Consistent practice with CEN Practice Questions is essential for achieving a high score on the exam.
Question 1.
The emergency nurse is providing education regarding prevention of urinary tract infections. This would include all of the following EXCEPT:
[a] wipe from the back to the front of the perineum.
[b] drink plenty of fluids on a daily basis.
[c] voiding immediately following intercourse.
[d] avoiding bubble baths and hot tubs.
Answer:
[a] wipe from the back to the front of the perineum.
Nursing Process: Evaluation
Rationale:
Wiping after using the toilet should be done from the front to the back of the perineum. Drinking fluids, voiding after intercourse, and avoiding bubble baths and hot tubs as well as voiding frequently, not “holding it” and being cautious with feminine products that are irritating are appropriate prevention techniques for urinary tract infections.
Question 2.
Which of the following is the most common etiology for urinary tract infection?
[a] Streptococcus
[b] Neisseria gonorrhoeae
[c] Escherichia coli
[d] Chlamydia trachomatis
Answer:
[c] Escherichia coli
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Escherichia coli (E.Coli) is the most common cause. This is due to the close proximity of the rectum and the E. coli that is found in the stool. The remaining choices can also be causes of a urinary tract infection, although not as common.
Question 3.
A patient experiencing epididymitis may experience relief of pain by elevation of the scrotum. This is known as which of the following signs?
[a] Kehr’s
[b] Prehn’s
[c] Kernig’s
[d] Brudzinski’s
Answer:
[b] Prehn’s
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Pain associated with epididymitis is relieved by elevation of the scrotum. This test can be used as a diagnostic tool as well and is called Prehn’s sign. Kehr’s sign is diagnostic in splenic injuries and any other condition that causes irritation to the diaphragm. It causes referred pain to the left shoulder. Kernig’s sign and Brudzinski’s sign are both signs of meningeal irritation. They include inability to straighten the leg without pain with the hip flexed while supine (Kernig’s) and involuntary flexion of arms, hips, and knee with passive flexion of the neck (Brudzinski’s).
Question 4.
Priapism may be caused by all of the following disease processes EXCEPT:
[a] sickle cell crisis.
[b] spinal cord injury.
[c] bladder cancer.
[d] trichomonas.
Answer:
[d] trichomonas.
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Priapism is a prolonged erection in the absence of stimulation. Trichomonas is a sexually transmitted disease and does not cause this. Sickle cell crisis, spinal cord injury, and bladder cancer can cause this symptom. Other causes include fat embolism, cauda equina, and leukemia.
Question 5.
Pain that occurs as a transient mid-cycle, sudden sharp and unilateral pain is known as:
[a] dysmenorrhea.
[b] endometriosis.
[c] appendicitis.
[d] mittelschmerz.
Answer:
[d] mittelschmerz.
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Mittelschmerz pain occurs during ovulation and is caused by increasing ovarian capsular pressure before the follicle erupts; therefore, the unilateral pain. Dysmenorrhea is pelvic pain during menses. Endometriosis is a condition where endometrial tissue develops outside of the uterus and causes pain during menses. Appendicitis does not occur in conjunction with menses or ovulation.
Question 6.
Which of the following conditions occurs when the normal bacterial flora in the vagina is replaced with “bad” bacteria due to a decrease in lactobacillus?
[a] Bacterial vaginosis
[b] Candidiasis
[c] Trichomoniasis
[d] Herpes simplex
Answer:
[a] Bacterial vaginosis
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Bacterial vaginosis is an infection that is believed to be caused by a decrease in the organism Lactobacillus. This helps to maintain the acidic enviroment that is necessary for a healthy vagina. When the count of this organism is lowered, “bad” bacteria can grow and cause problems. Although this is not considered a sexually transmitted disease (STD), it can create a situation where the potential for STDs is increased. Candidiasis is an airborne fungal colonization, trichomoniasis is a protozoan infection that is sexually transmitted, and herpes simplex is a viral STD.
Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis are vaginal odor; thin, whitish discharge; and irritation to the vulva. This can be associated with recent antibiotic use, douching, the use of IUD’s, and increased sexual activity. Remember that “natural or lambskin” condoms do not offer effective protection against sexually transmitted infections.
Question 7.
In certain cases, which of the following medications may be used to medically manage an ectopic pregnancy instead of surgery?
[a] Doxycycline (Vibramycin)
[b] Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
[c] Methotrexate (Trexall)
[d] Metronidazole (Flagyl)
Answer:
[c] Methotrexate (Trexall)
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Methotrexate (Trexall), a cytotoxic medication, is a folic acid antagonist and inhibits further duplication of fetal cells. Doxycycline (Vibramycin), ceftriaxone (Rocephin), and metronidazole (Flagyl) are antibiotics and not used for this condition but are used in the treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Methotrexate is used on embryos that are less than 4.0 cm in diameter or greater than 3.5 cm with a heart-beat, which makes it then a relative rather than absolute contraindication. Patients receiving this medication must have serial beta-human chorionic gonadotropins (BHCGs) drawn to make sure it is effective. Every hospital should have written policies on the administration of methotrexate.
Question 8.
A pregnant patient presents with complaints of heavy vaginal bleeding and severe abdominal cramping. Further diagnostic testing reveals that she has a positive pregnancy test and an open cervical os. Which of the following diagnoses would the emergency nurse expect?
[a] Threatened abortion
[b] Inevitable abortion
[c] Missed abortion
[d] Septic abortion
Answer:
[b] Inevitable abortion
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
An inevitable abortion would present with an open os, which indicates that there is no way to save the pregnancy. A threatened abortion is defined as vaginal bleeding, mild cramping, and a closed or slightly opened cervical os. In a missed abortion, the fetus has not formed or has died at some point in the process but remains within the uterus along with the placenta. A septic abortion is characterized by severe abdominal cramping, high fever, and malodorous vaginal discharge after an elective abortion has occurred.
Question 9.
A 35-week pregnant patient presents with complaints of a headache, vision changes, and decreased urination. The emergency nurse assesses her and discovers edematous hands, legs, and feet. Her vital signs are as follows:
Blood pressure - 160/100 mm Hg
Heart rate - 80 beats/minute
Respirations - 14 breaths/minute
Pulse oximetry - 98% on room air
Temperature - 98.2° F (36.7° C)
Which of the following medications would the emergency nurse expect the provider to prescribe to prevent seizure activity?
[a] Lorazepam (Ativan)
[b] Diazepam (Valium)
[c] Calcium gluconate
[d] Magnesium sulfate
Answer:
[d] Magnesium sulfate
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Magnesium sulfate is a smooth muscle relaxant and is the most effective preventive treatment for the preeclamptic patient. Lorazepam (Ativan) and diazepam (Valium) are given to stop seizures. They would not be the first choice for seizure prevention in the preeclamptic patient. Calcium gluconate is given to counteract a magnesium sulfate toxicity.
Continuous fetal monitoring should be done for the preeclamptic patient. Vital signs, especially respirations and deep tendon reflexes, should be checked at least every 15 minutes. Do not take responsibility for fetal monitoring unless you have been trained in this piece of equipment! Leave it to the Labor and Delivery folks!!
Question 10.
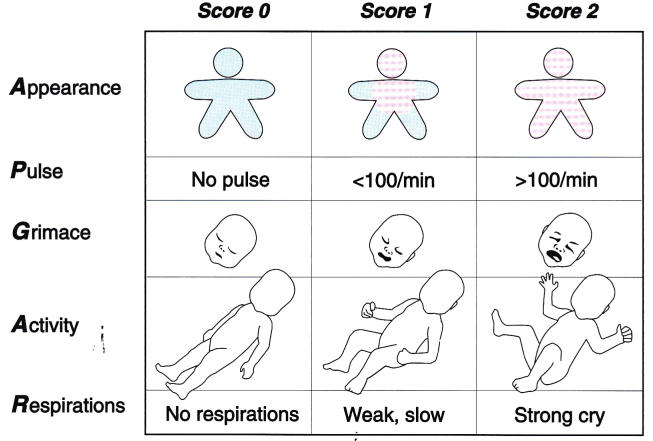
A delivery occurs in the emergency department. The baby presents with blue limbs, pink body, heart rate of 142 beats/minute, some flexion, some motion, and a weak cry. What is this infant’s APGAR score?
[a] 10
[b] 9
[c] 7
[d] 6
Answer:
[d] 6
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
According to the APGAR scoring scale, this infant would receive 1 point for the flexion (Activity or muscle tone); 2 points for Pulse rate, which is over 100 beats/minute; 1 point for the' motion activity (Grimace or reflex irritability); 1 point for the blue limb color with the pink body (Appearance); and 1 point for the weak cry (Respirations). This equals a scoring of 6.
Question 11.
The parents of a learning impaired child report the child has been crying with urination and an odor has been noted from his penis. Which of the following diagnoses would be the highest suspicion for this child?
[a] Urinary tract infection
[b] Foreign body in the urethra
[c] Hypospadias
[d] Hyperspadias
Answer:
[b] Foreign body in the urethra
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Foreign bodies are often placed in orifices as a means of exploration, especially in the developmentallly impaired. One might suspect a urinary tract infection in this patient as well, but they are less common in male patients. Hypospadias is a birth defect in which the urinary meatus is located inferior/below the glans penis and may actually be near the scrotum. Hyperspadias is also a congenital defect in which the urinary meatus is located on the superior/upper surface of the penis.
Question 12.
An emergent urologic consult has been made for a patient with a penile amputation. Which of the following actions should the emergency nurse take to preserve the amputated penis?
[a] Place it directly on ice.
[b] Place it in a clean towel.
[c] Place it in a dry gauze dressing.
[d] Place it in a saline-soaked gauze dressing.
Answer:
[d] Place it in a saline-soaked gauze dressing.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Proper care for an amputated part is to place it in a saline-soaked dressing, which will keep the tissue moist. A sterile bag will keep it clean and then placing it on ice will help keep the tissue viable. Placing the amputated part directly on ice may damage the tissue. Placing it in a dry towel or gauze may dry out the edges, making it difficult to reattach.
Question 13.
The absence of the cremasteric reflex has a high sensitivity but low specificity for which of the following conditions?
[a] Penile foreign body
[b] Testicular torsion
[c] Urethral tear
[d] Epididymitis
Answer:
[b] Testicular torsion
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
The cremasteric reflex is characterized by the normal elevation of the testes that occurs when the upper medial thigh is stroked. This will not be present if there is a testicular torsion. A penile foreign body, urethral tear, or epididymitis does not have this as a manifestation of these processes.
Question 14.
A patient is recovering from a transurethral resection of the prostate. The nurse is comfortable that the patient understood his postoperative discharge instructions when he presents to the emergency department with complaints of which of the following?
[a] Bright red blood in the urine
[b] Passing small blood clots in urine
[c] Inability to urinate
[d] Low-grade fever
Answer:
[c] Inability to urinate
Nursing Process: Evaluation
Rationale:
Patients are told to seek attention if an inability to urinate occurs, as there may be a clot obstructing the flow. Discharge instructions for this surgical procedure should direct the patient to expect the urine to be bloody and have some small clots. He may even expect to run a low-grade fever, but should contact the physician for a fever above 102° F (38.9° C).
Urologists should instruct their postoperative TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate) patients to drink more water if their urine becomes the consistency of ketchup.
Question 15.
The emergency nurse should suspect which of the following types of injury if a 22-year-old patient presents with a history of falling on to a balance beam from a standing position on the beam?
[a] Hangman’s injury
[b] Straddle injury
[c] Chance fracture
[d] Salter-Harris fracture
Answer:
[b] Straddle injury
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Straddle injuries occur when patients fall onto objects while their legs are apart. Serious injuries can occur to the perineum. Among these are urethral tears, vulvar hematomas, and extensive ecchymosis to the perineum. Surgical intervention may be required to repair tears or evacuate hematomas.
A hangman’s injury is a fracture of the second cervical vertebrae or subluxation of C2 or C3 caused by an accidental or violence-related hanging. A chance fracture is a spinal fracture that extends through all three spinal columns (anterior, middle, and posterior) and is very unstable requiring surgical intervention. Salter-Harris is a classification that is associated with fractures that extend through the epiphysis (growth plate).
Question 16.
Which of the following conditions is manifested by frequent sustained vomiting, often resulting in dehydration and weight loss of the pregnant patient?
[a] Cyclical vomiting
[b] Gastroenteritis
[c] Hyperemesis gravidarum
[d] Ulcerative colitis
Answer:
[c] Hyperemesis gravidarum
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Hyperemesis gravidarum is more extreme than morning sickness and is experienced by 70% to 80% of women early in their pregnancy. This condition often continues throughout pregnancy and is thought to be caused by the rise of hormone levels.
It may lead to hospitalization for rehydration. Cyclical vomiting occurs as sudden and repeated episodes of vomiting but is not associated with pregnancy. Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestine, and ulcerative colitis is inflammation of the colon with ulcers.
Question 17.
Which of the following blood tests detects fetal red blood cells in the maternal circulation indicating fetal hemorrhage through the placenta?
[a] Kleihauer-Betke test
[b] Fecal occult blood test
[c] Adrenal stress profile
[d] Thromboelastogram
Answer:
[a] Kleihauer-Betke test
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
The Kleihauer-Betke assay is a necessary test anytime a pregnant patient is involved in a trauma situation because it detects a disruption in the feto-maternal circulation. The presence of fetal red cells in the maternal circulation is a positive test. The fecal occult blood test would check for blood in the stool.
An adrenal stress profile would check for adrenal hormone levels assisting in the diagnosis of adrenal insults. Cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) hormones are measured in this test. A thromboelastogram test deals with the recognition of acute coagulopathies and also assists with the use of blood products during resuscitative events.
Question 18.
Which of the following is NOT a normal physiologic change that occurs in pregnancy?
[a] Resting heart rate increases.
[b] Peripheral resistance increases.
[c] Circulating plasma increases.
[d] Oxygen consumption increases.
Answer:
[b] Peripheral resistance increases.
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Peripheral resistance decreases during pregnancy causing a slight decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The resting heart rate actually increases 10 to 20 beats/minute and the circulating blood volume increases by 30% to 50%. Respirations increase to help accommodate for the increased oxygen consumption during pregnancy.
Cardiac output increases during pregnancy and can elevate to 50% greater than pre-pregnancy by the 16th to 20th week. Increases in stroke volume and heart rate are also present. Remember that the formula for cardiac output is: CO = SV X HR (cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate).
Question 19.
Which of the following is NOT an indicator that the placenta is ready to deliver?
[a] Umbilical cord advances 2” to 3”.
[b] Fundus rises upward.
[c] Uterus becomes soft.
[d] Small gush of blood noted.
Answer:
[c] Uterus becomes soft.
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Delivery of the placenta may take some time after the baby appears. Evidence that delivery of the placenta is imminent includes the uterus becoming firm and globular in nature. The umbilical cord will advance a few inches, the fundus will rise, and a gush of blood will occur.
It is important when the placenta is delivering to not pull or tug on it too hard. Just exert a small amount of traction on it and have the mother bear down. Counteraction is important in this part of the delivery process. Pulling too hard could pull the uterus inside out (uterine inversion) causing the necessity of an emergent hysterectomy.
Question 20.
A patient enters the emergency department complaining of nausea, vomiting, restlessness, and severe right-sided lower back pain with sudden onset 1 hour ago. The patient appears slightly pale and is diaphoretic. Vital signs are as follows:
Blood pressure - 140/92 mm Hg
Pulse - 120 beats/minute
Respirations - 32 breaths/minute
Pulse oximetry - 96% on room air
Temperature - 98° F (36.7° C)
Which of the following would be subjective data supporting a diagnosis of renal calculi?
[a] Mild flu symptoms last week
[b] Coffee-ground emesis
[c] Dark, scant urine output
[d] Right upper quadrant pain
Answer:
[c] Dark, scant urine output
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Most patients with renal calculi have blood in the urine from the stone’s passing. The urine is dark, tests hemoccult positive (which would be objective data), and is usually scant. Coffee-ground emesis refers to an upper gastrointestinal bleed. Right upper quadrant pain is a manifestation of cholecystitis. Mild flu symptoms are not a precipitating factor related to renal calculi.
Question 21.
Which of the following laboratory values supports a diagnosis of pyelonephritis?
[a] Myoglobinuria
[b] Ketonuria
[c] Pyuria
[d] Leucopenia
Answer:
[c] Pyuria
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Pyelonephritis is diagnosed by the presence of leukocytosis (increased white blood cell count), hematuria, pyuria, and bacteriuria. Myoglobinuria indicates the muscle protein, myoglobin, is being released in the process of rhabdomyolysis; ketonuria is present in diabetics; and leukopenia indicates a decrease in white blood cell counts.
Pyelonephritis can often develop into sepsis. It is important to make sure that if these patients arrive and cannot be bedded immediately, they understand the importance of waiting for treatment. Treating pyelonephritis early can help decrease their chances of the greater worry of a septic event.
Question 22.
A patient with a history of heart failure and
sepsis is at risk for which of the following genitourinary
complications?
[a] Renal calculi
[b] Urinary retention
[c] Acute renal failure
[d] Urethral stricture
Answer:
[c] Acute renal failure
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Heart failure and sepsis can decrease cardiac output. Decreased perfusion to the kidney can lead to acute renal failure. Renal calculi, urinary retention, and urethral strictures are urinary disease processes dealing with obstruction in the renal urine collection system.
Question 23.
Which of the following is an appropriate intervention for a patient with a renal calculus?
[a] IV fluids at 100 mL/hour
[b] Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
[c] Indwelling urinary catheter
[d] Nasogastric tube
Answer:
[b] Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
The medication of choice to treat the pain associated with kidney stones are the NSAIDS. Ketorolac (Toradol) can be used intravenously and is often used with great success for this disease process. Opioids can be used but, the movement, of course, is away from opioid use. Intravenous fluids are important as well, but the rate is wrong in the option. Some believe that increased fluids would be needed to encourage passage of the stone. There is some controversy on this aspect, but the general train of thought is hydration with intravenous fluids. Indwelling urinary catheter and nasogastric tubes are not necessary.
Question 24.
Which of the following is a virus in which there are more than 100 types and may present with tall, pinkish-gray lesions or genital warts?
[a] Bacterial vaginosis
[b] Gonorrhea
[c] Herpes simplex
[d] Human papillomavirus
Answer:
[d] Human papillomavirus
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Human papillomavirus is part of a family that contains more than 100 different types. Each of these types can cause different processes. Types 6 and 11 are associated with genital warts, whereas types 16, 18, 31, 33, and 35 are seen with cervical neoplasms. Bacterial vaginosis is an infectious process due to a depletion of normal vaginal flora. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that is one of the main causes of pelvic inflammatory disease. Herpes simplex has two strains—HSV-1 causes oral herpes (cold sores) and HSV-2 causes genital herpes. The sores associated with genital herpes appear as blisters.
Question 25.
Which of the following is a gynecologic/obstetric condition that must be considered as a potentially dangerous situation for every female presenting with abdominal pain during childbearing years?
[a] Ectopic pregnancy
[b] Ovarian cyst
[c] Ovarian torsion
[d] Dysmenorrhea
Answer:
[a] Ectopic pregnancy
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy occurring outside of the uterus) usually manifests before 12 weeks’ gestation, produces pelvic pain, and shock if ruptured. It is considered a true emergency and is a major cause of maternal death. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac in the ovary that may be painful, is usually self-limiting, but may develop hypovolemia when it ruptures/ Ovarian torsion occurs when the ovary twists itself around the stalk, that contains the blood vessels feeding the ovary and the fallopian tube. Pain is due to ischemia and requires surgical intervention. Dysmenorrhea is defined as painful menstruation in the absence of any other pelvic condition.
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, be sure to initiate a large-bore intravenous line. It is much easier to obtain this before the pregnancy ruptures and the patient is hypovolemic and in shock! And be sure to be suspicious of this in every woman of childbearing age with lower abdominal pain. Do not lower your concern for this potentially fatal process!
Question 26.
Which of the following is NOT a disease process that HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome can mimic and needs to be part of the differential diagnosis?
[a] Thrombocytopenic purpura
[b] Pyelonephritis
[c] Hepatitis
[d] Crohn’s disease
Answer:
[d] Crohn’s disease
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
HELLP syndrome is a potentially life- threatening form of preeclampsia that occurs when the patient develops multisystem organ failure. Symptoms of Crohn’s disease are not part of the picture of HELLP syndrome. Thrombocytopenic purpura, pyelonephritis, and hepatitis are all part of the differential diagnosis that must be done because the symptoms are similar with HELLP syndrome.
HELLP stands for Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, and Low Platelets. One of the most important things to remember is that this syndrome, as well as preeclampsia, can occur in the postpartum period!
Question 27.
Which of the following statements made by a patient being discharged with a diagnosis of trichomonas and placed on a regimen of metronidazole (Flagyl) indicates that instructions were understood?
[a] “I'm very glad that I don’t have to tell anyone about this.”
[b] “I'm so excited that I just found out that I am pregnant.”
[c] “I should not drink alcohol while I am taking this medication.”
[d] “The doctor said this would not impact my coumadin medication.”
Answer:
[c] “I should not drink alcohol while I am taking this medication.”
Nursing Process: Evaluation
Rationale:
Alcohol should not be used while the patient is taking metronidazole (Flagyl). It will cause extreme vomiting, headaches, and flushing. Patients who are diagnosed with trichomonas must share this information with their sexual partners and they should be treated as well. Patients who are in the first trimester of pregnancy should not take metronidazole (Flagyl). Metronidazole (Flagyl) can potentiate the effects of warfarin (Coumadin), resulting in a prolonged prothrombin time.
Question 28.
A patient with scrotal pain that has been present for 2 days is admitted to the emergency department. Which of the following signs would indicate a diagnosis of epididymitis rather than testicular torsion?
[a] Hypoperfusion on testicular scan
[b] Leukopenia on complete blood count
[c] Bacteriuria in urinalysis
[d] Elevated creatinine level
Answer:
[c] Bacteriuria in urinalysis
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Epididymitis is suggested by hyperperfusion on the testicular scan, an elevated white blood cell count, and the presence of bacteria in the urine. Flypoperfusion or no perfusion would indicate testicular torsion. Leukopenia indicates a decrease in white blood cell count. An elevated creatinine level is an indicator of renal, not scrotal disease.
Epididymitis, an inflammation of the epididymis, can be seen in any age group but is more common in those aged 14 to 35 years. Testicular torsion is a disease process seen more in prepubertal and pubertal-aged boys. Never leave a young boy with complaints of scrotal pain in the waiting room! Request an ultrasound if no beds are available.
Question 29.
Which of the following orthostatic vital sign readings would be of concern for a patient suspected of internal hemorrhage from a possible ruptured ectopic pregnancy?
[a] Lying—blood pressure, 120/64 mm Hg; heart rate, 82 beats/minute
Sitting—blood pressure, 114/60 mm Hg; heart rate, 72 beats/minute
Standing—blood pressure, 132/84 mm Hg; heart rate, 92 beats/minute
[b] Lying—blood pressure, 92/40 mm Hg; heart rate, 64 beats/minute
Sitting—blood pressure, 94/60 mm Hg; heart rate, 72 beats/minute
Standing—blood pressure, 86/54 mm Hg; heart rate, 78 beats/minute
[c] Lying—blood pressure, 128/52 mm Hg; heart rate, 74 beats/minute
Sitting—blood Pressure, 96/48 mm Hg; heart rate 94 beats/minute
Standing—blood pressure, 72/40 mm Hg; heart rate, 120 beats/minute
[d] Lying—blood pressure, 116/80 mm Hg; heart rate, 76 beats/minute
Sitting—blood pressure, 120/76 mm Hg; heart rate, 82 beats/minute.
Standing—blood pressure, 130/64 mm Hg; heart rate, 88 beats/minute
Answer:
[c] Lying—blood pressure, 128/52 mm Hg; heart rate, 74 beats/minute
Sitting—blood Pressure, 96/48 mm Hg; heart rate 94 beats/minute
Standing—blood pressure, 72/40 mm Hg; heart rate, 120 beats/minute
Nursing Process: Evaluation
Rationale:
Orthostatic hypotension can be a sign of hemorrhage and a precursor to hypovolemic shock. An increase in the pulse of 20 beats/minute or a systolic drop of 10 to 20 mm Hg is a positive indicator of occult blood loss. A negative orthostatic test does not rule out the possibility of bleeding. The other options do not indicate these changes.
When discharging a patient with a kidney stone, be sure to send them home with a strainer to catch the offending stone. If no strainer is available, a coffee filter can be substituted. presented that recommends the measurement of vital signs in supine and then standing at 1 minute and 3 minutes. Positive indicators are systolic change decrease of 20 mm Hg; diastolic change- decrease of 10 mm Hg; heart rate—increase by 20 beats/minute.
Most clinicians adhere to the older version of orthostatic vital signs. Be aware that negative readings do not mean that the patient is “OK. ” One of the best types of patients to perform this easy test on is the one who arrives to the emergency department days after a traumatic event with vague symptoms of “not feeling well” along with possible diaphoresis and nausea or vomiting.
Question 30.
A patient is being treated for urinary calculi and his urine pH is reported to be 4.8. Which of the following types of renal calculi would this patient most likely have?
[a] Magnesium
[b] Struvite
[c] Calcium phosphate
[d] Uric acid
Answer:
[d] Uric acid
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Uric acid crystals precipitate in a pH condition less than 5.5, leading to stone formation. Magnesium, ammonia, and phosphate stones (also called triple phosphate, struvite or infection stones) develop when the urine pH is higher than 7.2 and ammonia is present in the urine. Calcium phosphate stones also develop in alkaline urine (pH greater than 7.2).
Question 31.
All of the following are possible complications of an ovarian cyst EXCEPT:
[a] adhesions.
[b] peritonitis.
[c] ischemic ovary.
[d] mittelschmerz.
Answer:
[d] mittelschmerz.
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
An ovarian cyst can cause adhesions and peritonitis from leakage of cystic contents. An ovary can become ischemic from torsion that occurs when a cyst is twisted on its pedicle. Mittelschmerz occurs in the form of abdominal pain at ovulation; it needs to be considered in the differential diagnosis of an ovarian cyst.
Question 32.
Which of the following medications in the patient’s medical history can increase the risk of dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)?
[a] Antibiotics
[b] Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
[c] Steroids
[d] Muscle relaxants
Answer:
[c] Steroids
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding can be caused by hormone replacement therapy, steroids, androgens, digitalis, and anticoagulants. Nonsteroidals may increase bleeding after it has started. Antibiotics and muscle relaxants are not known to cause dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Question 33.
In which of the following positions should the patient be placed to achieve the most accurate diagnostic bladder ultrasound result?
[a] Prone
[b] Supine
[c] Semi-Fowler’s
[d] Lithotomy
Answer:
[b] Supine
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
A diagnostic bladder ultrasound is performed to determine bladder volume. The bladder is most easily accessed with the patient in a supine position. Accurate determination of bladder volumes can guide the need for bladder aspiration or catheterization. The prone (lying on the abdomen), semi-Fowler’s (sitting up at a 30- to 45-degree position), and lithotomy (pelvic examination position) positions will not achieve accurate results.
Question 34.
Zovirax (Acyclovir) is the drug of choice for the treatment of genital herpes lesions. The mechanism of action includes all of the following EXCEPT:
[a] providing bactericidal functions.
[b] relieving local and systemic pain.
[c] diminishing the interval of viral shedding.
[d] decreasing the formation of new lesions.
Answer:
[a] providing bactericidal functions.
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Herpes is a viral, not bacterial, infection (although a secondary bacterial infection can occur), and acyclovir is not bactericidal. Acyclovir relieves systemic pain, diminishes the interval of viral shedding, and decreases the formation of new lesions.
Question 35.
Which of the following is an ovarian cyst that usually contains hair and teeth?
[a] Corpus luteum
[b] Teratoma
[c] Endometrioma
[d] Chocolate cyst
Answer:
[b] Teratoma
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
A teratoma, or dermoid cyst, is produced from all three germ layers and usually contains hair and teeth, although it can contain tissue from any body structure. Teratoma cysts usually occur during the active reproductive years. A corpus luteum cyst is caused by cystic changes in an ovary from hemorrhage in a mature corpus luteum. It can cause bleeding and hemorrhage. An ovarian endometrioma is a chocolate cyst and occurs when endometrial tissue in an ovary cyclically bleeds with monthly periods and collects blood and blood clots.
Question 36.
The provider has diagnosed a patient with a hydatidiform mole. The emergency nurse will expect the human gonadotropin level to be:
[a] zero.
[b] very low.
[c] very high.
[d] normal for gestational age.
Answer:
[c] very high.
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
A hydatidiform mole or gestational trophoblastic tumor demonstrates an extremely elevated human chorionic gonadotropin level. Other signs include snowstorm pattern on ultrasound, early preeclampsia, absence of fetal heart tones, bleeding or spotting, and enlarged uterus.
Question 37.
Which of the following test results provides” information that is important immediately following a sexual assault?
[a] Negative serologic test for syphilis
[b] Normal complete blood count
[c] Rhogam test for blood type
[d] Negative pregnancy test
Answer:
[d] Negative pregnancy test
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
It is important to know if the patient was pregnant when the attack occurred. If she is not pregnant, the appropriate “morning after” medication (ethinyl estradiol and norgestrel) can be given within 72 hours. If the patient chooses to use plan B (morning after pill), they will need a prescription for an antiemetic as the medication can cause nausea. Other treatments for the patient would include prophylactic antibiotic therapy. Cultures and tests for syphilis will not be resulted for several days. A complete blood count does not provide vital information unless the patient is injured and hypovolemia is suspected. Rhogam will provide information regarding the Rh of the mother. This test is not indicated in this situation.
Question 38.
As part of the sexual assault examination, which of the following should be done with the victim’s clothing?
[a] Place it in a paper bag and seal it with evidence tape.
[b] Return it to the patient after examining it.
[c] Place it in a plastic bag and seal it with paper tape.
[d] Shake it out carefully to look for hidden evidence.
Answer:
[a] Place it in a paper bag and seal it with evidence tape.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Clothing that was worn by the patient and obtained during the sexual assault examination should be placed in a paper bag and secured with evidence tape to ensure that no tampering occurs. When performing a sexual assault examination and collecting the clothing, each piece of clothing should be placed in a separate paper bag. Also, the patient should stand on a sheet and then that sheet should also be sent as evidence.
The emergency nurse should also put their name or initials across the fold of the bag to assist with knowledge of non tampering as well. The patient’s clothing should be carefully removed, but not shaken out; microscopic evidence may be lost. All clothing should be given to the police; it is their responsibility to determine if evidence is present.
Clothing should not be placed in plastic bags, which can cause mildew and moisture retention, both of which can cause loss of evidence. All evidence collected should be labeled with the victim’s name, site of collection, date and time of collection, and the name of the person collecting the evidence.
The nurse collecting the evidence should be sure to follow chain of custody to the "T”! All individuals touching the evidence must be documented with great care and the exchange to law enforcement of the kit must be clearly represented in the charting.
Question 39.
Which of the following should NOT be collected during a sexual assault examination?
[a] Fingernail scrapings
[b] Pubic hair
[c] Saliva specimen
[d] Upper thigh scrapings
Answer:
[d] Upper thigh scrapings
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Any potential foreign material, such as suspected semen, blood, or saliva, should be collected with a cotton swab moistened with sterile water, not by scraping. However, evidence under the fingernails must be obtained by scraping or clipping. Pubic hair samples and saliva specimens are all part of routine evidence collection.
Never chart subjective information! Always remain objective. Never chart anything like, “No evidence of sexual assault. ” Be prepared for sexual assault questions on the test! They are always there!
Question 40.
A direct blow to the male groin will most likely result in which of the following?
[a] Right testicular injury
[b] Left testicular injury
[c] Penile fracture
[d] Urethral tear
Answer:
[a] Right testicular injury
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Possibly due to its higher position, the right testicle is more prone to injury following a blow to the male groin. Penile fracture occurs following trauma while engorged. Urethral tear is more likely with a shearing-type injury as opposed to a direct blow.
Question 41.
A trauma patient with a diagnosis of a ruptured bladder has two large-bore intravenous lines, oxygen, a nasogastric tube, and an indwelling urinary catheter in place. Initial vital signs are as follows:
Blood pressure—120/54 mm Hg
Pulse—120 beats/minute
Respirations—28 breaths/minute
Pulse oximetry—95% on room air
Temperature—98.2° F (36.7° C)
Which of the following might indicate impending hypovolemic shock?
[a] Pulse of 100 beats/minute
[b] Restlessness
[c] Blood pressure of 110/64 mm Hg
[d] Request for pain relief
Answer:
[b] Restlessness
Nursing Process: Evaluation
Rationale:
Restlessness is typically the first sign of impending hypovolemic shock or hypoxia. A pulse rate of 100 beats/minute is actually a decrease compared with the original 120 beats/minute, and the blood pressure has not dropped significantly. Requests for pain relief are normal for a trauma patient.
If you are caring for a patient who is constantly pulling on or trying to remove their oxygen cannula or mask, they are probably hypoxic and confused. These are the patients who need their oxygen the most. Be ready to intubate this patient!
Question 42.
Which of the following indicates the possibility of a urethral injury during a rectal examination of a trauma patient?
[a] Low-riding prostate
[b] High-riding prostate
[c] Absent sphincter tone
[d] Positive hemoccult test
Answer:
[b] High-riding prostate
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
When the urethra is torn, a hematoma or collection of blood separates the two sections of the urethra. This may feel like a boggy mass on rectal examination and the prostate becomes "high riding." A palpable prostate gland usually indicates an intact urethra. Absent sphincter tone would refer to a spinal cord injury. The presence of blood in the rectum would probably correlate with a GI bleed or colon injury.
Question 43.
Which of the following vaginal infections does NOT require treatment of sexual partners?
[a] Neisseria gonorrhoeae
[b] Candida albicans
[c] Trichomonas vaginalis
[d] Chlamydia trachomatis
Answer:
[b] Candida albicans
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Candida albicans is a yeast (fungal infection) treated with Mycostatin (nystatin) and does not require sexual partner treatment. Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas vaginalis, and Chlamydia trachomatis all are sexually transmitted diseases that necessitate partner treatment and thorough patient education.
Question 44.
A patient sustains an 8-foot fall landing on his buttocks. Along with possible spinal compression fractures, which of the following signs would be present indicating possible genitourinary vascular trauma?
[a] Bruit at the second lumbar vertebra
[b] Suprapubic pain on palpation
[c] Slowly escalating hypertension
[d] Decreased or absent bowel sounds
Answer:
[a] Bruit at the second lumbar vertebra
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
A contrecoup injury can occur to the kidney after a fall that exerts force above the kidney. The force tears the renal pedicle and causes a bruit that can be auscultated at the first or second lumbar vertebra. Suprapubic pain accompanies a bladder injury, not a vascular disruption. Hypertension may occur after a renal injury has been repaired. Decreased or absent bowel sounds would occur with an abdominal insult that created an ileus.
Question 45.
Which of the following diluents helps to decrease discomfort of an IM injection of ceftriaxone (Rocephin)?
[a] Sterile water
[b] Dextrose 5% in water (D5 W)
[c] Sterile normal saline
[d] 1% Lidocaine plain
Answer:
[d] 1% Lidocaine plain
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) injections are very painful. Lidocaine is recommended as the diluent of choice. Sterile water, DW, and sterile saline do not have any numbing properties.
Do not use intravenous ceftriaxone (Rocephin) with lactated ringers or other solutions that contain calcium as a precipitate can occur. Do not use this medication in infants under 28 days of life with high bilirubin levels. Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) can displace the bilirubin from binding sites, adding to the disease process and producing encephalopathy.
Question 46.
4 pregnant patient has been diagnosed with a chlamydial infection. Cesarean birth is usually the delivery method of choice because it decreases the infant’s risk of developing which of the following disease
processes?
[a] Endocarditis
[b] Hepatitis
[c] Pneumonia
[d] Encephalitis
Answer:
[c] Pneumonia
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
A mother infected with Chlamydia can pass the organism to her infant during its passage through the cervix. Potential complications for the infant include conjunctivitis and chlamydial pneumonia. Endocarditis, hepatitis, and encephalitis are not passed through Chlamydia.
Question 47.
A patient complains of a foul-smelling vaginal discharge and intermittent vaginal bleeding. She normally has irregular menses and does not recall the date of her last menstrual cycle. Her triage vital signs are as follows:
Blood pressure—104/62 mm Hg
Pulse—118 beats/minute
Respirations—22 breaths/minute
Pulse oximetry—99% on room air
‘Temperature—102.4° F (39.1° C)
Which of the following should the emergency nurse suspect?
[a] Septic abortion
[b] Pyelonephritis
[c] Vaginitis
[d] Ovarian cyst
Answer:
[a] Septic abortion
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
A patient with a septic abortion will present with prolonged retained products of conception, resulting in foul-smelling vaginal bleeding or discharge, abdominal pain, and fever. Pyelonephritis does not produce a foul-smelling discharge. Vaginitis is not generally associated with bleeding and the discharge is typically frothy or curd-like. Ovarian cysts are not generally associated with discharge.
Many times, patients who have had a recent abortion will not share this information readily. The emergency nurse must be able to ask important questions without making the patient feel uncomfortable. The emergency nurse should also understand the signs and symptoms so that suspicion can lead the nurse down the right pathway.
Question 48.
A teenaged boy comes to the emergency department after waking with severe pain to his left testicle. Examination reveals the following vital signs:
Blood pressure—110/72 mm Hg
Pulse—120 beats/minute
Respirations—30 breaths/minute
Pulse oximetry—98% on room air
Temperature—98.5° F (36.9° C)
His left testicle is slightly elevated and firm. Which of the following would be the most appropriate intervention?
[a] Send patient for ultrasound.
[b] Apply ice packs to the scrotum.
[c] Prepare to transfuse blood products.
[d] Elevate scrotum to 45-degree angle.
Answer:
[a] Send patient for ultrasound.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
This patient has signs and symptoms of testicular torsion. Testicular torsion results from congenital maldevelopment between the testis and the posterior scrotal wall. This is an emergency situation and an emergent ultrasound must be done. Twisting of the spermatic cord compromises the circulation causing severe pain that is not relieved by ice or elevation. There is no blood loss associated with testicular torsion, so blood products are not indicated.
Young boys may not want to tell nurses that they have testicular pain. They may describe the pain as being in the lower abdomen. Also, the testicle in testicular torsion can cause an upwardly retracted testicle, making the pain seem to be in the lower abdomen. Be suspicious with pubertal and prepubertal boys! No fever is usually present with this process.
Question 49.
A patient presents with a history of benign prostatic hyperplasia and an inability to void for 12 hours. Which medication could contribute to his urinary retention?
[a] Ibuprofen (Motrin)
[b] Terazosin (Hytrin)
[c] Vitamin C
[d] Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
Answer:
[d] Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) is an alpha-adrenergic agonist that increases urinary resistance. The effect is minimal but can contribute to urinary retention in combination with bladder outlet obstruction (enlarged prostate gland). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen (Motrin) are associated with hematuria and acute renal failure, but not urinary retention. Terazosin is an alpha-adrenergic blocker used to improve bladder neck dyssynergia (improve bladder outlet). Adverse effects of vitamin C include acidic urine, oxaluria, and renal stones.
Question 50.
Which of the following patients would the emergency nurse expect to be admitted to an inpatient area?
[a] A 3-year-old child diagnosed with a grade I kidney contusion and microscopic hematuria
[b] A 19-year-old woman diagnosed with her second urinary tract infection in the past year
[c] A 45-year-old man with hypertension (150/100mm Hg) and acute onset of urethritis
[d] A 32-year-old woman, 30 weeks pregnant, diagnosed with fever and pyelonephritis
Answer:
[d] A 32-year-old woman, 30 weeks pregnant, diagnosed with fever and pyelonephritis
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
A pregnant patient with pyelonephritis requires aggressive treatment. She could quickly develop acute renal failure or sepsis. Children with renal injury can usually be managed as an outpatient. A young patient with an uncomplicated urinary tract infection can be discharged with thorough discharge instructions and treatment. Urethritis in a male patient is likely caused by a sexually transmitted disease and can be treated orally or intramuscularly.
Question 51.
A patient arrives in the emergency department stating that she was sexually assaulted multiple times over the past 12 hours. She is tearful and accompanied by a friend. The emergency nurse knows that which of the following is the most important piece of information from this patient at this time?
[a] She notified the police.
[b] She uses birth control.
[c] She has changed clothing.
[d] She has been sexually assaulted before.
Answer:
[c] She has changed clothing.
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Whether the patient has changed her clothes, or even brushed her teeth since the attack, is critical to evidence collection and preservation. It is also helpful if the patient has not showered, urinated, or defecated. Determining if the patient has notified the police is also important, but does not affect the assessment. It is not relevant to know if she has been previously sexually assaulted or if she is using a method of birth control at this time.
Question 52.
When caring for a sexually assaulted patient, the highest priority would be:
[a] evidence collection and preservation.
[b] report of the crime to the authorities.
[c] caring for injuries sustained in the assault.
[d] updating her family and friends.
Answer:
[c] caring for injuries sustained in the assault.
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
The patient’s well-being is always the priority. Evidence collection and preservation and encouraging police involvement are important, but is not the priority. Notifying family and friends is up to the discretion of the patient.
Question 53.
Which of the following responses indicates understanding of discharge instructions by the sexual assault victim?
[a] “I will need to have follow-up care regarding my test results for possible STDs.”
[b] “I will stay at home with my family and friends until | get my test results.”
[c] “I will return to the emergency department in a few days to get rechecked.”
[d] “This is all my fault. 1 am ashamed of myself.”
Answer:
[a] “I will need to have follow-up care regarding my test results for possible STDs.”
Nursing Process: Evaluation
Rationale:
Sexual assault patients typically receive prophylaxis for sexually transmitted diseases and pregnancy when undergoing treatment. To ensure the treatment was adequate, follow-up with either the local health department or the patient’s primary care physician is necessary. A return visit to the emergency department would not be warranted for follow-up care. While some sexual assault victims blame themselves for the attack, this certainly is not a healthy coping mechanism. Secluding herself in her home is also not a healthy option.
When caring for sexual assault victims, encourage the use of local rape crisis departments. These individuals can help the victim through the entire process. Also, encourage reporting to the proper authorities. Even if the patient does not want to file charges, it can help identify the perpetrator if subsequent events occur.
Question 54.
A patient complains of abdominal pain. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. Which type of pain is usually associated with a ruptured ectopic pregnancy?
[a] Lower quadrant pain radiating to the shoulder
[b] Sharp, right upper abdominal pain
[c] Unilateral flank pain with hematuria
[d] Colicky, diffuse abdominal pain
Answer:
[a] Lower quadrant pain radiating to the shoulder
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
Ectopic pregnancies that are leaking or have ruptured result in referred pain to the shoulder from blood irritating the diaphragm. Pain with an ectopic pregnancy occurs in either the left or right lower abdominal area. Sharp upper abdominal pain is too high for pain caused by an ectopic pregnancy. Flank pain and hematuria may be caused by a kidney infection or kidney stones. Colicky, diffuse abdominal pain is commonly associated with intestinal disorders.
Question 55.
A patient in her 34th week of pregnancy comes to the emergency department and complains of sudden onset of bright red vaginal bleeding. Her uterus is soft, and she is not experiencing any pain. Fetal heart tones are 120 beats/minute. Based on this history, the emergency nurse should suspect which of the following conditions?
[a] Abruptio placentae
[b] Preterm labor
[c] Placenta previa
[d] Threatened abortion
Answer:
[c] Placenta previa
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Placenta previa is associated with painless vaginal bleeding that occurs when the placenta, or a portion of the placenta, covers the cervical os. Serious hemorrhage can occur. In abruptio placentae, the placenta tears away from the wall of the uterus before delivery. The patient usually has pain and a board-like uterus. Preterm labor is associated with contractions and should not involve bright red bleeding. By definition, threatened abortion occurs during the first 20 weeks of gestation.
Question 56.
Following a fall down a flight of stairs, a patient in her 38th week of pregnancy is brought to the emergency department. Unless contraindicated, she should be placed in which position during assessment?
[a] Trendelenburg
[b] Supine
[c] Left lateral recumbent
[d] Knee-chest
Answer:
[c] Left lateral recumbent
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
The left lateral recumbent position avoids compression of the inferior vena cava; compressing the vessel may result in decreased uterine blood flow, fetal hypoxia, and maternal hypotension. Trendelenburg or supine position would compress this vessel. If a pregnant patient must lie flat on a backboard for spinal evaluation, a wedge may be placed under the back board to tilt it, or manual manipulation of the uterus may also be done by a provider. The knee-chest position is used to avoid compressing the umbilical cord when it is prolapsed.
Vena cava syndrome, when the fetus is lying on the vena cava, can reduce maternal cardiac output by 30% causing hypotension. The uteroplacental bed is already vasoconstricted, which then places the fetus in danger as well.
Question 57.
Which of the following interventions is NOT considered appropriate for a patient with placenta previa?
[a] Performing a pelvic examination to determine cervical dilatation
[b] Maintaining strict bed rest and observing for further bleeding
[c] Monitoring for signs of shock
[d] Preparing the patient for ultrasound
Answer:
[a] Performing a pelvic examination to determine cervical dilatation
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
A pelvic examination should not be performed on a pregnant patient with vaginal bleeding in the third trimester. This can cause further bleeding and damage the placenta. The patient should be placed on bed rest, monitor a pad count, and be admitted if bleeding is heavy and persists. A pelvic ultrasound is useful for detecting placenta previa.
Question 58.
Delivery of an infant is imminent in the emergency department. Meconium is noted in the amniotic fluid: Upon delivery, the neonate is limp and not responding to stimuli. Which of the following actions should be taken first?
[a] Simulation of the neonate
[b] Suctioning of the oropharynx and the nasopharynx
[c] Endotracheal (ET) intubation with suction
[d] Placement of an umbilical line
Answer:
[c] Endotracheal (ET) intubation with suction
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Meconium-stained amniotic fluid can be an emergency for the neonate; therefore, endotracheal (ET) intubation with suction applied to the ET tube should be performed. Stimulating the neonate will cause more amniotic-stained fluid to enter the lungs. It is no longer recommended to routinely perform oropharynx and nasopharynx suctioning for neonates born to mothers with meconium-stained fluid. Placing an umbilical line is not necessary at this time.
Question 59.
A patient in her 34th week of pregnancy presents to the emergency department. Her blood pressure is 180/110mm Hg and she complains of headache and blurred vision. During treatment of this patient, the emergency nurse should be prepared for which of the following complications?
[a] Precipitous delivery
[b] Vaginal bleeding
[c] Cardiac dysrhythmias
[d] Seizure activity
Answer:
[d] Seizure activity
Nursing Process: Evaluation
Rationale:
This scenario provides information for symptoms associated with pregnancy-associated hypertension; the patient has a potential for seizure activity because of central nervous system irritability. Seizure precautions should be instituted. Precipitous delivery, vaginal bleeding, and cardiac dysrhythmias are not complications of pregnancy-associated hypertension.
Question 60.
Postpartum hemorrhage can occur immediately after delivery or can be delayed by as much as 6 weeks. Which of the following is NOT a cause of postpartum hemorrhage?
[a] Retained products of conception
[b] Vaginal or cervical tear
[c] Failure of uterus to contract to normal
[d] Amniotic fluid embolism
Answer:
[d] Amniotic fluid embolism
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Postpartum hemorrhage is defined as blood loss greater than 500 mL and is a common complication of labor and delivery. Amniotic fluid embolism, a complication experienced by the mother, is caused when amniotic fluid leaks into the mother’s venous circulation during labor and delivery. It does not cause postpartum hemorrhage. Retained products of conception or placental fragments can interfere with involution or return of the uterus to normal size. Vaginal or cervical tears can be a cause of postpartum bleeding.
Question 61.
Which of the following indicates imminent delivery?
[a] Need to bear down by the mother
[b] Rupture of membranes
[c] Loss of mucus plug
[d] Lengthening of contractions
Answer:
[a] Need to bear down by the mother
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
The desire to bear down or push usually indicates that delivery is near (especially in the multiparous mother). Other signs of imminent delivery are heavy bloody show and a bulging perineum. Rupture of membranes may occur before labor begins. Loss of the mucus plug is likely to occur up to a month before delivery. Lengthening of contractions does not necessarily indicate that delivery is imminent.
Question 62.
A patient has been diagnosed with pregnancy-induced hypertension. She is being transported to another facility. Which of the following measures would be important for the transport crew to follow?
[a] Have cabin lights well-lit.
[b] Read her a story of her choice.
[c] Dim lights and earplugs may decrease stimulation.
[d] Run ambulance lights and siren to facility.
Answer:
[c] Dim lights and earplugs may decrease stimulation.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Dimming lights and wearing earplugs may decrease stimulation, which would help to decrease the potential for seizures. Noise, vibration, and light may increase blood pressure. Reading her a story would be nice, but it may or may not lower her blood pressure. Even watching TV is sometimes considered too much stimulation. Having the cabin lights lit and the siren on would cause overstimulation.
Question 63.
The perineum totals approximately 1% of the total body surface area. Treatment options for a patient who has experienced a burn to this area would include which of the following?
[a] At home after explicit discharge instructions
[b] At a local physician’s office
[c] At a community emergency department or urgent care
[d] At a tertiary a burn center
Answer:
[d] At a tertiary a burn center
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Burns that involve the face, eyes, ears, hands, feet, major joints, genitalia, or perineum should be transferred to a burn center. These patients need special attention to prevent infection, scarring, and contractures. Care at home, with a local physician or in the emergency department, is not adequate.
Question 64.
Prophylactic treatment of sexually transmitted infections for the sexually assaulted victim usually includes all of the following EXCEPT:
[a] ceftriaxone (Rocephin).
[b] metronidazole (Flagyl).
[c] zosyn (Piperacillin).
[d] azithromycin (Zithromax).
Answer:
[c] zosyn (Piperacillin).
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Although Zosyn (Pipericillin) is a wide-spectrum antibiotic, ceftriaxone (Rocephin), metronidazole (Flagyl), and azithromycin (Zithromax) are usually prescribed prophylactically for possible sexually transmitted diseases. Remember that metronidazole (Flagyl) should not be taken with alcohol. This medication may be needed to be started the next day depending on the circumstances.
Question 65.
Which of the following is the most common injury associated with a pelvic fracture?
[a] Urethral tear
[b] Bladder rupture
[c] Fractured penis
[d] Fractured femur
Answer:
[a] Urethral tear
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
A urethral tear is more common in males because the urethra is longer with more exposure. Bladder rupture can occur with a pelvic fracture, but is less common. A fractured penis usually derives from a direct blow or injury during an erection, not necessarily a pelvic fracture. Femur fractures may occur depending on the mechanism of injury.
Suspect urethral tears early in the trauma assessment to avoid further injury by insertion of a urethral catheter. Blood found at the urinary meatus along with an abnormal prostate examination is indicative of this injury. A cystogram can be done to rule out injury in the acute setting.
Question 66.
The diaphragm is pushed upward by the expanding gravid uterus. Which of the following areas would be correct for chest tube placement in the pregnant patient?
[a] First to second intercostal space
[b] Third to fourth intercostal space
[c] Fourth to fifth intercostal space
[d] Sixth to seventh intercostal space
Answer:
[b] Third to fourth intercostal space
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
The gravid uterus will push the diaphragm upward, the lungs will shorten, and the functional reserve decreases. The chest tube should be placed one to two intercostal spaces higher than the standard fourth to fifth intercostal space. The first and second intercostal space would be too high. Anything distal would be too low.
Question 67.
Increased capillary engorgement heightens the risk of bleeding with the insertion of which of the following tubes during pregnancy?
[a] Urinary catheter
[b] Oral endotracheal tube
[c] Nasogastric tube
[d] Arterial line
Answer:
[c] Nasogastric tube
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Capillary engorgement of the upper respiratory passages increases the risk of nasopharyngeal bleeding and airway obstruction. This does not increase bleeding upon insertion of the urinary catheter, oral endotracheal tube, or arterial line.
Question 68.
A 42-week pregnant patient arrives in active labor and will be staying in a small community emergency department until after delivery. Assessment reveals that she has been taking narcotics throughout her pregnancy and appears impaired at this time. The emergency nurse would expect to perform which of the following interventions?
[a] Administer intravenous Narcan (Naloxone) immediately.
[b] Observe patient’s respirations and, assist intubation as needed.
[c] Allow patient to take her normal street drugs.
[d] Keep it a secret so she does not get in trouble.
Answer:
[b] Observe patient’s respirations and, assist intubation as needed.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Observation of the patient’s respiratory status is of highest importance. Narcotics suppress respiratory effort and the patient may need to be intubated. Administering Narcan to this patient may lead to rapid withdrawal and seizures in the newborn. Not reporting the situation and allowing the patient to continue her normal activity with illicit drug use are not appropriate interventions.
Question 69.
Which of the following heart rates indicates the point at which chest compressions should be initiated in the newborn?
[a] 60 beats/minute
[b] 80 beats/minute
[c] 100 beats/minute
[d] 110 beats/minute
Answer:
[a] 60 beats/minute
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
The normal neonatal heart rate is 120 to 160 beats/minute. Heart rates below 60 beats/minute necessitate chest compressions and ventilatory support.
Question 70.
The emergency nurse should determine an APGAR score on the neonate at 1 minute and again at 5 minutes. Which of the following parameters are assessed with this scoring?
[a] Heart rate, muscle tone, reflexes, respiratory effort, and color.
[b] Heart rate, temperature, reflexes, respiratory effort, and color
[c] Heart rate, muscle tone, weight, respiratory effort, and color
[d] Heart rate, muscle tone, reflexes, respiratory effort, and swallowing ability
Answer:
[a] Heart rate, muscle tone, reflexes, respiratory effort, and color.
Nursing Process: Assessment
Rationale:
The APGAR score should be determined at 1 and 5 minutes and should include assessment of heart rate, muscle tone, reflexes, respiratory effort, and color. A score of 7 to 10 is favorable.
Question 71.
Which of the following is the most common risk factor for an ectopic pregnancy?
[a] Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
[b] Spontaneous abortion
[c] Fertility difficulties
[d] Multiple pregnancies
Answer:
[a] Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Nursing Process: Analysis
Rationale:
Ectopic pregnancies are typically related to scarring of the fallopian tubes secondary to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Spontaneous abortion and multiple pregnancies are not associated with this condition. Scarring from PID may also result in fertility difficulties.
Another complication of pelvic inflammatory disease is called Fitz-Hugh-Cmtis syndrome. This is also known as gonococcal perihepatitis, which causes an inflammatory disease process on the lining of the liver. Other organs that can be affected are the peritoneal lining and the diaphragm.
Question 72.
An emergency nurse is suctioning an infant’s airway upon delivery due to respiratory distress in the infant. Which of the following is the correct procedure?
[a] Use a bulb syringe to suction the oral pharynx first.
[b] Use a bulb syringe to suction the nares first.
[c] Do not suction the infant’s airway.
[d] Lower the neonate’s head to assist drainage of fluid.
Answer:
[a] Use a bulb syringe to suction the oral pharynx first.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Although more recent information shows that all infants should not be routinely suctioned at birth, if the situation arises that suctioning was necessary, it is important to suction the mouth first, followed by the nose. Infants are obligate nose breathers, which means they prefer breathing through their nose. This will help clear the oral airway, before the infant takes their first breath through the nose. The neonate’s head should be kept level with the rest of the body.
Question 73.
During an emergency delivery in the emergency department what should the emergency nurse do during the delivery of the neonate’s head?
[a] Instruct the mother to hold her breath until the provider arrives.
[b] Instruct the mother to pant and apply gentle pressure to the perineum.
[c] Instruct the mother to push for a count of 10.
[d] Apply fundal pressure to assist with delivery.
Answer:
[b] Instruct the mother to pant and apply gentle pressure to the perineum.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Risk of perineal tears is increased if the mother pushes at the moment of delivery. Having the mother pant while applying gentle pressure to the perineum decreases the risk of tears. Fundal pressure is not necessary and may cause damage to the uterus. The mother should not attempt to not push when the baby is ready to deliver.
When delivering an infant be sure to place two clamps! And cut in between!
Question 74.
A trauma patient who is 36 weeks pregnant is brought to the emergency department in full spinal immobilization. She was involved in a one-car motor vehicle crash. She was wearing her seatbelt and paramedics report minor damage to the vehicle. She has no complaints, but the paramedics report her vital signs as follows:
Blood pressure—86/50 mm Hg
Heart rate—120 beats/minute
Respirations—16 breaths/minute
Pulse oximetry—95% on room air
Temperature—98.8° F (37.1° C)
Which of the following measures should the emergency nurse perform to improve her vital signs?
[a] Place the patient in Trendelenburg’s position.
[b] Remove the patient from spinal immobilization.
[c] Tilt the patient to the left side.
[d] Tilt the patient to the right side.
Answer:
[c] Tilt the patient to the left side.
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
The patient should be tilted on her left side to relieve pressure on the vena cava by the gravid uterus. Trendelenburg’s position is contraindicated for this patient. Tilting to the right side is preferable to lying flat, but is not as beneficial as tilting to the left. It will be appropriate to remove spinal immobilization as soon as possible, but must be under the direction of the provider. The preferable position would be on her left side or sitting as soon as the backboard is removed.
Question 75.
A paraplegic patient presents to the emergency department with diaphoresis, inability to urinate, and has not had a bowel movement for the past 3 days. His blood pressure reading is noted 180/96 mm Hg. Which of the following nursing interventions would the emergency nurse expect to be ordered?
[a] Insertion of a rectal tube
[b] Administration of intravenous hydralazine (Apresoline)
[c] Insertion of a urinary catheter
[d] Administration of oral magnesium citrate
Answer:
[c] Insertion of a urinary catheter
Nursing Process: Intervention
Rationale:
Early insertion of a urinary catheter is essential for this patient. These are symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia. The increase off sympathetic responses causes cutaneous vasodilatation above the cord lesion (diaphoresis and flushing) and cutane-ous vasoconstriction below the lesion (blanching, coolness, and elevated blood pressure).
A distended bladder is one of the most common precursors and can be caused by pressure from stool in the rectal vault. Insertion of a rectal tube will not remove the fecal impaction. Administration of hydralazine (or any anti-hypertensive) is not the cure for the problem. Laxatives may stimulate a bowel movement, but is not really the treatment for this patient.
Autonomic dysreflexia is usually caused by Gl or GU problems and these issues must be rectified before the hypertensive episode will resolve. While constipation and impaction are common problems, urinary retention, renal calculi, and catheter malfunction are also very common. Most patients with spinal cord injuries are aware of this possibility and understand the importance of “fixing” the underlying problem immediately.