Engaging with NCLEX PN Study Guide on a regular basis can help students identify areas of weakness and focus their study efforts accordingly.
NCLEX Gerontology/Geriatric Nursing Questions - NCLEX Questions on Gerontology/Geriatric Nursing
Gerontology/Geriatric Nursing NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
Mrs. Alvin is an 85-year-old woman who has come to the clinic for a routine check-up. As a nurse, which of the following statements regarding communicating with older adults is correct?
(a) Address client with respect: “Good morning, Mrs. Jones."
(b) Orient the client to the purpose and length of the interview.
(c) Give the older adult time to respond because verbal response slows with age.
(d) Choose words based on the client’s sociocultural background and formal education; do not use slang or jargon.
Answer:
(c) Give the older adult time to respond because verbal response slows with age.
Explanation:
Option (a) is a valid statement as it is important to address the client with respect, but it is not the best answer to this question.
Option (b) is also a valid statement, as it is important to orient the client to the purpose and length of the interview, but it is not the best answer to this question either.
Option (c) is the correct answer, as it is important to give the older adult time to respond because verbal response slows with age. As people age, their processing time may slow down, so they may take longer to respond to questions. It is important for the nurse to be patient and give them enough time to answer questions.
Option (d) is not the correct answer, as while it is important to choose words based on the client's sociocultural background and formal education, this is not the best answer to this question. The main concern here is to give the older adult enough time to respond to questions, rather than the choice of words used.
Therefore, the correct answer is C.
Question 2.
Mr. Saigrace is a 70-year-old male who has been diagnosed with dementia. He is currently living at home with his wife, who has been his primary caregiver. Recently, his wife has noticed that Mr. Saigrace has been increasingly forgetful, often misplacing items and becoming disoriented. He has also become more agitated and irritable than usual. The nurse has been called to assess Mr. Saigrace’s condition.
Question 2 Which of the following statements of Mr. Saigrace needs nursing intervention?
(a) Mr. Saigrace has personality changes
(b) Mr. Saigrace has agnosia
(c) Mr. Saigrace has Alzheimer's disease
(d) Mr. Saigrace has Pick disease
Answer:
(a) Mr. Saigrace has personality changes
Explanation:
Dementia is a progressive neurocognitive disorder that affects cognitive functioning, including memory, judgment, abstract thinking, and social behavior. It is characterized by a decline in intellectual functioning, loss of memory, difficulty performing familiar tasks, changes in mood or behavior, and deterioration of judgment and ADLs.
Option (a) which states that Mr. Saigrace has personality changes, is correct. Personality changes are a common symptom of dementia and can be challenging for the patient and their caregiver to manage. Nurses can intervene by providing emotional support and counseling to the patient and their family to cope with the changes.
Option (b) which states that Mr. Saigrace has agnosia, is incorrect. Agnosia is a symptom of dementia that affects the ability to recognize objects or people, but it is not one of the four As of cognitive impairment (agnosia, amnesia, apraxia, and aphasia). Therefore, this option is not the best answer.
Option (c) which states that Mr. Saigrace has Alzheimer's disease, is incorrect. Alzheimer's disease is one type of dementia characterized by the presence of beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. However, the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease cannot be made based on the given information, and it is not a nursing intervention.
Option (d) which states that Mr. Saigrace has Pick disease, is incorrect. Pick disease is a type of frontotemporal dementia that affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in behavior, language, and personality. However, the given information does not provide enough evidence to support this diagnosis, and it is not a nursing intervention.
In conclusion, the correct answer is (a) Mr. Saigrace's personality changes require nursing intervention, which can include providing emotional support and counseling to him and his family to cope with the changes associated with dementia.
Question 3.
Which of the following statements are appropriate nursing interventions for a client with dementia? (Select all that apply)
(a) Administer screening tools for depression and cognitive impairment.
(b) Keep the client functioning and actively involved in social and family activities for as long as possible.
(c) Maintain an orderly, almost ritualistic, schedule to promote a sense of security.
(d) Maintain a regularly scheduled reality orientation on a daily basis.
Keep the client oriented as to time, place, and person (repeatedly). Keep a calendar and clock within sight at all times (e). Keep familiar objects, such as family pictures, in the older adult’s environment to promote a sense of continuity and security (f). Administer prescribed drugs to reduce emotional lability, agitation, and irritability or prescribed antidepressant, as indicated.
Answer:
(a) Administer screening tools for depression and cognitive impairment. (Correct) (b). Keep the client functioning and actively involved in social and family activities for as long as possible. (Correct) (c). Maintain an orderly, almost ritualistic, schedule to promote a sense of security. (Correct) (d). Maintain a regularly scheduled reality orientation on a daily basis. (Incorrect)
Keep the client oriented as to time, place, and person (repeatedly). (Correct) Keep a calendar and clock within sight at all times. (Correct) (e). Keep familiar objects, such as family pictures, in the older adult's environment to promote a sense of continuity and security. (Correct) (f). Administer prescribed drugs to reduce emotional lability, agitation, and irritability or prescribed antidepressant, as indicated. (Incorrect)
Explanation:
(a) Administer screening tools for depression and cognitive impairment: This is a correct intervention, as early detection of cognitive and emotional changes can help to manage the symptoms effectively.
(b) Keep the client functioning and actively involved in social and family activities for as long as possible: This is also a correct intervention, as social engagement and activities can help to maintain cognitive and physical functioning and improve the quality of life.
(c) Maintain an orderly, almost ritualistic, schedule to promote a sense of security: This is also a correct intervention, as a structured routine can help to reduce confusion and agitation and provide a sense of security to the client.
(d) Maintain a regularly scheduled reality orientation on a daily basis: This is incorrect, as repeatedly orienting the client to reality can be frustrating and ineffective, and may cause distress. Keep the client oriented as to time, place, and person (repeatedly). This is a correct intervention, as repeated orientation to time, place, and person can help to reduce confusion and improve the client's sense of security. Keep a calendar and clock within sight at all times: This is also a correct intervention, as visual cues can help to reinforce orientation and reduce confusion.
(e) Keep familiar objects, such as family pictures, in the older adult’s environment to promote a sense of continuity and security: This is also a correct intervention, as familiar objects can help to provide a sense of continuity and security to the client.
(f) Administer prescribed drugs to reduce emotional lability, agitation, and irritability or prescribed antidepressant, as indicated: This is incorrect, as medication should only be prescribed after a thorough assessment and evaluation, and should not be the first-line intervention for managing emotional and behavioral symptoms. Non-pharmacological interventions should be tried first, and medication should only be prescribed if other personality Disorders
Question 4.
Which of the following statements from the member of patient's family indicates that they may be aware of elder abuse or neglect?
(a) "We haven't noticed any injuries or bruises on our loved one."
(b) "Our loved one has been having frequent falls, but we assume it's just due to their age."
(c) "Our loved one is dependent on their caregiver for all aspects of care."
(d) "Our loved one has been showing signs of depression lately."
(e) "We have noticed that our loved one's finances seem to be dwindling without explanation."
(f) "We have never heard of elder abuse laws in our state."
(g) "We have heard of elder abuse laws in our state and are aware of their purpose."
Answer:
(c) "Our loved one is dependent on their caregiver for all aspects of care."
(e) "We have noticed that our loved one's finances seem to be dwindling without explanation."
Explanation:
Option (c) indicates that the patient is dependent on the caregiver for some aspect of care, which is a common characteristic of typical elder abuse victims. Option (e) refers to financial abuse, which is one of the forms of elder abuse described in the passage.
The other options are either incorrect or do not necessarily indicate awareness of elder abuse or neglect. Option (a) and (b) may indicate that the family is not aware of any abuse or neglect, while option (d) may indicate a possible symptom of abuse but not necessarily awareness. Option (f) indicates a lack of knowledge about elder abuse laws, while option (g) only indicates awareness of such laws.
Question 5.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she understands how to assess for elder abuse?
(a) "Elder abuse is only associated with substance abuse."
(b) "It's not necessary to report cases of suspected elder abuse if there is no direct evidence."
(c) "Elder abuse is typically reported to authorities and not often repeated."
(d) "The majority of elder abuse victims are young men with high income."
(e) "Emotional abuse involves physical harm or injury."
(f) "Financial abuse is the most common form of elder abuse."
(g) "Assess physical injuries for abuse, including multiple injuries or fractures, bruises or bums, and sprains or dislocations."
(h) "Question the caregiver only if the client appears to be a victim."
Answer:
(g) "Assess physical injuries for abuse, including multiple injuries or fractures, bruises or bums, and sprains or dislocations."
(a) "Elder abuse is only associated with substance abuse."
Explanation:
Option (g) is correct because assessing physical injuries for abuse is an essential aspect of evaluating for elder abuse. The nurse should look for multiple injuries or fractures, bruises or burns, and sprains or dislocations. These can be signs of physical abuse.
Option (a) is correct because abuse of elders is associated with substance abuse, caregiver strain, and depression. Substance abuse can cause a caregiver to be more likely to mistreat an elder, while caregiver strain and depression can lead to unintentional neglect and abuse.
Option (c) is incorrect because elder abuse is often not reported to authorities, and there is usually a pattern of repetition.
Option (d) is incorrect because most elder abuse victims are older women with limitations in one activity of daily living, are widowed, and have a low income.
Option (e) is incorrect because emotional abuse does not involve physical harm or injury but includes verbal harassment, intimidation, denigration, or isolation.
Option (f) is incorrect because financial abuse is one of the five forms of elder abuse, but it is not the most common.
Option (h) is incorrect because the nurse should question both the client and the caregiver if there are any signs of abuse.
Question 6.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that they understand their responsibility regarding suspected elder abuse cases?
(a) Elder abuse is rare and seldom reported to authorities.
(b) Nurses are not required to report suspected elder abuse cases.
(c) Majority of states do not have laws designed to protect older or vulnerable adults from abuse.
(d) Nurses are required to report cases of suspected elder abuse to the ombudsman.
Answer:
(d) Nurses are required to report cases of suspected elder abuse to the ombudsman.
Explanation:
The passage mentions that the majority of states require nurses and other healthcare providers to report cases of suspected elder abuse to the ombudsman. This is important as reporting suspected abuse can help protect older or vulnerable adults from further harm. Option (a) is incorrect because the passage mentions that elder abuse is estimated to affect over 1 million older adults and is often not reported.
Option (b) is incorrect as the passage clearly states that nurses are required to report suspected elder abuse cases. Option (c) is also incorrect as the passage mentions that all states have enacted elder abuse laws designed to protect older or vulnerable adults from abuse.
Question 7.
Ms. Ranjan, an 80-year-old woman with a history of congestive heart failure and COPD, was admitted to the hospital for worsening shortness of breath. Despite aggressive treatment, her condition continued to deteriorate, and her medical team determined that she was unlikely to recover. The family has been informed of her prognosis and is considering hospice care. The nurse caring for Ms. Ranjan is discussing the care of old gatients with the family.
Which of the following statements from the family of the patient indicates that they understand the physiological changes associated with aging ?
(a) "Why is my mother's heart rate increasing? Isn't that a bad sign?"
(b) "I don't understand why my father can't hear us anymore. He was never like this before."
(c) "Why is my mother having difficulty breathing? Shouldn't she be getting better with the oxygen?"
(d) "I noticed that my mother's skin feels cooler to the touch. Is that normal?”
Answer:
(d) "I noticed that my mother's skin feels cooler to the touch. Is that normal?”
Explanation:
The physiological changes associated with aging and dying patinets can include a decrease in body temperature and increased susceptibility to hypothermia. The other options in the question relate to changes in heart rate, hearing, and breathing, which are not necessarily indicative of understanding the physiological changes associated with aging, Option (b) suggests confusion about hearing loss, and option (c) suggests a lack of understanding about the progression of Ms. Ranjan's condition despite treatment.
Question 8.
Mr. Ranjan, a 75-year-old man. is admitted to the palliative care unit with a diagnosis of metastatic lung cancer. The nursing staff is responsible for providing care for Mr. Ranjan during his end- of-life journey. As his condition deteriorates, the nursing staff must provide comfort care, manage his symptoms, and support his family.
One morning, while the nurse is checking Mr. Ranjan's vital signs, she notices that his blood pressure has dropped significantly, and his respiratory rate has increased. She then makes the following statement:
"Mr. Ranjan's vital signs are changing, and his breathing is becoming more labored. I think it's time to notify the physician and start administering oxygen."
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she understands the care of dying patients?
(a) "We need to do everything we can to prolong Mr. Ranjan's life."
(b) "We should avoid talking to Mr. Ranjan about his condition, as it may upset him."
(c) "We should continue to administer medications even if they are not relieving Mr. Ranjan's symptoms."
(d) "Mr. Ranjan's vital signs are changing, and his breathing is becoming more labored. I think it's time to notify the physician and start administering oxygen.”
(e) "We should encourage Mr. Ranjan to eat and drink as much as possible, even if he doesn't feel like it.
(f) "We should move Mr. Ranjan to a more comfortable room with a better view."
(g) "We should ask Mr. Ranjan's family to leave so that he can rest."
Answer:
(d) "Mr. Ranjan's vital signs are changing, and his breathing is becoming more labored. I think it's time to notify the physician and start administering oxygen.”
(e) "We should encourage Mr. Ranjan to eat and drink as much as possible, even if he doesn't feel like it.
Explanation:
Option (a) is incorrect because the goal of care for a dying patient is not to prolong their life but to provide comfort care and manage their symptoms. Option (b) is incorrect because it is important to communicate with the patient about their condition and involve them in decision making to the extent possible.
Option (c) is incorrect because administering medications that are not relieving symptoms can cause unnecessary side effects and discomfort for the patient. Option (d) is correct because the nurse is monitoring Mr. Ranjan's vital signs and recognizes the need for oxygen to manage his symptoms.
Option (e) is also correct because encouraging Mr. Ranjan to eat and drink as much as possible can help maintain his comfort and prevent dehydration. Option (f) is incorrect because moving Mr. Ranjan to a different room may cause unnecessary discomfort and stress. Option (g) is incorrect because it is important to involve the patient's family in their care and allow them to provide support and comfort during this difficult time.
Question 9.
Ms. Williams is a 72-year-old female who was diagnosed with stage IV lung cancer three months ago. She has been undergoing chemotherapy but her condition has worsened over the past few weeks. She is now experiencing increased pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. The healthcare team has determined that she is approaching the end of her life and has decided to transition her care to hospice. As her nurse, you have been tasked with providing comfort measures and symptom management to Ms. Williams during this difficult time.
Which of the following statements from the patient indicates that she is experiencing a common physiological change related to aging?
(a) "I can't hear anything you're saying, can you speak up?"
(b) "My skin feels warmer than usual, could I have a fever?"
(c) "I feel like I'm always crying these days, even when I'm not sad."
(d) "I can't see as well as I used to, everything seems blurry."
Answer:
(d) "I can't see as well as I used to, everything seems blurry."
Explanation:
The passage states that as people age, they may experience changes in their vision including presbyopia, decreased visual field, decreased color discrimination, and distorted depth perception. This statement from the patient indicates that she is experiencing a change in her vision, which is a common physiological change related to aging. Option (a) relates to hearing loss which is also a common physiological change in aging, but is not indicated by the patient's statement. Option (b) and (c) are not related to the physiological changes mentioned in the passage.
Question 10.
Which of the following statements from the member of the patient's family indicates that they understand the difference between delirium and dementia?
(a) "I'm not sure what's wrong with my loved one. They seem confused and disoriented."
(b) "My loved one has been forgetful lately, and their behavior has changed."
(c) "I heard that delirium is a leading cause of institutionalization in older people."
(d) "I didn't realize that dementia can be reversible in some cases."
(e) "I think my loved one's symptoms are related to depression."
(f) "I read that pseudodementias are a type of reversible dementia."
(g) "I don't know if my loved one has false delirium or not."
Answer:
(c) "I heard that delirium is a leading cause of institutionalization in older people."
(f) "I read that pseudodementias are a type of reversible dementia."
Explanation:
Option (a) indicates that the family member is unsure about the patient's condition and does not show an understanding of the difference between delirium and dementia. Option (b) mentions forgetfulness and behavior changes, which are common symptoms of dementia, but does not show an understanding of the difference between delirium and dementia. Option (c) correctly identifies delirium as a leading cause of institutionalization in older people, indicating an understanding of the difference between delirium and dementia.
Option (d) mentions the reversibility of dementia, which is true, but does not demonstrate an understanding of the difference between delirium and dementia. Option (e) suggests that the symptoms may be related to depression, which can cause pseudodementia, but does not show an understanding of the difference between delirium and dementia.
Option (f) correctly identifies pseudodementias as a type of reversible dementia, indicating an understanding of the difference between delirium and dementia. Option (g) suggests that the family member is not sure if false delirium is present, but does not show an understanding of the difference between delirium and dementia. Therefore, the correct options are (c) and (f).
Question 11.
Mrs. Ranjan, a 75-year-old female, was admitted to the hospital with confusion, agitation, and disorientation. The nursing staff noticed that she was unable to recognize familiar feces and was unable to communicate effectively. She also had difficulty sleeping, and her appetite had decreased significantly. Her daughter reported that Mrs. Ranjan had been experiencing similar symptoms for the past few days.
On examination, Mrs. Ranjan appeared to be dehydrated, and her electrolyte levels were found to be abnormal. Her blood tests showed that her kidney function was compromised. After conducting a thorough evaluation, the medical team diagnosed Mrs. Ranjan with delirium.
Which of the following statements from the passage is correct regarding delirium?
(a) Delirium is an irreversible condition.
(b) Delirium is characterized by long- and short-term memory loss.
(c) Delirium is a cognitive disorder that may be reversible.
(d) Delirium is the leading cause of institutionalization in older people.
(e) Delirium is caused by drug side effects, depression, and nutritional deficiency.
(f) Delirium is a type of irreversible dementia.
Answer:
(c) Delirium is a cognitive disorder that may be reversible.
Explanation:
Delirium is a sudden and usually temporary state of confusion and disorientation. It can be caused by a wide range of factors, such as drug toxicity, alcohol withdrawal, or an underlying medical condition. Symptoms of delirium can include confusion, agitation, hallucinations, and changes in sleep patterns. Delirium is often reversible if the underlying cause is treated.
Dementia, on the other hand, is a progressive and often irreversible decline in cognitive function. It is caused by damage to brain cells and can result in memory loss, impaired judgment, and a decline in language and communication abilities. Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia, but there are other types as well, such as vascular dementia and Lewy body dementia.
Unlike delirium, which can be caused by a variety of factors, dementia is typically caused by degenerative brain diseases. Although some types of dementia may be treatable, there is currently no cure for dementia and it typically worsens over time.
"Delirium is a cognitive disorder that may be reversible." This statement is mentioned in the first sentence of the passage, where delirium is defined as a cognitive disorder that can be reversible, as opposed to dementia, which is irreversible.
Option (a), "Delirium is an irreversible condition." is incorrect because delirium is a reversible cognitive disorder.
Option (b), "Delirium is characterized by long- and short-term memory loss." is incorrect because memory loss is a characteristic of dementia, not delirium. Option (d), "Delirium is the leading cause of institutionalization in older people," is incorrect because it is a characteristic of dementia, not delirium.
Option (e), "Delirium is caused by drug side effects, depression, and nutritional deficiency," is partially correct because it mentions the causes of false delirium, but not the actual causes of delirium. Option (f), "Delirium is a type of irreversible dementia," is incorrect because delirium and dementia are two distinct cognitive disorders with different characteristics and causes. Delirium and dementia are both cognitive disorders that affect the brain and can cause significant impairment in daily life. However, there are some key differences between the two conditions.
Question 12.
Ms. A is a 70-year-old woman who presents with a gradual decline in cognitive function, memory impairment, and difficulty with abstract thinking. She has been having trouble with simple tasks such as getting dressed, preparing meals, and paying bills. Her family members have also noted that she seems withdrawn and increasingly confused, and is frequently disoriented. Based on these symptoms, she is diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease.
Ms. A's physical health is relatively stable, and she is able to walk without assistance. However, she has difficulty with grooming and hygiene tasks, and is incontinent. Her motor ability is also declining, and she is at risk for falls.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that the client with suspected Alzheimer's disease may have impaired abstract thinking or impaired judgment?
(a) "The client is incontinent."
(b) "The client is restless and agitated."
(c) "The client is able to perform grooming and hygiene tasks."
(d) "The client has difficulty producing sentences."
(e) "The client shows no awareness of memory loss."
(f) "The client has a history of aluminum toxicity."
(g) "The client is unaware of confusion noted by others."
(h) "The client attempts to find the right answer early in the disease but not later."
(i) "The client recognizes staff and family."
Answer:
(d) "The client has difficulty producing sentences."
(g) "The client is unaware of confusion noted by others."
(h) "The client attempts to find the right answer early in the disease but not later."
Explanation:
Option (d) suggests that the client is experiencing language difficulties that could be indicative of cognitive impairment. Option (g) describes a lack of awareness of confusion noted by others, which may be indicative of impaired judgment. Option (h) describes a progression of cognitive decline that may be observed in Alzheimer's disease. The other options do not directly relate to impaired abstract thinking or impaired judgment, or are not specific to Alzheimer's disease.
Question 13.
Which of the following statements from the family member of the patient indicates that the patient may be in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease?
(a) "The patient is unaware of their memory loss."
(b) "The patient is agitated and paranoid."
(c) "The patient frequently wanders around at sundown."
(d) "The patient does not recognize staff or family."
Answer:
(a) "The patient is unaware of their memory loss."
Explanation:
The history reveals that the patient begins with recent memory loss, later having problems with coding and retrieving information. In the early stages of the disease, the patient will attempt to find the right answer, but later will not understand the question. The patient is also oblivious to failures. Therefore, option (a) is correct as it suggests the early stages of Alzheimer's disease where the patient is unaware of their memory loss.
Option (b) is incorrect as it indicates the patient is agitated and paranoid, which may happen in later stages. Option (c) is incorrect as it suggests wandering behavior, which may happen at any stage of Alzheimer's disease. Option (d) is incorrect as it suggests that the patient does not recognize staff or family, which may happen in later stages.
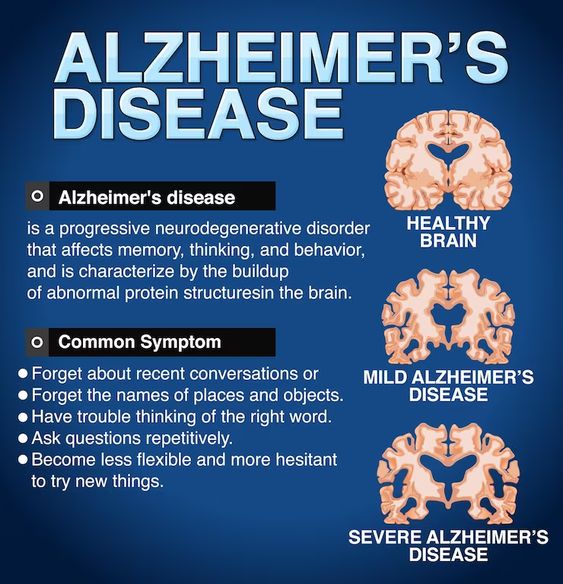
Question 14.
Mary is a 70-year-old widow who lives alone in her apartment. Her daughter, Sarah, has noticed that Mary seems more withdrawn than usual and doesn't take pleasure in activities she used to enjoy. Mary has lost weight, has difficulty sleeping, and complains of physical pain. Sarah is concerned that her mother may be depressed and at risk for suicide.
Which of the following statements from Sarah indicates that Mary may be at risk for suicide?
(a)"My mother has lost weight and doesn't seem interested in food."
(b) "My mother has difficulty sleeping."
(c) "My mother complains of physical pain."
(d) "My mother seems more withdrawn than usual."
(e) "My mother doesn't take pleasure in activities she used to enjoy."
(f) "My mother is a widow who lives alone."
(g) "My mother is 70 years old."
(h) "I am concerned that my mother may be depressed and at risk for suicide."
Answer:
(d) "My mother seems more withdrawn than usual."
(h) "I am concerned that my mother may be depressed and at risk for suicide."
Explanation:
Mary’s withdrawal is a symptom of depression and a warning sign of suicide risk. Sarah's concern for her mother's mental health is also indicative of the possibility of suicide risk. Options (a), (b), (c), (e), (f), and (g) describe symptoms and circumstances that are commonly associated with depression in older adults but do not directly indicate an increased risk of suicide.
Mrs. Vimal, an 80-year-old female, has been admitted to the hospital with complaints of sadness, difficulty sleeping, loss of appetite, and reduced sexual desire. She has also been complaining of memory loss and physical pain. Upon assessment, the nurse notes that Mrs. Vimal has a history of multiple losses, including the death of her spouse and friends, as well as a loss of normal physical functioning and social interaction. She has also been taking medication for high blood pressure and diabetes.
Quesion 15.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that Mrs. Vimal may be at risk for suicide?
(a) Mrs. Vimal has a history of multiple losses.
(b) Mrs. Vimal has been taking medication for high blood pressure and diabetes.
(c) Mrs. Vimal has been complaining of physical pain.
(d) Mrs. Vimal has been experiencing memory loss.
(e) Mrs. Vimal has been admitted to the hospital with complaints of sadness.
(f) Mrs. Vimal has been experiencing reduced sexual desire.
(g) Mrs. Vimal has been experiencing difficulty sleeping.
(h) Mrs. Vimal has been complaining of loss of appetite.
Answer:
(a) Mrs. Vimal has a history of multiple losses.
(e) Mrs. Vimal has been admitted to the hospital with complaints of sadness.
Explanation:
Option (a), "Mrs. Vimal has a history of multiple losses," is correct because according to the passage, the most significant risk factor for suicide in the older population is recent loss of a major relationship, and Mrs. Vimal has experienced the death of her spouse and friends. Option (e), "Mrs. Vimal has been admitted to the hospital with complaints of sadness," is correct because depression and suicidal ideation are strongly linked. Depression increases the risk of suicide, and individuals who experience depression are more likely to consider and attempt suicide.
Option (b) is incorrect because medication for high blood pressure and diabetes is not a risk factor for suicide. Option (c) is incorrect because complaints of physical pain are not necessarily a risk factor for suicide. Option (d) is incorrect because complaints of memory loss are not necessarily a risk factor for suicide.
Option (f) is incorrect because reduced sexual desire is not necessarily a risk factor for suicide. Option (g) is incorrect because difficulty sleeping is not necessarily a risk factor for suicide. Option (h) is incorrect because loss of appetite is not necessarily a risk factor for suicide.
Question 16.
Mrs. Ranjan is an 80-year-old woman who has been admitted to the hospital for pneumonia. During her stay, the nurse notices that she is experiencing urinary incontinence. Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she understands the assessment process for urinary incontinence?
(a) "Urinary incontinence is a normal consequence of aging."
(b) "Urinary incontinence is only a problem for those living in nursing homes."
(c) "Urinary incontinence is caused by bladder contractions."
(d) "Urinary incontinence can be caused by a variety of factors, including decreased bladder tone and medication side effects."
(e) "Urinary incontinence is only a problem for women."
(f) "Urinary incontinence is always caused by bladder obstruction."
(g) "Urinary incontinence is always caused by a urinary tract infection."
(h) "Urinary incontinence is always treated with surgery."
Answer:
(d) "Urinary incontinence can be caused by a variety of factors, including decreased bladder tone and medication side effects."
Explanation:
The correct statements are "Urinary incontinence can be caused by a variety of factors, including decreased bladder tone and medication side effects." This statement demonstrates an understanding of the assessment process for urinary incontinence, which involves identifying the underlying causes. Option (a) is incorrect because urinary incontinence is not a normal consequence of aging.
Option (b) is incorrect because urinary incontinence can affect anyone, regardless of where they live. Option (c) is incorrect because bladder contractions are only one potential cause of urinary incontinence. Option (e) is incorrect because urinary incontinence can affect both men and women.
Option (f) is incorrect because urinary incontinence can be caused by a variety of factors, not just bladder obstruction. Option (g) is incorrect because while a urinary tract infection can cause urinary incontinence, it is not the only cause. Option (h) is incorrect because surgery is not always necessary for the treatment of urinary incontinence.
Question 17.
A 72-year-old woman visits her primary care physician complaining of urinary incontinence. She reports that she frequently leaks urine, particularly when she coughs, sneezes, or laughs. She also feels the urge to urinate frequently and sometimes doesn't make it to the bathroom in time. She mentions that she has been experiencing these symptoms for about six months and that they are becoming more frequent and severe. The patient denies any pain or discomfort during urination and reports no history of urinary tract infections or other urologic conditions.
Which of the following statements from the patient indicates that she is likely suffering from stress incontinence?
(a) She leaks urine before reaching the toilet
(b) She experiences a constant dribble of urine
(c) She reports difficulty urinating due to an obstruction
(d) She feels the urge to urinate frequently
(e) She reports pain or discomfort during urination
(f) She has a hi story of urinary tract infections
(g) She experiences urine leakage during sexual activity
(h) She leaks urine when coughing, sneezing, or laughing
Answer:
(h) She leaks urine when coughing, sneezing, or laughing
Explanation:
Stress incontinence is characterized by the involuntary release of urine during physical activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or laughing.
Options (a), (b), (c), (d). (e), (f), and (g) are not consistent with stress incontinence. Option (a) describes urge incontinence, option (b) describes overflow incontinence, option (c) may indicate obstruction, option (d) may indicate urge incontinence, option (e) may indicate a urinary tract infection, option (f) may indicate a predisposition to urinary tract infections, and option (g) may indicate sexual dysfunction.
Question 18.
Mrs. Vimal is an 80-year-old patient who has been admitted to the hospital for a hip replacement surgery. During the admission assessment, the nurse noticed a pressure ulcer on her sacrum. On further assessment, the nurse noted that the ulcer was at stage 2 and had signs of infection. The nurse noted the patient's medical history and found out that she has a history of anemia and edema. The nurse provided interventions to relieve pressure, maintain good skin hygiene, and provided adequate nutrition and fluid intake.
Which of the following statements from the patient indicates that the interventions provided by the nurse are effective in preventing further pressure ulcers?
(a) "I feel dizzy when I stand up."
(b) "I am not hungry and don't feel like eating."
(c) "My skin feels itchy and irritated."
(d) "I feel pain when I move my legs."
(e) "I feel a tingling sensation in my sacrum area."
(f) "I am sleeping for longer hours now."
(g) "I feel that my skin is less dry than before."
(h) "I feel a warm sensation around my sacrum area."
Answer:
(e) "I feel a tingling sensation in my sacrum area."
(g) "I feel that my skin is less dry than before."
Explanation:
Option (a) is incorrect because feeling dizzy when standing up is not related to the prevention of pressure ulcers. Option (b) is incorrect because the patient's appetite is not related to the prevention of pressure ulcers. Option (c) is incorrect because itchy and irritated skin does not indicate that pressure ulcers are prevented. Option (d) is incorrect because pain when moving legs is not an indicator of pressure ulcer prevention.
Option (f) is incorrect because sleeping longer hours is not related to the prevention of pressure ulcers. Option (e) is correct because feeling a tingling sensation in the sacrum area indicates increased blood flow to the area, which is a sign of effective prevention of pressure ulcers. Option (g) is correct because less dry skin indicates that the interventions provided by the nurse to keep the skin dry are effective in preventing further pressure ulcers.
Question 19.
A 70-year-old patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of pain and redness on the sacral area. The nurse on duty assessed the patient's skin and found a stage 2 pressure ulcer on the sacrum. Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she understands the assessment and implementation of pressure ulcer management?
(a) "I will give the patient a massage on the sacral area to relieve pain and discomfort."
(b) "I will turn the patient every 4 hours to prevent the formation of new pressure ulcers."
(c) "I will avoid using an alternating-air-pressure mattress for the patient."
(d) "I will inspect the skin frequently and document the stage of the ulcer."
(e) "I will encourage the patient to avoid fluid intake to reduce the risk of infection."
Answer:
(d) "I will inspect the skin frequently and document the stage of the ulcer."
Explanation:
Options (a), (b), (c), (d), and (e) represent different management strategies for pressure ulcers. Option (a) is incorrect because massaging bony prominences can increase the risk of developing pressure ulcers. Option (b) is incorrect because turning the patient every 4 hours is not frequent enough to prevent the formation of new pressure ulcers.
Option (c) is incorrect because an altemating-air- pressure mattress can help prevent and treat pressure ulcers. Option (d) is correct because inspecting the skin frequently and documenting the stage of the ulcer are essential aspects of pressure ulcer management. Option (e) is incorrect because encouraging fluid intake is important to maintain good hydration and prevent dehydration, which can impede the healing process of the ulcer.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) "I will inspect the skin frequently and document the stage of the ulcer." and (e) "I will encourage the patient to avoid fluid intake to reduce the risk of infection." because inspecting the skin and documenting the stage of the ulcer are essential for pressure ulcer management, and encouraging fluid intake is important for hydration and preventing infection.
Question 20.
A 65-year-old male patient was admitted to the hospital after a fall resulting in a hip fracture. He underwent surgery and is now immobilized. The nurse noticed that the patient is experiencing bladder dysfunction, and she is implementing bladder retraining as part of the patient's treatment plan.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she understands the purpose of bladder training in this patient?
(a) "Bladder training is only necessary to prevent urinary tract infections."
(b) "Bladder training is not important because the patient is already wearing protective underwear."
(c) "Bladder training is intended to prevent skin breakdown from prolonged contact with urine."
(d) "Bladder training is unnecessary because the patient is unable to walk."
(e) "Bladder training is important to preserve renal function and maintain social acceptance."
Answer:
(e) "Bladder training is important to preserve renal function and maintain social acceptance."
(a) "Bladder training is only necessary to prevent urinary tract infections."
Explanation:
Option (a) is partially correct. One of the purposes of bladder training is to prevent urinary tract infections, but it is not the only purpose. Bladder training also aims to preserve renal function and maintain social acceptance.
Option (b) is incorrect. Wearing protective underwear is not a substitute for bladder training. It only helps to keep the patient dry and odor-free. Option (c) is incorrect. Although skin breakdown can occur as a result of prolonged contact with urine, it is not the primary purpose of bladder training in this patient.
Option (d) is incorrect. Bladder training is still necessary even if the patient is unable to walk. Therefore, options (e) and (a) are the correct answers. Bladder training is important to preserve renal function and maintain social acceptance, and it also helps to prevent urinary tract infections.
Question 21.
A 68-year-old patient with a history of chronic constipation is admitted to the hospital with complaints of abdominal pain and distention. The patient reports having only one bowel movement in the last seven days. Upon assessment, the nurse notes that the patient's abdomen is distended and tender to palpation. The patient is also experiencing nausea and vomiting. The healthcare provider orders a CT scan, which reveals a fecal impaction. The nurse implements bowel training to manage the patient's constipation. Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she is implementing bowel training correctly?
(a) "I will give the patient a laxative once a day until the impaction is resolved."
(b) "I will encourage the patient to drink more fluids and eat more fiber-rich foods.”
(c) "I will tell the patient to hold their breath and push hard when they feel the urge to have a bowel movement."
(d) "I will administer an enema to the patient every day until the impaction is resolved."
(e) "I will restrict the patient's fluid intake to prevent further distention."
Answer:
(b) "I will encourage the patient to drink more fluids and eat more fiber-rich foods.”
(d) "I will administer an enema to the patient every day until the impaction is resolved."
Explanation:
Option (a) Incorrect. While laxatives can help relieve constipation, using them daily is not a recommended bowel training technique. Option (b) Correct. Encouraging the patient to increase their fluid and fiber intake is an appropriate intervention for bowel training to prevent constipation.
Option (c) Incorrect. Instructing the patient to hold their breath and push hard can cause strain, which can lead to further complications, such as hemorrhoids or rectal prolapse.
Option (d) Correct. Enemas can be an effective intervention for fecal impaction, and using them daily until the impaction is resolved is an appropriate intervention for bowel training. Option (e) Incorrect. Restricting fluid intake can worsen constipation and cause further complications, such as dehydration.
Question 22.
Mary is an 80-year-old female who has been hospitalized for the treatment of a leg fracture. She has been immobile and has been confined to her bed for an extended period of time. Mary has developed hypostatic pneumonia, which is a type of pneumonia caused by a stagnation of blood flow in the dependent portion of the lungs due to prolonged bed rest. The nurse is responsible for the implementation of the appropriate interventions to prevent further complications.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she understands the implementation of appropriate interventions for hypostatic pneumonia? (Select two)
(a) "We should restrict fluids to prevent further accumulation of secretions in the lungs."
(b) "We need to turn the patient every two hours to promote lung expansion."
(c) "The patient should remain in bed to prevent further exertion."
(d) "We need to limit the patient's oxygen use to prevent oxygen toxicity."
(e) "Postural drainage is not necessary in the treatment of hypostatic pneumonia."
Answer:
(b) "We need to turn the patient every two hours to promote lung expansion."
(c) "The patient should remain in bed to prevent further exertion."
Explanation:
(a) Incorrect. Restricting fluids can lead to dehydration and thicker secretions in the lungs, worsening the condition. (b) Correct. Turning the patient every two hours promotes lung expansion and prevents the accumulation of secretions in the dependent portion of the lungs. (c) Correct. Remaining in bed for prolonged periods can lead to hypostatic pneumonia, so getting the patient out of bed can help prevent further complications.
(d) Incorrect. Limiting the patient's oxygen use can compromise the patient's oxygen saturation levels, which can worsen the condition. (e) Incorrect. Postural drainage can help mobilize secretions in the lungs, preventing further complications in hypostatic pneumonia.
Question 23.
Mrs. Jones is an 80-year-old woman who presents to the clinic with complaints of chronic pain in her knees and hips. She has a history of hypertension and is currently taking lisinopril. She is also taking over-the-counter ibuprofen for pain relief. During the assessment, the nurse reviews her medication list and notices that she is taking ibuprofen. Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she understands the potential risks associated with this medication in an older client?
(a) "Ibuprofen is safe for older adults and should be continued for pain relief."
(b) "We should consider switching Mrs. Jones to a stronger NSAID for better pain relief."
(c) "NSAIDs are generally safe for older adults but can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding."
(d) "Ibuprofen can increase the risk of cardiovascular events and renal dysfunction in older adults."
(e) "We should increase the dose of ibuprofen to provide better pain relief."
Answer:
(d) "Ibuprofen can increase the risk of cardiovascular events and renal dysfunction in older adults."
(c) "NSAIDs are generally safe for older adults but can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding."
Explanation:
The correct answer is (d) and (c). Ibuprofen and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be used with caution in older adults due to their increased risk for adverse effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding, cardiovascular events, and renal dysfunction. Answer choice A is incorrect because it is not true that ibuprofen is safe for older adults.
Option (b) is incorrect because switching to a stronger NSAID may increase the risk of adverse effects. Option (e) is incorrect because increasing the dose of ibuprofen can further increase the risk of adverse effects. Option (c) is partially correct as it acknowledges the potential risk of NSAIDs in older adults but does not specifically mention ibuprofen.
Question 24.
Mrs. Vimal is a 78-year-old female who was admitted to the hospital with complaints of severe pain in her left hip. She has a history of hypertension and osteoarthritis. The physician has ordered analgesics to manage her pain. The nurse is reviewing Mrs. Vimal's medications and medical history to ensure that she does not receive any medications that could potentially cause harm.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she has a good understanding of medications to avoid in the older client?
(a) "I will administer indomethacin to Mrs. Vimal for her hip pain."
(b) "Ketorolac is a safe NSAID to give to older clients."
(c) "Meperidine can cause confusion and is not recommended for older adults."
(d) "Tricyclic antidepressants are a good option for treating depression in older clients."
(e) "First-generation antihistamines are safe to use in older adults."
(f) "Alpha 1-blockers and centrally acting alpha2-agonists are safe for older adults with hypertension."
(g) "Oxybutynin and tolterodine are effective medications for treating urge incontinence in older adults."
(h) "Barbiturates and benzodiazepines are safe to use as sedative-hypnotics in older adults."
Answer:
(c) "Meperidine can cause confusion and is not recommended for older adults."
(e) "First-generation antihistamines are safe to use in older adults."
(f) "Alpha 1-blockers and centrally acting alpha2-agonists are safe for older adults with hypertension."
Explanation:
(a) "I will administer indomethacin to Mrs. Vimal for her hip pain." This statement is incorrect as indomethacin is a NSAID that should be avoided in older adults due to its potential to cause gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcers, and kidney damage.
(b) "Ketorolac is a safe NSAID to give to older clients." This statement is incorrect as ketorolac is also a NSAID that should be avoided in older adults due to its potential to cause kidney damage and gastrointestinal bleeding.
(c) "Meperidine can cause confusion and is not recommended for older adults." This statement is correct as meperidine is a medication that can cause confusion, delirium, and other adverse effects in older adults due to its metabolites accumulating in the body.
(d) "Tricyclic antidepressants are a good option for treating depression in older clients." This statement is incorrect as first- generation tricyclic antidepressants can cause several adverse effects, including anticholinergic effects, orthostatic hypotension, and cardiac arrhythmias, which can be dangerous for older adults.
(e) "First-generation antihistamines are safe to use in older adults." This statement is incorrect as first-generation antihistamines can cause sedation, confusion, and other adverse effects in older adults, increasing the risk of falls and accidents.
(f) "Alphal-blockers and centrally acting alpha2-agonists are safe for older adults with hypertension." This statement is incorrect as both medications can cause orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, and falls, which can be dangerous for older adults.
(g) "Oxybutynin and tolterodine are effective medications for treating urge incontinence in older adults." This statement is incorrect as both medications can cause anticholinergic effects, dry mouth, constipation, and confusion, which can be dangerous for older adults.
(h) "Barbiturates and benzodiazepines are safe to use as sedative- hypnotics in older adults." This statement is incorrect as both medications can cause sedation, confusion, falls, respiratory depression, and other adverse effects in older adults, which can be life-threatening.
Question 25.
Mrs. Vimal, an 82-year-old client, was admitted to the hospital with pneumonia. She was started on antibiotics, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids, which were all given orally. Due to her age and condition, the nurse assessed Mrs. Vimal's risk for aspiration before administering the medications. The nurse found that Mrs. Vimal had a decreased level of consciousness and was unable to swallow, cough, or gag.
Which of the following statements from the nurse indicates that she is taking appropriate actions for administering oral medications to Mrs. Vimal?
(a) The nurse should give Mrs. Vimal the medications in their original form.
(b) The nurse should give Mrs. Vimal the medications all at once.
(c) The nurse should mix the medications with applesauce or pudding.
(d) The nurse should crush the sustained-release tablets.
(e) The nurse should use a straw to help Mrs. Virnal drink the liquid medications.
(f) The nurse should thicken the liquids if indicated.
(g) The nurse should administer the medications in the form that is easiest to swallow.
(h) The nurse should collaborate with the health care provider and speech therapist before administering the medication.
Answer:
(c) The nurse should mix the medications with applesauce or pudding.
(f) The nurse should thicken the liquids if indicated.
(h) The nurse should collaborate with the health care provider and speech therapist before administering the medication.
Explanation:
Option (a) is incorrect because the original form of the medications may not be the easiest form for Mrs. Vimal to swallow. Option (b) is incorrect because administering all the medications at once increases the risk of aspiration. Option (d) is incorrect because sustained-release tablets should not be crushed. Option (e) is incorrect because the use of straws increases the risk of aspiration. Option (g) is incorrect because the easiest form may not be the safest form for Mrs. Vimal.
Option (c) is correct because mixing the medications with applesauce or pudding may make it easier for Mrs. Vimal to swallow. Option (f) is correct because thickening the liquids may make it easier for Mrs. Vimal to swallow and reduce the risk of aspiration. Option (h) is correct because collaborating with the healthcare provider and speech therapist before administering the medication can help ensure the safest administration for Mrs. Vimal.
Question 26.
Mrs. Ranjan is a 78-year-old client with a history of stroke and dysphagia, who is receiving oral medications for hypertension. The nurse is responsible for administering the medications and ensuring client safety.
Which of the following statements from the patient indicates that she is at risk for aspiration during medication administration?
(a) "I take my medication with a sip of water every morning."
(b) "I always crush my pills before swallowing them."
(c) "Sometimes I cough when I drink water."
(d) "I have no trouble swallowing my medication."
(e) "I prefer to take my medication with a straw."
(f) "I feel a lump in my throat when I swallow."
(g) "I have to take my medication on an empty stomach."
(h) "I drink coffee with my medication to help it go down easier."
Answer:
(c) "Sometimes I cough when I drink water."
(f) "I feel a lump in my throat when I swallow."
(h) "I drink coffee with my medication to help it go down easier."
Explanation:
Option (a) is incorrect because taking medication with water does not necessarily indicate aspiration risk. Option (b) is incorrect because crushing pills without consulting a healthcare professional may alter the medication's effectiveness. Option (c) is correct because coughing while drinking water can indicate an increased risk for aspiration. Option (d) is incorrect because stating no trouble swallowing does not necessarily rule out aspiration risk.
Option (e) is incorrect because using a straw may increase aspiration risk. Option (f) is correct because feeling a lump in the throat while swallowing can indicate an increased risk for aspiration. Option (g) is incorrect because taking medication on an empty stomach does not necessarily indicate aspiration risk.
Option (h) is correct because drinking coffee with medication may increase the risk for aspiration. Therefore, options (c), (f), and (h) are the correct answers because they indicate an increased risk for aspiration during medication administration in a client with dysphagia.
Read More:
