PN NCLEX Questions cover a wide range of nursing specialties, including obstetrics, geriatrics, community health, and psychiatric nursing.
NCLEX Emergency and Disaster Nursing Questions
Emergency and Disaster Nursing NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
A co-worker brings a colleague to the emergency department with a headache, weakness, and slight confusion. The health care provider diagnoses carbon monoxide poisoning. What should the nurse
do first?
(a) Initiate gastric lavage.
(b) Maintain body temperature.
(c) Administer 100% oxygen by mask.
(d) Obtain a psychiatric referral.
Answer:
(c) Administer 100% oxygen by mask.
Explanation:
Carbon monoxide poisoning develops when carbon monoxide combines with hemoglobin. Because carbon monoxide combines more readily with hemoglobin than oxygen does, tissue anoxia results. The nurse should administer 100% oxygen by mask to reduce the half-life of carboxyhemoglobin. Gastric lavage is used for ingested poisons. With tissue anoxia, metabolism is diminished, with a subsequent lowering of the body’s temperature; thus, steps to increase body temperature would be required. Unless the carbon monoxide poisoning is intentional, a psychiatric referral would be inappropriate.
Question 2.
Three hours ago, an adult was thrown from a car into a ditch. The client is now in the emergency department in a stable condition. Vital signs are within normal limits. The client has an open fracture of the right tibia. For which sign should the nurse be especially alert?
(a) hemorrhage
(b) infection
(c) deformity
(d) shock
Answer:
(b) infection
Explanation:
Because of the degree of contamination of the open fracture and the time that has passed since the accident, the risk of infection is very high. Therefore, the nurse should be especially alert for signs and symptoms of possible existing infection or early signs of infections, such as debris in the wound site, temperature abnormalities, results of laboratory studies (such as complete blood cell count and wound culture and sensitivities), or heat or redness around or in the wound.
Because the client’s vital signs and cardiovascular status are stable at this time, hemorrhage is not the primary concern. The client is talking coherently at this point, which does not suggest shock. However, the nurse should continue to assess the client for signs and symptoms of hemorrhage and shock. The fracture would be corrected by surgery as soon as possible, thereby minimizing the risk of deformity.
Question 3.
A client admitted to the emergency department with atrial fibrillation has a heart rate of 160 bpm. The nurse should implement which prescription first?
(a) Administer a heparin bolus.
(b) Administer a beta-blocker.
(c) Administer oxygen via nasal cannula.
(d) Prepare the client for an immediate cardioversion.
Answer:
(c) Administer oxygen via nasal cannula.
Explanation:
The nurse should first administer oxygen; in atrial fibrillation, the workload of the heart is increased, and as a result, myocardial oxygen demands are also increased. A heparin bolus may be prescribed; it is not clear how long the client has been in atrial fibrillation, and it is critical to deter-mine this before treatment is initiated. Beta-blockers and cardioversion are not primary interventions, and it is important first to determine if the client is hemodynamically stable and the length of time the client has had atrial fibrillation.
Question 4.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with atrial fibrillation and does not recall how long the rapid pulse and irregular heart rate has been occurring. The nurse should include which goals of care at this time? Select all that apply,
(a) Convert the heart rate to sinus rhythm.
(b) Decrease cardiac output and workload.
(c) Limit activity to being out of bed.
(d) Maintain a ventricular response below 100 bpm.
(e) Prevent an embolic stroke.
Answer:
(c) Limit activity to being out of bed.
(d) Maintain a ventricular response below 100 bpm.
(e) Prevent an embolic stroke.
Explanation:
(c), (d), (e) Clients who experience atrial fibrillation for more than 48 hours are at an increased risk of developing blood clots due to stasis of blood in the atria. Initially, it will be important to maintain a ventricular heart rate of <100 bpm and prevent complications related to clot formation including an embolic stroke. It is not necessary to limit activities; the client can resume normal activities and slowly increase exercise tolerance. Treating the atrial fibrillation and decreasing the heart rate will help to increase exercise tolerance.
Atrial fibrillation causes a decrease in cardiac output, and a goal of therapy would be to increase cardiac output. It is imperative to determine the length of time a client has been in atrial fibrillation prior to performing a cardioversion. If a client has been in atrial fibrillation longer than 48 hours and a cardioversion is performed, a clot may be dislodged and find its way to the brain, lungs, or coronary arteries.
Question 5.
The nurse is discharging a client who had a fish hook embedded in the eye. The fish hook was removed surgically in the emergency department, but the client currently has no vision in that eye. The surgeon has informed the client that a corneal transplant may restore some vision but the surgery cannot be performed for 6 to 8 weeks and only if no infection occurs. What information should the nurse include in the discharge teaching plan?
(a) resting to reduce strain to the eye and promote healing after surgery
(b) washing hands carefully to keep the area clean and decrease risk of infection
(c) verbalizing feelings regarding vision loss
(d) eating a healthy diet to promote healing and prevent constipation
Answer:
(b) washing hands carefully to keep the area clean and decrease risk of infection
Explanation:
Infection prevention is the immediate priority for this client in order to promote healing and successful corneal transplant with potential restoration of vision. Rest and a diet rich in nutrients and fiber to prevent straining due to constipation are important considerations as well as allowing the client to discuss feelings regarding vision loss. However, these are currently lower priority than infection prevention.
Question 6.
A client is in the emergency department with sneezing and coughing. The client is in the triage area, waiting to be seen by a health care provider. To prevent spread of infection to others in the area and to the health care staff, what should the nurse do?
(a) Place the client in an isolation room.
(b) Ask the others in the area to move away from the client.
(c) Give the client a surgical mask to wear.
(d) Ask the client to wash the hands before being examined.
Answer:
(c) Give the client a surgical mask to wear.
Explanation:
In order to prevent infections in hospitals, the nurse institutes measures to contain respiratory secretions in symptomatic clients. The nurse gives the client a mask to wear and tissues; the nurse instructs the client to dispose of used tissues in a no-touch receptacle. It is not necessary to place the client in isolation. It is not appropriate to ask others to move away from the client, but the nurse can ask the client to keep 3 feet away from others in the waiting room, if there is room.
The nurse instructs the client to perform hand hygiene after blowing his nose or touching his nose or face, but doing so is not a prerequisite for being examined by the HCP E3. The nurse and HCP also use hand hygiene practices when caring for this client.
Also Check: 16 Food Sources To Get All the Boron You Need!
Question 7.
There has been a car accident involving four vehicles on a remote highway. The nearest emergency department is 15 minutes away. Which victim should be transported by helicopter rather than an ambulance to the nearest hospital?
(a) a 10-year-old with a simple fracture of the femur, who is crying and cannot find his parents
(b) a middle-aged female with cold, clammy skin, heart rate of 120 bpm, and is unconscious
(c) middle-aged male with severe asthma, heart rate of 120 bpm, and is having difficulty breathing
(d) an older adult with severe headache, but conscious.
Answer:
(b) a middle-aged female with cold, clammy skin, heart rate of 120 bpm, and is unconscious
Explanation:
The middle-aged female is likely in shock; she is classified as a triage level I, requiring immediate care. The child with moderate trauma is classified as triage level III, urgent, and can be treated within 30 minutes. The man with asthma and the man with the severe headache is classified as emergent, triage level II, and can be transported by ambulance and reach the hospital within 15 minutes.
Question 8.
The nurse notices a fire in a wastebasket in a client’s room. In which order of priority from first to last should the nurse perform the actions? All options must be used.
(a) Confine the fire by closing the door to the client’s room.
(b) Extinguish the fire.
(c) Remove the client from the room.
(d) Pull the fire alarm at the alarm pull station.
Answer:
(c) Remove the client from the room.
(d) Pull the fire alarm at the alarm pull station.
(a) Confine the fire by closing the door to the client’s room.
(b) Extinguish the fire.

Explanation:
(c), (d), (a), (b) The nurse uses the RACE procedure to manage a fire: Rescue, Alarm, Confine, Extinguish.
Question 9.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with a full-thickness burn to the right arm. Upon assessment, the arm is edematous, fingers are mottled, and radial pulse is now absent. The client states that the pain is 8 on a scale of 1 to 10. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Administer morphine sulfate IV push for the severe pain.
(b) Call the health care provider (HCP) to report the loss of the radial pulse.
(c) Continue to assess the arm every hour for any additional changes.
(d) Instruct the client to exercise the fingers and wrist.
Answer:
(b) Call the health care provider (HCP) to report the loss of the radial pulse.
Explanation:
Circulation can be impaired by circumferential burns and edema, causing compartment syndrome. Early recognition and treatment of impaired blood supply is key. The HCP should be informed since an escharotomy (incision through full-thickness eschar) is frequently performed to restore circulation. Pain management is important for burn clients, but restoration of circulation is the priority. Assessments should be performed every 15 minutes when there is the absence of the radial pulse. Exercise will not restore the obstructed circulation.
Question 10.
A client is brought to the emergency department with abdominal trauma following an automobile accident. The vital signs are as follows: heart rate, 132 bpm; respirations, 28 breaths/min; blood pressure, 84/58 mm Hg: temperature, 97.0°F (36.1°C); and oxygen saturation 89% on room air. Which prescription should the nurse implement first?
(a) Administer 1 L 0.9% normal saline IV.
(b) Draw a complete blood count with hematocrit and hemoglobin.
(c) Obtain an abdominal X-ray.
(d) Insert an indwelling urinary catheter.
Answer:
(a) Administer 1 L 0.9% normal saline IV.

Explanation:
The client is demonstrating vital signs consistent with fluid volume deficit, likely due to bleeding and/or hypovolemic shock as a result of the automobile accident. The client will need intravenous fluid volume replacement using an isotonic fluid (e.g., 0.9% normal saline) to expand or replace blood volume and normalize vital signs. The other prescriptions can be implemented once the intravenous fluids have been initiated.
Question 11.
A middle-aged man collapses in the emergency department waiting room. What should the nurse do first?
(a) Ask the client to state his name.
(b) Perform the head tilt/chin lift to open the victim’s airway.
(c) Feel for any air movement from the victim’s nose or mouth.
(d) Watch the client’s chest for respirations.
Answer:
(a) Ask the client to state his name.
Explanation:
Calling the victim’s name and gently shaking the victim is used to establish unresponsiveness. The head-tilt, chin-lift maneuver is used to open the victim’s airway. Feeling for any air movement from the victim’s nose or mouth indicates whether the victim is breathing on his own. The rescuer can watch the victim’s chest for respirations to see if the victim is breathing.
Question 12.
A client is experiencing an allergic response. The nurse should perform the actions in which order from first to last? All options must be used.
(a) Assess for urticaria.
(b) Assess the airway and breathing pattern.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
(d) Active the rapid response team.
Answer:
(b) Assess the airway and breathing pattern.
(a) Assess for urticaria.
(c) Notify the health care provider (HCP).
Explanation:
(b), (a), (c) If a client is experiencing an allergic response, the nurse’s initial action is to assess the client for signs/symptoms of anaphylaxis, first checking the airway, breathing pattern, and vital signs, with particular attention to signs of increasing edema and respiratory distress.
The nurse should then assess for other indications of anaphylaxis, such as urticaria, feelings of impending doom or fright, weakness, sweating (because a severe systemic response to an allergen can result in massive vasodilation), increased capillary permeability, decreased perfusion, decreased venous return, and subsequent decreased cardiac output. The nurse should call the rapid response team Q and then notify the HCP
Question 13.
Proper hand placement for chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is essential to reduce the risk of which complication?
(a) gastrointestinal bleeding
(b) myocardial infarction
(c) emesis
(d) rib fracture
Answer:
(d) rib fracture
Explanation:
Proper hand placement during chest compressions is essential to reduce the risk of rib fractures, which may lead to pneumothorax and other internal injuries. Gastrointestinal bleeding and myocardial infarction are generally not considered complications of CPR. Although the victim may vomit during CPR, this is not associated with poor hand placement, but rather with distention of the stomach.
Question 14.
A visitor to the hospital has a cardiac arrest. When determining to use an automated external defibrillator (AED), the nurse should consider that AEDs are used in cardiac arrest in which circumstances?
(a) early defibrillation in cases of atrial fibrillation
(b) cardioversion in cases of atrial fibrillation
(c) pacemaker placement
(d) early defibrillation in cases of ventricular fibrillation
Answer:
(d) early defibrillation in cases of ventricular fibrillation
Explanation:
AEDs are used for early defibrillation in cases of ventricular fibrillation. The AHA and Canadian Heart and Stroke Foundation place major emphasis on early defibrillation for ventricular fibrillation and use of the AED as a tool to increase sudden cardiac arrest survival rates.
Question 15.
Indicate on the illustration where the nurse would place the other electrode of the automated external defibrillator on a victim who has collapsed and does not have a pulse.
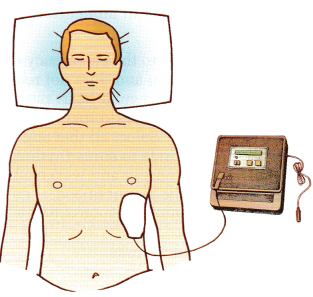
Answer:
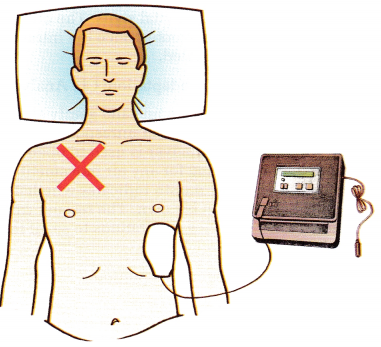
Explanation:
One electrode is placed to the right of the upper sternum just below the right clavicle. The other is placed, as shown, over the fifth or sixth intercostal space at the left anterior axillary line.
Question 16.
An adult has been admitted to the emergency department diagnosed with food poisoning following an outdoor picnic. What should the nurse do? Select all that apply.
(a) Tell the family to discard contaminated food.
(b) Collect specimens for laboratory examination.
(c) Assess vital signs.
(d) Initiate support for the respiratory system.
(e) Monitor fluid and electrolyte status.
(f) Provide antiemetics, as prescribed.
Answer:
(b) Collect specimens for laboratory examination.
(c) Assess vital signs.
(d) Initiate support for the respiratory system.
(e) Monitor fluid and electrolyte status.
Explanation:
(b), (c), (d), (e) Food poisoning is a sudden illness that occurs after ingestion of contaminated food or drink. The nurse should first assess vital signs and then ensure that the client is not in respiratory distress because death from respiratory paralysis can occur with botulism, fish poisoning, and other food poisonings. Measures to control nausea are important to prevent vomiting, which could exacerbate fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
Because large volumes of electrolytes and water are lost by vomiting and diarrhea, fluid and electrolyte status needs to be continuously monitored. The key to treatment is determining the source and type of food poisoning. If possible, rather than discarding the food, the suspected food should be brought to the medical facility and a history obtained from the client or family.
Question 17.
A client is admitted to the emergency department after being found in a daze walking away from her burning car after an accident. She was not injured in the accident, but the other driver died. She states, “I can't handle it anymore. There’s no point to it all.” The crisis nurse recommends hospital admission based on the identification of which concern?
(a) The client was walking around in a daze.
(b) The client has a lack of knowledge of what to do next.
(c) The client is having delusions and is not in touch with reality.
(d) The client is expressing helplessness and hopelessness and is a risk for suicide.
Answer:
(d) The client is expressing helplessness and hopelessness and is a risk for suicide.
Explanation:
The client is demonstrating helplessness and hopelessness during a crisis, as evidenced by her statement, “I can’t handle it. There’s no point to it.” Feelings of helplessness and hopelessness are common factors associated with suicidal ideation. Therefore, the client must be hospitalized to ensure safety to herself. There is not sufficient information to know if the client has a lack of knowledge of what to do next. The client is not having delusions, which would be evidenced by statements such as ‘‘The devil set my car on fire,” not just the inability to think clearly.
Question 18.
The nurse in the emergency department reports there is a possibility of having had direct contact with blood of a client who is suspected of having HIV/AIDS. The nurse requests that the client have a blood test. Consent for HIV testing can only be completed when which circumstances are present? Select all that apply.
(a) An emergency medical provider has been exposed to the client’s blood or body fluids.
(b) Testing is prescribed by a health care provider (HCP) under emergency circumstances.
(c) Testing is prescribed by a court, based on evidence that the client poses a threat to others.
(d) Testing is done on blood collected anonymously in an epidemiologic survey.
(e) An HCP who is taking care of a client suspected of having HIV/AIDS requests a blood test.
Answer:
(a) An emergency medical provider has been exposed to the client’s blood or body fluids.
(b) Testing is prescribed by a health care provider (HCP) under emergency circumstances.
(c) Testing is prescribed by a court, based on evidence that the client poses a threat to others.
(d) Testing is done on blood collected anonymously in an epidemiologic survey.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) Upon an HCP’s D written prescription requesting an HIV test for a client, consent y3 for HIV testing must be obtained. Consent exceptions include the following: testing is prescribed by an HCP under emergency circumstances, and the test is medically necessary to diagnose or treat the client’s condition; testing is prescribed by a court, based on clear and convincing evidence of a serious and present health threat to others posed by an individual; testing is done on blood collected or tested anonymously as part of an epidemiologic survey; or an emergency medical provider has been exposed to the client’s blood or body fluids.
Question 19.
Thirty people were injured in a train derailment. Which client should be transported to the hospital first?
(a) a 20-year-old who is unresponsive and has a high injury to his spinal cord
(b) a BO-year-old who has a compound fracture of the arm
(c) a b-year-old with a laceration on his leg
(d) a 25-year-old with a sucking chest wound
Answer:
(d) a 25-year-old with a sucking chest wound
Explanation:
During a disaster, the nurse must make difficult decisions about which persons to treat first. The guidelines for triage offer general priorities for immediate, delayed, minimal, and expectant care. The client with a sucking chest wound needs immediate attention and will likely survive.
The 80-year-old is classified as delayed; emergency response personnel can immobilize the fracture and cover the wound. The 10-year-old has minimal injuries and can wait to be treated. The client with a spinal cord injury is not likely to survive and should not be among the first to be transported to the health care facility.
Question 20.
An explosion at a chemical plant produces flames and smoke. More than 20 persons have burn injuries. Which victims, all adults, should be transported to a bum center? Select all that apply.
The victim who has:
(a) chemical spills on both arms
(b) third-degree burns of both legs
(c) first-degree burns of both hands
(d) respiratory distress
(e) inhaled smoke
Answer:
(a) chemical spills on both arms
(b) third-degree burns of both legs
(c) first-degree burns of both hands
(d) respiratory distress
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) Victims with chemical burns, second-and third-degree burns over more than 20% of their body surface area, and those with inhalation injuries should be transported to a burn center. The victim with first-degree burns of the hands can be treated with first aid on the scene and referred to a health care facility.
Question 21.
An apartment fire spreads to seven apartment units. Victims suffer burns, minor injuries, and broken bones from jumping from windows. Which client should be transported first?
(a) a woman who is 5 months pregnant with no apparent injuries
(b) a middle-aged man with no injuries who has rapid respirations and coughs
(c) a 10-year-old with a simple fracture of the humerus who is in severe pain
(d) a 20-year-old with first-degree burns on her hands and forearms
Answer:
(b) a middle-aged man with no injuries who has rapid respirations and coughs
Explanation:
The man with respiratory distress and coughing should be transported first because he is probably experiencing smoke inhalation. The pregnant woman is not in imminent danger or likely to have a precipitous birth. The 10-year-old is not at risk for infection and could be treated in an outpatient facility. First-degree burns are considered less urgent.
Question 22.
There is a shooting in a shopping mall. Three victims with gunshot wounds are brought to the emergency department. What should the nurse do to preserve forensic evidence? Select all that apply.
(a) Cut around blood stains to remove clothing.
(b) Place each item of clothing in a separate paper bag.
(c) Hang wet clothing to dry.
(d) Refrain horn documenting client statements.
(e) Place bullets in a sterile container.
Answer:
(b) Place each item of clothing in a separate paper bag.
(c) Hang wet clothing to dry.

Explanation:
(b), (c) Preserving forensic evidence is essential for investigative purposes following injuries that may be caused by criminal intent. The nurse should put each item of clothing in a separate paper bag and label it; wet clothing should be hung to dry. The nurse should not cut or otherwise unnecessarily handle clothing, particularly clothing with such evidence as blood or body fluids.
The nurse should document carefully the client’s description of the incident and use quotes around the client’s exact words where possible. The documentation will become a part of the client’s record and can be subpoenaed for subsequent investigation. The nurse should not handle bullets from the client because they are an important piece of forensic evidence
Question 23.
An airplane crash results in mass casualties. The nurse is directing personnel to tag all victims. Which information should be placed on the tag? Select all that apply.
(a) triage priority
(b) identifying information when possible (such as name and age)
(c) medications and treatments administered
(d) presence of jewelry
(e) next of kin
Answer:
(a) triage priority
(b) identifying information when possible (such as name and age)
(c) medications and treatments administered

Explanation:
(a), (b), (c) Tracking victims of disasters is important for casualty planning and management. All victims should receive a tag, securely attached, that indicates the triage priority, any available identifying information, and what care, if any, has been given along with time and date. Tag information should be recorded in a disaster log and used to track victims and inform families. It is not necessary to document the presence of jewelry or next of kin.
Question 24.
Four people who have been injured in a car accident are admitted to the emergency department. Using the emergency severity index (ESI), in which order from first to last should the victims be seen by a health care provider (HCP)? All options must be used.
(a) an adult with severe bleeding from a lacreation in the leg.
(b) a child with lacreations on the arm and legs.
(c) an adult with a history of asthma and respiration of 30 breaths/min.
(d) an older adult with normal vital signs, but is confused.
Answer:
(a) an adult with severe bleeding from a lacreation in the leg.
(b) a child with lacreations on the arm and legs.
(c) an adult with a history of asthma and respiration of 30 breaths/min.
(d) an older adult with normal vital signs, but is confused.
Explanation:
(a), (b), (c), (d) Using the ESI, the nurse should triage the clients to be seen by an HCP Q as follows: the adult with severe bleeding is categorized as level 1, life threatening and should be seen first; the adult with asthma and rapid bleeding is in the emergent category and should be seen next; the child with lacerations is categorized as less urgent and can be seen next; and the older adult has vital signs within normal range and is assessed as being nonurgent and can be seen last.
Question 25.
A small airplane crashes in a neighborhood of 10 houses. One of the victims appears to have a cervical spine injury. What should first aid for this victim include? Select all that apply.
(a) Establish an airway with the jaw-thrust maneuver.
(b) Immobilize the spine.
(c) Logroll the victim to a side-lying position.
(d) Elevate the feet 6 inches (15.2 cm).
(e) Place a cervical collar around the neck.
Answer:
(a) Establish an airway with the jaw-thrust maneuver.
(b) Immobilize the spine.
Explanation:
(a), (b) The victim of a neck injury should be immobilized and moved as little as possible. It is also important to ensure an open airway; this can be accomplished with the jaw-thrust maneuver, which does not require tilting the head. The victim should not be rolled to a side-lying position nor have his feet elevated. Both actions can cause additional injury to the spinal cord. Placing a cervical collar causes movement of the spinal column and should not be done as a first aid measure.
Question 26.
Thirty-two children are brought to the emergency department after a school bus accident. Two children were killed along with the three people in the car that caused the crash. Before the victims arrive, in addition to ensuring that the hospital staff are prepared for the emergency, which step should the nurse anticipate carrying out?
(a) calling the nearest crisis response team
(b) alerting the news media
(c) notifying the hospital volunteer office
(d) calling the school to inform teachers of the accident
Answer:
(a) calling the nearest crisis response team
Explanation:
The children and their families are at risk for experiencing a crisis. Disaster teams are available for crisis intervention in such emergencies. Usually, the news media monitors emergency radio frequencies and most likely are aware of the accident already. Although volunteers may help in some ways, they are not responsible for crisis intervention. Calling the school might be done, but the emergency issues take precedence.
Question 27.
The nurse in the emergency department is triaging victims of an airplane crash. Prioritize the clients in the order in which they should be treated from first to last. All options must be used.
(a) a 75-year-old with a 2-inch (5.1-cm) laceration to the left forearm
(b) a 22-year-old with a 2-inch (5.1-cm) laceration j to the left temple, slightly confused
(c) a 14-year-old with a 2-inch (5.1-cm) laceration to the chin, history of asthma, respirations 26 breaths/min, audible wheezing
(d) a 22-year-old female, 36 weeks pregnant with contractions every 10 to 15 minutes
Answer:
(c) a 14-year-old with a 2-inch (5.1-cm) laceration to the chin, history of asthma, respirations 26 breaths/min, audible wheezing
Explanation:
(c), The 14-year-old with asthma needs immediate, lifesaving interventions for the wheezing and should be seen first. The 22-year-old who is confused should be seen next to assess for head injury; the location of the laceration could indicate a significant blunt force traumatic injury. The pregnant female requires assessment but is not urgent unless other symptoms appear. The 75-year-old is nonurgent and can wait safely for several hours.
Question 28.
A suspected outbreak of anthrax has been transmitted by skin exposure. A client is admitted to the emergency department with lesions on the hands. The health care provider prescribes antibiotics and sends the client home. What should the nurse instruct the client to do? Select all that apply.
(a) Take the prescribed antibiotics for 60 days.
(b) Avoid contact with other members of the family during the treatment period.
(c) Wear a mask for 60 days.
(d) Expect the skin lesions to clear up within 1 to 2 weeks.
(e) Wash hands frequently.
Answer:
(d) Expect the skin lesions to clear up within 1 to 2 weeks.
Explanation:
Anthrax is treated with antibiotics, and the client must continue the prescription for 60 days, even if symptoms do not persist. The client may have skin lesions at the point of contact, with macula or papule formation; the eschar will fall off in 1 to 2 weeks. Clients with anthrax are not conta-gious; the client does not need to follow isolation procedures at home. Anthrax from skin exposure is not transmitted by respiratory contact, and the client does not need to wear a mask.
Question 29.
A severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) epidemic is suspected in a community of 10,000 people. As clients with SARS are admitted to the hospital, what type of precautions should the nurse institute?
(a) enteric precautions
(b) handwashing precautions
(c) reverse isolation precautions
(d) airborne precautions
Answer:
(d) airborne precautions
Explanation:
Transmission of SARS can be contained by airborne precautions that include an isolation room with negative pressure, use of N95 respirator, and use of personal protective equipment. The disease is spread by the respiratory, not enteric, route. Handwashing alone is not sufficient to prevent transmission. Reverse isolation (protection of the client) is not sufficient to prevent transmission.
Question 30.
Several clients who work in the same building are brought to the emergency department. They all have fever, headache, a rash over the entire body, and abdominal pain with vomiting and diarrhea. Upon initial assessment, the nurse finds that each client has low blood pressure and has developed petechiae in the area where the blood pressure cuff was inflated. Which isolation precautions should the nurse initiate?
(a) contact isolation with double gloving and shoe covers
(b) respiratory isolation with positive pressure rooms
(c) enteric precautions
(d) reverse isolation
Answer:
(a) contact isolation with double gloving and shoe covers
Explanation:
The nurse should institute treatment for hemorrhagic fever viruses, including contact isolation with double gloving and shoe covers, strict hand hygiene, and protective eyewear. The nurse should start respiratory isolation with negative pressure rooms, not positive pressure rooms. Enteric precautions are not needed because the vims is spread by droplet and contact. Reverse isolation protects the client; in this situation, the health care team also needs protection.
Question 31.
Eight farm workers are admitted to the emergency department after they were splashed with “a couple of chemicals” at work 30 minutes ago. They have watery/itchy eyes, slight cough, diaphoresis, and constricted pupils and are conscious and oriented. Their clothes are wet. What action should the nurse do first?
(a) Apply oxygen at 3 L per nasal cannula.
(b) Remove their clothing.
(c) Begin decontamination shower.
(d) Isolate the clients.
Answer:
(d) Isolate the clients.

Explanation:
The safety of the staff and others is the first priority. Isolating reduces the chance of contaminating others (secondary contamination). Vital signs can be obtained when it is safe after protecting staff, clients, and visitors from secondary contamination. Oxygen is not indicated for any of the listed symptoms. Removing clothing is important to prevent further exposure to the client, but must be done in a safe manner to prevent secondary contamination to others.
The clients can remove their own clothes and place them in plastic bags. After the safety of the staff and others is addressed, and the facility is prepared and properly trained staff is ready, the clients can be given a decontamination shower. If the staff is not trained, 911 may be the most appropriate response. Finding out which chemicals were involved is important but does not take priority over preventing secondary contamination
Question 32.
The nurse is triaging victims of an earthquake who were removed from a building following its collapse. Which victims should be classified as red? Select all that apply.
(a) a 10-year-old male with crushing chest wound, tachypnea with labored breathing, unconscious, impaled object in the forehead.
(b) a 49-year-old male with crushing chest pain radiating to the jaw, is diaphoretic, nauseated, and has an open fracture of the left wrist.
(c) a 75-year-old female with obvious fracture of the femur, absent pedal pulses on the affected side; heart rate 110 bpm, respirations 34 breaths/min, skin diaphoretic; awake/alert, states pain is 10 on a scale of 1 to 10.
(d) a 32-year-old female who is unconscious, 3-inch (7.6-cm) laceration to her forehead, ecchymosis behind the ears, respiratory rate 10 breaths/min and shallow; radial pulse is weak/thready/rapid; no breath sounds on the right side.
Answer:
(b) a 49-year-old male with crushing chest pain radiating to the jaw, is diaphoretic, nauseated, and has an open fracture of the left wrist.
(c) a 75-year-old female with obvious fracture of the femur, absent pedal pulses on the affected side; heart rate 110 bpm, respirations 34 breaths/min, skin diaphoretic; awake/alert, states pain is 10 on a scale of 1 to 10.
Explanation:
(b), (c) The client with crushing chest pain has an acute cardiac condition and can have a successful outcome if immediate interventions are initiated. The client with the open fracture could be stabilized and is not a significant factor in triage in a mass casualty incident. The client with a displaced femur fracture can also be classified as immediate because the fracture can impair circulation. There are also signs of shock and severe pain.
All conditions can improve with interventions. In a mass casualty incident, the goal is to do the greatest good for the greatest number which sometimes means that limited resources are not allocated to the very critically injured who have a very low probability of survival. The other two clients are categorized as “black”/ expectant because of their critical injuries and the unavailability of advance trauma care.
Question 33.
The nurse is assessing the client (see photo) who has recently returned from a 2-month mission in Africa. What type of respiratory protection is appropriate for the staff?
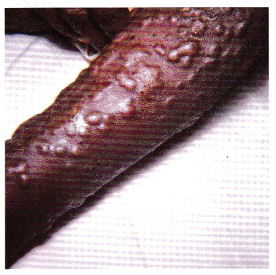
(a) N95 particulate respirator
(b) double-layered surgical mask
(c) surgical mask with eye shield
(d) no respiratory protection needed
Answer:
(a) N95 particulate respirator
Explanation:
Any type of blistering lesion, such as smallpox, requires extreme care to prevent exposure. Transmission-based precautions for smallpox includes airborne, droplet, and contact precautions. The N95 mask filters at least 95% of airborne particles. To prevent exposure through the respira-tory tract, the N95 mask must be fitted and worn properly.
Question 34.
A client who was a victim of a gunshot wound was treated in the emergency department and died. What should the nurse direct the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) to do during postmortem care? Select all that apply.
(a) Remove all tubes and IV lines.
(b) Cover the body with a sheet.
(c) Notify the family.
(d) Transport the body to the morgue.
(e) Notify the chaplain.
Answer:
(b) Cover the body with a sheet.
(d) Transport the body to the morgue.
Explanation:
(b), (d) The UAP can cover the body and transport it to the morgue. Deaths by gunshot wound are considered reportable deaths. All evidence in a reportable death, including tubes and IV lines, should remain intact until the coroner has been contacted. The health care provider (HCP) should be the one to notify the family. The nurse should be the one to notify the chaplain.
Question 35.
The nurse in the emergency department is administering a prescription for 20 mg intravenous furosemide, which is to be given immediately. The nurse scans the client’s identification band and the medication barcode. The medication administration system does not verify that furosemide is prescribed for this client; however, the furosemide is prepared in the accurate unit dose for intravenous infusion. What should the nurse do next?
(a) Contact the pharmacist immediately to check the prescription and the barcode label for accuracy.
(b) Administer the medication now, knowing the medication is labeled and the client is identified.
(c) Report the problem to the information technology team to have the barcode system recalibrated.
(d) Ask another nurse to verify the medication and the client so the medication can be given now.
Answer:
(a) Contact the pharmacist immediately to check the prescription and the barcode label for accuracy.
Explanation:
The nurse should contact the pharmacist first to be sure the medication is labeled for administration to this client. The nurse should not administer the drug until all safety precautions have been observed; the nurse should also not ask another nurse to verify the medication or client. Later, if the problem cannot be resolved with relabeling the medication, the nurse or pharmacist can contact the information technology team to check the barcode system.
Question 36.
The nurse notices a pair of nervous-acting individuals entering the emergency department. When reporting suspicious activity, the nurse should include which information in the report? Select all that apply.
(a) vehicle/vehicles description
(b) current location of parties involved
(c) names and phone numbers of parties involved
(d) relationship to hospitalized client
(e) tone of voice of each party involved
Answer:
(b) current location of parties involved
Explanation:
All suspicious individuals or activities should be reported as soon as possible to the security department. When reporting an incident, nurses/employees should provide the following: (a) type of incident, (b) persons involved/physical description, (c) vehicles involved and description, (d) date and time the incident occurred, (e) location where the incident occurred, (f) weapons involved, and (g) current location of parties involved. All reports of threats, actual episodes of violence, or suspicious individuals or activities must be investigated.
Question 37.
There has been an increase in medication errors and errors in prescribing laboratory studies in the emergency department. The nurse manager is conducting a staff education session on when to use “read-back” procedures. “Read-back” procedures should be performed in which situations? Select all that apply.
(a) when a medication prescription or critical laboratory result is received verbally or over the telephone
(b) when any verbal or phone prescription is received
(c) whenever a written prescription or printed critical test result is received
(d) when the unit secretary takes a phone prescription
(e) when the agency uses computerized health care records
Answer:
(a) when a medication prescription or critical laboratory result is received verbally or over the telephone
(b) when any verbal or phone prescription is received
Explanation:
(a), (b) A goal of client safety is to improve the effectiveness of communication among caregivers. For verbal or telephone prescriptions, or for telephone reporting of critical test results, one must verify the complete prescription or test result by having the individual receiving the information record “read-back” the complete prescription or test result. The unit secretary is not a licensed health care professional who has a scope of practice or the authority to receive prescriptions or results. The type of charting system used by the health care agency is not a factor in using “read-back” prescriptions.
Question 38.
Which client admitted to the emergency department should the nurse see first?
(a) a client experiencing a “ripping” sensation in the chest
(b) a client with a blood pressure of 170/95 mm Hg
(c) a client with a urine output of 240 mL in 12 hours
(d) a client taking anticoagulants with bloody stool
Answer:
(a) a client experiencing a “ripping” sensation in the chest
Explanation:
A client experiencing a “ripping” sensation in the chest is indicative of a ruptured thoracic aneurysm and warrants an immediate intervention. While a blood pressure of 170/95 mm Hg is high, there is not enough information that suggests that this client is a higher priority than the others. A urine output of 240 mL in 12 hours is < 30 mL/h; however, this is this client’s only problem now, and the nurse can investigate the cause next. A client experiencing bloody stools will need to be seen; however, no other information is present that would warrant this client being seen first.
