Practicing with NCLEX Exam Questions enables students to develop efficient test-taking strategies, such as elimination techniques and time management.
NCLEX Endocrine System/Endocrine Disorders Questions
Endocrine System/Endocrine Disorders NCLEX Questions Test Strategies
NGN Case Study
Patient A 38-year-old female presents with symptoms of salt cravings, irregular menstrual cycle, fatigue, and weakness. The patient also reports experiencing weight loss and postural hypotension.
Nurse's Notes:
- Assessed patient's vital signs (BP: 100/60 raraHg, HR: 90 bpm. RR: 18 breaths/min)
- Patient reported salt cravings, irregular menstrual cycle, fatigue, and weakness
- Observed skin pigmentation and reported weight loss and postural hypotension
- Reviewed patient's lab results, including high Calcium and Potassium levels, and low sodium levels
Physician’s Order:
- Ordered blood tests.
- Prescribed replacement therapy for adrenocortical hormones Advised patient to follow a high-sodium diet and avoid activities that may cause dehydration
Lab Values:
- Sodium (Na): 130 mEq/L (normal range: 135-145 mEq/L)
- Potassium (K): 5.0 mEq/L (normal range: 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) Calcium (Ca): 10.2 mg/dL (normal range: 8.5-10.5 mg/dL)
Question 1.
What is the most likely diagnosis for the patient in this case study based on the presented symptoms and lab results?
(a) Hypothyroidism
(b) Addison's disease
(c) Hyperparathyroidism
(d) Cushing's syndrome
Answer:
(b) Addison's disease
Explanation:
Option (a) Hypothyroidism can cause fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin, but it does not typically cause salt cravings or high calcium levels.
Option (b) Addison's disease, a condition where the adrenal gland does not produce enough hormones, presents with symptoms such as salt cravings, irregular menstrual cycle, fatigue, weakness, weight loss, and postural hypotension. The lab results show low sodium levels and high calcium and potassium levels, which are consistent with this diagnosis.
Option (c) Hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which the parathyroid glands produce too much parathyroid hormone, causing high calcium levels. It does not typically cause salt cravings or postural hypotension.
Option (d) Cushing's syndrome is a condition in which the body produces too much cortisol. It can cause weight gain, fatigue, and weakness, but it does not typically present with salt cravings, postural hypotension, or low sodium levels.
Question 2.
The nurse notes that the patient has salt carvings. Why may a patient with Addison's disease crave salt?
(a) Low levels of cortisol increase sodium excretion, leading to salt cravings.
(b) High levels of aldosterone increase sodium excretion, leading to salt cravings.
(c) Low levels of aldosterone decrease sodium excretion, leading to salt cravings.
(d) High levels of cortisol decrease sodium excretion, leading to salt cravings.
Answer:
(c) Low levels of aldosterone decrease sodium excretion, leading to salt cravings.
Explanation:
Addison's disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. Aldosterone is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that regulates the body's sodium and potassium balance. It does this by increasing the reabsoiption of sodium by the kidneys, leading to increased blood volume and blood pressure. In Addison's disease, the lack of aldosterone leads to decreased sodium reabsorption and increased sodium excretion by the kidneys, which can cause a decrease in blood volume and blood pressure.
Salt craving is a common symptom in patients with Addison's disease because the body is trying to compensate for the low’ levels of aldosterone by increasing salt intake. The body needs more salt to maintain its sodium balance, and this craving is a result of the body's attempt to maintain homeostasis.
Option (a) is incorrect because low levels of cortisol do not increase sodium excretion; rather, they decrease it by decreasing the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the kidneys, leading to decreased urine output and increased sodium reabsorption. Option (b) is incorrect because high levels of aldosterone increase sodium reabsorption, not sodium excretion, which would lead to decreased sodium levels in the blood, and thus not cause salt cravings.
Option (d) is also incorrect because high levels of cortisol do not decrease sodium excretion; rather, they increase it by increasing the GFR in the kidneys, leading to increased urine output and decreased sodium reabsorption. Therefore, the correct answer is option (c).

Endocrine System/Endocrine Disorders NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
A 35-year-old female presents to the clinic complaining of fatigue, weight gain, and hirsutism. She reports increased thirst and urination, and her blood pressure is found to be elevated. Upon further investigation, her fasting blood sugar is found to be elevated, her sodium level is elevated, and her potassium level is decreased. Her cortisol level is also elevated. Based on these findings, the patient is diagnosed with Cushing syndrome.
What is the most common symptom of Cushing syndrome?
(a) Irritability
(b) Restlessness and fatigue
(c) Tremors and tachycardia
(d) Polyuria and polydipsia
Answer:
(d) Polyuria and polydipsia
Explanation:
Polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia are the three Ps of diabetes, and they are consistent with increases in hunger, urination, and appetite indicating elevation in blood glucose levels. These symptoms are most commonly associated with Cushing syndrome, making option (d) the correct answer.
Options (a), (b), and (c) are not commonly associated with Cushing syndrome. Based on the information provided in the case study, the patient is experiencing increased thirst and urination, which are common symptoms of Cushing syndrome.
Rationale:
A patient presents to the clinic with the following symptoms: irritability, restlessness and fatigue, tremors and tachycardia, diaphoresis and depression. They also have moonface appearance, buffalo hump, obese trunk, pendulous abdomen, thin extremities, acne and striae, increased masculinity in females, and hirsutism.
Upon examination, the patient has decreased sodium levels and increased potassium levels in their blood. They also have a low' fasting blood sugar and a decreased plasma cortisol level. Based on these symptoms, the patient is diagnosed with Addison's disease.
Question 2.
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of Addison's disease?
(a) Polyuria
(b) Irritability
(c) Diaphoresis
(d) Polydipsia
Answer:
(a) Polyuria
Rationale:
Polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia are the three Ps of diabetes and are not listed as symptoms of Addison's disease. The other options are all listed as symptoms of Addison's disease.
Question 3.
Which of the following is NOT a predisposing factor for Addison's disease?
(a) Atrophy of the Adrenal gland
(b) Hyperplasia of the Adrenal gland
(c) Fungal infections
(d) Tubercular infections
Answer:
(b) Hyperplasia of the Adrenal gland
Rationale:
Atrophy of the Adrenal gland and fungal infections are listed as predisposing factors for Addison's disease. Hyperplasia of the Adrenal gland and tubercular infections are listed as predisposing factors for Cushing's syndrome.
Question 4.
Which of the following is NOT a diagnostic criterion for Cushing's syndrome?
(a) Elevated fasting blood sugar
(b) Decreased potassium levels
(c) Elevated sodium levels
(d) Decreased cortisol levels
Answer:
(a) Elevated fasting blood sugar
Rationale:
Elevated fasting blood sugar, elevated sodium levels, decreased potassium levels, and elevated cortisol levels are all listed as diagnostic criteria for Cushing's syndrome.
Question 5.
Which of the following is NOT a nursing intervention for Addison's disease?
(a) Administering corticosteroids
(b) Monitoring electrolyte levels
(c) Administering insulin
(d) Providing emotional support to the patient
Answer:
(c) Administering insulin
Rationale:
Administering corticosteroids, monitoring electrolyte levels, and providing emotional support to the patient are all listed as nursing interventions for Addison's disease. Administering insulin is not listed as a nursing intervention for either Addison's disease or Cushing's syndrome.
Question 6.
Which of the following lab values is commonly seen in individuals with Addison's disease?
(a) Elevated serum sodium
(b) Elevated serum potassium
(c) Elevated serum cortisol
(d) Elevated serum aldosterone
Answer:
(b) Elevated serum potassium
Explanation:
In Addison's disease, the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone, leading to low levels of these hormones and an increase in potassium levels.
Question 7.
Which of the following properties are associated with Addison's disease?
(a) Hypercortisolism
(b) Hypotension
(c) Hyperpigmentation
(d) Moon facies
(e) Hirsutism
(f) Hypokalemia
(g) Hypernatremia
(h) Weight gain
Answer:
(b) Hypotension
(c) Hyperpigmentation
(f) Hypokalemia
Explanation:
Addison's disease is a condition where the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, weight loss, and hypotension. Hyperpigmentation may also occur, particularly in areas of the body exposed to the sun, due to increased production of melanin-stimulating hormone (MSH) from the pituitary gland. Hypokalemia is common in Addison's disease due to the lack of aldosterone, which normally helps the kidneys retain potassium.
In contrast. Cushing's syndrome is a condition where the body is exposed to high levels of cortisol for an extended period. The options associated with Cushing's syndrome are (a) Hypercortisolism, (d) Moon facies. (e) Hirsutism, (g) Hypernatremia, and (h) Weight gain.
Hypersecretion of cortisol can lead to a range of symptoms, including weight gain, particularly in the trunk and face (causing moon facies), hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and hypernatremia (elevated serum sodium levels). It is important to note that Cushing's syndrome and Addison's disease are opposite conditions in terms of cortisol production, and as such, their symptoms are often diametrically opposed.
Question 8.
Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing intervention for a patient with Addison's disease experiencing an acute adrenal crisis?
(a) Administering IV fluids containing dextrose
(b) Administering high doses of glucocorticoids
(c) Administering a potassium-sparing diuretic
(d) Administering beta-adrenergic blockers
Answer:
(b) Administering high doses of glucocorticoids
Explanation:
An acute adrenal crisis can occur when the patient experiences a sudden and severe worsening of symptoms due to stress or illness. Nursing management of a patient with Addison's disease during an acute adrenal crisis is critical, and it involves prompt intervention to prevent life-threatening complications.
(a) Administering IV fluids containing dextrose: This option is partially correct as it addresses the fluid and electrolyte imbalances that can occur during an acute adrenal crisis. Addison's disease patients may experience hypotension, dehydration, and hyponatremia, which can be corrected with the administration of fluids containing dextrose. However, this option does not address the underlying cause of the crisis.
(b) Administering high doses of glucocorticoids: This option is the correct answer as it addresses the underlying cause of the crisis, which is the lack of cortisol production. Patients with Addison's disease need lifelong replacement therapy with glucocorticoids, and during an acute adrenal crisis, high doses of glucocorticoids are necessary to prevent life-threatening complications such as hypotension, shock, and renal failure.
(c) Administering a potassium-sparing diuretic: This option is incorrect as it does not address the underlying cause of the crisis. Potassium-sparing diuretics are used to treat hypertension and edema and can be harmful to patients with Addison's disease who are already experiencing electrolyte imbalances.
(d) Administering beta-adrenergic blockers: This option is incorrect as it can worsen the patient's condition. Beta-adrenergic blockers are contraindicated in patients with Addison's disease as they can mask the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, which can be life- threatening in these patients. Furthermore, beta-adrenergic blockers can exacerbate the hypotension that occurs during an acute adrenal crisis.
Question 9.
Which of the following conditions can cause high potassium levels in the blood?
(a) Hyperparathyroidism
(b) Addison's disease
(c) Chronic kidney disease
(d) Diabetic ketoacidosis
Answer:
(c) Chronic kidney disease
Explanation:
High potassium levels in the blood, also known as hyperkalemia, can be caused by various conditions, as mentioned in the provided information. Among the options provided, chronic kidney disease can lead to high levels of potassium in the blood.
The kidneys play a crucial role in removing excess potassium from the body. In chronic kidney disease, the kidneys are not functioning correctly, leading to an accumulation of potassium in the blood. This can result in muscle weakness, nausea, and abnormal heart rhythms.
Hyperparathyroidism can cause high levels of calcium in the blood, not potassium. Addison's disease leads to low levels of sodium and high levels of potassium in the blood. Acute kidney injury can also cause high potassium levels, but chronic kidney disease is a more common cause. Diabetic ketoacidosis can cause an increase in potassium levels, but this is due to the acidosis and not directly related to the kidney's function. Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
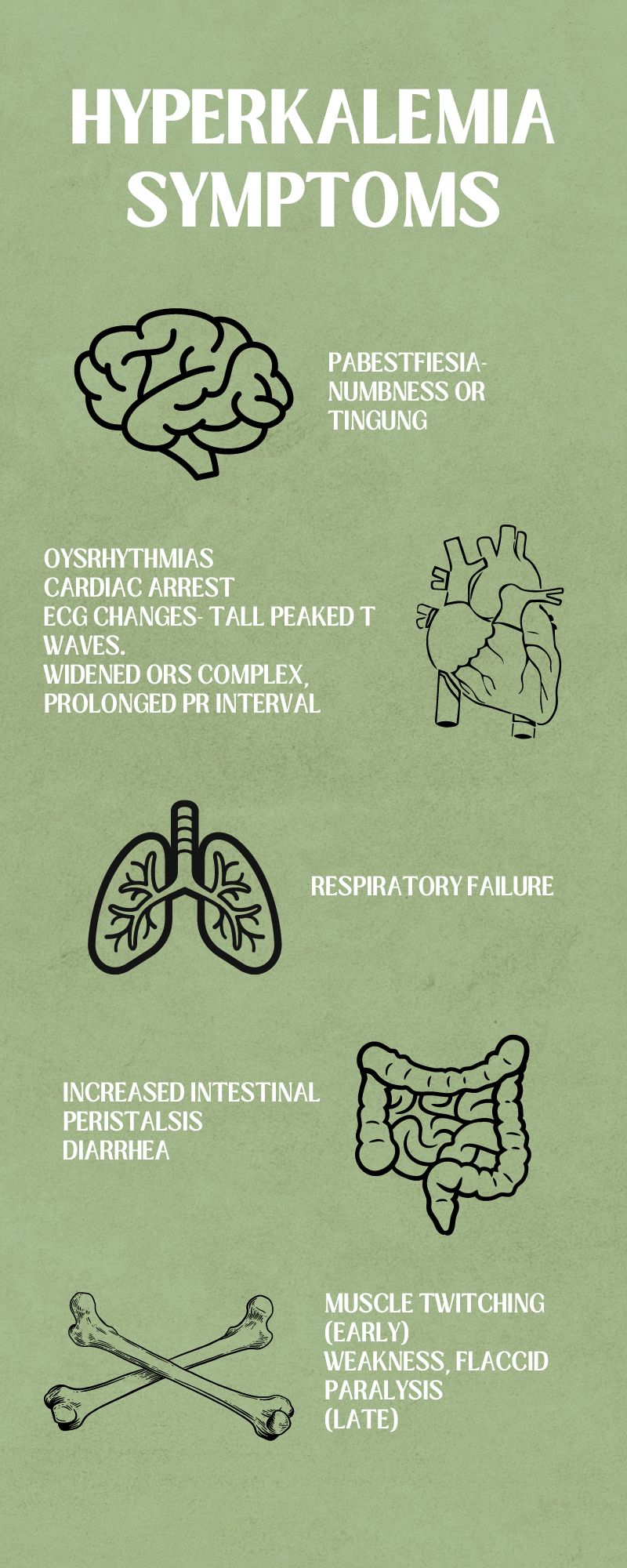
Question 10.
A patient who left taking antithyroid drug for a long time is admitted with symptoms of thyroid storm. Which of the following symptoms can a nurse anticipate to observe for the patient ?
Your options are:
(a) The patient is feeling very cold and feverish.
(b) The patient has a heart rate of 115 bpm.
(c) The patient has feels irritated, confused and restless,
(d) The BP of the patient is 85/60.
Answer:
(a) The patient is feeling very cold and feverish.
(b) The patient has a heart rate of 115 bpm.
(c) The patient has feels irritated, confused and restless,
Explanation:
The correct answer to this question is option number (a), (b) and (c) Option (d) is not correct. One of the symptoms of thyroid storm is systemic hypertension and tachycardia. All the possible symptoms that occur in hyperthyroidism is also a symptom of thyroid storm. It's just that it is a emergency medical situation.
Question 11.
A patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus needs insulin therapy for treatment. Which of the following type of insulin is safest to use in bedtime?
(a) Humulin R and novolin R
(b) Humalog
(c) NPH
(d) Glargine
Answer:
(d) Glargine
Explanation:
(d) Glargine is a long acting insulin. Long acting insulin with Glargine and detemir have a duration of action of 12 to 24 hours. Note that this is only the safest insulin for use in bedtime as it has very little chances of sleep hypoglycemia.
(b) Humalog is a ultra short acting insulin with the duration of 3 hours. It cannot be given at bedtime due to low duration of action.
(c) NPH. This is a intermediate acting insulin. As it has 12 hours of action it is given twice in a day but remember, not to give at bedtime as this can cause hypoglycemia at bedtime. As a nursing intervention, you should remember that it forms a cloudy suspension and can precipitate so it cannot be given IV as if it precipitates, it can cause under or overdose.
(a) Humulin R and Novolin R are regular insulin. They have a quick onset of 1 hour, reaching peak at 2 hours and has 4 hours of duration. They also are not safe to be given at bedtime as frequent waking and injecting insulin may be necessary.
Question 12.
A patient with long history of diabetes mellitus is prescribed metformin. Which of the following is not correct for its right use ?
(a) Discontinue metformin 48 hours after any contrast test.
(b) Give supplemental vitamin B12.
(c) Tell patient not to take alcohols during its use.
(d) Take with (after food).
Strategy: This is purely a knowledge based multiple choice question. We have to select a negative answer (incorrect answer) for this question. Metformin which falls in the biguanide group. Metformin works by decreasing the glucose production in liver and increasing glucose uptake by the body cells.
Answer:
The option we have to choose is the (a) option because it is not correct. You should ask patient to discontinue the drug 48 hours before (not after) any contrast test. Contrast dye such as iodine contrast procedure for cardiac catheterization can affect the kidney function of the patient which would be pronounced by metformin as it causes lactic acid build up.
So, combination of these 2 would be disaster. This is the reason why metformin is stopped on the day or at 48 hours before contrast procedures
(b) option, patient may be supplemented with vitamin B12. The reason is : vitamin B12 is correlated with vitamin B12 deficiency.
(c) option, alcohol shouldn't be consumed concomitantly with metformin because it causes hypoglycemia.
(d), to avoid the GI effect, it shouldn't be taken in an empty stomach. That means it should be taken with food.
