The process of reasoning through Practice NCLEX Questions sharpens students' clinical judgment and decision-making abilities.
NCLEX Cardiovascular System/Circulatory Disorders Questions
Cardiovascular System/Circulatory Disorders NCLEX Practice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following diagnostic studies is most useful in providing a definitive diagnosis of angina?
(a) Electrocardiography
(b) Stress testing
(c) Cardiac enzyme and troponin levels
(d) Cardiac catheterization
(e) Magnetic resonance imaging
Answer:
(d) Cardiac catheterization
Explanation:
Cardiac catheterization (Option d) is the most useful diagnostic study in providing a definitive diagnosis of angina as it provides information about the patency of the coronary arteries. This test involves inserting a catheter into the heart and injecting contrast dye to visualize the coronary arteries. Electrocardiography (Option a) can provide important information about the heart's electrical activity during an episode of pain, but it is not a definitive diagnostic tool for angina.
Stress testing (Option b) can also provide information about the presence of myocardial ischemia, but it is not as definitive as cardiac catheterization. Cardiac enzyme and troponin levels (Option c) are useful in diagnosing myocardial infarction but are not diagnostic for angina. Magnetic resonance imaging (Option e) can provide detailed images of the heart and blood vessels but is not routinely used in the diagnosis of angina.
Question 2.
Mrs. Alvin has recently had a pacemaker implanted. Which of the following should be included in her client education?
(a) Wear tight clothing over the pacemaker site.
(b) Participate in contact sports.
(c) Inform airport security about the pacemaker.
(d) Operate electrical appliances directly over the pacemaker site.
Answer:
(c) Inform airport security about the pacemaker.
Explanation:
The correct answer is C. Inform airport security about the pacemaker. This is important as the pacemaker may set off the security detector, and it's necessary to inform the security personnel before going through the detector. This helps to avoid unnecessary delays and inconvenience.
Option (a) is incorrect because Mrs. Alvin should wear loose-fitting clothing over the pacemaker site to avoid any discomfort or pressure on the pacemaker.
Option (b) is incorrect because Mrs. Alvin should avoid contact sports to prevent any damage to the pacemaker or leads.
Option (d) is incorrect because Mrs. Alvin should not operate electrical appliances directly over the pacemaker site as this can interfere with the functioning of the pacemaker. Instead, she should maintain a distance of at least 6 inches from electrical devices and avoid transmitter towers and antitheft devices in stores.
Therefore, the correct answer is (c). Inform airport security about the pacemaker, as it is crucial for ensuring the safe passage of Mrs. Alvin through security and preventing any complications.
Question 3.
A patient’s blood profile showed high blood level of triglycerides (525 mg/dl). He is prescribed with Atorvastatin to manage the high Triglyceride and LDL level. Which of the following advice would you give to the patient ?
(a) Do not take supplemental vitamin B3 when you are taking atorvastatin.
(b) Take the medicine early at morning.
(c) Take a moderate amount of alcohol during the treatment.
(d) Take plenty of fluids and grapefruit juice during treatment period.
Answer:
(a) Do not take supplemental vitamin B3 when you are taking atorvastatin.
Strategy:
This question requires specific knowledge about Atorvastatin. This is a type of anti-lipid that reduce the level of lipids and lipoproteins in the blood. They reduce the cholesterol. So these are basically used in the coronary artery diseases. Also, remember, whenever, you see options where grapefruit juice is mentioned there is high probability of interaction between the drug in question and the ‘grapefruit juice’ as it interacts with many drugs.
One of the side effects of anti-ipids is muscle soreness. Consuming niacin (vitamin B3) supplements along with a statin medication may worsen muscle soreness.
For option (b), These drugs are basically given at night because most cholesterol is synthesised when dietaiy intake is at its lowest. For option (c), Statins affect the liver and so does alcohol.
Statins should not be taken if you have severe liver disease or if blood tests suggest that your liver may not be working properly or alcohol should be stopped during the therapy. For option (d), With grapefruit juice, the statins level in the blood can increase so you should not give grapefruit and statins at the same time to a patient.
Question 4.
A patient with a history of heart attack is on warfarin drug therapy. Which of the following can be advised to the patient ?
(a) Proper oral care by brushing with soft brashes and hygiene should be followed.
(b) Change your diet to nutritious green leafy vegetables such as spinach, cabbage, broccoli, collard greens, lettuce etc.
(c) Alcoholic beverages can be taken occassionally only.
(d) Side effects such as blood in the stool and urine are normal for drags in this class.
Answer:
(a) Proper oral care by brushing with soft brashes and hygiene should be followed.
The drug may cause bleeding from the gums. Proper oral hygiene and brushing with soft bristle brushes should be done. Option (b) is incorrect. Changes in diet or use of other drugs can alter their risk of bleeding and/or clotting, sudden change in diet such as spinach, cabbage, broccoli, collard greens, lettuce which contains vitamin k should be avoided.
Option (c) is incorrect. The patient shouldn't take any alcoholic beverages as it interferes with the drug. Option (d) is incorrect. A black box warning is the FDA's most stringent warning for drugs and medical devices on the market. Warfarin can cause major or fatal bleeding. So whenever, you see such conditions the health care worker must be informed.
Question 5.
Ms. Ranjan, a 45-year-old woman, was diagnosed with hypertension during her recent visit to her healthcare provider. She was prescribed medications and advised to follow a treatment plan to control her blood pressure. You are her nurse and have been assigned to educate her about her condition and the importance of compliance with the treatment plan.
Which of the following instructions should be included in the education plan for Ms. Ranjan?
(a) Explain the disease process, emphasizing that symptoms usually develop early on.
(b) Advise Ms. Ranjan to engage in heavy weight-lifting and isometric exercises to improve her blood pressure.
(c) Encourage Ms. Ranjan to express her feelings about daily stress and assist her to identify ways to reduce stress.
(d) Instruct Ms. Ranjan to stop taking her medication if she experiences uncomfortable side effects.
(e) Provide a list of high-fat and high-calorie foods that are allowed in her diet.
(f) Instruct Ms. Ranjan to consume canned foods to ensure freshness.
(g) Stress the importance of follow-up care and regular monitoring of her blood pressure.
Answer:
(c) Encourage Ms. Ranjan to express her feelings about daily stress and assist her to identify ways to reduce stress.
(g) Stress the importance of follow-up care and regular monitoring of her blood pressure.
Explanation:
(a) is incorrect because hypertension is often asymptomatic until it has progressed to a more serious stage. (b) is incorrect because heavy weight-lifting and isometric exercises can cause a sudden increase in blood pressure and should be avoided by individuals with hypertension. (d) is incorrect because stopping medication without consulting with a healthcare provider can have serious consequences on the management of hypertension.
(e) is incorrect because a diet high in fat and calories can lead to weight gain and further complications in hypertension. (f) is incorrect because canned foods often contain high amounts of sodium and should be avoided in the diet of someone with hypertension. (c) is correct because reducing stress is important in managing hypertension, and expressing feelings and identifying ways to reduce stress can be beneficial. (g) is correct because follow up care and monitoring of blood pressure are essential in ensuring that the treatment plan is effective and preventing complications.
Question 6.
A patient with blood loss from an accident is transfused with blood. The patient complains of headache, tachycardia and chest pain. Upon investigation, circulatory overload was suspected. Which of the following nursing procedure would you follow ?
(a) Increase the rate of infusion so that the blood transfusion can be done quickly.
(b) Stop the blood transfusion immediately.
(c) Give IV deferoxamine.
(d) Decrease the rate of infusion and keep the patient in upright position.
Answer:
(d) Decrease the rate of infusion and keep the patient in upright position.
Explanation:
Circulatory overload is caused by administration of blood volume at a rate greater than the circulatory system can tolerate. If circulatory overload is suspected, the rate of infusion must be slowed and patient must be kept in upright position. IV deferoxamine is treatment of choice for iron overload. It can be given to remove the iron from the body. You must tell the patient that its completely normal for the urine to turn red as this is the excreted iron from the body.
Question 7.
A registered nurse at critical care division is assessing an electrocardiogram rhythm strip. She observes the following reading Regular P wave, QRS wave and T wave.
Heart rate 69 beats per minute
PR interval = 0.14
QRS interval = 0.08 seconds
QT interval = 0.2 seconds
What can she infer from these readings?
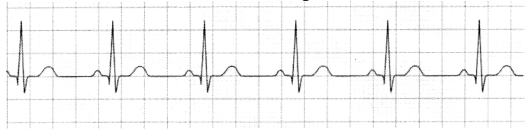
(a) This is a normal sinus rhythm.
(b) There is a problem with rhythmic contraction of ventricles.
(c) The PR interval is not normal.
(d) The QRS interval is not within the requirement for normal sinus rhythm.
Answer:
The first option is correct answer here. The conditions for normal sinus rhythm are:
- P width should be 0.12 to 0.20 seconds
- QRS width is 0.04 to 0.12 seconds
- Q-T interval < 0.4 seconds
Since the parameters given obeys all the acceptance criteria for normal sinus rhythm, it is a normal sinus rhythm.
Question 8.
Can you identify the criteria for which the following diagram doesn't obey the normal sinus rhythm from this ecg strip?
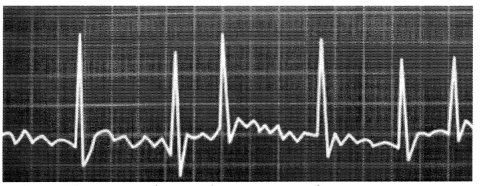
(a) The waves interval are not regular,
(b) The amplitude of the wave varies.
(c) The QRS interval is out of shape.
(d) The P wave is missing at some places.
Answer:
The correct answer to this question is 'the intervals are not regular' this is quite obvious from the diagram too.
Question 9.
A client is complaining of dizziness and has shortness of breath. She shows heart rate of 42 beats per minute and upon reading, the BP it is clear than hypotension with a reading of 85/55. Which of the following could be the causes of this problem?
(a) Her blood glucose level of 100
(b) She is prescribed atropine
(c) She could be suffering from some viral ever.
(d) She is prescribed digoxin
Answer:
(d) She is prescribed digoxin
Explanation:
The correct answer to this question is the last option that is 'She is prescribed with digoxin'. We learnt that certain drugs such as digoxin cause bradycardia and these all symptoms that she is showing such as dizziness, shortness of breath and hypotension are the symptoms of bradycardia.
Question 10.
A patient is feeling weak, lethargic and dizzy. Look at the following ECG strip reading. What problem can you identify the problem with this ecg reading?
S PR interval 0.18 seconds
QRS interval 0.06 seconds
S QT interval 0.2 seconds.
S Heart rate = 50 BPM
BP 80/60 Your options are :
(a) She has a normal sinus but low pressure
(b) She has bradycardia
(c) She has tachycardia
(d) She could have some heart blockade.
Answer:
The correct answer to this question is She has bradycardia. She shows the symptoms of bradycardia and her vital EKG details also matches to that of bradycardia.
Question 11.
The nurse notices some symptoms of supraventricular tachycardia such as sudden drop in BP to the level of 65/40 and feeling dizziness with a heart rate of 220 beats per minute. What should the nurse do as a management approach?
(a) Administer Beta Blocker
(b) Administer Atropine
(c) Administer Epinephrine.
(d) Administer Adenosine.
Answer:
(d) Administer Adenosine.
Explanation:
Options (a) is incorrect as betablockers can further decrease the blood pressure. The patient is already suffering from hypotension. Second option, atropine is also not correct as it can increase the heart rate. The heart rate is already very high and may lead to heart failure. The 3rd option epinephrine is also out of box as there is no use of it and it further increase the heart rate.
The last option that is administration of adenosine is correct one. Adenosine is given in rapid intravenous (IV) bolus injection into a vein or into an IV line. When given as a rapid IV bolus, adenosine slows cardiac conduction particularly affecting conduction through the AV node. Remember, to watch out for too frequent QRS complexes with P wave completely absent or masked by T waves in the EKG strip to identify the supraventricular tachycardia with underlying symptoms such as very high heart rate and low BP and Dizziness in patients.
Question 12.
Which of the following EKG strip shows the atrial fibrillation?
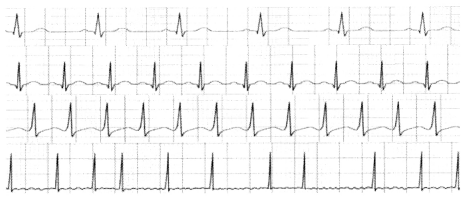
Answer:
- The first strip is for normal sinus.
- The second for sinus tachycardia.
- The third is for supraventricular tachycardia and the correct answer is the last option.
You can see that the strip for supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation is lot similar but still you can identify it with supraventricular tachycardia as atrial fibrillation is very unrythmic. We know that supraventricular tachycardia has normal rhythm and supraventricular tachycardia shows frequent QRS complex. So, you won't see much any other waves in between these QRS complex in supraventricular tachycardia.
Question 13.
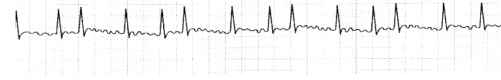
In which of the following conditions is the P wave absent? The options are:
(a) Tachycardia
(b) Atrial Fibrillation
(c) Bradycardia
(d) Atrial Flutter.
Answer:
(b) Atrial Fibrillation
(d) Atrial Flutter.
Explanation:
The correct answer to this question is atrial fibrillation. Options Tachycardia and bradycardia are not correct nor is atrial flutter. In atrial flutter, in fact, we see multiple P waves in between each QRS complex as shown in the figure below:
Question 14.
Which of the conditions can you infer from the following EKG Strips? ’
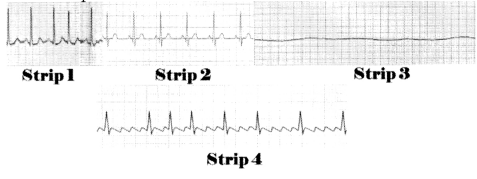
Answer:
Strip 1:
This is an atrial fibrillation. As we see, the P wave is absent, the rhythm is irregular and frequent in atrial fibrillation. You should see the following multiple small blunt waves and also as we discussed these wave patterns are very irregular.
Strip 2: This could be normal sinus. There is normal P QRS complex and T wave. Also, we are given normal heart rate of 75 BPM w'hich is between the resting heart rate of 60 to 100 BPM.
Strip 3: This is asystole, there is not any electrical activity or any wave patterns in EKG strip.
This is atrial flutter. As we discussed, this can be identified with identifiers such as:
- Extremely high heart rate between 250-350 beats per minute.
- The rate is regular.
- The P waves are well defined and shows a saw-tooth pattern.
Question 15.
The EKG strip of client shows following reading:
Which of the following is true regarding this condition?
(a) Could be better with defibrillation.
(b) This is Aystole.
(c) The QRS complex is weak and not rythmic.
(d) The heart rate is very low in this condition.
Answer:
(b) This is Aystole.
Explanation:
(a) and (c) Option are not correct. The P wave and QRS complex are totally absent in asystole. (d) option is incorrect. The rate is 0.
Question 16.
Which of the following could be nursing intervention for the patients with MI ?
(a) Administer Morphine
(b) Administer supplemental oxygen.
(c) Sedate the patient.
(d) See ECG findings to help to identify Ml and locate the position of MI
Answer:
(a) Administer Morphine
(b) Administer supplemental oxygen.
(d) See ECG findings to help to identify Ml and locate the position of MI
Question 17.
Which of the following ecg reading is of Mayocardial infarction.
You are given with 4 types of heart blocks in EKG strip. Your job is to identify the type of heart block.
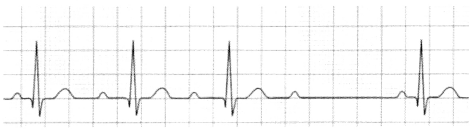
This is grade 2 type 1 heart block. In this EKG strip, we can see progressive increase in PR interval.
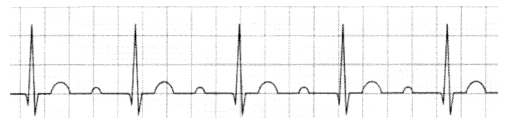
This is type 1 AV block. We can see that the PR interval is constant but wider.
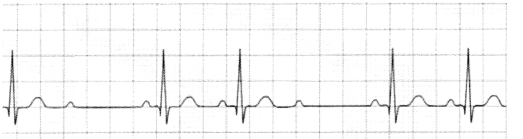
This is grade 2 type 2 heart block. We are seeing 2 normal PR and then the P wave is not followed by QRS complex.
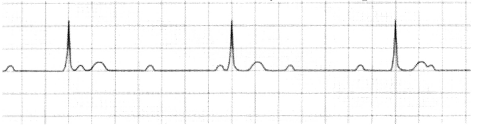
This is grade 3 heart block. P wave is multiple and few QRS complex. There is a complete dissociation or no relation between occurrence of P wave and QRS complex.
Question 18.
A patient is admitted to the emergency room with a myocardial infarction. The patient’s blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg. Upon assessing the patient, what should the nurse expect to find as an early assessment for this patient?
(a) Heart rate 130 bpm
(b) Troponin I 0.02 ng/mL
(c) Right arm pain
(d) Respiratory rate at 10 bpm
Answer:
(a) Heart rate 130 bpm
Explanation:
A myocardial infarction occurs when a coronary artery is blocked. This reduces the oxygenated blood supply to a portion of the myocardium (heart muscle). The affected muscle starts to infarct, or die, decreasing its ability to contract. This leads to decreased cardiac output. Typical signs and symptoms include hypotension, tachycardia, decreased oxygen saturation, chest pain, shortness of breath, left arm pain and numbness, nausea, vomiting, and anxiety.
Rationale:
(a) is correct because when blood pressure is decreased, baroreceptors in the aortic arch sense the decreased pressure within the vessels. In response, the parasympathetic system lessens sinoatrial node inhibition, thereby increasing heart rate as well as respiratory rate. Tachycardia is an early sign that begins before blood pressure is critically low. The heart is beating faster as a compensatory mechanism.
(b) is incorrect because it is a normal Troponin I level. The nurse would expect to see increased Troponin I within 4 to 6 hours after the myocardial infarction.
(c) is incorrect because left arm pain is a common symptom in patients experiencing an MI, not right arm pain. The nerves that supply the heart and the left arm are from the same spinal segment. The pain originates from the left chest (since the heart is slightly tilted left) and can radiate to the left arm, left nape of the neck, and left jaw.
(d) is incorrect because increased respirations occur as part of the compensation process, not decreased respirations.
Question 19.
A patient is given a beta blocker according to the healthcare provider’s orders. When the nurse assesses the patient later, which findings should be expected?
(a) Blood pressure change from 100/40 mmHg to 140/80 mmHg
(b) Respiratory rate change from 24 bpm to 16 bpm
(c) Oxygen saturation level change from 86% to 98%
(d) Pulse rate change from 110 bpm to 76 bpm
Answer:
(d) Pulse rate change from 110 bpm to 76 bpm
Explanation:
Beta blockers are administered to block stimulation of beta-i 000. This blocks sympathetic response, which decreases the heart rate as well as blood pressure. Ventricular filling time is increased due to the decrease in heart rate.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because beta blockers will decrease the heart rate causing decreased cardiac output and decreased blood pressure. These medications do not generally cause hypertension. On the contrary, they are used to treat hypertension.
(b) is incorrect because there is usually no effect on beta-2 adrenergic receptor sites or respiratory status.
(c) is incorrect because there is usually no effect on beta-2 adrenergic receptor sites or respiratory status. An increase in SpO2 is a good outcome for the patient, but it is not a direct action of beta-blockers.
Question 20.
The nurse on the medical-surgical floor is assessing patients. Which of the following patients is at greatest risk for cardiovascular disease?
(a) 74-year-old woman admitted for asthma exacerbation
(b) 66-year-old man, recently immigrated from Japan, admitted for colon cancer
(c) 53-year-old African American man admitted for diabetes mellitus
(d) 62-year-old postmenopausal woman taking hormone therapy
Answer:
(c) 53-year-old African American man admitted for diabetes mellitus
Explanation:
Coronary artery disease and hypertension are more prevalent in American Indians than whites and Asian Americans. Risk of hypertension and coronary artery disease is increased with diabetes mellitus patients. African Americans and males are also at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. So, this patient has two risk factors. Modifiable risk factors include hypertension, tobacco use, physical inactivity, hyperlipidemia, and overweight/obesity.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because asthma does not lead to increased risk of cardiovascular disease. This patient has one risk factor: increased age. Men are more at risk for cardiovascular disease than premenopausal women.
(b) is incorrect because colon cancer does not lead to increased risk of cardiovascular disease. This patient has no risk factors. Immigrants from eastern Asian countries are at less risk for cardiovascular disease. Their children and grandchildren, however, typically have increased risk for cardiovascular disease than the original immigrants due to adopting the western lifestyle.
(d) is incorrect because hormone therapy does not increase risk of cardiovascular disease. The risk for cardiovascular disease increases after women reach menopause. So, this patient has one risk factor.
Question 21.
The nurse is assessing a 65-year-old patient with several chronic diseases. The patient’s heart rate is noted to be 47 bpm. What is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Document the finding
(b) Prepare to externally pace the patient
(c) Review medications in the patient’s chart
(d) Administer 1 mg of atropine
Answer:
(c) Review medications in the patient’s chart
Explanation:
The conduction system of the heart is made up of pacemaker cells, which decrease in number as we age and can cause bradycardia. Medication reconciliation should be checked first to identify medications that decrease heart rate, then the healthcare provider should be informed.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because documentation must be performed, but not as a priority. The nurse should care for the patient first and document when care has been completed.
(b) is incorrect because external pacing is not indicated for this patient.
(d) is incorrect because although atropine may be indicated for treatment of bradycardia, the nurse should first check the medication to determine if the patient takes anything that can cause the decreased heart rate.
Question 22.
The nurse obtains a health history from a patient in the emergency room. Which of the following statements made by the patient could indicate heart failure?
(a) “Climbing stairs makes me short of breath.”
(b) “I can see halos floating above my head.”
(c) “My memory is troubling me these days.”
(d) “I’ve lost several pounds over the last few weeks.”
Answer:
(a) “Climbing stairs makes me short of breath.”
Explanation:
An early manifestation of heart failure includes dyspnea upon exertion, such as climbing stairs. Other symptoms include peripheral edema, decreased cardiac output and blood pressure, irregular cardiac rhythm or palpitations, fatigue, and cough.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because halos in the line of sight are not specific to early signs of heart failure. Halos can indicate glaucoma or cataracts. Visual halos can be an adverse effect of digoxin.
(c) is incorrect because memory trouble is not specific to early signs of heart failure.
(d) is incorrect because loss of weight is not specific to early signs of heart failure.
Question 23.
The nurse is obtaining the health history of a new patient on the medical floor. Which patient statement should alert the nurse to the presence of edema?
(a) “I have to get up at night to go to the bathroom.”
(b) “By the end of the day I have to take off my shoes; they’re so tight.”
(c) “My wedding ring keeps slipping off my finger.”
(d) “My intake includes 18 glasses of water daily.”
Answer:
(b) “By the end of the day I have to take off my shoes; they’re so tight.”
Explanation:
Fluid accumulation within interstitial spaces, also known as edema, can cause weight gain. Fit of shoes and rings for tightness should be noted, as well as any indentations in the legs from socks.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because nighttime bathroom trips are not indicative of edema.
(c) is incorrect because edema will often cause the fingers to swell, making it harder to get rings on and off.
(d) is incorrect because increased water intake is not necessarily indicative of edema, (although it may cause peripheral fluid retention). This patient is taking in more than the recommended amount of daily fluid. This statement needs to be investigated further by the nurse. Increased fluid intake can lead to fluid volume overload.
Question 24.
The nurse is assessing a 75-year-old patient. Which of the following assessments will cause the nurse to suspect a myocardial infarction?
(a) Complaint of chest pain with inspiration
(b) Complaint of weakness in the left arm and hand
(c) Confusion and disorientation
(d) Complaint of pounding headache
Answer:
(c) Confusion and disorientation
Explanation:
Myocardial infarction can cause decreased cardiac output, resulting in decreased cerebral blood supply. This can lead to confusion and disorientation, especially in older adults.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because chest pain on inspiration is an indication of pleurisy, not MI. Pleurisy (also known as pleuritis) is inflammation of the pleural lining of the lungs and the thoracic cavity.
(b) is incorrect because unilateral weakness and difficulty with fine motor control can be a sign of a stroke, not MI. MI can cause pain in the left arm, neck, and jaw but not weakness.
(d) is incorrect because myocardial infarction does not often cause a severe headache. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, cold sweats, and lethargy.
Question 25.
A patient is recovering from cardiac angiography with left femoral artery access. When assessing the patient’s left foot, the nurse determines the pedal pulse is weak. What is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Bend the left leg slightly and apply sandbag pressure to the femoral access site
(b) Increase the patient’s IV fluid rate
(c) Assess the left leg for color and temperature
(d) Document left pedal pulse 1+/4
Answer:
(c) Assess the left leg for color and temperature
Explanation:
Pulse loss distal to access site for angiography could indicate an arterial obstruction or hemorrhage. The nurse should assess both lower extremities and compare pulses. The nurse should also compare pulses to the pre-procedure assessment. Decreased pulse, cyanosis, pallor, and cool skin indicate decreased circulation. The healthcare provider should be notified once peripheral and vascular assessments are performed and data obtained.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the leg should remain straight. Sandbag pressure (or a pressure dressing) must be applied for 4-6 hours post procedure to prevent bleeding or hematoma to the site.
(b) is incorrect because increasing the rate of IV fluid infusion is not indicated at this time. If hemorrhage is identified, IV fluids will be needed, but the nurse must complete the assessment before addressing fluid replacement needs.
(d) is incorrect because documentation of findings without notifying the healthcare provider is inappropriate.
Question 26.
A patient recovering from left-sided cardiac catheterization is assessed by the nurse. Immediate intervention is required for which of the following findings?
(a) Intake exceeds output
(b) Bruising at the access site
(c) Confusion
(d) Pain at the access site
Answer:
(c) Confusion
Explanation:
Cerebral vascular accident (CVA) is a specific risk of left-sided cardiac catheterization. Changes in neurologic status require immediate action.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because although the dye used during cardiac catheterization can affect kidney function, causing decreased urine output, this is not the greatest concern. The confusion related to hemorrhage or CVA is the nurse’s priority at this time.
(b) is incorrect because bruising at the access site is expected.
Note: The patient should have a sterile dressing over the access site and the nurse does not remove the dressing to check for bruising. The doctor removes the dressing for the first time, and then the nurse can remove subsequent dressings as needed for dressing changes. (d) is incorrect because pain at the access site is expected.
Question 27.
The nurse is preparing a patient scheduled for cardiac catheterization. Which of the following is the priority for the nurse before the catheterization?
(a) Assess anxiety level of the patient
(b) Incentive spirometry education
(c) Heart rate and rhythm
(d) Iodine based agent allergies
Answer:
(d) Iodine based agent allergies
Explanation:
Allergy to iodine agents must be documented prior to cardiac catheterization as the contrast used for the procedure is based in iodine. A life-threatening allergic reaction can occur, making it high-priority.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because anxiety is a psychosocial assessment. It is more important for the nurse to assess for physical complications or contraindications related to the procedure.
(b) is incorrect because although it is important for the nurse to teach incentive spirometry, this is preventative treatment. Assessing for allergies is more important. If the patient does have an allergy to the dye, that would pose more of an actual problem than potential atelectasis related to immobility after the catheterization.
(c) is incorrect because obtaining a baseline cardiac status prior to the procedure is important, but not as important as assessing for allergies. If this patient is allergic to iodine, the catheterization procedure may need to be canceled or performed without contrast.
Question 28.
The nurse is preparing a patient for a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart. The patient has a pacemaker due to a previous myocardial infarction. What action should be taken by the nurse?
(a) Obtain an ECG prior to the MRI
(b) Notify the healthcare provider before the MRI is scheduled
(c) Draw cardiac enzymes prior to the MRI
(d) Encourage the patient to drink more fluids before the MRI
Answer:
(b) Notify the healthcare provider before the MRI is scheduled
Explanation:
In the past, MRI was contraindicated in all patients with implanted cardiac devices. Due to the magnetic field used in the MRI procedure, the pacemaker can be deactivated, device components can be damaged, and rapid pacing can be triggered. The MRI can also cause inappropriate shocks, burning the skin over the pacemaker implantation site.
The healthcare provider should be notified of the patient’s pacemaker so another diagnostic test can be ordered. MRI is only used with patients who have pacemakers when other alternative radiologic tests have been unsuccessful in making a diagnosis.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because an ECG prior to the MRI is not necessarily indicated.
(c) is incorrect because cardiac enzymes are not necessarily indicated.
(d) is incorrect because increased fluids are not indicated for this patient. The patient does not need to be NPO prior to the procedure either, but increased fluids are not a requirement.
Question 29.
A patient admitted to the medical unit for myocardial infarction has a pulmonary artery pressure of 24/13 mmHg. What is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Compare current pressure to previous readings
(b) Increase IV fluid infusion rate
(c) Notify the healthcare provider immediately
(d) Document the pressure in the patient’s chart
Answer:
(a) Compare current pressure to previous readings
Explanation:
PA pressures are obtained through use of a pulmonary artery catheter or Swan-Ganz catheter. This number indicates pressure within the pulmonary artery. Normal PA pressure is between 15-26 mmHg systolic and 5-15 mmHg diastolic. This patient’s pressure is normal, but the nurse is responsible for assessing for trends, which may indicate the need for intervention.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because IV fluids do not need to be increased for normal PA pressures. Low PA pressure can indicate fluid volume depletion, thus indicating the need for a higher rate of IV fluid infusion.
(c) is incorrect because the healthcare provider does not need to be notified of normal PA pressures. The nurse will notify the healthcare provider if the PA pressure drops or increases significantly.
(d) is incorrect because PA pressures should be documented after comparison to previous readings.
Question 30.
The nurse cares for a patient with 80% blockage of the right coronary artery (RCA). The patient is awaiting coronary bypass surgery. Which pre-operative intervention should the nurse be prepared to implement?
(a) IV furosemide administration
(b) External pacemaker
(c) Endotracheal intubation
(c) Central venous catheter placement
Answer:
(b) External pacemakers
Explanation:
The RCA is the supplier for the right atrium and ventricle, inferior left ventricle, and AV node. In 50% of people, the RCA also supplies blood to the SA node. When the RCA is completely (or nearly completely) occluded, the conduction system of the heart is affected, leading to heart block necessitating external pacing in an emergency.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because furosemide will have no effect on AV or SA node stimulation.
(c) is incorrect because endotracheal intubation is not indicated for this patient pre-operatively. The anesthesia team will intubate and connect to mechanical ventilation during the OR procedure.
(d) is incorrect because central venous catheter access will not help stimulate AV or SA node electrical activity.
Question 31.
A patient with diabetes has a body mass index of 42 and is at high risk for coronary artery disease. Which nutrition-related statement should the nurse include in the patient's teaching?
(a) “A low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet is the best method for weight loss.”
(b) “Weight loss and consuming necessary nutrients should be balanced.”
(c) “I will have the nutritionist come and talk to you about heart-healthy dietary measures.”
(d) “If you increase your exercise to five times per week, fewer dietary modifications will be needed.”
Answer:
(b) “Weight loss and consuming necessary nutrients should be balanced.”
Explanation:
The American Heart Association dietary guidelines should be followed by patients who are at risk for cardiovascular disease. The nurse should encourage consumption of vegetables and fruits, unrefined whole-grain, and fat-free dairy during weight loss. The nurse can include the following tips when teaching about a heart-healthy diet:
- Control portion sizes (a serving of pasta is V2 cup, a serving of meat is 2-3 oz)
- Limit unhealthy fats: less than 14 g saturated fat daily and less than 2 g trans fat daily (for people on a 2,000 calorie/daily diet)
- Drink at least eight glasses of water daily
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because high-protein low-carb diets are usually high in calories and fat, which is unhealthy for people at risk for cardiovascular disease.
(c) is incorrect because the nurse needs to address the patient’s risks. While it is acceptable to consult with the nutritionist, the nurse should first address the patient’s needs directly, to avoid “passing the buck.”
(d) is incorrect because together, a healthy diet and exercise are integral for reducing risk for cardiovascular disease. Increased exercise does not, alone, compensate for an unhealthy diet.
Question 32.
A patient with advanced cardiac disease tells the nurse she has difficulty sleeping at night. What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “I will notify the healthcare provider so a sleep study can be ordered to determine the problem.”
(b) “While sleeping, you are hypoxic, so we will provide you with a nasal cannula with oxygen to use at home.”
(c) “A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) mask can help you breathe while you are sleeping.”
(d) “Elevate your head with pillows while you sleep.”
Answer:
(d) “Elevate your head with pillows while you sleep.”
Explanation:
Orthopnea (shortness of breath due to lying flat) is likely being experienced by this patient. The patient should be taught by the nurse to raise their head and chest with a pillow(s) or use a recliner to sleep.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because it is not necessary to order polysomnography (sleep study) to identify the problem for this patient. This test measures brain activity, oxygen saturation, heart rate, breathing, and eye/leg movements. It is commonly used to diagnose sleep disorders.
(b) is incorrect because orthopnea is not relieved with oxygen therapy.
(c) is incorrect because orthopnea is not relieved with CPAP. A CPAP device is used to relieve obstructive sleep apnea. This machine increases airway pressure upon inhalation so the throat doesn’t collapse while lying down.
Question 33.
A 52-year-old man patient recovering from myocardial infarction tells the nurse, “I probably need to eat less chili to prevent the return of that awful indigestion pain that brought me in here.” What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “It’s a good idea to cut chili out of your diet because it is high in calories and fat.”
(b) “You now have an antacid prescribed that you will take each morning.”
(c) “Tell me what you understand about what happened.”
(d) “When did this indigestion start?”
Answer:
(c) “Tell me what you understand about what happened.”
Explanation:
After a patient suffers an extreme life-threatening event such as a myocardial infarction, they may exhibit defense mechanisms as a way of protecting themself from the actual anxiety they are feeling about the experience. This patient is likely in denial about what happened to them. Denial is a defense mechanism in which a patient fails to acknowledge a particular thought, feeling, or experience.
The nurse should ask the patient about their understanding of what happened and what it means to them, as a way of beginning a therapeutic conversation in which the patient can be presented with the facts related to what they experienced.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because it does not assess the patient’s knowledge regarding the experience, nor does it help address the MI.
(b) is incorrect because it does not address the patient’s knowledge regarding the experience, nor does it help address the MI. The patient may be started on an antacid if they experience gastro-esophageal reflux, but this is not directly related to an MI.
(d) is incorrect because it is a closed-ended question which will only give the nurse one piece of information. This is an appropriate question to ask at some point, but it does not address the denial indicated by the patient’s statement.
Question 34.
The nurse cares for a patient being prepared for coronary artery bypass graft surgery. The patient tells the nurse, “I am afraid of potential complications after the procedure. I am not sure I want to follow through with this.” What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “The risk of complications with this surgery is relatively low.”
(b) “Can I call the chaplain for you to speak with before the surgery?”
(c) “What are your concerns regarding the surgery?”
(d) “You will need assistance after the surgery. Tell me about your support system.”
Answer:
(c) “What are your concerns regarding the surgery?”
Explanation:
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a complex surgery that improves blood flow to the heart. Potential complications include wound infection, bleeding, reaction to anesthesia, heart attack, stroke, and even death. The procedure requires general anesthesia, excision of a vein from the leg or chest wall, and placement of the excised vein over the blocked coronary artery to restore blood flow to the myocardium.
The patient’s concerns and feelings related to the surgery should be discussed with the nurse. The nurse is capable of clarifying concerns related to common procedures and surgeries. After the nurse addresses concerns, the healthcare provider may need to be called.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because this is an untrue statement and provides false reassurance. The nurse must address the patient’s concerns. Even after the consent form has been signed, the patient legally still has the right to change their mind.
(b) is incorrect because the concerns of the patient should not be directed to the chaplain, as this is “passing the buck.” The nurse should address the patient directly before consulting another member of the healthcare team.
(d) is incorrect because this dismisses the patient’s current concerns. After the nurse addresses the fear and the complications, then support systems can be discussed.
Question 35.
The nurse in the emergency department is triaging four patients who have presented with chest discomfort. Which patient should be assessed by the nurse first?
(a) 45-year-old female, describes her pain as an “aching dullness” with numbness of the fingers
(b) 50-year-old male in moderate pain that increases with inspiration
(c) 54-year-old female whose pain is described as substernal radiating to the abdomen
(d) 60-year-old male whose pain is described as intense stabbing spreading across the chest
Answer:
(d) 60-year-old male whose pain is described as intense stabbing spreading across the chest
Explanation:
All patients complaining of chest pain must have a thorough assessment. In order to determine which patient must be seen first, common differences in descriptions of pain must be understood. Stabbing, squeezing pain that spreads across the chest, arms, jaw, back, or neck indicates a possible myocardial infarction. This patient should be seen by the nurse first.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because aching dullness and numb fingers is usually anxiety related.
(b) is incorrect because pain that worsens upon inspiration is usually a pleuropulmonary issue such as pleuritis (infection or inflammation of the lining of the lungs and thoracic cavity).
(c) is incorrect because pain radiating to the abdomen could be an esophageal or gastric issue, especially when experienced by a male patient. This type of pain could be myocardial-related when experienced by a female patient. All these patients should be seen, but the patient complaining of stabbing pain spreading across the chest is the highest priority.
Question 36.
Which statement by the patient in an outpatient clinic would cause the nurse to suspect left-sided heart failure?
(a) “five drank more water lately than I usually do.”
(b) “I have to get up at night to urinate.”
(c) “When taking the stairs, I have to stop halfway and catch my breath.”
(d) “Several times my vision has been blurry.”
Answer:
(c) “When taking the stairs, I have to stop halfway and catch my breath.”
Explanation:
Left-sided heart failure, also known as left-ventricular heart failure, is the failure of the left ventricle to maintain a normal output of blood. The left ventricle does not empty completely, therefore, it cannot accept the full volume of blood returning from the lungs via the left atrium. This causes engorgement of the pulmonary veins, and fluid seeps out of these vessels into the tissues of the lungs, causing pulmonary edema. Patients report fatigue or weakness while performing activities of daily living when experiencing left-sided heart failure. They may also experience coughing and difficulty breathing or feel the need to “catch their breath” due to fluid moving into the alveoli.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because water intake and thirst are not indicative of left-sided heart failure. This statement by the patient indicates a need for investigation, however. Increased fluid intake could potentially cause fluid volume overload.
(b) is incorrect because nocturia or having to urinate at night is often experienced by patients with right-sided heart failure. Other symptoms include dependent edema, liver enlargement, bloating, abdominal tenderness, coolness of extremities, and weight gain.
(d) is incorrect because heart failure is not characterized by blurry vision.
Question 37.
A patient on the cardiac unit is assessed by the nurse. Which patient statement would cause the nurse to suspect right-sided heart failure?
(a) “I have four pillows under my head when I sleep.”
(b) “My shoes have been so tight lately.”
(c) “Every night I wake up coughing.”
(d) “I have a hard time catching my breath lately.”
Answer:
(b) “My shoes have been so tight lately.”
Explanation:
Systemic congestion is a sign of right-sided heart failure. Fluid retention causes a build-up of pressure in the venous system, which leads to peripheral edema. This is due to the decreased ability of the heart to pump blood effectively in right-sided heart failure. Other symptoms include dependent edema, liver enlargement, bloating, abdominal tenderness, coolness of extremities, and weight gain. Treatment includes digoxin, antihypertensives, low-sodium diet, and diuretics.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because respiratory symptoms including paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea and orthopnea are seen in left-sided heart failure. In this condition, the left ventricle fails to maintain a normal output of blood, leading to pulmonary edema.
(c) is incorrect because coughing is related to left-sided heart failure due to fluid accumulation in the lung tissue.
(d) is incorrect because difficulty breathing could be related to left-sided heart failure.
Question 38.
A patient on the cardiac unit is assessed by the nurse. When an S3 gallop is noted, what is the next action the nurse should take?
(a) Assess for symptoms of left-sided heart failure
(b) Document the S3 gallop as a normal finding
(c) Notify the healthcare provider immediately
(d) Arrange to transfer the patient to intensive care
Answer:
(a) Assess for symptoms of left-sided heart failure
Explanation:
Typical heart sounds are noted as Si and S2. If there is a third heart sound, it is called S3, or S3 gallop. This is typically caused by blood flow suddenly slowing as it flows from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Early diastolic filling is indicated by S3 gallop and signifies increasing left ventricular pressure as well as left ventricular failure.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because an S3 gallop is an abnormal finding. Any abnormal finding should be a concern to the nurse. Appropriate nursing actions are to further assess or perform an appropriate nursing intervention if no further assessment data is warranted.
(c) is incorrect because the healthcare provider should be notified once the full assessment is completed. The healthcare provider is called when the nurse has enough assessment information or in a case of a medical emergency.
(d) is incorrect because a full assessment should be completed to see if a higher level of care is warranted. Transferring this patient to ICU without further assessment is “passing the buck.”
Question 39.
A patient diagnosed with right-sided heart failure asks why daily weights are important. What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Daily weights are the best indicator of fluid loss or gain.”
(b) “Daily weights will tell us if you’re eating a healthy diet.”
(c) “Hospital protocol requires daily weights of all inpatients.”
(d) “Daily weights help you lose weight which can decrease heart failure incidence.”
Answer:
(a) “Daily weights are the best indicator of fluid loss or gain.”
Explanation:
Fluid loss or gain is indicated by daily weights, which should be documented daily with heart failure patients. 2.2 pounds equals 1 liter of fluid. This excess fluid typically collects in the periphery in right-sided heart failure and is seen as edema in the legs and arms. The other responses by the nurse do not address the importance of fluid monitoring.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because daily weights do not necessarily indicate a healthy diet.
(c) is incorrect because it does not appropriately answer the patient’s question. This may be a true statement, but it doesn’t address the situation in the question.
(d) is incorrect because weight loss is not the goal for this patient.
Question 40.
A patient with heart failure has a new prescription for enalapril (Vasotec), and the nurse is performing teaching. Which statement should be included by the nurse for this patient’s teaching?
(a) “You need to avoid using salt substitutes.”
(b) “Take this medication with food.”
(c) “Avoid using products containing aspirin.”
(d) “You must check your pulse every day before taking the medication.”
Answer:
(a) “You need to avoid using salt substitutes.”
Explanation:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors including enalapril inhibit excretion of potassium, which can lead to hyperkalemia. This can be a life-threatening situation, so patients must be taught to limit their potassium intake. Salt substitutes contain potassium chloride and can further lead to increased serum levels of potassium.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because ACE inhibitors do not have to be taken with food.
(c) is incorrect because aspirin is not contraindicated when taking ACE inhibitors and is often prescribed in conjunction. Remember: aspirin should not be administered to patients with risk for bleeding or those who have clotting disorders. Aspirin is also contraindicated in patients under 21 years of age due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome.
(d) is incorrect because ACE inhibitors have no impact on heart rate. Patients taking beta-blockers are taught to check their pulse before taking their medication and hold if the heart rate is below 60 bpm.
Question 41.
A patient has been given a first dose of captopril for heart failure, and the nurse is implementing interventions to prevent complications. Which is a priority intervention for this patient?
(a) Give the medication with food to prevent nausea and increase absorption
(b) Teach the patient to call for help with getting out of bed
(c) Ask the unlicensed assistive personnel to assist the patient with bathing
(d) Assess potassium levels and for symptoms of hypokalemia
Answer:
(b) Teach the patient to call for help with getting out of bed
Explanation:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors block the conversion from angiotensin I to angiotensin II in the lungs, causing decreased blood pressure. These medications also cause decreased aldosterone secretion and sodium and fluid loss. ACE inhibitors are indicated for heart failure and hypertension. The initial dose of an ACE inhibitor can cause severe hypotension, termed the “first-dose effect.” The patient must be taught to call for help before getting out of bed to prevent postural hypotension and a fall. This risk is greatest after the first dose is taken.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because ACE inhibitors do not have to be taken with food. Food actually blocks the absorption of ACE inhibitors, so they should be taken one hour before or two hours after a meal.
(c) is incorrect because hygiene and collaboration with the unlicensed assistive personnel is not priority. Activities of daily living should be performed as independently as possible for this patient.
(d) is incorrect because hyperkalemia can occur with ACE inhibitors, not hypokalemia, especially in patients with renal insufficiency.
Question 42.
A patient is assessed by the nurse an hour after taking isosorbide mononitrate. The patient states they have a headache. Which intervention should the nurse perform?
(a) Start oxygen therapy
(b) Hold the next scheduled dose of isosorbide mononitrate
(c) Encourage the patient to drink water
(d) Administer acetaminophen
Answer:
(d) Administer acetaminophen
Explanation:
Isosorbide mononitrate is a vasodilator that relaxes smooth muscles in blood vessel walls, making it easier for blood to flow through. Headaches commonly occur with this medication due to the vasodilatory effects, especially during the beginning stage of therapy. Patients should be informed of this and instructed to take acetaminophen if a headache occurs.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the patient does not have hypoxia, and oxygen will not treat or prevent headaches.
(b) is incorrect because the medication must be taken as prescribed to prevent angina and should not be discontinued abruptly.
(c) is incorrect because the patient is not dehydrated, and drinking water will not treat or prevent headaches with this medication.
Question 43.
A patient is being taught about digoxin by the nurse. Which statement should be included in the patient's teaching?
(a) “Do not take aspirin or aspirin-containing products.”
(b) “Limit the intake of foods that contain potassium in your diet.”
(c) “If your pulse rate is less than 80 bpm, do not take the medication.”
(d) “Do not take an antacid within an hour of taking the medication.”
Answer:
(d) “Do not take an antacid within an hour of taking the medication.”
Explanation:
Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside prescribed for heart conditions including atrial fibrillation, flutter, and heart failure. Gastrointestinal absorption of digoxin can be erratic. Antacids interfere with absorption of digoxin. Adverse reactions to digoxin include anorexia, nausea, bradycardia, visual disturbances, and confusion.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because aspirin will have no impact on the absorption of digoxin.
(b) is incorrect because hypokalemia can potentiate digoxin toxicity. Patients taking this medication should be instructed to increase their intake of potassium-rich foods such as: bananas, potatoes with skin-on, sweet potatoes, white beans, avocado, dark leafy greens, dried apricots, and acorn squash. The nurse should monitor renal function and electrolytes.
(c) is incorrect because patients are taught to not take digoxin when bradycardic, but a heart rate of 80 bpm is within normal limits and not an indication to hold digoxin.
Question 44.
A nurse is teaching a patient about caring for themself at home after being diagnosed with heart failure. Which statement is most important for the nurse to include in the patient's discharge teaching?
(a) “Limit your fluids to less than three quarts per day.”
(b) “Be sure to consume three balanced meals daily.”
(c) “Take an additional diuretic when you feel short of breath.”
(d) “Record your weight daily wearing the same amount of clothing.”
Answer:
(d) “Record your weight daily wearing the same amount of clothing.”
Explanation:
Patients with heart failure must weigh daily to identify worsening heart failure and avoid complications early. Increasing dyspnea, intolerance of activity, symptoms of cold, and nocturia are also signs of worsening heart failure. The patient should eat a heart-healthy diet, balance intake of fluids with output, and take their medications as ordered. Daily weight and hypertension control are the most important points to teach patients with heart failure.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because intake of too much fluid can worsen symptoms of heart failure. Three quarts is over 2.8 L of fluid. A normal daily fluid intake is 2-2.5 L/day, so a heart failure patient may be on fluid restriction, such as 1.5 L/day.
(b) is incorrect because fluid balance is a greater priority than nutritional intake. Patients with heart failure often experience bloating and nausea due to abdominal ascites, so eating smaller frequent meals may be indicated.
(c) is incorrect because medications including diuretics should be taken as prescribed. Diuretics are not generally prescribed PRN. If the patient experiences symptoms such as shortness of breath, the healthcare provider should be notified.
Question 45.
A patient with type I diabetes is experiencing heart failure exacerbation. As the nurse admits the patient to the cardiac unit, what is the first action the nurse should take?
(a) Assess the respiratory' status of the patient
(b) Assess the patient’s serum electrolytes
(c) Administer intravenous furosemide
(d) Call the healthcare provider to obtain orders
Answer:
(a) Assess the respiratory' status of the patient
Explanation:
Respiratory assessment and oxygenation status are the most important to assess for this patient. Heart failure exacerbation or decompensation is characterized by ejection fraction less than 40%, hypotension, pulmonary congestion, worsening fatigue, dyspnea with or without activity, and coughing with pink or blood-tinged sputum. The nurse’s greatest priority is assessment of the current (baseline) airway status. The lungs will continue to be monitored closely as interventions are initiated. Respiratory and cardiac arrest are both complications that the nurse will be anticipating.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because electrolyte monitoring is important for heart failure patients but not priority over respiratory status.
(c) is incorrect because administration of diuretics is important for heart failure patients but not priority over respiratory status. The nurse must assess lung sounds before giving furosemide so the effect of the medication can be measured after the patient diuresis fluid.
(d) is incorrect because assessment of the current respiratory status is more important than obtaining orders for patient care. The nurse needs to remain focused on the patient at the bedside.
Question 46.
A patient with a history of mitral valve stenosis is on the cardiac unit. When assessing the patient, which clinical manifestation should the nurse recognize as progression of stenosis?
(a) Oxygen saturation level of 92%
(b) Fatigue and shortness of breath on exertion
(c) Systolic murmur
(d) Rheumatic fever
Answer:
(b) Fatigue and shortness of breath on exertion
Explanation:
The mitral valve (also known as the bicuspid) is the atrio-ventricular valve in the left side of the heart. Shortness of breath or dyspnea on exertion manifests as the mitral valve orifice is narrowed (stenosed) and the pressure in the lungs increases. The heart has decreased ability and capacity to pump blood to the lungs and periphery, causing backup of blood in the lungs and fatigue due to the extra work of breathing. Medications to help treat symptoms of mitral valve stenosis include diuretics and blood-thinners (to prevent clots from forming).
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because oxygen saturation levels are not directly related to mitral valve stenosis.
(c) is incorrect because a systolic murmur is not related to mitral valve stenosis.
(d) is incorrect because rheumatic fever is not a sign of worsening mitral valve stenosis. Rheumatic fever is a complication of untreated strep throat or scarlet fever and is the most common cause of mitral valve stenosis.
Question 47.
A patient is recovering after valve replacement surgery using a prosthetic valve. The patient asks why anticoagulants must be taken for the rest of their life. What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “You are at greater risk of a heart attack with the prosthetic valve.”
(b) “Artificial replacement valves form blood clots more than tissue valves.”
(c) “You have reduced circulation in your leg where they took the vein.”
(d) “There are small clots located in your heart and lungs due to the surgery.”
Answer:
(b) “Artificial replacement valves form blood clots more than tissue valves.”
Explanation:
Platelets can collect easily on synthetic valves and scar tissue, initiating formation of blood clots. Artificial valves are long-lasting as they are made of durable material, but there is an increased risk of clot formation necessitating the use of long-term anticoagulation medication. Thus, the patient is at higher risk for bleeding.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because there is not a greater risk of myocardial infarction with a prosthetic valve. Complications after a valve replacement include valve failure and prosthetic valvular endocarditis (PVE.)
(c) is incorrect because veins are not harvested from the leg for valve replacement surgery.
(d) is incorrect because valve replacement surgery does not generally cause thrombi or clots to form in the heart or lungs. The purpose of life-long anticoagulation therapy is to prevent clots.
Question 48.
A patient had mitral valve replacement surgery and has been prescribed warfarin. When the nurse performs discharge instructions, which patient statement demonstrates the need for more teaching?
(a) “I can carry heavy loads after six months.”
(b) “I will go to the dentist in two weeks to have my teeth cleaned.”
(c) “I shouldn’t eat foods like spinach that are high in vitamin K.”
(d) “I should use an electric razor instead of a straight blade.”
Answer:
(b) “I will go to the dentist in two weeks to have my teeth cleaned.”
Explanation:
Patients are placed on anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin, to prevent blood clots from growing on a new valve. Patients should be instructed to avoid going to the dentist for six months after valve replacement surgery as there is an increased risk of bleeding, even from minor dental procedures.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because heavy lifting should be avoided for six months after valve surgery, indicating patient understanding.
(c) is incorrect because if warfarin is prescribed, the patient should avoid consuming foods with high levels of vitamin K, indicating patient understanding. (Vitamin K is the antidote to warfarin, and can lessen the anticoagulant effects of the medication, increasing risk for blood clots.)
(d) is incorrect because patients should be instructed to use an electric razor while on anticoagulant therapy, indicating patient understanding. Other bleeding precautions include using a soft-bristled toothbrush, avoiding contact sports or activities that have a high risk for falling. Bruising, falls, diarrhea, rash, severe or unusual headache, and fever should be reported to the healthcare provider.
Question 49.
In order to safely care for the patient with infective endocarditis, which infection control precautions should be used by the nurse?
(a) Standard precautions
(b) Bleeding precautions
(c) Reverse isolation
(d) Contact isolation
Rationale:
Answer:
(a) Standard precautions
Explanation:
Infective endocarditis can be caused by several different organisms including streptococci, staphylococcus aureus, and fungi. This can be due to a skin abscess, infected gums, urinary tract infection, IV drug abuse, and even medical and surgical procedures. Infective endocarditis has no specific threat for transmission of causative organism. Standard precautions are sufficient for this patient.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because although thrombosis is an element of infective endocarditis, anticoagulation therapy is contraindicated. Bleeding precautions are required, and they are not a form of infection control precautions.
(c) is incorrect because the patient with infective endocarditis is not immunocompromised and does not need to be shielded from potential infection. Reverse isolation is necessary to prevent immunocompromised people from becoming infected by others or objects. This type of isolation may be used for those undergoing chemotherapy, awaiting bone marrow transplant, or on neutropenic precautions. Note: the CDC no longer recognizes reverse isolation as effective because of the negative psychosocial effects on patients.
(d) is incorrect because there is no specific threat for transmission of causative organism with infective endocarditis. Contact precautions are required for patients with infections from multi-drug resistant organisms (MRSA, VRE), C-diff, RSV, rotavirus, and Hep A.
Question 50.
The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with pericarditis. Which of the following assessment findings should be expected?
(a) Heart rate fluctuation between bradycardia and tachycardia
(b) Friction rub at the left lower sternal border
(c) Regular gallop rhythm
(d) Crackles in bilateral lung bases
Answer:
(b) Friction rub at the left lower sternal border
Explanation:
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium and can be characterized by pericardial friction rub and stabbing chest pain that typically worsens with deep inspiration and coughing. The pericardium is made up of three layers: an outer fibrous layer and two inner serous membrane layers. Pericarditis may cause pericardial friction rub at the left lower sternal border as a result of the inflamed inner pericardial layers rubbing together.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because heart rate changes are not specific to pericarditis.
(c) is incorrect because regular gallop rhythm is not specific to pericarditis. Complications the nurse will monitor for include heart palpitations and low-grade fever.
(d) is incorrect because crackles in lung bases are not specific to pericarditis. These symptoms are more indicative of left-sided heart failure or fluid volume overload.
Question 51.
The nurse cares for a patient who has received a heart transplant. The nurse teaches the patient that they should change positions slowly. When the patient asks why it is important, what is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Quick position changes may cause shear and friction which can tear out internal vascular sutures.”
(b)“The vascular connections are sensitive to changes in position, which can increase intravascular pressure and cause dizziness.”
(c) “The new heart is not connected to your nervous system and cannot respond to changes in blood pressure from changes in position.”
(d) “As your heart recovers, your blood flow is diverted away from your brain which increases your risk for stroke upon standing.”
Answer:
(c) “The new heart is not connected to your nervous system and cannot respond to changes in blood pressure from changes in position.”
Explanation:
The new transplanted heart is not connected to the nervous system, so baroreceptors and compensatory mechanisms do not function in response to position changes. This can lead to orthostatic hypotension, which can cause light-headedness and dizziness when changing positions quickly. This can be uncomfortable for the patient and increase risk for falls.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because it is an untrue statement.
(b) is incorrect because the vascular changes can cause decreased intravascular pressure, not increased.
(d) is incorrect because it is an untrue statement and does not specifically address the patient’s question.
Question 52.
A patient who had heart transplant surgery is prescribed cyclosporine. Which statement should be included by the nurse in the patient's discharge teaching?
(a) “Don’t floss and use a soft toothbrush.”
(b) “Avoid crowds and sick people.”
(c) “Position changes should be done slowly to avoid hypotension.”
(d) “We will draw blood periodically to check for pancreas damage while you are taking this medication.”
Answer:
(b) “Avoid crowds and sick people.”
Explanation:
Medications such as cyclosporine suppress the immune system, which puts the patient at risk for infection. These medications are required to prevent the immune system from attacking the transplanted organ and causing organ failure. The patient should avoid crowds of people where diseases may easily be transmitted. Other precautions include not consuming undercooked foods, avoiding contact with soil and live plants, washing fruits and vegetables thoroughly (or buy canned / frozen instead), good handwashing, and flossing and brushing teeth between meals.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because these are instructions for a patient who has a bleeding risk. Cyclosporine does not increase risk for bleeding. Cyclosporine may cause thrush, so the patient should use nystatin swish-and-swallow QID.
(c) is incorrect because there is no risk for orthostatic hypotension. An adverse reaction to cyclosporine is hypertension.
(d) is incorrect because cyclosporine does not affect the pancreas. BUN, creatinine, and liver function tests are necessary when taking cyclosporine.
Question 53.
A female patient with end stage heart failure is on the list for transplant. The patient seems depressed and tells the nurse, “I know this is my last chance, but if the surgery goes wrong, I really don’t want to end up with a tracheostomy for life.” What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Would you like for me to call the chaplain?”
(b) “I will arrange for the psychiatrist to come speak to you.”
(c) “We can remove you from the transplant list, if you choose.”
(d) “Can I provide you with information about advance directives?”
Answer:
(d) “Can I provide you with information about advance directives?”
Explanation:
The patient has verbalized fear or concern about outcomes of the surgery. Anxiety can have negative outcomes due to sympathetic stimulation. Allowing the patient to verbalize concerns and work on a positive outcome is the best action. The nurse can educate the patient about advance directives to help her plan her own care. A living will can indicate treatment or life-saving measures to be used if the patient is not able to make decisions for herself after surgery. A Durable Power of Attorney allows the patient to delegate another competent adult to make decisions for her, in the event that she becomes incompetent.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because the nurse should address this patient’s concerns at the bedside. Calling the chaplain at this time is “passing the buck.” The chaplain will be called to help address spiritual needs or concerns.
(b) is incorrect because the patient’s concerns should not be pushed off on the psychiatrist.
(c) is incorrect because although the patient has a right to choose, taking the patient off the transplant list is jumping to a conclusion that the patient does not want the surgery.
Question 54.
The clinic nurse is assessing a 58-year-old woman who lives alone with her dog. Her diagnosis is heart failure. Which is the best question for the nurse to ask in order to assess heart failure severity in this patient?
(a) “Are you able to play with your dog without any shortness of breath?”
(b) “Tell me about your morning routine at home and what it feels like when you’re getting ready each day.”
(c) “Do you have any problems at night?”
(d) “Do you feel heaviness in your legs?”
Answer:
(b) “Tell me about your morning routine at home and what it feels like when you’re getting ready each day.”
Explanation:
This is an open statement that will give the nurse information about whether the patient is symptomatic while arising from bed, getting dressed, walking around the house, and preparing/eating breakfast. Heart failure patients usually have negative findings, including shortness of breath, dizziness, and fatigue while active. The patient’s activity level needs to be assessed, and the nurse must determine if symptoms are present at rest, during mild exertion, or while fully active. This will indicate whether or not the heart failure has increased in severity.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because it is a closed-ended question and only gives the nurse one piece of information. The patient may be able to play with her dog while sitting in a chair, which does not require much physical activity. A better question to ask would be, “Are you able to take your dog for walks without complications?”
(c) is incorrect because nighttime breathlessness does not demonstrate the extent of heart failure. This is a yes/no question which does not give much information.
(d) is incorrect because peripheral edema is common in heart failure and does not determine extent.
Question 55.
An older patient with heart failure expresses concern about being dependent upon her daughter but is afraid to care for herself. She states she should probably die. What is the best response by the nurse?
(a) “Do you want to talk some more about your feelings?”
(b) “You’re lucky to have a devoted daughter.”
(c) “Your feelings of being a burden are normal.”
(d) “Perhaps a visit from pastoral care will be helpful. What is your religious preference?”
Answer:
(a) “Do you want to talk some more about your feelings?”
Explanation:
Patients with heart failure, especially older patients, can experience depression. This can be due to decreasing ability to care for themselves or loss of independence. Encouraging the patient to talk about her feelings is therapeutic. The nurse can then inform her of available resources to assist her as needed. Use of open-ended communication provides for honest responses by the patient.
Rationale:
(b) is incorrect because it doesn’t encourage the patient to talk about her concerns. This statement takes the focus off the patient.
(c) is incorrect because this answer is not as therapeutic as encouraging discussion in answer.
(d) is incorrect because this statement does not enhance the nurse-client therapeutic relationship. The nurse should focus on the patient at the bedside and address concerns before calling pastoral care.
Question 56.
A patient with heart failure is being taught by the nurse about energy conservation. Which statement should the nurse include in this patient's teaching?
(a) “Walk until you feel short of breath, then head back home.”
(b) “Before you begin chores, collect everything you need.”
(c) “Instead of pushing or carrying, pull items that are more than five pounds.”
(d) “Every day after dinner take a short walk to build strength.”
Answer:
(b) “Before you begin chores, collect everything you need.”
Explanation:
Energy conservation is important for heart failure patients as even the lightest activity can cause fatigue. Collecting supplies before starting a chore decreases energy use and allows the patient to complete the chores without needing to move around the home for forgotten items.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because it puts the patient in danger. The patient should be instructed to walk short distances, gradually increasing the distance, so that no shortness of breath is experienced.
(c) is incorrect because pulling requires more energy than pushing or cariying.
(d) is incorrect because it does not decrease energy use.
Question 57.
A patient admitted with acute pericarditis calls the nurse to report substernal precordial pain radiating to the left side of his neck. Which non-pharmacologic comfort measure should the nurse implement?
(a) Place an ice pack on the patient’s chest
(b) Provide neck rubs focusing on the left side
(c) Let the patient rest in bed with lights dimmed
(d) Have the patient sit up and lean forward on a pillow
Answer:
(d) Have the patient sit up and lean forward on a pillow
Explanation:
Laying supine can worsen pain from acute pericarditis. The pain is described as a stabbing chest pain that worsens with coughing and deep breathing in addition to lying down. The usual comfortable position is upright and leaning forward. Gravity helps to take pressure off the pericardial muscle to decrease pain.
Rationale:
(a) is incorrect because ice packs will only have a superficial effect and will not likely relieve the inner pain located within the lining of the heart in this patient.
(b) is incorrect because neck rubs are more likely to increase pain in this patient.
(c) is incorrect because it does not provide pain relief.
Read More:
