By simulating the exam environment, NCLEX Exam Questions help students develop the necessary stamina and concentration for the actual test.
NCLEX Eyes, Ears, Nose, and Throat Health Problems Questions
Eyes, Ears, Nose, and Throat Health Problems NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
The nurse is observing a spouse administer eye drops, as shown in the figure. What should the nurse instruct the spouse to do?
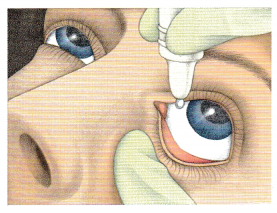
(a) Move the dropper to the inner canthus.
(b) Have the client raise the eyebrows.
(c) Administer the drops in the center of the lower lid.
(d) Have the client squeeze both eyes after administering the drops.
Answer:
(c) Administer the drops in the center of the lower lid.
Explanation:
The spouse has positioned the dropper and the client correctly to prevent injury to the client’s eye. The spouse should administer the drops in the center of the lower lid. Following administration of the eye drops, the client should blink the eyes to distribute the medication; squeezing or rubbing the eyes might cause the medication to drip out of the eye.
Question 2.
One day after cataract surgery, the client is having discomfort from bright light. What should the nurse advise the client to do?
(a) Dim lights in the house and stay inside for 1 week.
(b) Attach sun shields to existing eyeglasses when in direct sunlight.
(c) Use sunglasses that wrap around the side of the face when in bright light.
(d) Patch the affected eye when in bright light.
Answer:
(c) Use sunglasses that wrap around the side of the face when in bright light.

Explanation:
To prevent discomfort from bright light, the client should wear sunglasses that cover the front and side of the face, thus minimizing light that comes into the eye from any direction. It is not necessary to remain in dim light or inside. Attaching sun shields or sunglasses to existing glasses will not cover the eye sufficiently, and bright light will come in on the side of the face. It is not necessary to patch the affected eye.
Question 3.
The nurse is discharging a client who just had cataract removal and intraocular lens implantation. What statements indicate that the client understands discharge instructions? Select all that apply.
(a) “I understand the schedule for my eye drops and will use the medications.”
(b) “I feel good and am ready to drive home now.”
(c) “I will call in the morning if I cannot see clearly.”
(d) “I will wear the eye shield at night to protect my eye.”
(e) “I will avoid lifting or pulling anything over 15 lb (6.8 kg).”
(f) “I will call if I still have eye pain after taking acetaminophen. ”
Answer:
(a) “I understand the schedule for my eye drops and will use the medications.”
(d) “I will wear the eye shield at night to protect my eye.”
(c) “I will call in the morning if I cannot see clearly.”
(e) “I will avoid lifting or pulling anything over 15 lb (6.8 kg).”
Explanation:
(a), (d), (c), (e) To promote success of lens implant without complication (infection, inflammation, hemorrhage), it is important for the client to instill eye drops as prescribed, protect the eye, and avoid placing any stress on the eye by lifting, pulling, or pushing objects that weigh more than 15 lb (6.8 kg).
Pain should be minimal and relieved with acetamin-ophen; if not, the client should notify the health care provider (HCP) Q. Clients should not expect to drive or see clearly immediately following lens implant; it may take several days for vision to clear, and limitations will be discussed at the follow-up appointment.
Question 4.
A client is having a cataract removed and will use eyeglasses after the surgery. What information should the nurse include in the teaching plan? Select all that apply.
(a) Images will appear one-third larger.
(b) Look through the center of the glasses.
(c) The changes will be immediate.
(d) Use handrails when climbing stairs.
(e) Stay out of the sun for 2 weeks.
Answer:
(a) Images will appear one-third larger.
(b) Look through the center of the glasses.
(d) Use handrails when climbing stairs.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (d) The use of glasses following cataract surgery does not totally restore binocular vision. Glasses will cause images to appear larger, and peripheral vision will be distorted; the client should look through the center of the glasses and turn his or her head to view objects in the periphery. The client should also use caution when walking or climbing stairs until he or she has adjusted to the change in vision.
Changes in vision following cataract surgery are not immediate, and the nurse can instruct the client to be patient while adjusting to the changes. The client does not need to stay out of the sun but should wear dark glasses to prevent discomfort from photophobia.
Question 5.
The client has had a cataract removed. When explaining discharge instructions, what should the nurse tell the client to do?
(a) Keep the head aligned straight.
(b) Utilize bright lights in the home.
(c) Use an eye shield at night.
(d) Change the eye patch as needed.
Answer:
(c) Use an eye shield at night.
Explanation:
Using an eye shield at night prevents rubbing the eye. The head should be turned to the side to scan the entire visual field to compensate for impaired peripheral vision. Eye medications may initially cause sensitivity to bright light. The surgeon changes the eye patch on the second postoperative day.
Question 6.
The client with a cataract tells the nurse about being afraid of being awake during eye surgery. Which response by the nurse would be the most appropriate?
(a) “Have you ever had any reactions to local anesthetics in the past?”
(b) “What is it that disturbs you about the idea of being awake?”
(c) “By using a local anesthetic, you will not have nausea and vomiting after the surgery.”
(d) “There is really nothing to fear about being awake. You will be given a medication that will help you relax.”
Answer:
(b) “What is it that disturbs you about the idea of being awake?”
Explanation:
The nurse should give a client who seems fearful of surgery an opportunity to express his or her feelings. Only after identifying the client’s concerns can the nurse intervene appropriately. Asking the client about previous reactions to local anesthetics may be warranted, but it does not address the client’s concerns in this instance.
Telling the client that he or she will not have nausea or vomiting ignores the client’s feelings of fear and does not provide any data about the client’s feelings. More data would help the nurse plan care. Telling the client that there is nothing to be afraid of minimizes the client’s feelings and does not address his or her concerns. Premature explanations and cliches do not provide the needed assessment data and ignore the client’s feelings.
Question 7.
A client tells the nurse about the vision being blurred and hazy throughout the entire day. What should the nurse recommend that the client do?
(a) Purchase a pair of magnifying glasses.
(b) Wear glasses with tinted lenses.
(c) Schedule an appointment with an optician.
(d) Schedule an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
Answer:
(d) Schedule an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
Explanation:
An ophthalmologist is a health care provider (HCP) who specializes in the treatment of disorders of the eye, and the nurse should advise the client to see an ophthalmologist. An optician makes glasses, and it is not known at this point what the best treatment for the client is. Magnifying glasses, or glasses with tinted lenses, do not correct hazy or blurred vision. If glasses are needed to correct refractive errors, they should be prescription glasses.
Question 8.
The nurse is to instill drops of phenylephrine hydrochloride into the client’s eye prior to cataract surgery. Which is the expected outcome?
(a) dilation of the pupil and blood vessels
(b) dilation of the pupil and constriction of blood vessels
(c) constriction of the pupil and constriction of blood vessels
(d) constriction of the pupil and dilation of blood vessels
Answer:
(b) dilation of the pupil and constriction of blood vessels
Explanation:
Instilled in the eye, phenylephrine hydrochloride acts as a mydriatic, causing the pupil to dilate. It also constricts small blood vessels in the eye.
Question 9.
A short time after cataract surgery, the client has nausea. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Instruct the client to take a few deep breaths until the nausea subsides.
(b) Explain that this is a common feeling that will pass quickly.
(c) Tell the client to call the nurse promptly if vomiting occurs.
(d) Medicate the client with an antiemetic, as prescribed.
Answer:
(d) Medicate the client with an antiemetic, as prescribed.
Explanation:
A prescribed antiemetic should be administered as soon as the client has nausea following a cataract extraction. Vomiting can increase intraocular pressure, which should be avoided after eye surgery because it can cause complications. Deep breathing is unlikely to relieve nausea. Postoperative nausea may be common; however, it does not necessarily pass quickly and can lead to vomiting. Telling the client to call only if vomiting occurs ignores the client’s need for comfort and intervention to prevent complications.
Question 10.
The nurse is instructing the client about postoperative care following cataract removal. What position should the nurse teach the client to use?
(a) Remain in a semi-Fowler’s position.
(b) Position the feet higher than the body.
(c) Lie on the operative side.
(d) Place the head in a dependent position.
Answer:
(a) Remain in a semi-Fowler’s position.
Explanation:
The nurse should instruct the client to remain in a semi-Fowler’s position or on the nonoperative side. Positioning the feet higher than the body does not affect the operative eye; placing the head in a dependent position could increase pressure within the eyes.
Question 11.
After returning home, a client who has had cataract surgery will need to continue to instill eye drops in the affected eye. The client is instructed to apply slight pressure against the nose at the inner canthus of the eye after instilling the eye drops. What is the expected outcome of applying pressure?
Pressure:
(a) prevents the medication from entering the tear duct.
(b) keeps the drug from running down the client’s face.
(c) allows the sensitive cornea to adjust to the medication.
(d) facilitates the distribution of the medication over the eye surface.
Answer:
(a) prevents the medication from entering the tear duct.

Explanation:
Applying pressure against the nose at the inner canthus of the closed eye after administering eye drops prevents the medication from entering the lacrimal (tear) duct. If the medication enters the tear duct, it can enter the nose and pharynx, where it may be absorbed and cause toxic symptoms. Eye drops should be placed in the eye’s lower conjunctival sac. Applying pressure will not prevent the drug from running down the face as long as the drops are instilled in the eye. Pressure does not affect the cornea or facilitate the distribution of the medication over the eye surface.
Question 12.
To decrease intraocular pressure following cataract surgery, what should the nurse instruct the client to avoid?
(a) lying supine
(b) coughing
(c) deep breathing
(d) ambulation
Answer:
(b) coughing
Explanation:
Coughing is contraindicated after cataract extraction because it increases intraocular pressure. Other activities that are contraindicated because they increase intraocular pressure include turning to the operative side, sneezing, crying, and straining. Lying supine, ambulating, and deep breathing do not affect intraocular pressure.
Question 13.
After cataract removal surgery on the left eye, the client sits up and reports having sharp pain in the operative eye. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Cover the eye with a moist sterile sponge.
(b) Administer eye drops for pain.
(c) Have the client lie on the right side.
(d) Contact the health care provider.
Answer:
(d) Contact the health care provider.
Explanation:
Sudden, sharp pain after eye surgery may indicate that the client has intraocular hemorrhage. The nurse should immediately contact the health care provider (HCP) Covering the eye will not manage intraocular hemorrhage. Pain medication will not be effective in managing hemorrhage. The nurse should help the client return to a recumbent position.
Question 14.
The client is diagnosed with a detached retina in the right eye. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Apply compresses to the eye.
(b) Instruct the client to lie prone.
(c) Remove all bed pillows.
(d) Promote measures that limit mobility.
Answer:
(d) Promote measures that limit mobility.
Explanation:
Promoting measures that limit mobility may prevent further injury. Following surgical repair of a detached retina, cool or warm compresses are applied to edematous eyelids, if prescribed. The client should avoid lying face down, stooping, or bending preoperatively. It is not necessary to remove all pillows.
Question 15.
The nurse is placing patches on both eyes of the client with a detachment of the retina. What is the expected outcome of patching?
(a) reduced rapid eye movements
(b) decreased irritation caused by light entering the damaged eye
(c) protection of the injured eye from infection
(d) minimized eye strain on the uninvolved eye
Answer:
(a) reduced rapid eye movements

Explanation:
Patching the eyes helps decrease random eye movements that could enlarge and worsen retinal detachment. Although clients with eye injuries frequently are light sensitive, and preventing infection is important, the specific goal is to reduce rapid eye movements. Using the uninvolved eye would not cause eye strain, but random movements of one eye will involve the other eye.
Question 16.
The client with retinal detachment in the right eye is extremely apprehensive and tells the nurse, “I am afraid of going blind. It would be so hard to live that way.” What factor should the nurse consider before responding to this statement?
(a) Repeat surgery is impossible, so if this procedure fails, vision loss is inevitable.
(b) The surgery will only delay blindness in the right eye, but vision is preserved in the left eye.
(c) More and more services are available to help newly blind people adapt to daily living.
(d) Optimism is justified because surgical treatment has a 90% to 95% success rate.
Answer:
(d) Optimism is justified because surgical treatment has a 90% to 95% success rate.

Explanation:
Untreated retinal detachment results in increasing detachment and eventual blindness, but 90% to 95% of clients can be successfully treated with surgery. If necessary, the surgical procedure can be repeated about 10 to 14 days after the first procedure. Many more services are available for newly blind people, but ideally, this client will not need them. Surgery does not delay blindness.
Question 17.
Which statement would provide the best guide for activity during the rehabilitation period for a client who has been treated for retinal detachment?
The activity level is:
(a) increased gradually; the client can resume usual activities in 5 to 6 weeks.
(b) determined by the client’s tolerance; clients can be as active as they wish.
(c) restricted for several months; the client should plan on being sedentary.
(d) not restricted; clients can resume regular aerobic exercises.
Answer:
(a) increased gradually; the client can resume usual activities in 5 to 6 weeks.
Explanation:
The scarring of the retinal tear needs time to heal completely. Therefore, resumption of activity should be gradual; the client may resume usual activities in 5 to 6 weeks. Successful healing should allow the client to return to a previous level of functioning.
Question 18.
Which goal is a priority for a client who has undergone surgery for retinal detachment?
(a) Control pain.
(b) Prevent an increase in intraocular pressure.
(c) Cleanse the eye with soap and water.
(d) Maintain a darkened environment.
Answer:
(b) Prevent an increase in intraocular pressure.
Explanation:
After surgery to correct a detached retina, prevention of increased intraocular pressure is the priority goal. Control of pain with analgesics is a secondary goal. The client should avoid getting soap and water in the eye when bathing. Maintaining a darkened environment is not necessary for this client.
Question 19.
A client with glaucoma is to receive 3 gtt of acetazolamide in the left eye. What should the nurse do?
(a) Ask the client to close the right eye while administering the drug in the left eye.
(b) Have the client look up while the nurse administers the eye drops.
(c) Have the client lift the eyebrows while the nurse positions the hand with the dropper on the client’s forehead.
(d) Wipe the eyes with a tissue following administration of the drops.
Answer:
(b) Have the client look up while the nurse administers the eye drops.
Explanation:
The client should look up while the nurse instills the eye drops. The client will need to keep both eyes open while the nurse administers the drug. If the client raises the eyebrows while the nurse’s hand is positioned on the eyebrows, the movement of the forehead may cause the dropper to move and injure the eye. The client should gently blink the eyes after the eye drops have been instilled. Using a tissue to wipe the eyes could remove some of the medication; excess fluid can be removed with a cotton ball.
Question 20.
A client who has been treated for chronic open-angle glaucoma for 5 years asks the nurse, “How does glaucoma damage my eyesight?”What should the nurse tell the client?
“Your glaucoma:
(a) results from chronic eye inflammation.”
(b) causes increased intraocular pressure.”
(c) leads to detachment of the retina.”
(d) is caused by decreased blood flow to the retina.”
Answer:
(b) causes increased intraocular pressure.”
Explanation:
In COAG, there is an obstruction to the outflow of aqueous humor, leading to increased intraocular pressure. The increased intraocular pressure eventually causes destruction of the retina’s nerve fibers. This nerve destruction causes painless vision loss. The exact cause of glaucoma is unknown. Glaucoma does not lead to retinal detachment.
Question 21.
A client has chronic open-angle glaucoma. What should the nurse ask the client about when conducting a focused assessment?
(a) eye pain
(b) excessive lacrimation
(c) colored light flashes
(d) decreasing peripheral vision
Answer:
(d) decreasing peripheral vision

Explanation:
Although COAG is usually asymptomatic in the early stages, peripheral vision gradually decreases as the disorder progresses. Eye pain is not a feature of COAG but is common in clients with angle-closure glaucoma. Excessive lacrimation is not a symptom of COAG; it may indicate a blocked tear duct. Flashes of light are a common symptom of retinal detachment.
Question 22.
What information should the nurse provide when preparing the client for tonometry?
(a) Oral pain medication will be given before the procedure.
(b) It is a painless procedure with no adverse effects.
(c) Blurred or double vision may occur after the procedure.
(d) Medication will be given to dilate the pupils before the procedure.
Answer:
(b) It is a painless procedure with no adverse effects.
Explanation:
Tonometry, which measures intraocular pressure, is a simple, noninvasive, and painless procedure that requires no particular preparation or postprocedure care and carries no adverse effects. It is not necessary to dilate the pupils for tonometry.
Question 23.
A client uses timolol maleate eye drops. What is the expected outcome of this drug?
(a) constricting the pupils
(b) dilating the canals of Schlemm
(c) reducing aqueous humor formation
(d) improving the ability of the ciliary muscle to contract
Answer:
(c) reducing aqueous humor formation
Explanation:
Timolol maleate is commonly administered to control glaucoma. The drug’s action is not completely understood, but it is believed to reduce aqueous humor formation, thereby reducing intraocular pressure. Timolol does not constrict the pupils; miotics are used for pupillary constriction and contraction of the ciliary muscle. Timolol does not dilate the canal of Schlemm.
Question 24.
The nurse observes the client instill eye drops. The client says, “I just try to hit the middle of my eyeball so the drops do not run out of my eye.” What should the nurse tell the client about this method of instilling eye drops? This method may cause:
(a) scleral staining.
(b) corneal injury.
(c) excessive lacrimation.
(d) systemic drug absorption.
Answer:
(b) corneal injury.

Explanation:
The cornea is sensitive and can be injured by eye drops falling onto it. Therefore, eye drops should be instilled into the lower conjunctival sac of the eye to avoid the risk of corneal damage. The drops do not cause scleral staining or excessive lacrimation. Systemic absorption occurs when eye drops enter the tear ducts.
Question 25.
Which clinical manifestation should the nurse assess when a client has acute angle-closure glaucoma?
(a) gradual loss of central vision
(b) acute light sensitivity
(c) loss of color vision
(d) sudden eye pain
Answer:
(d) sudden eye pain
Explanation:
Acute angle-closure glaucoma produces abrupt changes in the angle of the iris. Clinical manifestations include severe eye pain, colored halos around lights, and rapid vision loss. Gradual loss of central vision is associated with macular degeneration. The loss of color vision, or achromatopsia, is a rare symptom that occurs when a stroke damages the fusiform gyrus. It most often affects only half of the visual field.
Question 26.
A client has been diagnosed with an acute episode of angle-closure glaucoma. The client asks the nurse what will be done. What should the nurse tell the client about this health problem?
Acute angle-closure glaucoma:
(a) frequently resolves without treatment.
(b) is typically treated with sustained bed rest.
(c) is a medical emergency that can rapidly lead to blindness.
(d) is most commonly treated with steroid therapy.
Answer:
(c) is a medical emergency that can rapidly lead to blindness.
Explanation:
Acute angle-closure glaucoma is a medical emergency that rapidly leads to blindness if left untreated. Treatment typically involves miotic drugs and surgery, usually iridectomy or laser therapy. Both procedures create a hole in the periphery of the iris, which allows the aqueous humor to flow into the anterior chamber. Bed rest does not affect the progression of acute angle-closure glaucoma. Steroids are not a treatment for acute angle-closure glaucoma; in fact, they are associated with the development of glaucoma.
Question 27.
The nurse should assess an older adult with macular degeneration for:
(a) loss of central vision.
(b) loss of peripheral vision.
(c) total blindness.
(d) blurring of vision.
Answer:
(a) loss of central vision.
Explanation:
Macular degeneration generally involves loss of central vision. Gradual blurring of vision can occur as the disease progresses and may result in blindness; however, loss of central vision is the most common finding. Tiny yellowish spots, known as drusen, develop beneath the retina. Loss of peripheral vision is characteristic of glaucoma experience with the disease process. Improving his vision may not be possible.
Question 28.
A client has a history of macular degeneration. What is the priority nursing goal while the client is in the hospital?
(a) Provide education regarding community services for clients with adult macular degeneration (AMD).
(b) Provide health care related to monitoring the eye condition.
(c) Promote a safe, effective care environment.
(d) Improve vision.
Answer:
(c) Promote a safe, effective care environment.
Explanation:
AMD generally affects central vision. Confusion may result related to the changes in the environment and the inability to see the environment clearly. Therefore, providing safety is the priority goal in the care of this client. Educating him regarding (OmmufliLy resources or monitoring his AMD may have been done at an earlier claie or can be done after assessing his knowledge base and experience with the disease process. Improving his vision may not be possible.
Question 29.
Which measure should the nurse teach the client with adult macular degeneration (AMD) as a safety precaution?
(a) Wear a patch over one eye.
(b) Place personal items on the sighted side.
(c) Lie in bed with the unaffected side toward the door.
(d) Turn the head from side to side when walking.
Answer:
(d) Turn the head from side to side when walking.
Explanation:
To expand the visual held, the partially sighted client should be taught to turn the head from side to side when walking. Neglecting to do so may result in accidents. This technique helps maximize the use of remaining sight. A patch does not address the problem of hemianopsia. Appropriate client positioning and placement of personal items will increase the client’s ability to cope with the problem but will not affect safety.
Question 30.
The nurse is assessing a client with macular degeneration. Identify the illustration that best depicts what clients with this disorder typically see.

Answer:

Explanation:
In macular degeneration, the center vision is blackened out, and only the outer visual fields are clear.
Question 31.
The nurse is assisting a client who has new- onset vision loss to transition to home from the hospital. The client can see shadow and light in the right eye only. When at home, what is the client’s greatest risk?
(a) loss of sensory perception
(b) injury from falls
(c) denial of changes in vision
(d) isolation from social activities
Answer:
(b) injury from falls
Explanation:
Because of the client’s recent vision loss, the client is at high risk for injury. Sensory alterations often affect other areas of functional ability, including leaving clients with sensory deficits at risk for injuries as a result. Disturbed sensory perception, denial of and difficulty adjusting to the vision loss, and social isolation may also be of concern and may accompany changes in sensory function, but they are not of higher priority than risk for injury.
Question 32.
A young adult is admitted for elective nasal surgery for a deviated septum. Which sign would be an important indicator of bleeding even if the nasal drip pad remained dry and intact?
(a) presence of nausea
(b) repeated swallowing
(c) rapid respiratory rate
(d) feelings of anxiety
Answer:
(b) repeated swallowing
Explanation:
Because of the dense packing, it is relatively unusual for bleeding to be apparent through the nasal drip pad. Instead, the blood runs down the throat, causing the client to swallow frequently. The back of the throat can be assessed with a flashlight. An accumulation of blood in the stomach may cause nausea and vomiting but is not an initial sign of bleeding. Increased respiratory rate occurs in shock and is not an early sign of bleeding in the client after nasal surgery. Feelings of anxiety are not indicative of nasal bleeding.
Question 33.
The client is ready for discharge after surgery for a deviated septum. Which instruction would be appropriate?
(a) Avoid activities that elicit Valsalva’s maneuver.
(b) Take aspirin to control nasal discomfort.
(c) Avoid brushing the teeth until the nasal packing is removed.
(d) Apply heat to the nasal area to control swelling.
Answer:
(a) Avoid activities that elicit Valsalva’s maneuver.
Explanation:
The client should be instructed to avoid any activities that cause Valsalva’s maneuver (e.g., straining at stool, vigorous coughing, exercise) to reduce stress on suture lines and bleeding. The client should not take aspirin because of its anti-platelet properties, which may cause bleeding. Oral hygiene is important to rid the mouth of old dried blood and to enhance the client’s appetite. Cool compresses, not heat, should be applied to decrease swelling and control discoloration of the area.
Question 34.
Which statement indicates that the client who has undergone repair of the nasal septum has understood the discharge instructions?
(a) “I shouldn’t shower until my packing is removed.”
(b) “I will take stool softeners and modify my diet to prevent constipation.”
(c) “Coughing every 2 hours is important to prevent respiratory complications.”
(d) “It’s important to blow my nose each day to remove the dried secretions.”
Answer:
(b) “I will take stool softeners and modify my diet to prevent constipation.”
Explanation:
Constipation can cause straining during defecation, which can induce bleeding. Showering is not contraindicated. The client should take measures to prevent coughing. The client should avoid blowing the nose for 48 hours after the packing is removed. Thereafter, the client should blow the nose gently using the open-mouth technique to minimize bleeding in the surgical area.
Question 35.
To approach a deaf client, what should the nurse do first?
(a) Knock on the room’s door loudly.
(b) Close and open the vertical blinds rapidly.
(c) Talk while walking into the room.
(d) Get the client’s attention.
Answer:
(d) Get the client’s attention.
Explanation:
The nurse should avoid startling the client who is deaf and should obtain the attention of the client before speaking. The client who is deaf cannot hear knocking on the door or talking. Opening the blinds is not a helpful way to get the client’s attention.
Question 36.
A 7 5-year-old client who has been taking furosemide regularly for 4 months tells the nurse about having trouble hearing. What should the nurse do?
(a) Tell the client that at age 75 years, it is inevitable that there will be hearing loss.
(b) Report the hearing loss to the health care provider.
(c) Schedule the client for audiometric testing and a hearing aid.
(d) Tell the client that the hearing loss is only temporary; when the body adjusts to the furosemide, hearing will improve.
Answer:
(b) Report the hearing loss to the health care provider.
Explanation:
Furosemide may cause ototoxicity. The nurse should tell the client to promptly report the hearing loss, dizziness, or tinnitus to help prevent permanent ear damage. Hearing loss is not inevitable, and it is inappropriate to make assumptions about the cause of symptoms without a thorough evaluation. The client’s system will not “adjust,” and hearing loss will not resolve.
Question 37.
The nurse is providing preoperative instructions to a client who is deaf. Which strategy is most effective in assuring that the client understands the information?
(a) Stand in front of the client, and slowly explain the instructions.
(b) Provide instructions to the spouse, and have the spouse explain them to the client.
(c) Give the client written material to read, and follow up with time for questions.
(d) Show the client a DVD with instructions.
Answer:
(c) Give the client written material to read, and follow up with time for questions.
Explanation:
A client who is deaf benefits most from reading information and then having an opportunity to ask questions and follow up. Verbal communication, while appropriate, may not be sufficient. The spouse can be included in the teaching, but the nurse is responsible for ensuring that the client understands the instructions. DVDs may be helpful, but unless they have closed captioning, key points may be missed in the audio portion.
Question 38.
A client who is prescribed by the health care provider (HCP) to take aspirin daily in order to prevent thrombus formation reports ringing in the ears. The nurse advises the client to take which measure?
(a) Increase fluid intake.
(b) Stop taking the aspirin.
(c) Use acetaminophen instead.
(d) Contact the HCP.
Answer:
(d) Contact the HCP.

Explanation:
Because aspirin is ototoxic, the ringing in the ears is likely caused by long-term aspirin use. The nurse advises the client to contact the HCP if the aspirin is to be discontinued, and other drugs may be ordered. The client is not instructed to stop taking the drug without discussing the change with the HCP. Acetaminophen does not have the same antithrombotic properties as does aspirin. Increasing fluid intake will not stop the ringing in the ears
Question 39.
The son of an older adult reports that his father just “stares off into space” more and more in the last several months but then eagerly smiles and nods once the son can get his attention. What further assessments should the nurse make?
(a) dementia
(b) hearing loss
(c) anger
(d) depression
Answer:
(b) hearing loss

Explanation:
Blank looks decreased attention span, positioning of the head toward sound, and smiling/ nodding in agreement once attention is gained are all behaviors that indicate hearing loss in adults. It is common to confuse sensory deficits for a change in cognitive status. The nurse should focus assessments of sensory function on considering any pathophysiology of existing or new-onset deficits and consider all client factors that might contribute to deficits. The blank looks do not indicate that this client is angry with his son.
Question 40.
The nurse has been assigned to a client who is hearing impaired and reads speech. Which strategies should the nurse incorporate when communicating with the client? Select all that apply.
(a) Avoid being silhouetted against strong light.
(b) Do not block out the person’s view of the speaker’s mouth.
(c) Face the client when talking.
(d) Have bright light behind so the individual can see.
(e) Ensure the client is familiar with the subject material before discussing.
(f) Talk to the client while doing other nursing procedures.
Answer:
(a) Avoid being silhouetted against strong light.
(b) Do not block out the person’s view of the speaker’s mouth.
(c) Face the client when talking.
(e) Ensure the client is familiar with the subject material before discussing.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e) When working with a client who is hearing impaired and reads speech, the presenter must face the person directly and devote full attention to the communication process. In addition, it will be useful for the client that the speaker not be too silhouetted against strong light, that the speaker’s mouth not be blocked from the client’s view, and that there are no objects in the mouth of the speaker. Finally, it is recommended that the presenter provide the client with the needed information to study before reviewing. This will provide the client with the ability to use contextual clues in speech reading.
Question 41.
Ear drops have been prescribed to be instilled in the adult client’s left ear to soften cerumen. To position the client, what should the nurse do?
(a) Have the client lie on the left side.
(b) Pull the auricle lobe up and back.
(c) Pull the ear lobe down and back.
(d) Chill the ear drops prior to administering.
Answer:
(b) Pull the auricle lobe up and back.
Explanation:
The nurse should have the client lie on the side opposite the affected ear. To straighten the client’s ear canal, pull the auricle of the ear up and back for an adult. For an infant or a young child, gently pull the auricle down and back to the nasopharynx. The ear drops should be administered at body temperature.
Question 42.
Sensorineural hearing loss results from which condition?
(a) presence of fluid and cerumen in the external canal
(b) sclerosis of the bones of the middle ear
(c) damage to the cochlear or vestibulocochlear nerve
(d) response to a traumatic experience
Answer:
(c) damage to the cochlear or vestibulocochlear nerve
Explanation:
A sensorineural hearing loss results from damage to the cochlear or vestibulocochlear nerve. Presence of fluid and cerumen in the external canal or sclerosis of the bones of the middle ear results in a conductive hearing loss. Hearing loss resulting from a traumatic experience is called a psychogenic hearing loss.
Question 43.
What should the nurse instruct a client who has cerumen buildup in the ear to do? Select all that apply,
(a) Wash the external ear with a washcloth,
(b) Instill cerumenolytic drops in the ear canal.
(c) Use cotton-tipped applicators to remove the wax from the ear canal.
(d) Use small forceps to extract the wax.
(e) Irrigate the ear with sterile water after softening the wax with a cerumenolytic solution.
Answer:
(a) Wash the external ear with a washcloth,
(b) Instill cerumenolytic drops in the ear canal.
(e) Irrigate the ear with sterile water after softening the wax with a cerumenolytic solution.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (e) The nurse can advise the client with cerumen that is impacted in the ear to use a washcloth to clean the exterior part of the ear. The client can also instill cerumenolytic drops to soften the earwax. The client can then irrigate the ear canal with sterile water using a small bulb syringe. The client should not use cotton-tipped applicators as they often push the cerumen further into the ear canal. The client should never put forceps in the ear.
Question 44.
A client is about to have a tympanoplasty and asks the nurse what the surgical procedure involves. What should the nurse do first when answering the question?
(a) Assess the client’s understanding of what the healthcare provider has explained.
(b) Describe the surgical procedure.
(c) Tell the client that the procedure will close the perforation and prevent recurrent infection.
(d) Explain that the procedure will improve hearing.
Answer:
(a) Assess the client’s understanding of what the healthcare provider has explained.

Explanation:
The nurse should first assess the client’s knowledge base. Working within the framework of the client’s knowledge and educational level, the nurse then can describe the procedure and its benefits.
Question 45.
An older adult takes two 81-mg aspirin tablets daily to prevent a heart attack. The client reports having a constant “ringing” in both ears. How should the nurse respond to the client’s comment?
(a) Tell the client that “ringing” in the ears is associated with the aging process.
(b) Refer the client to have a Weber test.
(c) Schedule the client for audiometric testing.
(d) Explain to the client that the “ringing” may be related to the aspirin.
Answer:
(d) Explain to the client that the “ringing” may be related to the aspirin.
Explanation:
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) is an adverse effect of aspirin. Aspirin contains salicylate, which is an ototoxic drug that can induce reversible hearing loss and tinnitus. The nurse should explain this to the client and then encourage the client to inform the health care provider (HCP) Q of the symptom. Tinnitus is not a function of aging. The Weber test and audiometric testing are useful for determining hearing loss but are not necessarily helpful in the management or diagnosis of drug-induced tinnitus.
Question 46.
An older adult has vertigo accompanied with tinnitus as the result of Meniere’s disease. The nurse should instruct the client to restrict which dietary element?
(a) protein A
(b) potassium
(c) fluids
(d) sodium
Answer:
(d) sodium
Explanation:
Meniere’s disease is commonly seen in older women; the disorder is caused by pressure within the labyrinth of the inner ear as a result of excess endolympha resulting in swelling in the cochlea. Therefore, the nurse should instruct the client about dietary restrictions of sodium to reduce fluid retention. Pharmacologic treatment includes
anti vertiginous drugs and diuretics. If the client is prescribed a diuretic, the fluid and electrolytes are monitored. The amount of protein does not have a direct influence in this disease process.
Question 47.
A client has vertigo. Which goal would be most appropriate to prevent injury related to altered immobility and gait disturbances? Select all that apply.
The client:
(a) assumes a safe position when dizzy.
(b) experiences no falls.
(c) performs vestibular/balance exercises.
(d) demonstrates family involvement.
(e) keeps the head still when dizzy.
Answer:
(a) assumes a safe position when dizzy.
(b) experiences no falls.
(c) performs vestibular/balance exercises.
(e) keeps the head still when dizzy.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (e) Assessment of vertigo, including history, onset, description of attacks, duration, frequency, and associated ear symptoms, is important. Vestibular/balance therapy or exercises should be taught and practiced. The client needs to be instructed to sit down when dizzy and decrease the amount of head movement. The client will benefit from recognizing whether he or she experiences an “aura” before an attack so appropriate action can be taken.
Finally, it is recommended that the client keep the eyes open and look straight ahead when lying down. These expected outcomes will prevent the problem of injury. Family involvement is essential when dealing with a client experiencing vertigo but is not essential for this client who must manage the vertigo with or without family involvement,
Question 48.
The client with Meniere’s disease is instructed to modify the diet. The nurse should explain that what is the most frequently recommended diet modification for Meniere’s disease?
(a) low sodium
(b) high protein
(c) low carbohydrate
(d) low fat
Answer:
(a) low sodium
Explanation:
A low-sodium diet is frequently an effective mechanism for reducing the frequency and severity of the disease episodes. About three-quarters of clients with Meniere’s disease respond to treatment with a low-salt diet. A diuretic may also be prescribed. Other dietary changes, such as high protein, low carbohydrate, and low fat, do not have an effect on Meniere’s disease.
Question 49.
Which statement indicates the client under-stands the expected course of Meniere’s disease?
(a) “The disease process will gradually extend to the eyes.”
(b) “Control of the episodes is usually possible, but a cure is not yet available.”
(c) “Continued medication therapy will cure the disease.”
(d) “Bilateral deafness is an inevitable outcome of the disease.”
Answer:
(b) “Control of the episodes is usually possible, but a cure is not yet available.”
Explanation:
There is no cure for Meniere’s disease, but the wide range of medical and surgical treatments allows for adequate control in many clients. The disease often worsens, but it does not spread to the eyes. The hearing loss is usually unilateral.
Question 50.
The risk for injury during an attack of Meniere’s disease is high. The nurse should instruct the client to take which immediate action when experiencing vertigo?
(a) “Place your head between your knees.”
(b) “Concentrate on rhythmic deep breathing.”
(c) “Close your eyes tightly.”
(d) “Assume a reclining or flat position.”
Answer:
(d) “Assume a reclining or flat position.”
Explanation:
The client needs to assume a safe and comfortable position during an attack, which may last several hours. The client’s location when the attack occurs may dictate the most reasonable position. Ideally, the client should lie down immediately in a reclining or flat position to control thier.
The danger of a serious fall is real. Placing between the knees will not help prevent a fall and is not practical because the attack may last several hours. Concentrating on breathing may be a useful distraction, but it will npt help prevent a fall. Closing the eyes does help prevent a fall.
Question 51.
Following a laryngectomy, the nurse notices that the client has saliva collecting beneath the skin flaps. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Place an absorbent dressing over the area.
(b) Circle the area and monitor for increased accumulation of saliva.
(c) Ask the client to expectorate the saliva into an emesis basin.
(d) Notify the health care provider.
Answer:
(d) Notify the health care provider.
Explanation:
The nurse should next notify the health care provider. A salivary listula is suspected when there is saliva collecting beneath skin flaps or leaking through the suture line or drain site. Salivary fistula or skin necrosis usually precedes carotid artery rupture. Using a dressing, observing for increased drainage or having the client expectorate the saliva are not appropriate actions until the health care provider has determined the presence and extent of a fistula.
Question 52.
The nurse is developing a care plan with a client who had a laryngectomy 3 days ago. What steps should the nurse take to assure adequate client nutrition? Select all that apply.
(a) Weigh weekly and report weight loss.
(b) When eating, sit and lean slightly forward.
(c) Have serum albumin level checked regularly.
(d) Receive enteral tube feedings as prescribed.
(e) Manipulate the nasogastric tube daily.
Answer:
(a) Weigh weekly and report weight loss.
(b) When eating, sit and lean slightly forward.
(c) Have serum albumin level checked regularly.
(d) Receive enteral tube feedings as prescribed.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) The nurse should monitor nutritional status through frequent weighing and checking the serum albumin level. The nurse also should administer enteral tube feedings until there is sufficient healing of pharynx and the client can consume sufficient oral feedings to meet body needs. The nurse should avoid manipulation of the nasogastric tube during this time so it does not disrupt the suture line. The nurse should place the client in a sitting position, leaning slightly forward, which allows the larynx to move forward and the hypopharynx to partially open; the epiglottis normally prevents fluid and food from entering the larynx during swallowing.
Question 53.
The client with a laryngectomy is being dis-charged. The nurse should determine that the client understands the need for which self-care measures? Select all that apply.
(a) Provide humidification in the home.
(b) Use a protective shield over the stoma for bathing.
(c) Consume a liberal intake of fluids (2 to 3 L/day).
(d) Limit spicy seasonings on food.
(e) Follow a low-fiber diet.
Answer:
(a) Provide humidification in the home.
(b) Use a protective shield over the stoma for bathing.
(c) Consume a liberal intake of fluids (2 to 3 L/day).
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c) The nurse should advise the client to provide humidification at home. Instruct the client to use a protective shield for bathing, showering, or shampooing or cutting hair to prevent aspiration. The nurse can also encourage the client to obtain a fluid intake of 2 to 3 L daily to help liquefy secretions. To counteract any loss of smell and impairment of taste sensation, the client can add additional seasoning to food. The client should follow a high-fiber diet and use stool softeners because the client may not be able to hold their breath and bear down for bowel movements.
Question 54.
After a total laryngectomy, the client has a feeding tube. What is the purpose of the feeding tube?
The feeding tube:
(a) provides nutrition.
(b) minimizes aspiration.
(c) prevents fistula formation.
(d) maintains an open airway.
Answer:
(a) provides nutrition.
Explanation:
The goaf of postoperative care is to maintain physiologic integrity. Therefore, inserting a feeding tube is a strategy to ensure the fluid and nutritional needs of the client as the surgical site is healing. The feeding tube does help prevent aspiration by preventing ingested fluid from leaking through the wound intofihe trachea before healing occurs; however, the primary rationale is to meet the client’s nutritional and fluid needs. A tracheoesophageal fistula is a rare complication of total laryngectomy and may occur if radiation therapy has compromised wound healing. A feeding tube does not help maintain an open airway.
Question 55.
Which is a priority nursing goal for the hospitalized client who 2 days earlier had a total laryngectomy with creation of a new tracheostomy?
(a) Decrease secretions.
(b) Learn to care for the tracheostomy.
(c) Relieve anxiety related to the tracheostomy.
(d) Maintain a patent airway.
Answer:
(d) Maintain a patent airway.
Explanation:
The main goal for a client with a new tracheostomy is to maintain a patent airway. A fresh tracheostomy frequently causes bleeding and excess secretions, and clients may require frequent suctioning to maintain patency. Decreasing secretions may be a component of a client’s care after laryngectomy and tracheostomy, and relieving anxiety is always an important goal; however, the primary goal is to maintain a patent airway. Instruction in the care of a tracheostomy is a priority later in the client’s recovery.
Question 56.
The client with glaucoma is scheduled for a hip replacement. Which prescription would require clarification before the nurse carries it out?
(a) Administer morphine sulfate.
(b) Administer atropine sulfate.
(c) Teach deep-breathing exercises.
(d) Teach leg lifts and muscle-setting exercises.
Answer:
(b) Administer atropine sulfate.
Explanation:
Atropine sulfate causes pupil dilation. This action is contraindicated for the client with glaucoma because it increases intraocular pressure. The drug does not have this effect on intraocular pressure in people who do not have glaucoma. Morphine causes pupil constriction. Deep breathing exercises will not affect glaucoma. The client should resume taking all medications for glaucoma immediately after surgery.
Question 57.
What should the nurse do to ensure safety for a hospitalized blind client?
(a) Require that the client has a sitter for each shift.
(b) Request that the client stays in bed until the nurse can assist.
(c) Orient the client to the room environment.
(d) Keep the side rails up when the client is alone.
Answer:
(c) Orient the client to the room environment.
Explanation:
The priority goal of care for a client who is blind is safety and preventing injury. The initial action is to orient the client to a new environment. Taking time to identify the objects and where they are located in the room can achieve this goal. It is unrealistic to have someone stay with the client at all times or for the client to stay in bed until the nurse can assist. Using side rails creates unnecessary barriers and may be a safety hazard.
Question 58.
The nurse is taking care of a client who had a laryngectomy yesterday. To assure client safety, the nurse should give hand-off of care reports at which times? Select all that apply.
(a) change of shift
(b) change of nurses
(c) when the nurse goes to lunch
(d) when the unit clerk goes to a staff meeting
(e) when new medication prescriptions are written
Answer:
(a) change of shift
(b) change of nurses
(c) when the nurse goes to lunch
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c) Effective communication is essential when managing client safety and preventing errors. “Hand-off reports” should be made at shift change, when there is a change of nurses or when the nurse leaves the unit, and when the client is discharged or transferred to another unit. There does not need to be a hand-off report when the unit clerk leaves the unit or when new medication prescriptions are written.
Question 59.
The nurse is admitting a client with glaucoma. The client brings prescribed eye drops from home and insists on using them in the hospital. What should the nurse do?
(a) Allow the client to keep the eye drops at the bedside and use them as prescribed on the bottle.
(b) Place the eye drops in the hospital medication drawer and administer as labeled on the bottle.
(c) Explain to the client that the health care provider (HCP) will write a prescription for the eye drops to be used at the hospital.
(d) Ask the client’s wife to assist the client in administering the eye drops while the client is in the hospital.
Answer:
(c) Explain to the client that the health care provider (HCP) will write a prescription for the eye drops to be used at the hospital.

Explanation:
In order to prevent medication errors, clients may not use medications they bring from home; the HCPQ will prescribe the eye drops as required. It is not safe to place the eye drops in the client’s medication box or to permit the client to use them at the bedside. The nurse should ask the wife to take the eye drops home.
Question 60.
The nurse is assigned to care for a client with an ocular prosthesis who is having surgery under a local anesthetic. Prior to surgery, what should the nurse do?
(a) Maintain surgical asepsis when caring for the prosthesis.
(b) Leave the prosthesis in place.
(c) Cleanse the ocular prosthesis with full-strength hydrogen peroxide.
(d) Instruct the client to cleanse the prosthesis daily.
Answer:
(b) Leave the prosthesis in place.
Explanation:
The nurse should maintain medical asepsis to care for an ocular prosthesis. Because the client will have a local anesthetic, the nurse should leave the prosthesis in place. Daily removal and cleansing is not necessary and may be irritating to the socket removal for cleansing once or twice a month is sufficient. The nurse should never use anything stronger than liquid soap and water to cleanse an ocular prosthesis.
Question 61.
A client has been diagnosed with insulin-requiring diabetes. The nurse should instruct the client about which factors that can contribute to the risk for diabetic retinopathy. Select all that apply.
(a) poor control of blood sugar
(b) nearsightedness
(c) length of time of being diagnosed with diabetes
(d) hypertension
(e) elevated cholesterol
Answer:
(a) poor control of blood sugar
(c) length of time of being diagnosed with diabetes
(e) elevated cholesterol
Explanation:
(a), (c), (e) Risk for diabetic retinopathy increases for clients with diabetes who have poorly controlled blood sugar, the longer the client has had the disease, and if the client has other health problems such as hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Being near-sighted is not a risk factor. The nurse should include information about risk factors and how to prevent or minimize them when developing a teaching plan for all clients with diabetes.
