Important Tests during pregnancy help check the baby's growth and health, as well as the mother's well-being.
A Biophysical profile or BPP is a simple and painless process that combines ultrasound imaging with a nonstress test to assess the well-being of a fetus in the uterus. This test is generally done after the 28 weeks of pregnancy. It measures the baby’s movements, muscle tone, breathing movement, heart rate and amniotic fluid level.
Look at the complete details about BPP such as a biophysical profile test, its purpose, and test details.
- What is a Biophysical Profile?
- Purpose of Biophysical Profile
- Biophysical Profile (BPP) Parameters
- Detailed Procedure of Biophysical Profile Test
- Results of Biophysical Profile
- What is a good Biophysical Profile Score?
- Pros and Cons of BPP
- What are the 5 parameters of a biophysical profile?
- What is the difference between BPP and NST?
- What is a normal BPP score?
- What are the tests on ultrasound for biophysical profile?
What is a Biophysical Profile?
A biophysical profile (BPP) is a test that combines a nonstress test with an ultrasound to check the fetus’s health. A nonstress test measures the fetal heart rate in response to fetal movements.
An ultrasound is a diagnostic technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of the fetus. Biophysical profile testing is usually performed in the last trimester of pregnancy. It is non-invasive and low risk.
Learn About: Iron Profile Test During Pregnancy
It uses a scoring system to rate the fetus in these areas:
- Body movement: The fetus moves its limbs or body.
- Breathing movements: The fetus has continuous, rhythmic breathing.
- Muscle tone: The fetus opens and closes its hands or bends and extends its arms or legs.
- Amniotic fluid volume: There is a pocket of amniotic fluid that measures at least 1 cm across and 2 cms vertically.
Sometimes are nonstress test is needed if one or more of the areas aren’t met. Your healthcare provider may perform a modified BPP test pregnancy instead of the complete biophysical profile.
Purpose of Biophysical Profile
Your care provider may order a biophysical profile if your pregnancy is high risk or goes beyond 40 weeks. They may also recommend biophysical profile test if you have any of the following conditions:
- Hypertension, lupus, renal disease or thrombocytopenia.
- There’s a decrease in the fetus’s movements.
- Previous stillbirth or other negative pregnancy outcomes.
- Expecting multiples (twins or triplets).
- Pregnancy-related hypertension (high blood pressure) or preeclampsia.
- Possible intrauterine growth restriction. (The fetus is measuring smaller than average.)
- Diabetes before pregnancy or diabetes associated with pregnancy (gestational diabetes).
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid.
- You’re Rh negative.
- You’re 35 or older at the time of delivery.
- You have obesity (a body mass index, or BMI, of 30 or higher).
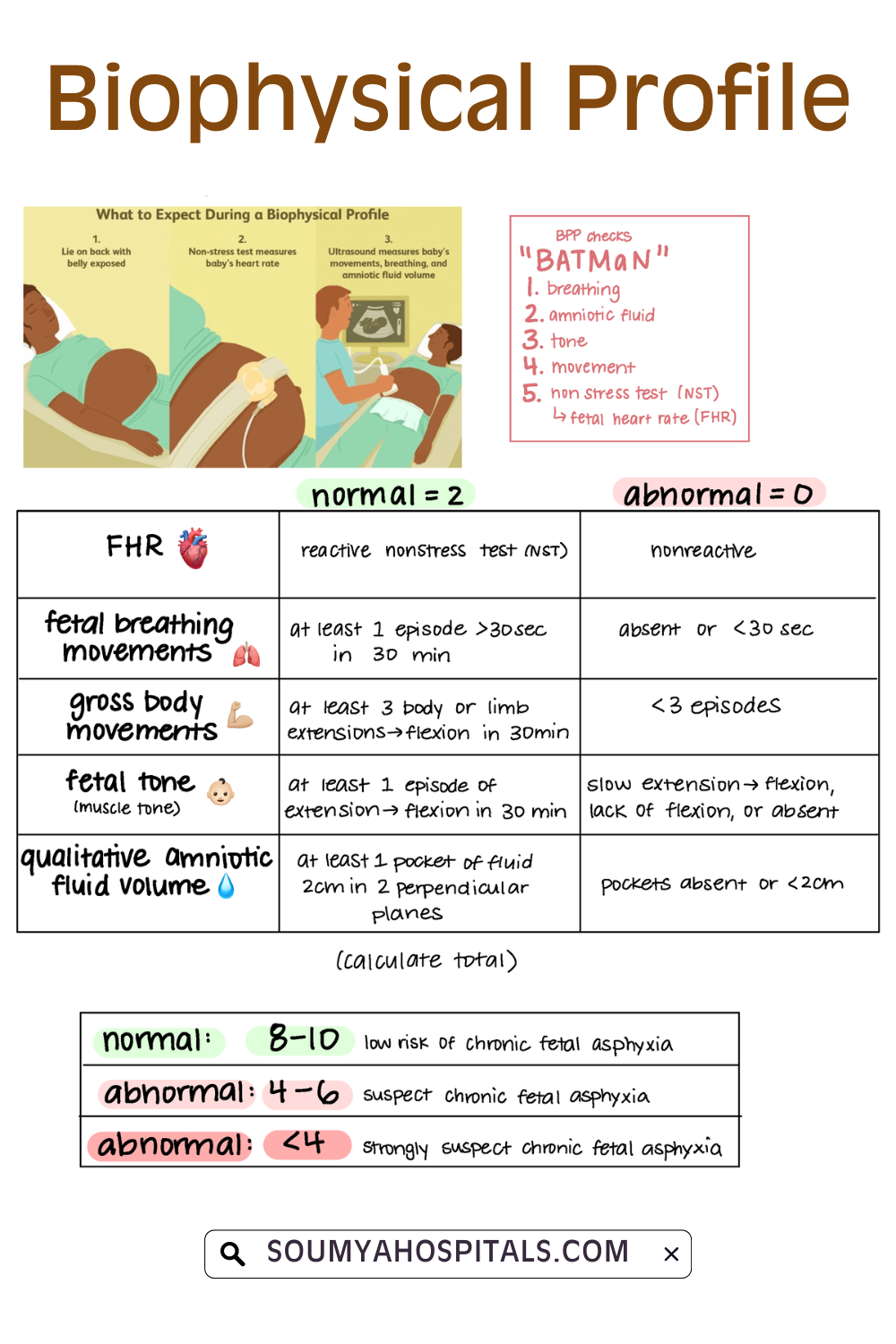
Biophysical Profile (BPP) Parameters
There are five parameters to a biophysical profile. The first is a nonstress test, which assesses the fetus heart rate in response to its movement or contractions. The other 4 parts are assessed by ultrasound. They are as follows:
- The fetus breathing movements
- The fetus body movements
- The fetus muscle tone
- The amount of amniotic fluid
Detailed Procedure of Biophysical Profile Test
The following steps are performed as part of a biophysical profile:
Ultrasound examination: During an USG, you’re lying down or reclining on an exam table. Your provider moves a device named transducer or probe on your abdomen to produce sound waves. The transducer converts the sound waves to images that can be seen on the screen.
Nonstress test: An electronic fetal monitor measures the fetus’s heart rate while you are reclining on an exam table. Your provider places a belt with an electronic sensor around your abdomen. Then, sensor measures your fetal heart rate.
The test usually takes about 20 minutes, but can extend to 40 minutes based on fetal activity. There should be 2 or more accelerations in their heart rate. If there are fewer than two, it may indicate the fetus is asleep.
In that situation, your provider may use a buzzer or a loud noise to stimulate movement. In some cases, your provider will place a second monitor with a sensor around your abdomen. This monitor measures and records your uterine contractions.
Results of Biophysical Profile
Every component receives either zero or two points. You can’t get one point. The maximum you can score is 8 points. The highest you score, the better health the fetus is assumed to be in.
The criteria to earn two points for each component are:
- Fetal muscle tone: One or more episodes of active extension and flexion of an arm or leg or the opening and closing of a hand in 30 minutes.
- Fetal gross body movement: Three or more separate movements of the fetus’s body or limbs in 30 minutes.
- Fetal breathing movements: At least one episode of continuous breathing that lasts at least 30 seconds during the 30-minute test.
- Amniotic fluid volume: At least one pocket of amniotic fluid that measures 1 cm across 2 cms vertically.
Any component that doesn’t meet the criteria above is considered irregular and receives a score of zero points.
No need to worry if the BPP pregnancy results are abnormal. Certain conditions and factors could affect your score. This is when your provider may suggest a nonstress test.
In a nonstress test, there need to be at least 2 episodes of heart rate acceleration in 20 minutes. This means when the fetus moves, its heartbeat should increase. This is similar to how your heartbeat rises when you walk upstairs. If two accelerations occur, you get an additional two points.
What is a good Biophysical Profile Score?
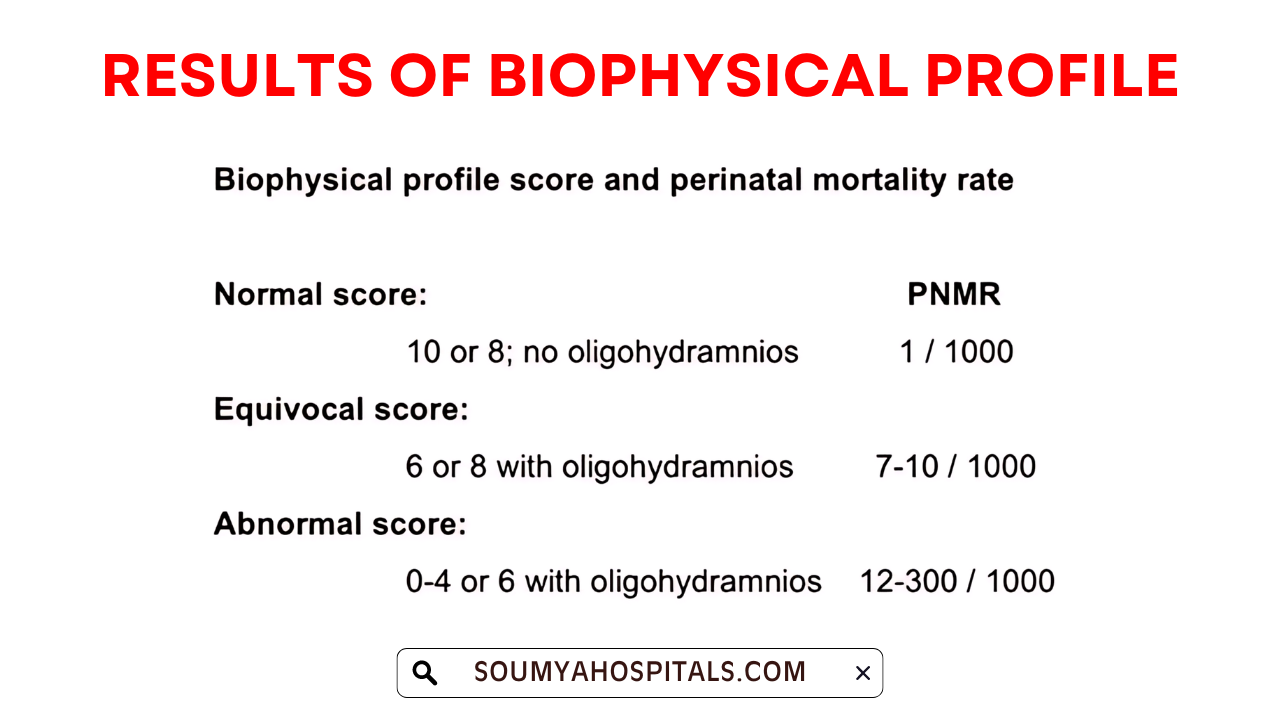
Your biophysical profile score says the following things:
- A score of 8 points with good amount of amniotic fluid volume is regarded as reassuring which means normal.
- A score of 6 indicates that there may be problems and additional testing is needed. This could mean repeating the test in 12 to 24 hours or considering an early delivery.
- A score of 4 or less, your provider may need to deliver your baby right away. In some cases, further testing is required and delivery can be delayed until necessary.
Closer monitoring is always needed if your amniotic fluid level is very low, even if other scores are normal.
Pros and Cons of BPP in Pregnancy
The advantages of the biophysical profile include:
- There is a little risk to you or the fetus.
The disadvantages include:
- It’s not as reliable when its performed between 32 weeks of pregnancy.
- The results may be affected by corticosteroids. The fetus breathing may increase and its movement may decrease for several days after you are treated with corticosteroids.
- The test may need to be repeated more than once.
FAQs on Biophysical Profile
1. What are the 5 parameters of a biophysical profile?
The 5 parameters of a biophysical profile are body movement, muscle tone, breathing movement, heart rate and amniotic fluid level.
2. What is the difference between BPP and NST?
A biophysical profile is a test that combines a nonstress test with ultrasound to check the fetus health. A nonstress test measures the fetal heart rate in response to the fetus movements.
3. What is a normal BPP score?
A normal BPP score ranges between 8 and 10.
4. What are the tests on ultrasound for biophysical profile?
The tests to be performed on ultrasound for biophysical profile are nonstress test, assessment of fluid index, fetal breathing movements, total body movements, and limb tone demonstrated by flexion and extension of the limbs.
Key Takeaways
A biophysical profile is a safe test that has no risks to you or the fetus. It allows your team to assess the fetus health and determine if delivery is necessary. Get to know about other pregnancy tests at our page.