Important Tests during pregnancy help check the baby's growth and health, as well as the mother's well-being.
The Ultrasound NT scan or Nuchal Translucency scan is a safe and non-invasive test performed during the first trimester of pregnancy. The ultrasound identifies the risk of several chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. Those can be Down syndrome, Edward's syndrome, trisomy 13 and other heart diseases.
An NT scan is an important test to be done during pregnancy. Get to know the complete details about Ultrasound NT Scan in the following sections of this page.
Also Check: Vitamin D Test During First Trimester Pregnancy
- Highlights of Nuchal Translucency Scan
- What is NT Scan?
- Reasons to Perform Ultrasound NT Scan
- Ultrasound Nuchal Translucency Preparation
- How NT Scan is Done?
- When to take the Ultrasound NT Scan?
- Ultrasound NT Scan Results
- Is a NT Scan painful?
- Can a NT ultrasound tell gender?
- What is NT scan full form?
- What a normal NT scan value at 13 weeks?
Highlights of Nuchal Translucency Scan
| Also Known As | USG NT SCAN, Nuchal Translucency Scan, NT NB Scan, Ultrasound Level 1 |
| Purpose | To estimate the risk of chromosomal abnormality in a developing fetus |
| Preparation | No special preparation is required. You may need to drink water 1 hour before the test to have a full bladder. |
| Fasting | No |
| Machine Used | Ultrasound/ Sonography Machine |
| Timing | 11-13th Week of Pregnancy |
What is Nuchal Translucency?
Nuchal translucency (NT) is an ultrasound scan that measures the amount of fluid behind your baby's neck in the first trimester of pregnancy. Measuring the amount of fluid can be helpful to calculate your fetus's chances of having a chromosomal or genetic variant.
NT ultrasound is a screening test and it doesn't diagnose your health condition. It only helps your doctor to determine if your baby is doing well or if further tests should be recommended.
Reasons to Perform Ultrasound NT Scan
The NT Ultrasound should be done at the different stages of pregnancy for the following reasons.
- To accurately date the pregnancy: This is most useful for the women with an irregular menstrual cycle or one who has conceived during breastfeeding, or someone who doesn't remember her last menstruation date.
- To diagnose multiple babies in your belly.
- Aneuploidy disorders diagnose such as Down syndrome, Edward's syndrome (trisomy 18), Patau's syndrome (trisomy 13), and Turner's syndrome.
- Congenital heart disease: It is a genetic defect in which the heart of the child is not formed correctly during the gestation period.
- Skeletal dysplasia: It is an abnormality caused by the abnormal formation of the bones in the baby's body.
- Congenital diaphragmatic herniation: This is an abnormality in which the diaphragm is not accurately formed during the development of the fetus.
- VACTERL association: It is the group of numerous anomalies that can happen during the development of the child in the gestation period.
- Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome: The inability to synthesize cholesterol is called Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.
All these disorders may be fatal for the child as well as the mother. Hence they are diagnosed early to either treat the developing embryo or the child after being born.
Ultrasound Nuchal Translucency Preparation
There is no preparation required. you can eat anything normally before taking the screening test. It may be advised that you have to drink 600 to 800 mL of water at least 1 to 2 hours before the test. You should have some fluid in the bladder, but not full.
This ensures that the inside of the abdominal area is seen clearly on the ultrasound images. It is also advised that you wear comfortable clothing that gives easy access to your lower abdominal area.
Ultrasound NT Scan Procedure
The NT scan ultrasound can be performed through the vagina or abdomen. The procedure of the ultrasound is as follows:
- The transabdominal scan is similar to the normal abdominal ultrasound and is done on the lower abdomen of the pregnant woman.
- The cream applied to the lower abdominal area and the sonographer will move the transducer on the skin.
- In most cases, the ultrasound scan is done just by moving the transducer on the skin, and the images of the developing child will appear on the machine screen. However, if that does not happen then the vaginal scan has to be done.
- The length of the fluid in the neck area of the baby is measured. It appears as a black fluid under the skin.
- The images are enough to identify the risk of abnormalities in the developing baby.
- If your scan is done transvaginally, a small, lubricated ultrasound probe is gently inserted into your vagina. The probe may create little discomfort but usually isn't painful. Scans done this way can give more detailed pictures because the probe goes closer to the uterus.
The entire ultrasound scan may take around 20 to 40 minutes.
When to take the Ultrasound NT Scan?
The USG NT scan is usually performed by the end of the first trimester. The baby should be in a period between 11 weeks and 13 weeks in 6 days of gestation. The test done before the 11th week can be too early and not give accurate results.
The crown-rump length of the baby should be between 45mm and 84mm. It is also advised to not delay the scan beyond 14 weeks since by then the fluid starts to move to the lymphatic system and may not show an accurate image.
Ultrasound NT Scan Results
The Nuchal Translucency Ultrasound measures the thickness of the translucent region behind the baby's neck, which shows the fluid in the nuchal fold of the developing baby.
Normal Values
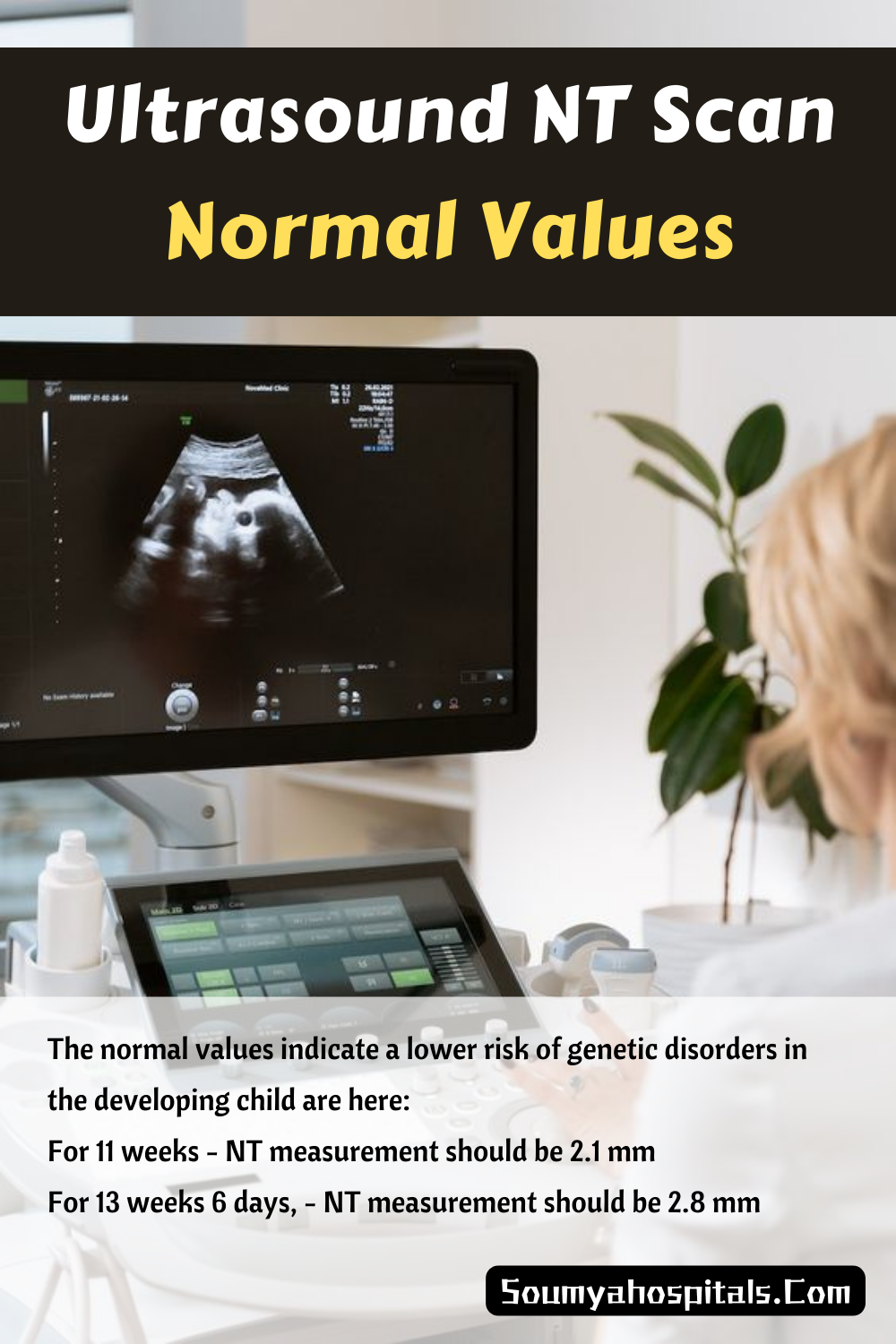
The normal values indicate a lower risk of genetic disorders in the developing child are here:
For 11 weeks - NT measurement should be 2.1 mm
For 13 weeks 6 days, - NT measurement should be 2.8 mm
Abnormal Values
Normal NT Scan report of more than 2.8 mm denote more fluid than usual. The higher the fluid measurement, the higher the risk for genetic disorders like
- Down Syndrome
- Congenital heart disease
- Patau Syndrome
- Edwards Syndrome
- Turner Syndrome
FAQs on NT Ultrasound
No, USG NT Scan is not a painful process. If your scan is done through your vagina, the sonographer will gently insert a small, lubricated USG probe. The probe may be a little uncomfortable but isn't usually painful.
2. Can a NT ultrasound tell gender?
No, the NT scan cannot determine the baby's gender. It measures fluid thickness at the baby's neck, potentially indicating chromosomal abnormalities.
The ultrasound NT scan full form is Nuchal Translucency. It is an ultrasound that measures the amount of fluid behind your baby's neck in the first trimester of pregnancy.
4. What a normal NT scan value at 13 weeks?
If the fetus is 13 weeks old, the fetal ultrasound measures the nuchal translucency will usually be less than 2.8 mm.
Conclusion
The ultrasound NT scan is a safe test that doesn't cause any harm to you and your baby. The scan is quite an accurate process to determine the risk of abnormalities in the developing fetus. Even though it is a recommended test in the first trimester, few women skip this test as they don't want to know their risk.
Your NT scan results can be combined with blood tests to give a more accurate estimate of your risk. Bookmark our site to know more tests that should be done during pregnancy.
