit is preparing a bed assignment for a stable client diagnosed with necrotizing fasciitis. The client has a history of diabetes and hepatitis. There are four beds available. The nurse knows that the best roommate for this client is which of the following?
(a) a client with gout in the large toe
(b) a client with fever, vomiting, and diarrhea
(c) a client with MRSA
(d) a client with severe dementia with a tendency to wander
Answer:
(a) a client with gout in the large toe
Rationale:
The best roommate for this client is a client with gout in the large toe. Necrotizing fasciitis is worse in immunocompromised clients, and this client has a history of diabetes and hepatitis. This leaves the client vulnerable to worsening the infection or developing a new infection on top of the necrotizing fasciitis. Gout is not a communicable illness, so this is the best roommate choice for this client. A client with fever, vomiting, and diarrhea may potentially have a contagious condition that can worsen the outcome for the client.
The client with MRSA is not a good choice because there is a chance that the MRSA could infect the client with necrotizing fasciitis. The client with severe dementia and the tendency to wander is at risk of cross-contamination and further infecting the client with necrotizing fasciitis because of her inability to perform hand hygiene. Clients with necrotizing fasciitis are generally not contagious to healthy persons, but contact and universal precautions, along with hand hygiene, prevents them from further colonization by bacteria.
Question 45.
The nurse is caring for a client who is post-op day 1 for a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). The nurse knows that continuity of care for this client is ensured by doing which of the following? Select all that apply.
(a) using standardized handoff reports
(b) knowing how to perform a chart check
(c) following up on outstanding lab reports and incomplete orders
(d) knowing the proper procedures to transfer clients to another floor
(e) telling the next shift that they will need to draw blood that was due on the current shift
Answer:
(a) using standardized handoff reports
(b) knowing how to perform a chart check
(c) following up on outstanding lab reports and incomplete orders
(d) knowing the proper procedures to transfer clients to another floor
Rationale:
The nurse understands that continuity of care only occurs when all people involved in client care maintain open, two-way communication so that nothing is overlooked or forgotten. Using standardized handoff reports ensures that all important data is conveyed to each following shift, without any omissions. Daily chart checks involve reviewing all orders written during the previous shift and ensuring that they have been completed or ordered, such as a series of daily labs. The nurse should follow up on incomplete orders or outstanding labs before the end of shift so that the next shift does not have to assume responsibility.
Knowing proper procedures and forms needed to transfer clients helps to ensure that all orders "follow" the client to the next area. Telling the next shift that they need to draw labs that were due on the current shift is poor nursing practice and may affect treatments and medications ordered by the health care provider.
The nurse must ensure that all orders on clients are carried out, even if that means staying over to finish that shift's work. Unless informed otherwise by the charge nurse or facility policy regarding overtime, the nurse is expected to finish all work for his shift before leaving.
Question 46.
The nurse reports to work and finds that a client from the previous day has been assigned to another nurse. The nurse had a great rapport with the client and wonders how he did during the night. She decides to look at the client's chart to read the progress notes. Which statement is correct regarding the nurse's actions?
(a) She should go to the client's room and see how he is doing.
(b) She has legal access to the client's chart since she was involved in his care.
(c) The nurse is violating HIPAA regulations and should not be accessing the client's chart.
(d) She should wait and ask the other nurse how the client is doing and not view the client's chart.
Answer:
(c) The nurse is violating HIPAA regulations and should not be accessing the client's chart.
Rationale:
Even though the nurse cared for the client the previous day, she is no longer assigned to the client. Accessing the chart, even if she cared for the client previously, is a HIPAA violation in this instance. The nurse may not realize it, since she cared for the client previously. It is important to not become complacent about HIPAA compliance. The nurse should not go to the client's room unless she is called in there to help turn or perform another action.
She does not legally have access at this time to view the chart. The nurse should not ask the current nurse about the client's condition, since this is still illegally sharing information that she is not privy to. HIPAA violations are not limited to viewing charts; any sharing of information about a client that the nurse is not caring for violates HIPAA regulations
Question 47.
A nurse is talking to a nursing student about quality improvement and nurse-sensitive indicators. The nurse knows that the nursing student understands quality improvement when she identifies which to be nurse-sensitive indicators? Select all that apply.
(a) fall injury rates
(b) restraint utilization rates
(c) staying within the unit budget
(d) upgrading computer charting programs
(e) pressure ulcer prevalence and incidence
(f) client satisfaction with pain management
Answer:
(a) fall injury rates
(b) restraint utilization rates
(e) pressure ulcer prevalence and incidence
(f) client satisfaction with pain management
Rationale:
Nurse-sensitive indicators in a quality improvement program consist of measurements of client care that are directly impacted by nursing care. Fall injury rates, restraint utilization rates, pressure ulcer prevalence and incidence, and client satisfaction with pain management are just a few.
These are areas in which nurses assess diligently and know when to intervene. While staying within the unit budget is always a goal, it is not a nurse-sensitive indicator. Upgrading computer charting programs is not a nurse-sensitive indicator.
Question 48.
The nurse is charting on his client, who had an open appendectomy the previous day. Which are appropriate nursing documentation entries? Select all that apply.
(a) The client appeared anxious when several family members came to visit.
(b) The client appeared angry when the health care provider changed her medications.
(c) The client tolerated 80% of the lunch tray with no complaints of nausea or stomach cramping.
(d) The abdominal dressing is clean, dry, and intact with a 3-cm area of light staining noted in the center.
(e) The client ambulated 200 feet in the hall with a cane. No dyspnea or syncope noticed. Tolerated well.
Answer:
(c) The client tolerated 80% of the lunch tray with no complaints of nausea or stomach cramping.
(d) The abdominal dressing is clean, dry, and intact with a 3-cm area of light staining noted in the center.
(e) The client ambulated 200 feet in the hall with a cane. No dyspnea or syncope noticed. Tolerated well.
Rationale:
Charting should always contain only objective facts regarding what the nurse sees, hears, or feels. Noting that the client tolerated 80% of the lunch tray with no complaints of nausea or stomach cramping is an objective observation. It is important to note how well the client tolerated the meal. If the client complained of nausea while eating, this observation would be noted, preferably in the client's own words, such as "I started to get nauseated when I tried to eat."
The observation about the abdominal dressing is factual and objective, noting the size of the area of light staining. When a client ambulates in the hall, it is important to chart the distance, whether assistive devices were used, and how well the client tolerated it. The nurse states that no dyspnea or syncope was noted. Statements that the client appeared anxious when family came to visit infers that the client was anxious due to the family's visit.
This is presumptive on the nurse's part, as the client could be appearing anxious from unvoiced thoughts. Likewise, the nurse makes it sound as if the client is angry because her medications were changed, when there is no evidence that this is the case. The nurse should avoid charting that a client "appears" to have a certain type of reaction to an event, and chart only those objective facts without speculation.
Question 49.
The ED nurse has triaged a client who was in a severe motor vehicle accident. He is unconscious with fractures to the left femur and left humerus and ulna. CT also reveals a large amount of internal hemorrhaging. No identification was found on the client at the scene.
What is the correct action by the nurse?
(a) prepare the client for emergency surgery
(b) try to obtain informed consent from a family member
(c) wait until the client is conscious, and then obtain the consent
(d) ask police to run the tag number so the client can be identified
(e) inform the health care provider that consent cannot be obtained at this time
Answer:
(a) prepare the client for emergency surgery
Rationale:
In an emergency situation where the client is suffering a potentially life-threatening event, it is not necessary to obtain consent. Trying to obtain consent from a family member wastes valuable time, since the client's identity is unknown. The client may not gain consciousness, so waiting until he can be roused is not the correct action.
Asking the police to run the tag number wastes precious time that the client needs to be prepped for surgery, and is not a feasible option. Informing the health care provider that consent cannot be obtained does not apply in an emergency situation. The client is at high risk for death from internal bleeding.
Question 50.
The nurse notices an increase in the prevalence of deep vein thrombosis among clients in a surgical unit. The nurse collects data, develops a preventative program with peers, and works with her manager to implement a new policy and procedure. Which of the following best describes the nurse's actions?
(a) collaboration
(b) consultation
(c) informatics
(d) performance improvement
Answer:
(d) performance improvement
Rationale:
The nurse is using evidence-based decision-making to improve performance. Methods within performance improvement include collaboration and consultation. Informatics addresses processing data in an organized method to allow for storage and retrieval.
Question 51.
The nurse is caring for an elderly client with osteoporosis who has fractured her mid-shaft clavicle. Which nursing intervention would be included on the plan of care?
(a) immobilize the affected shoulder with a sling
(b) encourage weight-bearing exercise
(c) increase fluids to 1,500 cc/day
(d) prepare for surgical repair
Answer:
(a) immobilize the affected shoulder with a sling
Rationale:
A mid-shaft clavicle fracture needs to be immobilized to prevent further damage to the joint. Weight-bearing exercise is associated with a fracture in the lower extremities. An intake of 1,900 cc/day is the recommended amount for a healthy individual, making 1,500 cc/day suboptimal. Surgical repair for a fractured mid-shaft fracture is typically not required.
Question 52.
The nurse is caring for a client admitted for right-sided renal artery stenosis. Where should the nurse anticipate auscultating for a renal bruit?
(a) right renal artery
(b) right iliac artery
(c) left renal artery
(d) left iliac artery
Answer:
(a) right renal artery
Question 53.
The school nurse is monitoring the diet of a child with celiac disease. What lunch menu item would the nurse recommend to the family?
(a) ham and cheese sandwich
(b) chef salad with oil and vinegar dressing
(c) chili with corn bread
(d) vegetarian pizza with lactose-free cheese
Answer:
(b) chef salad with oil and vinegar dressing
Rationale:
While celiac disease is incurable, persons with the disease typically are able to control their symptoms when they follow a gluten-free diet. A chef salad with oil and vinegar dressing is the best option as it contains no gluten protein.
Question 54.
The role of the nurse as patient advocate is accurately identified in which of these statements?
(a) Nurses evaluate only the negative outcomes of patient advocacy.
(b) Nurses provide only physical and emotional support.
(c) Advocacy practices are limited to within health care settings.
(d) Nurses work with patients, their families, other health care team members and third- party persons.
Answer:
(d) Nurses work with patients, their families, other health care team members and third- party persons.
Rationale:
Nurses work with patients and their families along with a variety of relevant health care team members and third-party persons. Evaluation of both positive and negative outcomes of patient advocacy should be addressed by the nurse. Providing physical, emotional, and spiritual support is within the scope of the nurse as an advocate. Advocacy practices may extend outside health care settings.
Question 55.
Which statement concerning informed consent is false?
(a) Persons 17 years of age and younger may not give informed consent.
(b) A married minor may not give informed consent.
(c) A pregnant minor may give informed consent.
(d) An adult 18 years of age and older may give informed consent.
Answer:
(b) A married minor may not give informed consent.
Rationale:
A married minor may give informed consent. The remaining statements are true.
Question 56.
Identify the position in this diagram.
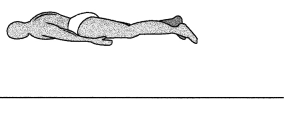
Answer:
prone
Question 57.
Identify the position in this diagram.
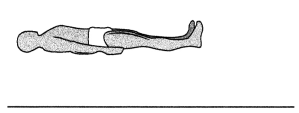
Answer:
suprine
Question 58.
Identify the position in this diagram.
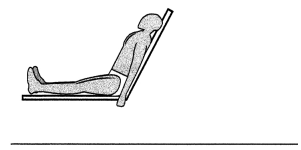
Answer:
Follower's
Question 59.
Identify the position in this diagram.
Answer:
right lateral recurtiment
Question 60.
Identify the position in this diagram.
Answer:
left lateral recurtiment
Question 61.
Identify the position in this diagram.
Answer:
Trendelenburg's
Question 62.
The nurse is delegating tasks to on unlicensed ossislive personnel (UAP), Which client task
should the nurse delegate to the IJAP?
(a) a client whose IV infiltrated and needs replacing
(b) a client on BIPAP who needs arterial blood gases (ABGs) drawn
(c) a client with mild dementia who needs assistance with her food tray
(d) a client who needs a wet4o.dry dressing change on on abdominal incision
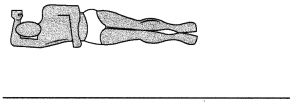
Answer:
(c) a client with mild dementia who needs assistance with her food tray
Rationale:
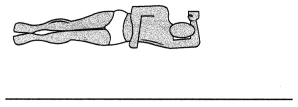
Assessing the IV site and inserting an IV is beyond the scope of practice for a UAP and should be performed only by the licensed nurse. Drawing ABGs should be performed by the licensed nurse or respiratory therapist per facility policy. Assisting a client with a meal tray is within the scope of practice for a UAP. Dressing changes should be performed by the licensed nurse. UAPs may not provide direct nursing care or perform nursing interventions requiring specialized nursing knowledge, judgment, or skill.
Question 63.
A nurse is preparing o client scheduled for a right mastectomy. which statement indicates the
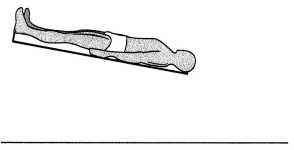
need for further intervention?
(a) The client refuses to sign the blood consent since she is o Jehovah’s Witness.
(b) The client identifies the right breast os the surgical site for a right mastectomy.
(c) The client signs the consent form witi, an X, which is witnessed by two licensed perfonnel.
(d) The client expresses doubt over her decision and asks the nurse to explain more about the procedure.
Answer:
(d) The client expresses doubt over her decision and asks the nurse to explain more about the procedure.
Rationale:
Expressing doubt and asking further questions of the nurse indicates that the client may not be fully informed and should confer further with the health care provider. The nurse may clarify facts, but it is the health care provider's responsibility to give detailed information about the surgical procedure.
The nurse is responsible for ensuring that the client has been adequately informed. A client may refuse to sign a blood consent due to religious beliefs prior to surgery. The client has correctly identified the surgical site, which is to be expected. The client who cannot write may sign with an X as long as it is witnessed by two people.
Question 64.
An external weather disaster has flooded the emergency deportment with several new clients.
Which client should the nurse see first?
(a) the client complaining of chest pain and nausea who is diophoretic
(b) the client with o simple fracture of the radius from o fall on o staircase
(c) the client complaining of slight redness and itching at the IV site ¡n his hand
(d) the client presenting with a sprained ankle from a tree branch Foiling on him
Answer:
(a) the client complaining of chest pain and nausea who is diophoretic
Rationale:
Triage works on the principle that clients with the highest acuity have priority over clients with injuries or conditions that are not considered life-threatening. Chest pain, nausea, and diaphoresis indicate a possible myocardial infarction, which can be life-threatening and requires immediate intervention. Fractures and sprains are nonurgent and can wait for treatment. Redness and itching at an IV site indicates a need to assess the site and remove and replace the IV, but is not immediately life- threatening.
Question 65.
A nurse is working with an unlicensed ossistive personnel (UAP) to perform a bed bath on a client. The nurse notes the smell of alcohol on the UAP’s breath. Which is the priority nursing action?
(a) Work closely with the UAP during the shift and observe for any signs of impairment.
(b) Complete the bed both without comment. The unit is already short one staff member.
(c) Offer chewing gum lo the UAP. Since she does not give medications, she can do her job is she does not appear impaired.
(d) Call for another nurse to complete the bath and immediately report the UAP to the charge nurse or unit manager.
Answer:
(d) Call for another nurse to complete the bath and immediately report the UAP to the charge nurse or unit manager.
Rationale:
The professional nurse works under the framework of six ethical principles. Nonmaleficence emphasizes protecting the client from harm. Client safety is always a priority. Another nurse may step in and complete the bath, ensuring that the client is not left alone with impaired personnel.
Options (a), (b), and (c) allow the impaired UAP to remain on duty, possibly causing harm to the client. The nurse also has an ethical and legal duty to report situations that may cause client danger. Failure to do so may result in disciplinary action by the board of nursing for the nurse involved, regardless of whether harm comes to the client.
Question 66.
The nurse has received report on the ossigned night-shift clients. Which client should the nurse see first?
(a) a mildly confused client due for o dressing change on o diabetic ulcer to the heel
(b) an elderly, stable client who just returned from on MRI to rule out a kidney moss
(c) a client whose IV pump has started beeping, indicating that the antibiotic has completed infusing
(d) a client complaining of sudden warmth and poin at an appendectomy incision site 48 hours after surgery
Answer:
(d) a client complaining of sudden warmth and poin at an appendectomy incision site 48 hours after surgery-specific
Rationale:
Classic signs of localized infection include sudden warmth, redness, pain at the site, and swelling caused by the inflammatory process. This client should be assessed first due to the risk of infection following surgical procedures. The health care provider should be notified immediately so that lab work can be ordered and an appropriate course of treatment started.
The client needing a dressing change is not as urgent as a client with infection. A stable client returning from MRI is not the priority. The client with an IV pump beeping can be seen once the health care provider has been notified. The risk of infection and subsequent complications take priority over a beeping IV pump.
Question 67.
The nurse is working triage in the ED when four clients present at the some time. Which client should be seen first.
(a) a 45-year-old female on oral contraceptives with unusually heavy menstrual bleeding
(b) a 24-year-old with o dog bite to the leg from the family dog who is current on rabies shots
(c) on irritable 4-month-old with o peiechiol rash, riuchol rigidity, and temperature of 103.4c F
(d) a 16-year-old football player with o twisted ankle who has no deformity and a pedal pulse
Answer:
(c) on irritable 4-month-old with o peiechiol rash, riuchol rigidity, and temperature of 103.4c F
Rationale:
Petechial rash, nuchal rigidity, and fever are signs of meningitis, which is a medical emergency, especially in an infant. The client with heavy menstrual bleeding is not as urgent as the infant. Dog bites from a known pet current on rabies shots are less urgent than bites from a dog with an unknown rabies status. A twisted ankle with a pedal pulse and no deformity is not life-threatening and can be seen after more urgent clients.
Question 68.
The nurse is caring For clients on o medical-surgical floor. Which tasks related to pain management con be delegated lo unlicensed assislive personnel (LJAP)? Sel.ct all that apply.
(a) assessing the pain level ono scale of 1 - 10
(b) reminding clients to report pain immediately
(c) reporting facial grimacing in unresponsive clients
(d) asking clients directly, MAre you having any pain right now?
(e) giving ocetominophen (Tylenol) alter the nurse obtains the medication but is interrupted to attend a code blue before she administers il
Answer:
(b) reminding clients to report pain immediately
(c) reporting facial grimacing in unresponsive clients
(d) asking clients directly, MAre you having any pain right now?
Rationale:
Asking clients if they currently have any pain and reminding clients to report pain are within the scope of practice for the UAP. The UAP may also report facial grimacing to the nurse, who can then assess the pain. Assessing pain using the pain scale should be done by the nurse, as assessment is a nursing action. No medications, even over-the-counter ones, may be given by anyone other than the licensed nurse.
If the nurse is interrupted for an emergency, another nurse may administer the medication after assessing the client's pain and checking the chart for any allergies, if facility protocols permit this. The nurse is ultimately responsible for the task that has been delegated.
Question 69.
A newly graduated nurse is woricing in the pediatric unit. Which client assignment is most
appropriate fof this nurse?
(a) a 2-year-old with hemophilia A who has suddenly become less responsive
(b) a 15-year-old wiih sickle cell disease comploining of lower right quadrant abdominal poin
(c) a 6-year-old who ¡ust hod o tonsillectomy 2 hours earlier and is frequently swallowing
(d) a 12-year-old with newly diognosed type 2 diabetes whose parents need teoching on insulin
Answer:
(b) a 15-year-old wiih sickle cell disease comploining of lower right quadrant abdominal poin
Rationale:
Clients with sickle cell disease commonly present with pain during a crisis. The newly graduated nurse is qualified to assess the client's pain and administer ordered pain medications. A client with a clotting disorder and a decreased level of consciousness is an emergency situation due to possible intracerebral bleeding and is not appropriate for an inexperienced nurse.
Swallowing after a tonsillectomy indicates possible bleeding and should be assessed by the more experienced nurse. Client teaching is an important and more advanced skill that takes time to develop. Insulin is a high-alert drug, and incorrect information from the new nurse may cause harm to the client.
Question 70.
The nurse s preparing to transfer o client From the ICU to the floor. W1h of the following
ensures continuity of core for the client? Select oil that appiy.
(a) using approved abbreviations in documenting core
(b) providing report on the client using standard hond-off reports
(c) informing the receiving nurse of pending lob results and when they ore expected
(d) informing the receiving nurse of ony core that needs to be done, such as bathing
(e) telling the receiving nurse thai the family is demanding and asks too many questions
Answer:
(a) using approved abbreviations in documenting core
(b) providing report on the client using standard hond-off reports
(c) informing the receiving nurse of pending lob results and when they ore expected
(d) informing the receiving nurse of ony core that needs to be done, such as bathing
Rationale:
Ensuring continuity of care is especially important when the client is being transferred to another area of the hospital. Options (a), (b), (c), and (d) are guidelines that ensure continuity of care. Addressing pending lab results, listing client requests that the nurse was unable to do, and informing the receiving nurse of upcoming medications or glucose checks that will need to be done shortly after the client arrives make it easier for the receiving nurse to be sure that upcoming tests or medications are not missed.
Complaining about the family is unprofessional and takes the focus away from client needs. A smooth transition is essential to ensure that no orders are overlooked. The nurse should be prepared to answer questions from the receiving nurse if needed for clarification after the client is transferred.
Question 71.
A client has been admitted to the oncology unit and hos a large amount of cash, several credit cards, and several pieces of expensive-looking gold iewelry in her possession. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate?
(a) tell the client to hide everything in her purse or a bog and put it In the closet
(b) ofFer to take her belongings to the charge nurse’s office where they can be locked up
(c) suggest that the client put her valuables in a sock and place it in the bottom of the bedside table under some clothing
(d) inform the client of the hospital policy regarding valuables and suggest that she give them to a trusted family member or to security for safekeeping
Answer:
(d) inform the client of the hospital policy regarding valuables and suggest that she give them to a trusted family member or to security for safekeeping
Rationale:
Most hospitals provide security to lock up client's valuables, along with a receipt or form for identification for claiming the items. All items placed in security must be documented on the admission form and signed. The facility is not responsible for valuables left in the room by clients, and the nurse should be sure that the client is aware of this policy and understands it.
Options (a) and (c) still leave the valuables subject to theft. Locking them up in the charge nurse's office is not an appropriate option, as this places the charge nurse in a position of responsibility. Many hospital admissions are unplanned, and the best advice the nurse can give a new client is to send home anything of value.
Question 72.
(d) inform the client of the hospital policy regarding valuables and suggest thai she give them to a trusted family member or to security For safekeeping The nurse is coring for o 7-year-old child who presents lo the D with multiple bruises, a fractured ankle, and cigarette bums on the arms. Which action by the nurse is most
appropriate?
(a) ask the parents if they burned the child with cigarettes
(b) ask the client to tell you what happened to couse the bruising and bums
(c) inForm the parents iha they cannot leave with the child until they talk to the police
(d) notiFy the charge nurse immediately so thot the suspected child abuse can be reported
Answer:
(d) notiFy the charge nurse immediately so thot the suspected child abuse can be reported
Rationale:
Any suspected cases of abuse and neglect must, by law, be reported to the authorities. The ED will have policies and procedures to guide staff on appropriate responses to suspected child abuse cases. Option (a) assumes that the parents are responsible for the burns and may provoke a violent response. While it is appropriate to ask the client what happened, the nurse should be aware that many abused children are coached to say that they fell off a swing or had another type of accident when asked about their injuries by authority figures.
Option (c) is both presumptive and accusatory. Additionally, it may also provoke a violent response. The nurse must objectively assess the client and chart the findings, including descriptions of injuries. Child abuse cases require collaboration among nurses, physicians, social workers, police, and family services. The nurse should remain alert to verbal or nonverbal cues that the situation may intensify, and follow facility guidelines.
