Hepatitis B is a viral infection called HBV infection, which affects liver function and causes some complications during pregnancy. With the rising impact of this HBV infection across the globe, pregnant women should be aware of the risks of Hepatitis B, how Hep B can affect pregnancy, and what are the HBV treatment options.
Overall, this comprehensive guide helps in delivering a useful understanding of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy. Let’s Dive In!
What is Hepatitis B and Pregnancy?
As you heard earlier Hepatitis B is a viral infection, caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). This virus infection can cause both acute and chronic liver disease. This virus can spread via direct contact with infectious body fluids like blood, semen, or vaginal secretions.
Hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted to children from their mothers during pregnancy, especially while giving birth. So, it is even more important for mothers to understand the consequences of Hepatitis B during pregnancy.
Before that, let’s see what are the common hepatitis B virus symptoms from the next modules. Also, click on this informative guide called Hepatitis C in Pregnancy to understand the symptoms, causes, risks, management, and treatment.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
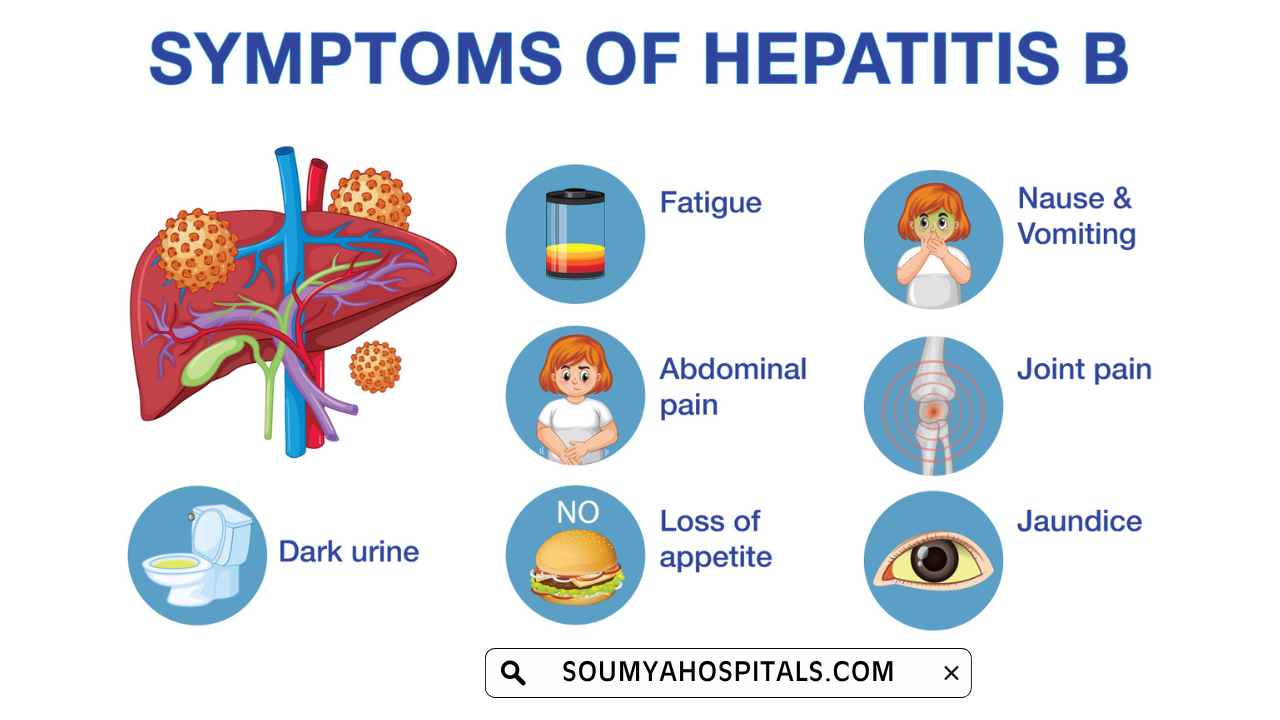
During pregnancy, expected women have some of the common Hep B symptoms as an early sign of pregnancy. Many of them may get confused or mistaken with typical pregnancy discomforts.
Hence, visit for the regular screening of hepatitis B once you find out any of the following symptoms of HBV during pregnancy and prevent transmission to your infants:
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Dark urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain
Risks Associated with Hepatitis B in Pregnancy
Any infection that affects pregnant women leads to certain risks during or after pregnancy in both mother and baby. Hence, look at the risks associated with HBV infection for parent and baby from here:
Maternal Risks
Expected women or mothers with acute or advanced chronic Hepatitis B would be at risk of several complexities, including:
- Liver Damage: Over time, this HBV chronic infection may cause liver cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Preterm Birth: A few surveys say that an active Hepatitis B infection may show the biggest impact of preterm labor among mothers.
- Increased Bleeding Risk: Liver dysfunction may give you the risk of bleeding during delivery.
Risks to the Baby
The main risk of Hep B virus infection in the baby is vertical transmission of infection during childbirth. Yes, there is a possibility of transmitting the virus to the baby during delivery from the HBV-infected mother.
The transmission rate differs as the mother has active viral replication:
- High Viral Load: Mothers with high HBV DNA levels had a high chance of transmitting the infection to the baby.
- Low Viral Load: Mothers with low viral loads or HBV DNA levels have a minimum possibility of transmitting the virus to the infants.
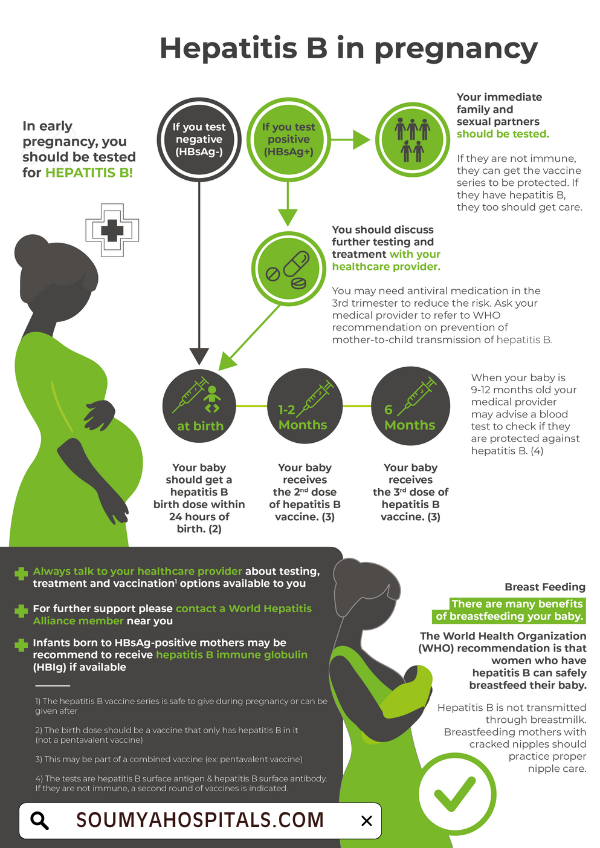
Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission of HBV
To stop the risk of mother-to-child transmission, you can try the following measures:
- Screening: During the initial prenatal visit, every conceiving woman should go through the hepatitis B screening tests.
- Antiviral Therapy: One of the best preventive measures is treating pregnant women with high viral loads with antiviral medications in the third trimester. This measure can help you minimize the risk of transmission.
- Vaccination: HBV-positive mothers who are given childbirth should get the vaccine-related to Hepatitis B and Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) before 12 hours of birth.
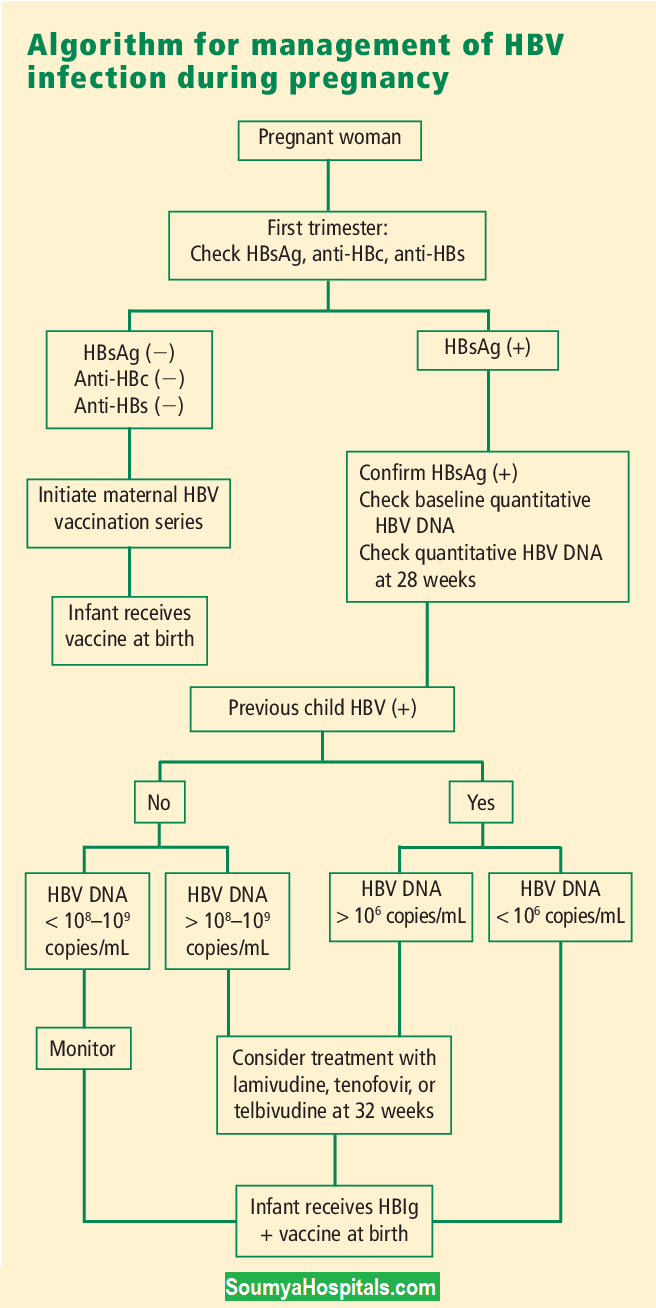
Diagnosis of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy
If you are pregnant and find out that you have hep B virus then the following diagnosis should be done before treating the infection. Hence, check on the Hepatitis B Screening Tests and follow-up tests to get clarity during the actual tests.
Hepatitis B Screening Tests
To diagnose Hepatitis B in pregnant persons, the following tests are performed commonly:
- HBV DNA Test: This DNA test is simple and precise in detecting the amount of virus currently available in the blood. It helps to evaluate the risk of mother-to-child transmission.
- HBsAg Test: You can perform this test to identify the existence of Hep B surface antigen (HBsAg) in the blood, showing an active infection.
- Anti-HBs Test: It is mainly used to measure the antibodies opposing Hep B and suggests vaccination or recovery.
HBV Follow-Up Testing
If a pregnant woman tests positive for HBsAg, further testing may be necessary to determine her viral load and assess liver function through tests such as:
- Liver Ultrasound: To determine the structure of the liver and identify the abnormalities, testing with imaging scan technology is beneficial.
- Liver Function Tests: This helps evaluate the blood proteins and enzymes that signify liver health.
Learn More On Blood Tests During Pregnancy First Trimester
Management & Treatment of Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
Managing the Hep B-affected persons can be possible by treating the virus using the best possible options mentioned below:
Antiviral Treatment Options
Chronic hepatitis B-infected pregnant women are considered to be treated with antiviral medications. These medications can be sorted separately from person to person based on their viral load and overall health status.
Below are the commonly used antiviral medications for chronic HBV pregnant women:
- Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (TDF): A much-chosen medication to treat hep B because of its safety profile during pregnancy and significance in lowering viral load.
- Entecavir: If TDF is not right for any patient, then the alternative option to consider is Entecavir.
Timing of Treatment
What is the best time to treat Hepatitis B? Is the most commonly asked query in any search platform. If you’re one among them then here is the answer to it.
The best time to initiate the Antiviral therapy for Hep B treatment is nearly 28 weeks gestation (during the third trimester) with high viral loads. The treatment should go on until delivery to reduce mother-to-child transmission risks.
Delivery Considerations
There are two delivery modes to be considered by pregnant women with Hepatitis B. They are:
- Vaginal Delivery: For mothers with well-controlled HBV infection, vaginal delivery is typically considered safe.
- Cesarean Section: If there are concerns about the mother's health or if there are signs of active viral replication at delivery, a cesarean section may be suggested.
Postpartum Care and Follow-Up
After giving birth, it's crucial for new mothers diagnosed with Hepatitis B to take care of their liver health and to follow up on antiviral treatment as necessary. Moreover, newborns need to get the following care:
- Hepatitis B Vaccine: This vaccine should be administered within 12 hours after the baby is born to protect against Hepatitis B.
- HBIG Administration: Along with the first dose of the vaccine, the baby should also receive Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) to further protect against the virus.
Long-Term Monitoring
Monitoring the Hepatitis B infection for long term results in the awareness of the condition about their liver function and estimates possible complications related to chronic Hepatitis B infection.
Conclusion
Hepatitis B poses significant risks during pregnancy. Proper screening, management, and treatment strategies can effectively mitigate these risks. Pregnant women should have open discussions with their healthcare providers about their HBV status and any concerns they may have.
Understanding how Hepatitis B affects maternal and infant health can help expectant mothers take proactive steps toward ensuring a safe pregnancy outcome. For more such information on pregnancy screenings & tests, visit our website @soumyahospitals.com regularly.
